Many people use alcohol, as they put it, “to warm up.” Indeed, under the influence of alcohol, blood vessels dilate, and a pleasant warmth spreads throughout the body. But, having warmed up quickly, you can freeze just as quickly, so you need to be careful with alcohol, especially in the open air in winter.
When drinking large amounts of alcohol, you may encounter another problem - dehydration, which is accompanied by headaches, nausea and weakness. To understand that you or your loved ones are suffering from alcoholism, you need to know the causes of its occurrence, types and stages of the disease.
Alcoholism refers to the physical and psychological craving for alcoholic beverages. Alcoholics drink in order to achieve a pleasant and relaxed state - intoxication. The effect of alcohol on the body depends on the characteristics of a person - his gender, weight, stage of alcoholism and, of course, on the strength and dose of alcoholic beverages consumed. Exceeding the normal dose leads to loss of coordination, memory loss and unpleasant physical sensations.
Prices for Ultramed clinic services
Types of alcoholism
From the point of view of doctors, an alcoholic is not the usual man with a fume who can barely stand on his feet. Anyone can suffer from a drinking addiction, regardless of gender, age or income level. If a person constantly drinks alcohol and cannot imagine his life without it, this type of alcoholism is called chronic. Acute alcoholism means severe poisoning with alcoholic beverages in the event of a single use. As a rule, acute intoxication is experienced by light drinkers who accidentally “had too much” during a feast.
Middle stage of the disease
The second stage of alcoholism is characterized by the same symptoms as the first. Only the manifestations become more vivid. When stage 2 begins, a person begins to realize that problems still exist, and it is necessary to get rid of it. But in most cases, the patient does not give up alcohol, but continues to drink it in large quantities. How to determine the stage of alcoholism at the second stage? The patient begins to show active performance while intoxicated, which is not typical for him in a sober state.
The second stage of alcoholism is determined by the amount of alcohol consumed. If the previous stage was characterized by a dose 3-4 times higher than normal, then at the next stage the patient takes approximately 5-10 times more than is typical for the body in a normal state. Intoxication becomes a common state, and a period of “pseudo-binge” begins. Strong drink is present in everyday life every day. At this stage of alcoholism, a sober state can only be observed if it is necessary to complete an important job or task. Sleeping without a “dose” is also not possible for the patient.
The signs become more and more pronounced. The patient feels constant memory lapses and an inadequate state appears. At this stage of alcohol addiction, not only psychological, but also physiological addiction begins. The patient cannot control the amount of drink, a hangover appears, as the body feels physical and moral exhaustion. In the morning the condition is bad, severe headaches occur. At this stage of alcoholism, severe poisoning can occur.
Chronic alcoholism
Regular consumption of alcoholic beverages begins unnoticed, but soon very quickly drags a person on. Almost always, chronic alcoholism is not a secret to others, since the alcoholic does not hide it and constantly comes up with reasons for drinking. The end of the work week, the payment of a salary, a meeting with an old friend - all this is an excuse to get drunk again. The dependence of chronic alcoholics is psychological in nature, therefore it must be treated accordingly, protecting the person from their usual lifestyle.
Chronic alcoholism can be recognized by the following signs:
- The appearance of a hangover syndrome;
- Outbursts of aggression and loss of self-control;
- The appearance of mental disorders;
- Increasing the volume of alcohol consumed.
A hangover, the most well-known symptom of chronic alcoholism, reminds you of itself with a rapid heartbeat, increased sweating and low mood.
Symptoms of the third stage
The third stage of alcoholism can lead to death from:
- alcoholic delirium;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- liver and kidney diseases.
Before this, a person undergoes physical, mental, and social degradation. The character of the patient changes - cynicism, aggressiveness, cruelty, anger become the “framework” of the addict’s personality. It is difficult for close people and acquaintances to recognize him - it’s as if the person has been replaced.
The severity of withdrawal syndrome in the third stage of alcoholism is more severe. Reduced tolerance to alcohol leads to rapid intoxication from small doses, and true binges appear - daily continuous drinking of alcohol. Loss of appetite and dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract lead to weight loss.
The brain, kidneys, liver, and heart undergo serious changes. There is a loss of vital interests, intoxication ceases to give the expected sensations. The moral side of the individual suffers no less.
Alcoholism can be cured!
We know how to do it! Sign up for a consultation:
The intellectual and emotional spheres undergo the following changes:
- decreased intelligence, deterioration of thinking, primitiveness;
- misunderstanding of humor;
- refusal of intellectual stress, irritation;
- severe irritability, conflict;
- touchiness, tearfulness;
- stubbornness, selfishness;
- loss of interests.
The deterioration of the financial situation inevitably leads to the replacement of alcohol with a surrogate. A person uses it and is instantly intoxicated and loses control over himself.
The last stage of alcoholism has an unfavorable prognosis - a high probability of death, exhaustion of organs and systems, severe depression, and the possibility of suicide.
It is important to know what stages of alcoholism your loved one has gone through in order to prevent something irreparable.
Methods for treating alcohol addiction
Since chronic alcoholism appears due to various reasons, methods of its treatment are also divided into several groups:
- Treatment with medicines and drugs;
- Psychotherapy;
- Social rehabilitation;
- Detoxification;
- As well as complex methods that include elements of the listed groups.
The first group of methods is aimed at eliminating the physiological causes of alcoholism. A drug that is incompatible with alcohol is injected into the patient’s body. If a person drinks a little during treatment, he will experience severe poisoning. The fear of repeating the same sensations makes a person give up alcohol. Since a severe overdose of alcohol can lead to serious consequences, including death, treatment with such methods is carried out only with the consent of the patient.
The work of psychotherapists is to consolidate in the patient’s mind a negative attitude towards drinking, and the awareness of the fact that the person no longer drinks gives him even more strength and vitality. Social rehabilitation is no less important than the use of medications, since it determines how a person will communicate with people after returning to normal life. To prevent yesterday's alcoholic from becoming addicted again, control from relatives and psychologists is very important during the rehabilitation period.
Alcohol detoxification is used to relieve a hangover and is not an independent treatment for alcoholism. During detoxification, alcohol is replaced with substances that have similar chemical properties, but are less dangerous to the body. Complex methods include all of the listed treatment options.
How to Determine If You Have Alcoholism
Diagnosing alcoholism in yourself is very difficult. To do this, you need to have a high degree of awareness and self-control, and they simply will not let you go on a binge. If control over your desires is weak, then you are unlikely to admit to yourself that you have a problem. Listen to your loved ones: urgent requests to contact a narcologist can save your life. The first symptoms of alcoholism appear in relation to addiction:
- ignoring social problems due to abuse;
- ignoring diseases that are aggravated by drinking alcohol.
All tissues and cells of the body are destroyed under the influence of alcohol. The most vulnerable are the nervous system, pancreas, and liver. Exacerbation of chronic diseases due to alcohol intake should stop you
If you feel that all your attention is focused on drinking, and career and family issues do not concern you, it’s time to consult a specialist.
Binge drinking
Binge drinking is drinking alcohol for several days or weeks in a row, followed by periods of “sobriety.” If a person drinks a little and not every day, it is still alcoholism, but not yet binge drinking. When drinking alcohol continues for many days in a row (and sometimes months), this is a reason to sound the alarm. Having coped with the binge (usually with the help of doctors, since it is very difficult to do this on your own), the alcoholic lives an ordinary life for some time, but then again takes up the old ways. The onset of binge drinking is caused by psychological reasons, and then “chemistry” takes over - the body demands one portion of alcohol after another, reacting painfully to their absence.
The last stage of the disease
The third stage of alcoholism is the final and most severe. Here it is necessary to begin serious and long-term treatment. If this is not done, the consequences can be fatal. Quite often, patients die from delirium tremens, heart failure and cirrhosis.
If the body still manages to cope with a large amount of alcohol at this level of alcoholism, the changes appear quite clearly and pronounced.
Complete personality degradation begins, rudeness and cynicism appear, the person cannot control aggression.
The third stage of alcoholism is characterized by a painful hangover, constant nausea and vomiting. The body becomes less resistant to alcohol. Intoxication can begin even from a small dose, and short-term binges develop into long periods. The patient loses appetite and weight also decreases. Stage 3 of alcoholism is characterized by the strong impact of alcohol on important organs, which over time may simply fail and cease to function fully.
It is impossible to say exactly how long such patients live. In most cases, the last stage of alcoholism ends in death. Some people refuse treatment and experience frequent depression, which can lead to suicide. They do not try to understand the problem they are faced with and prefer alcohol.
Treatment of binge drinking
First of all, it is necessary to find out for what reasons a person began to drink without stopping - this will help in
later, when the body is cleansed of toxins, a psychologist will talk with the patient. Then you should take care of the patient directly: you need to sober him up by waiting until he falls asleep. Be careful: sometimes this may require sleeping pills, so trust the treatment only to a narcologist. After this comes the stage of removing toxins. The patient is prescribed special medications for oral administration, and in case of complications, droppers with saline solution. Sobering up a person and cleansing the body takes 3-4 days.
If everything is so bad, why do people drink?
And in fact, who is right, doctors and researchers or friends of the “green serpent”? Observe people who drink and their behavior after drinking. The state of intoxication has several characteristic properties:
- after drinking alcohol, a person feels euphoric and elated;
- Alcohol is a good tranquilizer - it eliminates stress, fears, and causes a state of carelessness.
Are many people ready to give up their elated, serene state?
No!
The trouble is that not everyone is able to assess the situation and control themselves. Not everyone has an authoritative or simply interested person who will tell you, or even take you by the hand and tell you: “Stop!”
Hidden and beer alcoholism
Often people do not want others to know about their addiction to the bottle. Typically, women and successful wealthy people carefully hide their alcoholism, for whom the craving for alcohol is a stain on their reputation. But, unfortunately, for them, everything secret becomes clear: after some time, it is no longer possible to hide negative changes in appearance and character from family and work colleagues. Not wanting to reveal themselves, secret alcoholics resort to new tricks - they either drink rarely, but very much, or switch to low-alcohol drinks and beer.
Drinking beer, despite its apparent harmlessness, is much more dangerous than other types of alcoholism. With beer alcoholism, a person drinks almost every day, and the average dose rarely falls below one liter. At first, it does not affect a person’s health in any way, but the attachment to beer is much stronger than, for example, to wine or vodka. In the future, drinking beer leads to a transition to stronger drinks, binge drinking and serious diseases of the internal organs. Based on the strength and volume of alcohol consumed, alcoholism is divided into:
- Daily consumption of weak alcohol;
- Rare consumption of weak alcohol;
- Extremely rare consumption of strong alcohol and in large doses.
Stages of alcoholism by gender
It is customary to distinguish alcoholism by stages and rarely by gender, since the stages are the same for both men and women: the difference is only in some manifestations.
The male body is characterized by relatively greater resistance, so the stages of alcoholism in men can transform into each other for a long time. Among mental manifestations, aggressive behavior, outbursts of anger, and cruelty towards loved ones are statistically more common. If you are the spouse of a drinker, the article: how to rid your husband of alcohol may be useful to you.
The stages of alcoholism in women proceed faster due to reduced resistance. Representatives of the fairer sex are more likely to show apathy, irritability, tearfulness, and touchiness. The main distinguishing feature is secrecy - the initial stage of alcoholism occurs unnoticed by loved ones, since female alcoholism is socially condemned.
The difference may be determined by the cause of the disease. A man can start drinking alcohol in company, and also often drinks at critical moments in his life, gradually increasing the dose and becoming dependent. Women often start using after failures in their personal lives - breakup, divorce, infidelity of a spouse.
The above information equally applies to beer alcoholism; strong drinks are not the only form of addiction.
The stages of alcoholism are quite easy to recognize, starting from the second, but signs at 0 and 1 may not be enough to create a complete picture. Relatives of a potentially alcoholic person should pay attention to indirect symptoms and other differences in behavior and appearance.
Etiological process
According to the theory, which has been repeatedly tested by research, the basis for the development of a chronic form of alcoholism is “burdened” heredity, caused by a lack of the enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase and the presence of cells, damage to which leads to the development of dependence syndrome.
In addition, people with a certain personality type are prone to illness - easily suggestible and unable to withstand life's difficulties and conflicts, prone to cyclothymia (mood fluctuations). Their initial perception of alcohol is influenced by culture, upbringing, family traditions, status and position in society.
The systematic influence of alcohol on the body leads to poisoning and drug intoxication of the central nervous system, the structural elements of brain tissue, which are responsible for the mechanism of physiological formation of affects and feelings, are disrupted. Subsequently, this becomes the cause of alcohol addiction (alcoholomania) and dramatic changes in the response of cells to alcohol.
This is manifested by failures of chemical reactions in the body and damage to internal tissues and organs at the proliferation level. The most toxic compound that poisons the body is ethanal, produced by the liver as a result of the oxidation of ethanol-containing drinks. It is not for nothing that chronic alcoholism during pregnancy is an indication for termination.
Treatment and prevention of alcoholism
Like any other disease, alcoholism needs treatment. And the sooner it is started, the more effective the result will be. The problem of treating alcoholism is often complicated by the reluctance of the patients themselves to free themselves from the addiction. In such cases, treatment of a patient with alcoholism occurs under pressure from the family or administrative services. It is carried out in a drug treatment hospital and consists of several stages.
At the very beginning of therapy, a patient with alcoholism is helped to get rid of a hangover with medication. Isolation in a drug dispensary in this case is necessary to eliminate the minimal likelihood of the patient coming into contact with alcohol. The second stage in the treatment of alcoholism lasts months or even years and consists of restoring general health, spoiled by regular drunkenness. During this stage of alcoholism treatment, various coding methods are usually additionally used - implantation of drugs under the skin that cause aversion to alcohol. And at the third stage, social rehabilitation of the alcoholic patient occurs with the help of a psychotherapist and a sobriety society, as well as with the support of the family.
Unfortunately, successful recovery from alcoholism does not always provide a 100% guarantee against relapse of the disease. Prevention of alcoholism in a person with a history of alcohol dependence continues throughout life and involves complete abstinence from alcohol.
Prevention of alcoholism in healthy people, especially among young people, is the task of the state, public organizations, medical institutions, families, and schools. In the fight against a dangerous disease, all methods of preventing alcoholism are good: explanatory conversations, promotion of a healthy lifestyle, restrictions on the sale of alcohol, etc.
Stages and clinical picture of the disease
Drunkenness is inherently a social problem, but when ethanol destroys the drinker’s brain and health over time, a biosocial pathology develops, and it can only be gotten rid of through a set of therapeutic measures. The structure of the disease consists of 3 stages: the formation of mental, physical dependence, the final stage
Stage I of chronic alcoholism – formation of mental dependence
The main symptom of this first “stage” of the disease process is obsessive cravings. It is manifested by the presence of a constant craving for alcohol. The patient himself may deny its presence, but his thoughts, conversations, desires, and actions return his attention to the desire to take the next dose.
Therefore, under the guise of various reasons, the patient begins to drink alcohol-containing products more and more often. He develops tolerance - the need to take increasingly larger portions to obtain the desired euphoric effect. This stage can last 5-7 years.
Stage II – physical dependence
The signs described above are accompanied by a binge form of abuse - a period of many days of drunkenness, against the background of which the patient is unable to engage in normal activities. Sobering up is accompanied by severe withdrawal symptoms (hangover).
Abstinence is manifested by the development of a severe psychophysical state (depression, anger, aggressiveness, hysteria, trembling throughout the body, fear, pain). These manifestations can only be eliminated by taking a small dose of alcohol, which brings the person back to “normal.”
Following the “improvement” of health, the patient continues massive alcoholism (physical cravings). The binge cycle continues until the body’s adaptive forces are completely exhausted. Coming out of binge drinking is very difficult. Against this background, complications appear. Particularly dangerous are acute psychoses and epileptic seizures, which without treatment often result in cerebral edema, causing high mortality.
Patients at this stage of the disease quickly deteriorate. Huge doses of strong alcohol progressively destroy the brain, heart, liver and other important organs. The duration of the stage of physical dependence is up to 10-12 years.
III final stage
Clinical manifestations and symptoms of this phase of the disease are characterized by a change in the form of intoxication. Binges are going away, and their place is taken by the constant intake of weak alcohol in small doses. The patient “sinks” morally and physically. Mental degradation reaches its climax. He has sloppiness, parasitism, lack of interest in everything except the desire to drink. Alcohol is integrated into metabolism. You can help such a person only by mitigating the problems he has. As a rule, in such a situation, people can no longer stop drinking.
Psycho-emotional (mental) state
The long-term influence of toxins on the cells of brain structures causes rapid death (necrosis) of nerve cells. Mental disorders manifest themselves in a quarter of binge alcoholics in the form of:
- acute hallucinosis;
- paranoid states;
- affect and anxiety;
- focal seizures (epileptic).
Psychopathic signs manifest themselves during periods of heavy drinking and periods of sobering up. The destructive influence of alcohol causes partial memory loss, a complete inability to concentrate, leads to dementia and complete degradation. Family and morality become abstract concepts.
Is it possible to treat alcoholism at home and without the knowledge of the patient:
Parasitic life, constant dependence on alcohol, are accompanied by unreasonable fear, imaginary danger, anxiety and suicidal tendencies. The only thing that calms the patient is constant “feeding” of alcohol. Without another dose of booze, no activity is possible.
Chronic alcoholics initially have a weak character (asthenics), develop an inferiority complex, an increased sense of uncertainty and timidity, and neurasthenia. Personalities of a hysterical nature are characterized by a tendency towards deceit and bravado. Most patients with chronic illness experience difficulty sleeping, which leads to the progression of nervous exhaustion.
Second
In the second phase of the disease, old symptoms intensify and new ones are added to them. Perhaps the drunkard is aware of his addiction and even attempts treatment. Most often, they are unsuccessful: psychological dependence has already been formed, and it is impossible to do without medical help.
The greatest ability to work is observed only in a state of mild intoxication. Resistance to alcohol during this period is maximum: the required dose increases by 6-8 times. Although this indicator is individual and depends on the characteristics of the body.
Signs
Recognizing an alcoholic in the second stage is not difficult. This phase can be characterized by the appearance of binge drinking: the patient drinks for several days in a row, interrupting for work. He falls asleep only after taking it to the chest. At the second stage, many alcoholics lose their jobs - it is rare that an employer is willing to put up with systematic absenteeism.
The need for a drinking companion disappears, the person begins to drink alone. In this case, serious memory damage occurs: individual episodes or the entire evening from the first to the last glass may be forgotten. As a rule, all unpleasant moments are forced out of memory. Physical dependence on alcohol begins to form. The patient ceases to control the dose of alcohol, and the next morning he is tormented by a severe hangover.
If an alcoholic loses his job or family, personality degradation accelerates significantly.
Treatment
To get rid of alcoholism in the second stage, you need to stay in a hospital. A narcologist conducts an examination and individually selects symptomatic treatment tailored to the patient’s characteristics.
Stages preceding the formation of alcoholism
What is alcoholism and what precedes it? The formation of alcohol dependence is preceded by certain stages that at first glance seem harmless. At first these are periodic feasts, at first they are irregular and occur for some reason. After such evening events, a person feels very bad in the morning and is tormented by a hangover. Having completely sobered up, he returned to his normal lifestyle.
Start
The second stage is regular feasts, which require the presence of alcohol on the tables. Such events can drag on for several days, and for this reason a person may not go to work.
The third stage is the so-called household alcoholism, which manifests itself in frequent drinking at home for the most insignificant reasons. A person drinks more than a couple of times a week and moves towards the initial stage of alcoholism. How long it will take is an individual question. For men, this process can occur over several years, while for women it takes much less time. As a rule, the development of chronic alcohol dependence is preceded by a long period of irregular drinking. Due to the peculiarities of physiology in women, some stages of alcoholism are replaced by others faster than in men.
Causes of alcoholism
Alcohol addiction is a disease. The reasons for the abuse are still unknown. The cravings experienced by an alcoholic can be as strong as the need to eat food or drink water. There are a number of factors that can lead to alcohol dependence in a person:
- Genetic predisposition. Research shows that people who have parents or other close relatives who were addicted are at risk of becoming addicted to alcohol.
- Physiological reasons. People who start drinking at an early age are more likely to develop alcohol dependence. Also, various ailments can become a factor in the development of addiction. For example, liver diseases, head injuries, mental disorders.
- Psychological trauma. An addiction to alcohol can develop against the background of traumatic events or difficult periods of life.
Female alcoholism
Female alcoholism is an even more acute social problem and a serious disease. The identification of female alcoholism as a separate type of disease is forced by the congenital poor tolerance of alcohol by the woman’s body. The clinical picture of female alcoholism and its complications differs significantly from male alcoholism.
So, for example, if a man needs up to 10 years of regular drinking to become an alcoholic, for a woman the first stage of alcoholism lasts no more than 3 years. And then there is an accelerated increase in symptoms and the manifestation of complications associated with female alcoholism: hepatitis, pancreatic necrosis, cirrhosis of the liver. Personality changes also occur quickly: touchiness, anger, hysteria, and sexual promiscuity develop. Female alcoholism today is less common than male alcoholism, but under unfavorable social circumstances, strong emotional shocks, working in a drinking establishment or with relatives who abuse alcohol, a woman becomes an alcoholic earlier than a man.
Coding by photo
Today, coding is very popular, which is carried out using photographs. This coding method is good because a person who is addicted to alcohol does not even know that he is being relieved of this addiction. The fact is that many people suffering from alcoholism do not want to seek help, so they try in every possible way to avoid it. In addition, this coding method does not have the slightest side effects, and it does not pose any harm to health. It is also equally important that the person does not have to go to hospital for inpatient treatment.
The only disadvantage of such therapy is that its effectiveness has not yet been confirmed, and for many it raises doubts and mistrust. Therefore, there is no guarantee that this procedure will produce results. Based on this, people who resort to this technique agree to it, being prepared in advance for the fact that it will not help. It is best to use this technique in combination with medication and psychotherapeutic coding. In this case, the results will be clear.
Consequences of alcoholism
The most dangerous and common problems with alcoholism are alcoholic psychoses. Among them there are acute and chronic. The most famous acute psychosis is “delirium tremens” (delirium tremens), which occurs in 75% of complications. Most often it affects patients in advanced stage 2 of alcoholism.
Clinical manifestations of this pathology occur after 2-3 days of complete abstinence, an abrupt end after prolonged drinking. Patients become restless, they develop fear, illusions and hallucinations. Externally – severe trembling in the body, pronounced heartbeat, sweating. Symptoms are increasing. Patients can scream, hide, talk to invisible enemies, fantastic creatures, or run away from them. The acute period lasts several days. In severe cases and without treatment, death occurs. The reason for this complication of alcoholism is cerebral edema.
Please note: an interesting fact is that after recovering from delirium tremens, patients vividly remember their hallucinatory experiences and can describe in detail all their visions and sensations.
Delirium tremens may recur.
A complication of alcoholism such as alcoholic hallucinosis occurs more mildly. With this type of psychosis, the patient, against the background of emerging visions and hallucinations, maintains a more or less critical attitude towards them.
Chronic alcoholic psychoses last for months. Characterized by milder hallucinatory experiences and often with delusions of jealousy.
Complications of alcoholism from internal organs
The incidence of internal diseases in persons suffering from addiction to drinking is almost 2 times increased.
These data were established during a study of working enterprises in Moscow back in 1975 by N.Ya. Hoof. But there are specific damage to both internal organs and the nervous system that are characteristic of the long-term toxic effects of alcohol. The toxic effect of alcohol has a destructive effect on all organs and systems, but mainly the “weak link” is attacked, that is, an existing pathology or a predisposition to it. Most often affected:
- nervous system (brain and peripheral parts);
- the cardiovascular system;
- digestive.
The complications that alcohol gives to the brain and psyche during alcoholism are described above. In addition to degradation, alcoholics develop alcoholic polyneuropathy. The manifestation of this complication is expressed by complaints of numbness, “pins and needles”, nagging pain in the limbs, muscle weakness, cramps, trembling in the hands.
The next target is the heart and blood vessels. Patients develop alcoholic cardiopathy - damage to the heart muscle caused by the effect of alcohol on cardiac cells. As a result of this effect, a number of metabolic problems arise in the tissues of the heart, which lead to disruption of muscle nutrition. Heart failure gradually develops, aggravated by the negative effects of nicotine, since most patients smoke. This is due to a lack of thiamine, which is destroyed by alcohol, as well as metabolic disorders.
Cardiopathy in alcoholism is manifested by shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, interruptions, and swelling. When the patient abstains from alcohol and undergoes treatment, the heart symptoms gradually disappear.
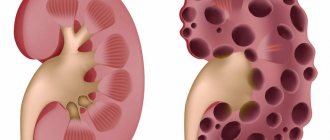
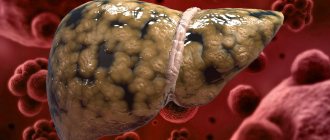
Liver problems are also a very common complication of alcoholism. Alcohol has a direct damaging effect on liver cells - hepatocytes. All types of exchange are disrupted.
The mildest degree of liver damage, alcoholic fatty degeneration, rarely occurs. It is found by chance during examination of the patient and is characterized by an enlarged liver and increased density. With a sober lifestyle, the pathology undergoes reverse development.
Alcoholic hepatitis is more serious. Manifested by complaints of belching, dull pain in the right hypochondrium, bloating, nausea. The liver is denser and enlarged than with dystrophy, and is painful. In the tests, alkaline phosphatase activity is noticeable. The patient's appearance is exhausted, vomiting, fever, diarrhea, and jaundice occur. If you give up alcohol, the disease partially goes away, but the consequences still remain.
The most dangerous complication is alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver. Patients experience:
- lack of appetite,
- sudden weight loss
- depression of mood,
- enlarged spleen.
In more severe cases, fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity (ascites), jaundice, bleeding, and liver failure develop. The prognosis is unfavorable.
The toxic effect of alcohol on the pancreas leads to the development of a serious complication of alcoholism - pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas). The disease is often combined with liver problems and gives a complex picture of complaints and clinical manifestations. Particularly characteristic are severe girdling pains in the abdomen, radiating to the back.
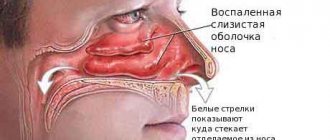
The stomach and intestines suffer from alcoholism. Gastritis, enteritis, enterocolitis are frequent companions of the disease.
These are the sad consequences that can result from the destructive passion of drinking alcohol.
You will receive more detailed information about the formation of dependence on alcohol, the effect of ethyl alcohol on the body and the consequences of alcoholism by watching the video review:
Lotin Alexander, narcologist
15, total, today
( 195 votes, average: 4.75 out of 5)
Schizophrenia - types, forms and clinical manifestations
Treatment of schizophrenia at home
Related Posts
A hangover as a sign of alcoholism
Contrary to popular belief, a hangover in itself is not a sign of alcoholism in men or women. It occurs due to excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages, which is already an alarming sign. Regular drinking of alcohol is a direct road to the development of addiction and the appearance of symptoms of alcoholism.
The basis of a hangover is the entry into the bloodstream of an intermediate metabolite (acetaldehyde). It is formed due to poor-quality processing of ethyl alcohol. Any alcoholic drink contains acetaldehyde, a substance toxic to the human body. When drinking ethyl alcohol, the liver begins to break it down into carbon dioxide and water, but when drinking a large amount of alcohol, this protective function only partially manifests itself, which leads to a deterioration in well-being.
Due to incomplete processing of alcohol, acetaldehyde is formed, causing characteristic signs of a hangover syndrome:
- pain in muscles and joints;
- physical weakness;
- strong thirst;
- severe headache;
- obsessive desire to drink alcohol.
Sometimes a hangover is confused with the withdrawal syndrome of alcoholism, the symptoms of which appear every time after drinking alcohol and taking a short break. Headaches, muscle pain, weakness, swelling on the face - this is not just a hangover, but a cry from the body for help, visible manifestations of alcohol poisoning and intoxication.