Medical Consultant Gastroenterology Intestinal hernia: causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention of the disease
An intestinal hernia is a disease in which part of the intestine comes out of the abdominal wall or moves within the abdominal cavity. Protrusion of an organ or part of it can occur under the skin, into an area free of muscle tissue, into internal pockets and cavities. The occurrence of the disease is facilitated by the presence of a defective area of abdominal wall tissue and increased intracavitary pressure. The risk of the disorder is approximately 3 times higher in men than in women.
- Causes
- Symptoms and diagnosis
Features of the course of the disease in men and women
- Lifestyle recommendations
- Horizontal bar
Reasons for the development of pathology
An intestinal hernia can be congenital; it occurs due to abnormalities in the development of abdominal organs during the period the fetus is in the womb. In addition, this pathology can be acquired. Predisposing factors are excessive physical activity along with frequent constipation, excess weight and postoperative complications. In addition, the factors for the development of the disease include the following reasons:
- The presence of diseases of the internal organs of the digestive system along with human exhaustion.
- Sustaining mechanical injuries to the anterior abdominal wall.
- Presence of genetic predisposition.
- The appearance of a prolonged and hysterical cough.
- The presence of lumbago (acute pain radiating to the lower back in the form of lumbago).
Diagnostics
As a rule, the diagnosis of this disease does not cause complications, since the clinical picture has quite specific signs.
A standard diagnostic program may include the following:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- general urine analysis;
- diagnostic laparoscopy;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- radiography of internal organs;
- MRI.
The treatment tactics are strictly prescribed by the doctor, after receiving the diagnostic results and identifying the etiology of the development of this disease.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of an intestinal hernia may vary depending on where the pathological process began to develop. In the event that it is small in size, and it itself grows slowly, practically not developing, the overall symptomatic picture will be weakly expressed. It will manifest itself in the form of minor short-term disturbances in the digestive and genitourinary systems.
If pathological processes develop, the first symptom of an intestinal hernia will be pain, which can be aching, strong, acute or weak. This may occur under the influence of provoking factors or may be constantly present.
Symptoms
At the initial stage of development, an intestinal hernia may be asymptomatic. As it develops, the following symptoms can be observed:
- dull, stabbing, cramping pain, which can intensify with physical activity or coughing;
- feeling of fullness in the stomach;
- symptoms of intestinal obstruction;
- nausea, which is rarely accompanied by vomiting;
- belching, often with an unpleasant odor or taste of recently eaten food;
- feeling of incomplete bowel and bladder bowel movements;
- unstable functioning of the gastrointestinal tract - attacks of diarrhea can be replaced by prolonged constipation;
- signs of general intoxication of the body;
- anointing.
Separately, the clinical picture of this pathological process in women should be highlighted:
- frequent urge to urinate, which does not bring relief;
- discharge of mucus from the vagina;
- exacerbation of chronic gynecological diseases, if any;
- nagging pain in the back;
- heaviness in the vaginal area;
- discomfort in the groin area;
- discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse.
It should be noted that with a small hernia there may not be pronounced symptoms. Pathology is most often detected by ultrasound of the abdominal organs in relation to another disease or during a routine examination.
If you have the above clinical picture or symptoms of intestinal obstruction, you should seek medical help. You cannot self-medicate or ignore this disease, as this can lead to irreversible changes.
General signs
The following general symptoms of intestinal hernia in women and men are noted:
- The presence of disorders of the digestive system.
- The appearance of pain in the lower abdomen.
- The presence of bloody clots in the stool.
- The appearance of nausea and vomiting.
- The appearance of swelling in the area of location.
Classification and varieties
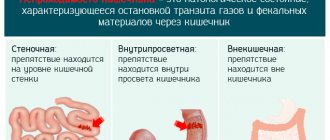
It is customary to distinguish several types of intestinal hernias. Classification depends on the location of the hernial sac:
- Inguinal. Develops in the area of the inguinal canal. It can form inside, go under the skin, or be diagnosed in both places at the same time.
- Umbilical. This type of education is typical for newborn babies. Caused by an underdeveloped umbilical ring. Also, a hernia can form in women during pregnancy and after childbirth.
- Femoral. Located in the upper part of the anterior thigh. Typical for older people.
- Linea alba. In most cases, it is represented by several small hernias located in close proximity to each other.
- Ventral (postoperative). Formed in an area of thinned scar tissue.
- Sliding. Formed as a result of partial overlap of the intestine with peritoneal tissue.
Patient management tactics depend on the type of hernia
Diagnosis of intestinal hernia
Diagnosis of a tumor formation in the presence of symptoms of an intestinal hernia, as a rule, includes interviewing the patient about complaints; in addition, a thorough anamnesis, that is, a history of pathology, can be compiled. An examination is carried out through palpation, so the doctor determines the degree of intensity of pain by studying the size of the hernia. If necessary, a consultation with related specialists is prescribed, such as a gastroenterologist, proctologist, gynecologist, and so on.
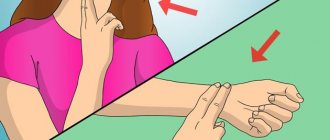
In order to confirm the diagnosis of intestinal hernia in men and women, a cough impulse is used. This technique is carried out in this way: the doctor places his palm on the place where the hernia is located and asks the patient to try to cough. If during a cough the formation begins to move under the skin, then the diagnosis is confirmed.
Complications
A hernia can provoke dysfunction of the organs of the system in which the hernial sac is located. If the pathology is located on the white line, then the person’s digestive system is disrupted. The patient may suffer from frequent constipation, and the development of ulcerative pathology in the stomach along with gastritis and colitis is possible.
In the presence of an inguinal hernia, diseases of the organs in the genitourinary system may occur. The most common complication is the inability to reduce the hernial sac. If the size of the protrusion is small, there are no complications. And against the background of this, a person, taking a horizontal position, will notice that the wandering hernia is simply hiding.
This condition is called a wandering sac, since against the background of a change in body position, the organs that fell into the hernial sac begin to return to their original position. If the patient lies down and the bulge on the body does not decrease, this indicates the development of severe complications. They are dangerous because over time, the hernia can begin to divide into several sectors at once, into each of which a segment of the intestine will fall out.
Against the background of the development of an inguinal hernia, the functioning of the rectum can be completely disrupted. Often, the only method of normalizing digestion is an anal colostomy, which is an operation to create an alternative anal passage.
A complication of inguinal hernia in women and women, which poses a health risk, is strangulation. This pathological condition is characterized by the fact that the hernial sac may suddenly become trapped in the hernia gate. Strangulation is an emergency requiring surgical intervention. This condition is accompanied by severe pain and may be the reason that gangrene develops, since when pinched, blood circulation in this area may be disrupted. Other possible complications are intussusception (that is, intestinal obstruction) and the development of diverticulosis of the sigmoid colon (against the background of which pockets form in segments of the large intestine).
How does a postoperative (ventral) hernia manifest?
Symptoms of the disease depend on the degree of reducibility of the hernial contents and the presence of strangulation in the area of the hernial orifice.
In the initial, uncomplicated stages, these may be:
- periodic appearance of a protrusion (subcutaneous round formation) near the postoperative scar;
- painfulness of the emerging formation when palpated and when coughing or straining;
- in the absence of complications, a hernia in a horizontal position can be reduced independently.
In the future, as the situation worsens, when intestinal loops are pinched in the hernial orifice, chronic inflammatory changes are formed, and more formidable symptoms may appear:
- constipation;
- intestinal obstruction;
- bloating of the intestines due to stagnation of contents and impaired gas discharge;
- vomiting, sometimes mixed with blood;
- nausea;
- increase in general body temperature, other signs of intoxication (lethargy, lack of appetite).
A hernia that appears is not always a consequence of surgery. This may be a hernia of the white line or an umbilical hernia that occurs spontaneously. The surgeon will be able to differentiate the origin of the hernia and choose the correct treatment tactics after examination and using additional diagnostic methods. Most often, this is an ultrasound of the hernia, herniography, radiography of the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract), gastroscopy or endoscopy (esophagoduodenoscopy), CT scan of the abdominal organs.
Treatment of intestinal hernia
Pathology, depending on the stage, is treated with conservative methods or surgical operations. Drug therapy, as a rule, is aimed at relieving painful symptoms, and in addition, at preventing the further development of pathological processes. But it will be possible to completely get rid of the hernia only by performing a surgical operation.
If the bag does not increase in size, then there are no complications at all. Such patients are prescribed physical therapy aimed at strengthening the muscles in order to prevent subsequent organ loss. It is mandatory to wear a bandage.
Traditional medicine techniques, along with herbal decoctions, in the treatment of the pathological condition in question are used only as part of additional therapy to reduce the overall intensity of pain symptoms. It is worth noting that conspiracies in the treatment of hernia will definitely not give any therapeutic effect.
Types of surgical intervention for inguinal hernia
There is only one way to cure an inguinal hernia in men - surgery. Folk remedies, bandages, and medications will ease the course of the disease, but these remedies cannot completely get rid of the disease.
Hernia surgery is called herniography. It is performed in two main ways: open (removal through an incision) or laparoscopy (removal through a small hole). The second method is more gentle on the body. This happens due to the fact that many people seek help from a doctor at fairly advanced stages of the disease.
Usually the operation lasts up to one and a half hours. The hernia can be completely removed, but its cavity can also be cleaned and the muscle wall strengthened with a special mesh. The operation can be performed under local or general anesthesia, the doctor will decide this depending on the chosen method of intervention and the patient’s condition. In all cases, a preliminary examination, blood and urine tests are carried out, and when underlying diseases are diagnosed, their correction is carried out. At the time of the planned operation there should be no exacerbations of chronic diseases, no infections or colds.
Laparoscopy (endoscopy) is a modern minimally invasive (gentle) surgical method. It involves suturing a hernia using a laparoscope (endoscope) through a small hole (up to 1.5 cm in diameter). An endoscope is an instrument with a system of special lenses connected to a video camera. As a rule, not one puncture is made, but 3-4 - to insert clamps and other necessary tools.
"Important! Laparoscopy is indicated for the patient in cases where there are no complications, but sometimes complex manipulations are performed using this method.”
The general scheme of the operation is as follows: a small puncture is made in the tissue to access the hernial sac with the introduction of carbon dioxide, the hernial sac is removed and cleaned, and sutures are applied. The recovery period in the hospital lasts 6-7 days. There are no scars left and no painful sensations are observed.
Operation
Surgical interventions aimed at removing a hernia of the small intestine are performed endoscopically and openly:
- Traditional open surgery is performed primarily in cases of strangulation, when the patient urgently requires quick and effective measures.
- Endoscopy is a method of planned surgical interventions, which have a lower risk of complications and a fairly quick recovery period, since it does not require a cavity incision, as is the case with traditional surgery.
Traditional operation
During the operation, the doctor excises the ligaments and muscle corset, returning the internal organs that have fallen into the hernial sac to their place. In the event that there was an infringement that led to necrosis and circulatory disorders, the damaged part of the intestine is completely removed.
An obligatory stage of the traditional operation is the plastic surgery of the hernial orifice, carried out by placing a mesh implant that supports the muscles. This measure is guaranteed to prevent the recurrence of a hernia. The tension method can also be used. In this case, the hernial orifice can be closed by the patient’s tendons and muscles.
How is an intestinal hernia removed by endoscopy?
Classification depending on the location of the pathological process
Based on this criterion, it is customary to divide hernias into external and internal hernias. In turn, internal ones are divided into intra-abdominal and diaphragmatic. External ones are more common and have an unfavorable prognosis. The most dangerous of external hernias are inguinal and umbilical hernias, due to their tendency to pinching.
It just so happens that the most dangerous hernias are the most common. Unfortunately. So you need to remember about their most characteristic manifestations and go to the hospital in time.
Endoscopic surgery
The doctor makes several small punctures in the skin through which a surgical instrument is inserted. They also introduce an endoscope, which is a tube with a camera attached to the end; it transmits the image to the monitor. This method of surgery for intestinal hernia is much more preferable, since it is less dangerous and does not injure the body as much. During it, the doctor cuts off the edges of the hernial sac from the tissue, the doctor returns the prolapsed organs to their place and sutures the gate.
Strangulated hernia: what is the danger?
With a strangulated hernia, parts of the internal organs that have fallen into the slit-like cavity cannot be straightened and returned to their place. They become pinched, often compressed, which leads to necrosis (death of tissue), suppuration and intoxication of the body. Therefore, a person with a strangulated hernia has, in whole or in part, signs of an inflammatory process or poisoning. He turns pale, shudders, and feels nauseous. There is vomiting and intestinal obstruction. The skin in the affected area turns red or blue, and severe pain is felt in this area.
"Important! If urgent measures are not taken to save the patient, this condition threatens with peritonitis - inflammation of the walls of the peritoneum, which can lead to death.”
Rehabilitation
After surgical removal of an intestinal hernia (after surgery), the patient must wear a bandage, which reduces the likelihood of relapses. The patient’s diet must be adjusted and all kinds of physical activity excluded. To relieve pain, which always occurs during the postoperative period, painkillers are prescribed.
They recommend spending as much time as possible in the fresh air, walking at a leisurely pace. Physical activity is usually allowed after two months. In the absence of complications, doctors allow cardio exercises along with swimming, which does not put any stress on the operated area, helping and promoting the restoration of muscle tone, which in itself serves as a fairly good prevention of recurrences of the hernial sac.
A very important place in the entire rehabilitation program is given to daily changing of the dressing and treating the surgical wound with antiseptic drugs. Drinking alcohol along with smoking during the rehabilitation period is strictly excluded.
What should the diet be like?
In order to prevent complications, a patient diagnosed with an intestinal hernia must adjust his diet along with his diet. It is necessary to completely exclude from the menu foods that cause constipation along with excessive gas formation.
It is necessary to follow the eating regimen. In this case, you need to eat food up to six times a day, but nutritious portions must be very small. It is strictly forbidden to overeat. You should finish eating with a feeling of slight hunger. Avoid foods that provoke fermentation processes in the intestines.
The diet in the presence of a hernia, as a rule, excludes the intake of heavy food; in addition, you should not eat fatty meat and fish, and at the same time smoked meats. All food must be steamed or boiled. Food must be chewed very thoroughly. Any products must undergo mandatory heat treatment.
It is very important to follow the correct regime of fluid intake; you should drink at least two liters of water per day. After eating food, drinking water is strictly prohibited. Dinner is allowed no later than three hours before going to bed.
Carrying out prevention
An intestinal hernia is a serious condition that can be prevented through a variety of preventive measures. They are aimed at minimizing the risks of increased pressure within the abdominal region.
The main preventative measure is proper nutrition along with adherence to food intake. Excess weight, which is caused by unlimited consumption of fried foods, flour products, and also carbonated drinks, is the main cause of the appearance of a pathological bag.
Frequent overeating leads to increased pressure inside the abdominal wall and can provoke a hernia. It is also recommended to avoid frequent constipation. If bowel movements are frequent, it is necessary to identify the causes and carry out appropriate treatment.
People who professionally engage in heavy sports must wear a special bandage when undergoing active physical activity. The use of such a device is also recommended for pregnant women when their uterus is rapidly enlarging, putting pressure on the abdominal organs, which often causes an inguinal hernia.
Muscles must be in good tone; therefore, for prevention purposes, it is necessary to take regular exercise as a habit. This could be, for example, a simple exercise that helps keep the body toned and in shape.
Prediction and prevention of hernia formations
The prognosis for an intestinal hernia, if complications are not allowed, is very favorable, and with proper surgical treatment, a complete cure is often observed. When the anomaly is strangulated, the prognosis is determined by timely surgical intervention, competent choice of treatment tactics and adequate elimination of intestinal fragments that have undergone necrotization.
Today, methods of simplified removal of intestinal fragments are considered the most unfounded, since in such cases the risk of postoperative complications is quite high.
Prevention of intestinal hernia is considered to be a rational diet, which will ensure regular bowel movements and maintaining an appropriate weight. Experts also advise balancing the appropriate level of strength loads, which will ensure proper support for the muscular frame of the peritoneum.