Why do you need a biopsy test?
Diagnostics helps determine the scope of upcoming operations, the nature and nature of pathological tissues. It is supplemented with radiography, immunological analysis, and endoscopy. Indications for sampling:
- precancerous changes, cancer;
- detection of HPV - human papillomavirus;
- genital warts, papillomas on the genitals;
- endometriosis;
- inflammation, polyps;
- deviations in the functioning of organs.
The analysis provides complete information about the structure of cells and helps determine the morphological signs of diseases. The technique is used to confirm the suspected diagnosis. It is indicated if the results of other diagnostic procedures are not enough to diagnose it. The method is also used to study the nature of the tumor and control cancer treatment.
How to obtain biopsy material
The biomaterial obtained during the biopsy process is called a biopsy sample. This is a piece of tissue or a small amount of blood or bone marrow for testing. According to the method of collection, the procedure is divided into types:
- trephine - obtaining a biopsy using a special thick needle;
- brush – diagnostics using a catheter, inside of which a string with a brush is installed;
- fine-needle aspiration - a minimally invasive procedure that uses a syringe that sucks out biomaterial from tissues;
- loop – excision of pathological tissues with biopsy sampling with an electric or thermal loop;
- liquid – technology for identifying tumor markers in blood and lymph;
- radio wave – a gentle technique using the Surgitron apparatus;
- open – involves open access to tissues;
- preskalennaya - taking a biopsy sample through the lymph nodes and lipid tissues at the angle of the jugular and subclavian veins.
Excisional lymph node biopsy: indications, procedure and result
This type of procedure involves the complete removal of the gland that has undergone abnormal modifications. There are a large number of indications for open diagnosis of lymph nodes.
The grounds for conducting this diagnostic study are:
- suspicion of cancer of the lymph node;
- continuous growth of the gland, accompanied by its pronounced compaction and swelling;
- the need for differential diagnosis of diseases such as sarcoidosis or tuberculosis.
Excisional biopsy of a lymph node is performed by making small incisions on the skin and subcutaneous tissue, and complete removal of the affected gland through them is not only an informative diagnostic procedure, but also an adequate therapeutic measure. This type of surgery allows you to completely remove an organ affected by malignant cells.
Types of biopsy
The procedure is divided according to the type of biopsy sample taken. The most famous types:
- excisional biopsy - removal of an entire organ or tumor;
- stereotactic - a minimally invasive method that involves constructing a special access scheme to the suspicious area after scanning;
- puncture biopsy - obtaining samples using a puncture with a fine needle;
- transthoracic – obtaining biomaterial from the lungs through the chest using an open or puncture method;
- incisional biopsy - removal of part of an organ or tumor during surgery;
- wedge-shaped (conization) - carried out to study the cervix using a scalpel or laser beam;
- curettage – removal of cells from the canals with a curette.
What organs and tissues are examined during excisional and incisional biopsies?
Total and partial diagnostics, consisting of taking a biopsy during surgery, are the most justified step in diagnosing a large number of diseases of an oncological and infectious nature that develop in various internal organs and systems. Excisional and incisional biopsies make it possible to identify pathological processes, the nature and nature of which are not determined using non-invasive diagnostic techniques. Typically, materials obtained from an open biopsy are used for microscopic examination (histology).
Histological study of biological material collected intravitally is the main and only way to make a final diagnosis of almost all oncological processes.
Most often, incisional and excisional biopsy is prescribed when there is a need for adequate examination of the following organs:
- breast, thyroid and prostate glands;
- mucous membrane of the digestive tract;
- female reproductive system;
- skin;
- bone marrow;
- lymph nodes;
- bronchi and lungs.
Methods for studying biopsy material
The obtained biopsy specimen is studied using several methods - histological or cytological. The first is considered more accurate, since tissues are studied, not cells. Both methods involve the use of microscopic technologies.
Histological examination
Tissue sections are studied, placed in a specialized solution, paraffin, and then stained. The latter procedure is necessary so that cells and their areas are better distinguished under a microscope.
If urgent research is necessary, the biopsy is frozen, sectioned and stained. The procedure lasts 40 minutes.
Cytological
If histology studies tissue sections, then cytology examines cellular structures in detail. The technique is performed if it is not possible to obtain a piece of tissue. Diagnosis is carried out to determine the nature of the formation - benign or malignant, reactive, inflammatory, precancerous. A smear is made on glass using the biopsy specimen and examined under a microscope. The procedure is faster and simpler than histology.
Contraindications
If the gynecologist discovers any inflammatory processes in the vagina, the biopsy is postponed until they are eliminated. If the cause of the disease is clear, the gynecologist will immediately suggest a treatment regimen. Otherwise, additional tests will be needed to understand what is causing the inflammation. The procedure is not carried out during menstruation.
Sometimes during pregnancy, the doctor may suggest this test, taking into account the risks and benefits. It is most dangerous to perform a biopsy before 12 weeks, as it can lead to miscarriage. If the procedure is performed in the last weeks of pregnancy, there is a risk of premature birth. The most optimal period is the second trimester of pregnancy.
Procedure for performing manipulations
Methods for collecting biomaterial differ depending on the organ being studied. This affects the procedure for studying the biopsy specimen. The procedure is approximately the same: preparing the patient, collecting tissues or cells, studying under a microscope.
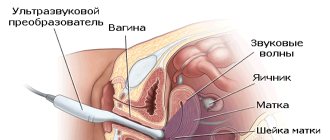
Biopsy of the reproductive system
Women's cervixes are often examined. The biopsy is done under local anesthesia or general anesthesia. For pain relief, lidocaine spray, epidural or intravenous drugs are used. Procedure for collecting material:
- A dilator is inserted into the vagina, the cervix is grabbed with forceps closer to the entrance, and treated with acetic acid or iodine to detect suspicious areas.
- The pathological tissue is removed using forceps or a scalpel. If there are several suspicious foci, 3-4 samples are taken. To do this, a wedge-shaped area is cut out with a scalpel at the border of the healthy and changed part of the tissue (5 * 5 mm).
- Sometimes the radio wave method is used. Conchotomic and diathermic biopsy methods are prohibited.
- After the procedure, self-absorbing sutures are placed on the wound, and a hemostatic sponge or tampon soaked in fibrin is inserted into the vagina to stop bleeding.
- The resulting tissue sample is fixed in a formaldehyde solution and sent to the laboratory.
During a circular biopsy (conization), a large amount of tissue is removed. In this case, the neck is circularly excised with a special scalpel. Such a study is indicated for lesions of the cervical canal, precancer, or suspected tumor growth.
The method helps to determine pathologies of the uterine cervix and body, endometrium, vagina, and ovaries. In gynecology, other methods of obtaining a biopsy may additionally be used:
- incisional;
- aiming;
- aspiration;
- laparoscopic;
- endometrial.
When examining the bladder, cold and TUR biopsy are used. The first method involves penetration through the urethra and taking a biopsy with special forceps. During a TUR biopsy, the entire tumor and some healthy tissue are removed.
Organs of the gastrointestinal tract
The choice of method for collecting biomaterial depends on the nature and location of the area under study. Colonoscopy with biopsy is most often used. Tissue collection from the small and large intestines is carried out using the following methods:
- puncture;
- loop;
- trepanation;
- incisional;
- plucked;
- scarification (from the surface).
When analyzing the pancreas, fine-needle aspiration, transduodenal, laparoscopic, and intraoperative methods are used. Indications for a biopsy include the need to determine morphological changes in cells in the presence of tumors and identify pathological processes.
Organs of the cardiovascular system
Myocardial biopsy helps detect and confirm myocarditis, cardiomyopathy, and ventricular arrhythmia. She will detect rejection after organ transplantation. Right ventricular intervention is most often performed. Access to the muscle is through the jugular, femoral or subclavian vein. To control the manipulations, fluoroscopy and an electrocardiogram are needed.
A catheter is inserted into the vein and brought to the desired area. On the bioptome, tweezers are opened and a small piece of tissue is removed. To avoid thrombosis, a special medicine is given.
A bone marrow biopsy is performed for malignant tumors, leukemia, iron deficiency, thrombocytopenia, splenomegaly, and anemia. The doctor takes a red bone marrow biopsy - a small piece of bone tissue - with a needle. The procedure is carried out using aspiration or trepanation methods.
Bone tissue
A bone biopsy is performed to identify malignant tumors and infectious processes. Manipulations are carried out percutaneously, using a thick or thin needle, or surgically.
Organs of vision
An eye exam can help detect retinoblastoma, a malignant tumor that is common in children. A biopsy helps to obtain a complete picture of the pathology and determine the size of the lesion. Aspiration technique with vacuum extraction is used.
Preparing for biopsy sampling and performing the procedure
Excision and incisional procedures are common surgical interventions performed on various organs, therefore, before performing surgical procedures, the patient must undergo urine and blood tests, as well as undergo tests prescribed by the attending physician. Due to the fact that any surgical procedure is performed under general or local anesthesia, the main preparatory stage is to refuse food at least 8 hours before the operation. All other recommendations will be given by the attending physician, since they vary depending on which organ the surgical manipulation will be performed on.
The technique for performing an open biopsy is as follows:
- The patient is placed on the operating table and given general anesthesia or local anesthesia.
- The surgeon makes a tissue incision over the pathological area and removes from it, during the incisional type of biopsy sampling, a certain fragment of the modified structure, and during the excision type, he cuts out the entire pathological area or resects the affected organ.
How to prepare for a biopsy
In order for the results of the study to be reliable, you need to properly prepare. Helpful Tips:
- A cervical biopsy is performed 5–7 days after the first day of menstruation. During the day, douching, tampons, medicated suppositories or creams, and intimate hygiene products are canceled.
- Before the study, blood and urine tests are taken, the levels of bilirubin, creatinine, urea, and sugar are determined. A coagulogram is taken and, if necessary, a smear.
- If an infectious process is detected, a biopsy is done after it has been eliminated.
- For 2 weeks, you should stop taking Aspirin, Warfarin, Ibuprofen.
- One day before, you need to stop smoking and eliminate alcohol.
- During anesthesia, food and liquid intake is canceled 12 hours before.
Well-being
The gynecologist will try to carry out the examination as comfortably as possible, so you should expect quite tolerable pain or discomfort. As mentioned above, after a biopsy, bleeding of varying degrees of abundance will appear, depending on the chosen research method. During this period, you can only use pads, not tampons. If you develop a fever, you must contact the doctor who performed the procedure.
Typically, sexual rest is prescribed for 7 days. In rare cases - for two weeks. It is best to wait until the cervix is completely healed and the bleeding and pain have subsided.
Decoding the results
Using histological or cytological examination, the doctor determines the presence of altered cells that can threaten serious consequences or be signs of precancer and tumors. According to the World Health Organization classification, there are mild, moderate, severe dysplasia and carcinoma - an early stage of cancer.
Decoding the results classifies the detected changes into one of the groups:
- Background – does not turn into precancer, but causes the development of diseases.
- Precancerous – there is no malignant tumor activity yet, but approximately 50% of cases, if left untreated, transform into cancer.
- Cancer is a malignant formation. Divided into preclinical (early stage without symptoms), clinically expressed.
The reliability of biopsy data is 98.5%. This means that errors are virtually eliminated. Biopsy under the control of colposcopy (for the cervix) or colonoscopy (for the intestines) increases the quality of diagnosis, according to reviews, by 25%. Repeated use of the procedure is highly undesirable, because scar changes are formed that impede the normal functioning of the organ.
Interpretation of results
The results of a prostate biopsy are usually available in 2-7 days, your doctor will tell you and ask you to come in for a consultation.
The report will include:
- number of biopsy samples taken;
- whether the samples are negative, have benign results, are suspicious (and if so, why), or are cancerous;
- if cancer is present, the percentage of cancer in each sample;
- Gleason score, which indicates the aggressiveness of the cancer.
Let's look at the possible sampling results in more detail.
Negative
A negative biopsy means that there is no evidence of benign changes, suspicious-looking cells or cancer cells in the area where the biopsy was taken.
Benign changes
There are several benign findings that may be noted on a biopsy. Some of them:
- Atrophy: Atrophy (including focal atrophy or diffuse atrophy) simply refers to the shrinkage of prostate tissue and is common in men who have undergone hormone therapy.
- Inflammation: both chronic and acute prostatitis can occur.
- Adenosis: Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia, or adenosis, is another benign finding.
Contraindications for analysis
The procedure is highly informative, but has a number of contraindications. These include:
- blood pathologies, clotting problems, thrombocytopenia, hemophilia;
- intolerance to anesthesia;
- chronic heart failure;
- inflammatory, infectious diseases in the acute phase;
- epilepsy;
- diabetes;
- pregnancy.
Indications and contraindications for skin biopsy
A skin biopsy is often purely diagnostic in nature, but if the procedure completely removes the altered area of the skin, it can also be called therapeutic. Indications for skin biopsy are:
- Infectious lesions;
- Inflammatory process of unknown nature;
- Neoplasms;
- Autoimmune pathology, vasculitis (systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, etc.);
- Cutaneous tuberculosis;
- Psoriasis;
- Suspicion of amyloidosis;
- Darier's disease;
- Lymphomas of the skin;
- Deep fungal infections.
In addition to diseases, the reason for a biopsy may be to monitor the treatment performed.
Contraindications to skin biopsy are:
- Pathology of blood clotting;
- Acute inflammatory process at the site of tissue collection;
- Pustular lesion;
- Acute infectious general disease;
- Allergy to local anesthetics.
Possible consequences of manipulation
With proper care after manipulation, the risk of complications is minimized. Measures taken:
- to relieve pain, take painkillers;
- to prevent infectious complications - use antibiotics prescribed by the doctor, antiseptics to treat the wound, - agents that accelerate the healing of scars;
- after a cervical biopsy - wear cotton underwear, use absorbent pads, use fragrance-free soap, dry the perineal area;
- After any procedure, you cannot drive a car, lift heavy objects, take a bath (shower only), or visit swimming pools or saunas.
The most common complications after a biopsy are pain and prolonged wound healing. They are harmless and go away on their own. More severe consequences are:
- bleeding from the vagina, delayed menstruation;
- scar formation;
- strong pain;
- high body temperature;
- deterioration of general condition, weakness;
- coating on the tongue;
- back pain after anesthesia;
- copious suspicious vaginal discharge;
- urticaria, Quincke's edema, anaphylactic shock.
Risk factors that increase the likelihood of complications include:
- obesity;
- smoking;
- elderly age;
- hyperglycemia;
- dysfunction of the kidneys, liver, heart;
- chronic lung disease;
- autoimmune diseases;
- weak immunity.
Postoperative period and possible complications
In most cases, after a cervical biopsy, women feel satisfactory, possible pain is relieved by analgesics, and their ability to work is not impaired. Regardless of the method of taking tissue, after its excision bleeding appears of varying intensity and duration.
The discharge after the biopsy is not too heavy and lasts for several days. In the case of minimally invasive methods of tissue sampling, they bother you for the next 2-3 days, while a loop biopsy, electroconization or knife technique gives quite pronounced bleeding within a week, and then the discharge becomes spotting and may be present for another 2-3 weeks.
After a biopsy, doctors strongly do not recommend using tampons, douching, or resuming sexual activity until the bleeding stops completely. You should avoid visiting the pool, bathhouse, sauna, or lifting weights of more than 3 kg in the next 2 weeks after the study or longer if the discharge has not stopped.
Among the complaints presented by patients who have undergone a cervical biopsy may be pain in the lower abdomen and genital tract. They are associated with a cervical injury and, as a rule, go away quickly on their own. In some cases, gynecologists recommend taking analgesics in the first few days after the procedure.
Negative consequences after a cervical biopsy are very rare, but still not excluded. Among them, the most likely are bleeding and infection, as well as scar deformation in the long-term period after resection with a scalpel, conchotome or electric current.
A woman should be alerted to heavy bleeding, discharge for more than 2-3 weeks, fever, cloudy and foul-smelling discharge from the genital tract. These symptoms are a reason to urgently consult a doctor.
Biopsy analysis: what is it?
Biopsy - what it is in oncology is well known. The short answer to the question of why a biopsy is done is as follows: to identify tissue pathologies and determine their benign or malignant nature.
Undeniable advantages of the procedure:
- Studying a biopsy sample (removed material) under a microscope allows one to determine the cytology of tissues - providing complete information about the presence of the disease and the extent of its spread.
- Allows you to identify the disease at the earliest stages, when alternative diagnostic methods are not yet effective.
- Allows you to identify the area of the lesion, and therefore predict the complexity of the upcoming operation.
To clarify the clinical picture, other diagnostic methods can be used: immunological analysis, x-rays, endoscopy, but they are only of an auxiliary nature - the main thing remains what the biopsy shows.
Often, a biopsy analysis is prescribed during the treatment process - to assess its effectiveness and monitor the dynamics of the disease.
Having found out: biopsy analysis - what it is, you also need to find out when this analysis cannot be done. Contraindications for the procedure are:
- problems with blood clotting;
- chronic heart disease;
- the possibility of using less traumatic diagnostic methods;
- written refusal of the patient from the procedure.
What diseases can the study identify?
The study of biomaterial is carried out within 10 days. The analysis makes it possible to differentiate benign prostatic hyperplasia from adenocarcinoma.
If carcinoma has already been diagnosed, a biopsy is used to determine the stage, nature and extent of prostate damage, which, in turn, helps to correctly choose further treatment tactics.
How does this happen?
It will be useful to learn not only what a biopsy is, but also how a biopsy is taken. The term “biopsy”: what it is in oncology, deciphering the meaning is known to many. Literally, this is the excision of a living organism (in this case, tissue).
A biopsy can be removed from almost any part of the body. This is done under anesthesia - general or local. The second option is preferable because it is less traumatic to the body, but sometimes the collection of material requires only general anesthesia.
When asked how long it takes to perform a biopsy, experts answer that the procedure itself does not last long. How long does a biopsy take specifically - from 10 to 20 minutes.
If you know where to take the biopsy test and it is a difficult place to reach, the procedure can last up to 40 minutes. But how long does it take to analyze a biopsy - that is, study the obtained material - this depends on the nature of the study.
Biopsy is the general name for one of the types of diagnostics of body cells. This procedure has several subtypes, depending on the size of the extracted biopsy, the location of the problem area, and the medical instruments used.
When studying what a biopsy is and what this word means, it is necessary to note that today there are about 14 types of biopsies.
Based on the method of impact on the patient’s body, the following types of biopsy are distinguished:
- An excisional biopsy is the removal of an entire tumor or an entire organ. This type of diagnosis allows not only to examine the affected element, but also to remove it from the patient’s body - it turns out that this procedure has not only a diagnostic, but also a direct therapeutic effect.
- An incisional biopsy is the removal of only part of a tumor or an affected organ. An incisional biopsy allows you to determine the presence or absence of the disease, as well as assess the extent of organ damage for planning further treatment procedures.
- A puncture biopsy is the collection of a biopsy material by puncturing the formation under study with a hollow needle. The method is used if getting to the affected area is problematic or the organ is too delicate (in particular, this includes tongue biopsy). As a result of the puncture, cells of the object under study remain on the needle, which are used to diagnose health conditions. A puncture biopsy can be performed with a thin (aspiration) or thick (trephine) needle. Often the procedure must be carried out based on the data of an ultrasonic sensor, endoscope or radiograph - otherwise it is unlikely to hit the desired target.
Biopsy - research methods
When cells are collected for analysis, or a piece of organic tissue is obtained, the material is sent to the laboratory. Depending on the purpose of the study, the type of samples available and the preliminary diagnosis, either cytology or histology is performed. Definitions of what a biopsy is, in the context of this classification, are different. In the first case, cells are analyzed, in the second - tissues.
Cytological examination
The most painless biopsy, analysis involves scraping, washing off the affected areas, or studying biological fluids (blood, urine, punctures from serous cavities). The obtained materials are subjected to research using the following methods:
- Optical (light).
Cells are examined under a microscope. What is assessed during the analysis: general plan, movement, movement of cytoplasm, division processes. There are several subtypes of this cytology - ultraviolet, dark and light field, fluorescent and others. - Electronic.
The concept of what a biopsy is, in the presented case, coincides with the previous research technique, only a different microscope is used. Electronic equipment provides the maximum available magnification of material, so with its help you can even examine the structure of cell membranes, track viruses and their particles, and observe the interaction of antibodies and antigens. To increase information content and improve the contrast of samples, they are “etched,” which means they are exposed to heavy metal salts. - Centrifugation.
This technology involves preliminary fragmentation of cells into their component parts (organelles) in a special device (homogenizer). The resulting sample is placed in a centrifuge and subjected to rotation, which ensures the separation of the material into fractions, from which individual components and subcellular formations are extracted. - Atom labels.
To study biochemical processes in cells, carbon, oxygen, and other elements are replaced with radioactive isotopes. They behave identically, but are easier to track. - X-ray diffraction analysis.
This research helps to determine the spatial arrangement of protein chains, RNA and DNA, which helps determine their properties. - Cultural technique.
The resulting cells are placed in a nutrient medium and grown, after which they are studied. - Microsurgery of the specimen.
Various organelles are artificially implanted or removed into the material, which makes it possible to evaluate the cell response to the “invasion.”
Histological examination
Tissue analysis is necessary to determine their quality; it is used mainly in oncological practice. Histological examination of biopsy material is carried out in several stages:
- Dehydration.
Using special solutions (wiring), moisture is removed from tissues and made fat-soluble. - Impregnation.
The prepared mass is placed in paraffin cubes. - Receiving a sample.
Using a microtome (an apparatus with a sharp knife that allows for the removal of very thin layers, up to 3 microns), sections are made. - Removing paraffin.
The remaining fats and paraffin are removed from the tissue layers, soaked in ethanol, and transferred to microscope glass. - Study.
Samples are exposed to different dyes to make cells, their elements and intercellular substance distinguishable. - Conclusion.
The pathohistologist (pathomorphologist) makes the final diagnosis.
In some cases, urgent histology is required. What is a biopsy in this situation - a sample of the material, immediately after its receipt, is frozen in water without preliminary testing. Further actions are similar to standard histological analysis (sections and examination under a microscope). This study takes about half an hour and is carried out directly during the operation.
Types of biopsy examination
Many people are interested in how long it takes to do a biopsy. Indeed, after a biopsy is performed, how many days later can the results be seen? Of course, I would like to have express results instantly. But this is not always possible.
Biopsy analysis - what is it? Biopsy examination is carried out using two methods:
- Histological - microscopic examination of a tissue section, which is first placed in a pharmacological solution, then in paraffin, and then the biopsy specimen is stained and sections are taken. Staining allows cell layers to be distinguished when examined under a large-scale microscope. How long does it take to prepare a biopsy if a histological examination is performed? Usually the result is obtained in 4-14 days. If an immediate response is important, the biopsy is taken immediately after removal - before the end of the operation - frozen, stained and sectioned. Such a histological examination requires more experience, and the result will be ready in 40-60 minutes.
- Cytological - the study of individual cells and their structures. The technique is used for puncture sampling of material, washings and smears, when it is not possible to remove an entire piece of the formation. It is more efficient, but it provides superficial information - it allows you to determine the benign or malignant nature of the formation, the presence of inflammatory, reactive or precancerous processes - and nothing more. How many days does the biopsy take in this case? The results will be available within 1-3 days, and often within an hour after the start of the study.
Usually, if a biopsy is prescribed, the timing of the analysis is agreed upon in advance, taking into account the workload of the laboratory and the urgency of making a diagnosis. But in general, you need to be prepared for the fact that the biopsy examination will take several days.
After the examination
Your doctor will give you specific instructions about what you will need to do after the procedure, but will usually be allowed to return to your normal diet and bathing routine when you return home. It is also recommended to drink more water during the first few days to cleanse your urinary system.
You may also be advised to continue taking antibiotics until the course is completed. If you were taking blood thinners that were stopped before the procedure, you will likely be asked to put them off for at least a few more days.
Managing side effects.
After the biopsy, you may have rectal pain for several days. It can be relieved by applying warm compresses to the area. Some men experience mild bleeding or blood spots in their stool or urine. If the amount of bleeding is small and stops after a few days, this is considered normal. Blood stains in semen are also common and may persist for several weeks after the biopsy.
You should call your doctor if you notice any moderate or heavy bleeding (more than a teaspoon at a time) from the rectum, bladder, or semen. You should also contact your doctor immediately if you experience fever or chills, significant abdominal or pelvic pain, difficulty urinating, or nonspecific symptoms such as dizziness, confusion.
Blood biopsy - what is it?
Often, before removing the biopsy, the doctor may order a blood test for a biopsy. If you tell the average person about a biopsy - what kind of procedure it is, and then ask: what does a blood test for a biopsy show, it is logical to answer that this study shows the presence of an oncological disease in the blood itself. In fact, this is not entirely correct.
Blood biopsy test: what is it and why is it often prescribed? Another name for the procedure is a biochemical blood test.
Blood biopsy - what does this procedure show? A blood biopsy examines enzymes, minerals and organic substances, and all this makes it possible to judge the state of the body, and, accordingly, to identify dysfunctions in the functioning of a variety of organs: the heart, liver, kidneys, pancreas, blood vessels and even skeletal muscles.
Taking a biopsy in this case involves taking up to 10 ml of venous blood. It is recommended to do this on an empty stomach, and not to buy or take medications several hours before the procedure.
Blood for biopsy - what is it? The key aspects of a biochemical blood test are: glucose level, bilirubin, transaminases, cholesterol, protein, creatinine, urea, amylase, various microelements. A blood biopsy is a test that is used both to determine oncological processes and to assess the general condition of the body.
Attention! If you notice an error or typo in the text, please let us know using the feedback form!
Elimination of infectious and inflammatory processes
If a man has problems with blood clotting, as well as in the presence of infectious and inflammatory processes, it is strictly prohibited to perform a prostate biopsy. This is explained by the fact that diagnostic results may be distorted or the procedure may provoke the development of complications. Therefore, until a person gets rid of inflammation and infections, doctors will not allow him to undergo the procedure.
It is possible to restore erectile function! Proven FOLK CARE ... Reviews My story spotenciey.ru
Treatment of PROSTATITIS using a new method To restore the functions of the prostate, you need every day... Website Interview with a doctor bezprostatita.ru
The problem of the small size of the dignity has been solved. The mechanism of erection has been revealed... Official website Recovery bigbigrazmer.ru
To combat infectious and inflammatory processes, complex therapy is used, which includes the following measures:
Taking antibiotics
- taking antibiotics;
- increasing the protective functions of the body;
- undergoing physiotherapeutic procedures;
- lifestyle change.
The main role in the fight against infections and inflammation is given to antibacterial drugs. The selection of a drug is carried out by the attending physician after the patient has undergone bacteriological culture to test the sensitivity of the microflora to the active ingredients of a particular drug.
The duration of treatment depends on the type of disease and its complexity. So, if the provocateur of inflammation is acute prostatitis, then therapy with antibacterial drugs takes from 10 to 14 days. In the presence of a chronic form of prostatitis, treatment is slightly more complicated and takes place over 6-8 weeks. The treatment uses several medications, the course of each of which varies from 1.5 to 2 weeks.
Prostate magnetic therapy
After getting rid of the symptoms of inflammation, a man may be prescribed a prostate massage. It is recommended to do it in order to remove pathogens from the body. A completed course of massage will help improve blood circulation, saturate cells with oxygen and nutrients, and strengthen the immune system.
In some cases, doctors prescribe patients to undergo certain physiotherapeutic procedures:
- magnetic therapy;
- ozone therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- microwave thermotherapy.
You can speed up the healing process by following a diet (excluding fatty, smoked, spicy foods from the diet) and exercising.
It is these manipulations that must be performed to undergo a prostate biopsy if the patient has inflammatory or infectious processes. After completing all stages of therapy, the man must undergo a general blood and urine test, as well as urine culture for flora.
Only after reviewing the test results will the doctor decide whether the man can be allowed to undergo a prostate biopsy.
Female oncology: cervical biopsy
Cancers specifically affecting women include cervical cancer and breast cancer. If to prevent the second type it is enough to visit a mammologist once a year and periodically feel the mammary glands (a breast biopsy may be required), then with the cervix it is more difficult - you cannot do without an examination by a specialist. The “insidiousness” of this disease is that it may have no symptoms - only visual signs.
Indications for a cervical biopsy are as follows:
- suspicious changes in its surface;
- the presence of erosion or ectopia;
- colposcopy results.
How is a biopsy taken? This procedure involves pinching or cutting off a piece of tissue from a suspicious formation. These tissues are then examined for the presence of malignant or precancerous signs.
So, a biopsy - how is it performed in this case:
- trephine biopsy - epithelium is collected from various parts of the cervix;
- conization - a cone-shaped section of the epithelium is removed with a laser beam or scalpel;
- endocervical procedure - mucus is scraped out from the cervical canal using a medical instrument - a biopsy sample.
The implementation of any of these procedures is preceded by certain preparation: a general blood test, a blood test for major infections and coagulation; taking gynecological smears, which will help to understand the health of the patient’s reproductive system; written consent to the procedure.
Many doctors even perform procedures such as cauterization of erosions only after a biopsy test has been performed. How quickly a woman’s health can be improved directly depends on how long it takes to prepare a biopsy. The most informative is colposcopy. It is this that can provide the basis for carrying out this procedure.
What are the important reasons:
- identification of iodine-negative zones on the surface of the cervix;
- the epithelium reacts to acetic acid - it becomes white.
There are also significant contraindications for this procedure: the presence of inflammatory processes in the body or poor blood clotting.
Indications for biopsy
If a tumor develops in the human body, a number of studies are carried out that make it possible to establish its exact location, size, and a biopsy is used to determine the nature of the tumor (benign or malignant). In addition, the procedure is also necessary during organ transplantation or the detection of autoimmune diseases or infections. There are many indications for a biopsy, and they all depend on the affected organ and the type of procedure. The most popular of them:
- Breast biopsy. Allows you to determine the nature of neoplasms in the breast.
- Bone tissue examination. The procedure is carried out to identify pathological changes in the bones and detect an infection affecting them. A biopsy is performed using needles that are inserted through the skin.
- Endometrial analysis. The study is carried out to identify the causes of uterine bleeding and clarify the general condition of the endometrium.
- Bone marrow biopsy. An indispensable procedure for diagnosing blood diseases - leukemia, anemia. A sample of bone tissue and red bone marrow is removed for examination.
- Biopsy to examine the kidneys, liver, thyroid gland and skin.
One type of procedure is chorionic villus biopsy. This study is carried out on a living fetus that is developing in utero. For such a biopsy there must be compelling indications, which include:
- Severe hereditary diseases that are associated with the gender of the unborn child.
- Gene mutations that are observed in one of the parents.
- The expectant mother is over 35 years old.
- Presence of children with chromosomal abnormalities in the family.
Carrying out a biopsy also has its contraindications:
- Blood clotting disorder.
- The ability to make an accurate diagnosis without a procedure.
- The patient's refusal to undergo a biopsy in writing.
- The presence of tumors that are similar to melanoma.
Chorionic villus biopsy is not performed if there is a threat of miscarriage, there is bleeding, or there is an inflammatory process in the mother’s body, accompanied by a high temperature.
Analysis during pregnancy
Is it possible to perform a similar examination of the cervix in pregnant women? Sometimes the doctor considers it necessary to do this without delaying it until the postpartum period.
Such procedures for taking material from the cervix in the early stages of pregnancy often lead to miscarriage, so they are not performed until the 12th week. In the later stages, they also stimulate labor - there is a risk of premature birth. The most acceptable period is from 13 to 28 weeks of pregnancy.
We hope that this article has covered the topic “Biopsy - what kind of analysis is it” a little, and the reader, having reached these lines, can tell what a biopsy test is, as well as how a biopsy is done, why a biopsy or blood is taken for a biopsy, and also what is a biopsy and how long does it take to test for a biopsy?
Risks and contraindications
As with other medical tests, a prostate biopsy carries potential risks and reasons why this test should not be performed.
Potential Risks
Some risks of a prostate biopsy may be more concerning for some people than others, so be sure to discuss them with your doctor.
- Difficulty urinating. Some men may have difficulty or inability to urinate after the procedure and will need a catheter until the swelling goes down (usually two to three days).
- Rectal bleeding: Sometimes rectal bleeding can be excessive and require treatment such as surgery.
- Infection. infections can occur and account for about 75 percent of hospitalizations within 30 days of prostate biopsy, making it the most common reason for hospitalization for complications. Infections appear to be less common with MRI/targeted biopsies (since fewer samples are taken), but infections associated with prostate biopsies are currently on the rise.
- With MRI/targeted biopsies, there is a rare risk of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis —a rare, sometimes fatal disease that affects the skin and organs—due to the contrast agent used (gadolinium), but the risk primarily affects men with very poor kidney function. Doctors should take this into account.
What is a biopsy
Essentially, this is the collection of biological material for further examination under a microscope. The main goal of the invasive technique is to timely detect the presence of cancer cells. Therefore, biopsy is often used in the complex diagnosis of cancer. In modern medicine, it is possible to actually obtain a biopsy from almost any internal organ, while at the same time removing the source of pathology.
Due to its pain, such laboratory analysis is performed exclusively under local anesthesia; preparatory and rehabilitation measures are required. A biopsy is an excellent opportunity to promptly diagnose a malignant neoplasm at an early stage in order to increase the patient’s chances of maintaining the viability of the affected organism.
Complications
The most common complications include infections and bleeding. You should immediately consult a doctor if the bleeding does not go away for a long time, or if it is very profuse, with clots, or an unpleasant odor.
After receiving the biopsy results, you must make an appointment with your doctor. He will not only decipher the incomprehensible words on the analysis form, but will also calm you down by prescribing the appropriate treatment. Remember, the earlier the pathology is detected, the easier it is to cope with it!
If, during a gynecological examination or hardware diagnostics, various pathological changes were identified on the vaginal surface of the cervix or in the thickness of its tissues, it is necessary to use such precise research methods as biopsy.
During this manipulation, a small volume of tissue from the patient is collected for subsequent examination under special conditions. By staining the sample with special pigments and using special markers, specialists will examine it for the presence of benign and malignant neoplasms, as well as to detect precancerous conditions.
If during a biopsy it turns out that changes in the cervix are oncological in nature, doctors and laboratory technicians establish the most accurate diagnosis using a tissue sample. Thanks to this, you can choose the most effective treatment method and select the best drugs.
Why do they take it?
A biopsy is prescribed for the timely and rapid detection of cancer cells and the pathological process accompanying their presence. Among the main advantages of this invasive technique performed in a hospital setting, doctors highlight:
- high accuracy in determining tissue cytology;
- reliable diagnosis at an early stage of pathology;
- determining the extent of the upcoming operation in cancer patients.
Painful biopsy and waiting for results
Since the collection of material is associated with damage to the patient’s tissue, albeit to a small extent, specialists use various painkillers - anesthetics. The cervix is a part of a woman’s body in which many nerve endings are intertwined, but there are no pain receptors among them. Therefore, the duration of anesthesia during biopsy and the selection of drugs to reduce its pain depend on the individual characteristics of the patient.
In addition, the choice of anesthetics and pain relief techniques depends on the scale of the intervention, that is, the specific method of collecting material. Of course, general anesthesia is considered the most effective. But this is a serious drug effect that can negatively affect the patient’s condition.
Therefore, specialists often use local anesthesia, that is, the introduction of lidocaine and other agents. Also in some cases (for example, during surgical sampling of material), spinal anesthesia is used. This is an injection into the lumbar region with which a special substance is injected that blocks pain sensitivity in the lower half of the body.
When performing a cervical biopsy, the patient needs to relax all muscles as much as possible and not experience emotional distress. This will avoid complications and pain resembling contractions.
What is the difference between histology and biopsy
This diagnostic method studies cells and their potential mutation under the influence of provoking factors. A biopsy is a mandatory component of diagnosing cancer and is necessary to take a tissue sample. This procedure is performed under general anesthesia using special medical instruments.
Histology is considered an official science that studies the structure and development of tissues of internal organs and body systems. The histologist, having received a sufficient fragment of tissue for examination, places it in an aqueous solution of formaldehyde or ethyl alcohol, and then stains the sections using special markers. There are several types of biopsy, histology is carried out in a standard sequence.
In case of prolonged inflammation or suspected oncology, it is necessary to perform a biopsy to exclude or confirm the presence of an oncological process. It is first necessary to perform a general analysis of urine and blood to identify the inflammatory process, and implement instrumental diagnostic methods (ultrasound, CT, MRI). The collection of biological material can be carried out in several informative ways, the most common and popular among them are presented below:
- Trephine biopsy. It is carried out using a thick needle, which in modern medicine is officially called a “trephine”.
- Needle biopsy. The collection of biological material is carried out by puncturing the pathogenic neoplasm using a thin needle.
- Incisional biopsy. The procedure is carried out during a full-fledged operation under local anesthesia or general anesthesia and involves the productive removal of only part of the tumor or affected organ.
- Excisional biopsy. This is a large-scale procedure, during which a complete excision of an organ or malignant tumor is performed, followed by a rehabilitation period.
- Stereotactic. This is a diagnosis carried out by preliminary scanning for the further construction of an individual scheme for the purpose of surgical intervention.
- Brush biopsy. This is the so-called “brush method”, which involves the use of a catheter with a special brush for collecting biopsy material (located at the end of the catheter, as if cutting off the biopsy material).
- Loop. Pathogenic tissues are excised using a special loop (electric or radio wave), in this way a biopsy sample is taken for further research.
- Liquid. This is an innovative technology for identifying tumor markers in liquid biopsy, blood from a vein, and lymph. The method is progressive, but very expensive, and is not carried out in all clinics.
- Transthoracic. The method is implemented with the participation of a tomograph (for more careful control) and is necessary for collecting biological fluid mainly from the lungs.
- Fine needle aspiration. With such a biopsy, the biopsy material is forcibly pumped out using a special needle to conduct exclusively cytological examination (less informative than histology).
- Radio wave. A gentle and absolutely safe technique, which is carried out using special equipment - Surgitron in a hospital setting. Does not require long-term rehabilitation.
- Preskalennaya. This biopsy is used to diagnose the lungs and consists of taking a biopsy sample from the supraclavicular lymph nodes and lipid tissues. The session is carried out with the participation of a local anesthetic.
- Open. Officially, it is a surgical procedure, and tissue collection for examination can be done from an open area. It also has a closed diagnostic form, which is more common in practice.
- Core. Soft tissue sampling is performed using a special trephine with a harpoon system.
What should the patient do after the biopsy?
After taking a fragment of skin for pathological examination, the patient will have to carefully care for the resulting wound to prevent infection and suppuration. If stitches are not applied, then the wound is covered with a sterile napkin for several days, water procedures, baths, saunas, and solariums are excluded.
In the case where the biopsy is completed by suturing, the patient will have to daily treat the wound with an antiseptic and remove the suture threads on days 7-10, which is performed by the surgeon. It is better not to take a bath until the stitches are removed, although a regular hygienic shower is possible. Baths, saunas, open reservoirs, swimming pools are prohibited until complete healing.
Usually the main question of patients after a biopsy is whether and how they can wash themselves, because no one has canceled their usual daily hygiene. On the first day after tissue collection, it is better not to wet the damaged area of skin, then depending on the situation: if the wound is dry and clean, then you can take a shower. After washing, the biopsy site should be treated with an antiseptic and covered with a bandage. It is better not to touch the skin with your hands; you should absolutely not stretch it. Complete healing will occur after one to two weeks.
If a biopsy of the skin of the face or head was performed, then it makes sense to spend a couple of days at home, avoiding going out into the open sun. In addition, damage to the skin on visible areas of the skin and, especially on the face, creates some psychological inconvenience, albeit temporary.
In the next few days after the biopsy, some complications may appear, which should be a reason to consult a doctor. These are:
- Bleeding;
- Increased swelling, pain at the biopsy site;
- The appearance of pus-like cloudy discharge;
- Violation of the general condition - increased body temperature, chills.
If there are complications, the specialist will prescribe the necessary treatment - anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, painkillers, local wound-healing drugs. Self-medication is strictly unacceptable!
A skin biopsy is performed free of charge if indicated, but if the patient himself wants to undergo the study as an additional diagnostic measure, then he can do this for a fee. A referral for a biopsy is given by a dermatologist.
Waiting for results can take from 7-10 days to several weeks. If the morphological picture is complex and ambiguous, an immunohistochemical study and additional consultations with pathomorphologists from large clinics are required - the wait will be longer. Complex biopsies can be consulted even remotely if the patient lives at a considerable distance from a diagnostic center of the required level.
The result of a biopsy helps clarify the nature of tumor growth, exclude or confirm cancer, but often this is not even the question that worries the patient and his doctor. Long-term non-healing ulcerative lesions, progressive hardening or pigmentation of the skin, vascular disorders, unexplained hair loss, lack of effect from numerous tried medications are only a small part of the reasons that cause not only physical, but also psychological suffering to their owner. In such cases, it is a biopsy that can put the final point in the diagnostic search and help determine a truly effective treatment.
How they do it
The features and duration of the procedure itself completely depend on the nature of the pathology and the location of the suspected focus of the pathology. Diagnostics must be monitored by a tomograph or ultrasound machine, and must be carried out by a competent specialist in a given direction. Below are described options for such a microscopic examination depending on the organ that was rapidly affected in the body.
In gynecology
This procedure is appropriate for extensive pathologies not only of the external genitalia, but also of the uterine cavity, its cervix, endometrium and vagina, and ovaries. Such laboratory research is especially relevant for precancerous conditions and suspected progressive oncology. The gynecologist recommends undergoing the following types of biopsy strictly for medical reasons:
- Sighting. All actions of the specialist are strictly controlled by extended hysteroscopy or colposcopy.
- Laparoscopic. More often, the technique is used to take biological material from the affected ovaries.
- Incisional. Involves careful excision of affected tissue using a classic scalpel.
- Aspiration. In this case, the biopsy can be obtained using the vacuum method using a special syringe.
- Endometrial. Carrying out a pipel biopsy is possible with the assistance of a special curette.
This procedure in gynecology is an informative diagnostic method that helps to identify a malignant neoplasm at an early stage, initiate effective treatment in a timely manner, and improve the prognosis. With progressive pregnancy, it is advisable to abandon such diagnostic methods, especially in the first and third trimesters; it is first important to study other medical contraindications.
Blood biopsy
Such laboratory testing is considered mandatory if leukemia is suspected. In addition, bone marrow tissue is collected for splenomegaly, iron deficiency anemia, and thrombocytopenia. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia or general anesthesia, performed by aspiration or trepanobiopsy. It is important to avoid medical errors, otherwise the patient may suffer significantly.
How is a biopsy performed?
Most people are afraid of the upcoming procedure because it is similar to surgery. It is important, even before the manipulation, to ask the doctor in detail how the biopsy is performed, how painful it will be and what the risks are. The described diagnostic method is considered minimally invasive and involves minimal tissue damage; recovery is very fast.
Biopsy in gynecology
Inflammatory “female” diseases, erosions and ulcers can become malignant, which requires their timely and correct identification. In gynecology, the technique in question is used to study different parts of the uterus and its cervix. The following procedure options are used:
- endometrial aspiration biopsy;
- curettage (smear);
- chromodiagnostics (Lugol's staining of the cervix and reaction assessment).
If gynecological disorders lead to hormonal imbalance and provoke mammological problems, an additional analysis of breast tumors is prescribed:
- core and trephine biopsy;
- aspiration;
- incisional and excision sampling of material.
Thyroid biopsy
Tissue collection for examination of the endocrine organ is carried out in two ways. The classic option is fine needle aspiration. Puncture is performed under ultrasound guidance and takes about 10-15 minutes. If the use of aspiration is inappropriate or uninformative, an open (excisional) biopsy is performed. This manipulation involves direct access to the thyroid gland. The extracted tissue is sent for analysis immediately.
Lymph node biopsy
Access to this organ for research is similar to the techniques used in diagnosing the thyroid gland. Fine needle aspiration is preferred; it is a quick, almost painless and very informative technique. Express analysis involves excisional manipulation. The results of an open biopsy will be known after 20-30 minutes. This is the optimal solution if a malignant tumor is suspected or if there is a need to conduct research directly during surgery.
Biopsy of internal organs
Samples of the digestive or excretory system are made using two methods - punch and puncture. A biopsy of the stomach and esophagus is performed during fibrogastroduodenoscopy. After examining the mucous membranes and identifying the affected areas, a small piece of tissue is pinched off. A biopsy of the pancreas is also performed using this technique. In other cases, percutaneous access to the test material is practiced. A biopsy of the liver, kidneys and other internal organs is performed by puncture. Tissue samples are obtained using a needle and piston syringe.
Bone marrow biopsy
In modern practice, the collection of the described material is performed either by aspiration or puncture. Some patients, who do not understand well what a biopsy is, are terrified of bone marrow manipulation. If a detailed study of the procedure technique and a description of its process does not help, sedation is performed first, the effect of which lasts another 1-2 hours after the biopsy.
Options for obtaining samples:
- Aspiration.
The syringe is inserted into the sternum or pelvic bone. The soft tissues are numbed with local anesthetic. - Trephine biopsy.
The pelvic iliac bone is pierced with a needle. This manipulation lasts about 5 minutes.
Brain biopsy
One of the most dangerous diagnostic methods, which carries a risk of damage to nerve structures. There are 3 ways to take material:
- Open
– an operation during which the surgeon has direct access to the organ. - Aspiration
– an incision is made in the scalp and a small hole is drilled into the skull bone. A needle is inserted into the resulting hole to take a sample. - Stereotactic brain puncture
is a procedure almost identical to the previous technique, but a micro-camera is additionally inserted into the hole, as during laparoscopy.
Skin biopsy
The technique is selected depending on the size and location of the tumor that needs to be diagnosed. In most cases, the definition of what a skin biopsy is involves scarification or loop sampling of tissue. The surgeon either scrapes off the desired area or cuts it out with a radio knife. This method performs a biopsy of the skin of the face, neck, and other areas with surface defects. If it is necessary to take deep-lying tissue for analysis, puncture, core procedure or aspiration is used.
Bone biopsy
Solid material is collected using two techniques; the choice of technique depends on the conditions and purposes of the study. Classical biopsy involves trepanation. The tissue column is removed by inserting a harpoon system after local anesthesia. What is a bone biopsy during surgery or if puncture is not possible - cutting or scraping. Having direct access, the doctor collects samples directly at the site of the lesion and immediately sends them for rapid analysis.
The essence of a biopsy
This study is intended to clarify a diagnosis or clarify an existing one. The accuracy of the biopsy is almost 100%. During the study, a small area is taken from any organ, depending on the location of the tumor and pathology.
If cancer is suspected, a biopsy is prescribed first. During a biopsy, biological material is taken and examined under a microscope. If there is the development of a cancerous tumor or other pathological process, then changes always begin in the tissues that simply cannot be missed under a microscope.
Preparation and stages of biopsy
Conization of the cervix
Tissue collection for examination is carried out quite quickly, from one or several areas of the cervical pharynx. Before a cervical biopsy, it is necessary to take a hygienic shower and also avoid lifting heavy objects - this can cause increased blood loss during tissue sampling.
- Initially, the doctor examines the patient using a gynecological speculum. This is necessary for a preliminary assessment of the scale of minimally invasive intervention.
- The cervix is stained with Lugol's solution, iodine or acetic acid solution. The gynecologist looks at the tissue reaction: suspicious areas will remain white and not stained. From there a piece of tissue will be taken for examination.
- A biopsy needle is inserted into the vagina, and then the doctor pinches off a piece of mucous membrane from the external pharynx. Many women are interested in whether it hurts to take a cervical biopsy? The fence is, of course, sensitive, but not critically so. In most cases, the patient only feels a pinch (or several pinch) that lasts 1 to 2 seconds. Within a few minutes after the biopsy, stinging pain may occur.
- The cervix and vagina are treated with an antiseptic solution. After 2 - 3 minutes, the woman can leave the gynecological chair and go home.
If you become familiar with how a biopsy is performed in advance, this will help to avoid unnecessary fears before this procedure, because of which women sometimes hesitate to begin treatment for polyps or ectopia.
Condition of the cervix after the procedure
Because the surgery is minimal, severe bleeding almost never occurs. In the first hours after the procedure, the pharynx swells slightly and turns red. Over the next day, the wound heals.
Bloody discharge after a cervical biopsy is not observed in most cases. Only sometimes, 2–3 hours after the intervention, women find a few brown drops of blood on their panty liner.
It is recommended to refrain from lifting heavy objects for a week - this can cause slow healing of the edges of the wound.
How to perform a biopsy using endoscopic techniques
During endoscopic collection of biological material, the doctor uses a thin and flexible tube instrument (endoscope), which has a special backlight to identify the internal structures of the body. This tube is used to surgically remove cancerous tissue.
The endoscope can be inserted into the mouth, rectum, urethra, or small incision in the skin. This research technique makes it possible to identify cancer diseases with the least trauma to the body.
Repeat biopsy
If, based on the results of the analysis of the obtained biopsy, there are no signs of cancerous degeneration of cells, then the result is considered negative. However, in some cases, a repeat biopsy is prescribed after 3-6 months. Indications:
- Intraepithelial neoplasia is the proliferation of cells in the ducts and acini of the prostate.
- High growth rates of PSA (more than 0.75 ng/mg per year). This is typical only for prostate cancer.
- Suspicion of an unsatisfactory result of radiation therapy, local relapse.
- If compactions appear during subsequent control palpations or ultrasound of the gland.
During a repeated procedure, a biopsy sample is taken not only from the peripheral, but also from the transition zone (these are two lobes on either side of the seminal tubercle just above it).
Where can I undergo the procedure, what is its cost and patient reviews?
A biopsy should be performed only in municipal medical institutions or private clinics of the appropriate profile upon the direction of the attending physician. The price depends on the organ being examined, the equipment and reagents used during the procedure. It is worth saying that in public medical institutions it can be done for free if you have a policy, but the waiting period for the biopsy procedure and results takes a very long time due to their workload. It is best to contact a private institution and perform all the manipulations for a fee, but quickly.
According to patient reviews, a biopsy is an extremely necessary procedure that helps to make a correct diagnosis in a timely manner and there is no need to be afraid of possible pain, because, if necessary, local anesthesia is performed or general anesthesia is given.
Types of diagnostic tests
Samples of pathologically altered tissues are taken for examination both from the skin and epithelium of internal organs, and from inside them. In each case, certain tools are used.
The type of biopsy prescribed to a patient is directly related to the location from which the sample will be taken:
- Puncture. The procedure is used when it is necessary to obtain biological material from abnormal lesions located in close proximity to the skin.
- Aspiration. This diagnostic technique is used to obtain tissue from internal organs.
- Trepanation. The sample is taken from the bones.
According to the method of obtaining the material
In clinical practice, histological and cytological examination of biopsy material is used to make a diagnosis. In the first case, the structure of the tissue is studied. Typically, this diagnostic method is the first to be used to find a dangerous process.
For histological examination, biological material is obtained in one of the following ways:
- Excision. For further study, during open surgery, the entire pathological structure or organ is excised if the tumor is gigantic.
- Incisional. Laboratory testing requires a part of the organ in which pathological changes are detected. Biopsy material is obtained during minimally invasive surgical interventions.
- Trephine biopsy. This method is used when examination of a dense tumor or bone tissue is required. Abnormal structures are removed from the body using a trephine, a hollow tube with pointed edges.
- Core (cutting or core biopsy of soft tissues). For manipulations, a trephine is also used, only a special type of it, equipped with a harpoon system.
- Scarification (superficial). Used to obtain pathological samples from the skin. A scalpel is used for manipulation.
- Plucked. Small pieces of biopsy material are pinched off with special forceps (punch-biopsy).
The biosubstrate intended for cytological research must be collected in completely different ways. Due to the fact that cytology studies cells, the biopsy procedure often does not involve invasive intervention in the patient’s body and is almost painless for him.
This biopsy is performed using the following technologies for obtaining biopsy material for further cytological examination:
- fine-needle biopsy (puncture) from various organs, including the spinal and bone marrow;
- obtaining a biosubstrate from the gastrointestinal tract during an endoscopic examination;
- scrapings from ulcers, wound (inflamed) and eroded surfaces;
- smears and swabs from the cervical canal, uterine cavity;
- smears-imprints from external pathological structures;
- collection of sputum, saliva, urine, blood.
Types of biopsy accuracy control
This procedure is classic, when the doctor receives biopsy samples “blindly”. This method is widely used in clinics where there is no specialized equipment to monitor the process or where the study is planned on an organ that is difficult to visualize. Such a biopsy often gives inaccurate results due to errors in taking the biopsy sample, so recently, whenever possible, a targeted biopsy examination is used, which is carried out under visual control.
There are several main varieties:
- Stereotactic. It is carried out in one of two ways: using neuronavigation or using a stereotactic frame. The first method is simpler and more convenient for both the patient and the surgeon, and the second, considered classic, has high accuracy.
- Under X-ray control. This type of examination is used to monitor pathological processes in the mammary gland and involves the use of a mammograph.
The photo shows a breast biopsy under ultrasound guidance.
- Under ultrasound control. Such a biopsy is a highly accurate and safe method of collecting biomaterial, since the insertion of the needle is controlled by the most modern ultrasound machines.
- Endoscopic. It is carried out using an endoscope equipped with a camera with a light source, and is used mainly on the hollow organs of the gastrointestinal tract.
“Cervical biopsy: indications, preparation and consequences of the procedure”
A cervical biopsy is the removal of a tissue sample from the surface of the cervix for examination to detect cancerous cells. This procedure is performed not only in cases where the gynecologist suspects cancer, but also when a woman has to undergo a procedure to remove a polyp or ectopia (erosion).
A biopsy is the most reliable method for determining the presence of a cancerous tumor. In its accuracy, it surpasses even cytology (collection of cells using scraping from an affected or suspicious area of the mucous membranes).
Without a biopsy, it is absolutely impossible to judge whether a tumor is malignant, which is why the procedure often precedes medical procedures that the gynecologist plans to carry out in the future.
Methods for collecting biological material
Depending on the location of the tumor, doctors use one or another method of taking material.
Fine needle biopsy. With this type, the material is taken using a needle, which is inserted into the pathological area.
Imprint smears are taken from the cervix if cancer is suspected.
A thick-needle biopsy involves obtaining a larger amount of tissue, for example, if cancer of the liver, prostate, or mammary glands is suspected.
Aspiration biopsy. The material is collected using an aspirator. This method allows you to obtain several tissue fragments simultaneously.
The collection of material can be carried out under scanning control, this can be X-rays, MRI or ultrasound. They allow the doctor to control the position of the needle.
A biopsy may be performed during surgery.
Collection of material during endoscopy or fibrogastroduodenoscopy. This method is often practiced when cancer of the colon, stomach, or esophagus is suspected.
Taking into account the severity of the pathology and its localization, the doctor decides on the method of collecting material for cytological examination.
Biopsy results
The removed piece of tissue is sent for microscopic examination. Usually the result is ready no earlier than after 2 - 2.5 weeks. Based on the data obtained, the doctor determines a treatment regimen for the disease that was discovered in the patient. The results of a uterine biopsy may include the following:
- The absence of pathological processes means that the mucous membranes of the external pharynx are healthy, do not require additional treatment and do not interfere with the treatment of the underlying disease.
- Benign changes - endometriosis, endocervicitis, eroded ectropion, benign polyps or cysts. This analysis result allows the patient to be treated without risking her life.
- Precancer – most often this includes cervical dysplasia, which occurs due to advanced erosion. This analysis result signals the gynecologist that the woman needs urgent conization of the external pharynx so that the tumor does not affect the entire cervical canal.
- Malignant changes - microscopic examination reveals cancer cells in the layers of the epithelium. This result means that the doctor needs to conduct a more serious examination, establish the stage of the cancer and determine a treatment regimen.
You should not interpret the cervical biopsy yourself. It is better to show the analysis to a doctor and be confident in its accurate interpretation. Menstruation after this procedure usually comes without delay, since tissue sampling does not disrupt the woman’s hormonal levels.
How is a biopsy done in a particular organ?
Patients always want to know how exactly the biopsy will be taken? All manipulations are carried out with very sharp instruments. This allows you to reduce the duration of the procedure to a minimum.
The nature of the upcoming manipulations depends on the organ on which they will be performed:
- If the surgeon has to excise an organ in which the tissue structures are compact and have a fairly uniform arrangement (pancreas, spleen, liver), sampling is done from any part, capturing the parenchyma and capsule.
- Tissues from hollow organs are taken from their walls, and all layers are necessarily captured.
- In kidneys, the cut should contain both the medulla and the cortex.
The organs that most often require a biopsy to clarify their diagnoses will be discussed below.
Biopsy in gynecology
Biopsy sampling from the female genital and reproductive organs is often required. This procedure is necessary not only to diagnose oncology, but also to find out the reasons for not carrying a child to term and to detect the preconditions that provoke uterine bleeding.
Several methods are used to perform a biopsy in gynecology:
- thick-needle puncture, with the help of which a column of pathological tissue is obtained;
- electrosurgical, using a wire loop under current;
- endocervical curettage, scraping of the cervical mucosa using a curette;
Intestinal biopsy
The main tool for obtaining the required amount of biopsy material is special rectal forceps, which are inserted into the intestine through a retroscope or anoscope. This method of studying the digestive organs is the most common. In addition to the pinch biopsy method, scarification, incisional or loop biopsy can be used. During the procedure, the patient must be admitted to the hospital.
Pancreatic biopsy
Most often, percutaneous fine-needle and thick-needle puncture biopsy is performed on this organ.
They are performed using a biopsy gun, but in some cases other biopsy technologies can be used:
- Laparoscopic allows you to take a biopsy from exactly the area of the gland from which it needs to be taken.
- Endoscopic biopsy. The biopsy sample is taken with a thin needle located in the endoscope through the duodenum.
- Intraoperative biopsy. This procedure involves taking a piece of tissue from the area of the body and tail of the gland during surgery.
Muscle biopsy
This biopsy is a fairly simple procedure that does not require complex manipulations from the doctor. Usually one of the areas of the muscle corset is biopsied: biceps (biceps muscle), quadriceps femoris or deltoid shoulder.
Muscle tissue biopsy is performed on an outpatient basis, with local anesthesia, in one of the following ways:
- fine needle puncture;
- open biopsy (an incision is made into the skin and a small, no more than 1 cm3, piece of muscle tissue is cut out).
The site for the biopsy is selected using a previously performed tomography.
Heart biopsy
Obtaining tissue for research from this organ is carried out by introducing into the chest cavity through the blood vessels a special device, a bioptome, equipped with instruments for taking a biopsy sample. The movement of this device and all manipulations are controlled by an ultrasound scanner. To perform a biopsy of the left ventricle, the biopsy is advanced through the femoral artery, and the right ventricle is advanced through the subclavian vein.
Bladder biopsy
Bladder biopsy is performed only using 2 technologies:
- Cold way. Biting off a biopsy sample with special forceps during transurethral penetration.
- TUR biopsy. The entire tumor is removed, and then a biopsy sample is taken from it.
Blood test
A biopsy of this body fluid is the same biochemical analysis familiar to any person. This study allows you to assess the functioning of internal organs, obtain information about lipid and carbohydrate metabolism and determine the body's need for microelements.
Tissue biopsy of the galaxy
Only a fine-needle biopsy is performed on the retina, orbit or vitreous body of the organ of vision. It is indicated for eye tumors that are difficult to diagnose with other types. TIAB biopsy reduces the risk of injury to the eyeball. But it can still lead to blindness. Therefore, it is prescribed only in extreme cases. When without this study, vision loss is inevitable.
Bone biopsy
Bone biopsy is used to detect infection of bone structures or the development of cancerous lesions in them. The procedure involves obtaining a biopsy sample through a needle puncture. The material is collected using a biopsy gun, which facilitates manipulation.
Oral biopsy
A biopsy of the oral mucosa is performed by oral surgeons, dentists or otolaryngologists. All manipulations are performed under local anesthesia. The instruments used for this procedure are various needles, a trephine dissector or a scalpel. The material is collected by excision of tissue from pathological areas, after which the patient is given self-absorbing sutures.
Clinics and prices
A biopsy should only be done on the recommendation of a doctor . The procedure can be carried out free of charge under the compulsory medical insurance policy (usually no more than 6 puncture points are made per referral) or at your own expense in any clinic that provides similar services. Analysis of the obtained biomaterial is performed only by institutions with their own laboratory and specialists. Clinics and prices:
- "ABC Clinic" (Moscow): material collection - 5500 rubles, analysis - 1500 rubles;
- "Euromed" (St. Petersburg): biopsy without analysis - 10,500 rubles;
- "Central Clinical Hospital" RAS (Moscow): biopsy - 8000 rubles;
- Clinic "Andromeda" (St. Petersburg): biopsy from 3 points - 1700 rubles, from 12 points - 3500 rubles, histological examination - 700 rubles;
- Research Institute of Oncology named after. Petrova (St. Petersburg, Pesochny village): histology – 8000 rubles, material collection – 2620 rubles;
- “Invitro”: comprehensive histological examination (+ immunohistochomic) – 10,990 rubles;
- “Helix”: histology of 12-16 samples – 5200 rubles, histological and immunohistochomic – 18315 rubles;
- “Hemotest”: histological examination of up to 12 samples – 4400 rubles.
When choosing an institution for a biopsy, it would be useful to find out whether it has the right to issue certificates for the tax office. On their basis, expenses can be reimbursed (order 289, Ministry of Taxes of the Russian Federation No. BG-3-04/256 dated July 25, 2001).
Diagnostic equipment, what is it?
To ensure that the biopsy is safe for humans and does not provoke the development of any complications, specialists carry out the procedure only with the help of special equipment. Currently, oncologists in most clinics use a modern disposable needle biopsy kit.
It includes the following tools:
- Needles for puncture biopsy of three types (cutting, modified, aspiration). The set includes cannula needles (pointed at one end of the tube) of various diameters.
- Disposable plastic guides (syringes) for 20 and 30 ml;
- Test tubes filled with saline and ampoules with lidocaine.
- Gel for filling the space between the ultrasound sensor and the skin.
In addition to disposable kits, biopsy guns are used to carry out this diagnostic procedure, allowing shots to be fired with a thin, sharp needle, which acquires high speed and cuts tissue at the site of the lesion. With the help of such a gun, puncture biopsy of soft tissues of various internal organs is effectively performed: liver, prostate, mammary, pancreas and thyroid glands, kidneys, etc.
In most specialized oncology clinics and specialized medical centers, ultrasound-guided puncture biopsy is performed using the latest equipment used to visualize manipulations performed on internal organs - Kretz 530 and HP SONOS-5500 ultrasound scanners.
Preparing for a breast biopsy
The procedure for collecting material does not require special preparation in a hospital setting. 2-3 days before diagnosis, you must stop taking medications that affect blood clotting and drinking alcohol. If the patient is taking any medications systemically, the attending physician must be notified.
On the day of the biopsy, you should not use cosmetics that are applied directly to the breast or armpit skin (deodorants, lotions). It is also worth taking care of your underwear: the bra should be comfortable to hold the cooling element at the puncture site, but not put too much pressure on the chest.
The main condition that determines the timing of a biopsy is the menstrual cycle. It is not recommended to collect material for research immediately before the onset of menstruation and during the period 1-4 days of the cycle. The optimal time for manipulation is 7-14 days of the cycle.
Types of biopsy
The types of biopsies can be different, they can even differ depending on the field of medicine:
- Puncture biopsy. For research, biological material is taken using a syringe or aspiration gun.
- Strokes-imprints. Such a biopsy involves applying a glass slide to the surface of the tumor to obtain some material for study.
- Excisional biopsy involves complete removal of the tumor along with surrounding tissue.
- An incisional biopsy is the removal of biological material from the tumor itself.
- Trephine biopsy. It is carried out using special needles, with their help a column of tissue is obtained from the neoplasm.
Not only are there different types of biopsies, but also methods for taking biological material for research.
results
The biopsy result (result of histological examination) will be ready in 7-10 days . Its accuracy (the diagnostic value of the procedure) depends on how correctly the biopsy specimen was taken, as well as on the qualifications of the pathologist examining it. It is he who must evaluate the malignancy of the cells of each column (the degree of their difference from normal) from 1 to 5 according to the Gleason scale.
Appearance of cells according to Gleason score (by degree of malignancy)
Adenocarcinoma (prostate cancer) on glass under a microscope
After evaluating the biopsy results, two samples of dominant cellular forms (which cells are the most abundant) are selected and their values are added. The first number is the most important, it indicates which cells are dominant.
Example of evaluation of 10 biopsy samples
Results after addition (Gleason number):
- 2-4: cells differ slightly from normal (low degree of differentiation).
- 5-7: average risk of developing cancer.
- 8-10: high probability of cancer.
Photo of the histological report
Based on the results of the Gleason biopsy, treatment tactics are chosen:
- Less than 6: a wide range of treatment options is possible. If less than 2 columns are identified, in which the degree of cell damage does not exceed half, then it is recommended to monitor the dynamics of tumor development using PSA, rectal palpation, ultrasound, and MRI.
- 6-7: there is a risk of tumor spreading to other organs. Indirect signs are the presence of cancer cells surrounded by fat, PSA more than 20 ng/ml, a Gleason score greater than 8, more than 2/3 of the columns, in which cancer cells make up 30% of the length. Removing the prostate with these results can be very dangerous. With a PSA less than 20, the risk of spread is low. Medicines, radiation therapy, and removal of the prostate are recommended.
- 8-10: aggressive form of tumor. Immediate treatment is required.
For any biopsy result, the decision on treatment is made only by the attending physician, who is responsible for it.
What diseases can be detected with a biopsy?
This study allows you to diagnose any organ. Although the main purpose of a biopsy is to establish the malignant nature of the process and precancerous conditions, it can be used to identify congenital pathologies and a large number of benign diseases of an infectious and inflammatory nature. Based on tissue samples taken from the patient for examination, the doctor will be able to accurately say which microorganisms provoked the disease, and what caused the onset of inflammation.
Cost of the procedure
The price of a cervical biopsy depends on the chosen method of taking biomaterial. You can check this with the administrator of our clinic.
Indications for cervical biopsy:
- cervical erosion
- negative smear cytology result
- detection of atypical abnormalities that were diagnosed during colposcopy (acetowhite epithelium, iodine-negative areas)
- presence of polyps, condylomas, tumor formations
- leukopathy
A biopsy is performed on days 7-13 of the menstrual cycle.
Contraindications for biopsy:
- detection of inflammatory foci during an appointment with a gynecologist that require further examination and treatment
- the beginning of the menstrual cycle
- You must inform your doctor about pregnancy in advance.
Preparing for a cervical biopsy.
Before the procedure, it is necessary to undergo a number of examinations and tests in order to reduce the risk of the occurrence and complications of infectious diseases.
Gynecologists recommend taking the following tests before the procedure:
- general blood analysis
- coagulogram (blood clotting test)
- flora smear (the ability to identify diseases of the reproductive system)
- smear for cytology
- perform a colposcopy
- tests for hidden infections (which have no external manifestations)
- tests for HIV, hepatitis, syphilis
In addition, before the procedure itself, it is recommended to avoid medications that are introduced into the vaginal cavity, the use of tampons, douching, and sexual intercourse 2 days before the procedure.
Contraindications to cervical biopsy:
- inflammatory diseases of the cervix
- pregnancy (1st and 3rd trimester)
In these cases, the biopsy will have to be postponed.
Is it possible to have a cervical biopsy during pregnancy?
Cases when a cervical biopsy is required during pregnancy occur when your attending physician notices suspicious changes in the cervical area and decides that it is impossible to wait until childbirth; a biopsy is performed during pregnancy. Before 12 weeks, a biopsy carries the risk of increasing the likelihood of miscarriage, and in the later stages it increases the likelihood of premature birth, so a cervical biopsy during pregnancy is performed in the second trimester, when the risk is lower. If detected changes in the cervix do not require prompt diagnosis, then manipulation can be postponed until the postpartum period, no earlier than 6 weeks after birth.
Results of histological and cytological examination of the material
After a needle biopsy is performed, laboratory examination of the biopsy sample takes several days.
The pathologist's response may contain the following information:
- Norm. There are no cells with abnormal changes in the studied material.
- Non-malignant changes. There are altered cellular structures, but there are no signs of malignant degeneration.
- There is an oncological lesion. The material under study contains cells with an altered shape and structure that arise during the process of malignant degeneration.
- Not enough information. The amount of biopsy material submitted for examination was not enough to determine the pathological process, so the procedure must be repeated.
Important! If, as a result of examining tissue taken from internal organs using a puncture type of minimally invasive procedure, pathological signs are discovered, you should not immediately make a terrible diagnosis. Their appearance does not always indicate the development of a serious disease.
Biopsy during colonoscopy
The most common procedure performed during a colonoscopy is a biopsy. Through a special hole-tube in the endoscope, forceps are brought to the required place, which remove a small piece of tissue. Further assessment of the state of the structure of the resulting tissue is carried out under a microscope in the laboratory.
If the altered tissue suggests an infectious origin, then a biopsy during colonoscopy can be performed in order to further cultivate a bacterium, virus, microorganism, or microscopically identify the parasite.
If a colonoscopy was prescribed for intestinal bleeding, then it can be used to determine the source of its occurrence, as well as take the necessary measures to stop it.
Today, when determining polyposis in the colon, a biopsy is a mandatory procedure for their further removal, since this is the most effective method of preventing the development of colorectal cancer.
It should be said here that each additional procedure is painless in most cases and it is not at all necessary to carry it out to determine the presence of oncology.
What is trephine biopsy: features of the method
For such research, special needles are used; they have threads on the outside. When such a needle is inserted into the tissue of a tumor or internal organ, it is screwed into them like a screw, after which the doctor sharply removes the instrument. Tissue samples remain on the thread, which are sufficient for research.
Our clinic has the most modern equipment for performing biopsies, including special guns with sets of needles. Thanks to good equipment, we can ensure not only the effectiveness of the procedures performed, but also comfort for patients, which is no less important.