Treatment of hematemesis
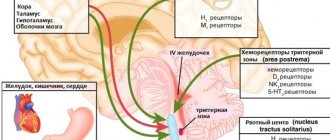
The vomiting reaction is always formed “in the head,” specifically in two zones of the medulla oblongata.
One of the zones is called the vomiting center; a response is formed there to the transmitted impulses in the form of a command to contract muscles in some organs or relax in others. The second area, the chemoreceptor trigger zone (CHZ), also collects “nauseous” impulses from the underlying sections and sends them to the vomiting center for response. When impulses to the medulla oblongata come from special sensitive cells of the intestinal mucosa, this mechanism is designated as peripheral. Signals coming from the cerebral cortex or from biologically active or toxic substances circulating in the blood directly to the chemoreceptor zone form the central mechanism of nausea and vomiting. In a cancer patient, both mechanisms are activated separately or together.
The central mechanism is believed to occur in the following clinical situations:
- increased intracranial pressure due to tumor or metastatic lesions of the brain is complicated by visual and neurological disturbances, as well as a gag reaction when turning the head, and in severe cases even with synchronous opening of the eyes;
- high concentration of calcium in the blood - hypercalcemia when bone tissue is destroyed by multiple metastases or when the parathyroid glands are involved in a conglomerate of thyroid cancer;
- tumor intoxication, when toxic waste products of a cancer tumor and decay products of a tumor node are constantly released into the blood and poorly eliminated;
- psychogenic vomiting reaction due to fluctuations in psycho-emotional state or from fear of imminent nausea and uncontrollable vomiting during chemotherapy.
The peripheral mechanism is involved in the following cases:
- complications of the use of chemotherapy drugs that are toxic to nerve tissue, causing a significant decrease in intestinal motor activity until contractions stop—intestinal paresis;
- intestinal obstruction or stenosis - narrowing of the outlet of the stomach by a malignant neoplasm;
- tumor damage to the liver with a significant decrease in functionality.
The interaction of both signaling pathways to the vomiting center provides radiation and chemotherapy, in which toxic metabolites circulate in the blood and irritate the sensitive cells of the intestinal mucosa. When using high doses of narcotic analgesics, the effect of metabolites is complemented by a decrease in gastrointestinal motility, but gagging is less of a concern than almost constant nausea.
Oncology has achieved considerable success in the treatment of chemotherapy vomiting, despite an incomplete understanding of the mechanism of action of antiemetics. Not only standard prevention and treatment regimens have been developed, but also basic principles for taking antiemetic drugs:
- early prediction of the intensity of complications and individual selection of a combination of antiemetics;
- start taking it not when a complication develops, but ahead of time and strictly on an hourly basis;
- the advantage of intravenous and rectal forms over those taken orally - orally;
- adding tranquilizers for nervousness;
- introduction of PPI drugs into the regimen that protect the mucous membrane;
- adequate levels of microelements in the blood and a sufficient volume of circulating plasma are maintained by intravenous drips.
When vomiting, the likelihood of gastric contents refluxing into the respiratory tract in a conscious patient is minimal. If the patient is unconscious, which is possible in the terminal stage of cancer, especially with metastases to the brain or liver, the head is turned to the side, trying to tilt it lower.
It is impossible to interrupt the urge to vomit; interference with the process will worsen its course and irritate the patient. After vomiting, it is advisable to rinse your mouth and replenish lost fluid throughout the day by drinking cool water with electrolytes - rehydron - and only in small sips.
In all cases of the development of an emetic reaction, it is necessary to prescribe antiemetic drugs; an initially effective combination does not guarantee a constant result; constant monitoring of the condition and regular adjustment of the regimen are important.
All patients with hematemesis are referred for urgent gastroscopy, during which they try to detect the source in the form of a gaping vessel and carry out conservative measures to stop the bleeding.
Many methods have been developed for local control of bleeding during endoscopy; often several methods are used in one patient. They resort to hypothermia with an ice solution, hemostatic agents and various methods of coagulation and vascular embolization. It is especially difficult with profuse leakage, when the blood seems to be oozing from the wall and not a single damaged vessel is visible.
The frequency of relapses after endoscopic control of blood loss is also significant, so the possibility of performing surgery on a cancer patient is mandatory. A radical measure is removal of the stomach, but emergency intervention immediately after the bleeding has stopped results in high postoperative mortality, therefore, if possible, the patient is actively prepared for a planned surgical intervention within several days.
Treatment of a bleeding stomach is a very difficult task, requiring only an individual therapeutic approach with the clinic being well equipped with modern operating and diagnostic equipment. To this, our clinic adds vast experience in endoscopic interventions in complex cancer patients.
Approximately 50% of people with malignant tumors experience nausea, which is either a symptom of the cancer itself or a consequence of anti-cancer treatment.
Nausea in cancer is defined as an unpleasant feeling of the need to vomit and is often accompanied by autonomic disorders:
- pale skin;
- cold sweat;
- increased salivation;
- dizziness;
- tachycardia.
This is a more stable state of the body than vomiting, which can occur on its own. Difficult to control, therefore it may cause interruption of therapeutic measures.
- Intestinal obstruction is a common complication of common malignant neoplasms. It leads to obstruction, mechanical compression, motility disorders, etc. It may be a consequence of anticancer therapy.
- Side effect of chemotherapy. Occurs immediately after treatment or after some time. In this case, toxic substances are located in the gastrointestinal tract. They stimulate a number of receptors: 5HT3, neurokine-1, cholecystokinin-1.
- In 20% of cases, the state of nausea precedes therapeutic measures. It has a lot to do with the psychological aspect. Therefore, pharmaceutical drugs are often not effective. The only remedy that combats premature nausea is a benzodiazepine. You can also use the following methods:
- behavioral changes;
- systematic desensitization;
- progressive muscle relaxation;
- hypnosis;
- acupuncture and acupressure.
- Radiation therapy may cause nausea in cancer patients depending on a number of factors:
- irradiation sites;
- total dose;
- fractionation;
- volume, etc.
Nausea with stomach cancer
Stomach cancer is accompanied by the following additional symptoms:
- general persistent disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, in particular heartburn, pain and discomfort;
- bloating and vomiting that occurs soon after eating;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- as if something was stuck in the stomach.
Drugs for the treatment of nausea in stomach tumors are prescribed according to its causes. They usually contain phenothiazines, butyrophenones and other drugs that have antihistamine and antimuscarinic properties.
Nausea with liver cancer
Often occurs due to systemic poisoning of the body by an oncological formation or the spread of a tumor beyond the primary localization. The altered chemical balance of the blood interferes with the performance of its main functions. At the same time, blood contaminated with toxic substances circulates throughout the body. It penetrates the blood vessels, transmits signals to the brain about the presence of abnormal cells and affects the corresponding receptors.
Treatment of nausea in liver cancer consists of the use of antiemetic tablets, which are determined depending on the complexity of the lesion. Steroids are often used to alleviate the general condition. They improve appetite and add energy.
Stopping methods
To control the gag reflex, special antiemetic medications and other aids are used.
Medicines
Selected depending on the cause of the side effect:
- in case of excessive production of the vagus nerve stimulator (5-HT3), partial obstruction of the stomach or esophagus, consequences of chemotherapy or radiation, Metoclopramide, Ondasetron, Granisetron, Tropisetron are prescribed;
- in case of adverse effects of the tumor itself, peripheral drugs “Cerukal”, “Reglan”, “Domperidone”, “Motilium”, “Dimetpramide”;
- for cancer with metastases - glucocorticoid hormone "Dexamethasone" or "Cortisone", antipsychotics "Amitriptyline", "Risperidone", "Olanzapine", "Quetiapine";
- for hypercalcemia - selective medication "Haloperidol";
- to act directly on the emetic.
What to do without using medications?
What to do to reduce the number of gags? Recommended:
- rest and peace;
- small-portion fractional meals;
- light food;
- taking restorative fluids.
After an attack, it is important to drink 25 ml of light broth, water, juices and jelly.
After an attack, in the first hour it is important to drink 25 ml of light broth, water, weak non-acidic juices, liquid jelly every 15 minutes. The consumption of soda and other “spicy” drinks is prohibited. If a person cannot drink liquid, frozen juices, broths, and water in the form of chips are allowed. If intestinal blockage has developed, it is recommended to install a tube to remove vomit.
Other supporting measures:
- acupuncture, acupressure;
- breathing relaxation techniques;
- homeopathy.
Traditional methods
You can fight vomiting with the help of proven folk remedies, such as:
- ginger powder: tea is brewed with it, cookies are made, food is seasoned with it;
- chamomile tea;
- mint in the form of teas, tablets, capsules.
Types of vomiting as the disease progresses
In the medical literature, there is no classification of emetic reactions by type, since the clinical manifestation is always the same: a sharp contraction of the diaphragm and stomach with the release of gastric contents.
The appearance of the vomit itself can suggest the root cause of the pathological symptom, but not in all situations, including because as cancer progresses, the appetite suffers, the patient does not experience hunger, on the contrary, an aversion to food is characteristic, therefore the scarcity of vomit makes it difficult to analyze.
Depending on the time of occurrence of vomiting after eating, the following types are possible:
- When the passage of food through the gastrointestinal tract is blocked, vomiting mainly occurs some time after eating, when the food masses have already undergone partial digestion; brown inclusions can be detected in them - altered blood.
- During a meal or immediately after eating, the release of stomach contents is caused by an increase in pressure in the brain, psychomotor agitation, and tumor damage to the esophagus.
- In case of intoxication, metastases in the liver, complications of drug and radiation therapy, the release of vomit is possible at any time.
With some degree of probability, the appearance of the vomit can suggest the leading cause of the complication:
- almost unchanged food - cancer of the esophagogastric junction or esophagus;
- partially digested contents smelling sour - swelling of the lower third of the stomach;
- an admixture of bile is characteristic of damage to the initial parts of the small intestine;
- brown - “coffee grounds” occurs when bleeding in the stomach;
- bitter yellow contents are possible when liver function is impaired as a result of tumor damage.
How to provide first aid?
With profuse, continuous black vomiting, it is very important to provide the patient with the correct first aid. First of all, the patient should be put to bed and ensure absolute rest. Directly during a vomiting attack, the patient should be carefully turned on his side and his head slightly tilted down to prevent vomit from entering the respiratory tract.
If bleeding in the lungs is suspected, cold should be applied to the chest area. In order to avoid dehydration, it is necessary to give the patient plenty of fluids. It is better if it is herbal infusions or warm sweet tea. To maintain the so-called electrolyte balance, saline solutions are used.
Vomiting after radiation and chemotherapy
Severe nausea and frequent vomiting discredit an effective method of treating malignant neoplasms, so prevention and prevention of extremely unpleasant complications are no less important than selecting the optimal combination of anticancer drugs.
During chemotherapy, an acute vomiting reaction occurs during the first 24 hours, and a delayed vomiting reaction occurs in the following days after the administration of the cytostatic. There are indomitable or breakthrough vomiting and refractory vomiting, that is, not preventable by special antiemetics - antiemetics.
For all chemotherapy drugs, the emetic - emetogenic potential and methods for its prevention and treatment have been determined, and prevention must begin from the first day and be completed 2-3 days after the end of the course.
Every fourth woman after the first course may develop a reflex - psychogenic vomiting reaction; this type of vomiting is not typical for men. To stop a possible reflex reaction on the eve of the course, tranquilizers are used, acupuncture and psychotherapeutic techniques help.
During irradiation, an emetogenic - vomiting reaction does not have typical symptoms; it often depends on the irradiation zone and the patient’s internal mood. The frequency of complications is influenced by being female, youth, nervousness and life experience in the occurrence of vomiting and nausea from other causes.
At what stage of cancer does nausea and vomiting develop?
Nausea appears at the fourth stage of oncology. It can occur after eating, when the food consumed has not yet begun to be digested.
If the condition is a rare occurrence and does not contain blood impurities, it is enough to take antiemetic drugs to ensure peace for the patient. In some cases, the body's rejection of vomit leads to death. Frequent urges cause complications:
- dehydration of the body;
- constant nausea contributes to the development of pathological conditions of the cardiovascular system;
- internal bleeding;
- the appearance of thrombosis.
If the discharge turns black or contains blood clots, this is a reason for urgent medical intervention. Signs indicate bleeding, which, if not stopped in a timely manner, leads to death.
Vomiting mainly occurs with stage 4 cancer. This is due to the following reasons:
- with a brain tumor at the last stage, metastases completely affect the organ, due to which intracranial pressure increases;
- complications after anticancer drugs;
- taking painkillers based on narcotic substances;
- intoxication that occurs when a malignant tumor enlarges or metastases are activated;
- psychological reasons associated with a long struggle for life, stress and depression.
A dangerous condition is if the urge occurs more than 3 times during the day. When the tumor disintegrates, nausea appears randomly.
Treatment methods for symptoms of cancer depend on the etiology of the process. There is definitely no universal remedy that is equally successful for different patients. Despite the huge list of various medications intended to relieve the gag reflex, doctors advise starting or combining drug therapy with physical procedures. Non-drug therapy includes:
- A massage that allows the patient to relax.
- Swimming in warm water in the absence of contraindications.
- Walking in the fresh air without overworking the body.
- Mint tea.
- Light gymnastics.
Such treatments are useful as a calming factor - the process of fighting cancer is stressful. Patients become depressed and live with a constant feeling of fear and uncertainty.
It is necessary to treat nausea not only for reasons of comfort. Such pathological conditions cause negative consequences, such as exhaustion of the body, large loss of fluid and drug intoxication. Together with the vomit, the patient loses the strength the body needs in the fight against cancer. Doctors often advise sticking to a balanced diet and replenishing the water-salt balance.
Antiemetic therapy is represented by a large number of drugs in the form of tablets, solutions, syrups and injections. The attending physician, who is aware of the dynamics of the disease, should select the type and class of the drug. Self-prescribing medications is prohibited; some medications will be useless.
To relieve nausea, the following is prescribed:
- Antagonists. It affects the vomiting center, blocking the urge.
- M-cholinergic receptor blockers affect the muscles of the stomach and pancreas. The drugs relax and slow down the reflux of contents.
- Glucocorticosteroids have a wide range of effects and are good at blocking vomiting syndrome, preventing it in the future.
- Prokinetics that block dopamine receptors.
The choice of antiemetic drugs is large, the range of actions lies in the restoring effect of water balance.
Loading …
If the doctor suspects that the patient has liver cancer, he will definitely order additional tests to clarify the diagnosis. Ultrasound is used for this
, radioisotope scan of the liver. But the most accurate method is laparoscopy. This is a small operation during which a 1-2 cm hole is made in the abdominal cavity. A narrow tube with a camera is inserted into it. Additional equipment allows you to take material for a biopsy. This helps to accurately determine the size and type of tumor.
After diagnosis, the oncologist determines the stage of tumor development. It is designated by Roman numerals from I to IV.
Stage I: The cancer can be any size. It is solitary, does not extend beyond the liver, does not grow into blood vessels, neighboring organs and lymph nodes.
There are practically no external manifestations at this stage. A person may feel weakness, fatigue and minor discomfort in the upper right part of the abdomen. After just a few weeks, the liver increases in size.
Stage II: A solitary tumor that grows into blood vessels and can be any size. This stage also includes cases where there are several tumors in the liver that do not exceed 5 cm in diameter. They do not spread to lymph nodes or distant organs.
This stage is manifested by nausea, vomiting, and aching pain in the right hypochondrium. The patient experiences long-term indigestion and diarrhea for no reason. The liver is noticeably enlarged in size, dense to the touch. The person looks weakened and complains of chronic fatigue.
Stage III has 3 substages.
- Stage IIIA. Several tumors were found in the liver. At least one of them exceeds 5 cm in diameter. The malignant neoplasm does not spread to nearby lymph nodes and distant organs.
- Stage IIIB. One of the tumors grows into the large veins of the liver - the portal or hepatic veins. Lymph nodes and other organs are not affected.
- Stage IIIC. The tumor metastasizes to nearby organs, except the bladder. This substage includes cases when the tumor grows into the capsule that surrounds the liver from the outside. Distant organs and nearby lymph nodes are not affected by metastases.
External manifestations: jaundice, swelling of the legs and lower back, redness of the palms and spider veins on the skin. Chills and fever appear. It ranges from 37 to 39°C; antipyretic drugs hardly bring it down. Exhaustion begins, the patient loses weight sharply, and facial features become sharper.
Stage IV has two substages.
- Stage IVA. Any number of tumors can be found in the liver. They grow into blood vessels and surrounding organs. Lymph nodes are affected. Metastases are not found in distant organs.
- Stage IVB. The tumor affects nearby and distant organs and lymph nodes. The number and size of neoplasms can be any.
A person loses a lot of weight. The bones are visible, which contrasts with the swollen abdomen. The skin becomes pale yellow, dry and inelastic. Severe swelling of the lower body is associated with poor circulation and compression of the inferior vena cava by blood clots and lymph nodes. The person feels exhausted and experiences acute pain.
Depending on the stage of development of the disease, the doctor chooses the most effective treatment methods.
In cancer patients, especially in the last stages, their worldview changes significantly. They evaluate life differently, treat loved ones differently. A person can be self-absorbed, or, conversely, show increased vital activity. These social changes depend on the patient's age, experience, social status, education, and many other factors. It is impossible to predict in advance what the condition of a cancer patient will be; everyone experiences this disease in their own way.
Many people do not realize the criticality of their situation until the very end and try to lead an active lifestyle. When severe weakness develops, such a person falls into a state of depression because he cannot engage in usual activities. Often people become embittered and aggressive. Hepatic encephalopathy, which changes the character and intelligence of the patient, is also important.
There are people who, after the diagnosis is announced, become depressed and lose their zest for life. This accelerates the development of cancer and worsens the prognosis. It is extremely rare to encounter patients who adequately perceive their diagnosis and follow all medical recommendations.
Liver cancer symptoms before death can be divided into several stages. In each of them, certain changes occur in the body, ultimately leading to death. All of them are theoretically reversible, but in practice death usually occurs.
- Predagonia. Severe drowsiness, lethargy, loss of orientation. A dying person stops talking, moving, and eating. The skin turns pale and has a bluish tint. Blood pressure decreases and urination stops.
- Agony. There is a complete loss of consciousness. Symptoms include a lack of response to any irritants, deep, rare breathing, a slow pulse and low blood pressure. All these are signs of hepatic coma. The skin is bluish, the sphincters relax - the bladder and rectum are emptied.
- Clinical death. Lack of breathing, consciousness and pulse. This condition is still reversible within 5-7 minutes.
Then comes biological death - irreversible suppression of vital functions.
Liver cancer causes death very quickly, within a few years. Against this background, all body functions are suppressed, immunity is reduced, which together leads to death. Patients in the final stages of the disease lose the ability to even self-care, so they need careful care. Psychological support for such patients is also extremely important. To alleviate the pre-death state, there are special hospices.
What type of cancer can cause bleeding?
The first symptom of bleeding in cancer is most often sudden vomiting of characteristic contents. Bleeding is possible with a large or very small tumor located next to a large vessel. In almost 70% of patients with a complicated course of the disease, the size of the malignant lesion corresponds to stages 3 and 4 of cancer.
Initially, gastric bleeding in carcinoma is rarely pronounced; as a rule, the vessel corroded by the cancerous tumor periodically secretly sneaks in for some time, leading to anemia or aggravating existing anemia. With cancerous infiltration, the tissues become “hard” and the likelihood of vascular walls sticking together due to thrombosis is minimal, so seven out of ten asymptomatic bleeding patients eventually develop serious bleeding, and one in nine – up to shock due to rapid and severe blood loss. In every fifth patient, bleeding is combined with wall perforation or cancer growth into adjacent anatomical structures.
The most common type of gastric carcinoma is infiltration with ulceration or ulcerative-infiltrative type; the size of the lesion and ulcerative defect can be any size, up to total damage to the organ. A cancer ulcer has rough, protruding and uneven boundaries; its walls and bottom form a kind of folded funnel. Saucer-shaped carcinoma is distinguished when the ulcer has very clear and uniform boundaries.
In addition, cancerous infiltration can pass through the gastric wall and penetrate into the pancreas and pull the abdominal omental bursa into the conglomerate. Even with tiny early cancer with a minimal ulcerative defect, organ-preserving surgery - mucosal resection - is excluded, because the true boundaries of the tumor are in the deep layers of the gastric wall.
The ulcerative form of cancer in appearance is almost no different from a banal chronic gastric ulcer, and that is why during each gastroscopy, a biopsy is taken from the edges of the mucosal defect from all absolutely ulcer patients.
It is almost impossible for carcinoma growing outside the stomach to bypass the vessel, because in the thickness of the wall the arterial vessels form four interconnected vascular networks: inside and under the mucous layer, between the muscular and under the serous layers. That is why bleeding is the most common complication of the disease.
Late symptoms of liver cancer
Late symptoms of liver cancer appear:
- in endocrine disorders (for example, Cushing's syndrome may develop), which arise due to the synthesis of hormone-like substances by tumor cells,
- in the appearance of jaundice,
- in a significant enlargement of the liver, which can be felt upon palpation.
If liver cancer develops against the background of cirrhosis, the patient’s condition begins to rapidly deteriorate, severe pain appears, and ascites occurs - a process in which fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity, as a result of which the abdomen increases in volume.
In approximately 15% of patients, intra-abdominal bleeding occurs, followed by the development of shock. Symptoms of cancer include:
- frequent nosebleeds,
- cutaneous telangiectasias are small spots on the skin filled with a network of small blood vessels.
Clinical signs of blood loss
Severe blood loss is manifested by a rapid decrease in blood pressure and associated progressive weakness. Exsanguination is manifested by pronounced waxy pallor with blue lips against the background of an increasing heartbeat, which the cancer patient feels like hammer blows inside the chest.
The most common sign of gastric bleeding is bloody vomit, commonly referred to as “coffee grounds.” Bloody vomit is typical for damage to the vessels of the respiratory tract; a sign of acute gastrointestinal pathology is dirty-brown food masses with an unpleasant odor, which may also contain dark clots of coagulated blood.
As blood passes through the intestinal tube, iron released from dead red blood cells will color the stool and the color of the stool will also change to black, again due to fermentation by intestinal secretions. Often, in a cancer patient, the stool liquefies and comes out in the form of a tarry paste with an extremely unpleasant odor. Increased frequency of stools with changes in consistency and color is called “melena.”
The combination of dark vomiting food masses and black feces are the leading signs of gastric bleeding of any etiology, including carcinoma. Foul-smelling vomit is typical of gastric or colonic outlet obstruction, but its color is not dark brown, although it differs from the food eaten the day before.
What does black vomit mean?
The eruption of brown vomit with foamy impurities may indicate pulmonary hemorrhage, characteristic of oncological diseases of the respiratory system. The appearance of profuse, continuous black vomiting is a serious phenomenon that poses a potential threat to the life and health of the patient. Black vomiting is especially dangerous, accompanied by the following symptoms:
- increased body temperature;
- signs of intoxication of the body;
- sharp pain in the abdominal area, with a tendency to increase;
- vomiting in masses that have been in the gastric cavity for several days.
If at least several of the above alarming signs are present, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance, and before the doctors arrive, provide the patient with all possible first aid. In addition, black vomit may be a sign of intestinal obstruction or acute internal bleeding, which, if not promptly taken, can cause death.
Why does nausea occur with cancer? Causes
The urge to vomit is caused by toxins entering the bloodstream, which attack healthy cells. The place of formation of attacks of nausea is the central nervous system. It processes alarm signals that come from the body. Those, in turn, are sent to the necessary parts of the human body (gastrointestinal tract, brain, etc.) and provoke a feeling of nausea. It may end in vomiting, but this does not always happen.
It should be borne in mind that the feeling of nausea is also caused by other diseases or temporary disorders of the digestive system.
Nausea is a sign of cancer when the condition is constant and does not improve over time, but rather worsens. It is also accompanied by other complex manifestations, such as:
- unexplained loss of weight or appetite;
- persistent fatigue and headaches;
- low-grade body temperature (37° – 37.2°);
- frequent infectious diseases;
- chronic pain syndrome in bones or other areas of the body.
Death symptoms
Cancer is a disease that is extremely rarely curable today. Many patients die from the rapidly growing tumor. The near-death state can last a long time, or it can be lightning fast. How people die from liver cancer can be seen from the characteristic symptoms.
- Constant drowsiness, being in a stupor. This condition is caused by inhibition of brain activity due to intoxication. The liver can no longer perform a neutralizing function, so the brain is affected by various waste substances. This condition is also called hepatic encephalopathy.
- Lack of appetite. It is also caused by intoxication, as well as severe weakness and intense pain.
- No movement. Exhaustion leads to the fact that a person not only stops performing daily activities, but cannot even get out of bed.
- Mental disorders. Again associated with brain damage from toxins. The patient's speech becomes slow and slurred. He stops recognizing close people and is not oriented in place and time. Hallucinations may develop.
- Respiratory disorders. They are caused by the accumulation of fluid in the lungs, as a result of which a person experiences attacks of suffocation and moist rales.
- Urinary disorder. Associated with a small volume of fluid intake and low physical activity.
How to help a patient?
General tips for relieving cancer nausea include:
- Use of any medications prescribed without a prescription:
- “Meclozine” (“Antivert” or “Bonine”);
- “Dimenhydrinate”;
- Antihistamine.
- Drinking enough liquid. Drink in small sips and often.
- Meals should be divided into 6-8 small portions.
- Avoid salty, fried, too sweet or spicy foods.
- At the next attack, suck on a mint candy or refreshing chewing gum.
- Drink teas and decoctions of medicinal herbs, in particular ginger, mint, lemon balm, milk thistle, and flax.
Antiemetic therapy
Your doctor will tell you what to do if negative symptoms that affect your quality of life appear. Today, oncology uses a large number of antiemetic medications in the form of solutions, tablets, suppositories, syrups and injections. The doctor selects the most effective drug in each specific case. In case of brain cancer, antiemetics are powerless; in this case, a high dose of hormones and diuretics are prescribed. Fluid intake is limited during treatment. For stomach and intestinal cancer, a special diet is prescribed along with medications. If a person develops vomiting due to metastasis of cancer cells from leukemia (leukemia), he is prescribed a high dose of hormones and peripheral anti-nausea and vomiting medications, such as Motilium.
Note! Nausea and vomiting cannot always be controlled, and 70% of people who receive radiation therapy are at risk.
Today, various methods and recipes are used to treat and prevent vomiting in cancer pathologies. But the most effective are serotonin receptor antagonists, which include Ondansetron and Zofran. They help improve the quality of life of patients. They also provide the opportunity to undergo chemotherapy at home. They are taken half an hour before using the cytostatic drug.
Medicines to eliminate
Dealing with nausea due to cancer is not easy. First you need to establish the exact cause, and then take action. Traditional medicine is not always able to give the desired result. Therefore, it is important to know the remedies that effectively affect and eliminate nausea. These include:
- 5-HT3 antagonists block the action of serotonin on the surfaces of nerve endings: “Dolasetron”, “Granisetron”, “Ondansetron”, “Tropisetron”.
- Corticosteroids. Dexamethasone has a special effect. The drug gives a positive result for many causes of nausea (even with chronic nausea of a metastatic cancer process).
- Anti-NK1 receptor agents, e.g. They control the production of elements in the brain stem and gastrointestinal tract.
- Simultaneous use of the three named drugs.
- Prokinetic agents, in particular Metoclopramide, which affects the muscular lining of the intestines.
- Drugs that block dopamine: Haloperidol, Olanzapine, Levomepromazine, etc.
- Antihistamines (“Promethazine”, block D2), affecting the mechanisms that cause vomiting and the vestibular nuclei.
- Anticholinergic drugs (“Scopolamine”). Relieves tension in the stomach muscles and reduces the secretion of gastric juice.
- Analogues of “Somatostatin”, which are used for palliative purposes.
Nausea with cancer is common. It requires careful choice of management, since it can greatly aggravate the condition of a person with cancer.
Reasons for appearance
The painful condition in cancer patients can be caused by the following factors:
- Tumor growth in the stomach. As the volume of the tumor increases, muscle tissue decreases. If cancer develops near the inlet or outlet, it can become blocked, causing gastric obstruction and vomiting. When a tumor affects the gastric walls, internal mobility is disrupted and the functioning of the organ is interrupted, as a result of which the accumulated food and liquid will be released back.
- Surgery that can cause intestinal blockage.
- Narrowing of the esophageal tube.
- Metastasis.
There are 2 scenarios for the development of vomiting:
- The occurrence of nausea and vomiting immediately after eating. In this case, the food bolus appears in its original form without traces of digestive juice.
- Sudden onset of vomiting without eating food and nausea. The reason is poisoning of the body by dead tumor cells during its disintegration. The number and strength of spasms determine the power of the vomit flow and its concentration.
The color and consistency of the etched masses determines the degree of development of stomach cancer. Bloody vomiting is considered the most dangerous, as it indicates the development of bleeding and blood plasma entering the stomach. In this situation, urgent hospitalization is needed to provide emergency measures. Unreasonable vomiting indicates the early stages of cancer, especially if it is accompanied by accompanying symptoms.
THIS IS REALLY IMPORTANT! Right now you can find out a cheap way to get rid of stomach pain. FIND OUT >>
Why is this condition dangerous?
Any vomiting is a loss of fluid and electrolytes. Frequent and profuse vomiting of bile leads to dehydration. A severe loss of potassium and sodium ions will cause cardiac arrest. Therefore, if such a condition occurs, you should urgently call an ambulance.
If you have any of the above reasons, you need to know how to stop vomiting bile. First aid will help prevent the development of complications, and maybe even save a person’s life.
The most dangerous complication is Mallory-Weiss syndrome. Strong straining during vomiting can tear the esophageal mucosa. Then fresh blood will appear in the vomit. If measures are not taken in time, the esophagus can completely rupture.
Additional treatments
There are also alternative therapies that help control nausea and are used as an adjunct to primary treatment. Such activities include acupuncture, massage, hypnosis and relaxation. Doctors do not advise using herbal remedies and biological supplements, as they can cause a decrease in the effect of antiemetic treatment.
Note! Be sure to drink enough fluids during therapy to reduce the risk of dehydration. All medications must be taken on a full stomach.
oncoved.ru
How to determine bile
How can you tell if you are vomiting bile? Vomit will have characteristic signs:
- dark green;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- yellow-brown coating on the tongue;
- liver smell.
The severity of the condition will be determined by the frequency and volume of vomiting. If you vomited 1-2 times, then this is considered a mild condition. But if you feel sick and vomit more than 10 times a day, then this is already an indication for hospitalization.
What other symptoms may there be:
- heat;
- girdle pain in the abdomen;
- dizziness and tinnitus;
- unstable blood pressure.
Vomiting with bile during exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis is a bad prognostic sign. This may indicate the death of pancreatic tissue (pancreatic necrosis). Especially if it is accompanied by low blood pressure.
Treatment in adults
Only a doctor has the right to make predictions, diagnoses and prescribe treatment. You should not take medications without his recommendation.
While waiting for an ambulance, the patient is helped:
support the patient psychologically throughout the period of illness; after vomiting, it is important for the patient to remain in bed, with the head elevated; It’s better to lay it on its side and cover it with a warm blanket; try to force you to drink as much water as possible; be sure to ask about his well-being, pain sensations in order to convey information to the doctor; measure the patient’s blood pressure and pulse every five minutes in case of discharge of a large amount of blood; If you faint, be sure to lie on your side.
There are general care recommendations:
- give more liquid so that severe vomiting does not cause dehydration; the liquid will be plain water, decoctions, natural drinks, fruit drinks;
- the patient is allowed to eat a diet; the stomach should not be overloaded after such stress and tension; with the doctor’s permission, it is allowed to consume chicken broth and light types of porridges cooked in water.
You cannot treat a patient at home, this will worsen the situation.
Diagnosis and treatment
Modern medicine has a very wide range of fight against the blood gag reflex. To begin with, the doctor will carry out a standard procedure for diagnosing the disease. As a rule, it consists of the following stages:
- First, the doctor will interview the patient, find out the nature of the problem, the frequency of vomiting attacks, and ask questions about nutrition.
- This will be followed by laboratory tests. Clinical analysis will allow you to accurately diagnose the essence of the problem. Blood biochemistry, metabolism, glucose - all this will be carefully studied.
- An X-ray and ECG will be performed.
- An ultrasound and computed tomography will be performed.
After diagnosis, the treatment process begins. Its goal is to eliminate the cause that caused the vomiting reaction. Treatment that will begin after the disease is diagnosed includes:
- Use of medications prescribed by a doctor. Various drugs are used as treatment: tranquilizers (phenozepam), antipsychotics (haloperidol). Antihistamines are used. Drugs such as Cerucal, Granisteron and many others are effective in treatment. Often, treatment uses saline solutions that are administered intravenously.
- When the disease process has passed a deep stage, the doctor decides on instrumental intervention. Drugs are injected into the area of the mucous membrane with a syringe to help stop the gag reflex. The doctor may use an electric current to dry the tissue.
- If the cause of the disease is a progressive ulcer, then surgical intervention will be used. This is a gastric resection. Using the cutting method, ulcerative secretions are separated from healthy organisms.
- Alternative treatments for vomiting. They include the use of boiled herbs: valerian, mint, lemon balm, soothing chamomile, dill. Green tea, water with lemon, vodka mixed with salt, and orange juice are suitable for drinking. Often such rather exotic methods are very effective.
- The doctor prescribes a special diet, which must be followed for a certain time. The diet excludes foods that can in one case or another cause a gag reflex, and fatty and spicy foods are excluded from the diet. Food should always be warm and liquid. After progress in treatment, the list of acceptable foods expands, and eggs are included in the menu. The patient gradually returns to normal life.
The most important thing is that ignoring the problem and refusing timely treatment can result in very bad consequences, including neglect of the disease, constant pain and even death. Therefore, you should never neglect your health
A gag reflex with blood is a very alarming sign, the very sign when you need to see a doctor immediately.
Features of first aid
With this pathological condition, it is important not to get confused and start acting. The condition, well-being and even life of a person will depend on how timely and correctly emergency care is provided.
- The first thing to do is call an ambulance.
- Then you need to rinse your stomach.
- Next, place the patient in bed on his side, cover him with a warm blanket and elevate his legs.
- Prepare a container (it is quite possible that the attack will be repeated) and do not leave the person unattended.
- Give him more fluids. This will help prevent dehydration.
What not to do
Never give food or any medications to the sick person. The maximum that can be given to the victim is an antiemetic. It is impossible to stop vomiting in case of poisoning.
You cannot carry out any measures if you suspect illnesses such as a perforated ulcer or brain injury.
Further treatment is carried out by a qualified specialist in a hospital setting, after examination and clarification of the cause - the underlying disease.
Vomiting blood in a pet: causes, first aid
Not only people get sick, cats and dogs also often suffer from various pathologies. But if a person can indicate what and where it hurts, then an animal cannot. You can tell that something is wrong with a dog or cat by their behavior and condition.
Bloody vomiting in an animal is often a signal of gastric bleeding. In this case, it is necessary to quickly take the pet to a veterinary clinic. The occurrence of an illness in a dog may be due to:
- the presence of a foreign body in the gastrointestinal tract;
- intoxication of the body;
- parasitic infestations;
- diseases of an infectious nature: hepatitis, leptospirosis;
- hypoadrenocorticism;
- oncological pathologies;
- stomach ulcer;
- eating disorders;
- renal failure;
- uremia.
Often this condition is accompanied by lethargy, a sharp decrease in appetite, frequent belching, upset stomach, and fever.
The discharge of vomit containing blood in cats can be provoked by: helminthic infestations, infectious pathologies, poisoning with poor quality food or poisons, postpartum diseases, pregnancy, ketosis, uremia, inflammatory processes, liver and kidney diseases, intestinal obstruction, ear diseases, stomach ulcers.
This pathology in cats is usually accompanied by: weight loss, diarrhea, abdominal pain, pale gums, rapid breathing, malaise, lethargy, collapse, shock.
If you notice vomiting in your pet (no matter cats or dogs), do not hesitate, start taking action. The animal needs your help more than ever
Observe how often the vomit is discharged and what is contained in it. If vomiting is repeated and does not go away, administer an antispasmodic and antiemetic drug to the animal (No-shpu, Cerucal). This will make your pet feel better.
The main thing when administering medications is not to exceed the dosage, otherwise you will only worsen the situation. Then give the animal an adsorbent - activated carbon, Enterosgel. If your pet does not feel better within 24 hours, take him to the veterinarian. The doctor, after the examination, will prescribe the necessary treatment.
For 24 hours (after the attack has stopped), you should not feed the animal. If the condition improves, rice water can be added to the diet. Further, if the attacks no longer recur, you can slowly give your pet his usual food.
Getting sick is unpleasant for both people and animals. But both we and our smaller brothers face different pathologies. Bloody vomiting is an unpleasant illness. However, timely and appropriate assistance and subsequent therapy will help normalize the condition. The main thing is not to hesitate and go to the hospital or veterinary clinic in time.