Anomalies
6965
no comments
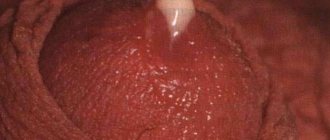
Hypospadias is recognized by experts as a common disorder of the urethra, usually observed in male newborns, and in rare cases in girls. According to statistics, the pathology is observed in 2-3 children out of 125. What kind of anomaly is this? With the disease, there is a shift in the external opening of the urethra towards the coronary sulcus, scrotum, perineal area, and trunk of the organ, as in the photo. Hypospadias of the penis is characterized by the following phenomena:
- Organ deformation;
- Difficulty urinating;
- Irritation of the skin of the perineal area;
- The presence of psychological discomfort;
- Violation of the functionality of the reproductive structure.
This anomaly in children implies the presence of a list of certain signs, the main of which is considered to be the unconventional location of the hole. There may also be a frequent urge to urinate and difficulties in carrying out this process. In adult males, as a result of the development of this pathology, sexual apathy can occur, and deformation of the penis is noticeable.
Causes of hypospadias
This developmental anomaly is congenital. It is formed at the stage of intrauterine development of the fetus, approximately from 7 to 14 weeks of pregnancy.
The external genitalia of female and male embryos are no different until the eighth week; then, under the influence of testosterone, the genitals in boys begin to develop according to the male type. During the growth of the penis, the urethral groove shifts from the base of the shaft to the base of the glans. The urethral layer, which lines the groove between the cavernous (cavernous) bodies on the lower surface of the penis, closes along the midline, forming the urethral tube. The process of this closure occurs towards the head of the penis from its base.
The formation of the foreskin occurs in the form of a fold of skin that grows in lateral directions at the base of the head, covering it. With this pathology, the process of formation of the foreskin is disrupted and it is displaced in the posterior direction. Often, together with hypospadias, there are cords (chords), which lead to curvature of the penis due to an imbalance in the growth of tissues of its different parts.
What is "hypospadias"?
Hypospadias is a congenital defect of the genitourinary system in men. With this pathology, the opening of the urethra in men is shifted towards the base of the head of the penis towards the scrotum or perineum. Such a structural anomaly entails unpleasant symptoms, trauma to the child’s psyche, as well as impaired development of the penis.
Due to internal structural changes, a man's penis becomes curved, which leads to impaired sexual function. Incorrect placement of the urethra causes urination problems and skin irritation. Correction of the pathology is possible only by surgical methods.
The opening of the urethra can be shifted to different distances relative to the norm. Possible variations of hypospadias are shown in the photo:
The incidence of the pathology is approximately 2% of newborn boys. At the same time, hypospadias also occurs in women, but it is extremely rare.
Pathology belongs to the field of urology, treatment is carried out by a urologist. It is imperative to correct the structural anomaly. The problem is noticeable immediately after childbirth and in the future can lead to improper development of the genital organ. The operation helps prevent complications and will enable the future man to feel full.
The main signs of hypospadias are:
- the opening of the urethra is shifted towards the perineum;
- curvature of the corpora cavernosa is observed;
- Dysplasia of the foreskin is diagnosed.
The main reasons for the development of hypospadias
- Genetic factors. The risk of hypospadias is significantly higher if the father or grandfather of the child has a similar anomaly.
- Endocrine disorders. Impaired development of the external genitalia, including hypospadias, can be caused by a decrease in androgen levels. Also associated with the development of congenital defects of the scrotum and penis are mutations in the hormone 5-alpha reductase, which converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone, which has a more powerful effect. The incidence of this pathology in children conceived in winter is higher, which is associated with changes in the functioning of the hypothalamic-pituitary system at this time in response to changes in daylight hours.
- Unfavorable environmental factors can provoke the development of hormonal imbalance and abnormalities in the formation of the urethral canal. The influence of pesticides and taking contraceptive medications after conception has also been proven to increase the likelihood of hypospadias.
- The combined influence of several of the following factors:
- drinking alcohol during pregnancy;
- toxicosis in early pregnancy;
- endocrine diseases in the mother;
- action of toxic substances;
- chromosomal diseases;
- presence of hypospadias in the family;
- too young or late age of the mother;
- low birth weight.
A similar anomaly is quite often observed in boys conceived by in vitro fertilization (IVF). Hypospadias is often combined with disorders such as inguinal hernia, hydronephrosis, cryptorchidism (undescended testicles into the scrotum).
An interesting fact is that among the white population the incidence of this pathology is higher.
Causes of the disease
The development of this pathology can be provoked by the following phenomena:
- Incorrect development of the fetus (from 7 to 15 weeks) - this period is characterized by the beginning of the creation of the human sexual structure;
- Genetic, chromosomal abnormalities;
- The presence of complications caused by viral diseases occurring during pregnancy - rubella, influenza;
- Illiterate use of hormonal substances;
- Infections of intrauterine nature;
- Presence of stressful situations;
- Insufficient food intake;
- Alcohol abuse during pregnancy.
Classification
Depending on the degree of underdevelopment of the urethra, hypospadias is classified into the following forms:
- coronal hypospadias – the opening of the urethra is located in the area of the coronary groove;
- capitate - the outlet of the urethra is located at the base of the head;
- stem - the hole opens onto the shaft of the penis;
- perineal - the outlet of the urethra is located in the perineum;
- scrotal – the hole is located on the scrotum.
Considering the degree of displacement of the external opening of the urethra, anterior, middle and posterior hypospadias are distinguished.
The anterior one includes capitate and coronal forms. They occur in approximately half of all cases of the disease. The posterior includes scrotal-trunk, scrotal and perineal forms of pathology (accounts for approximately 30% of cases). Average hypospadias (trunk) occurs in 20%.
Consequences and complications
Hypospadias is complicated by irritation of the skin that constantly occurs at the end of the urethra, infections of the genitourinary system, and impaired fertility. An operation to eliminate the anomaly can be fraught with the following negative consequences:
- urethral fistula;
- narrowing of the internal lumen of the urethra;
- diverticula of the excretory duct;
- decreased or complete absence of sensitivity of the head of the penis.
Serious consequences of the disease are most often characteristic of perineal and scrotal forms of hypospadias. They reduce a man’s quality of life and lead to mental disorders.
Symptoms of hypospadias
The symptoms of the disease are directly influenced by the location of the urethra and the nature of the curvature of the penis.
The capitate form of hypospadias is the most common and mildest. The opening of the urethra is narrowed, which makes urination difficult. There may be increased curvature of the penis during puberty, as well as after the onset of sexual activity.
With the coronal form of the pathology, urination is difficult, urine flows out in a thin stream due to the narrowed opening, and the curvature is quite pronounced. In order to avoid getting liquid on his feet, the child in the toilet is forced to lift his penis up.
The trunk form is manifested by the fact that children have to lift the penis up, and sometimes it is even easier to urinate while sitting. The deformation of the penis is very noticeable, and erection may be painful. During sexual intercourse, depending on the location of the urethra, sperm may not enter the vagina.
The scrotal form is considered the most severe. With this arrangement of the urethra, the penis is often curved and underdeveloped. The urethral opening divides the scrotum into two parts, making it somewhat similar to the female labia majora. Sexual activity with this form of hypospadias is impossible, and urination is only possible while sitting. Urine almost always gets on the skin, causing irritation and even inflammation.
In patients with the perineal form of the pathology, underdevelopment of the penis and its small size are noted.
It is often quite difficult to determine the sex of the child at birth, since such an anomaly is confused with adrenogenital syndrome in girls. In some cases of the disease, the congenital defect consists only of a shorter length of the urethra, and its external opening is located normally. This form is called “hypospadias without hypospadias.”
Hypospadias
Hypospadias is one of the most common malformations of the penis. There is an average of 1:200 newborn boys. The pathology is characterized by varying degrees of ectopia (displacement) of the external opening of the urethra to the base of the head, coronal sulcus, shaft of the penis, scrotum, and perineum. The disease may be accompanied by curvature of the corpora cavernosa of the penis in 25-30% of patients, and disturbances in urination and sexual function are often observed. The foreskin, as a rule, does not surround the head circularly; it is split and is a fleshy flap in the form of a hood located along the dorsal (posterior) surface.
There are opinions about hereditary predisposition to this disease. Studying the issues of inheritance of hypospadias, N.E. Savchenko (1974) observed hypospadias in four generations, and ED Smith (1990). at six. The main cause of hypospadias is considered to be hormonal disorders of the development of the penis. As a result of insufficient production of male hormones - androgens - by the testes and placenta, or an enzyme deficiency in the process of converting testosterone into dehydrotestosterone or defects in the sensitivity of androgen receptors in the penis. A “breakdown” at any point in the androgen stimulation chain can also cause various intersex conditions Devine CJ (1977) JPMurphy (1998),
The diagnosis of hypospadias is not always easy. A false, blindly ending hole at the top of the head often misleads doctors. The true opening of the urethra can be located significantly lower and be narrowed. Therefore, all children with impaired anatomy of the genital organs must be examined at the time of urination. A special place in diagnosis and treatment is occupied by children with severe forms of hypospadias 17-20% (scrotal, perineal with gross curvature of the penis). Indirect signs of intersex anomalies in these patients can be a combination of hypospadias with bilateral cryptorchidism (non-descending testicles), micropenia (underdevelopment of the penis, its small size), penis-scrotal transposition or bifurcation of the scrotum. - in appearance resembling the labia majora in girls. Such boys may have a urogenital sinus, the rudiment of the uterus, which in rare cases can reach 20-50 ml. All these are signs of false male hermaphroditism. To clarify the genetic sex, the child’s chromosome set (XX or XY) should be determined by karyotyping, sex chromatin should be assessed using a buccal smear, or by Y-fluorescence (which allows one to identify the long arm of the Y chromosome).
Surgical treatment of hypospadias is considered a complex task in plastic surgery. The operation involves not only the complete straightening of the corpora cavernosa, but also the creation of the missing part of the urethra from the child’s own tissues. It is necessary to form a sealed tube from the skin of the shaft of the penis or foreskin through which urine will flow under pressure. It is important that the newly created area of the urethra is well supplied with blood, does not have defects (urinary fistulas), there are no cicatricial stenoses (narrowings) that impair urination or diverticulum-like expansions where stagnant urine accumulates. When correcting hypospadias, it is necessary to strive to comply with strict modern cosmetic requirements - smooth corpora cavernosa, the external opening of the urethra at the top of the glans (and not at its base), the absence of excess skin on the foreskin and shaft of the penis.
That is why the treatment of hypospadias is considered a complex complex problem, which most surgeons solve in stages. Performing a series of sequential operations, straightening the penis, preparing a supply of skin on the shaft of the penis, creating an artificial urethra piece by piece.
However, there are more complex one-step techniques that combine several stages of treatment for this complex defect. In the Department of Pediatric Urology of the Research Institute of Urology of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, one-stage methods of treatment of all existing forms of hypospadias are used, the original operations of Prof. Yu.E. Rudin are used. of which five (5) are protected by a Russian patent. The results of the treatment meet modern international cosmetic requirements and were reported at international scientific congresses of pediatric urologists in Russia, England, Austria, Germany, Latvia and Turkey.
Should surgery be performed if there are minimal changes to the penis? If there is no deformation of the corpora cavernosa of the penis, there is coronal hypospadias and a hooded foreskin. Do! However, under no circumstances agree to perform circumcision without urethroplasty; these proposals can very often be heard from doctors who have little knowledge of the problems of hypospadias. The foreskin is necessary as a plastic material during operations to create the missing part of the urethra.
All forms of hypospadias are operated on in all civilized countries. A boy’s penis should not differ from the norm; it is a special organ for a man and any deviations in its structure, even minor ones, can cause self-doubt. That is why it is advisable to complete the treatment of hypospadias before the age of 3-4 years, so that the child does not remember the problems that existed in his life. If the boy is much older, it is advisable not to focus on the fact that he has a penile defect and it is important to convince the child of the possibility of a complete cure.
At what age should surgery be performed? In our clinic, operations begin at the age of 10-11 months, provided that the size of the penis is at least 30 mm and there is no gross combined pathology that increases the risk of anesthesia (anesthesia)
Surgical treatment of hypospadias is a serious test for the child and his loved ones.
The task of the operating surgeon, doctors and medical staff is to help get through this difficult period with the least amount of difficulty.
What information do you need to have? Surgeries on the penis are painful (the organ has many sensitive receptors, especially on the head); in modern practice, local anesthetics, blockades and analgesics are used (including narcotics in the first day after surgery), however, some pain remains that may bother the child.
Urine diversion when correcting hypospadias (in 90% of cases) involves installing a urethral catheter (a tube passed through the urethra into the bladder). Most children react minimally to the presence of a catheter, but some patients experience discomfort, the urge to defecate, and aching pain in the lower abdomen.
After surgery, to prevent the development of severe tissue edema and prevent infection of the postoperative wound, circular bandages are applied to the penis, which are impregnated with special compounds that improve healing. Changing the bandage is also a rather painful procedure, despite the use of painkillers. Many parents are scared when they hear information that children are tied to a bed for a long period of time. This is wrong. The child can be restrained only for a short time until he finally wakes up from long-term anesthesia. Further, at the request of the parents, all fixing bandages are removed, the patient is put on a double diaper and the child can be picked up. The main thing is to ensure reliable fixation of the drains with wide adhesives (so that the child does not remove the tube prematurely)
However, all these difficulties can be solved in the conditions of a professional team of doctors and nurses who have extensive experience working with patients of this profile. There are schemes that have been proven over the years to reduce all the risks of surgery and postoperative management of children with hypospadias
As an example, the results of treatment of patients with hypospadias are presented.
| Fig. 1 A. A 5-year-old boy with distal hypospadias of the stem form. B. Photo of the same child after the operation. B. The same boy 2 years after the operation. He urinates freely in a wide stream, there are no fistulas. |
| Fig. 2 A. Photo of a 1.5 year old child with scrotal hypospadias and penile deformity. B. Photo of the same child 1 week after surgery. |
| V.G. The same child 6 months later. after operation. A wide, tense stream indicates a freely patent urethra and the absence of urinary fistulas. |
| Fig. 3. A 3-year-old boy with coronary hypospadias A. The same child 5 months later. after surgery B. Another example is the treatment of a very complex variant of perineal hypospadias with gross deformation of the cavernous and complete absence of the urethra on the head, shaft of the penis and scrotum |
| Fig. 4 A 1-year-old boy with proximal hypospadias perineal form A. The same child after a successful simultaneous operation, straightening the corpora cavernosa and urethroplasty with a tubularized flap of foreskin skin. B. The same child 1 month later during urination (no fistulas). |
It is necessary to understand that one-stage operations to correct all manifestations of the defect in hypospadias are not an end in themselves. Of course, it is preferable that the curvature of the penis, lack of urethral length, narrowing of the urethra and scars from previous surgical interventions are eliminated in one operation. Unfortunately, this is not always possible and often increases the risk of postoperative complications. That is why we must not forget about stage operations.
Recent developments by foreign and domestic surgeons offer new methods for correcting complex and complicated forms of hypospadias. They allow the use of free (non-blood-supplied) flaps: tissue of the foreskin, the mucous membrane of the cheek in the form of a supply of plastic material, which are moved to specified locations (in the area of the urethra) and implantation (engraftment) of these tissues is achieved
This approach makes it possible to prepare a sufficient amount of plastic material on the shaft of the penis to create a tube of the required diameter. The supply of tissue helps to cover the new urethra securely with minimal risk of fistula formation and narrowing of the urethra. We have long mastered these methods and recommend using these two-stage treatment methods in the most difficult cases of hypospadias correction. The use of these reliable techniques in the hands of professionals can reduce the number of surgical complications to 2-3%.
Rice. 1 Method of two-stage treatment of proximal hypospadias.
Stage 1 – straightening of the corpora cavernosa and implantation of a free flap of the foreskin.
| A | B |
A. A 1-year-old boy with penoscrotal proximal hypospadias and deformation of the penile shaft. B. Test with artificial erection (deformation of the corpora cavernosa by 65 degrees)
| IN | G |
V. G. Complete straightening of the corpora cavernosa and mobilization of the tissue of the head (wings of the head) of the penis, mixing of the fleshy membrane of the foreskin. Preparation of a free flap of foreskin
| D | E |
D. Implantation and fixation of a free flap of foreskin along the ventral surface of the penis. E. Pressing the flap to the turunda with levomikol using interrupted sutures.
| AND |
G. The result of the first stage of treatment of proximal hypospadias. View of the penis after 6 months. after straightening the penis and implanting a free flap of foreskin.
Rice. 2 The second stage of two-stage treatment of proximal hypospadias. Urethroplasty according to Duplay.
| A | B |
A. Cutting out a flap along the ventral surface of the penis. B. View of the penis after surgery.
| IN |
B. The same patient 2 months later. after surgery during the act of urination.
A clinical example of two-stage treatment of scrotal hypospadias and penoscrotal transposition in a 1.5-year-old child K.
Fig.3. A. B. The penis of a 1.5 year old child with scrotal hypospadias and penoscorotal transposition before surgery. V.G. The result of straightening the corpora cavernosa of the penis. D. A free flap of foreskin is implanted into the urethral pad. E. The flap is pressed with a turunda and guiding sutures onto the skin of the shaft of the penis.
Rice. 4. A.B. The same patient 12 months later. after stage 1 of the operation. B. Dissection of the urethral platform to form the urethra. D. Incisions in the skin of the scrotum for correction of penoscorotal transposition. D. View of the penis after surgery. E. Free urination from the top of the head.
Rice. 5. The first stage of two-stage treatment of scrotal hypospadias in a 2-year-old child G.
A. Appearance of the penis before surgery. B. Deformation of the cavernous bodies before correction. B. The penis after excision of the chord and plication of the tunica albuginea. D. Multiple superficial transverse notches on the tunica albuginea along the ventral surface of the penis D. Final view of the penis after implantation of a free flap of the foreskin into the area of the urethral area.
Fig.6 . The second stage of two-stage treatment of scrotal hypospadias in a 2-year-old boy G. A. View of the penis after 10 months. after the first stage of treatment. B. Cutting out a flap in the area of the urethral platform. B. Formation of the urethra using a continuous 6\0 PDS suture. D. Appearance of the penis after the end of the operation. D. Urination in a free wide stream from the top of the child’s head D. After 3 months. after the second stage of treatment.
Fig. 7 Clinical example of treatment of coronoid hypospadias. A. View of the penis before surgery, view of the penis after urethroplasty.
Yu.E.Rudin ,
Literature:
- Y. Rudin, D.Marukhnenko, N.Poljkov, D.Aliev, G.Lagutin, A.Vardak “Augmentation of the glans and distal urethra affective method of coronal urethral fistulas correction” (PP) 30th Congress of the ESPU 24- 27th April 2019 Lyon France p.23
- Rudin Yu.E. Methods of correction and features of surgical treatment of hypospadias in childhood. Study guide.2019, "Uromedia" 75 p.
- Y. Rudin. D.Marukhnenko, D.Aliev, G.Lagutin, A.Vardak “RETROSPECTIVE REVIEW OF PROXIMAL HYPOSPADIAS REPAIR: TWO-STAGE VS ONE-STAGE TECHNIQUES” (PP) 27th Congress of the ESPU June 22-25th 2016 Harrogate,Yorkshire, UK p.58
- Rudin Yu.E., Marukhnenko D.V. Optimization of urethroplasty in the treatment of children with distal and mid-trunk hypospadias. Russian Bulletin of Pediatric Surgery, Anesthesiology and Reanimatology. 2019. T.5, No. 4, pp. 20-26
- Rudin Yu.E., Romikh V.V., Garmanova T.N., Marukhnenko D.V. Functional results of hypospadias correction based on urodynamic examination data. Experimental and clinical urology. 2019 No. 3, pp. 88-91
- Rudin Yu.E., Marukhnenko D.V., Sayedov K.M. Choice of method for correcting proximal hypospadias in childhood J. Experimental and clinical urology. 2019. No. 1, pp. 81-88
- Rudin Yu.E., Marukhnenko D.V., Garmanova T.N.. Application of an analog-digital scale in the preoperative assessment of the condition of the penis in patients with hypospadias Experimental and clinical urology. 2013.№4, pp.110-115.
- Rudin Yu.E., Marukhnenko D.V., Garmanova T.N., Sayedov K.M. Choice of urethroplasty method in patients with distal and mid-trunk hypospadias. Urology. 2013. No. 1. 92-96.
- Rudin Yu.E., Marukhnenko D.V., Garmanova T.N. Sayedov K.M. New method of plastic surgery of the glans penis in patients with hypospadias Experimental and clinical urology. 2013.№1, pp.87-89.
- Rudin Yu.E., Marukhnenko D.V., Garmanova T.N., Sayedov K.M.Plasty of the glans penis in accordance with normal anatomy is the key to successful correction of hypospadias. Urology, 2013. No. 3. 74-78.
- Rudin Yu.E., Marukhnenko D.V., Garmanova T.N.. Comparative analysis of three urethroplasty techniques in patients with distal and trunk forms of hypospadias. Experimental and clinical urology. 2012.№2, pp.61-65
- Rudin Yu.E., D.V.Marukhnenko, S.V.Bachiev, R.N.Makeev, Garmanova T.N.Simultaneous urethroplasty with an increase in the area of the glans penis in the treatment of hypospadias in children. Experimental and clinical urology 2010. No. 3, pp. 66-69.
Diagnostics
The presence of hypospadias in a child is diagnosed immediately after birth. A neonatologist examines a newborn and determines the form of pathology. If an anomaly in the development of the genital organs does not allow one to accurately determine the sex of the baby, then in this case an ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the pelvic organs is performed, and sometimes even a determination of the chromosome set.
After the disease is identified, the child is sent for consultation with a geneticist, since such a disorder may be accompanied by other congenital pathologies. Additionally, an ultrasound scan of the bladder and kidneys is performed to assess their structural condition. Quite often, problems are also found there. Further observation is carried out by several specialists: urologist, endocrinologist, etc.
A thorough examination of the baby is carried out to determine the localization of the pathology, urination disorders, as well as the degree of curvature of the penis. Before the examination, the parents are found out about the presence of a similar pathology in close relatives, and information about possible risk factors is clarified.
During the examination, the doctor pays attention to the location and diameter of the external opening of the urethra, the size of the penis, the appearance of the foreskin, the presence of separation of the cavernous bodies and bends of the shaft during erection. He then examines the scrotum to rule out cryptorchidism and the presence or absence of a congenital inguinal hernia.
Severe hypospadias in combination with other pathologies of the genital organs requires a full endocrinological and genetic examination immediately after the birth of the child in order to exclude disorders of sexual development.
Additional instrumental methods for diagnosing hypospadias can include magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the pelvic organs, urethroscopy, and urethrography.
Treatment of the disease
The main method of eliminating hypospadias in a child is surgery. The operation is aimed at restoring the shape of the penis and the correct position of the urethra. There are various intervention options, selected for each boy individually.
When talking about how long the operation lasts, doctors call the time frame from 1 to 3 hours. This depends on the form of the pathology and the presence of concomitant developmental anomalies. Surgical interventions with plastic surgery lead to restoration of the shape of the penis. This can be seen in the photos before and after the operation. Children tolerate surgical procedures without complications.
Parents are worried about how much the surgery will cost. Surgery is performed free of charge, as it is the recommended method of treating the disease.
Preventive actions
Due to the fact that the causes of the pathology are not fully established, specific prevention has not been developed.
Doctors recommend that a pregnant woman adhere to the following general recommendations:
- eliminate bad habits: drinking alcohol, smoking and drug addiction;
- treat infectious diseases, primarily sexually transmitted infections;
- avoid heavy physical activity and stress;
- Do not use medications on your own. Medicines may be contraindicated during pregnancy, as they can cause developmental abnormalities in the child.
If symptoms of illness appear during pregnancy, you should consult a gynecologist. The specialist will conduct an examination and prescribe therapy.
Conclusion
The prognosis for hypospadias in boys is positive. Detection of pathology after birth and surgical correction of the defect can normalize the development of the external genitalia and prevent complications of the disease.
Feedback from parents about the treatment is positive. The operations do not require long-term hospitalization for children and are safe for them.
Treatment of hypospadias
Elimination of this disease is possible only through surgery. This requires joint work between a plastic surgeon and a urologist. The goal of treatment is to eliminate cosmetic defects and restore penile function. It is possible to achieve the most positive results with early surgery (from one to three years). Such children may not even remember their problem in the future. The correction can be done in stages or all at once.
To establish indications for surgical treatment, it is necessary to first determine what results should be achieved and the disorders eliminated - functional and/or cosmetic.
Functional disorders that are indications for surgery include:
- posterior hypospadias;
- stenosis of the external opening of the urethra;
- deflection and splashing of the stream when urinating;
- curved penis.
Cosmetic indications for surgery:
- abnormal development of the foreskin;
- abnormal location of the urethral opening;
- split head of the penis;
- split scrotum.
Any surgical intervention is accompanied by a risk of complications, so the child’s parents must carefully explain the indications for it and the possible consequences before the operation.
For hypospadias, surgery is performed to restore the normal shape of the penis, eliminate its curvature, form a new urethra, and also bring its external opening to the tip of the head.
In the postoperative period, attention is paid to caring for the installed urinary catheter and wound, since regular dressings are necessary. To prevent infectious complications, antibacterial therapy is prescribed until the urinary catheter is removed.
The baby's parents are given detailed instructions on how to properly apply antibacterial ointment to the area of the operated head. This is done with every diaper change and after every urination. In the presence of pain, non-narcotic analgesics can be prescribed.
Boys with very small penis sizes may be prescribed hormonal therapy before surgery. Growth accelerates when taking testosterone and human chorionic gonadotropin.
Pathology treatment options
If you suspect this disorder, you should consult your doctor. The standard treatment option in this situation is not enough - surgery eliminates this disease. Surgical intervention is recommended in a certain age period - it is recommended to operate on children from six months to 1.5 years, some experts push this period to 3 years. During this time period, any physical procedures are most effective; they are easily tolerated by the baby.
If hypospadias was not eliminated in childhood, then it can be eliminated in the adult period of a male representative’s life.
The presence of signs of disease does not always indicate that the patient needs surgical intervention - this process is performed only in a situation where severe deformation of the organ is observed, also if a narrowed opening is noted.
Treatment of this anomaly is a difficult task for urology and plastic surgery, because their task is to restore the functional usefulness of the organ and correct a cosmetic defect in representatives of the stronger half of humanity. Today, a large number of different one-stage, stage-by-stage surgical methods for correcting the anomaly are used.
Slight dystopia of the meatus with meatostenosis - in this case, meatotomy should be used, in other situations - plastic correction of the urethra is performed.
Stages of the operational option:
- Correction of penile curvature;
- Urethroplasty is the creation of a section of the urethra that does not exist;
- Meatoplatisk – restoration of the usual location of the meatus.
Also, if cryptorchidism is present, then the process of testicular descent occurs in the scrotal area. The operating process takes 1-3 hours.
The postoperative period is characterized by urine diversion - catheterization of the bladder is performed, and after the operation a cystostomy is placed (1-2 weeks). As prescribed by the doctor, bougienage of the urethra is performed.
The surgical technique achieves effectiveness in 75-95% of situations. An early corrective method of eliminating pathology ensures restoration of the urination process, good development of the organ, and prevents mental trauma to the child.
Complications of the surgical method may include:
- Urethral fistula;
- Diverticulum of the urethra;
- Urethral strictures;
- Loss of sensation in the head of the organ.
Typically, negative consequences occur with proximal types of disorders - perineal, scrotal type.
A child who has undergone surgery to eliminate this anomaly is under medical supervision until the end of the development of the reproductive organs.
Forecast
Modern techniques achieve positive results in approximately 80% of cases. In this case, it is possible to restore the desired appearance of the organ and functional abilities.
Early correction of the pathology guarantees normal development of the penis, as well as the exclusion of psychological trauma in the boy. After the operation, until the growth and formation of the penis is completed, such patients continue to be observed by a urologist.
Principles of treatment
The main method of correcting the defect is surgery .
The operation is most often performed at an early age, when the child reaches 2 years of age . In this case, the chances of a successful outcome increase.
Surgery is necessary to:
- restore the process of urination;
- prevent violations of the structure and functionality of the genitourinary system;
- to preserve intimate function in the future;
- to eliminate an aesthetic defect and prevent the development of associated psychological problems.
What are stem and scrotal forms of deviations?
The stem form of the anomaly is characterized by the location of the urethra on the trunk of the genital organ. In such patients, over time, severe deformation of the penis occurs, and the process of urination itself causes enormous problems. The fact is that during the process the jet is directed downward. Therefore, with every urge to go to the toilet, people with a similar diagnosis have to literally pull their manhood to the abdominal area.
Scrotal hypospadias (a photo of this disease can be found in our article) involves a congenital displacement of the canal either to the scrotum itself or to the line of its demarcation from the trunk of the organ. Patients with this form of anomaly subsequently acquire severe deformation of the penis and can defecate exclusively while squatting.
Coronal hypospadias
The deviation of the external opening of the urethra towards the groove is called coronal. When urinating, the stream of urine is directed at an angle to the penis. The coronal form of hypospadias is different:
- developed foreskin with additional folds;
- the formation of a “pocket” of skin folds;
- change in the position of the curved genital organ.
Step-by-step plastic surgery of the new urethra allows you to create an opening on the head of the genital organ
Forms of pathology
Hypospadias is divided into several types, depending on the degree of underdevelopment of the urethra.
Next, we will consider each of the forms in detail. It would not be superfluous to note that each of them is classified into 3 groups: As for the female gender, hypospadias is divided into 2 degrees:
- The urethral opening is located in the middle region of the vagina.
- The opening of the urethra in the area of the lower vaginal region.
Capitate
This type of pathology practically does not bother me in childhood, there are no complaints, the penis is visually straight. Often people with this form of disease consider themselves to be healthy.
In this case, the opening of the urethra is located slightly lower than it should be, and the lower adjacent wall of the urethral tract is thin. Typically, discomfort appears when the urination process begins to be disrupted:
- splashing urine;
- narrowing of the stream;
- mandatory sitting position while emptying the bladder.
Capitate hypospadias may be a precursor to the development of genital warts and nonspecific urethritis.
Stem
This type of pathological condition is characterized by the location of the urethral opening on the body of the penis (its stem part) at an arbitrary distance from the head of the organ. The further from the head of the phallus it is formed, the greater the underdevelopment and deformation of the reproductive organ.
Scrotal
The following characteristics are characteristic of this species:
- visually the scrotum is divided in half, as if enlarged labia;
- the opening is located between the split parts of the scrotum.
With this type of pathology, the male member is underdeveloped, looks similar to the female clitoris, and urination occurs like a female.
Hypospadias in the absence of displacement of the urethral canal
In medicine there is such a thing as “hypospadias without hypospadias.” This type of anomaly is extremely rare, occurring in approximately 8% of cases. In this case, the hole is located in the right place, but the penis is curved. When examining a child, the hole is located in the upper part of the head, or near the coronary groove. Basically, the foreskin looks like a “hood” and is placed behind. In some boys it looks anatomically correct, completely covering the head of the penis.
The main reason for the modification of the penis of this type of pathology is the occurrence of compacted connective tissue scars between the cavernous bodies, which are called chords. It was discovered that they are formed from altered spongy (spongy) tissue of the urethra.
Normally, periurethral spongy tissue takes part in the stretching and elasticity of the walls of the urethral tract. With this form of hypospadias in 40% of children, the urethra itself is a thin film and has deviations in structure.
Venechnaya
Coronary hypospadias is the most common form of the pathological condition, reaching 70% of cases. When such an anomaly is detected, the opening of the urethral tract is shifted and is located parallel to the coronary sulcus. The opinion of doctors is that for coronary hypospadias, surgical intervention is not necessary, provided that no curvature of the penis is detected. If there is a curvature, surgery is advisable, since the defect does not allow for a full intimate life.
Diagnosis of anomaly
For an experienced neonatologist, it is not difficult to suspect a disease in a child in the first days after birth. If in doubt, a urologist is called for a consultation. Diagnostic methods:
- a careful examination of the penis of a boy or an adult man is necessary; for girls, a consultation with a pediatric gynecologist;
- genetic research with determination of sex chromatin helps to determine the cause;
- An ultrasound of the urinary organs may be required to exclude other internal anomalies;
- A urine test will reveal signs of inflammation;
- urography using radiopaque agents more fully reflects the structure of the urinary system.
Doctors experts point out the need to take X-rays of the baby at the time of erection. In children, it occurs in the morning upon awakening, when the bladder is full. The lateral projection allows you to determine the angle of deviation of the penis and the severity of the deformation of the cavernous bodies. This is an important procedure for deciding whether surgery is needed and choosing a tactic for the surgeon.
Symptoms of the disease
One of the most obvious and visually distinguishable signs of the described pathology is the nonspecific localization of the excretory duct of the bladder. The disease negatively affects the process of emptying. Often, with abnormal development, narrowings are observed in the urethra, which negatively affect the process of emptying: the procedure requires tension in the transverse abdominal muscle, and the stream of biological fluid itself is very weak.
Hypospadias of coronal, scrotal, stem forms and other varieties can provoke the following defects:
- absence of the corpus cavernosum;
- member deviation;
- genitals are underdeveloped;
- the head is forked and others.
The lower the end section of the urinary tract is, the more pronounced the clinical picture of the described urological disease.
Symptoms and consequences
The main symptom of hypospadias is a change in the shape of the penis, the location of the urethral opening in an unusual place. Against the background of the disturbed form, the patient experiences:
- discomfort or pain when urinating;
- frequent urination;
- impaired erection during puberty, infertility in marriage;
- decreased sexual needs.
Lack of specialized medical care can lead the patient to develop:
- dropsy of the testicles (hydrocele), when fluid accumulates between the membranes;
- inguinal hernia;
- changes in the development of the foreskin;
- urinary tract infections.
In the case of women with the disease, the following are often observed:
- chronic cystitis and urethritis;
- vulvovaginitis;
- pronounced signs of pseudohermaphroditism.
Surgical treatment
Taking into account psychological factors, anesthetic management and technical aspects of surgical treatment, the optimal age for correction is from 6 to 18 months. For small penis and glans sizes, preoperative hormonal therapy is advisable.
Preparatory activities
To reduce the child’s stress during treatment, we use preoperative sedatives, a minimum period of the child’s absence from the mother, and caudal anesthesia, which provides prolonged pain relief after the intervention for up to 6-8 hours.
Progress of the intervention
Also, during correction, our department uses absorbable suture material that does not require the removal of sutures. During the entire postoperative period, the child wears two diapers, which allows the little patient’s discomfort to be minimized, thereby ensuring full activity. All of the above contributes to the maximum possible elimination of stress in the child before the intervention, during and in the postoperative period.
Surgical treatment in our clinic is carried out using the most modern techniques. Microsurgical instruments, optical magnification and absorbable suture material are used.
Thus, we do everything possible to reduce stress as much as possible for the little patient and obtain the best functional and cosmetic result.
Consequences of the disease
Like any other disease, hypospadias has a list of consequences that lead to a deterioration in the quality of life, and sometimes even more serious problems. They are especially pronounced in the scrotal form of the disease. Consequences of the pathology:
- systematic irritation of the skin in the area of the urethral canal;
- infectious diseases of the genitourinary system;
- serious problems with reproductive function.
After surgery, a number of the following complications may occur:
- urethral fistula;
- narrowing of the lumen of the urethra (stricture);
- protrusion of the wall (diverticulum) of the urethral canal;
- insensitivity of the head of the genital organ.
Why does hypospadias occur?
It is impossible to point to one specific reason for the formation of the anomaly. A connection between the development of the anomaly and several risk factors has been established. The fetus is most sensitive at 7–15 weeks of pregnancy, at which time the genitals are formed.
Violations may depend on:
- from a chromosome mutation present in the body of a pregnant woman, hereditary genetic predisposition;
- past viral infections (the most dangerous are rubella and influenza);
- poor nutrition, lack of vitamins;
- consumption of alcoholic beverages, drugs, smoking;
- treatment during this period with hormonal drugs;
- intrauterine infections of the fetus;
- stressful situations.
Hypospadias in children is most often caused by mothers who were exposed to a combination of more than one factor during pregnancy.
Congenital anomalies differ in form, likelihood of developing complications, and tactics of the treatment approach. Let's look at the main types found.
Forms and degrees
There can be three forms of trunk hypospadias in children. Let's look at them in more detail. Classifications of the disease:
- Distal truncal hypospadias - with the meatus located closer to the coronary sulcus.
- The central form is the urethral canal in the center of the shaft.
- Proximal forms of truncal hypospadias in children - the meatus is located closer to the scrotum.
According to the severity of the pathology, the following classification:
- Mild stage - the penis is only slightly curved or normal. This is most often observed in the coronoid form of hypospadias.
- Middle stage - the penis is curved, and this is visually determined. This degree is often observed in the proximal form.
- Severe degree - urine output occurs immediately near the perineum, the penis is not only curved, it is hyperplastic.
Prevention
Since it is not known exactly what exactly causes the development of hypospadias, as a preventative measure for this disease, it is recommended to avoid taking foods and external negative factors that negatively affect the development of the fetus because they disrupt the normal hormonal state of the body. Also, hormonal drugs, which, for example, are prescribed when there is a threat of miscarriage, can negatively affect the development of the fetus (such drugs can block the synthesis of male hormones, which contribute to the formation of male genital organs). Traditional methods are useless to use to treat this disease, since hypospadias is a congenital pathology that can only be corrected through surgery.
Capitate form of hypospadias in children: cost of surgery
| Service | Price |
| Hypospadias, capitate form, surgical treatment of I category of complexity | 65000 |
| Hypospadias, capitate form, surgical treatment of category II complexity | 89000 |
| Hypospadias, capitate form, surgical treatment of III category of complexity | 135000 |
The price list published on the website is not a public offer agreement. The provision of services is carried out on the basis of an agreement for the provision of medical services. You can find out the cost of the service during the consultation.
*The cost of the operation includes:
- all disposable surgical consumables and instruments
- constant telephone communication with a doctor
- examination any day in the clinic within 30 days after surgery
The cost of surgical treatment does not include:
- permanent placement
- anesthesia care
- diagnosis and treatment of concomitant diseases and their complications
- preoperative examinations and tests (performed in our clinic with a 50% discount)
** This is not a public offer agreement. Check the cost of services on the day of consultation.
Don't waste your precious time - call!
Our specialists will be happy to answer all your questions
+7
Reviews
Twins, Maxim and Vadim, our miracle, our joy! We were born, diagnosed with coronal hypospadias - Vadim, hypospadias of the chord type, curvature of the penis - Maxim. Vadim’s first operation took place on March 2, 2018 at the Filatov Hospital. Just a terrible rehabilitation period, tied to a bed for 10 days, the result is that after a year smegmal stones have formed, a second operation is needed! The decision was made unequivocally - only the best surgeon, the best specialist in this field! 10/03/2019 The operation was performed on both of them! The result is excellent! 6 days and we are home! The children feel great both physically and psychologically! Thank you very much from our entire family to Asaad Akhmadovich! For his golden hands! For his kindness! For his patience! Thanks to Nadezhda Alexandrovna! Thanks to the entire clinic team for the warmth and attention to patients and their parents! Thank you for the health of our boys!
- Ksenia Hypospadia, curvature of the penis
Thank you for your invaluable work, for the opportunity for us and our son to live a happy life. I appeal to parents of children who had or have special needs!
- Hidden penis Hidden penis
We spent a long time looking for someone to circumcise our newborn son, because we wanted everything to be done both according to tradition and at a high medical level. We considered several options, incl. and Dr. Matara A.A, whom our Mullah recommended to us. When we arrived for the consultation and met Asaad Akhmadovich, we decided that we would definitely have circumcision done by him. On the day of the operation, everything went very clearly, neatly and relatively quickly. We really liked the result! Everything is done very carefully and beautifully! Now I will recommend Dr. Matar to everyone I know!
- Ashad Circumcision
I would like to share my words of gratitude to Matar Asaad Akhmadovich for performing a complex operation on my child in 2009, when he was 3 years old. The diagnosis is very serious. Distal form of hypospadias.
- Olga, Dmitrov Distal form of hypospadias
I sincerely express my gratitude to the pediatric surgeon - director of the International Pediatric Andrological Hypospadias.
- Lena Dalyuk Hypospadias
Our advantages
Experienced surgeons
Individual approach
Without pain and fear
Comfortable conditions
Causes
In 20% of cases, familial cases of pathology are detected, that is, it can be inherited. Presumably, the formation of such an anomaly occurs in the 7-14th week of embryogenesis. This is due to the influence of various factors on the mother’s body, as a result of which the urethral groove does not close correctly and the process of formation of the cavernous bodies of the penis is disrupted. What risk factors can cause such deviations?
The following teratogenic factors can affect the fetus:
- Hormonal imbalances;
- Endocrine diseases;
- Drinking alcohol, smoking, drug addiction;
- Early severe toxicosis;
- Taking toxic medications;
- Bad ecology;
- Previous chickenpox or rubella;
- Cytomegalovirus, toxoplasmosis;
- Severe flu;
- Chemical poisoning;
- Congenital syphilis;
- Radiation;
- Radiation therapy, x-ray examinations;
- Serious stress.
Phthalates, which are contained in hairsprays, are very harmful to the fetus, so abuse of such cosmetics can also provoke the development of hypospadias. Negative effects are also noted from exposure to household chemicals and paints.
An abnormal structure of the penis is more often observed in boys conceived through IVF and in multiple pregnancies. In some cases, hypospadias is not isolated, but is part of a complex of diseases - Patau syndrome, Edwards syndrome.
Problems in adults with hypospadias
Due to hypospadias, adult men experience difficulties in sexual relations. Curvature of the penis prevents a full erection. Sex brings discomfort instead of pleasure.
Curvature of the penis causes ridicule and contempt among peers. Because of this, many representatives of the stronger half fall into stress, have complexes, and become neurotic. In addition, hypospadias can directly lead to infertility. If the skin of the scrotum was taken during the reconstruction of the urethra, it begins to become covered with hair during puberty. Urate salts will settle on them to form stones. This will disrupt the urination process.
With age, if left untreated, the penis continues to curve even more, and urination turns into a very unpleasant, problematic ritual. The urine that pours down will stain your clothes and feet. Such patients must literally pull their penis towards their stomach every time they visit the toilet to urinate.