Fish – a source of opisthorchiasis infection and its types
Opisthorchiasis in fish is a source of intestinal obstruction, cancer, and liver cirrhosis. In order not to run into trouble, you need to scrupulously control the products caught and comply with the required preparation standards.
The main cause of infection with worms is opisthorchiasis fish and the ingestion of other products that received bacteria during cutting.
If the processing and preparation process is not followed, opisthorchis retain vital activity in dried, raw, smoked, lightly salted river products for a long period. When lightly boiling, baking, or frying, the risk of infection is high. Do not forget the rules for salting, cooking, smoking the prepared dish.
The list of fish carrying worms is growing. Due to frequent migration (high waters, floods), helminths were found among the carp family, in pike, perch, peled, pike perch, burbot, sterlet, pink salmon, omul, vendace, bream, carp and others.
Let us systematize the factors that increase the frequency of infection:
- geography - a dangerous place with the risk of infection with cat fluke;
- poaching – uncontrolled fishing, storage, transportation, sale;
- non-compliance with production technology when freezing semi-finished products, smoking, drying;
- amateur fishing - improper preparation of a fish dish at home.
Risk factors for opisthorchiasis infection
Fish from the carp family are often infected. Factors determining the risk of disease:
- Place of capture. The rivers of Thailand, Vietnam, India, the North of Russia and Siberia have been identified as the most dangerous places for infestation of the Siberian fluke. The main reason is the consumption of products in raw (stroganina) or half-raw form (sushi, smoked, dried) by humans and animals.
- Presence of illegal fishing. Some sellers have little interest in the health of potential buyers. When catching fish products, storage technologies, sanitary processing, and tests for the presence of Siberian fluke are not followed; the temperature regime during salting and drying is violated - an insufficiently smoked, salted product ends up on the markets.
- Unfair attitude of small enterprises towards cooking technology, expressed by:
- Buying cheap, contaminated fish (lack of checking for the presence of Siberian fluke);
- Savings on the rules of processing and preparation of fish products;
- Neglect of hygienic, sanitary standards, cooling regime.
- Location of lakes and rivers within the city. There are a huge number of pathogens, and water is rarely tested for the presence of opisthorchid. Fishermen do not know whether the fish has an infection. The main route of infection in urban areas is fecal-oral. Human and animal feces are poured into a body of water where mollusks live - the primary carrier of the cat fluke, which are consumed by fish, becoming a secondary carrier of worms. Opisthorchiasis passes from fish to humans.
Proper processing of fish products does not guarantee complete protection against contamination. Extracted organs should not be given to cats; they should not be thrown into water; it is safer to bury them in the ground.
Vectors
In the muscle layer of the intermediate hosts, the fluke forms metacercariae - a capsule with a larval stage. This is an invasive form of helminth. Meat containing metacercariae of the parasite is dangerous for humans and animals.
In 1893, Brown proved that additional hosts for the cat fluke are most often representatives of the Karpov family.
Geographical prevalence of opisthorchiasis in Russia:
- Altai region;
- Khanty-Mansiysk Okrug;
- Tomsk region;
- Tyumen region;
- Omsk region;
- Novosibirsk region.
The main large rivers in which affected fish are caught are:
The main representatives of the Carp family, often eaten and containing opisthorchid metacercariae:
Massive infestation occurs in ide, roach, dace, and minnow. Bream, tench and crucian carp are less susceptible to infection.
Many sources claim that only Cyprinidae are carriers of the parasite. The infection of fish from other families by opisthorchis is controversial.
According to some data, northern representatives of the whitefish genus may be infected with the parasite:
These are delicious varieties that are usually eaten raw.
It is generally accepted that the cat fluke is not found in predatory species. Although many fishermen indicate that pike, pike perch, perch, and burbot are infected with helminths. The incidence of the disease in them is much lower than in other species, for example, cheese or muksun. But there is still a risk of getting a parasite from them.
The possibility of infection of pike, pike perch and burbot exists when they live in the same body of water with representatives of the Karpov family. Any freshwater fish runs the risk of becoming a carrier of opisthorchiasis. Isolated cases of damage to sturgeon and salmon (salmon, trout, pink salmon) have been recorded.
Opisthorchiasis of carnivores is found only in those reservoirs where the first intermediate host of the parasite, the Cadiella mollusk, lives. As a rule, these are small rivers or lakes with standing water - a favorite place for spawning. It is then that most of them become infected with helminths.
There are no causative agents of opisthorchiasis in marine life (for example, mackerel and herring).
It is impossible to independently determine whether the fish is infected. Metacercariae are not visible to the naked eye. Only special veterinary laboratories can accurately determine the presence of opisthorchid.
It should be remembered that fish not susceptible to opisthorchiasis can be carriers of other dangerous parasites.
Fish breeds most susceptible to infection
It is difficult to determine whether the Siberian fluke is present in the body of the fish or not. It has been established precisely: sea fish are too salty a habitat for opisthorchid larvae. The main carriers of liver flukes are freshwater individuals. List of species susceptible to infection:
- Fish of the carp family: dace, bream, carp, ide, roach, bleak, roach, spikefish, sabrefish, chebak, rudd, carp, bluefish, crucian carp, minnow, peled, ram, tench.
- Whitefish – muksun, vendace, cheese, shchekur, omul, nelma.
Pike, perch, burbot, pike perch, and smelt become carriers of the disease due to their cohabitation with carp species.
The presence of opisthorchid larvae in red and sea fish should be checked. Can be examined under a microscope in cheese, pyzhyan, chekura, nelma, and other types of salmon (chum salmon, trout).
Opisthorchiasis: what is it in humans?
Most people have no idea about the disease opisthorchiasis, what causes it and what measures should be taken to avoid irreversible consequences.
It is widespread in the Russian Federation (usually in Western Siberia). This disease is caused by worms from the class of cestodes. It is not so easy to identify this disease, because it has practically no clinical signs. It is important to make a diagnosis in time and not to confuse it with another disease. For example, opisthorchiasis can occur with the same symptoms as hepatitis B or oncology. Let's study this disease in more detail.
What it is?
To date, about 250 serovars of helminths have been identified that parasitize humans and cause the disease - helminthiasis. In Russia there are approximately 100 serovars of trematodes, about 20 of which are distributed everywhere. A large number of infections with Siberian (cat) fluke occur in the rivers of Russia - Ob, Kama, Irtysh.
In addition, parasites can be found in the Volga and Don. Statistics show that most often invasion occurs in the Amur region, Tomsk, Novosibirsk and other regions, as well as in the Altai Republic. One of the main places for the spread of opisthorchiasis is the Ob River - Irtysh Basin.
This is one of the largest catchment areas. In addition, the rapid development of the North of Western Siberia, as well as the development of oil and gas deposits, led to social and demographic changes. These changes caused some people to migrate from other areas of the country and the shift work method quickly spread. In the area of Western Siberia, according to statistics, about 80% of invasions in the country.
The ponds in the area are home to 29 types of fish, which belong to ten families. The commercial function is performed by nineteen species, the main ones being: muksun, peled, whitefish, white salmon, nelma, sturgeon, sterlet, ide, pike, dace, roach, perch, burbot.
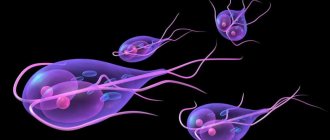
Opisthorchiasis is a widely occurring human helminthiasis. In Russia, about two million people suffer from this disease. The name of the pathogen is Siberian fluke (lat. Opisthorchis felineus). They are lanceolate flatworms ranging from 7 to 17 mm in length. This parasite lives in people and pets and is localized in the gallbladder, liver and pancreas.
Of no less importance is the functioning of the cat fluke of an allergic and mechanical nature on the human body, its larval stage and egg laying. In the process of excreting waste products of parasitic worms, allergies appear.
The action of a mechanical nature is expressed in the disruption of the bile and pancreatic ducts with the help of suckers of the mouth and peritoneum. As a result, the accumulation of trematodes in the bile duct impedes the flow of bile. Which is an excellent substrate for the development of re-infection of the bile excretory pathways.
The Siberian fluke was first isolated by Sebastian Rivolta, who lived in Italy, in 1884 in a cat's liver. In 1891, the Soviet scientist K.N. Vinogradov discovered it in humans and gave the name to the trematode “Siberian liver fluke.” In the 1930s, a scientist named Hans Vogel from Hamburg wrote a publication that described the entire life cycle of the Siberian fluke.
Opisthorchiasis
The disease is characterized by a protracted course, severe complications and often causes the development of dangerous tumors in the liver and pancreas. As noted earlier, the pathogen enters the human body by eating fish meat that has been improperly cooked and contains live cat fluke eggs. The parasite often enters the body when using cutting knives contaminated with fish meat.
Under the action of stomach enzymes, the larval shell dissolves. Then the larva enters the duodenum and is transported through the bile ducts to the liver, where it is localized. When diagnosed, worms are usually detected in the bile ducts and liver, accounting for 100% of cases. In the gallbladder, flukes are found in approximately 55% of patients, and in the pancreas, less so - in approximately 38% of cases.
As a result, the entire period of development of the parasite from the larva takes from four to five months, during which the egg transforms into a flatworm, then they lay eggs, and they are released into the external environment as waste products of the body. In the body of the definitive host, the disease worsens only when the pathogen enters the body a second time.
The lifespan of helminths in humans and animals can be from 20 to 25 years. The harmful effects of helminths on a sick body are as follows:
- Opistarchia cause a large number of physical wounds to the epithelium of the mucous membrane of the bile and liver canals, which leads to a decrease in blood flow to the organs of the digestive system.
- Helminths can accumulate in the liver canals, dilating them excessively, and also interfering with the outflow of bile and the enzyme pancreatin.
- Growth and reproduction of pathogenic microflora entering through the bloodstream or from the gastrointestinal tract. This leads to infection in the gallbladder and bile ducts. In medical practice, cases of the occurrence of such a disease as purulent cholangitis against the background of chronic helminthiasis are described. Purulent cholangitis is a disease that occurs due to inflammatory processes in the bile ducts of the liver. It is usually accompanied by severe pain and dyspepsia.
- The pathological effect of this helminth on the human body and animals, which are its final hosts, is the development of allergies. It occurs due to the body's intolerance to the waste products of worms.
- An illness not detected in time, which over a long period of time has developed into a chronic disease, can cause a pathology such as cholangiocarcinoma (liver cancer).
Is the pathology contagious?
The source of transmission of the pathogen is domestic animals, as well as fish from the carp family. Helminth eggs cannot enter another organism through airborne transmission. The only way is to go through its entire life period in the first, temporary host, and only then is it able to end up inside the body of the definitive host.
Helminth eggs accumulated in the body are released into the environment. They, along with the feces of a sick animal or person, enter the reservoir, where they are eaten by mollusks, which after 2 months are eaten by fish from the carp family.
Diagnostics
The volume of leukocytes in the blood increases, the number of eosinophils also increases, and a slight decrease in the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin is also observed. Cat fluke eggs are found in the pancreas, as well as in fecal matter.
Treatment is carried out using the following medications:
- khingamine 150 mg. 3 times a day;
- hloxylom - 60 mg. per kg 3 times a day, duration 5 days, consume 15-20 minutes after meals, wash down with milk;
- biltricide 20-60 mg per kg of body weight 3 times a day, consumed 1 time a day an hour after meals.
In addition, symptomatic treatment is carried out and immune stimulants and antioxidants are prescribed. There is a list of preventive measures, the implementation of which will help avoid infestations of humans and pets with opisthorchiasis.
Try not to eat raw or suspicious fish at all. When frying it in boiling oil, you need to fry it for at least 25 minutes. You also need to cook for at least 25 minutes. To preserve using salting, it is necessary to correctly calculate the amount of salt per mass. For 1 kg you need to take at least 290 g of table salt.
The fish must be kept in brine for at least 14 days. When drying, it is first salted and then kept for at least 22 days. When cutting, you should not give pets parts of the carcass that are not needed for cooking.
All rules for the prevention of opisthorchiasis are focused on the absolute elimination of thermally unprocessed fish from the menu, because it is meat and fish that contain opistarchis larvae. The question of how parasites behave under the influence of microwaves when preparing food in a microwave oven has not yet been studied.
Detection of opisthorchiasis is carried out using scatological examination of stool for the presence of helminth eggs. As soon as the diagnosis of opisthorchiasis is confirmed, the patient is prescribed antiparasitic therapy. With timely treatment, a person usually makes a complete recovery. If you suspect opisthorchiasis, you should consult a general practitioner or an infectious disease specialist.
Opisthorchiasis is differentiated from pneumonia, acute respiratory diseases, hepatitis, acute surgical and intestinal diseases.
Useful video
In conclusion, we suggest watching a short video about the dangers of opisthorchiasis:
Liver fluke survival rate
The temperature at which the Siberian fluke dies is interesting. You can get infected from untreated fish. Microorganisms are characterized by increased survivability in extreme conditions.
- Metacercariae die at a temperature of -12C after two weeks. The carcass must be frozen evenly. Quick freezing will not completely destroy parasite eggs. In the refrigerator, the larvae remain active for up to a month.
- When salting worms, salt in a concentration of 20% kills, otherwise the worms remain viable. The duration of canning with brine before drying and smoking should be 2-4 weeks, the strength should be above 22%.
- Thermal high-temperature treatment is recognized as the most effective disinfecting method. Helminths are killed by boiling for 20 minutes and frying for an hour.
- In the oven (during baking, smoking) at a temperature of 80C, metacercariae can be destroyed after 2 hours.
It is important to wash your hands, dishes, and cutting board after handling river fish products.
Opisthorchiasis infection
The main method of invasion is the consumption of opisthorchiasis fish. The number of helminths depends on the number of larvae that have entered the human body. The average lifespan of a worm in a person is 20 years. Cases have been recorded of opisthorchis living in the body of carnivores for 40 years.
External signs of helminthiasis in humans:
- the temperature rises sharply;
- pain appears in the joints, right hypochondrium, and abdomen;
- vomiting, nausea, diarrhea occurs;
- the liver and spleen enlarge;
- a skin rash appears;
- General weakness, headaches, dizziness, disturbed sleep, and fatigue are noted.
After one and a half to two months, the acute stage gives way to the chronic stage. Associated diseases develop: pancreatitis, duodenitis, gastritis, cancer, cirrhosis of the liver.
Antihelmintic medications help against opisthorchiasis: Trichopolum, Praziquantel, Albendazole. Before use, you should consult with your doctor who will prescribe the dosage and duration of the drug.
How dangerous is the disease?
The first symptoms of the disease are very similar to any infectious disease. There are no distinctive features that specifically characterize opisthorchiasis. This greatly complicates timely diagnosis and prompt assistance to the sick person. The parasites use the lost time to infect the liver and bile ducts.
After fluke larvae enter the human body, the disease does not manifest itself for a long time. This latent period does not allow the patient to even suspect that he has parasites. Later, the first signs appear, which also do not indicate a specific disease.
A doctor can diagnose bile stagnation and liver inflammation.
The patient complains of abnormal stool, heaviness after eating (and it occurs even after a light snack), unpleasant bloating, flatulence, and sometimes pain near the right hypochondrium. The pain can be of a different nature, depending on the severity of the patient's condition.
Most often it is an aching, nagging pain, sometimes there may be attacks of sharp pain. Palpation shows a significant enlargement of the liver. With such a clinical picture, the presence of opisthorchiasis does not manifest itself in any way.
The most unpleasant thing about this disease is the occurrence of complications. The inflammation covers a large area, the worms multiply quickly and block the bile ducts. This causes severe pain.
The waste products of parasites enter the blood, which leads to intoxication of the body, the temperature rises, weakness appears, and the patient’s general condition worsens. A very severe allergic reaction may also occur.
So how can we determine whether a patient has the disease? The most effective way is a blood test, which should show antibodies to a specific parasite. Unfortunately, it is not always effective. Often the body does not produce these same antibodies and does not fight the infection.
Then the most effective will be an ultrasound or radiography of the abdominal cavity.
Is cheese fish opisthorchiasis?
Cheese is not only the name of a curd dessert, but also the second name of peled - a fish that lives in lakes and rivers and is of great importance for the economy. This is a low-calorie and vitamin-rich fish, which many are afraid to eat for fear of contracting opisthorchiasis, caused by the presence of flatworms in the human body. The latter are especially common in Russia, Ukraine and the countries of Southeast Asia.
Curd fish
The cheese or peled belongs to the whitefish family, lives in the rivers and lakes of the Arctic Ocean and the Amur River, and is also artificially bred. Its average length is 40–55 cm, average weight is 2–3 kg, and can reach 4-5 kg. The fish feeds on plankton and on average can live up to 8–11 years.
It has a laterally compressed body and a silver color; there is a dark gray stripe on the back; the head and dorsal fin are covered with black dots. The whitefish differs from other species in having a terminal mouth, a slightly longer upper jaw compared to the lower one, and a large number of gill rakers.
Spawning occurs during all months of autumn and December. Fertility exceeds 80 thousand eggs. The “childhood” of peled lasts about six months. This time is enough for the fish to become an adult.
There are three forms of peled:
- grows and develops faster, matures by the age of 3. Most often lives in rivers.
- Common lake fish remain to live in their native lake and get the opportunity to develop normally.
- Dwarf lake fish live in small lakes where there is a lack of food, which is why they develop poorly. Its weight often does not exceed 0.5 kg.
Beneficial features
Like any fish, eating peled is quite beneficial for health and beauty. It consists of the following substances:
- A large amount of protein (19.1 grams) and a small amount of fat (5.5 grams of which 1.5 grams are saturated fatty acids).
- Vitamin RR.
- Minerals: magnesium, calcium, chromium, iron and a number of others.
- The calorie content of curd fish is 130 calories, which makes it a dietary product.
Thanks to its properties, the cheese helps:
- Normalize blood sugar levels and establish protein-carbohydrate metabolism.
- Normalize cholesterol levels and improve blood circulation.
- Get rid of insomnia, depression, depression and irritability.
- Fight against bad breath.
- Cope with constipation.
- Get rid of excess fat and significantly improve skin condition.
Harm of cheese
Despite the abundance of positive aspects, raw fish is not so safe:
- It is not recommended for use by children under one year of age.
- Frequent consumption, more than 4 servings per week, can cause allergic rashes, heaviness in the stomach and even cause nausea.
- Peled that has not passed sanitary control or is caught in dirty waters may be infected with opisthorchiasis worms.
However, this does not mean that you cannot eat fish. As with any product, it is important to use caution and moderation, paying attention to how your body reacts.
Opisthorchiasis: general information
Opisthorchiasis is a series of diseases caused by parasitic flatworms of the genus Opisthorchiasis. They are especially common in Southeast Asia, as well as in Russia and some neighboring countries. In Western Europe and America, cases of infection are extremely rare.
Risk groups include humans and fish-eating animals, which people can also eat or keep at home. When worms enter the body, the ducts of the liver, pancreas and gall bladder are affected. The lifespan of worms is up to 20–30 years, and there is no way to get rid of them without medical help.
On the way to the human body, opisthorchia passes through several hosts, without ceasing to develop:
- Freshwater mollusks bithiniids swallow worm eggs, which end up in the reservoir along with silt raised from the bottom or metabolic products of the last host. The development process lasts 2 months; at the end, opisthorchis is selected from the mollusk and swallowed by fish.
- Once in the fish's body, the parasite continues to develop, clinging to the muscles and subcutaneous tissue.
- The last host of opisthorchid is a person or other large mammal that has eaten infected fish: fox, cat, dog, ferret. In the body of the last host, the worm penetrates through the small intestine into the liver and gall bladder, where it lays eggs. They do not live in the body for even 10 days, but once in the water along with waste products, parasitic eggs can live for almost a year.
The danger of opisthorchid
Opisthorchis poses a danger to humans at any stage of development:
- When moving and holding in place, they use suction cups and spines that pinch the mucous membrane. This leads to impaired blood circulation and tissue integrity.
- The accumulation of worms and their eggs in one place impedes the flow of bile, provokes dilation of the bile ducts and stagnation.
- Metabolic waste causes an allergic reaction in the body and poisons it. Long-term exposure can lead to the development of cholangiocarcinoma and proliferation of the bile duct epithelium.
- Worms can bring infection with them.
Symptoms of infection are:
- pain in muscles and joints;
- fever for no other reason;
- nausea, vomiting and diarrhea;
- pain in the stomach and intestines;
- dizziness, weakness, irritability, insomnia;
- allergic rashes;
- an increase in the size of the gallbladder, spleen and liver.
However, these symptoms are not unique and may be associated with other diseases. Tests reveal the parasite only after a month of its residence inside the body, when it begins to lay eggs.
Is cheese fish opisthorchiasis?
Previously, it was believed that worms could only settle in fish belonging to the carp family, but this is not so. Roach, dace, ide and other representatives are among the leaders in the number of infections, but recently worms have begun to be found more and more often in predatory fish - pike and the cheese itself. This may be due to the fact that the habitats of both predators and cyprinids are the same, and the parasites calmly cling to everyone.
Prevention of infection
It is easier to prevent than to treat - this motto is perfect for preventing opisthorchiasis infection.
It is necessary to carefully select fish prepared for consumption, especially if it was caught in a potentially dangerous place. It is strictly forbidden to eat raw, unprocessed fish: it must be boiled, fried, smoked or salted before consumption. The same applies to preparing cheese for pets: they should not eat raw fish.
Getting opisthorchiasis is not particularly difficult, but getting rid of it is much more difficult. If the thought of parasites living inside you does not seem attractive to you, you should take care in advance not to swallow them along with the fish. Carefully select cooking methods and do not hesitate to throw away a carcass that seems suspicious. However, before doing this, you should make sure that it will not be eaten by any animal.
1parazit.ru>
How can you get infected?
Why is opisthorchiasis so common? Fluke larvae are adapted to survive in different conditions. They do not die either when frozen or at high temperatures.
To destroy parasites, you need to keep the fish in the freezer for at least three weeks or heat it for a long time while preparing the dish. The risk zone applies to those who like to eat dried fish (peled).
How to treat fish for parasites
The best way to get rid of any infections that may be in fish meat is heat treatment. However, it is also acceptable to eat it in other forms. You should know how to salt fish to kill opisthorchiasis and what safe cooking methods exist.
The most dangerous for consumption is stroganina - raw fish meat cut into thin pieces. In this case, it is not processed, so there is a possibility of contracting opisthorchiasis and any other parasitic or bacterial infection.
Treatment methods
Since it is almost impossible to diagnose opisthorchiasis in a timely manner, doctors are most often faced with a serious condition of the patient. The presence of a large number of parasites leads to serious intoxication, which can often only be relieved during hospitalization.
Treatment consists of supporting the liver, removing toxins, killing parasites and helping the body recover. Specific drugs are used to kill worms. In parallel, the patient receives restorative therapy. Since at the same time the body can contain both larvae and adults. The course of treatment is designed in several stages.
The best treatment is prevention.
This includes careful processing of the product, as well as objects in contact with it, for which you should select a separate board and knife.
What is better - a blood test or other methods?
All diagnostic methods are necessary. In this case, it will not be possible to limit yourself to one research method. A blood test will help quickly determine the presence of opisthorchiasis. Other methods help confirm the diagnosis.
Duodenal intubation is considered one of the most reliable research methods. It is recommended to carry it out without fail.
The slightest suspicion of helminth infection requires immediate medical attention. Opisthorchiasis is a serious disease, provokes many complications and easily becomes chronic.
Therefore, it is very important to buy fish from places where there are certificates for it, and also to consume it after sufficient heat treatment. Then the risk of infection is reduced.
List of dangerous fish
Opisthorchiasis, found in river fish, is one of the most common types of helminthic infestations. It affects a large number of the world's population. There is especially a lot of it in the northern regions of Russia. We can safely say that all river fish are affected by this disease. Worm larvae are concentrated among muscle tissue and are found in fish of the carp family.
Thus, you can make a list of fish that, when consumed, are highly likely to become infected. Among them are: bream, carp, peled, ram, ide, bluefish, nipper, roach, omul, rudd, cheese, and other representatives of the carp fish family.
Opisthorchiasis, which species of fish occurs most often?
These are the fish that people like to put on the table on weekdays and holidays. The advantage, as already mentioned, is in the carp family.
In what territory does the opisthorchiasis pathogen live?
Opisthorchiasis parasites live mainly in freshwater fish. Many countries are at risk. A special place is occupied by countries in southeast Asia, as well as the territories of Russia, Ukraine and Kazakhstan. Within Russia, infected fish live in fresh rivers in the following rivers:
Thus, many regions fall within the zone of spread of the disease. Every year many cases of people with opisthorchiasis are registered. Treatment of parasites is a long and not very pleasant process, so it is better to worry about prevention.
What fish suffers from opisthorchiasis?
It is generally accepted that only fish of the carp family are infected with the pathogens of opisthorchiasis, but in fact it turns out that other species of fish living in fresh waters can also get sick.
The question often arises: is it possible to become infected by eating predatory fish species that live in the same bodies of water as infected ones? As a rule, predatory fish are not carriers of opisthorchiasis. The fact is that the body of each fish has a special antibacterial protection, which is ensured by the content of cholic acid.
Predatory fish contain much more acid, and therefore cope with parasites, preventing them from developing. However, there are known cases of opisthorchiasis after eating predatory fish. There are very few of them, however, you should not take risks and eat fish without heat treatment.
List of fish in which opisthorchiasis occurs:
Sea fish is safe to eat. Since seawater contains quite a lot of salt, parasites simply cannot survive in such an environment. Therefore, it is sea fish that is used in dishes without heat treatment.
Opisthorchiasis, which fish definitely doesn’t have it?
Opisthorchiasis can be present in river fish, but the only fish that definitely doesn’t have it is sea fish!
Salmon. This royal dish is bought for the table quite often. In addition to taste, it can also boast of its beneficial properties. It compensates for the deficiency of omega acids in the human body.
Which fish is completely safe?
Marine. The infection cannot develop in salt water. Therefore, if you want to know exactly which types of fish are free of parasites, then all types of sea fish can be consumed in any form without fear of infection.
Fish is one of the indispensable products on our table. It is important that it is always of high quality. If you have the slightest doubt about the product, it is better to refuse consumption or subject the dish to additional processing.
For those who enjoy eating fish, the question often arises - how to determine which fish has opisthorchiasis, where to find a list with photos and names of healthy and sick individuals? These questions are becoming increasingly acute, because the number of people who become infected with these helminths is increasing every year. In order to understand which species to be most careful with, you need to know the ideal conditions for the development of flatworms.
It is necessary to know what the causative agent of the disease is and why it is dangerous, as well as what types of fish are most susceptible to infection with opisthorchiasis. Various ways to determine infestation and prevent opisthorchiasis infection should be considered.
Prevention
The main prevention of opisthorchiasis is aimed at an additional host - fish.
People who eat raw or frozen fish (stroganina) are at greatest risk of infection. These include the peoples of the North, fish factory workers, cooks and housewives tasting uncooked minced fish.
The main rule for preventing infection with opisthorchiasis is proper treatment, especially of representatives of the Karpov family.
Freezing
Death of metacercariae occurs when frozen only after 1.5-2 weeks. Minimum temperature minus 12 degrees. It must be evenly distributed throughout the body, otherwise some of the parasites may survive.
Affected fish should not be quickly frozen at very low temperatures. There is a high probability that the metacercariae will be viable when thawed.
A household refrigerator preserves larvae for a month.
Pickling
To completely destroy the larvae, salting must occur in at least a 20% salt solution for a week to a month.
Small quantities of product are disinfected much faster than large quantities.
Drying
Before drying, long salting is required: at least two weeks in a concentrated salt solution. By decreasing the salting time, the drying time increases to 3 weeks.
Heat treatment
The most destructive thing for opisthorchids is exposure to high temperatures.
It is better to boil or fry fish in small pieces. Complete disinfection occurs during heat treatment at 100 degrees in 15-20 minutes. You should not try dishes that are not fully cooked. Large pieces or whole fish must be boiled or fried for at least 40-60 minutes.
Baking in the oven is carried out for an hour. Smoking is only possible using a hot method. At a temperature of 80 degrees it should last at least two hours. When cold smoking, you must first salt it in the same way as when drying.
It is very difficult to disinfect ide in any way.
Purchasing fish products in stores and markets with a veterinary certificate reduces the risk of opisthorchiasis infection to a minimum.
Other methods of prevention include sanitary education, epidemiological control over pollution of water bodies, and timely deworming of sick people and animals.
Do you still think that getting rid of parasites is not easy?
Worms can live asymptomatically in your body for years and their waste products will interfere with the functioning of your body and cause other diseases, the course of which often becomes chronic.
You are familiar with the following symptoms firsthand:
- nausea;
- gases and bloating;
- frequent colds;
- poor sleep;
- weight problems;
- excessive nervousness;
- fatigue;
- skin problems?
Getting rid of parasites without serious consequences for the body is easier than it seems, see this from the article by V.V. Dvornichenko, Candidate of Medical Sciences, on how to remove worms from the body forever. Read the article >>
A federal program to rid the population of parasites has been launched! It’s hard to believe, but an effective drug for cleansing the body is financed by the budget and special funds. Terrible statistics show that 850 THOUSAND people in Russia die every year due to parasites! To avoid this you need to take a cheap remedy.
Opisthorchiasis is an invasive disease caused by the liver fluke, which parasitizes the gallbladder and liver. A person can become infected by eating infected fish. The pathogen is capable of parasitizing in the human body for up to 30 years. It destroys the mucous membranes of the pancreatic and bile ducts, prevents bile from leaving, releases toxins, causes allergies, and leads to the appearance of tumors
Therefore, it is very important to prevent the disease or detect it in a timely manner if helminths do enter the body.
To avoid infection, it is important to know what kind of fish can be eaten and how long to cook it.
The causative agent of the disease
Some fish are carriers of opisthorchiasis. This type of parasite belongs to flatworms, or more precisely, to digenetic flukes. The final carriers are mammals that feed on fish, as well as humans. An adult individual has a flattened body, 0.8-1.4 cm long, equipped with two suction cups that fix it in the host’s body.
In humans, parasites live in the following places:
- hepatic ducts;
- biliary tract;
- gallbladder;
- pancreas;
- pancreatic ducts.
Nutrients are obtained using suction cups, sucking them out of the tissues to which they are attached. These flukes are equipped with two pairs of reproductive organs (hermaphrodites). An adult can lay up to 800-900 eggs per day.
Species susceptible to opisthorchiasis infection
Parasites pass through the entire food chain of fresh water bodies. Initially, the eggs are swallowed by shellfish, which then enter the body of fish. Previously, it was believed that herbivorous fish that received infected shellfish in their food were most susceptible to this. It is now known that such fish entered the stomachs of predatory species and infected them with worms. Therefore, many freshwater fish species are in the danger zone and can become carriers of the disease. To know from which fish you can become infected with opisthorchiasis, you need to consider the main families of freshwater fish eaten by humans.
You need to look at the list of which fish contain opisthorchiasis in order to be careful with their consumption. These fish species are grouped into families.
Fish from the carp family that can be infected with opisthorchiasis:
- Carp.
- Bream.
- Verkhovka (oatmeal).
- Carp.
- Roach, with such common subspecies as ram and roach.
- Crucian carp, common or silver.
Among perciformes, the following species most often suffer from invasion:
Sturgeon are also susceptible to helminths, the main carriers being:
Salmonids are also carriers, especially freshwater species:
- Karelian trout.
- Muksun.
- Grayling, all subspecies.
- Nelma.
- European vendace (ripus, kilets).
- Arctic omul.
- Belorybitsa.
Peled
Disputes continue among fishermen as to whether peled is an opisthorchiasis fish or not. In order to understand this, you need to know better about their habitats and diet. Cheese, another name for peled. It spends most of its life in lakes; only a few individuals live in rivers, which do not have a special impact on the population. Due to the fact that fresh water in such reservoirs is replaced slowly, when parasite eggs enter, gradual infection of all inhabitants begins. The cheese feeds on the first stage of larval carriers - zooplankton, and therefore has a greater likelihood of being infected than predatory fish species. In peled, opisthorchiasis is also transmitted through eggs.
Precautionary measures
Even when properly cooked fish is not guaranteed to be completely safe. There are a number of rules that are not
are always observed, and several more carriers act between fish and humans.
What you must do:
- Do not give raw fish to pets, they are also the final hosts for worms.
- When cutting, use only metal boards.
- All utensils involved in cooking should be treated, preferably with boiling water.
- When washing your hands, lather up to the elbow, it is best to use laundry soap.
Knowing which species can be carriers and how to properly prepare them, you can protect yourself from infection. But if after 7-10 days unpleasant or painful sensations arise in the right hypochondrium, you should immediately contact a gastroenterologist. The doctor must be told about suspicions of opisthorchiasis so that tests can be carried out. The sooner the problem is identified, the easier it will be to treat.
Opisthorchiasis is a common helminthic infestation that, without proper treatment, can cause significant harm to the body. The causative agent of the infection is the liver fluke, which lives in river shellfish and fish, and when eating poorly processed thermal products, it can enter the human body. Such flatworms are capable of parasitizing the bile ducts and liver, causing irreversible changes in vital human organs. In this article we will tell you about which fish can become infected with these worms and whether opisthorchiasis is present in perch. We will also tell you at what temperature opisthorchiasis dies.
Studies have shown that opisthorchiasis larvae prefer the muscle tissue of fish belonging to the carp family. Whereas predators and sea fish can be eaten almost without fear. Massive foci of infection with these helminths are located in Vietnam, Cambodia and Thailand. In post-Soviet countries, this disease is common in Kazakhstan and the Russian Federation. According to statistics, the most disadvantaged regions are Omsk, Tomsk, Tyumen and Novosibirsk regions. Also, an increased number of patients with opisthorchiasis are observed in the Altai Territory and the Yamalo-Nenets District. It is important to know from which fish you can become infected with opisthorchiasis.
Methods for determining infestation
To detect opisthorchiasis in fish, fishing enterprises use several diagnostic methods simultaneously. To do this, several samples are caught, at different stages of development, if possible, and if the reservoir is large, in different places. Which fish is infected and whether there is opisthorchiasis in the eggs can only be found out through clinical trials.
Types of laboratory tests:
- Physico-chemical, detect deviations in the interaction of ammonia released from decomposed fish and hydrochloric acid.
- Sanitary and microbiological, fish muscle tissue is checked by applying rosolic acid, coloring healthy areas in shades of pink. Uncolored areas indicate the presence of infection.
- Parasitological, muscle fibers and subcutaneous tissues are checked under a microscope. Only with the help of special equipment can you see what opisthorchiasis looks like, which fish contain opisthorchiasis, and record them in a photo.
- Organoleptic, a rarely used type of research, is carried out only when there is a significant deviation in the development of fish.
Life cycle of a parasite
The parasite has a complex life cycle, requiring the presence of intermediate hosts. A person or any warm-blooded mammal is the final host, and in addition, a source of infection. Because part of the parasite's life cycle occurs in the intestines, its eggs and, to some extent, larvae, are excreted in the feces.
If infected feces fall on the soil, their intermediate host becomes a snail that leads a semi-aquatic lifestyle. It is she who transfers the parasite eggs into the water. There they are swallowed by carp fish. They can also be present in water and in free form. They infect fish, their larvae are present in all its meat.
It is not always possible to determine visually whether a pike (or another breed) has opisthorchiasis. Therefore, the contaminated product can be eaten by humans. This is how the parasite enters the oral cavity. From there, the eggs penetrate into the stomach, and from there into the intestines. There the larvae hatch, penetrate through the mucous membrane into the local bloodstream, and from there into the general bloodstream. They migrate through the portal vein to the liver, where they develop and begin to multiply. Since during the cooking process it is impossible to determine which fish is infected with opisthorchiasis, each one must be processed very carefully.
Processing fish before consumption
To enjoy your favorite fish dishes, you need to know how to destroy opisthorchiasis in pike, pike perch, muksun, cheese, and other types of commercial fish. Helminths are very tenacious, and the treatment process must be carefully followed. If the preparation is of poor quality or insufficient time, fish opisthorchiasis persists and is transmitted to humans.
Unreliable ways to kill opisthorchia in fish:
- dry, so dried fish should be preferred to more heavily processed ones;
- cold smoking;
- lightly salt;
- It is not enough to boil or bake;
- raw frozen fish (used by some residents of Karelia);
- fry in thick pieces.
Reliable ways to cook fish:
- long-term heat treatment;
- freezing;
- hot smoking;
- salting
Each type of preparation has its own characteristics, and they must be considered separately in order to understand how to kill opisthorchiasis.
Heat treatment
The first thing you need to know is at what temperature opisthorchiasis dies. For frying it is 120, for cooking 100 degrees. The main thing in cooking is that the pieces of fish are small, not exceeding 100 grams, otherwise the temperature will not kill the parasites located in the depths. The smaller and thinner the processed fillet, the faster the fish infected with opisthorchiasis will become edible.
- Cooking - at least 20-30 minutes in boiling water.
- Frying - from 15 minutes on both sides.
- Stewing – 2-3 hours.
Freezing
To destroy opisthorchid larvae and eggs, pieces of fish are frozen for at least 14-21 days at temperatures below -12. With a shorter duration, viable individuals may remain. Naturally, such a duration is inconvenient, and sometimes it is necessary to increase the speed of disinfection. Then the temperature is lowered to -30 degrees, and the fish is frozen for 3-4 days. To get safe food and not to contaminate other food stored in the freezer, you need to follow sanitary standards.
Rules for storing fish:
- Cleaning the entrails and head (wearing protective gloves).
- In muksun and other large species, the bones must be removed.
- Mandatory cutting into pieces.
- Place in containers with tight-fitting lids (this will prevent contact with other products).
Salting
The longest method of disinfection. It will take 30-50 days to destroy all the larvae. Salting begins with removing the fish's giblets, after which it is cut into small pieces, no more than 2-3 cm in diameter. When the base is ready, 0.5 cm of salt is laid out at the bottom of the container, on which fish pieces are placed. After the entire surface is occupied, salt is poured again and the fish continue to be laid out. And so on until 2-3 cm remains to the edge of the dish. The workpiece is tightly closed and put in a dark place, with a temperature not exceeding 7-8 degrees, for at least 45-50 days.
The second method, which enhances the salting of fish, uses oppression. Then you should leave more space in the container, which will be occupied by the inserted plate and weighting agent. Thanks to constant pressure, the fish is better and faster saturated with salt, and the time until ready is reduced to 30-35 days. In pike perch, opisthorchiasis dies the fastest - in 25-28 days.
Prevention
The main prevention of opisthorchiasis is aimed at an additional host - fish.
People who eat raw or frozen fish (stroganina) are at greatest risk of infection. These include the peoples of the North, fish factory workers, cooks and housewives tasting uncooked minced fish.
The main rule for preventing infection with opisthorchiasis is proper treatment, especially of representatives of the Karpov family.
Freezing
Death of metacercariae occurs when frozen only after 1.5-2 weeks. Minimum temperature minus 12 degrees. It must be evenly distributed throughout the body, otherwise some of the parasites may survive.
Affected fish should not be quickly frozen at very low temperatures. There is a high probability that the metacercariae will be viable when thawed.
A household refrigerator preserves larvae for a month.
Pickling
To completely destroy the larvae, salting must occur in at least a 20% salt solution for a week to a month.
Small quantities of product are disinfected much faster than large quantities.
Drying
Before drying, long salting is required: at least two weeks in a concentrated salt solution. By decreasing the salting time, the drying time increases to 3 weeks.
Heat treatment
The most destructive thing for opisthorchids is exposure to high temperatures.
It is better to boil or fry fish in small pieces. Complete disinfection occurs during heat treatment at 100 degrees in 15-20 minutes. You should not try dishes that are not fully cooked. Large pieces or whole fish must be boiled or fried for at least 40-60 minutes.
Baking in the oven is carried out for an hour. Smoking is only possible using a hot method. At a temperature of 80 degrees it should last at least two hours. When cold smoking, you must first salt it in the same way as when drying.
It is very difficult to disinfect ide in any way.
Purchasing fish products in stores and markets with a veterinary certificate reduces the risk of opisthorchiasis infection to a minimum.
Other methods of prevention include sanitary education, epidemiological control over pollution of water bodies, and timely deworming of sick people and animals.
Do you still think that getting rid of parasites is not easy?
Worms can live asymptomatically in your body for years and their waste products will interfere with the functioning of your body and cause other diseases, the course of which often becomes chronic.
You are familiar with the following symptoms firsthand:
- nausea;
- gases and bloating;
- frequent colds;
- poor sleep;
- weight problems;
- excessive nervousness;
- fatigue;
- skin problems?
Getting rid of parasites without serious consequences for the body is easier than it seems, see this from the article by V.V. Dvornichenko, Candidate of Medical Sciences, on how to remove worms from the body forever. Read the article >>
A federal program to rid the population of parasites has been launched! It’s hard to believe, but an effective drug for cleansing the body is financed by the budget and special funds. Terrible statistics show that 850 THOUSAND people in Russia die every year due to parasites! To avoid this you need to take a cheap remedy.
Eating products of animal origin, including fish, always carries the risk of infection with various types of helminths. Insufficient heat treatment increases the likelihood of helminthic infestation for humans.
Cooking methods such as drying and cold smoking allow the eggs and larvae of parasitic worms found in muscle tissue and eggs to remain viable for a long time.
Among the most dangerous types of helminthiases that develop as a result of eating fish is opisthorchiasis, which is usually transmitted to the carrier during consumption of fish from the carp family and some other species. When answering the question whether peled is an opisthorchiasis fish or not, as well as in relation to other species, one should consider its belonging to a specific family and genus of fish.