Our intestines are the place to digest food and remove waste products. His work is a kind of “litmus test” for the functioning of the body. After all, even acne on the face is a sign of a malfunction in the intestines, and what can we say about the state of immunity and health? The work of this organ is important: here nutrients are absorbed into the blood, and food “waste” is formed into feces and excreted. The intestines are inhabited by tiny microorganisms - bacteria, and they bear the burden of digesting food. Analysis of stool for the intestinal group will determine how balanced the “population” of the intestine is, and which microflora predominates - normal or pathogenic? The study identifies intestinal diseases. to choose the right treatment.
Intestinal group: what does it include?
Content
The human intestine is a densely populated organ of the body. More than five hundred species of bacteria live in the intestines; they are divided into groups:
- Normal microorganisms are normally represented by the majority (90%) of bacteria, mainly lactobacilli and bifidobacteria, whose role is to secrete acids against “harmful” microbes and protect the body.
- Opportunistic microflora, represented by entobacteria, candida fungus, staphylococcus, etc., which are harmful. Their numbers are regulated by beneficial bacteria. Conditional pathogens - do not cause harm until favorable factors for their reproduction occur.
- Pathogenic microflora, which, growing in the body, causes infectious diseases, common representatives are salmonella, brucella, shigella, etc.
In other words, the intestinal group of each person is the collection of bacteria that inhabit the intestines. Since the ratio of microorganisms is constantly changing, it is important to monitor the “population” of the digestive tract, and the analysis of the intestinal group helps with this.
Don’t be shy, ask our consultants questions, right here on the website. We will definitely answer. Leave commentsGo
Disturbance of intestinal microflora
The main part of the microenvironment is concentrated in the large intestine - the lower zone of the intestinal part of the digestive tract. The microflora consists of several hundred microorganisms forming a symbiotic system. Bacteria are classified into three intestinal groups: beneficial, opportunistic and harmful (pathogenic).
A healthy intestine contains only representatives of the first two groups, in strictly balanced quantities. Their ratio is 9 to 1. An imbalance between beneficial and opportunistic bacteria causes dysbiosis (otherwise known as dysbiosis).
There should be no pathogenic microorganisms in the intestinal microflora. When they are introduced into the body, infectious processes of varying severity develop. The penetration of pathogens can provoke a state of severe intoxication that threatens the patient's life. Fecal analysis determines the qualitative and quantitative composition of each intestinal group.
| Classification | Form of existence | Norm in % | Representatives |
| group of beneficial bacteria | obligate anaerobes (oxygen-free existence) | 90 | bifidobacteria, bacteroides, lactobacilli, enterococci, Escherichia coli, eubacteria, etc. |
| group of opportunistic pathogens | facultative or non-strict anaerobes (capable of life with and without oxygen) | 10 | staphylococci (saprophytic, epidermal), yeast fungi (candida), peptococci, fusobacteria, bacilli, clostridia, etc. |
| pathogens | facultative anaerobes and aerobes (needing oxygen) | Pseudomonas aeruginosa, salmonella; Vibrio cholerae, invasive and toxigenic Escherichia coli, Shigella, etc. |
Infection with pathogenic bacteria most often occurs through consumption of contaminated products, failure to comply with sanitary and hygienic standards, or due to the spread of nosocomial (nosocomial) infections.
What the analysis can detect
For analysis of the intestinal group, feces are taken. The study detects if:
- Escherichia coli, it is the causative agent of colienteritis and escherichiosis;
- salmonella - the causative agent of typhoid fever, salmonellosis and paratyphoid fever;
- dysentery bacillus, etc.
In equipped laboratories, stool testing for intestinal flora is comprehensive, identifying the requested microorganisms and the quantitative ratio of representatives of the patient’s local microflora.
Indications for the study
Tests for the presence of intestinal infection are prescribed in cases of symptoms that indicate the presence of a bacterial pathogen:
- coli;
- staphylococcus;
- salmonella, which provokes the development of typhoid fever.
The presence of a particular pathogen in the gastrointestinal tract will be indicated by the following symptoms:
| Intestinal infection |
|
| Staphylococcal intoxication |
|
| Typhoid fever |
|
In case of a combination of the listed characteristic symptoms, an urgent consultation with an infectious disease specialist is necessary, who will prescribe the necessary laboratory tests.
How to take a stool test for the stool group
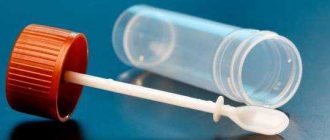
Since it is easy to correctly collect stool for analysis, patients do not experience any difficulties with this. Feces are collected, as for general or scatological analysis. It is collected little by little from different parts of the pile, mainly from the middle. It is more rational to use ready-made containers from the pharmacy - the jar is equipped with a special spoon for scooping out the biomaterial. But it is also allowed to use sterile glass containers of small volume. Feces are taken exclusively fresh. Since it is allowed to store a stool sample until the morning, it is allowed to collect bowel movements in the evening. It is worth remembering how long feces can be stored in the refrigerator for analysis: no more than 8 hours. If more time has passed since collection, it is not recommended to take such biomaterial to the laboratory - the result may be distorted.
Rules for collecting stool:
- defecation is natural and cannot be induced with an enema or laxative;
- the day before, abstaining from alcohol, medications, and spicy foods;
- It is recommended to stop taking antibiotics at least a week before the test;
- if there are purulent or bloody inclusions in the masses, it is recommended to make a fence from this part.
Since it is problematic to collect feces for analysis from a child of the first year of life who is not potty trained, it is allowed to use excretory material from panties or a diaper, but only immediately after emptying. The feces are collected in an airtight container and can be stored in a cool place for several hours.
By the way, read more on this topic: Stool analysis for scatology
Do I need special preparation for the analysis?
No special preparation required.
The optimal time for collecting material is as early as possible when symptoms appear, before taking any antibacterial drugs.
When taking an analysis to obtain a medical record, the biomaterial can be submitted at any time.
There is no special preparation for the study; it is recommended to refrain from using enemas and rectal suppositories in consultation with your doctor.
If the patient underwent an X-ray examination with a contrast agent the day before, it is advisable to postpone the test for several days. This is necessary due to the long-term removal of the radiopaque substance from the body.
The main thing when taking the test is to maintain sterility. The entry of foreign microorganisms into the material can significantly distort the results of the study.
Decoding the research results
If the study reveals foreign microorganisms (salmonella, E. coli, trichomanas, dysenteric amoebas, etc.), the patient is immediately prescribed appropriate treatment.
The most common diseases diagnosed during disgroup analysis:
- Dysentery (shigellosis) is an infection caused by bacteria from the genus Shigella. It is characterized by symptoms of general intoxication of the body and disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, especially the colon. The source of infection can be people who are carriers of the infection. Infection can also occur through food and water.
- Salmonellosis is an acute intestinal infection caused by bacteria of the genus Salmonella. The pathogen settles in the small intestine of a person, causing intoxication of the body and disruption of the gastrointestinal tract. There are several types of Salmonella, according to which the manifestation of infection may vary. For example, the presence of a group D pathogen signals typhoid fever. Pathogens of groups A, B and C are characteristic of paratyphoid fever. The infection is transmitted through soil, water and food, as well as through animals and, less commonly, people.
- Coli infection is a group of diseases caused by pathogenic serotypes of Escherichia coli. The infection is characterized by a disorder of the gastrointestinal tract; in children and people with weak immunity, lesions of the urinary tract (cystitis, pyelonephritis, etc.) may also occur. Infection occurs through contact and household contact from person to person.
We suggest you read: How to find bedbug nests in an apartment - expert advice
You can take a stool test without an appointment every day:
- Mon-Sat: 08:30–13:00 (first pick-up), 13:00–17:00 (second pick-up)
- Sun: 09:30—14:00.
To receive test results by email, you must leave written consent for sending with the administrators of the medical center.
To obtain reliable results, the patient should adhere to the conditions of preliminary preparation and the rules for collecting excrement for examination. One of the most important conditions of the preparatory stage is the prohibition on independent (without medical recommendations) use of:
- antibacterial therapy drugs;
- laxatives and fixatives;
- tablets that enhance peristalsis;
- sorbents (Polysorb, Activated carbon, Enterosgel, etc.).
The listed medications can destroy part of the intestinal microbiota. This will negatively affect the accuracy of the analysis results.
The patient's responsibilities during the preparatory period include the following. 2-3 days before donating the biomaterial, eliminate from the diet heavy fatty foods (meat, mushrooms, fatty sauces), foods that provoke flatulence (cabbage, milk, brown bread, legume dishes), carbonated drinks, sweet baked goods.
Variant of a pharmaceutical container with a spoon for collecting feces
For three days, eliminate the use of alcohol, stop using rectal suppositories, use microenemas, purchase a sterile sealed container with a spoon from the pharmacy for submitting excrement for analysis (for loose stools, you need to buy a pipette). If the patient is prescribed an X-ray of the digestive organs with contrast, the diagnosis should be made after submitting the excrement for analysis.
The radiation exposure and contrast agent administered to the body will affect the intestinal microenvironment, which may distort the final data. New foods (complementary foods) should not be introduced into the menu for infants. This can cause allergies or dyspeptic syndrome (digestive problems).
Important! It is prohibited to collect feces in non-sterile containers. Any foreign matter may make the material unsuitable for research.
The study of stool for disgroup involves two options for collecting material: independently at home in a pharmacy container, taking a rectal smear (or liquid substance) in a medical institution. The conditions for preparing the body are identical in both cases.
Morning stool samples are suitable for microbiological research. Before collecting biomaterial, you should perform hygiene of the anorectal area (without perfumed cleansers) and empty your bladder. Women are not recommended to collect stool during the first seven days of the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle. If an urgent examination is necessary, care must be taken to ensure that menstrual fluid does not get into the material being examined.
It is incorrect to collect feces directly from the toilet. It is necessary to use a vessel or ensure the sterility of excrement using plastic film or stationery paper. In infants, fresh feces can be collected from a diaper. In this case, care should be taken to ensure that no fibers of hygienic material get into the container.
Using the plastic spoon provided with the container, you need to move the feces fragments into the container. If there are pathological purulent, flaky or mucous impurities in the excrement, their particles must be sent for analysis. Fill the third part of the container and close the lid tightly.
The greatest information content of the data is ensured by the immediate delivery of excrement to the research site (to the laboratory). Samples should not be frozen or left at room temperature. Facultative anaerobes do not tolerate changes in temperature and may die. In this case, the study will lose its meaning.
A smear is taken in a medical facility using a swab. A sterile cotton swab is inserted into the rectum, rolled several times and removed. After this, the sample is placed in a laboratory container with liquid nutrient contents.
A sample of loose stool is collected through a catheter. This method is intended for collecting liquid feces. One end of the medical instrument is inserted rectally into the patient, the other is placed in a laboratory vessel. The procedure for collecting a rectal smear may cause minor temporary discomfort in the anorectal area.
Important! Neglect of the conditions of preparation for analysis and collection of biomaterial will not allow obtaining a reliable result. The prescribed treatment will be erroneous and ineffective.
How the research is carried out
Each type of bacteria prefers nutrient media, which is what laboratory technicians use. To determine the number of certain microorganisms, feces are inoculated on special liquid substances, creating favorable conditions for the life of bacteria. When the colony of microorganisms expands, it is transferred to a solid nutrient medium, where it is easier to differentiate by species. Additionally, microscopic analysis and biochemical tests are performed.
But the patient does not need to know these subtleties. All you need to do is collect the stool correctly, bring it to the laboratory, wait for the results, and then go to your doctor with them.
How much is a stool test for intestinal group done in a regular clinic and paid laboratory?
It takes several days for a colony of bacteria to grow for accurate differentiation. Therefore, the results of the analysis will have to wait. In paid laboratories (Invitro, Hemotest), the preparation of the result takes 4-6 days. In a regular clinic, it usually takes longer – sometimes up to 2 weeks. If pathogens are identified in order to determine their sensitivity to antibiotics, the preparation time for the analysis may be delayed.
Test results are valid for 6 months.
Opportunistic microorganisms that can cause intestinal infection
Increasingly, bacteria that constantly live in the human large intestine cause infections of various locations - the digestive tract, respiratory or genitourinary system. This is caused by a deteriorating environmental situation, uncontrolled use of antibiotics and other drugs, and the constant presence of bacteria in the human environment. As a rule, newborns and children in the first 6 months of life get sick.
You can perform a bacteriological analysis of stool in Invitro. This is a network of laboratories with branches in all major cities. Patients like the fact that test results can be obtained online, meaning there is no need to go to the laboratory to get them.
Decoding the analysis, evaluating the results
The attending physician interprets the tests. But you can also figure out for yourself whether everything is okay. Normal indicators are as follows (accounting in CFU):
- number of bifidobacteria: from 1*108;
- lactobacilli – from 1*106;
- Escherichia coli – up to 4*108;
- spore-forming anaerobes – no more than 1*103;
- enterobacter – up to 5%;
- cocci – no more than 25% of the total;
- no pathogenic flora should be detected.
In children of the first year of life, these indicators may differ, more often - to a greater extent.
The results are issued on a special form; if pathogens are present, this is marked with a plus sign in the appropriate column or recorded with a stamp.
What therapy is prescribed
Did stool tests reveal the presence of pathogenic microorganisms? The sooner treatment is prescribed, the better! The sick person is immediately removed from the team (work, school, kindergarten) and, if necessary, hospitalized. Therapy includes an integrated approach, the following are prescribed:
- antibiotics, the type of which is selected by appropriate analysis of the sensitivity of the flora to it;
- prebiotics – drugs that populate the intestines with beneficial microflora;
- drugs to support immunity and vitamins.
In this case, the diet prescribed by the doctor plays an important role. Since taking antibiotics is incompatible with drinking alcohol together, you should stop drinking alcohol!
Who should be tested for the “intestinal group”
Typically, an appointment for a stool test to determine the intestinal group is issued by a doctor. For what reasons? Before:
- if patients have complaints;
- when applying for a job, entering a preschool educational institution or school;
- representatives of professions: catering workers, teachers working with children, health workers.
In addition, persons in whose enterprises an outbreak of intestinal infection has been identified, as well as people who have been in contact with an identified case, are sent to the laboratory. If these requirements are neglected, an outbreak of an epidemiological disease may result, leading to quarantine or closure of the institution.
Analysis of stool for the intestinal group if a particular intestinal infection is suspected precedes the final diagnosis, allowing adequate treatment to be prescribed. For preventive purposes, such a study is carried out without appropriate indications.
What pathogenic microorganisms are most often detected?
A patient with an acute digestive disorder and suspected infection is sent to an inpatient infectious diseases department. Children are hospitalized together with their mothers. In a hospital setting, it is possible to isolate the patient and conduct the most complete examination and treatment.
The most common intestinal pathogens are manifested by the following diseases:
These examples show how important it is to timely analyze not only feces, but also food, drinking water, and swabs from the hands of personnel. Especially if the disease is detected in children's institutions.