FUS ablation is an operation during which myomatous nodes are removed using focused ultrasound without any tissue incisions, bloodlessly. After completion, the woman can move independently and feels well.
The essence of the procedure:
- During the preliminary examination, the location of the nodes is specified down to the millimeter.
- FUS ablation is performed on an MR machine, which is used for MRI. A beam of ultrasonic waves is focused strictly into the tumor, and it burns out without a trace.
- Upon completion of the procedure, an MRI is performed to monitor treatment.
The following fibroids are subject to FUS ablation:
- Single nodes. With multiple ones, it is difficult to predict the location and consequences of removal using ultrasound.
- With subserous and interstitial growth. The depth of their occurrence should not exceed 12 cm from the surface of the body in front and no further than 4 cm from the sacrum, otherwise the pelvic bones can be damaged.
- There should be no adhesions. If there is one, there is a risk of tissue burns (adhesions).
- The volume of an individual node that will undergo surgical intervention should not be more than 5000 cm3 according to ultrasound, CT, and MRI. Otherwise, the risk of only its partial disappearance is extremely high.
It is impossible to get rid of fibroids in a woman in this way if she is planning a pregnancy or is pregnant. The risks are too high and the prognosis is uncertain.
Contraindications for use:
- if the patient’s body weight is large and the patient’s waist circumference is more than 110 cm;
- if the patient suffers from intolerance to confined spaces;
- if a woman’s body has metal structures or a pacemaker;
- in the presence of serious diseases in the stage of decompensation.
The main advantage of FUS ablation is that it is not an operation, but a manipulation during which a woman gets rid of a tumor without incisions or anesthesia , since during the procedure she does not feel severe discomfort, but only heating in the affected areas. The advantages include the following:
- During the procedure, only the tumor is removed, the uterus itself remains intact;
- during FUS ablation there is no bleeding or threat to life;
- after removal of fibroids, no traces remain on the skin;
- FUS ablation can be performed on an outpatient basis. The rehabilitation period is much shorter than after standard operations.
Standard list of examinations before the procedure:
- General laboratory tests of blood and urine for coagulation, viral infections.
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs and CT, MRI at the discretion of the doctor.
- Curettage of the uterine cavity, if necessary, cervical biopsy, hysteroscopic examination.
- Examination by a therapist and, if necessary, specialists.
- Blood testing for tumor markers to exclude malignant diseases.
Uterine fibroids during MRI examination
The procedure generally takes about 180 minutes , sometimes it can take up to 6 hours or more. All this time, the patient remains in the magnetic resonance chamber in a prone position. A nurse is located next to the device to monitor the situation and provide first aid if necessary.
Stages of implementation:
- To ensure timely emptying of the bladder during the procedure, a catheter is placed.
- After the woman is laid on the table, it is forbidden to move anything that is below the waist. For example, you can make any movements with your hands. There is a panic button nearby to stop the procedure if necessary. For example, if it became bad, very painful, etc.
- A specialist at the computer directs the beams to the required point. It heats up the tissues for 20-30 seconds, after which the effect stops. Then everything is repeated until the formation is completely removed. At the same time, an MRI is performed to ensure accuracy of actions.
- At the end of the procedure, a contrast agent is injected into the vein and an MRI assessment of the result is performed. After this, the woman is transferred to a ward for observation.
FUS ablation of uterine fibroids
After ablation, it is necessary to monitor the effectiveness of treatment after 3, 6 and 12 months. The examination includes an MRI with the introduction of contrast, as well as a thorough ultrasound using expert-class devices.
FUS ablation is not normally accompanied by severe pain or discomfort. During the procedure, women feel:
- slight burning, heating in the lower abdomen or on the skin;
- mild nagging pain comparable to menstrual pain.
The occurrence of severe pain, increased burning or other suspicious sensations, as well as shooting, stabbing pains are indications for stopping the procedure and pressing the panic button.
Possible complications after surgery:
- tissue burns (occur due to adhesions between organs);
- injury to significant nerve endings (if the node selection criteria are not met);
- subsequent growth of tumor foci if the fibroid is not completely removed;
- uterine rupture along a scar during pregnancy. Women who want to undergo fibroid ablation are told that scars after manipulation have not been studied, so there is a risk of their failure as the myometrium grows during pregnancy.
Inconsistency of the uterine scar according to ultrasound data
The cost of FUS ablation of fibroids is from 50 thousand to 120 thousand rubles. There are programs and indications when the price can be reduced for a certain category of women.
Read more in our article about FUS ablation of uterine fibroids.
Features of FUS ablation
This is an operation during which myomatous nodes are removed using focused ultrasound without any tissue incisions, bloodless. After this operation, the woman can move independently and feels well.
Principle of FUS ablation
In general, the essence of the procedure can be described as follows:
- During the preliminary examination, the location of the nodes is specified down to the millimeter;
- FUS ablation of uterine fibroids is performed on an MR machine, which is used for MRI. A beam of ultrasonic waves is focused strictly into the tumor, and it burns out without a trace;
- Upon completion of the procedure, an MRI is performed to monitor treatment.
We recommend reading about the causes of large fibroids. From the article you will learn about the classification of fibroids, symptoms of large fibroids, possible complications, and treatment options. And here is more information about the signs and treatment of cervical fibroids.
Characteristics and description of the method
In the structure of gynecological diseases, uterine fibroids occupy one of the first places. They are the most common benign formations and, according to various sources, are diagnosed in 25-45% of women of reproductive age. When conducting random studies, myomatous nodes are detected on average in 70% of women.
Relatively recently, the main methods in their treatment were hormonal therapy, surgical myomectomy (removal of the node) and hysterectomy (amputation or extirpation of the uterus). However, the results of treatment with the first two methods are characterized by a high frequency of disease relapses, and hysterectomy is characterized by hormonal disorders and vegetative-vascular disorders.
In recent decades, new treatment methods have emerged - hysteroscopic resection of submucosal (submucosal) nodes, laparoscopic or temporary transvaginal uterine artery embolization (UAE), laser or cryodestruction of nodes. However, there is no universal method that can be applied to all patients. All these techniques are more or less invasive. The only non-invasive technology is fuse MRI ablation of uterine fibroids.
Physical basis and mechanisms of action
The term "ablation" means the destruction and partial removal of biological tissue. The general physical meaning of FUS ablation is the isolated thermal effect of focused ultrasound waves on areas of the organ, their evaporation and destruction. From conventional diagnostic waves used in ultrasound examination, therapeutic ultrasound waves differ in their lower frequency (on average 1 MHz) and higher power, amounting to 50-300 W.
It is assumed that the mechanism of influence of focused ultrasound on fibroids is:
- direct temperature effects resulting from the release of ultrasonic wave energy when meeting an obstacle; heating biological tissues to 55-60° for one second leads to their dehydration, denaturation (precipitation) of proteins, damage to vascular tissues and destruction of collagen structures;
- an indirect effect on the tumor, which consists of changing local blood flow and disrupting the nutrition of its tissues.
The use of ultrasonic waves of sufficiently high energy power for 10 seconds causes point necrosis (necrosis) of the tissue. The ablation zone, formed under the influence of one focused pulse, has a cylindrical shape. Its diameter next to the emitter is 2 mm, length is 4 mm, and at the greatest depth (15 cm) the minimum dimensions of the necrotic “cylinder” are 2 and 8 mm, the maximum are 10 and 20 mm, respectively.
Treatment of a benign tumor, in particular fibroids, does not require the destruction of every cell. It is enough to carry out coagulation of organ tissue in individual areas, usually at 30-50 points, which allows you to completely stop uterine bleeding and get rid of the symptoms of compression of the pelvic organs by a tumor.
As in the process of diagnostic ultrasound, ultrasound waves during FUS ablation penetrate tissue without damaging it. However, focusing the rays and duration of exposure for 1-30 seconds leads to heating of the tissue to 55-90o. The area of thermal coagulation is 0.6 mm in diameter and 2 cm in tumor depth and does not extend to adjacent areas. This effect is carried out repeatedly until the destructive process covers the entire planned volume of the area to be treated.
The highest selectivity, effectiveness and safety of FUS ablation in the treatment of uterine fibroids is explained by several factors:
- a significantly higher content of matrix (extracellular, connective tissue structures) in the tissue of most myomatous nodes, compared to neighboring tissues, in particular, the myometrium surrounding the tumor; the intercellular matrix has the properties of delay and high absorption of the energy of ultrasonic waves, and the muscle cells of the tumor are affected for the second time - as a result of heating the matrix;
- difference in blood perfusion (passage) in the tumor and in normal myometrium;
- location of the vascular network along the peripheral parts of the fibroid.
These properties explain the practical impossibility of causing damage to unchanged vessels and the muscular lining of the uterus, in which the fibroids are located. The device that generates waves allows you to configure focus parameters from small sizes (0.8 mm in diameter and 1 cm in length) to large ones (0.7 mm in diameter and up to 4.5 cm in length). In addition, the selectivity and effectiveness of the procedure is ensured by determining the exact location and volume of the tumor, and the ability to isolate impact segments in it using MRI (magnetic resonance imaging).
Cure of a myomatous node with a diameter of up to 2 cm can be achieved after 1-3 influences (sonications) during one procedure, and uterine fibroids measuring about 20 weeks - after 100 sonications. The duration of the procedure is on average 2.5-5 hours.
At the same time, the effect of FUS ablation is directly dependent on the structure of the fibroid, that is, on its magnetic resonance properties assessed in relation to the muscular layer of the uterus. Depending on this, tumors are divided into:
- hypointense, or “dark” - the histological structure corresponds to a simple myomatous node without the presence of edema of the connective tissue (stroma); they use low energy ultrasonic waves and a small number of impacts during one procedure (no more than 80);
- isointense, or “gray”, in which stromal edema is determined; their treatment, as a rule, takes place in two stages - “drying” and direct treatment;
- hyperintense, or “white”, therapy for which is usually ineffective, since they either do not absorb electromagnetic waves, or the degree of absorption of the latter is very low.
Formations with a heterogeneous structure, a large number of septa, zones of insufficient perfusion inside the node and the presence of calcifications are also difficult to treat with FUS therapy. The latter not only reflect the rays, but are capable of redistributing their energy, which can cause damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
Advantages of diagnostics and monitoring using MRI
At the initial stages of using the FUS ablation technique, fluoroscopy, ultrasound, and computed tomography were used. However, they did not allow constant dynamic control over the degree of temperature heating, which on average should be 60° and not exceed 100°.
If these conditions are not met, boiling of the interstitial (intercellular) fluid may occur with vaporization and the formation of gas bubbles, leading to damage and rupture of tissue bordering the ablation zone. In addition to constant thermometric monitoring, high-quality visualization of the tumor itself and precise determination of its location are also necessary.
It is the magnetic resonance imaging scanner, which is part of the hardware system for performing FUS ablation, that allows:
- pre-divide the pathological formation into conventional segments (segments);
- plan the duration and power of the impact;
- accurately bring the focus of high-power ultrasonic waves (up to 300 W) to the point of impact;
- selectively heat tissue to a high temperature without increasing it in adjacent healthy myometrial structures.
The degree of necrosis and volume of tissue ablated is assessed in real time using magnetic resonance temperature mapping. At the same time, the heterogeneity of the fibroid itself in many cases becomes an obstacle in calculating the required temperature at target points.
Thus, MRI is intended for:
- high-precision spatial planning of points and geometric parameters of each sonication (impact);
- accuracy of focusing of ultrasonic waves;
- control of each sonication individually and the entire procedure as a whole in real time;
- adequate assessment of the volume of destroyed tissue, for which a contrast solution based on gadolinium preparations is additionally introduced.
Evaluation of results
According to data from different authors, the results of treatment with FUS ablation are ambiguous. For example, some authors note an improvement in symptoms after the procedure in a period of six months to 1 year in 50% of patients, others in 79%, and some in 89% and even 92%.
The maximum reduction in the severity of symptoms of the disease was observed during the first 3 months after the procedure. At the same time, the estimate of tumor volume reduction according to different authors ranges from 13.5% to 48.7% of the initial volume.
The attitude towards the influence of this technology on fertility and pregnancy is also ambiguous, due to the insufficient number of observations. There are several separate descriptions of the successful course of pregnancy and childbirth. Despite the contraindications for women planning pregnancy, most researchers believe that FUS therapy helps restore female reproductive function.
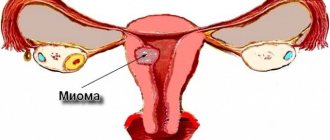
Which uterine fibroids can be removed?
Not all fibroids are subject to FUS ablation due to the peculiarities of the ultrasonic effect of this frequency on tissue. On the eve of the procedure, a thorough examination of the woman is carried out to confirm that her nodes can really be removed in this way. The following fibroids are subject to FUS ablation:
- It is desirable that these are single nodes, not multiple. In the latter case, it is difficult to predict the location and consequences of removal using ultrasound.
- Nodes should only have subserous and interstitial growth. The depth of their occurrence should not exceed 12 cm from the surface of the body in front and no further than 4 cm from the sacrum. If these rules are violated, damage to the pelvic bones may occur.
- There should be no adhesive process, that is, if any gynecological operations have been previously performed, it is dangerous to perform FUS ablation due to the risk of tissue burns (adhesions).
- The volume of an individual node that will undergo surgical intervention should not be more than 5000 cm3 according to ultrasound, CT, and MRI. Otherwise, the risk of only its partial disappearance is extremely high.
It is impossible to get rid of fibroids in a woman in this way if she is planning a pregnancy, or especially if she is pregnant. Cases of successful pregnancy have been described, but most researchers are inclined to believe that the risks are too high and the prognosis is ambiguous.
When is it possible and why not to perform FUS-MRI?
Uterine fibroids are one of the most common benign neoplasias in women of reproductive age. It provokes not only infertility, but also intense pain, bleeding, and dysfunction of the pelvic organs when large in size.
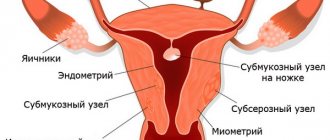
types of uterine fibroids
Myomatous nodes can be multiple, located both inside the myometrium and under the serous or mucous membrane. Subserous neoplasms may have a thin stalk, the torsion of which is fraught with necrosis of the node and the need for urgent surgical treatment. The volume and location of nodes can become a limiting factor for FUS ablation, so a thorough examination is required before treatment.
The reason for FUS ablation of fibroids can be either a single tumor node in the uterine body or multiple fibroids. In addition, it is indicated for:
- Combination of tumor with endometriosis;
- Heavy uterine bleeding due to fibroids;
- Pain syndrome, signs of compression of other organs.
The size of nodes for ultrasound ablation should not exceed 15 cm, and their number should not exceed 5 . In this way, it is possible to remove submucosal and intramural nodes, as well as those that grow from the muscular layer under the serous membrane of the organ.
FUS ablation of fibroids is relatively safe, but there are certain contraindications to it. So, it is not carried out when:
- Malignant neoplasms of the pelvic organs;
- Myomatous nodes growing on a thin stalk under the serous membrane;
- Volumetric processes in the ovaries;
- Strong bending of the uterus backwards;
- Endometrial hyperplasia (requires preliminary treatment);
- Infertility;
- Myoma size is less than 2 cm;
- The location of the nodes is closer than 4 cm from the sacrum and 10 cm from the anterior wall of the abdomen;
- Significant adhesions in the pelvic area;
- Pregnancy;
- The presence of acute or aggravated chronic inflammation of the genital organs;
- Decompensated somatic pathology - liver disease, kidney disease, heart failure, heart rhythm disorders;
- Body weight from 110 kg and waist circumference over 110 cm (obesity 2-3 degrees);
- Claustrophobia;
- The presence of metal prostheses inside the patient’s body;
- Implanted pacemaker;
- The presence of large, rough scar changes on the anterior surface of the abdomen, implanted polymer meshes;
- Previous plastic interventions (liposuction, abdominoplasty, etc.), endovascular embolization of tumor vessels;
- Installed intrauterine contraceptives.
Contraindications for use
Ultrasound ablation of fibroids is effective and safe only in cases where all the pros and cons are weighed, and the woman is carefully examined to identify contraindications to the procedure.
The method cannot be used in the following situations:
- if the patient’s body weight is large and the patient’s waist circumference is more than 110 cm. This is a limitation for carrying out in an MR installation;
- if the patient suffers from intolerance to confined spaces, which is a prerequisite for an MRI;
- if a woman’s body has metal structures or a pacemaker. The strong magnetic field of MRI will lead to complications in such cases;
- in the presence of serious diseases in the stage of decompensation, it is necessary to decide on the appropriateness of the treatment.
The presence of multiple subserous nodes on the pedicle is a contraindication to FUS ablation
Where and by whom is it carried out?
As a rule, the procedure for ultrasound treatment of fibroids is considered quite expensive, and that is why it is very often unavailable in budgetary and government institutions due to the lack of a magnetic resonance imaging scanner. To use this particular treatment method, a woman should go to a private clinic or medical center that has the necessary equipment within its walls.
Fusion ablation is performed by a qualified gynecologist under the strict supervision of a specialist working with MRI.
The procedure has been mastered and used by numerous clinics with modern equipment that provide medical services to the population. However, FUS ablation remains a rather expensive method, and not everyone is able to afford this method of treatment.
To perform FUS ablation, a woman goes to one of the private medical clinics, where there are experienced specialists and equipment to carry out the procedure. The need for hospitalization is determined individually, taking into account the nature of the fibroids and for a period of no more than two days. If the condition of the tumor does not pose a threat to health, then hospital stay after treatment is not required.
Advantages of ultrasound ablation of fibroids
The main advantage of FUS ablation is that it is, in fact, not an operation, but a manipulation during which a woman gets rid of a tumor. There is no need to make incisions or perform anesthesia, since during the procedure the woman does not feel severe discomfort, but only warming up in the affected areas. The advantages also include the following:
- During the procedure, only the tumor is removed, the uterus itself remains intact. Theoretically, a woman can carry a healthy baby, but with certain risks, of course.
- During FUS ablation there is no bleeding or threat to the woman’s life.
- After removing fibroids in this way, there are no marks left on the skin, scars, etc.
- FUS ablation can be performed on an outpatient basis. But most often, doctors prefer to observe the woman for several days. In any case, the rehabilitation period is much shorter than after standard operations.
Recovery period after surgery to remove uterine fibroids
After laparoscopic operations, 3 incisions 5-10 mm long remain on the skin of the abdomen. From the first day, patients begin to get out of bed and take liquid food. Discharge from the hospital occurs on the 2-3rd day.
After laparoscopic myomectomy (organ-conserving surgery), as a rule, light hormonal therapy is prescribed for 3-6 months to optimize reparative processes in the uterus. Dynamic observation by a gynecologist is necessary - examination, ultrasound after 1, 3 and 6 months. Pregnancy is possible after 6-8 months. It is advisable to first perform hysterosalpingography (x-ray assessment of the patency of the fallopian tubes and the condition of the uterine cavity). Depending on the size of the suture on the uterus, childbirth is possible either through the natural birth canal or by caesarean section.
After radical laparoscopic operations on the uterus, complete restoration of ability to work is largely due to the presence of concomitant pathology (hypertension, diabetes mellitus, obesity), as well as the severity of anemia before surgery. Typically, the recovery period corresponds to 12-21 days after surgery.
Sexual activity is possible about a month after the operation. If the patient does not consider it necessary to inform her husband about the extent of the operation undergone, then he will not be able to determine the degree of anatomical changes in the woman’s body.
Interview with Prof. Puchkov on Medical Channel 1 on the topic: “Prevention and treatment of adhesive disease”
The absence of a uterus in itself does not cause disharmony in the sexual life of spouses and does not cause a decrease in libido and sexual satisfaction in a woman. The only manifestation of the absence of a uterus will be the absence of menstruation and the possibility of becoming pregnant. Removal of the uterus for fibroids does not affect the approach and severity of the symptoms of menopause, since the uterus does not produce sex hormones, but is the target organ for them.
Examination before the procedure
The standard list of examinations includes the following:
- General laboratory tests of blood and urine for coagulation, viral infections, HIV, hepatitis, and syphilis.
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs and CT, MRI at the discretion of the doctor.
- Curettage of the uterine cavity, if necessary, cervical biopsy, hysteroscopic examination.
- Examination by a general practitioner and, if necessary, by specialized specialists.
- Blood testing for tumor markers to exclude malignant diseases.
Ultrasound of uterine fibroids
In each individual case, the list can be expanded at the discretion of the attending physician.
Main advantages and differences from traditional surgery
Laparoscopy is an alternative method for removing a uterine mass. Unlike open surgery, this procedure is more gentle, pain is less pronounced, the recovery period is much shorter, the patient’s hospitalization time in the hospital is reduced, and the quality of life improves. The effectiveness of the technique is not inferior to the results of standard methods.
The most important thing, especially for young and middle-aged women, is the best cosmetic effect. Scars after surgery are small, thin, and therefore less noticeable.
Laparoscopy requires specialized equipment, training and experience of doctors.
How does FUS ablation work?
The procedure generally takes about 180 minutes, sometimes it can take up to 6 hours or more. All this time, the patient remains in the magnetic resonance chamber in a prone position. There is a nurse next to the device to monitor the situation and provide first aid if necessary.
The stages of the operation are as follows:
- Due to the length of the procedure, it is necessary to empty the bladder in a timely manner, so a catheter is installed.
- After the woman is laid on the table, it is forbidden to move parts of the body that are below the waist. For example, you can make any movements with your hands.
- There is a panic button nearby to stop the procedure if necessary. For example, if it became bad, very painful, etc.
- A specialist at the computer directs the beams to the required point. It heats up the tissues for 20-30 seconds, after which the effect stops. Then everything is repeated until the formation is completely removed. In parallel, magnetic resonance imaging is performed to ensure accuracy of actions.
- At the end of the procedure, a contrast agent is injected into the vein and an MRI is performed to track how successfully everything went. After this, the woman is transferred to the ward for observation.
After ablation, it is necessary to monitor the effectiveness of treatment after 3, and then 6 and 12 months. The examination includes an MRI with the introduction of contrast to enhance tissue visualization, as well as a thorough ultrasound using expert-class machines.
Why us
Over many years of practice, doctors at the hospital’s gynecology and obstetrics department have only positive reviews from patients. By choosing us, you will receive the following benefits from our department:
- The doctors are constantly practicing gynecological surgeons, among whom are doctors of the highest qualification category, professors, holders of doctoral degrees, and have extensive experience in performing endoscopic, combined and vaginal operations.
- Safety - laparoscopic operations minimize the risks of bleeding, adhesions and other postoperative and intraoperative complications.
- Fast recovery - the time required to return to normal life and work is halved compared to abdominal surgery.
- Careful treatment of tissues - our surgeons treat healthy tissues sparingly, which ensures their rapid recovery and healing.
- Comprehensiveness - in addition to operations, the hospital offers programs for rapid preoperative examination and observation during the recovery period.
Hundreds of women who underwent laparoscopy in the department of gynecology and obstetrics have maintained their women's health and returned to a full life. Make an appointment with a gynecologist at the Yauza Clinical Hospital by calling the phone number listed on the website, using the feedback or appointment services.
How does a woman feel?
FUS ablation is not normally accompanied by severe pain or discomfort, so the procedure does not require anesthesia. Women often note the following:
- slight burning, heating in the lower abdomen or on the skin;
- mild nagging pain comparable to menstrual pain.
Expert opinion
Daria Shirochina (obstetrician-gynecologist)
The occurrence of severe pain, increased burning or other suspicious sensations, as well as shooting, stabbing pains are an indication to stop the procedure and press the panic button.
Complications after surgery
Possible complications include the following:
- Tissue burns. Usually occur during adhesions between organs. Treatment is different in each case.
- Injury to significant nerve endings . It is observed if the criteria for selecting nodes are not met when they are located too close to large nerve trunks, for example, the sciatic nerve.
- Subsequent growth of tumor foci. If the fibroid is not completely removed, its growth will soon resume; as a result, FUS ablation will not be a radical and ineffective operation.
- Uterine rupture along a scar during pregnancy . Women who want to undergo fibroid ablation are told that scars after manipulation have not been studied, so there is a risk of their failure as the myometrium grows during pregnancy.
Preparation
The most important preparation procedure is considered to be a thorough diagnostic examination, according to the results of which a medical professional will be able to determine the number of myomatous nodes, the diameter of the tumor formation, its nature and structure. In addition, you should make sure that the woman is not pregnant and that cancer is not progressing in her body.
Before the ultrasonic manipulation itself, you should avoid eating foods that cause gas formation. It is also necessary to perform hair removal in the peritoneal area to improve contact with radiation.
Before the procedure, it is necessary to undergo preoperative preparation, on which the effectiveness of the result depends. A thorough examination is carried out to determine the exact location of the fibroid, its nature, size and number of nodes. The exact distance from the tumor to the sacrum must be measured, since if the fibroid is located too close (less than four centimeters), the sciatic nerves can be damaged during treatment.
The method is not used if the fibroid is deepened from the abdominal wall by more than 10 cm and if its size exceeds 500 cm3.
On the day of the procedure, you can eat and drink, however, it is better to abstain from foods that increase gas formation. Routine tests and hardware diagnostics are required. The treatment area is also prepared, for which the skin is cleared of vegetation, if any, to prevent burns.
Other diseases that can be treated with this method
Initially, FUS ablation was invented and used to remove tumors that are difficult to approach with other types of interventions or have other limitations for major operations. Most often in oncology, FUS ablation is used for tumors in the following organs:
- bones (most often these are metastases);
- liver;
- brain and some others.
FUS ablation of the brain
Research on the possibilities of ultrasound treatment is still being carried out.
Contraindications
Even such a “miraculous” procedure as FUS ablation has specific contraindications, so it may not be performed on all patients.
This method of treating fibroids is not used:
- If the fibroid formation grows on a stalk;
- If there are more than 5 nodes;
- If the tumor area is too large;
- If the fibroid is intramural in nature (forms deep);
- If the patient weighs more than 110 kg and waist circumference is more than 110 cm;
- In the presence of adhesions in the pelvic area;
- History of abdominoplasty, cardiovascular problems;
- If an intrauterine device, pacemaker, metal or magnetic implants are installed;
- If you have claustrophobia or panic attacks;
- During pregnancy;
- For small fibroids (less than 1.5 cm).
Price of FUS ablation of uterine fibroids
The cost of FUS ablation of fibroids largely depends on the area and location (medical institution) of the procedure. In general, the price varies from 50 thousand to 120 thousand rubles. There are programs and indications when the cost of the service can be reduced for a certain category of women.
We recommend reading about why a coil is needed for fibroids. From the article you will learn about the types of IUDs, the effect of Mirena on fibroids, the therapeutic effect and the disadvantages of using an IUD for fibroids. And here is more information about whether uterine fibroids can develop into cancer.
Ultrasound ablation of fibroids is one of the promising options for removing nodes. Research in this area is ongoing. The procedure has a number of advantages, which include safety, low complication rates, bloodless surgery, and low recurrence rates when the nodes are completely removed. However, not all nodes can be removed this way, but only those with a certain location, size, and only if the woman is not planning a pregnancy.
average cost
Today, the average price of this unique and effective procedure remains quite high and ranges from 45 to 115 thousand rubles. The final cost determination depends on many factors, such as the area to be treated, the extent of the damage, the status of the hospital and the qualifications of the medical staff.
Despite the high price, the procedure is very popular among patients with fibroids, as it is a very effective alternative to surgical removal of fibroid nodes. Moreover, it is considered less traumatic, does not use incisions, does not use anesthesia in the form of anesthesia, and does not require a long recovery period. Based on all the positive aspects, FUS ablation is becoming increasingly popular.
Useful video
Watch this video about the method of performing FUS ablation of fibroids:
Similar articles
- Abdominal surgery for uterine fibroids and postoperative...
In some cases, abdominal surgery for uterine fibroids is necessary, the postoperative period after which depends on the type of intervention performed. Read more - Large fibroids: subserous, multiple...
The reason for the appearance of large fibroids is hormonal disorders. It can be subserous, submycotic. Multiple myomatous nodes are also detected. Treatment without surgery is almost impossible. Removal will not only help remove the node, but also minimize risks during pregnancy and childbirth. Read more
- Cervical fibroids: submucous, subserous...
Depending on the type, cervical fibroids can be submucous or subserous. The permissible size at which surgery can be avoided is a maximum of 6 cm. Symptoms up to 3 cm are imperceptible, pregnancy is almost impossible. Traditional methods can only be used in combination with hormonal treatment. Sometimes a hysterectomy is recommended. Read more
- Why do you need a spiral for fibroids?
Sometimes it is difficult to understand why coiling is needed for fibroids. The answer is simple - it is not only a means of contraception, but also a source of hormones, thanks to which you can relieve the unpleasant manifestations of nodes. The Mirena spiral is recognized as one of the best. Read more
Preparation for the procedure
Before performing FUS ablation, the patient undergoes a thorough examination, during which the number of fibroid nodes, their location, structure and size are determined. A complete gynecological examination is necessary. A physician's opinion may be required to confirm that women do not have severe chronic diseases.
An important point in diagnosis is determining the distance from the tumor to the sacrum. If the fibroid is located too close to the latter (less than 4 cm), then the sciatic nerves may be damaged during manipulation.
The attending physician prescribes a number of tests, including pregnancy tests and tumor markers. The patient undergoes ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging of organs located in the pelvis. A biopsy for uterine fibroids is performed through the anterior abdominal wall.
There are no restrictions regarding food and drink on the eve of FUS ablation. It is not recommended to eat heavy foods that cause gas. The hair on the abdomen should be shaved. This ensures better contact with the gel filling the pillow on which the patient lies.
Before being placed in the MRI chamber, the woman is given a sedative injection and a catheter is inserted into the bladder to drain urine. Prolonged stay in a stationary state leads to a slowdown in blood circulation in the lower extremities and the occurrence of venous stagnation. To reduce the risk of blood clots, you need to tighten your shins with an elastic bandage or use compression stockings.