Stool examination provides information about the patient's health. This method helps to identify various diseases and disorders in the body.
If the patient is scheduled to donate stool, a few days before the procedure you should go on a diet - this will allow you to get reliable results from the analysis.
Nutrition in preparation for diagnosis
In this case, it is necessary to stop consuming apples, white beans, cucumbers, spinach, cauliflower, horseradish, meat and fish products. Tomatoes, bell peppers and green vegetables are also prohibited.
Alcohol, sweet carbonated water, coffee, and black tea are prohibited from drinks. Pure still water is allowed.
Patients are allowed to consume potatoes, cereals, and dairy products. You need to eat in small portions without overeating. It is important to avoid frying; Instead, food is boiled, stewed or baked .
In what pathologies is hemoglobin found in feces?
The presence of occult blood is determined by the Gregersen reaction. It is carried out by determining altered hemoglobin in feces, since red blood cells themselves may not be detected microscopically, but the doctor suspects internal bleeding or diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, accompanied by blood leakage.
These include:
- Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum (ulcer may bleed).
- Helminth infections (helminths damage the intestinal walls).
- Malignant tumors of the stomach, intestines, esophagus.
- Varicose veins of the esophagus.
- Intestinal tuberculosis.
- Ulcerative colitis.
Basic principles
Basic principles of the methodology:
- It is necessary to exclude meat, fish, eggs, legumes and green vegetables from the diet.
- Portions should be small so that a person does not feel heavy in the stomach.
- During the diet, you should not take antibiotics or laxatives.
- It is allowed to consume dairy products, mashed potatoes, and oatmeal decoction.
- Instead of coffee and black tea, you should drink water, dried fruit compotes, and fresh juices.
Dishes are prepared by boiling, stewing, baking or steaming. Frying is strictly prohibited: such food can negatively affect the analysis results. The daily calorie content should not exceed 2200 kcal, the weight of the dishes should be 2.2−2.5 kg.
You need to eat food every two hours, but in small portions . There are 5-6 meals per day. The program lasts from 3 to 5 days - this is enough to prepare the body for the test.
General analysis (coprogram)
- 2 days before collecting biomaterial, discard tomatoes, tomato juice, pasta, beets, blueberries, pomegranates and other vegetables and fruits containing dyes.
- For 3 days, stop taking antibiotics, laxatives, and drugs that cause changes in intestinal motor function. Do not use rectal suppositories, ointments, or oils.
- Do not eat exotic fruits, vegetables and foods that are not typical for your diet as a whole. Do not overeat, exclude fatty, spicy, pickled foods.
- If you are taking medications containing iron and bismuth, they must be discontinued 2 days before stool collection.
Attention.
After radiography with a contrast agent (barium), collect feces for coprogram no earlier than 7–10 days after the examination. Women are not recommended to take the test during menstruation. Collect stool for examination in the morning, on an empty stomach. If this is difficult, you can prepare the sample in advance, but no more than 8 hours before submitting it to the laboratory. In this case, store the sample in the refrigerator (do not freeze!).
- Carry out hygiene procedures and first urinate in the toilet and flush.
- Place sterile paper (or an ironed sheet) or a disposable plastic plate in the bowl or bottom of the toilet and perform a bowel movement.
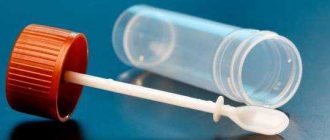
- Collect feces immediately after defecation from different places in a single portion with a special spoon mounted in the lid of a plastic container in a volume of 1–2 g (no more than 1/3 of the container’s volume). Avoid contact with urine and pieces of undigested food.
- Deliver the sample to the laboratory on the day of collection. Before delivering the sample to the laboratory, the container with stool should be kept in the refrigerator at 2–4 °C. Storage at 2-8 °C is allowed - up to 72 hours.
Its effect on the body
The technique is aimed at preparing the body for the test. It is cleansed of harmful substances, components that can negatively affect the result of the procedure are removed.
This diet normalizes digestion and reduces the load on its organs. By giving up fatty foods that are difficult to digest, discomfort and a feeling of heaviness in the stomach will disappear.
The person's condition will improve significantly . Excluding difficult-to-digest, high-calorie foods from the menu can lead to a decrease in body fat, and a person will lose a little weight.
When is a referral for analysis issued?
In addition to screening the age group over forty years, the doctor writes a referral for this test in the following cases:
- for abdominal pain
- nausea
- frequent heartburn
- with an iron taste in the mouth
- if you have no appetite
- if you experience sudden weight loss
- constant loose and mushy stools
- if you suspect an ulcer or gastritis.
The analysis reveals the slightest damage to the walls of the intestine. If an admixture of blood higher than normal is detected in the stool, the test is repeated and, if the result is confirmed, the patient is sent to see a proctologist or gastroenterologist.
Pros and cons of the method
Benefits include:
- High efficiency.
- Beneficial effect on the digestive organs.
- No need to starve.
- Help in obtaining reliable analysis results.
However, each diet has not only pros, but also cons: the patient is allowed to consume very few foods. They can get boring after a few days.
Most familiar dishes are excluded from the menu. The diet is not easy for all patients, but it is effective, so such restrictions are understandable .
This technique has no contraindications, but in the presence of chronic diseases, the doctor can adjust the diet, add or exclude certain foods. It is necessary to consult a doctor.
Test for intestinal dysbiosis
A study that allows you to assess the ratio of normal intestinal microflora and opportunistic microorganisms, as well as the presence of pathogenic bacteria. The study also reveals the sensitivity of pathogenic microbes to antibiotics and bacteriophages. Preparation for the analysis, in addition to following general recommendations, is not required, however, it should be noted that the accuracy of the result may be influenced by antibacterial therapy. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct research before taking antibiotics.
Sample menu
In order not to make mistakes in nutrition, you need to familiarize yourself with the menu compiled by experts:
| Diet day | First breakfast | Lunch | Dinner | Afternoon snack | Dinner |
| First | Rice porridge | Compote | Mashed potatoes | Kefir | Milk soup |
| Second | Buckwheat porridge | 50 ml milk | Vegetable stew | Compote | Potato casserole |
| Third | Cottage cheese | Kissel | Boiled rice | Peach | Low-fat yogurt |
Usually the diet is followed for three days. For breakfast it is better to eat porridge or low-fat cottage cheese. For lunch, mashed potatoes, non-green vegetable stew, or boiled rice are suitable.
For dinner, fruit salads, low-fat yogurt or cottage cheese are acceptable.
It is recommended to snack on dried fruit compotes, jelly or kefir.
When creating a menu, you should remember the lists of prohibited and permitted products.
The permitted products are very few in number and are included in the diet. The focus is on low-fat dairy products, cereals and non-green vegetables.
How is it carried out?
To confirm the presence of hidden blood in the stool, the Weber reaction is additionally performed - a test with guaiac resin.
The research technique is quite simple. To detect occult blood, the method of benzidine oxidation with hydrogen peroxide is used. Feces are tested for the Gregersen reaction in this way: the material for analysis is smeared on a glass slide and a few drops of the reactive substance are added. In this procedure, hidden blood acts as a catalyst for the release of oxygen and, due to the peroxidase action, it turns greenish or blue. If blood is present in the material being studied, then after the reaction its pigment necessarily changes its color. At the same time, the sensitivity of the reagent to hemoglobin is 1:100,000. This method of detecting occult blood allows you to quickly and accurately determine its presence or absence in the stool.
List of approved products
During the diet you can consume:
- Dairy products - milk, kefir, low-fat cottage cheese.
- Porridge - rice, buckwheat.
- Vegetables - potatoes, beets, carrots.
- Fruits - peaches, persimmons.
- Drinks - jelly, compote, berry juice.
It is allowed to add a little butter to dishes. During lunch or dinner, you can eat a slice of bread. The main thing is not to eat buns and flour products, they are prohibited. You can add a little sugar to tea, but you should not eat the sweets themselves .
Compotes made from dried fruits have a beneficial effect on the patient's condition. They are consumed throughout the day. This is a great addition to lunch or dinner or snack.
For carbohydrates
- Carry out hygiene procedures and first urinate in the toilet and flush.
- Place sterile paper (or an ironed sheet) or a disposable plastic plate in the bowl or bottom of the toilet and perform a bowel movement.
- Collect feces immediately after defecation from different places in a single portion with a special spoon mounted in the lid of a plastic container in a volume of 1–2 g (no more than 1/3 of the container’s volume). Avoid contact with urine and pieces of undigested food.
- Deliver the sample to the laboratory within 4 hours.
https://youtu.be/h4tcHaJCvzo
Attention Storing a stool sample for more than 4 hours, including in the refrigerator, is not allowed.
What not to eat
Patients should avoid the following:
- Vegetables and fruits are green.
- Meat and fish.
- Seafood.
- Nuts.
- Legumes.
- Dairy products - fermented baked milk, sour cream, yogurt.
- Drinks - alcohol, sweet carbonated drinks, coffee.
It is necessary to give up not only the food mentioned above, but also spices, flavorings, and sweeteners. Smoked meats, semi-finished products, and salted foods are also prohibited.
For the results to be reliable, you need to give up cereals such as barley, millet, wheat . They may negatively affect the diagnosis.
Indications for testing
In most cases, direct indications for performing a biochemical study of feces for the presence of occult blood in them are the presence of the following accompanying symptoms in the patient, indicating one of the possible gastrointestinal diseases:
- persistent pain in the abdominal cavity, which does not have a specific localization in terms of one of the organs of the digestive system;
- frequent and causeless occurrence of diarrhea, or constant defecation of highly liquefied feces;
- dyspeptic disorders, manifested in the form of prolonged heartburn, excessive gas formation, nausea, vomiting, lack of appetite;
- various types of disturbances in the digestion of food and its absorption with breakdown into nutrients;
- a sharp decrease in body weight against the background of the fact that a person continues to eat in the same volumes, and the energy and biological value of products remains unchanged;
- standard clinical diagnosis of stool does not detect the fact of internal bleeding, although the patient has a number of other signs that are a direct indicator of blood entering the gastrointestinal tract cavity.
Recommendations from nutritionists
During the diet, experts advise strictly adhering to the menu and not consuming prohibited foods. You can't go hungry or overeat. You need to eat every two to three hours, avoiding a feeling of heaviness in the stomach.
If the patient does not have kidney problems, you should drink 1.5 liters of water per day . This will help prepare the body for the procedure.
If a person takes any medications, they are abandoned during the diet. They may affect the result of the analysis.
Intense sports training is also not recommended; walking in the fresh air is acceptable.
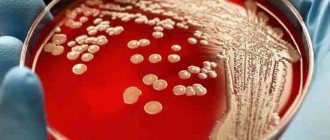
Culture for microflora and sensitivity to antibiotics
3-4 days before the study, it is necessary to stop taking laxatives, castor and vaseline oil, and stop administering rectal suppositories. Feces obtained after an enema, as well as after taking barium (during X-ray examination) are not accepted for examination!
Attention: Feces are collected before starting treatment with antibacterial and chemotherapy drugs.
Collection rules
- First urinate in the toilet and flush.
- Place sterile paper (or an ironed sheet) or a disposable plastic plate in the bowl or bottom of the toilet and perform a bowel movement.
- Collect feces immediately after defecation from different places in a single portion with a special spoon mounted in the lid of a plastic container in a volume of 1–2 g (no more than 1/3 of the container’s volume). Avoid contact with urine and pieces of undigested food.
- Deliver to the laboratory on the day of collection. If it is impossible to quickly deliver the sample to the laboratory, you can store it in the refrigerator for no more than 4 hours at 2-8 °C.
Duration
The duration of the technique is 3-5 days, no more. Typically, patients need three days to prepare for the test. The diet is stopped after the test.
To prevent the body from experiencing stress, switch to normal nutrition gradually. You cannot immediately switch to familiar dishes and products .
They are added in small quantities to the menu while continuing to consume healthy foods. This will allow you to switch to your usual diet without negative effects on the body.
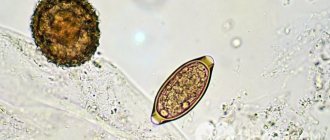
Examination of stool for protozoa and helminth eggs
A procedure also known as a worm or parasite test. This is another microscopic examination, the objectives of which are clear from the name - to detect signs of the presence of various parasites in the intestines. In this way, for example, eggs of roundworms, hookworms, trematodes and tapeworms, as well as cysts of amoebas, balantidia and other protozoa are detected. No special preparation is required for the analysis, with the exception of the general recommendations mentioned above.
Separately, a few words should be said about the analysis for enterobiasis, that is, for pinworms. This procedure does not apply to stool examination methods, since parasites lay eggs only externally - in the perianal area. Therefore, the generally accepted method for diagnosing enterobiasis is a scraping (imprint) from the skin.
Dairy diet option
The technique is often used due to its high efficiency. Its main principles include:
- During the day, a person consumes mainly dairy products, and fruits and vegetables in small quantities.
- It is allowed to consume cottage cheese, milk, kefir.
- Porridge is cooked with milk, and casseroles are made from cottage cheese.
- Adding sugar and sweet syrups to dairy products is prohibited.
The program lasts 3-5 days, the doctor can tell you exactly how long this diet will last. In addition to milk, you are allowed to drink water, compotes, jelly and berry decoctions .
You can add fruit to milk porridge and cottage cheese, but not green fruit. Peaches, pears, and persimmons are optimal. This diversifies the diet, making the diet easier for a person to tolerate.
Before donating stool for occult blood, a diet is necessary: it helps prepare for the test, cleanses the body, and has a beneficial effect on the human condition.
Knowing the principles of such nutrition, a person will do an excellent job of preparing the body for analysis, and the results will be reliable.
What does the analysis show (what is the point)?
The analysis allows you to determine the presence of hemolyzed hemoglobin, indicating “hidden” bleeding.
Hidden bleeding is called bleeding that cannot be seen with the naked eye or even with a microscopic examination. Often, when a bolus of food passes through the intestinal tract, red blood cells are destroyed, and bleeding can only be suspected by detecting their contents using a biochemical method.
The main component of the red blood cell, which is its marker, is hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is a protein-iron compound that can carry oxygen and carbon dioxide. Normally, it should not appear in the stool.
To obtain a reliable result, you must adhere to the delivery algorithm. It consists of the correct collection of material and preparation for analysis.
Before taking the test, it is necessary to warn the patient about a false positive result if the recommendations are ignored. For reliability, you must adhere to the preparation rules:
- follow dietary recommendations;
- brush your teeth carefully to prevent blood from gingivitis from entering the gastrointestinal tract;
- do not take the test during menstruation;
- avoid taking medications;
- feces should be obtained only in a natural way; the use of auxiliary means is unacceptable.
Culture for intestinal dysbiosis: details of the analysis
So, you can't:
- 3 days before the study, eat fish and meat dishes, seafood, foods containing iron (broccoli, apples, asparagus and others);
- a week before the study, exclude any laxatives: suppositories, micro- and regular enemas, oral laxatives;
- 3 days in advance, stop taking medications containing iron (for example, vitamin preparations), as well as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (aspirin, ibuprofen, paracetamol).
Preparing containers
A more budget-friendly option is to use food jars. It is preferable to use glass or plastic containers, which must first be boiled. Metal, especially iron, boxes are unacceptable, as a false result is possible.
Collection of material
- The container from which feces are collected must be clean, without additional impurities such as water, secretions, or urine.
Also, it should not be metal. It is recommended to purchase a plastic pot, which needs to be boiled before testing. Taking material from the toilet is prohibited! - It is advisable to collect morning feces from a sterile pot using a clean spatula.
- Sampling is carried out from different departments, several factions.
- About 2/3 of the volume is filled into the container (this is about half a teaspoon).
- Close the lid tightly.
Store the material at a temperature of 4-8 - this is the temperature of the refrigerator compartment. The shelf life of stool is up to 12 hours.
If the ambient temperature is higher, then the material must be delivered to the laboratory within two hours. Otherwise, the result will be unreliable.
Read on topic: Basic stool parameters for self-assessment
Different laboratories may use different techniques.
The basis is the presence of antibodies to human hemoglobin in the test system. The test is very sensitive and specific. It allows for quantitative determination, the range of which is from 0 to 50 ng/ml. The only disadvantage of the reaction is the inability to determine the presence of bleeding localized in the esophagus, since under the influence of digestive enzymes hemoglobin breaks down into structural components.
Gregersen reaction
If the diet is violated, false positive reactions are possible. In this case, you have to adhere to a strict diet, but using this reaction you can confirm the presence of bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract. This is due to the fact that the reagent determines the presence of iron, which is part of the hemoglobin of red blood cells.
Read on the topic: Stool color: norm and pathology
After the reaction, the laboratory technician evaluates the result of the occult blood test. The analysis is carried out quickly and answers can be provided within the current day, so the method is a rapid diagnosis.
If after the test the reagent does not change color, then the reaction is considered negative. If the patient has clinical manifestations, it is recommended to repeat the test three times.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Cerucal: instructions for use for children, dosage for children, analogues, price
The test has its own error and cannot accurately determine the absence of bleeding. The attending physician may prescribe an in-depth examination if in doubt.
If the result is positive, the reagent changes color. In this case, it is necessary to determine the source of bleeding. The reaction is only a marker; it determines the fact of damage; it is necessary to determine its location.
Further diagnosis is necessary, since often a stool test for occult blood is a marker of the development of dangerous diseases.
Possible reasons
The following pathological conditions may be the reasons for the appearance of occult blood in the stool as a result of enzyme immunoassay:
- polyposis of the intestinal tube;
- anal fissures;
- inflammation of hemorrhoids;
- autoimmune intestinal lesions (ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease);
- cancer (can be detected in early stages);
- helminthiases;
- infectious pathology accompanied by hemocolitis.
When performing the Gregersen reaction, you can additionally think about:
- peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum;
- dilation of the veins of the esophagus;
- ulcerative lesion of the esophagus.
Diagnostics
If the test is positive, the following studies are necessary:
- Blood clinic. Allows you to assess the degree of blood loss (anemic manifestations), suggest the presence of an inflammatory process (changes in the leukocyte formula) or an autoimmune process (increased ESR, eosinophilia).
- X-ray of the intestine with contrast (barium). Allows you to determine filling defects - ulcerations, space-occupying formations with approximate localization.
- CT or MRI. The presence of space-occupying formations and metastatic lesions in the abdominal organs is assessed.
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS). Allows you to visually evaluate the mucous membrane of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum. It is possible to take material for a biopsy.
- Colonoscopy. Evaluates the condition of the colon mucosa throughout its entire length. It is possible to take material for histological examination.
- Sigmoidoscopy. A visual assessment of the rectum is performed and tissue is taken for biopsy.
- Video capsule. An expensive examination that allows you to visually evaluate the gastrointestinal tract along its entire length.
Read on the topic: Intestinal biopsy: why and how is it done?
A screening test for blood in stool is carried out for the following indications:
- dyspeptic disorders of unknown etiology (frequent nausea, heartburn, flatulence, stool instability);
- regular pain in the abdominal area without a clear cause;
- anemia of unknown origin in a clinical blood test;
- rapid weight loss;
- loss of appetite;
- discomfort and pain during bowel movements;
- intoxication syndrome of unknown etiology (unmotivated rises in temperature, chronic fatigue syndrome due to decreased appetite, weight loss);
- age after 40 years;
- family history of cancer or autoimmune intestinal pathology.