Vomiting is the most common reflex process that every person has encountered at least once in their life. This condition can be caused by a large number of predisposing factors, which are not in all cases associated with damage to the digestive system. Moreover, some reasons may be completely harmless.
- Etiology
- Classification
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Prevention
The gag reflex is accompanied by a large number of clinical manifestations, including nausea, stool upset and increased body temperature.
Often, diagnosing vomiting does not cause difficulties, however, to determine the reasons for its occurrence, it is necessary to conduct a laboratory and instrumental examination. Treatment tactics are based on conservative techniques.
Mechanism of vomiting
Vomiting may accompany:
- pathological processes of the gastrointestinal tract;
- cerebrovascular accidents;
- thrombosis of blood vessels of internal organs;
- tumor neoplasms;
- acute kidney diseases;
- toxicosis (gestosis) of the first half of pregnancy;
- infectious (most often intestinal) diseases;
- diseases of the visual organs;
- vestibular disorders;
- acute forms of myocardial infarction;
- drug overdose, drug incompatibility.
The patient initially experiences nausea, excessive salivation, and increased breathing. Then the diaphragm lowers and the section of the stomach, which passes into the duodenum, begins to contract in the opposite direction (antiperistalsis), the upper “floor”, on the contrary, relaxes. Spasms of the diaphragm begin, pressure in the stomach cavity increases, and the glottis closes. After this, an eruption of gastric contents occurs through the esophagus into the oral cavity.
The patient turns pale, has cold, sticky sweat, dizziness and severe weakness often occur, and blood pressure may drop. Nausea is a sensation that occurs due to irritation of the vagus and splanchnic nerves. Excitation from them is transmitted to the vomiting center and from it the impulse goes to the organs that are involved in vomiting.
In fact, vomiting is a specific symptom, but depending on the causes of its occurrence and a number of other factors, it has many varieties and characteristics of its course.
Features of vomiting:
- vomiting not accompanied by nausea is characteristic of problems with the brain;
- vomiting with severe headache is a sign of migraine;
- Vomiting in the morning is typical for poisoning.
Other provoking factors
Sour vomiting may indicate the presence of gastritis. The disease can be asymptomatic for a long period. The pathology is characterized by inflammation of the mucous membranes of the digestive organ. The most common cause of the disorder is Helicobacter pylori infection and consumption of low-quality food. If not treated in a timely manner, an ulcer may form.
Another possible cause of sour vomiting is Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. In the presence of such a pathology, a tumor forms in the pancreas. The pathology is characterized by an increase in acidity levels. Treatment is only surgical.
Often sour vomiting is a symptom of gastritis
With this syndrome, vomiting cannot be eliminated with antiemetic drugs. Also, a sour gag reflex can signal:
- brain injuries;
- strokes;
- eating too much food.
Only a doctor can make a diagnosis. It is impossible to find out the cause of sour vomiting on your own.
Sour vomiting may indicate the presence of gastritis. The disease can be asymptomatic for a long period. The pathology is characterized by inflammation of the mucous membranes of the digestive organ. The most common cause of the disorder is Helicobacter pylori infection and consumption of low-quality food. If not treated in a timely manner, an ulcer may form.
Esophageal vomiting
Begins without nausea, in a lying position or when bending forward. Occurs due to retention and accumulation of food in the esophagus.
Food vomiting is typical for the following diseases:
- narrowing of the esophagus (tumor, post-burn, ulcerative);
- achalasia cardia (spasmodic tension of the lower esophagus);
- diverticula of the esophagus (bag-like protrusions of the walls);
- insufficiency of the sphincter (the muscle that compresses the passage from the esophagus to the stomach).
According to the timing of occurrence, the following are distinguished:
- early vomiting that occurs while eating, with pain in the chest. It is provoked by eating solid foods due to problems in the esophagus;
- late vomiting, which manifests itself 3-4 hours after eating (a sign of severe expansion of the lower parts of the esophagus);
- mixed. Occurs with ulcerative esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus with ulcers).
Sometimes there is night vomiting. Complicated by getting into the respiratory tract.
Signs of vomiting in diseases of the stomach and duodenum
Gastric vomiting makes itself felt almost immediately after a heavy meal, in case of pathology of the duodenum - after 2-3 hours.
Please note: the hallmark is relief immediately after vomiting and reduction in pain.
A narrowed opening of the outlet (pyloric) section of the stomach (with cancer, scar changes) causes frequent, voluminous vomiting with undigested food that has been in the stomach for several days, with a putrid odor.
If vomiting is repeated frequently and contains remnants of recently eaten food, then a spasm of the lower part of the stomach should be suspected. Occurs in case of poisoning with toxins, acute ulcerative process in the stomach, diseases and dyskinesia of the bile ducts, neuroses.
In cases of acute gastritis, patients often complain of vomiting - repeated, with pain in the epigastric region, which brings relief. Chronic gastritis is very rarely accompanied by vomiting.
Other diseases of the abdominal organs that cause vomiting
Acute appendicitis can also cause vomiting, especially in the presence of severe pain and fever.
Thrombosis of the peritoneal arteries is accompanied by vomiting of blood.
With peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum), repeated vomiting and fever are observed, bringing relief each time.
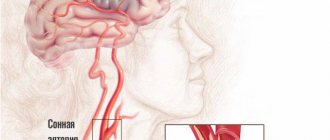
Phenomena indicating cerebral vomiting
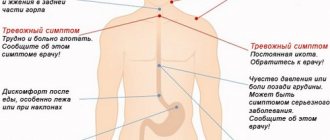
Occurs as a result of injuries and diseases of the brain, blood vessels and surrounding tissues. An increase in pressure in the diploic veins of the skull (intracranial pressure) gives characteristic vomiting with intense headaches that occur in the morning, when trying to get up or simply turning the head while lying down. These signs may be accompanied by disturbances in the functioning of the heart and breathing. Possible loss of consciousness (Bruns syndrome).
Vomiting and fever are characteristic of inflammatory diseases of the brain and membranes - meningitis and encephalitis. In these cases, intense pain in the head and specific neurological symptoms, which are determined by a neurologist, also occur. The development of paresis and paralysis is possible.
Meniere's disease is accompanied by damage to the vestibular apparatus with attacks of dizziness, hearing loss and periodic vomiting.
Many people suffering from hypertension periodically experience a sharp increase in blood pressure and a deterioration in their condition, accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
Atypical provocateurs of the gag reflex
Diagnosis of the condition is possible only by studying all the accompanying symptoms. Only they make it possible to identify diseases in which vomiting and nausea may manifest themselves as uncharacteristic symptoms.
These include hepatitis, brain diseases (tumors, hydrocephalus, intracranial hematoma), pathologies and functional failures of the cardiovascular system (vascular rupture), certain mental conditions and neuritis in diseases of the nervous system.
Nausea in such cases leads to pathological vomiting, indicating the onset of a state of severe severity.
How to artificially induce vomiting
For some diseases and conditions, it is necessary to be able to induce vomiting yourself. In case of overeating, poisoning, or consumption of poor quality food or water, it may be necessary to empty the contents of the stomach by inducing forced vomiting.
The most commonly used traditional method is pressure on the root of the tongue with two fingers or a spoon. To make the procedure easier, it is better to drink a solution of manganese. It is prepared from a small amount of potassium permanganate crystals and a liter of warm, boiled water. The solution must be stirred until a pink, uniform color is obtained. Then drink it and stimulate vomiting. The solution helps to rinse the stomach well and cleanse it. It also relieves discomfort during vomiting.
For the same purpose, you can use a solution of salt and soda in water (1 teaspoon per liter). Drink in one gulp and empty your stomach. In most cases there is relief.
What to do about the symptoms
The most affordable way to cope with the urge to vomit is to use special medications. An effective remedy is Omeprazole. It will reduce acidity in the stomach, relieve heartburn, nausea and the urge to vomit. Ibuprofen is also recommended.
In addition to medications, there are other ways:
- Rinse your mouth with a solution of salt or soda. Composition proportions: per teaspoon of dry matter, one glass of water. Soda dries out the gastric mucosa more strongly, which is why it causes discomfort in some people.
- Oral gels that cause mild numbness.
- Rinse your nose regularly. Saline solution or seawater drops are good for this. When the nose breathes freely, the risk of vomiting is several times less.
- If you are prone to nausea and require a visit to the dentist, avoid eating 3 hours before your appointment.
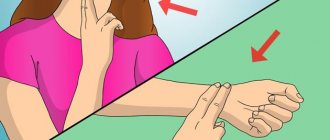
- An easy way to overcome the gag reflex is to clench your fingers into a fist.
If gagging occurs while brushing your teeth, the cause may be an allergy to the composition of the toothpaste.
If the cause of vomiting is a psychological problem, then breathing exercises, relaxation techniques, yoga, and Pilates will help overcome the attack. These methods will teach you to relax the body and keep your health under control.
Vomiting in children
Vomiting in a child is a common symptom that accompanies many childhood diseases.
As in adults, it happens:
- psychogenic;
- organic (caused by diseases).
In newborns in the first months of life, vomiting may occur due to excess food intake. It is often accompanied by swallowing air.
Please note: sometimes “chewing gum” occurs - regurgitation with repeated swallowing (rumination). Regurgitation differs from vomiting in the absence of muscle tension.
Vomiting in children is accompanied by:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- infectious diseases;
- poisoning;
- heart and vascular diseases;
- pathology of the nervous system.
A child may have cases of vomiting and diarrhea without fever of unknown etiology or as the first (single) symptoms of an incipient disease.
Diarrhea, vomiting and fever often accompany infectious pathology. Vomiting with blood (scarlet and dark), the presence of mucus, food debris, and intestinal parasites in the masses is a valuable diagnostic sign that allows the pediatrician to correctly construct diagnostic tactics and subsequent treatment.
Important: requires a mandatory determination of the cause - vomiting of bile. In children it is a sign of serious illness.
What to do about vomiting in children? The answer is in the video review:
Prevention methods
The simplest, but at the same time effective methods of prevention include:
- Try to relax. Anxiety and stress are present in everyone's life, but to prevent nausea, you should learn not to react to such situations.
- Try to rest more, you can practice meditation techniques, yoga.
- Avoid unpleasant odors, especially if your olfactory receptors are highly sensitive. For example, cigarette smoke, perfumes, products. They stimulate the urge to vomit, since the sense of smell is closely related to the gastrointestinal tract.
- Try to reduce the number of trips by transport. When the body cannot correctly orient itself in space, it gets motion sickness. So, a regular trip on a rough road or a boat ride can trigger the urge. To combat motion sickness, fix your gaze on a distant fixed point. This will calm the nervous system and relieve discomfort.
- Before drinking alcohol, drink 2-3 glasses of water. Alcohol contributes to dehydration, so you need to hydrate your body. Thanks to water, the alcohol will be diluted, absorbed more slowly and will not provoke such symptoms.
- Fatty foods also help when drinking alcohol. It works on the principle of water, slowing down the absorption of alcohol. It is important to distinguish between healthy and unhealthy fats. Healthy ones include: avocado, nuts, fish, flaxseed and olive oil.
If symptoms bother you for several days, consult a doctor, he will be able to determine the exact cause. In case of minor ailments, he will explain how to deal with poor health, and in case of diagnosing a serious illness, he will prescribe treatment.
Emergency measures and treatment methods for vomiting
The volume and nature of assistance must be taken into account depending on the reasons that caused vomiting.
Most cases require immediate gastric lavage by inducing artificial vomiting. It is strictly contraindicated to administer antiemetic drugs to the patient.
If there is blood in the vomit, then lavage of the stomach is prohibited. The patient can be given small pieces of ice for oral administration; it is better to place an ice bubble on the epigastric region. Urgent hospitalization in a supine position is required.
Subcutaneous atropine or metaclopramide can be used to stop vomiting. For indomitable vomiting, antipsychotics (etaperazine, meterazine, haloperidol) are prescribed.
Treatment of repeated vomiting with severe dehydration is supplemented by intravenous drip administration of isotonic solution, glucose, and other drugs.
Such patients are subject to hospitalization.
Lotin Alexander, radiologist
29, total, today
( 54 votes, average: 4.15 out of 5)
What can you eat if you have diarrhea?
Liver fibrosis: symptoms, treatment, prevention