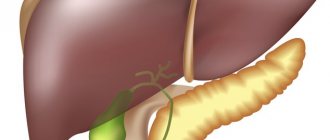
Even from school, many people know where the bladder is located, what it looks like and what its function is in the body. The bladder is an unpaired organ located in the lower abdomen, directly behind the pubic bone. It is one of the organs of the urinary system, which is responsible for the accumulation of urine from the body.
Innervation of the urinary organ allows you to form the urge to urinate, relaxes the muscles to drain urine and allows you to restrain its release for a certain period of time.
Where is the bladder located?
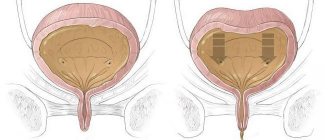
In humans, the bladder is located in the midline of the pelvis. The anterior wall borders the symphysis pubis, from which it is separated by a gap filled with loose fiber. The bladder is conventionally divided into four parts: the upper part, the body (middle part), the bottom - the lower expanded fragment and the neck, which, tapering, passes into the urethra. The location of the bladder varies depending on the degree of its fullness. When empty, it is located completely in the small pelvis. When filled with urine, the walls of the organ straighten and it rises above the pubis. At maximum filling, the top of the bladder reaches the navel.
The bladder is located mesoperitoneally relative to the peritoneum, that is, it is covered from above and from the sides by this serous membrane.
Prevention of cystitis
In the prevention of diseases of the genitourinary system, the main role is played by compliance with sanitary and hygienic rules and timely treatment of concomitant pathologies. To avoid bladder infections, you should:
- use hypoallergenic hygiene products;
- empty the bladder on time;
- change children's diapers promptly;
- eat a balanced diet;
- wear loose underwear;
- avoid hypothermia;
- exercise;
- wash your hands after every trip to the toilet;
- refuse casual sex.
Cystitis is a disease of predominantly infectious origin, which is accompanied by urination problems. At the initial stage it does not cause complications and is easily eliminated with medications. Therapy for acute inflammation takes no more than 7-10 days. Therefore, if you have difficulty urinating and pain in the suprapubic area, you should consult a doctor.
Features of the structure of the organ
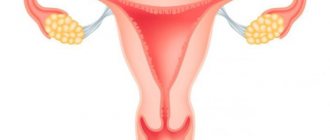
The shape and size of the bladder anatomy is somewhat different in men and women. For men it is spherical in shape and the volume reaches 700 ml, and for women it is in the form of an oval, placed horizontally, and the maximum capacity is 500 ml. Behind the posterior wall of the bladder in men are the final section of the large intestine - the rectum and vas deferens. The seminal vesicles are localized at the bottom. In women, the location of the bladder in the pelvic cavity determines its proximity to the genital organs - the uterus and vagina, which are delimited by a thin septum.
During pregnancy, the location of the uterus between the bladder in front and the rectum in the back can cause them to be compressed by the enlarged uterus and cause symptoms such as frequent urination and false urge to go to the toilet. The structure of the bladder is the same in both sexes.
The anatomy of the bladder is largely determined by its functions. Being a temporary storage for collecting urine (urine), its walls have increased elasticity, the ability to stretch and significantly increase in volume.
The structure of the bladder wall is multilayered, consisting of an inner layer - mucous, submucosal layer, muscle layer and outer shell.
- The mucous membrane of the empty bladder is folded, lined with a special transitional epithelium or urothelium, which is capable of changing its structure and depends on the stretching of the wall. It contains mucous glands and lymphatic follicles.
- Lymph nodes, blood vessels, and nerve receptors are distributed in the submucosa.
- The muscle layer is powerful, three-layered. The fibers in it are intertwined in three directions: circular, longitudinal and transverse. These muscle bundles form a single muscle of the bladder - the detrusor, which, by contracting, reduces the volume of the cavity, and urine pours out.
- The outer shell consists of connective tissue fibers.
The bottom of the bladder is secured in the pelvic cavity by fibrous ligaments and muscle bundles. In the frontal part of the fundus there are three openings: two from the ureters and one from the urethra. At the mouth of the urethra there is a sphincter that prevents urine from escaping. It is composed of smooth muscle and striated fibers. Smooth muscles are innervated by the sympathetic nervous system and contract involuntarily, while striated muscles contract from the spinal nerves. They open the sphincter only when the person wishes.
Diagnosis of inflammation
Confirmation of inflammation is possible after diagnostic studies:
- collection of anamnesis of inflammation;
- palpation of the abdomen - its lower zone (the patient feels discomfort and pain of varying intensity);
- urinalysis (UAM). In the presence of inflammation of the bladder, increased levels of protein, uric acid, red blood cells are observed in the urine, and mucus is present;
- general blood analysis. With a very violent infection, the level of leukocytes is greatly increased;
- biochemical blood test (BAC). When inflammation has spread to the kidneys, high levels of creatinine and urea are observed;
- examination by a gynecologist with collection of biomaterial for cytological, biological examination and PCR;
- Ultrasound. It shows the presence of inflammation by structural changes in the walls of the organ.
Functions performed
There are two functions of the bladder - temporary storage of urine and evacuation of it from the body. When the detrusor contracts, intravesical pressure increases and urine is removed from it. As the kidneys filter blood through the ureters, urine cycles into the bladder. The speed of filling is determined by several factors: the amount of water drunk, ambient temperature, and the emotional state of the person.
Evacuation of the contents of the bladder occurs when:
- contraction of the detrusor with significant overextension of the walls;
- stimulation of urethral mechanoreceptors when urine enters;
- irritation of the walls when the sphincter relaxes.
Normally, urination occurs 4-6 times per day.
The frequency of urination depends on food and water load, climatic conditions (cold, heat), and the condition of the pelvic organs and intestines.
The process of urination is very complex and is coordinated by the somatic and autonomic nervous systems.
When the bladder fills, its walls stretch, intravesical pressure increases, and baroreceptors are irritated. The nerve impulse follows to the brain, the person feels the urge to urinate. In the absence of pathology on the part of the detrusor and sphincter, a person is able to stop urinating for some time. Due to a signal from the brain, the detrusor contracts, and at the same time the sphincter relaxes, urine comes out. Normally, after urination, the bladder cavity contains up to 50 ml of residual urine. The sphincter closes when urine stops flowing into the urethra and the detrusor muscle relaxes.
Currently, four main bladder diseases have been studied and are widespread:
- Urolithiasis or urolithiasis.
- Cystitis.
- Neoplasms (benign and malignant).
- Secondary urinary disorders associated with other diseases.
Functions of the organ
There are 2 important functions: reservoir and evacuation. The reservoir function consists of the accumulation of urine flowing through the ureters from the pelvis with a frequency of 0.5 minutes.
The rate of urine flow from the right and left ureter may be different. The volume of fluid contained in the bladder depends on the amount of fluid that enters the body and the excretory capabilities of the kidneys. The time that urine is retained in the bladder depends not on the volume of incoming fluid, but on the speed of its inflow.
On average, the volume of the bubble is about 0.5 liters. In men, the organ capacity is greater than in women: from 0.35 to 0.75 liters, while in women this figure is from 0.25 to 0.5 liters. The desire to evacuate occurs when a fluid volume of 150-200 ml accumulates in the organ.
If the urine excretion process is disrupted, inflammation may develop - cystitis. This is the most common bladder disease. To reduce the likelihood of developing bladder diseases you should:
- maintain hygiene;
- prevent the development of diseases of the pelvic organs;
- avoid hypothermia;
- use linen made from natural fabrics;
- adhere to a healthy diet.
Urolithiasis disease
Urolithiasis is a common urological disease, the mechanism of development of which is not completely clear. Its widespread prevalence in society is explained by the consumption of poor-quality water, food and the negative influence of environmental factors.
Influencing factors
Factors influencing the development of urolithiasis are external (affect the body from the outside) and internal (physiological characteristics of the body).
External factors include:
- abuse of spicy, sour canned food with excess protein, which increases the acidity of urine;
- high content of calcium ions in drinking water;
- deficiency of vitamins B, A;
- long-term use of medications such as sulfonamides, steroid hormones, large doses of vitamin C.
Internal factors include:
- developmental anomalies of the urinary tract;
- lack of normal urine outflow due to obstruction (blockage) of the urethral outlet, infectious diseases of the kidneys and bladder (pyelonephritis, cystitis, urethritis);
- chronic pathologies of the digestive tract;
- intoxication;
- dehydration.
In the vast majority of cases, approximately 70-80%, stones are formed from inorganic calcium (phosphates, oxalates, carbonates), in 15% of cases - from uric acid - urates, in 5% of cases protein stones are formed.
Symptoms of urolithiasis
The clinical manifestations of the disease depend on the size and number of stones, as well as their location in the bladder. Sometimes stones are discovered by chance during an ultrasound examination of organs with other diseases.
If the stone is located at the mouth of the urethra and obstructs the passage of urine, severe pain occurs, intermittency of the urinary stream and the inability to completely empty the bladder. Stones moving through the bladder injure its walls. Hematuria (blood in the urine) appears of varying severity from microhematuria, diagnosed only by microscopy, to severe bleeding when the venous plexuses of the bladder are damaged.
If the stone is located near the internal sphincter, its incomplete closure occurs and, as a result, urine leakage occurs.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is based on medical history, patient complaints, results of laboratory and instrumental examinations.
Using bacteriological urine culture, pathogenic microorganisms and their sensitivity to various antibiotics are determined.
On ultrasound, stones appear as hyperechoic formations that move when the patient’s body moves.
Cystoscopy is a method that provides the opportunity to visually evaluate the mucous membrane of the bladder and foreign formations: stones, polyps, tumors.
The diagnosis is clarified using cystography, excretory urography and computed tomography.
Treatment
Some small stones and sand are freely excreted along with urine. If the stone is single, in the absence of symptoms, conservative therapy is prescribed: treatment with medications to alkalize urine (Blemaren, Xidifon, Potassium Citrate), and a diet is selected depending on the mineral composition of the stone.
If therapy is ineffective and there is a risk of complications, surgical methods for removing stones are used:
- Endoscopic lithoextraction.
- Stone crushing method, or cystolithotripsy - stones are crushed with a special instrument (laser, ultrasound), and small stone remains and sand are sucked out through a cystoscope.
- Removal of stones by open surgery - removal of stones is performed by suprapubic litholapaxy.
What is forbidden to do and what is possible in case of inflammation
For inflammation of the bladder and during treatment, women are not recommended to:
- apply a heating pad (a rush of blood occurs and inflammation is activated);
- put ice on your stomach;
- take a bath (with prolonged exposure to water, the mucous membrane becomes dry, and hot water increases blood flow, which provokes increased pain and activates inflammation);
- in the acute period, have sex (inflammation increases);
- use tampons during the acute period;
- swim in the pool, in open water.
Allowed for inflammation:
- take a warm shower;
- use pads during menstruation;
- adhere to the usual sports regime, go to the gym (but only during the period of follow-up treatment);
- you can have sex (when the acute period passes), but be sure to use condoms.
Cystitis
Cystitis is one of the most common diseases of the human genitourinary system. The frequent occurrence of cystitis in women is due to the specific anatomical structure of the urethra, which is about 5 cm long and 1.8 cm wide. Proximity to the anus and vagina determines easy infection by pathogenic microorganisms. Men suffer from cystitis much less frequently due to the structural features of the urethra: its length reaches 25 cm, and an infection that gets into the initial part of the urinary canal is more likely to cause urethritis in a man than cystitis.
Cystitis in most cases is caused by Escherichia coli, which belongs to the opportunistic microflora that lives in the intestines. Activated when immunity decreases, it is the causative agent of many infectious diseases, including cystitis.
Cystitis is also caused by other infectious agents: viruses, gonococci, streptococci, protozoa, and fungi. A feature of the inflammatory process in cystitis is that urine itself inhibits the proliferation of microbes, and even with a clear clinical picture of cystitis, when you suffer from frequent urge to go to the toilet and pain when urinating, there is never a significant increase in temperature. Human anatomy is designed in such a way that there is a close connection between the urinary system and the genital organs. Therefore, if fever occurs with such symptoms, it means that the infection has spread to other nearby organs (renal pelvis, in women - to the vagina, in men - to the prostate).
In addition to infection, cystitis can be caused by:
- Mechanical injuries.
- Burns – thermal, chemical.
- Food allergies.
- Tumors of the pelvic organs.
- Poor nutrition with a predominance of spicy and salty foods.
- Regular consumption of strong alcoholic drinks (vodka, whiskey, cognac).
- Hypothermia of the legs and pelvic area.
- Constant urinary retention in people of certain professions (drivers, dispatchers).
In women who are sexually active, cystitis often occurs after various types of unprotected sex (oral, anal), when the infection freely penetrates through the opening of the wide urethra, which opens in the perineum.
Symptoms of the disease
The most commonly observed symptoms of cystitis are:
- Usually, frequent urination begins (from several times an hour to every 5 minutes), after which there remains a feeling of incomplete emptying.
- Pain and pain in the urethral area, radiating to the groin and anus.
- Limited pain behind the pubis in the lower abdomen, which radiates to the back and perineum. The pain is nagging, aching, then stops, then intensifies again, especially at night.
- Lymphadenopathy (enlargement) of the inguinal nodes.
- Changes in the organoleptic properties of urine: the smell of ammonia, cloudiness due to a large number of impurities in the form of bacteria and mucus.
Diagnosis of cystitis is based on the patient’s complaints, the presence of red blood cells and leukocytes in the urine. With smear microscopy, it is possible to determine the causative agent of the disease, but not always if the infection is caused by a virus. In difficult cases, a serological test of blood serum is performed to detect antibodies against the pathogen.
An informational, safe and painless method is to examine the bladder using an ultrasound diagnostic device. There are several ways to carry out the procedure:
- Transabdominal, when ultrasound scans the organ being examined through the anterior abdominal wall.
- Transvaginal - performed in women when a sensor is inserted into the vagina.
- Transrectal, when a sensory device is inserted into the rectum.
- Transurethral - a probe is inserted into the urethra.
An unfilled human bladder is located in the small pelvis and is covered in front by the symphysis pubis. Dense bone tissue obscures it, and in this form it is impossible to scan it with an ultrasound sensor. When filled to the maximum, it rises above the womb to the navel and becomes available for examination.
Ultrasound reveals echo signs caused by inflammation of the bladder: a large number of tiny particles are concentrated in the organ cavity (epithelium from the walls, leukocytes, salt crystals), thickening of the walls and blood clots are noted.
Treatment
Therapy begins with the prescription of antibacterial agents to which microorganisms are most sensitive. These drugs include: Nolitsin, Monural, Palin, Furodonin.
To relieve pain and relax the smooth muscles of the dertrusor, antispasmodics Nosh-pu and Drotaverine are used.
Combined preparations based on the medicinal properties of plants can alleviate unpleasant and painful symptoms. Among the most effective are Canephron and Cyston.
For cystitis, a diet is recommended that includes limiting spicy, salty, and pickled foods. The diet should consist of dairy products, vegetables, and fruits. It is recommended to expand the drinking regime to include compotes and fruit drinks made from cranberries, blueberries, and lingonberries.
An attempt to independently treat cystitis leads to its transition to a chronic form, with an alternation of asymptomatic course and frequent exacerbations under the influence of unfavorable factors.
If the development of acute cystitis becomes chronic, it is necessary to prescribe longer courses of antibiotics, with a preliminary determination of the sensitivity of the pathogen to the drug. Considering the close connection between the urinary organs and the reproductive system, with inflammation in women - the vagina, uterus, ovaries, and in men - the prostate, the pathological process can also affect other neighboring organs. Therefore, simultaneously with cystitis, it is necessary to treat underlying diseases.
Types of inflammatory processes
Inflammation of the urinary tract is classified according to various criteria - origin, etiological factor, nature of changes in the wall of the organ. Along the way, cystitis occurs:
- Spicy. Accompanied by a pronounced clinical picture. In acute cystitis, there are complaints of severe pain in the affected area and dysuria - urinary disorders.
- Chronic. Symptoms are erased - pain is absent or mild, inflammation intensifies with a strong decrease in immunity.
Based on its origin, inflammation in the organs of the urinary system is divided into 2 types:
- primary – occurs independently due to local inflammation of the urinary wall;
- secondary – provoked by diseases, injuries, medical procedures, surgeries on the urinary tract, etc.
Depending on the etiological factor, 2 forms of the disease are distinguished:
- infectious – fungal, viral, bacterial, chlamydial;
- non-infectious - toxic, radiation, medication, nutritional, chemical.
Depending on the pathogen, infectious inflammation of the urinary tract occurs:
- Specific - provoked by pathogenic microorganisms that are not normal representatives of the microflora of the urinary system. These include gonococci, chlamydia, and Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
- Nonspecific - caused by the natural inhabitants of the urea microflora. Opportunistic microorganisms include staphylococci, candida, and streptococci.
Cystitis requires adequate and timely treatment.
It tends to become chronic, which is more difficult to treat. In its course, acute cystitis goes through 3 stages:
- Catarrhal is a relatively mild inflammation that is localized only in the mucous membrane of the bladder. Accompanied by moderate swelling and redness.
- Hemorrhagic - the submucosal layer along with the vessels is involved in inflammation. Damage to the capillaries leads to hemorrhages, which causes hematuria - blood in the urine.
- Ulcerative – ulcerations appear in the affected area, causing acute pain. In advanced cases, surgical intervention is required.
Inflammation of the bladder neck (cervical cystitis) is fraught with swelling of the mucous membrane, urinary tract obstruction and acute urinary retention. Sclerotic changes in the organ lead to its shrinkage.
Bladder neoplasms
Currently, benign and malignant neoplasms in the genitourinary system are widely diagnosed. Let's take a closer look at them.
Benign tumor
Benign tumors include tumors that develop from the epithelial layer - polyps, papillomas, and non-epithelial ones (fibromas, hemangiomas, neuromas), depending on the cellular structures from which the tumor was formed. The main reasons that provoke the tumor process are still unclear. The presence of occupational hazards (chemical production workers - varnishes, paints, gasoline) and prolonged stagnation of urine are recognized as significant factors. This is due to the presence of orthoaminophenols in the urine, which promote the proliferation of the urothelium that lines the urinary tract.
Men more often experience disturbances in the outflow of urine associated with compression of the urethra by the hypertrophied prostate, so the risk of developing tumor formations is higher in them than in women.
Bladder tumors such as polyps and papillomas can be single or multiple and exist unnoticed for a long time. The first signs are dysuria and the appearance of blood in the urine (hematuria). Dysuria, as a symptom, is associated with secondary cystitis and is manifested by increased frequency, difficulty urinating, painful false urges, and sometimes acute urinary retention. The characteristic pain is localized in the pubic area and groin, which intensifies at the end of urination.
A complication is torsion of the legs of the polyp or papilloma, which leads to disruption of their blood supply and necrosis. When the tumor ruptures completely, massive bleeding occurs.
The risk of papilloma malignancy in smokers increases significantly. Even removed papillomas are capable of frequent relapses.
To detect such neoplasms, modern diagnostic methods are used: ultrasound, cystoscopy, computed tomography (CT), taking a biopsy sample for histology.
Asymptomatic tumors are not treated; their development is periodically monitored with ultrasound and cystoscopy.
During the clinical presentation, papillomas and polyps are removed through the urethra using a cystoscope using the method of electroresection or electrocoagulation. The treatment regimen includes antibiotics, antispasmodics, and painkillers.
After tumor removal, dynamic monitoring of the patient is necessary: during the first year - once every 3 months with mandatory cystoscopy, then once a year.
Malignant tumor
Up to 95% of all malignant bladder tumors originate from epithelial tissues. Any part of the bladder can be affected.
One of the signs of oncology is that blood may appear in the urine, the urine looks like “meat slop,” and when a blood clot forms, acute urinary retention occurs. Pain is the next symptom when a tumor grows into the muscular and submucosal layers. It is localized in the pubic area, then spreads to the perineum and sacrum.
Diagnostics is carried out using the following methods:
- The cystoscopy method is used to examine the internal cavity of the bladder using an endoscope. You can determine which side the tumor is on using a contrast agent, which selectively accumulates in cancer cells. With special lighting of the place with the highest concentration, it begins to glow.
- Cytology of urine sediment, in which atypical cells are differentiated.
- A urine test for the presence of a specific VTA antigen, a test for nuclear matrix protein and others are not specific enough, their reliability is slightly more than 50%.
- Computed tomography is included in the mandatory list of examinations of patients with suspected infiltrative cancer to find distant metastases in the lymph nodes and pelvic organs. Since the bladder of men is located next to the prostate, metastasis can affect it too.
- The examination plan for cancer patients includes ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space, chest x-ray and excretory urography.
Treatment of diseases caused by malignant neoplasms depends on the stage, type of cancer, prevalence and degree of metastasis. Either minimally invasive surgery is performed in the form of transurethral resection of the tumor, or open resection of the pathological formation. The operation is performed as gently as possible so that bladder function is preserved.
The next stage is intravesical treatment with chemotherapy to prevent relapses.
For invasive forms of cancer, a radical method is used to completely remove the bladder, with a stoma placed on the anterior abdominal wall. Cystectomy in men is performed with the removal of the prostate and seminal vesicles; Women's uterus and appendages are removed.
If radical surgery is contraindicated, an alternative method of cystectomy is radiation therapy.
Urinary tract diseases, their causes and symptoms
Women are more susceptible to bladder diseases due to the characteristics of the body. However, its location, structure and functions, connection with neighboring organs are the cause of diseases in men as well.
Cystitis
This inflammation of the mucous membrane, mainly provoked by E. coli against the background of decreased immunity, appears more often in women. Among the signs: painful, frequent urination (up to 1 time in 5 minutes) or false urges, the appearance of blood in the urine, its turbidity, ammonia smell.
In the chronic form, manifestations are periodic.
Urolithiasis, or urolithiasis
The formation of calculi (stones) in the bladder occurs due to metabolic disorders, thyroid diseases, improper nutrition, and poor-quality water. Typical symptoms are dull aching pain in the lumbar region, intoxication, constant urge to urinate, the appearance of blood in the discharge, cloudy urine.
Leukoplakia
The disease, called “white plaque,” is an abnormal condition of the organ mucosa, the appearance of keratinized areas on it. The reasons are the penetration of infections into the bladder: gonococcus, mycoplasma, trichomonas, chlamydia. Symptoms are frequent urges, mainly at night, pain, burning after bowel movements, nagging pain localized in the lower abdomen.
Benign and oncological tumors
The reasons for the formation of hemangiomas, neuromas, papillomas, and polyps are still unclear, but in men they are caused by a hypertrophied prostate, which prevents the outflow of urine. The first symptoms are urinary retention, the presence of blood in it, and painful sensations in the groin. In the same way, cancerous tumors, diagnosed in only 5-10% of patients, make themselves felt.
SRMP
The causes of irritable bladder syndrome are nervous stress against the background of a constant negative environment. Signs of pathology:
- Frequent urination, but a small volume of discharge, despite a feeling of fullness;
- strong urges;
- pain when urinating, radiating to the perineum.
Hyperactivity
Urinary infectious diseases, neurological pathologies, prostate adenoma, prolapse of the vaginal wall, and neoplasms are often to blame for involuntary contraction of the detrusor. Manifestations: incontinence, frequent urination, including at night, an urge that cannot be tolerated.
Endometriosis
This is a rare pathology of the bladder, since the endometrium is the mucous membrane of the uterus. Sometimes it grows and reaches other organs. The cause is considered to be a hormonal factor. The symptoms are similar to those of cystitis: frequent urination, blood, flakes in the urine, pain in the pelvic area, urinary incontinence.
Atony
Provoke insufficient tone of the muscular lining of the bladder:
- menopause;
- nervous disorders;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- childbirth;
- injuries;
- cystitis.
Classic symptoms are incontinence, weak flow, the need to push hard, a feeling of insufficient emptying.
exstrophy
This is a birth defect in which the bladder is located outside the body. Both the anterior wall of the organ and the part of the peritoneum adjacent to it are missing. The specific causes of the anomaly are still unknown. It is believed that the risk increases if intrauterine infections appeared during pregnancy, the woman smokes, or takes illegal medications.
Polyps
The occurrence of these neoplasms is due to the uncontrolled growth of tissue on the inner lining of the organ. The cause of the phenomenon is unknown, but the predisposition of smokers and patients with cystitis has already been proven. Stagnation of urine is also in this category.
Polyps are typically asymptomatic. Rare manifestations include frequent urination, blood in the urine.
Cyst
This is a multi-chamber formation in the bladder duct - the urachus. It should heal by the 5th month of fetal development, but anomalies do occur. The reason for them has not been established. There is a version linking the pathology with impaired embryo development. Signs: intense pain during menstruation, problems with urination (incontinence), fever, constipation.
Diverticulum
Another anomaly is protrusion of the walls of the organ in the areas of the orifices of the ureters. Insufficient bladder muscle is to blame. The defect can be either congenital or acquired due to increased pressure inside the organ. Symptoms: long duration of emptying or complete retention of urine, discharge of blood and pus with it.
Weak bladder
It is synonymous with incontinence. Insufficient muscle tone provokes dysfunction. Causes:
- frequent childbirth;
- repeated infections;
- hernia;
- chronic constipation;
- stressful situations.
Signs: lack of control over urination, lack of urge and incontinence even with slight abdominal tension.
Omission
Cystocele - prolapse of the bladder - occurs in women due to insufficiently strong pelvic floor muscles or their overstretching. Anomalies are caused by structural features of the bladder (congenital muscle pathologies), long or multiple births, complications after them, heavy loads, tissue atrophy, and sudden weight loss. Symptoms: frequent urination, heaviness in the vagina, pain in the groin, back, and during sexual intercourse.
Urinary incontinence
Involuntary urination is of two types: false, when there is no urge, and true, if there is, but urine flows out without the participation of the patient. The culprits of the anomaly are increased intra-abdominal pressure, pathologies of the sphincter, bladder, ureters, impaired local circulation and central nervous system function.
Urinary disorders
Several reasons lead to disruption of the coordinated functioning of the detrusor and sphincter.
The neurogenic factor underlies diseases that cause damage to the central nervous system (CNS): brain and spinal cord injuries, Parkinson's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Other diseases not related to the innervation of the bladder: germination of a malignant tumor into the wall of the bladder, atony of smooth muscle muscles in old age, circulatory disorders.
Symptoms
Symptoms and treatment depend on the type of detrusor dysfunction.
With the hyporeflex type, the detrusor contracts weakly, and the hydrostatic pressure in the cavity is not enough to push urine out. Urine is poured out in portions, and a person has to strain to completely empty it. The muscles of the anterior abdominal wall are also involved. After the act of urination, the feeling of incomplete emptying persists. Such patients are not able to hold urine for a long time with a full bladder; they spontaneously release it.
With the hyperreflex type of detrusor dysfunction, frequent urination is characteristic, but the volume of urine released is small. In severe pathology, urgent urination syndrome is formed, when the urge is so strong that a person cannot tolerate it even for a short time.
Treatment
For diseases of the central nervous system, the underlying disease must be treated. To regulate the functioning of the muscular wall of the bladder, medications are prescribed that affect its receptors: either enhance or weaken the effect of neurotransmitters.
For hypofunction, acetylcholine blockers are used - Proserin, Kalimin. For hyperreflexia, Proroxan, Driptan, Sibutin are prescribed - drugs that act on the detrusor receptors and relax it. For pain relief, antispasmodics are prescribed - Nosh-pa, Spazmex.
The close interaction and location of the urinary and reproductive systems determined their unification into a single genitourinary system. Thus, the male urethra not only drains urine, but also delivers seminal fluid to the woman’s vagina during sexual intercourse. The external opening of the female urethra is located in the vestibule of the vagina. Because the genitourinary organs are located so close to each other, they are primarily at risk of infection.
The initial symptoms of diseases of the genitourinary system, including sexually transmitted diseases, are not specific (pain, pain when urinating, a slight increase in temperature). That is why, for proper diagnosis and treatment, you should consult a urologist, and women should also consult a gynecologist.
Epidemiology
The disease is diagnosed more often in women, which is associated with the hormonal and anatomical and physiological characteristics of the female body. Acute inflammation of the bladder is registered annually in Russia in an average of 30 million representatives of the weaker half, of which 35% experience a relapse within a year, and in 8–10% the disease takes on a chronically recurrent nature.
note
Inflammation of the bladder is more common in women of reproductive age, the second peak occurs over the age of 55 years, when postmenopause occurs.
Oncological diseases
Quite often, women are visited by such a terrible disease as bladder cancer. It is almost invisible and perfectly disguises itself as other diseases. That is why a benign disease turns into a malignant one, and this brings big problems to life. If you are at risk and at least 1-2 of the list of causes of diseases are familiar to you, do not be lazy to check the organ for the presence of a tumor in case of any discomfort. It's better to be a picky paranoid than a frivolous patient.
Very often, women suffer due to the fact that they are constantly faced with harmful working conditions. Printing house, waste recycling, chemical industry, gas enterprise - all this leads to an increased risk of cancer. The fundamental factors are considered to be the state of the environment and a history of previous diseases.
The most important reason that most often provokes the formation of a tumor is frequent contact with salts of heavy metals and amines and amino acids. This is typical for people who work or have worked in hazardous enterprises. Moreover, it happens that you left the chemical plant many years ago, and the tumor began to form only now. Therefore, if you have at least one dangerous enterprise in your work record, do not be lazy to go for preventive examinations at least once a year. This must be done constantly, because if necessary, expensive treatment is prescribed.
Cancer is caused by bad habits. Contrary to popular stereotypes, prolonged drinking can lead to more than just liver damage, and heavy smokers suffer from more than just lung cancer. All this together leads to a bladder tumor. Smoking has a particularly strong effect on the organ. Therefore, if you are a smoker who has discovered signs of any disease of the genitourinary system, contact a qualified specialist as soon as possible.
The tumor appears due to the presence of other bladder diseases. In particular, its formation can be provoked by untreated cystitis, which has turned into an acute form, especially if it appears due to kidney stones. An installed catheter may also be the cause.
Symptoms of the disease often appear when it is too late to treat them. This:
- Blood when urinating. If, when going to the toilet outside the menstrual cycle, blood clots are observed in the urine, this is a reason to consult a doctor as soon as possible for diagnosis and treatment of the disease.
- Pain when going to the toilet.
- Frequent discharge that is not typical for you, emitting an unpleasant odor.
- Regular pain in the pubic area.
Causes
Cystitis can be infectious or non-infectious in nature. Non-infectious diseases occur as a result of damage to the mucous membrane of the bladder. Irritants can be chemical components in the urine, medications, or foreign bodies. So, when washing the bladder with a chemical substance, a burn to its mucous membrane may occur.
Damage is often caused during endoscopic examination.
Typically, the inflammatory process occurs as a result of exposure to infection. The causative agents are: Escherichia coli, streptococcus, staphylococcus. Trichomonas vaginalis and chlamydia may be present in the urine of cystitis caused by infection. The cause of cervical cystitis can also be hypothermia.
In addition to the main causes, there are also triggers that provoke the onset of the disease. These include:
- decreased immunity;
- pyelonephritis;
- infectious diseases;
- urethritis, vulvitis, colpitis;
- the beginning of menstruation;
- diabetes;
- menopause;
- poor personal hygiene.
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis for the treatment of acute cystitis is favorable if you take all prescribed tablets and avoid hypothermia. A proper diet and hardening of the body to reduce sensitivity to low temperatures is also extremely important for a successful recovery.
In the recurrent form, the prognosis is ambiguous and depends on the woman’s correct understanding of the importance of preventive measures. Drinking medications, herbs, or undergoing physical therapy is not enough for this form of illness. To prevent relapse, you need to maintain overall physical and psychological health.
What types of cystitis are there?
There are several classifications. When compiling them, one of the determining factors of the disease was taken as a basis: the type of pathogen, the nature of the course. So, depending on how the disease progresses, the following types of cystitis are distinguished:
- Acute
– characterized by a sudden, sharp onset. - Chronic
– has mild symptoms and is considered as a complication of the acute form of the disease.
Depending on what caused cystitis, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- Specific cystitis
is caused by the presence of sexually transmitted infections. - Nonspecific
– caused by conditionally pathogenic microflora.
Depending on the nature of the pathogen, there are:
- Bacterial cystitis
- develops as a result of bacteria entering the urethra. - Non-infectious
- caused by other reasons.
The following types of non-infectious diseases are distinguished:
- interstitial – the cause cannot be determined;
- medicinal – develops when the body is exposed to drugs;
- radiation – the result of radiation therapy of the pelvic organs;
- chemical – when using unsuitable intimate hygiene products.
Clinical manifestations of cystitis
The classic symptoms of bladder inflammation in women may vary somewhat depending on physiological and age characteristics, factors that provoked the development of the disease, the presence of underlying diseases, as well as a number of other aspects. However, in the vast majority of cases in women, symptoms of cystitis manifest themselves as follows:
- Intense pain syndrome that occurs in the perineum and lower abdomen, intensifying at the time of urination or when the patient takes a certain position.
- Urine becomes cloudy, acquires a sharp, unpleasant odor, and is released in small portions.
- False urges to go to the toilet appear.
- A slight increase in temperature is possible.
- An uncontrollable urge to urinate due to the release of small portions of urine.
Despite the unpleasant signs of bladder inflammation in women, the general state of health during the development of this disease worsens slightly, and therefore it is possible to carry out treatment at home. Hospitalization is a necessary measure only if the illness is aggravated by the addition of any complications.
Prevention of pathologies
In order to never encounter all these symptoms, it is necessary to practice prevention. First of all, it is worth reducing the risk of developing cystitis, since it is the cause of many other pathologies.
Avoid hypothermia. Sometimes it’s better to just stand than sit on a cold bench. There is no need to freeze your genitals for the sake of crazy fashion. It is better to wear warm trousers and put off nylon tights with a short skirt until summer.
Never forget about hygiene. Wash yourself 1-2 times a day, change your underwear once a day. Wearing the same panties for a long time leads to the formation of an environment of harmful rotting bacteria.
Treatment: tablets and other forms of drugs
First of all, a woman must undergo a full diagnostic examination, based on the results of which the doctor will prescribe drug therapy. It is recommended to avoid sexual intercourse for the entire duration of treatment in order to restore the vaginal microflora.
To relieve spasms and eliminate severe pain, doctors usually prescribe Urolesan or Canephron.
How to get rid of cystitis? If the disease is infectious, the prescription of antibiotics is considered necessary. Currently, the following are especially popular among antibacterial agents: “Monural”, “Co-trimoxazole”, “Nitrofurantoin”. As a rule, the duration of the course is from three to seven days.
The choice of antibiotics must be approached with special attention. This is why it is so important to seek help from a qualified specialist. The doctor recommends medications based on test results. The tests carried out make it possible to identify a whole group of microorganisms in the patient that are sensitive to a particular medication. It is important to note that modern antibacterial agents have virtually no toxic effect on the body, so they can be used without fear for such ailments as acute cystitis.
Treatment of the disease is impossible without the use of herbal diuretics, uroantiseptics and immunostimulants. You can speed up the healing process through physical therapy.
It is equally important to follow a special diet for a certain time, which prevents the development of an aggressive urine environment. It is necessary to exclude alcoholic beverages, pepper, mustard, horseradish, marinades and pickles from the daily diet.
Not the least role in treatment is given to the drinking regime. For example, it is recommended to consume at least two liters of liquid per day. This can be the most common still water, tea with honey, decoctions of parsley leaves, the so-called kidney tea. Drinking plenty of fluids helps flush out existing infections from the bladder more quickly.
Traditional treatment of cystitis in women should not be carried out without consulting a specialist. Of course, today you can find many recipes for alternative medicine that are designed to help in the fight against this disease. However, in some cases they do more harm than good.
Complications of cystitis
If the bladder is not treated in a timely manner, there is a risk of developing serious complications, including, for example, inflammation of the urethra and kidneys. As a rule, this happens due to the penetration of urine contaminated with toxins and pathogenic microflora into the urinary tract. If intense pain occurs in the back, it is recommended to contact a medical facility as soon as possible to identify the causes of discomfort, make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Treatment at home with folk remedies
In addition to taking medications, patients are advised to drink plenty of fluids - more than two liters of fluid per day. It is good to use decoctions of lingonberry leaves, chamomile flowers, and rose hips. If possible, you should remain in bed and take thermal procedures to warm the lower abdomen.
Baths with decoctions
Among the most common folk recipes are baths with infusions of medicinal herbs. They promote personal hygiene, and are also effective for pain relief, have an anti-inflammatory and disinfectant effect.
The water for the procedure should not be too hot (no higher than 42 degrees), as high temperatures can worsen the condition. Take a bath until the water cools down comfortably, but no more than 30 minutes. Afterwards, it is recommended to insulate the lumbar area and rest for an hour in a warm bed.
For immersion baths, effective remedies are potassium permanganate, furacillin, baking soda, and herbal remedies. You can take a bath with chamomile infusion. 500 g of dried flowers are immersed in a bucket of hot water and allowed to brew. The composition is filtered. In a similar way, you can warm up using a decoction of dry horsetail (350 g of raw material per bath).
A pine bath is effective. Small pine and spruce cones and young shoots are placed in a 10-liter container, filled one third with water and boiled for half an hour. Strain and dilute with water. Not only sedentary baths, but also steam baths are recommended. The peculiarity of their adoption is as follows:
- the solution temperature should be about 90 degrees,
- the container into which the solution is poured should be such that it is comfortable to sit on: a bucket or large pan,
- while sitting on the container, you need to wrap up the lower part of the body,
- bath time – 20-30 minutes,
- the solution must be hot all the time. If necessary, add boiling water to it.
For steam baths, you can use a decoction of chamomile, St. John's wort, horsetail, as well as a pine decoction.
Cranberry juice for cystitis
In the initial stage of the disease, freshly squeezed cranberry juice helps well. It contains active substances that have an antibacterial effect on many microorganisms, including E. coli. Bacteria, entering the acidic environment created by cranberries, lose the ability to remain on the walls of the bladder and are excreted along with urine.
You can use fresh cranberries or dried cranberry extract from the pharmacy. Packaged juice is not suitable for treatment, since it does not contain microelements that will affect pathogenic microorganisms.
Parsley seeds
Parsley, in addition to other useful substances, contains B vitamins and folic acid, which have an antimicrobial effect. And the essential oils contained can relieve pain and have an anti-inflammatory effect.
For treatment, you can use parsley seeds, from which an infusion is prepared. To do this, pour 1 teaspoon of seeds into 2 glasses of warm water. Infuse in warmth and in the absence of light for 10 hours. Strain. The resulting infusion should be drunk within 24 hours. One-time dose – one tablespoon. Within 3 days, the pain and stinging when urinating disappears, and the burning sensation goes away.
Compresses on the stomach
Compresses on the abdominal area help relieve pain from cystitis. They can be used if there is no elevated temperature, as well as a predisposition to diseases that can cause bleeding. Below are the recipes for compresses:
- Add 2 drops of essential oil of sandalwood, eucalyptus and juniper to warm water.
- Dip a towel into the solution. Squeeze it and apply it to the lower abdomen for 5 minutes.
- You can make a honey compress. Honey is mixed with flour, preferably oatmeal. Roll out the resulting mixture into a flat cake and apply it just above the pubis. The top is covered with oilcloth and insulated.
- A clay compress helps a lot. The clay is diluted with warm water to a thick sour cream, spread on the lower abdomen, and covered with oilcloth.
Nutrition for cystitis
Diet is the most important component of treatment. In addition to medicine, therapy for the disease is carried out with folk remedies, herbs and food. Food can both contribute to recovery and lead to serious consequences.
The cystitis diet removes the following foods from the diet:
- low-alcohol, alcoholic, sweet carbonated drinks;
- dairy products, especially cheese and cottage cheese;
- tomato juice, paste and tomatoes;
- fatty foods, canned foods;
- dishes of unknown origin;
- nuts, raisins, dried apricots, peaches, bananas.
This diet is not strict, but will allow the body to quickly cope with acute or chronic inflammation without negative consequences. And by including infusions and decoctions, for which medicinal herbs are used, in your diet, you can comprehensively improve your health and relieve discomfort.
Treatment
Therapy must be comprehensive. It should be prescribed on an individual basis, taking into account the patient’s age, gender, and nature of the disease. Cervical cystitis can be treated both at home and in the hospital.
Treatment at home
In the acute form of the disease, the patient is recommended to rest in bed and drink plenty of fluids. It is useful to drink non-carbonated mineral water, alkaline drinks, herbal teas. If the disease is caused by microbes, the patient is prescribed antimicrobial medications. Anti-inflammatory therapy is also carried out. It is recommended for all inflammatory diseases, including myositis. If there is severe pain, taking antispasmodics is indicated.
Among the most popular drugs for the treatment of cystitis are the following:
- Collargol.
- Urolesan.
- Monural.
- Cyston.
- Furagin.
Antibiotic therapy is carried out for 3–7 days.
Homeopathic treatment also helps with cystitis of the bladder neck. Folk remedies have also proven their effectiveness. Patients are advised to take decoctions based on lingonberry, juniper and birch bud leaves. Drinking cranberry juice can reduce inflammation.
Vaginal suppositories are used to treat cystitis in girls and women.
Treatment in hospital
Sometimes installations are indicated, in which medications are injected directly into the bladder. This procedure can only be performed in a hospital setting.
If the disease is chronic and causes significant discomfort to the patient, surgical treatment may be performed. The operation is a plastic surgery of the external urethral opening. This hole is moved to a higher position. Thus, the path for bacteria to enter is blocked.
Treatment methods
If the patient has been diagnosed with cervical cystitis of the bladder, treatment may include the following measures:
- use of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs;
- taking painkillers;
- drinking plenty of fluids and bed rest;
- installation of the bladder;
- surgical intervention (in extreme cases);
- treatment using folk remedies.
Atypical forms of the disease
Rare types of the disease are diagnosed in 1-3% of all cases of cystitis. These pathologies are insidious and difficult to treat; their rare manifestation does not allow doctors to learn enough about them. We are talking about allergic, ulcerative, tumor-like, gangrenous, granulomatous and many other atypical variants of the disease.
Inflammation without an identified etiology occurs in little girls, during menopause, with diseases of the endocrine system, and after sexual intercourse. Cystitis can develop in anyone, of any form, but women make up the majority of patients. In some cases, patients must take medications for life in order to perform normal activities and work.
How is therapy carried out?
For cystitis, you can take the following medications:
- Antibiotics - antibacterial tablets are necessary to destroy unfavorable microflora and eliminate the root cause of pathology;
- Anti-inflammatory tablets should be taken to eliminate the acute inflammatory process that causes pain;
- Immunostimulating drugs - a vitamin complex and immunostimulating tablets must be prescribed, because inflammation can be a consequence of a decrease in the protective mechanism;
- Nutrition – a properly selected diet will improve a woman’s well-being and prevent relapse of the disease; diet is also important when you need to take antibiotics and other strong drugs;
- Painkillers and antispasmodic tablets - you need to drink for symptomatic therapy, they relieve pain, they can be supplemented with natural herbs and natural anesthetics.
You can take these medications only under the supervision of a specialist, because self-medication never gives guarantees. To prevent the spread of infection from the neck of the bladder to neighboring organs, medications should be taken to stimulate the restoration processes of the mucous membrane.
Symptoms
With cervical cystitis in women and men, the bottom of the bladder becomes inflamed. The muscles that are responsible for urine production stop functioning normally. In a healthy state, a person can open these muscles through willpower. If cervical cystitis occurs, the person cannot control the muscular system and control urination - urinary incontinence occurs.
With cervical cystitis, the symptoms are similar to those of other types of cystitis. Patients experience:
- Pain in the lower abdomen and pubic area.
- Stinging and burning during urination.
- Frequent urge to urinate.
- Difficulty urinating.
A characteristic symptom is urinary incontinence. Laboratory tests may reveal higher levels of white blood cells in the urine than normal.
The disease may be accompanied by general weakness, malaise, and in some cases, increased body temperature. Acute symptoms appear within a week.
Then they gradually subside. Some people are happy to feel better and do not pay attention to treatment. It is necessary to ensure that the disease does not pass into the chronic stage, in which the disease will manifest itself with a certain frequency constantly.
Complications
The disease in the acute stage has characteristic symptoms. In the chronic stage, it may not make itself felt. This is the danger, because the disease remains untreated and can cause complications.
One of the most common complications is secondary vesicoureteral reflux. Pyelonephritis also often develops. Less common are urethral stenosis, sclerosis of the bladder neck, paracystitis, urethritis and peritonitis.
Diagnosis and forms of pathology
Before treating cystitis, you need to do a urine test, ultrasound, and CT scan. These are the main ways to detect pathology, but not the only ones.
What needs to be done to confirm the diagnosis:
- general analysis of urine and blood;
- ultrasound examination of the bladder;
- Cytoscopy for suspected neoplasm and malignant process.
Diagnosing the disease is not difficult, but it is important to correctly determine its form in order to treat in the right direction. Therapy for the primary and secondary ailment is significantly different, and before treating cystitis, you need to remove its main cause, otherwise there will be no results, and the disease will return in the future. more aggressive form.
There are acute, chronic, recurrent cystitis. In case of an acute process, it is necessary to treat comprehensively, first the symptoms are eliminated, then the woman should take drugs to increase immunity and relieve the inflammatory process. In case of a chronic illness, you will have to take antibiotics and treat with folk remedies using medicinal herbs. Diet and lifestyle control with the elimination of bad habits are a must.
The recurrent form of the pathology loves the cold, and as soon as the woman becomes hypothermic, unpleasant symptoms begin. In this case, a constant diet and symptomatic treatment are indicated. You need to take antibiotics prescribed exclusively by a doctor, and also treat the bladder using herbs and folk remedies.
Prevention
As you know, absolutely any disease is easier to prevent than to treat later. In the case of cystitis, this is also true. To prevent the development of this disease, all women are advised to adhere to fairly simple rules. What should you not do if you have cystitis?
- Have an uncontrolled sex life.
- Neglect basic rules of personal hygiene.
- Constantly being hypothermic.
- Neglect treatment of genitourinary tract infections.
- Use tight underwear made of synthetic fabrics.
Disease statistics
According to medical statistics, cervical cystitis most often occurs in young women. This disease accounts for approximately 10–20% of other urinary tract diseases. Every year, 3–5 million people consult doctors with characteristic symptoms. 0.5–0.7 cases of the disease occur per woman. Among men, the incidence is noticeably lower. Out of 1000 people, the disease occurs only in 5–7 representatives of the stronger sex.
We recommend that you read:
- What is cystitis in women?
- How long does it take to treat cystitis in women?
- Treatment of cystitis in women - at home.