Stomatitis is a disease of the oral cavity, which is accompanied by inflammation of the mucous membranes, the appearance of painful ulcers, canker sores, and blistering rashes. Typically, treatment of stomatitis in adults and children is carried out at home using various forms of medications: tablets, drops, sprays, gels, lozenges, mouthwashes.
Types of stomatitis
Stomatitis is an inflammatory disease of the oral cavity. Visible manifestations of the disease can be different - wounds, ulcers, redness, white coating on the mucous membrane in the oral cavity. Visible signs of stomatitis depend on its type. There are several causes (pathogens) of stomatitis and, accordingly, several types of the disease:
- Viral stomatitis (or herpetic) , the causative agent is the herpes virus.
- Fungal stomatitis (or candidiasis) , the causative agent is candida fungus.
- Bacterial stomatitis (pathogen is pathogenic bacteria, those microorganisms that cause sore throat, scarlet fever, influenza, pneumonia, caries). The second name for bacterial stomatitis is microbial.
In addition, there are several other causes of stomatitis:
- Allergic stomatitis is formed due to an allergic reaction, which reduces the local immunity of the oral cavity and makes infection possible (viruses, fungi, bacteria, various microorganisms).
- Traumatic stomatitis - appears after trauma and injury to the mucous membrane inside the mouth. The resulting wounds become a gateway for infection (viruses, fungi or bacteria).
- Internal ill health of the body - vitamin deficiency, digestive diseases, dysbacteriosis after the use of antibiotics. These factors lead to a decrease in immunity and disruption of the microflora of the oral cavity, which creates conditions for further infection.
- Medicines or unsuitable toothpastes that reduce the local immunity of the oral cavity. For example, toothpaste with sodium lauryl sulfite reduces salivation and dehydrates the oral cavity. As a result, the oral mucosa becomes vulnerable to acids, bacteria, and viruses. Diuretics have a similar effect; they reduce saliva production.
- Insufficient personal hygiene - eating dirty, unwashed fruits and vegetables, eating with dirty hands, poor cleaning of teeth and the formation of plaque on them.
- Chronic poisoning of the oral mucosa (for example, from smoking or when working in hazardous industrial production).
- Mouth breathing dries out the oral mucosa and makes it easier to become infected.
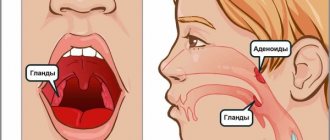
Inflammation and wounds can appear on any mucous surface - on the palate and tongue, on the cheek and inside of the lip, and even on the gum. The body's response to an infectious agent depends on the immune system. With weak immunity, stomatitis becomes extensive and forms deep wounds. If the immune system is strong, stomatitis can occur in a catarrhal form - without the formation of ulcers, in the form of superficial inflammation.
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis
A distinctive feature of this type of stomatitis is the appearance of so-called aphthae on the oral mucosa. These are small round ulcers with redness at the edges, the touch of which causes unpleasant painful sensations. Often occurs as a result of the activity of microorganisms (in particular, staphylococcus). Treating aphthous stomatitis at home is only recommended if it is not caused by a more severe illness. Often aphthous stomatitis occurs with problems with the immune system, liver and gastrointestinal tract.
Treatment methods
- Allergy therapy.
- Antiseptic therapy (treatment of aphthae with anti-inflammatory solutions, gels and ointments).
- Dental treatment and sanitation of the oral cavity (after dental treatment, stomatitis occurs less frequently than in the presence of carious lesions).
- Immunotherapy.
- Diet.
Stages of stomatitis: catarrhal, ulcerative, aphthous
Stomatitis in adults is manifested by inflammation of the mucous membrane and the formation of ulcers. According to clinical symptoms, stomatitis is divided into catarrhal and ulcerative. Catarrhal stomatitis is the onset of the disease. It affects the superficial layers of the mucous membrane. With catarrhal stomatitis, the mucous membrane turns red, swells, and becomes covered with plaque. An unpleasant odor from the mouth is formed. Catarrhal form is the initial stage of any stomatitis ( infectious, microbial, allergic, etc.
).
Ulcerative stomatitis affects the entire thickness of the mucosa. They can occur independently (for example, as a result of a herpes infection) or be the result of untreated catarrhal stomatitis. With ulcerative stomatitis, deep wounds are formed throughout the entire thickness of the mucous layer. Lymph nodes also enlarge, headache and fever appear. The smell becomes not just unpleasant, but rather putrid.
Note Ulcerative stomatitis often develops in people with diseases of the digestive system. The immunity and microflora of such patients are weakened, so the catarrhal form of stomatitis easily turns into ulcerative stomatitis.
A special form of stomatitis is called aphthous disease. This stomatitis often forms due to internal problems in the body ( gastrointestinal diseases, allergies
).
Aphthous stomatitis is accompanied by the formation of one or more large ulcers up to 1 cm in size (they are called aphthae). Aphthae have a round shape, clear boundaries with redness at the edges, are covered with a gray-yellow coating on top and are very painful.
After the aphtha heals, traces (scars) remain. Aphthous stomatitis often accompanies intestinal diseases. Canker sores often heal on their own, but are prone to recurring occurrences.
Types of disease
There are several forms of oral stomatitis in adults:
| Depending on the cause of appearance (causative agent) | According to external signs and clinical picture | According to the nature of the development of the disease |
|
|
|
Stomatitis acute and chronic
According to the nature of the manifestation of the disease, stomatitis can be acute and chronic ( recurrent
).
The acute condition corresponds to the full manifestation of symptoms: redness of the mucous membrane, its swelling, the formation of wounds and plaque. If the acute disease is not fully treated, and one’s own immunity is not strong enough, the pathogen remains in the oral cavity, and the inflammation becomes chronic and sluggish. With any decrease in immunity ( acute respiratory infections or acute respiratory viral infections, stress, antibiotics, hormones, pregnancy, malnutrition and vitamin deficiency
), microorganisms are activated and an exacerbation occurs.
Recurrences of herpetic stomatitis are especially unpleasant. They often accompany patients even after a complete (outwardly) cure. The herpes virus settles in the nerve endings of cells. A strong, healthy immune system limits the activity of the virus. With a temporary decrease in immunity, a relapse of the disease occurs.
In order to cure stomatitis, it is necessary to correctly determine its cause (source of infection) and the factor of decreased immunity. Incorrect identification of the infectious agent will lead to the wrong choice of drug. This means that the drug will be ineffective.
Healing agents
Drugs in this category are intended to accelerate the regeneration of damaged mucosa, providing a healing effect on ulcers.
Solcoseryl
The product is a dental paste that not only improves trophism, but also has a stimulating effect on the regeneration of damaged tissues.
For use in adults only. After eating, apply a small amount of the drug to the affected area using a cotton swab. The drug Solcoseryl is contraindicated during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Sea buckthorn and rosehip oil
The use of completely natural products significantly speeds up the healing process of the affected surface.
Used to lubricate ulcers and sores after meals up to four times a day.
Advice! For the treatment of uncomplicated stomatitis in children, it is recommended to use herbal remedies.
Olazol
The drug is a combined agent that, in addition to accelerating the regeneration of damaged tissue, also has an anesthetic and antibacterial effect.
The product includes:
- sea buckthorn oil;
- anesthesin;
- chloramphenicol;
- boric acid;
- lanolin;
- triethanolamine.
Olazol is contraindicated for use if there is an individual intolerance to one of the components of the product. The foam is applied to damaged areas of the mucous membrane using a cotton swab.
What does stomatitis look like in adults?
Primary diagnosis is based on examination of the oral cavity : the mucous surface of the cheeks (from the inside), palate, and tongue. It is necessary to analyze what color the mucous membrane is, if there is plaque, and in what sequence the wounds are formed. Based on the visible signs of stomatitis, the nature of the location of the wounds and their size, one can judge the source of infection. Is stomatitis viral, bacterial or fungal?
Here is a description of the different types of stomatitis, symptoms of an acute condition and characteristic signs of bacterial, fungal and viral stomatitis.
General recommendations regarding the use of tablets for stomatitis
Before starting treatment, you need to consult a doctor. The fact is that stomatitis can be of different etiologies - bacterial, fungal, viral. There are also forms such as radiation, allergic and chemical.
If a patient has an infectious disease of viral origin, and he takes tablets that are effective against fungal infection, the therapeutic effect will be weak. Only etiotropic treatment will help, which is almost impossible without preliminary diagnosis.
In order for tablets for stomatitis in the mouth to really help, and for the disease to go away within a few days, you need to take a smear and determine the type of pathogenic microorganism that caused the infection. It is better not to self-medicate, especially when it comes to the health of the child.
Also during treatment you need to follow the recommendations of specialists:
- Read the instructions carefully and do not violate the treatment regimen or exceed the dosage.
- Before taking the product, rinse your mouth with water or an aqueous solution of soda.
- The tablets must be taken exactly as indicated in the instructions. That is, you should not swallow or chew tablets if they are indicated to be dissolved.
- After taking the drug, you must refrain from taking any food or liquid for at least 60 minutes. Some medications are incompatible with substances contained in toothpastes, which can adversely affect the condition of your teeth.
Compliance with doctors’ recommendations will increase the effectiveness of therapy and you will cure stomatitis much faster.
Herpetic stomatitis
98% of the world's population is infected with the herpes virus. As a rule, infection with herpes occurs in childhood (chickenpox, oral herpes). Therefore, acute herpes stomatitis occurs more often in children, less often in adults.
Acute herpetic stomatitis in adults is a relapse. This disease develops with a seasonal decrease in immunity (spring and autumn), with the use of certain medications, poisoning, stress, and other unfavorable situations. In addition, the following factors contribute to a local decrease in immunity in the oral cavity and relapse of herpetic stomatitis:
- dental problems (plaque, tartar, caries);
- gingivitis (inflammation of the gum edge) and periodontitis (inflammation of the gums);
- inflammation of the nasopharynx (sinusitis, tonsil infection);
- mouth breathing;
- smoking.
Acute herpetic stomatitis and its relapse begin with redness of the oral mucosa. Afterwards swelling appears. They itch, burn, tingle. Already in the initial period of herpes stomatitis, enlarged lymph nodes can be felt (the herpes virus multiplies in the nearest lymphatic formations). After a couple of days, a cluster of bubbles appears at the site of the swelling. Blistering rashes inside the mouth are located in groups. Each bubble contains liquid.
After another two or three days, the bubbles burst and turn into wounds that merge with each other. The red surface of the wounds quickly becomes covered with a yellow-white coating.
This pattern is typical for the formation of a herpetic rash. In any part of the body (in the groin, on the lips or inside the mouth), herpetic rashes always form in the same way: first itching, then accumulations of small blisters, and then their merging into one wound.
Herpes stomatitis is painful. Difficulty eating, drinking, speaking (moving your tongue). Herpetic disease lasts up to 2 weeks and can be accompanied by general intoxication (weakness, malaise, muscle pain and headache). With low immunity, the temperature may rise.
Important: when diagnosing yourself, do not confuse herpes stomatitis with aphthous stomatitis. Their visible signs are similar in the late stage, when a large ulcer has formed. In the initial stage, herpes consists of small blisters. Treatment of herpes and aphthous stomatitis are different!
Often herpetic stomatitis is accompanied by inflammation of the gum edge - gingivitis. The gums along the teeth and the gingival papillae (the elevations between the teeth) become bright red and increase in size (swell).
Antiviral drugs
The most common cause of stomatitis is the herpes virus. Transmission occurs by airborne droplets. Sometimes household transfer of media is also possible. Here treatment must be carried out using antiviral agents.
Viru-merz Serol
The drug has a gel-like form. The active substance of the drug, tromantadine, is very active against the herpes virus.
Even after a single use, there is a significant reduction in the main pain sensations, as well as itching and burning. Ulcers and aphthae must be treated 2-3 times a day.
Bonafton
Since herpes stomatitis quite often forms on the lips, Bonafon is perfect for treating painful sores. The product is available in the form of an ointment. The active substance of the drug is bromonaphthoquinone. Damaged areas must be treated with the product 3-4 times during the day, leaving the ointment on for 5-10 minutes.
Acyclovir
Another antiviral ointment widely used in the treatment of herpes stomatitis. To relieve symptoms, damaged areas should be treated every four hours. Duration of treatment is 5-7 days.
Herpes stomatitis in adults: treatment
Treatment of herpetic stomatitis in adults uses antiviral agents and immunomodulators, as well as disinfecting rinses and wound-healing drugs. Herpes stomatitis differs from other types of disease. If in case of bacterial or fungal infection you can get by with rinses and gels, then the treatment of herpes stomatitis is more difficult. It is effectively suppressed only by antiviral drugs (internally and externally).
Antiviral drugs in tablets
The greatest effectiveness of antiviral drugs in the treatment of herpes stomatitis is achieved by early initiation of treatment (if the drug is started immediately after the burning sensation appears). Antiviral agents are used for the first 3-4 days
, until the bubbles burst and merge into a common wound. After the formation of erosions, taking antiviral drugs is ineffective; wound healing and regenerating gels are needed. How is herpetic stomatitis treated?
- Famciclovir is the most effective antiviral drug. Taken 1 or 2 times at the onset of the disease. For a single dose, the dose is 1500 mg, for a double dose - 750 mg every 12 hours.
- Valaciclovir is also taken during the first day of illness: 2000 mg every 12 hours.
- Acyclovir is characterized by the least effectiveness and low price. 60% of herpes virus strains are insensitive to acyclovir. Acyclovir is effective for primary herpetic stomatitis. In case of recurrent infection, stronger analogs are needed (valaciclovir, famciclovir).
Immunomodulators
Treatment of herpes stomatitis in adults is ineffective without means of boosting immunity. Therefore, immunomodulators are necessarily used.
Viferon is a complex drug, an immunomodulator and an antiviral agent. It contains human interferons and vitamins C, E. The effect of Viferon is manifested in a complex - it strengthens the immune system and counteracts the virus. Such a complex medicine is necessary for the treatment of herpetic stomatitis.
Viferon is available in the form of suppositories, ointments and gels. Suppositories are administered rectally (through the anus), absorbed into the blood through the intestinal walls and affect the entire body as a whole. Gels - used for local treatment of the oral mucosa. They are applied to the affected areas of the mucosa up to 4 times a day after preliminary drying (wiping the mucosa with a gauze swab). The treatment period is up to 7 days.
For the treatment of herpetic stomatitis, ointments and creams are not used, since they cannot be fixed on the mucous membrane for a long time.
Important to know: Viferon is effective only for herpetic stomatitis (the presence of a viral infection). This drug is ineffective for aphthous disease.
Other immune stimulants:
- Immudon is available in the form of lozenges. The course of treatment or prevention takes 20 days, up to 6 tablets of the drug must be dissolved daily;
- Amiksin is also available in tablet form. For a viral disease, adults take 1 tablet of 0.125 mg on the first and second days, then 1 tablet every other day. In total you need to take 20 tablets;
- Vitamins.
Antiviral rinses and gels
When treating herpes stomatitis in adults, the pathological virus is affected through the blood (general means - tablets) and place (rinses and ointments). The rinse solution used must have an antiviral effect. Miramistin is used for this. This remedy is effective against various microorganisms, and is especially effective against the herpes virus. Rinse your mouth with Miramistin solution 4 times a day for 1 minute. After rinsing, the mucous membrane is wiped with a gauze swab and Viferon-gel is applied (an immunostimulant and antiviral agent, which we discussed above).
It is important to know: simply disinfecting infusions and preparations are not effective in treating herpetic stomatitis. Therefore, for herpes in the oral cavity, do not rinse with herbal infusions or chlorhexidine.
Home remedies for stomatitis
Home treatment of stomatitis is based on natural components with bactericidal properties and alcohol-based medical antiseptics - it serves as an auxiliary therapy. The use of alcohol-containing products must be agreed with a doctor.
Recipes:
- Sea buckthorn berry oil. Apply to a sponge and apply to the affected areas of the mucous membrane or rinse your mouth with oil.
- Bactericidal decoctions of chamomile and sage. Mix the ingredients in equal proportions. 2 tbsp. l. Brew the mixture with 300 ml of boiling water, leave for an hour. Rinse your mouth 4-5 times during the day.
- White cabbage juice. Using a juicer, squeeze out the juice and dilute with boiled water 1:1. Rinse your mouth between meals.
- Methylene blue (blue). Medical alcohol antiseptic has antiparasitic, bactericidal, antimicrobial properties. It has no contraindications and can be used from infancy. For aphthous and ulcerative stomatitis, blue medicine disinfects and heals erosions in the oral cavity. Before using the bluing, remove plaque from canker sores and papules using a bandage soaked in an aqueous solution of soda. A cotton swab is dipped in blue and the affected areas are spot-treated 5-8 times a day.
- Honey-garlic mixture. The garlic is squeezed through a press, an equal amount of liquid honey is added, and mixed. Between meals, keep the paste in your mouth for several minutes.
- Calendula tincture with alcohol. A pharmaceutical bottle of tincture (25 ml) is designed for 5 uses. Dilute 1/5 part in a glass of water. Use the solution to rinse the mouth
A paste of garlic and honey is enough to place in the mouth for a few minutes.
Folk remedies are not used if there are allergic reactions to the ingredients of the recipe.
Allergic stomatitis: symptoms in adults
During an allergic reaction, the mucous membranes swell. Their blood supply is disrupted, causing dryness, itching or burning. Color changes and redness are possible. Allergy itself is not the cause of stomatitis. It reduces immunity, disrupts mucous microflora, resulting in infection. The causative agent of the infection determines the name of allergic stomatitis: allergic viral, allergic bacterial.
The main treatment for allergic stomatitis is to protect the body from exposure to the allergen (food product, household chemicals, cosmetics). After eliminating contact with the allergic substance, anti-inflammatory and anti-infective therapy is carried out. That is, they destroy the infection and treat inflammation.
The principle of action of the tablets
In most cases, tablets help to eliminate the clinical symptoms of the disease at any stage of its development as quickly as possible. The active substances of drugs have a negative effect on infectious agents and also have a beneficial effect on the oral mucosa.
Tablets for stomatitis in the mouth have the following effects:
- The inflammatory process is stopped.
- The activity and reproduction of pathogenic microflora is suppressed.
- The balance of the natural microflora of the oral cavity is restored.
- The severity of symptoms such as hyperemia, bleeding, and swelling of the mucous membrane is reduced.
- The pain syndrome becomes less intense.
- The mucous membrane is restored to its normal state, the number of ulcers and erosions decreases, and inflammation gradually disappears completely.
- Local immunity increases.
As a result, within a few hours after the start of treatment, the patient’s condition improves. After 1-2 days the situation stabilizes and by 5-7 days stomatitis is completely cured.
Aphthous allergic stomatitis
Aphthous stomatitis often occurs due to allergies. It is difficult to cure with antiseptic rinses alone. It is necessary to remove the cause that caused the disease - an allergen or a digestive disease. Therefore, if aphthous stomatitis occurs, you need to prescribe a diet for yourself: exclude citrus fruits, honey, red berries, chocolate from the menu, adjust medications (if they are taken), take antihistamines (anti-allergic) drugs (Suprastin, Diazolin, Claritin, Tavegil)
.
Further treatment of aphthous stomatitis uses disinfecting rinses and gels:
- Stomatophyte is an alcoholic extract of medicinal herbs (chamomile, sage, calamus, oak bark, mint). The drug contains alcohol and therefore cannot be used in the treatment of children, pregnant women and persons driving a car. Rinse your mouth with stomatophyte several times a day; for rinsing, the alcohol infusion is diluted in a ratio of 1:10. Stomatofit A (gel form of the drug with an anesthetic component) is widely used in the treatment of aphthous stomatitis.
- Miramistin is a solution for rinsing.
- Cholisal-gel is an antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory drug. It is ineffective against viral diseases. But it is widely used for the treatment of aphthous stomatitis, as it has an analgesic effect.
The gel is applied to the affected surface of the aphthae after rinsing. Thus, combine rinsing with Stomatofit and gel Stomatofit A. Or rinsing with Miramistin and Cholisal gel. To speed up wound healing, a regenerating gel is used - Solcoseryl.
Another cause of aphthous stomatitis is staphylococcal bacteria in dental plaque and cavities. Therefore, to prevent the formation of large aphthae, sanitation of the oral cavity is necessary - cleaning teeth from stone, plaque and treating all carious holes.
Healing medicines for stomatitis
Drugs that can heal mucous membranes should be included in therapy for stomatitis. They accelerate the healing of ulcers and do not allow them to grow, covering a large area.
No. 1. Imudon
Dispensed in tablets that need to be dissolved. The medicine contains special bacteria that accelerate the production of antibodies. The latter inhibit the activity of pathogenic microflora. The ulcers heal quite quickly if the tablets are used once every 2-3 hours. The duration of therapy is 7-10 days.
No. 2. Sea buckthorn oil
Stomatitis is treated with sea buckthorn oil. It speeds up the healing of mouth ulcers in adults. Preparations containing it are effective and affordable. It is enough to apply the oil to the affected mucous membranes 5 times a day using a cotton swab. After all manipulations, it is forbidden to eat or drink for several hours.
No. 3. Solcoseryl
Since the ointment has a greasy base, for stomatitis it is applied only to the inside of the lips and facial skin (if these areas are affected). The product will not adhere to the wet side of the cheeks. It is advisable to apply the ointment to dried sores. The product is also available in gel form. It is used to treat wet wounds.
Ulcerative-necrotizing stomatitis
This form of stomatitis is characterized by extensive ulcers and necrosis (death) of gum tissue. It is rare and requires medical treatment. First, the mucous membrane becomes dry, and gum bleeding appears. Then the temperature rises and a putrid smell from the mouth appears. Ulcers appear on the gingival papillae (the elevations between the teeth). Ulcers on the papillae become covered with plaque. The inflammation spreads to the tongue, palate and inner surface of the cheeks.
Antibiotics and antihistamines are used to treat necrotizing ulcerative stomatitis. One of the reasons for the necrotic process on the oral mucosa is allergic reactions of the body.
Treatment of ulcerative stomatitis
Ulcerative stomatitis very often occurs due to poor oral hygiene and bad habits (especially smoking). Often this type of stomatitis at its onset is confused with periodontitis and gingivitis, since it is characterized by inflammation of the gums, a grayish coating around the teeth and death of soft tissues. Often accompanied by fever and fever. One of the few forms of stomatitis, which often requires treatment by a doctor, and in the most advanced cases, surgical intervention.
Treatment methods
- Antibiotic therapy.
- Antibacterial treatment of affected areas.
- Surgical intervention (in severe cases, removal of areas of dead tissue and gum grafting).
Candidal stomatitis
Candidal stomatitis is a type of fungal disease of the oral cavity. The causative agent - Candida fungus - is always found in the human body on its mucous membranes. Its growth and reproduction is inhibited by lactic acid bacteria (bifido, lacto). In some conditions, the balance of microorganisms is disturbed, bifidobacteria die and Candida multiplies uncontrollably on the mucous membrane. In the mouth, candidiasis forms a white or yellow coating, in the vagina - thick white discharge. The second name for candidiasis is thrush. It reflects the type of changes taking place: the mucous membranes are covered with white “milk”. The most common cause of candidal stomatitis (thrush in the mouth) is taking antibiotics.
In the initial stage of the disease, warning signs appear:
- dryness;
- burning in the mouth;
- swelling of the mucous membrane;
- redness of the mucous membrane;
- white or gray coating;
- thick white discharge;
- bad breath or bad breath;
- pain when chewing and talking.
White plaque in the mouth can lie on the mucous membranes completely or in spots. If the plaque is carefully removed (wipe with a cotton swab), then underneath it will be the red, inflamed oral mucosa.
How to treat stomatitis in adults at home?
Treatment of candidal stomatitis is based on preventing the spread of the fungus. Any fungal infections multiply in an acidic environment. To prevent their proliferation, it is necessary to reduce the acidity of the environment and change the acidic environment to an alkaline one. The most readily available home alkalizer is baking soda.
It is necessary to rinse your mouth with a soda solution after eating and wipe the areas where plaque forms, as well as your teeth. Often candidiasis is hidden not only in plaque on the mucous membrane, but also in deposits on the teeth. Concentration of soda solution for rinsing - 1 teaspoon per half glass of water (100 ml)
.
In addition to rinsing with soda, the mouth is washed and treated with a solution of borax in glycerin.
The folk medicine cabinet for the treatment of candidal stomatitis uses infusions of antiseptic herbs: chamomile, sage, oak bark, St. John's wort, calendula.
Pharmacy medications for stomatitis with candidiasis offer the following drugs:
- Chlorhexidine solution (0.05%) . Chlorhexidine stops the growth and division of Candida fungi. Rinsing can be supplemented with local treatment of inflamed areas (cotton swabs soaked in a medicinal solution).
- Candida - contains the active substance clotrimazole (antifungal component). The drug is applied with a tampon to the affected areas of the oral mucosa up to 4 times a day for 10 days.
- Diflucan.
- Iodinol (blue iodine) - for rinsing and lotions.
- Borax (borax solution in glycerin).
As well as vitamin complexes and immunomodulators.
Stomatitis in a child: what to do and how to treat it
The children's body is more sensitive to drugs and their effects on internal organs, so not all drugs for stomatitis can be treated in children.
To treat diseases of the oral mucosa in children, use:
- Acyclovir. An antiviral drug, an effective remedy for herpetic stomatitis in the mouth in children over 2 years of age. For patients under two years of age, the drug can be used, but with a dosage halved.
- Spray Miramistin. An excellent antiseptic. Additionally, it has an antiviral and bactericidal effect. During the treatment period, the mucous membrane is irrigated with a spray 3-4 times a day.
- Lollipops Imudon. A powerful immunomodulating agent for adults and children. Used for the treatment and prevention of disease.
- Viferon. Immunostimulating, antiviral medicine for stomatitis in the mouth. Contains vitamins E, C. Produced in the form of suppositories, gels, ointments of various dosages.
- Suprastin. Belongs to the category of antihistamines. Its analogs Diazolin and Tavegil are also used to treat children.
- Vitamin solution Aekol. Used locally and externally. Aekol should be smeared on damaged areas that have been cleared of plaque. A relatively cheap and effective drug.
- Lollipops Carmolis. Shows high effectiveness in the treatment of gum inflammation. They have anti-inflammatory, antiseptic, immunomodulatory and antiviral effects. Can be used to reduce pain. The lollipops are inexpensive and suitable for children and the elderly.
It is allowed to use cheap and natural folk remedies in treatment, but this must be done after consultation with a doctor. Please note that such medications act as auxiliary, but not primary. Treating stomatitis with folk remedies alone is ineffective.
At the first symptoms of the disease, contact a specialist. This will help quickly cure the disease and prevent the development of complications.
Microbial carious stomatitis
Microbial stomatitis is a concomitant disease. It manifests itself during the development of infectious diseases. Let's give examples.
Signs of stomatitis in adults often appear due to dental problems ( caries, tartar, dental plaque
).
Plaque and open cavities are sources of infection. They multiply carious bacteria (staphylococci, streptococci). The oral mucosa is attacked by pathogens. When the mucous membrane is injured (biting, food burns), coccal caries infection causes stomatitis.
Stomatitis may accompany a sore throat or scarlet fever. With scarlet fever, a dense white coating appears on the tongue, which disappears after four days and reveals a bright red mucous surface.
. Such microbial stomatitis in scarlet fever is bacterial.
With purulent sore throat, the tongue is also covered with a dense white coating (the tongue is said to be “coated”). After this, inflammation can spread to the gums, they become bright red, swell, and hurt.
To effectively treat bacterial stomatitis, use antiseptic rinses (antiseptic herbs or pharmaceutical chlorhexidine solution).
Chlorhexidine - has high antimicrobial activity (higher than its analogue - Miramistin). After rinsing, chlorhexidine leaves a thin film on the surface of the mucous membrane, which continues its therapeutic effect. Chlorhexidine is effective specifically for bacterial and fungal stomatitis and provides almost no relief for viral diseases.
Other antimicrobial agents: chlorophyllipt, oxolinic ointment, blue or methylene blue.
Note It is important to know: the course of treatment with chlorhexidine should not exceed 10 days so as not to cause dysbiosis of the oral cavity.
Drug groups
Various medications are used in the treatment of stomatitis in adults. This:
- anesthetics;
- antibiotics;
- disinfectants and antiseptics;
- antiviral;
- antifungal;
- cell regeneration stimulators;
- antiallergic.
Traumatic stomatitis
Injuries to the mucous membrane cause infection and the development of stomatitis. The most common causes of injury are burns from hot food or drink, accidental biting, injuries from fish bones, scratches from chipped teeth, poorly fitting dentures, braces, and mechanical damage from sharp objects.
The visible signs of traumatic stomatitis depend on the nature of the infection - bacteria or virus. Traumatic stomatitis can be bacterial (then it is treated with antibactericidal rinses) or viral (then antiviral drugs are used - Miramistin, Viferon, Famciclovir).
Causes of stomatitis
Stomatitis can develop under the influence of the following factors:
- Viral and bacterial diseases, for example, scarlet fever, herpes simplex virus type 1.
- Insufficient or unbalanced nutrition. The diet of a healthy person should be balanced, enriched with vitamins and minerals. The daily menu must include foods rich in B vitamins, iron, zinc, protein, and folic acid.
- Injuries. Stomatitis can be caused by various types of trauma to the oral mucosa. Mechanical damage is possible when eating rough food, in the presence of sharp edges of artificial crowns or tooth fragments. Thermal - when consuming very hot food or drinks. Chemical - due to burns with acid or alkali.
- Incorrectly selected, incorrectly installed or made from allergenic materials dentures.
- Neglect of hygiene rules: washing hands, fruits, vegetables.
- Decreased immunity due to long-term treatment with antibiotics, chemotherapy, and other aggressive methods of therapy for cancer.
- Frequent use of toothpaste with sodium lauryl sulfate.
- Anemia, hormonal pathologies, gastrointestinal diseases, dehydration.
- Allergic reactions.
If symptoms indicating stomatitis occur, there is no need to try to diagnose the disease yourself and treat it at home. Stomatitis is a rather insidious disease, so it must be treated under the strict supervision of a specialist.
Antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory medications for stomatitis
For bacterial stomatitis, drugs are used to help fight microbes and inflammatory processes. Complex preparations restore the optimal balance of microflora and heal wounds of the oral mucosa.
Lugol spray
It is an aerosol that is used 4-6 times a day. The spray should be sprayed pointwise, with one click. The aerosol is not recommended to be swallowed. If a significant portion of the spray gets inside, you should consult a doctor. The active ingredients of the aerosol are potassium iodide and glycerol. Molecular iodine in the spray is effective in combating bacteria and fungi.
The average cost of the drug is 120 rubles.
Contraindications for the use of the spray include:
- pregnancy;
- lactation;
- chronic liver and kidney diseases;
- dermatitis herpetiformis;
- thyrotoxicosis.
Be careful! In case of overdose, it is possible to burn the mucous membranes of the cheeks and lips. You should strictly follow the instructions and use the medication as directed.
Vinylin
A complex drug that fights microorganisms, has an anti-inflammatory effect, and promotes the regeneration of mucosal tissue.
Vinylin is presented in the form of a viscous balm (also known as Shostakovsky's balm), which is rubbed into the lesions using a cotton swab. The balm is applied before bed and after meals 3 times a day.
Miramistin
It is a ready-made solution for rinsing. Treatment must be carried out within 7 days.
Rinsing should be done at regular intervals 4 times a day. It is recommended to carry out the procedure after eating.
When the solution comes into contact with the oral mucosa, a slight burning sensation may be felt.
The average price of the drug is 220 rubles.
Folk remedies
Treatment of stomatitis at home should be carried out as prescribed by a doctor, who will take into account the causes of the disease and the general condition of the body. After eliminating the cause, he will prescribe rinses, ointments, gels, and multivitamin preparations.
- Hydrogen peroxide. Rinse your mouth with 3% hydrogen peroxide diluted in the same amount of water 2-3 times a day for one to two weeks.
- Blue iodine. Dilute blue iodine in a 1:1 ratio with warm water. Rinse your mouth with a glass of water 3 times a day. Apply gauze bandages moistened with blue iodine to the affected areas for 5 minutes. Treat stomatitis with this method 3 times a day.
- Propolis tincture. After eating, rinse your mouth with hot water and then hydrogen peroxide to thoroughly clean out the sores. Some additionally dry them with warm air using a hairdryer. Then lubricate the affected areas with alcohol tincture of propolis diluted with water and dry again with warm air so that a film forms more quickly.
- Myrrh oil. As legend has it, ancient Greek warriors did not go on a campaign without a paste of myrrh resin. Thick oil prevents the spread of infection, treats various skin lesions, helps with coughs and colds, and has an anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effect for bacterial and viral lesions.
- Silver water. Used to treat stomatitis in children and adults. Rinse your mouth with warm water several times a day. To prepare silver water, place a silver item in water at room temperature for a day.
- Honey. Brew 1 tsp. green tea with a glass of boiling water in a teapot, leave for 45 minutes, strain. Melt 1 tbsp in a water bath. honey, add to green tea infusion. Rinse your mouth several times a day with warm infusion to treat stomatitis.
- Blueberry. Brew 0.5 liters of boiling water with 3-4 tablespoons. blueberries, cook for 15 minutes over low heat with the lid closed, let cool. Rinse your mouth with a decoction for stomatitis or irritation of the mucous membrane.
- Get 1 tsp. freshly squeezed onion juice, 1 tsp. Kalanchoe juice, add 3 tbsp to the juice mixture. water. Rinse your mouth several times a day.
Symptoms and causes
We list the main symptoms of stomatitis:
- sometimes there is a fever of up to 40 degrees;
- profuse drooling;
- refusal to chew and consume food, especially salty food, such foods further irritate the mucous membranes;
- bad breath;
- small sores, localized in groups or one at a time.
Causes of stomatitis:
- violation of the rules of hand and oral hygiene;
- insufficient protein intake;
- poorly fitted dentures;
- various oral injuries;
- allergies to certain medications;
- bacterial, fungal, viral infections;
- severe anemia;
- radiation exposure.
Healing of ulcers
The healing process may take too long. Bacterial plaque often appears on the oral mucosa, preventing normal treatment. To prevent the chronic form of the disease from developing, you need to cleanse it. For this purpose, antibacterial pastes are used, which are freely sold in pharmacies.
Stomatitis is accompanied by severe pain in any manifestation. This applies to severe cases with a large affected area and separately localized ulcers. The disease is accompanied by edema and swelling of the gums, and the appearance of aphthae on the mucous membranes. Eating is complicated by these tumors; you need to chew well.
Solid food injures inflamed gums and the inner surface of the cheeks, and it becomes painful to talk. Severe stomatitis occurs in children and often occurs due to neglect of oral hygiene rules, lack of B vitamins and folic acid in the body. This often occurs after illness and treatment with antibiotics.
Stomatitis is always accompanied by high fever, swelling and ulcers make it difficult to swallow and chew food. New growths are white and bright red, their sizes vary. They may not appear immediately after infection, but after some time. This circumstance complicates the early diagnosis of the disease. At first, stomatitis may be felt as discomfort in the oral cavity and may not manifest itself clearly.
This infection is contagious, so the sick person should use separate utensils and limit contact with others so as not to expose others to the risk of infection. This is especially true for the safety of children and those who are at risk, for example, those who have recently had a cold.
Diagnosis of stomatitis
A dentist should tell you how to treat stomatitis in adults in the mouth, and to determine the type of disease and prescribe effective treatment, a thorough diagnosis is carried out. When a patient contacts, the dentist studies the medical record and conducts an examination. Sometimes this is enough to determine the clinical picture of the disease.
But in order to determine the type of stomatitis, the causes of its occurrence and the connection with other pathologies in the body, the following tests are prescribed:
- simple blood and urine test, blood biochemistry test;
- stool analysis for dysbacteriosis;
- oral swab for bacteriological culture from the affected area;
- PCR diagnostics for fungal infection and herpes virus.
To exclude diabetes, in which stomatitis is a common concomitant symptom, a blood plasma glucose test is prescribed. If a severe weakening of the immune system is suspected, immunological tests are prescribed. If the patient has frequent relapses, the doctor recommends undergoing an ultrasound of the gastrointestinal tract, liver, and checking the condition of the ENT organs with an otolaryngologist.
Types of stomatitis
Let's look at the main types of the disease:
Catarrhal stomatitis . Pimples form on the mucous membrane due to caries, plaque, and poor brushing of teeth. Dysbacteriosis also provokes this condition. Redness in the mouth also indicates problems with the gastrointestinal tract or the formation of worms.
The ulcerative form is always more advanced. New growths appear in the mouth, and the disease can develop independently. Pain is felt while eating.
On the mucous membrane, the lesion appears completely, a high temperature of up to 38 degrees appears, the lymph nodes dilate, and a migraine appears. More often, people with ulcers, heart patients, and people with intoxication in the body after poisoning are susceptible to this disorder.
Candidal stomatitis manifests itself in the form of a fungus. It is more often diagnosed in children and the elderly. The main cause of such lesions is infection and the use of antibacterial agents. Candidal stomatitis can be contracted from another person.
Patients develop a light coating on the tongue and cheeks on the inside. Sometimes bleeding occurs. The sense of taste decreases or disappears completely. A burning sensation appears in the mouth and throat.
The herpetic form manifests itself in carriers of herpes infection. With a minor progression of the disease, a rash appears on the mucous membrane. With a complex form, swelling appears in the mouth, the lymph nodes dilate, the temperature rises, a lot of saliva is released, people often feel sick, it becomes painful to eat, and there is a burning sensation in the mouth. Herpes cannot be removed from the body by modern medications.
Aphthous stomatitis develops in acute or chronic forms. This is a serious illness that is provoked by rheumatism, allergies, viruses and gastrointestinal disorders. Aphthae appear in the mouth, covered with plaque, surrounded by swollen, reddened mucous membrane. The affected areas cause pain and weakness. Body temperature is always high.
Classification
Mouth ulcers, causes and treatment are determined primarily depending on the causative agent of the disease. There is a certain classification of the disease depending on what pathogen caused the white spots to appear. What stomatitis looks like in the mouth also depends to some extent on the pathogen.
| Type of stomatitis | Description |
| Viral | A consequence of infection by the herpes simplex virus (herpes stomatitis) Epstein-Barr (herpetic stomatitis). Such pathogens provoke the appearance of vesicular rashes containing clear liquid. Later, the addition of a secondary bacterial infection is noted. Then they open up and erosions appear. Similar mouth ulcers also appear with HIV. How to treat wounds is determined by the doctor, having found out the cause of the disease. |
| Bacterial | Manifests itself due to the action of staphylococci or streptococci. With this form of the disease, a purulent rash appears (easy to see in the photo), which subsequently quickly opens. As a result, ulcers and erosions form in the mouth. |
| Fungal | As a rule, it appears after a course of antibiotics with which the patient is trying to cure other diseases. Fungal stomatitis in the mouth, the photo of which clearly demonstrates a dense white coating, appears due to the action of the Candida fungus. After removing the white plaque in the mouth, painful erosions are observed on the tonsils. |
| Erosive | It appears after illness and is characterized by the occurrence of erosions. |
| Chemical | Consequences of burns produced by acid or alkali. Later, scarring and deformation of the mucosa occurs. |
| Ray | A consequence of radiation sickness also develops after chemotherapy. The patient develops erosions in the oral cavity, and the mucous membrane thickens in certain areas. |
Also, depending on concomitant diseases, syphilitic and streptococcal stomatitis are distinguished.
What helps in the treatment of stomatitis?
Compliance with the rules of oral hygiene and disinfectant rinses using herbal decoctions: sage, oak bark, chamomile and calendula.
How to quickly cure stomatitis? Solutions of chlorophyllipt and stomatophyte help well in relieving symptoms. It is more difficult for children to get rid of this disease due to the specificity of treatment methods and the localization of inflammation. Everything can be treated with medication; the virus can be defeated with the help of modern drugs and diagnostics.
It is important to treat stomatitis to the end, and not stop the procedure immediately after the condition improves . This threatens a new outbreak of the disease, then all treatment will have to start all over again.
After pain disappears and inflammation is relieved, it is recommended to take a course of restorative therapy, take vitamins, and strengthen the immune system to help the body become more protected and resistant to various viruses and infections.
Causes of stomatitis
Common current causes:
- untimely and poor-quality dental and oral hygiene;
- weakened immune system.
The main reasons for the appearance depending on the form:
| Catarrhal | Traumatic are divided into: 1. Mechanical:
2. Chemical – burns from chemicals, various types of acids, household chemical products 3. Thermal - burns from hot food and drinks |
| Infectious. Damage to the surface of the mucous membrane by microbes resulting from influenza, viral infection, measles, chickenpox. | |
| Symptomatic. Stomatitis as a concomitant symptom of the underlying disease. It is observed in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, nervous, endocrine and cardiovascular systems. | |
| Specific. Inflammation of the mucous membrane in certain diseases - tuberculosis, syphilis, leprosy. | |
| Aphthous | Herpes virus. When ingested, it causes the appearance and development of herpetic stomatitis. Relevant at the time of weakening of the immune system (during or after illness, with a lack of vitamins, frequent and prolonged drinking of alcohol and smoking) |
| Allergy. Irritants can be:
| |
| Genetic predisposition. According to statistics, if at least one of the parents has had stomatitis, there is a 90% chance of the child getting sick. | |
| Ulcerative | Lack of vitamins P, C and group B. According to research results, outbreaks of ulcerative stomatitis occur in the spring, when the body experiences an acute deficiency of vitamins. During the war period, the disease affected about 60% of the population. |
| Dental pathologies Caries, pulpitis, and tartar deposits create a favorable environment in the mouth for the development of bacteria, which leads to inflammation of the mucous membrane and the occurrence of stomatitis. | |
| Chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, throat and nose, and endocrine system provoke the occurrence of pathology. |
Treatment of stomatitis on the tongue in adults at home
Usually, treatment of the disease occurs at home, but in order to avoid complications, it is better to carry out home treatment after a preliminary examination by a doctor.
Methods to combat the disease depend on its degree and severity; in many cases, the complex use of medications is necessary.
When any of the listed types of stomatitis occur, oral irrigation and antiseptic methods are used to get rid of infection and disinfection:
- furatsilin;
- 0.05% chlorhexidine solution;
- 1.5% hydrogen peroxide solution;
- miramistin;
- 1% clotrimazole solution.
- 5% borax solution.
Ointment for stomatitis: classification, names of the best drugs
All topical remedies for stomatitis in the oral cavity can be divided into antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, universal and analgesic , necessary for local anesthesia. Therefore, before starting to use them, you need to decide on the type of disease. If fungal dental sores in the oral cavity are treated with antiviral ointment, the disease will continue to progress, which is fraught with the development of complications: tonsillitis or pharyngitis.
The type of disease is determined by the doctor based on a visual examination of the patient. Laboratory tests are carried out very rarely and only for the purpose of differential diagnosis.
Anesthetics
Painkillers do not affect fungi, bacteria and viruses. They are prescribed for stomatitis only to relieve pain and only if the disease is caused by an allergy. Since many antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs have their own anesthetic effect, stomatitis therapy that includes them can be carried out without the use of an anesthetic.
Kalgel
Kalgel gel cannot be called a purely anesthetic, but it is usually used specifically for pain relief. It contains 2 active substances: cetylpyridinium chloride, which has antiseptic properties, and the anesthetic lidocaine.
This drug can be used to treat large canker sores and small ulcers on the oral mucosa in both adults and children.
Holisal against aphthae
In addition to a strong anesthetic effect, Cholisal has antipyretic, antipruritic and anti-inflammatory effects. It can be used for all types of dental diseases, even when treating children under one year old and pregnant women. The drug is fast-acting, applied to ulcers no more than 3 times a day.
Solcoseryl
Solcoseryl is available in the form of a gel and ointment. Saliva has virtually no effect on its absorption, so it is indicated for various diseases of the oral cavity. This effect is achieved thanks to the unique composition of the drug: it contains elements of the blood of calves.
Positive effects after using Solcoseryl:
- blood supply in the oral cavity improves;
- damaged tissues are healed;
- the structure of the mucous membrane is restored;
- collagen synthesis is stimulated.
After lubricating the canker sores with Solcoseryl, a person can eat and drink, since the product is insensitive to saliva and liquid. But before applying the drug, it is recommended to clean the affected areas of the oral mucosa from pus and dead particles for better absorption of the drug.
Lidochlor
Lidochlor is used for superficial treatment of ulcers. It has few contraindications, but is used with caution to treat pregnant women and young children.
The prescription of Lidochlor is especially important if, in addition to dental ulcers, the patient has tartar. Purely for local anesthesia, this drug can be applied only once every 2 days.
Kamistad
The active ingredients of this medicine are lidocaine and chamomile extract. The gel not only relieves pain well, but also promotes healing of the oral mucosa, relieves inflammation and destroys pathogenic bacteria. The drug is not used in the treatment of children under 3 years of age and pregnant women.
Instillagel
Instillagel is an effective analgesic and healing agent with chlorhexidine. This drug kills yeast, dermatophytes, gram-negative and gram-positive microorganisms. The anesthetic effect is achieved 5–10 minutes after applying the medicinal gel.
Antibacterial agents
Antibacterial therapy is indicated in case of detection of concomitant infections (not only in the oral cavity), ulcers with purulent contents, bacterial or necrotizing ulcerative forms of the disease. Most often, for inflammation of the oral mucosa, the following ointments and gels with an antibacterial effect are prescribed:
- Lincomycin.
- Metrogyl Denta, synthesized on metronidazole. After using this drug, you should not drink plain water or any other liquid.
- Tetracycline ointment.
- Gentamicin.
- Kanamycin.
The use of antibacterial ointment against stomatitis is permissible only for medical reasons.
Tetracycline ointment
The active substance of the drug is tetracycline. The product has a wide antibacterial spectrum of action and is contraindicated for mycoses and leukopenia.
The use of tetracycline ointment is not recommended for the treatment of children under 8 years of age. The medication is available without a doctor's prescription, but it should be remembered that it is an antibiotic and therefore should be used with extreme caution.
Lincomycin
Lincomycin ointment for treating the oral mucosa is used for diseases caused by the activity of aerobic and anaerobic gram-positive bacteria. The medicine belongs to the group of lincosamides.
Lincomycin has the ability to be deposited (accumulate) in dental and bone tissue, due to which the drug not only eliminates all ulcers on the oral mucosa, but also helps to avoid the addition of a secondary infection.
Gentamicin
Gentamicin should not be taken for too long, as this may cause pathogens to become accustomed to it. The product helps in the treatment of diseases caused by gram-positive and gram-negative aerobic microorganisms. Gentomycin ointment should not be used to treat stomatitis caused by anaerobic bacteria, viruses or fungi.
The therapeutic effect of the drug lasts for 8–12 hours, so it is recommended to apply it no more than 2 times a day. The medicine should not be used in the treatment of small children and pregnant women. In addition, it is contraindicated to use gentamicin in combination with aminoglycoside-based agents for treating ulcerative surfaces.
Medicines against mycosis
Treatment of candidal stomatitis involves the use of special antifungal agents. These include:
- Clotrimazole, which instantly suppresses the growth of fungus in the oral cavity, provided it is applied at least 3 times a day.
- Candida, which can be called an analogue of Clotrimazole.
- Nystatin ointment, used with extreme caution due to the large number of side effects.
- And also Pimafucin, Miconazole, Daktarin, Levorin.
Clotrimazole
Clotrimazole, prescribed for stomatitis, has an antimycotic effect and is most active against:
- yeast-like fungi;
- dimorphic fungi;
- dermatophytes.
Clotrimazole blocks the synthesis of nucleic acids, ergosterol and proteins, which disrupts the structure of the cell membranes of the fungus and kills pathogenic microorganisms.
Pimafucin
Pimafucin healing cream for stomatitis contains natamycin, a broad-spectrum antibacterial drug that destroys the cell membrane.
The medication is effective against most fungi, with the exception of dermatophytes. The duration of its use is determined individually, but after the symptoms have resolved, the affected areas should be lubricated with the product for another 2-3 days.
Antiviral drugs
Stomatitis is a reaction of the body that can be triggered by absolutely any virus. Typically, viral stomatitis develops against the background of other diseases (measles, herpes, influenza, chickenpox) and is treated in combination with the underlying disease. For these purposes, the following ointments and creams are used:
- Oxolinic ointment, which fights influenza and herpes viruses.
- Zovirax is an effective remedy for herpetic rashes.
- Acyclovir is a wound-healing drug suitable for the treatment of primary and recurrent herpetic stomatitis.
- Metrogyl denta.
- Viferon.
- Methyluracil ointment.
Oxolinic ointment
The active ingredient of the drug is oxolin. This medicine has virtually no contraindications, with the exception of individual intolerance to the components of the drug. Due to this, oxolinic ointment is often used to treat stomatitis during pregnancy and lactation, as well as in childhood. The drug is applied to the sores 3-4 times a day until complete recovery.
Oxolin has antiviral properties against influenza viruses, herpes zoster and herpes. Available in the form of an ointment containing 0.3% and 0.25% of the active substance. But to treat inflamed oral mucosa, only a product with 0.25% of the active substance is used.
Viferon
Viferon is a remedy that enhances immunity. Due to its absolute harmlessness, the ointment can be used in the treatment of adults and children without restrictions. The drug contains interferon α-2, which stops the process of HPV synthesis and protects the body from secondary infection.
The ointment is often used for stomatitis in children. Its use is most productive at the very beginning of the disease, when blisters have not yet formed, but itching and burning are already present.
Methyluracil
Methyluracil is a substance that improves tissue trophism and increases its regenerative properties. The drug stimulates nucleic acid metabolism in the oral mucosa, due to which aphthae heal quickly. Methyluracil is contraindicated in the presence of malignant and benign tumor formations in the body.
Drugs for the treatment of stomatitis
Sometimes the pain of ulcers greatly interferes with the patient’s ability to lead a normal lifestyle and eat. Therefore, the doctor may recommend the use of some effective anesthetic drugs, such as:
| Drug name | Mechanism of action |
| Anestezin | local anesthetic for superficial anesthesia, available in the form of tablets for forming powder and powdering the affected area. |
| Hexoral tabs | is available in the form of lozenges; the drug contains Chlorhexidine and Benzocaine, which have a local antimicrobial and analgesic effect |
| Lidocaine Asept | an antiseptic with a local anesthetic effect, quite often used for aphthous stomatitis and for the treatment of erosive lesions of the mucosa. |
| Lidochlor | a drug of combined action in the form of a gel, which has a local anesthetic and antiseptic effect, pain relief and antimicrobial action occurs 5 minutes after applying the gel. |
| Folk remedies | A decoction of sage, calendula, chamomile, and colanchoe juice is used for pain relief and the treatment of ulcers. |
In addition, treatment must include mouth rinses, ointments, sprays, gels, absorbable tablets, and lozenges with antimicrobial action.
Here is a list of current and effective drugs for treating stomatitis at home:
- "Actovegin" is a gel that is used for the initial treatment of ulcers.
- "Eucalyptus M" - lozenges.
- "Kameton" - spray and aerosol.
- "Cholisal" is a dental gel with a combined analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effect.
- “Vinilin gel”, “Lugol spray”, “Hexoral spray”, “Inhalipt spray”.
- Hexetidine (Stomatidin) is an antiseptic with weak analgesic and antimicrobial effects.
- “Evkarom”, “Ingafitol” - a collection for rinsing the mouth and inhalations, consists of eucalyptus leaves and chamomile flowers.
- “Kamistad” is a dental gel with an anesthetic and antiseptic effect; it contains chamomile and lidocaine.
Antiviral, antifungal, antihistamine drugs are used depending on the cause of stomatitis, for herpetic stomatitis in adults, treatment consists of the use of antiviral agents in ointments, tablets, for fungal origin of stomatitis (thrush) antifungal agents are used, antihistamines should also be used for allergic stomatitis , and with other types of lesions of the oral mucosa.
- Antihistamines - in tablet form “Fenistil”, “Claritin”, “Loratodin”, “Cetrin”, “Suprastin”, “Tavegil”.
- Antifungals - “Mikozon”, “Daktarin”, “Mikonazole” gel, “Levorin”, nystatin ointment.
- Antiviral - oxolinic, bonaftone ointment, interferon, tebrofen ointment, Zovirax, Acyclovir, Viru-Merz Serol.
Agents that accelerate epithelial healing:
- Rosehip and sea buckthorn oil have a healing effect.
- Karotolin is an oil solution intended for external use with an antioxidant effect, vitamin A.
- Propolis spray is an additional remedy for the treatment of stomatitis in adults, which has a beneficial effect in the presence of various skin lesions, herpes, and ulcers.
- Shostakovsky's balm, or "Vinilin" - helps cleanse wounds and accelerates tissue regeneration and epithelization, has an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect.
- “Solcoseryl” is a dental paste that improves tissue trophism and stimulates epithelial regeneration in cases of stomatitis.
Prevention of stomatitis
Stomatitis in adults is considered a recurrent disease, that is, it is prone to return and relapse. In order to prevent a recurrence of the disease, it is necessary to adhere to the rules of prevention:
- treat caries promptly;
- treat the gastrointestinal tract in a timely manner;
- wash your hands before eating;
- remove tartar and plaque in a timely manner;
- choose the right toothpaste and mouth rinse;
- Provide yourself and your loved ones with a healthy diet, with a balanced combination of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and microelements.
Stomatitis is not a terrible, but very unpleasant disease of the oral cavity. Its occurrence can be effectively prevented. And timely treatment helps to quickly relieve yourself of painful symptoms.