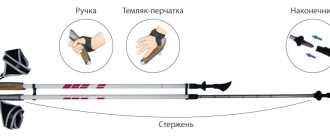
In some cases, medications are prescribed that have to be administered by injection. If the injection must be given into a vein, then going to the treatment room would be the best solution. But with intramuscular injections, you can simply ask one of your relatives or friends.
Giving yourself an injection in the buttock yourself is inconvenient and scary, so if your assistant does not know exactly how this is done, it is better to educate him.
Provide him with detailed instructions on how to properly give the buttock injection. In the event that you are not aware of this, both of you will have to study the issue.
In fact, getting an injection in the buttock at home is not that difficult, the main thing is to prepare for the procedure in advance. There are several steps, the correct implementation of which will lead to the most correct procedure.
In our material we will tell you step by step about all the steps to correctly performing an injection in the buttock.
Preparing for the procedure
The more thorough the preparation, the fewer complications during and after intramuscular injection. In order to correctly inject into the buttock, immediately before the procedure you need to:
- Ensure disinfection of both the injection site and the hands of the person giving the injection. Hands or medical gloves are treated with any skin antiseptic or wiped with special alcohol wipes. At home, you can use cologne or vodka as an antiseptic.
- Prepare a syringe that corresponds to the amount of drug administered (2 ml or 5 ml). 2 ml syringes are usually used when injecting children or thin people - those who have a very thin subcutaneous fat layer. For everyone else, the injection into the buttock is given with a 5 ml syringe.
- Prepare sterile alcohol wipes or cotton wool and skin antiseptic to treat the body surface before and after injection.
- Remove the ampoule/ampoules with the medicinal substance from the box, carefully check the name, concentration of the solution, expiration date and integrity of the ampoule/ampoules.
Be sure to ensure that the sterile packaging of the syringe is intact. Do not use a syringe whose packaging is damaged.
If the medicine has changed color, become cloudy, or a sediment has formed, it should not be used.
It is necessary to prepare suspensions from powdered drugs (antibiotics, etc.) or lyophilisates immediately before the injection. If a solvent is included in the medicine box, it is not advisable to use another solvent.
It is imperative to ask the patient if he is allergic to the medicine you are about to administer. If an allergic reaction was previously noted, the drug is not administered!
Step-by-step instruction
To correctly administer the solution for intramuscular injection, you need to perform the following sequential steps:
- The plate is disinfected with boiling water, and hands are washed with antibacterial soap;
- Tampons are formed from cotton wool, which need to be soaked in antiseptic. 5 pieces are enough;
- A closed syringe, cotton swabs, an ampoule with medicine or a jar with lyophilisate are placed on the plate;
- You need to wash your hands again, dry them on a towel and put on gloves;
- The ampoule is opened or the lyophilisate is diluted;
- All garbage remaining after preparing for the injection is thrown into a garbage bag;
- The package with the syringe is opened and the needle opens;
- The medicine is drawn into the syringe, then the needle is turned up and the air is released by pressing the piston. There should be a trickle;
- The patient's buttock is wiped with tampons soaked in antiseptic. It is necessary to disinfect a large area of skin, not just the injection site;
- Afterwards, you need to wipe the buttock with an antiseptic again, but now only the area where the needle was inserted;
- The needle is sharply inserted into the muscle at an angle perpendicular to the skin, but not all the way. There should be at least half a centimeter left on the surface;
- Under the pressure of the piston, the solution is gradually injected into the gluteal muscle;
- After quickly removing the needle, a swab soaked in antiseptic is applied to the wound.
Read:
36 most expensive sneakers
Upon completion of the procedure, all unnecessary instruments are thrown away, and hands are thoroughly washed with soap.
How to give yourself an injection in the buttock (diagram)
Having prepared everything for the manipulation and making sure that there are no contraindications for the injection, perform the injection according to the following algorithm:
- Open the syringe package, holding the needle, tightly secure the needle to the needle cone.
If the connection is not tight, the needle may come off during injection. This measure eliminates leakage of the drug, ensuring the administration of the exact amount of medication.
- Open the ampoule with a nail file from the package or, if provided by the manufacturer, along the break line.
- Draw the dose of the drug prescribed by the doctor into the syringe without touching the walls of the ampoule with the needle - this way you will not violate its sterility. Release the air from the needle and syringe. In this case, hold the syringe vertically, with the needle up.
- Ask the patient to lie on their stomach or side, exposing the buttock. Inspect the site of the future injection for wounds, tumors, skin lesions, and spider veins. If there are any, it is better to give the injection in the other buttock.
- Mentally draw your buttock crosswise into four zones. The upper outer zone in the diagram is the site of the future injection.
The injection cannot be given in other areas. There is a high risk of complications such as damage to arteries and nerves.
- Lubricate the skin of the buttock with a sterile alcohol wipe or cotton wool pre-moistened with an antiseptic. Treat the immediate site of the future injection with another napkin.
- If necessary, grab the skin into a small fold.
- With a confident movement, insert the needle at an angle of 90 degrees into the center of the upper outer zone to 2/3 of the depth. For obese people and when injecting drugs intended for deep intramuscular administration (as a rule, this is indicated in the instructions), the needle is inserted as deeply as possible.
If the syringe contains a suspension or oil solution, first pull the syringe plunger towards you. You cannot start injecting the solution if blood appears in the syringe - it may enter a blood vessel. Pull the syringe with the needle slightly towards you and then inject.
Inject the medicine slowly, monitoring the patient's sensations.
If the patient feels weak or ill, stop the procedure immediately and remove the needle.
After the medicine is injected, remove the needle with a smooth movement and apply a cotton swab with an antiseptic or an antiseptic wipe to the injection site.
Make the next injection in the other buttock or 1-1.5 cm away from the previous one. You cannot go beyond the upper outer zone.
Preparatory activities
Before giving an intramuscular injection to an adult, you need to take:
- Soap, preferably antibacterial;
- Clean cotton towel or sterile paper towels;
- Medical cotton wool;
- Antiseptic - alcohol or Chlorhexidine, hydrogen peroxide will not work;
- Disposable medical gloves;
- An additional needle (if you need to dilute the lyophilisate in the vial);
- A plate scalded with boiling water for placing tools;
- A sterile syringe, the capacity of which corresponds to the volume of the medication ampoule;
- Trash bag.
Selecting a location
The patient who needs to be given an injection must be placed on his stomach, so the place must be chosen that is level and not too soft. A hard couch, an unfolded sofa, or, in extreme cases, a table covered with a clean cloth will do. You cannot lie on the floor, as there are a lot of germs and dust there.
The person giving the injection must have free access to the table where there is a plate with a syringe, needles, medicine, etc. During the procedure, his hands must not come into contact with interior items. Only with the patient’s body and sterile instruments.
If you need to give yourself an injection, you should not lie down, but stand. In this case, it is better to position yourself in front of a mirror to see the back of your body and correct your actions.
Read:
Why do some people eat a lot and don't gain weight?
Hand washing
Before each injection of an intramuscular solution, the person giving the injection must wash their hands thoroughly. This is a mandatory hygienic procedure that prevents pathogens from entering the patient’s skin or wound. Also, washing your hands before touching another person's buttocks allows you to protect yourself from infection by germs, fungi and bacteria, especially if he is suffering from an infectious disease.
Interesting!
In addition to the buttock, intramuscular solutions can be injected into the brachialis muscle. But in this case it will be very painful.
Dilution of the lyophilisate
The medicine can be supplied to pharmacies either in the form of a ready-made solution or in powder form. In the latter case, it must be diluted with a 0.9% sodium chloride solution. This is done according to the following scheme:
- Sodium chloride is drawn up with a syringe;
- The protective cap of the jar is pierced with a needle and the solvent is poured in;
- Without removing the needle, shake the bottle thoroughly until the lyophilisate is completely dissolved.
Afterwards, the medicine is drawn into the syringe and the needle is replaced with a new one. You cannot use an old needle, because when you pierce the rubber cap, its end will become dull and it will be difficult to pierce the skin.
Determining the injection site
To avoid piercing a blood vessel or nerve of the sacral plexus, you must choose the correct injection site for the needle. To do this, half the butt is mentally divided into 4 parts. The outer area at the top is the zone where it is permissible to inject.
The medicinal solution can be injected into both the left and right buttock. If the patient is undergoing long-term drug treatment and needs frequent injections, then it is necessary to inject each time into a different gluteal muscle. For example, today the injection is given in the right half, tomorrow in the left, and the day after tomorrow again in the right.
Where else are intramuscular injections given?
Intramuscular injections are not always performed in the buttock. Sometimes this is not possible, for example, with bedsores or injuries to the buttocks, after surgery on the buttocks.
In addition to the gluteal muscle, the deltoid muscle of the shoulder and thigh muscles are used to administer the drug intramuscularly.
Complications with injections in the shoulder and thigh occur more often; injections into these places are more painful.
But when you need to inject yourself intramuscularly, it is more convenient to do it in the thigh area.
However, you can also use the buttock.
Important points - which injections you can’t do yourself
When inserting a syringe, the needle must cross the skin, subcutaneous fat and enter the muscle tissue. Therefore, zones are chosen for penetration where:
- Maximum number of myocytes.
- There are no large blood vessels.
- Few nerve endings.
In most cases, when an injection is performed by a stranger, he uses the gluteal region, its upper outer quarter. However, this is not the only place on the body where the drug can be administered. Suitable for self-treatment:
- Stomach. Here the medicine is injected into the subcutaneous tissue. A ten-centimeter circle around the navel is most suitable, departing from the center by four to five centimeters. To avoid perforation of internal organs and the wall of the abdominal cavity, before the puncture, a large fold of tissue is made into which a needle is inserted.
- Forearms. Use the side and back.
- Thighs. Front surface.
To protect against damage to the periosteum when a needle is inserted into the shoulder or leg, the muscle is also folded. The medication is administered lying or standing.
A little trick! Before injecting into the buttock, you need to slap it first. Muscles relax and nerve fibers are “distracted”. The puncture will be painless.
Certain nuances of the procedure may vary. Each physician uses his own tricks and features of gluteal injections. However, the basic sequence is maintained in all cases.
Injection into the buttock:
- Draw the solution into a syringe.
- Raise the needle up. If necessary, flick the sides of the syringe to release large bubbles. Then press the plunger lightly to release the air. In the final version, the needle should be filled with the substance to the very tip. To do this, press the plunger until splashes or droplets of medicine appear. Parietal bubbles may remain on the walls. It's not scary.
- Visually divide the buttock into four parts. You need the top outer one. If in doubt, place your left palm on your right buttock or your right palm on your left buttock, pointing toward your back. Move your thumb at a right angle to the rest. Between the index finger and the thumb there will be an area for the injection.
- Wipe the area with cotton wool and alcohol.
- Slap on the buttock.
- Holding the palm of your left hand on your butt, slightly stretch the skin in the desired area.
- Push the syringe firmly, inserting it strictly perpendicularly and holding it like a dart. The needle should go three-quarters of the way in.
- Using your thumb, slowly press the plunger to inject the medication.
- Having reached the end, apply cotton wool to the puncture site and sharply remove the needle at the same angle as it was inserted.
- Press down on the area with a cotton swab so that some of the medicine does not flow back out due to muscle tension.
Injection at other sites
Eliminate the third, fifth and sixth points from the procedure. Instead, pinch the fold of tissue with your thumb and forefinger, wipe with alcohol and, without letting go, insert the tip and inject the drug. Then follow the previous instructions.
Advice! When making a series of injections, alternate between the right and left sides and make the next puncture away from the previous one.
Young patients tend to cringe at the sight of a syringe. The child may become hysterical and difficult to calm down. Therefore, the preparation should be carried out without his knowledge. For the safety of the baby, you need to properly secure the body.
- If you are working with an assistant, he can pick up the child while standing, placing his head on his shoulder and turning his butt towards you. One hand of an adult tightly clasps the chest area or belt, the other fixes the legs just below the causal site.
- Second option: sitting pose. The child is placed between the legs with his face to the side, then tilted and bent over one knee, fixing his legs between his knees. Thus, the butt is raised up. Hands should support your back.
- When performing the manipulation yourself, the baby is placed flat on his stomach. They sit on his legs. Hold your back with one hand and insert the needle with the other.
The main task is to avoid sudden jerks from the patient. Otherwise, soft tissues will be damaged or the metal may break off.
The most common problem that arises during long-term treatment is the appearance of lumps and bumps at the injection sites of the drug. To minimize the problem, you should make an iodine mesh in the treated area. It is also useful to apply alcohol compresses at night.
- Hematoma. If you hit a capillary or small vessel, a hematoma appears. It will resolve over time. Injections should not be given at the site of the bruise. A large or increasing area of hemorrhage is a reason to consult a doctor.
- Abscess. Appears when sterility is violated. After consulting a surgeon, ointments (Vishnevsky, Ichthyol) are used to draw out the purulent contents.
- Nerve puncture. The limb becomes numb and, in rare cases, loses mobility. Treatment will require anti-inflammatory drugs, which will be prescribed by a doctor.
- Anaphylactic shock. The result of an immediate allergic reaction to the drug. Manifested by respiratory and cardiac arrest. It is necessary to perform artificial ventilation and cardiac massage, call an ambulance.
- Quincke's edema. Instant swelling of the tissues of the face and larynx. Another type of allergic reaction. Danger of suffocation. The “antidote” in this case is the administration of dexamethasone in ampoules. An adult has two cubes. For a child, depending on age, 0.3-1 ml. Be sure to call the doctors.
- Needle breakage. A very unpleasant event when the tip remains in the tissues. Removal is performed surgically. It is important to maintain a static position and call an ambulance.
Most of the troubles are associated with incorrect administration technique and self-medication without consulting a doctor. Therefore, it is important to strictly follow the instructions for the drug and the rules of manipulation.
Intramuscular injections are given in the area where some of the largest muscles in the body are located - the gluteal muscle, the outer thigh, or the deltoid muscle.
If you do a subcutaneous injection, then choose places with a good subcutaneous layer of fat - the abdominal area or the inner thigh is suitable for this purpose. It is convenient to give injections in these places and independently - for yourself.
Injections in the buttock or thigh area are made in such a way that the injection area is not repeated. That is, you cannot prick in the same place - it is both painful and fraught with the appearance of bruises or hardening.
Experts recommend choosing a two-cc syringe with a thin needle for injections - it is more convenient to administer the drug and does not leave any seals. Of course, such a choice is possible if there are no special instructions from the doctor. In this case, you must follow the specific recommendations issued.
Always carefully read the instructions for the injected drug - because some of them require additional components for injection. For example, lidocaine or a special aqueous solution.
Also, before each injection, you must wash your hands to prevent the possibility of foreign microorganisms getting into the wound. Despite the fact that the injection site is always treated with alcohol, this is not enough to ensure the necessary sterility.
Watch this video on how to properly give an intramuscular injection.
Many drugs, including antibiotics, are prescribed by injection - intramuscularly. The course of such injections can have different timing, and very often a situation arises when the injection must be given either early in the morning or late in the evening. At this time, the nearest clinic is no longer open, so it is very important to be able to give intramuscular or subcutaneous injections yourself.
Intramuscular injections are most often given in the buttock - this is one of the largest muscles in our body. There are also no nerve ganglia or large vessels in this area. It is recommended to do the injection while lying down - so that the muscles relax. This not only reduces the pain of the process, but also prevents the risk of accidentally breaking the needle.
Shake the ampoule, tap its top with your fingernail so that all the liquid is at the bottom. The ampoule cap is filed with a special file and the tip is broken off. The medicine is drawn into the syringe in the needle-up position, after which the syringe plunger is slowly pressed to push the air out of the needle. A sign of success in this case will be droplets of the drug at the tip of the syringe.
The injection is given in the upper part of the buttock, after palpating the area for the presence of lumps. Next, you need to fix the skin at the injection site with two fingers - the thumb and forefinger.
The injection itself is done as follows:
- The syringe is held with all fingers at once - vertically, with a slight inclination relative to the surface of the buttock. In one movement, the needle must be inserted to ¾ of its length - approximately 1 cm should remain on the surface.
- With one hand, hold the syringe in a stationary position, and with the thumb of the other hand, slowly press the plunger - while the drug is injected gradually. This is necessary in order to eliminate pain and the appearance of a lump at the injection site.
- After administering the drug, you need to press the alcohol-containing cotton wool to the point where the needle enters the skin and pull it out in one motion. The cotton wool is left at the injection site for some time for disinfection.
It is important to rub the injection site so that the drug spreads better throughout the body, as well as to avoid stagnation. Very often, patients complain of bruising or hardening at the injection site. To prevent such phenomena, you need to rub the injection area with light massage movements.
This useful skill will be useful to everyone, because it is not always possible to go to a clinic or use the services of a qualified nurse who would come to your home.
Despite the apparent complexity, the principle of action is the same as when you inject another person. The only difference is that you need to pay special attention to preparing for the injection.
In order to give yourself an injection into the gluteal muscle, you need to stand in front of a mirror so that you can clearly see your buttock.
Then you need to transfer the body weight from one leg to the other according to the following principle - if you, for example, give an injection in the left buttock, then the body weight should be transferred to the right leg.
How to properly inject yourself
In some cases, it is necessary to inject yourself. To properly inject yourself in the buttock, follow the following algorithm:
- Open the syringe package and tightly attach the needle to its tip.
- Open the ampoule with a nail file from the package or, if provided by the manufacturer, along the break line.
- Draw the dose of the drug prescribed by the doctor into the syringe, without touching the walls of the ampoule with the needle. Release the air from the needle and syringe.
- Stand or lie on your side, expose your buttock, examine and feel it for wounds, tumors, skin lesions, and spider veins.
- Treat the upper outer area of the selected buttock with an antiseptic.
- Grasp the skin in a fold and make a puncture at an angle of 90 degrees so that the needle enters 2/3 of the length.
- Slowly inject the medicine and remove the needle with a smooth movement.
- Treat the injection site with an alcohol wipe or cotton swab moistened with an antiseptic.
Complications are common when performing an injection in the buttock yourself, so it is better to entrust this procedure to someone else, ideally a medical professional.
Useful tips
There are several tips on how to give an intramuscular injection in the buttock without outside help. They will help you learn quickly and make the process as painless as possible.
- For the procedure, it is advisable to choose modern syringes with a rubber tip on the piston.
- The syringe is intended for single use only.
- If a course of injections has been prescribed, you should not inject in the same place.
- It is advisable to warm up ampoules with oil solutions first in your hands or under running warm water.
- After the needle is inserted into the muscle, you need to slightly pull the piston up. If blood enters it, it means that the vessel has been touched. The fix is simple. You just need to deepen the puncture a little.
Possible complications of the procedure
As with almost any medical procedure, intramuscular administration of the drug may have general and local complications.
- Allergy to a medicinal substance up to the development of anaphylactic shock, which can result in death. In case of allergies, the drug is not administered!
- Embolism. Entry of an air bubble or oil into the blood. The complication is fatal in most cases.
- Infiltrates. Tissue compactions after multiple injections into one buttock, with the introduction of large doses of solutions, oil solutions, magnesium sulfate. It also occurs when the solution gets into the subcutaneous fat layer instead of muscle, if a short needle was used (with a 2 ml syringe) or if the needle was inserted shallowly.
- Abscess. If aseptic and antiseptic measures are not followed during injection, microorganisms enter the skin and cause acute purulent inflammation. It is treated surgically.
- Broken needle. If the injection is performed roughly, the tip of the needle may break off and remain in the soft tissues. Treatment is surgical.
- Bleeding when a vessel is punctured. It happens when the injection site is chosen incorrectly.
- Nerve inflammation. It happens when the injection site is chosen incorrectly.
If it is not possible to entrust an injection into the buttock to a medical professional, it can be done at home. If you take precautions and follow the standard algorithm, performing an injection in the buttock correctly will not be difficult.
About the author : Sokolova Leila Aleksandrovna, senior nurse of the surgical department. 11 years of experience.
Which part of the buttock should the injections be given?
The upper (outer) part of the buttock is considered a suitable area. To avoid mistakes, the muscle must be visually divided into 4 equal parts. The upper square, namely its middle, will be the area where you need to place the injection.
The most suitable place for injection is in the buttock
The photo clearly shows the area that is best suited for administering medications. The location is far from the sciatic nerve, iliac bone and spinal column, which allows for safe manipulation.
The advantage of self-injection
If a person has mastered injecting himself in the buttock or another muscle and does them carefully and without unpleasant consequences, then this is more convenient for him than going to the treatment room.
- The patient himself can choose the time and place for the injection, gather his courage, and take a comfortable position. Nurses typically administer medications to patients in a standing position, which can be painful;
- Some drugs require slow administration. Procedure nurses quite often neglect this rule, since they have a whole line of patients outside the office door. By injecting yourself, you can administer the medicine at the speed needed;
- To reduce pain from an injection at home, you can use a special patch or gel with lidocaine. The patch is placed on the injection site for an hour, the gel is applied as a layer under a bandage or regular patch. After applying the anesthetic patch or gel, inserting the needle is almost painless. In a clinic setting, the use of patches and gels is almost impossible;
- Lidocaine should be used instead of water and saline when preparing solutions for injections. Then the injection will be less painful. but not all medications are combined with it, so you need to check with your doctor about this possibility;
- You can select needles whose insertion causes almost no pain, for example, triangular ones from outside the border. They instantly pierce the skin. It is also good to use syringes for administering insulin if the volume of the drug administered is small. In the clinic, the needles and syringes are domestically produced and not always of high quality;
- Nurses give the injection with the same needle that was used to draw the drug. At home, it is better to change the needle. Because when taking medicine through a puncture in a rubber cap or from a glass ampoule, the needle becomes dull upon contact with the cap or walls of the vessel, pierces the skin slowly and causes noticeable pain;
- The patient knows well where he had the site of yesterday’s injection of the medicine, a hematoma, a lump, so he injects himself into another part of the body. The nurse at the clinic does not know this and may administer the drug in the same place as last time. Firstly, it is much more painful, secondly, such an injection can lead to the formation of an abscess, and thirdly, the drug disperses worse through the blood if it is injected into a seal.
Choosing a site for IM self-injection
There are four main areas for intramuscular injections on the body, which are considered the safest and most effective for this procedure. Among them:
- Thigh: Vastus lateralis muscle (m. vastus lateralis) - although the degree of absorption of the drug administered in this way is often lower than when an injection is given in the shoulder, this is still the best area for IM self-injection.
- Buttock: Anterior gluteal region (ventrogluteal muscle) – This is a suitable place to perform an IM injection, since the fat layer here is thinner than on the buttocks themselves, which contributes to better absorption of medications. This area is also considered the safest if the procedure is followed correctly.
- Shoulder: Deltoid muscle (m. deltoideus) - The most common site of administration for many vaccines. When giving an injection to this area, you need to carefully measure the volume of the injection, because this area can accommodate a limited amount of the drug at a time. For adults, it is not recommended to exceed a dosage of 1 ml.
- Buttocks: Dorsogluteal muscle - Also an acceptable and widely used injection site. Although this area is significantly removed from major nerves and blood vessels, there is still a risk of damage to the sciatic nerve.
When choosing an area for an independent intramuscular injection, you need to take into account its accessibility and the volume of the drug used. The following questions should be answered:
- Do you give an IM injection alone?
- Can you ask someone to give you an IM injection?
- What dose are you using?
The best place for IM self-injection is considered to be the thigh due to its high accessibility and good visual control. You can also use a larger needle for this area compared to the shoulder. If you have skill and considerable maneuverability, you can independently give an IM injection in both the thigh and buttock.
To inject a large dose of medication, it is better to choose the thigh muscle, since in this zone the threshold for the maximum injection volume is higher. The maximum dose of the drug for the muscles of the buttocks and thighs is 4 ml, while no more than 1 ml can be injected into the shoulder (link). If the required amount of medication exceeds a single dosage for a particular area, you can divide this volume into several injections and place them in different places. This is quite optional for fat burner injections, because they are mainly recommended to be injected 1 ml at a time.
It is also worth changing the areas where injections are performed to avoid skin irritation and scarring. Whether you inject in different places or not, it is advised to allocate a zone with a radius of 2-3 cm for each procedure. It would not be amiss to write down the place and time of the last injection into the muscle. This way you can protect your skin from irritation and avoid complications caused by improper use.
Why are injections given in the buttock?
Most often, injections are given in the outer upper quadrant. The zone is selected because it is rich in subcutaneous tissue and has developed muscle fibers. There are few blood vessels and nerves here. A successful anatomical structure is less painful for the patient and convenient for the one who injects into the buttock.
The poverty of the capillary network makes the zone a good place for creating a medicinal depot. When an injection is given in the buttock, the medicine enters it. It accumulates and slowly enters the general channel. Gradually being absorbed, the solution spreads the therapeutic effect throughout the body, leading to an improvement in the patient’s condition.
Many people ask whether it hurts to inject antibiotics or vitamins. When positioned correctly and using a slow insertion technique, they do not cause any discomfort.
Intramuscular administration of drugs
Medicines prescribed by a doctor are introduced into the patient’s body enterally (through the digestive tract) and parenterally (bypassing the gastrointestinal tract).
One of the most popular methods of parenteral drug administration is intramuscular injection, a procedure that every nurse should be familiar with. Intramuscular injections are carried out in the treatment room of a hospital or outpatient medical facility, in the ward directly in the patient’s bed and at home as prescribed by the local doctor.
A specialist who has a state diploma of completion of a secondary or higher medical educational institution in the specialty: “Nursing”, “Midwifery”, “General Medicine”, “Pediatrics” has the right to administer intramuscular injections in medical institutions and at home.
The purpose of the procedure is to introduce a medicinal solution into muscle tissue.
Indications for intramuscular injections are determined exclusively by the attending physician or the doctor on duty.
Contraindications . Determined by a doctor. There should be no inflammatory and/or degenerative processes at the injection site (ulcers, rashes, burns, etc.)
Advantages of the method . Exact dosage. Rapid entry of the drug into the body, although not lightning fast (as with intravenous administration). Quite accurate dosage of the drug.
Risks of self-injection
The most common problem that people encounter when administering injections on their own is the formation of an infiltrate. To eliminate it as quickly as possible, you need to lubricate the area with heparin ointment, make magnesium compresses, and install a mesh with iodine.
If the injection site is chosen incorrectly, damage to the sciatic nerve or superior gluteal artery may occur. These cases require contacting a doctor for adequate help. If the dose is incorrectly calculated, if it is underestimated, the effect may not occur, and if it is overestimated, an allergic reaction may begin. In the second case, you should immediately call a doctor.
Let's make ourselves
For other adults or children, getting an injection in the butt correctly is not so difficult, but giving yourself injections, doing it correctly, is a real science. But this can also be solved, you just need to adapt well to inject. You need to turn around in front of the mirror and understand how it will be most convenient for you to inject and how to hold the syringe so that everything comes out. A little training and the problems will disappear; this is the only way to learn how to give injections correctly.
WE ADVISE YOU TO READ:
The insidious disease meningitis: whether or not to vaccinate against it
Previous article
Vaccinations for newborns - immunization calendar by month
Next article
Anatomical landmarks for performing IM injections
- Thigh : Divide the surface of the thigh into three equal parts. The middle portion of the muscle between the upper thigh and knee corresponds to the injection area. As you prepare to insert the needle, lift the muscle slightly off the bone.
- Shoulder : At the top of the arm, the bones form an inverted triangle. The apex of the triangle points to the midaxillary line, and its base lies along the acromial line. Inject into the center of the resulting triangle 3-5 cm below the acromial line.
- Buttock (front area): Lie on your side with the injection side facing up. Place your hand on the area where your gluteal muscle connects to your upper thigh. Turn your palm so that your thumb points toward your perineum and your remaining fingers point toward your head. Extend your index finger to form a “V” shape. Insert the needle into the center of this figure.
- Buttock (posterior area): Divide the buttock into four equal sections. The upper outer quarter is the injection site.
Selection of needle for intramuscular injection - caliber and length
First, you need to know that a syringe consists of three main elements:
- Needles: The part of the syringe that pierces the skin and penetrates the muscle (caliber and length will be discussed later)
- Cylinders: containers for measuring and containing medicinal solution
- Piston: element that controls the flow of the drug
The needle must be long enough to penetrate the muscle to the desired depth. The two main characteristics of a needle are gauge and length. The gauge corresponds to the diameter of the needle. The larger the gauge, the smaller the needle diameter. For intramuscular injections, 22-25 gauge needles are usually used.
The length of the needle is measured in millimeters (mm) and typically depends on the person's body type. However, the standard needle length for intramuscular injections ranges from 45-70 mm. Be sure to select the optimal gauge and length of needle for each injection site to prevent any pain that may result from improper needle insertion, tissue damage, or irritation.
Injectable preparations usually come in a kit with suitable needles. If in doubt, be sure to contact your healthcare provider to ensure that the gauge and length of the needle you are using is correct.
How to give an IM injection (infographics)
Disposal of needles and syringes
Needles and syringes should not be thrown away with general household waste or recycled. They are subject to government regulations regarding proper disposal. You can ask your doctor's office or purchase a special container for proper needle disposal. If necessary, you can use any durable container or plastic bottle with a tight-fitting lid for this. Be sure to check current laws regarding proper disposal.