October 20, 2019
- Creatinine in the blood - what is it?
- Norm for women, men and children
- Signs of impaired creatinine formation
- Laboratory diagnostic methods
- What does a low level mean?
- When creatinine is elevated
Hello, dear readers of the KtoNaNovenkogo.ru blog. One of the informative diagnostic procedures is a biochemical blood test.
It is difficult for a person without medical education to understand his testimony. After all, blood is not only formed elements - platelets (what are they?), red and white cells.
It is also an extensive complex of organic substances (lipids, proteins, including specifically colored ones, carbohydrates, vitamins and enzymes (what is this?), inorganic and low-molecular nitrogenous substances).
By the level of content in the blood plasma of each of them, one can judge the state of the human body and the pathological processes occurring in it.
Today’s topic is devoted to one of the representatives of low molecular weight nitrogenous substances – creatinine. What kind of substance is this, what role does it play in the body, what is the physiological norm, and what its imbalance can tell us.
What causes high creatinine?
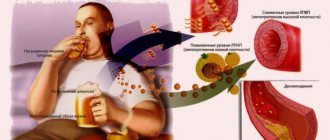
If the functioning of your kidneys is interrupted or impaired by any condition, this can cause your creatinine levels to increase. Some of the most common causes of chronic kidney disease or elevated creatinine levels in adults include:
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Urethral infection
- Kidney infections
- Abnormal muscle breakdown due to rhabdomyolysis
- Drugs such as cimetidine
- Consuming large amounts of dietary meat
Let us now look at the warning symptoms that may arise due to high creatinine levels in the blood.
Creatinine in the blood - what is it?
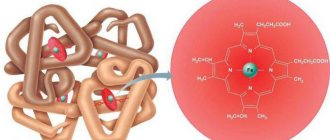
Creatinine belongs to the group of low molecular weight nitrogenous substances. In fact, it is an anhydride (chemical compound) of creatine (a nitrogen-containing carboxylic acid), which provides the body's muscle tissue with the necessary energy.
It is formed as a result of metabolic processes in the structure of muscle tissue by the cleavage of enzymatic proteins (dephosphorylation) and non-enzymatic dehydration (decomposition) of nitrogen-containing carboxylic acid.
The “energy raw materials” necessary for tissues are produced by the pancreas, kidneys and liver.
After its formation, it is delivered through the bloodstream to the cellular structure of muscle tissue. Here, as a result of a reaction with a kinase enzyme, it is converted into the form of creatine phosphate, or phosphocreatine. The addition of phosphate acids to the process results in the formation of powerful energy for muscle contractile function.
It is during the process of energy production that creatine is temporarily converted into creatinine. Subsequently, the substance is excreted from the body in urine.
Our body consistently produces creatinine and creotine in a certain amount, maintaining the necessary balance. Every day, up to 2% of creatine is converted to creaotinine. Its value in the body is constant, since muscle mass in humans is virtually unchanged.
Creatinine levels may vary depending on muscle mass, gender and age of the patient. Almost all of the energy substance is produced through glomerular filtration in the kidneys, only 15% is secreted by the renal tubules.
Since the substance is removed from the body through the urinary system, the creatinine clearance (the volume of blood passing through the kidneys and cleared of the substance in 1 minute) in urine can be used to judge the effectiveness of glomerular filtration processes and the performance of the kidneys themselves.
Therefore, the concentration of creatinine in the blood plasma, which does not go beyond a certain norm, is a good indicator of the functional viability of the kidneys, or a sensitive indicator of their pathologies.
This is interesting. Since fish and meat are considered the richest foods in creatinine, many “experts” believe that it is possible to provide the necessary energy to muscle tissue only through a balanced diet.
At the same time, completely unaware that for a normal “load” of creatinine into the body, you will need to include up to 5 kg in your daily diet over the course of a week, in addition to other foods. pure meat.
What are the symptoms of high creatinine?
The symptoms of high blood creatinine and kidney dysfunction often have similar symptoms. Some people may have severe kidney disease and high creatinine levels without any symptoms, while others usually have symptoms such as
- Swelling or inflammation
- Shortness of breath
- Loss of body fluid
- Fatigue
- Nausea and vomiting
It is important to have your kidneys checked periodically if you have any of these symptoms.
Options for reducing creatinine
If the concentration of the substance has increased slightly, and this was caused by minor changes in the body, then the situation can be corrected with the help of:
- Nutrition corrections. Add lean meat (turkey, rabbit) to the menu, eating it three times a week. To normalize digestion, porridge (oatmeal, millet) is suitable.
- Proper drinking regime. You need to take at least 2 liters of plain water per day.
- Decreased physical activity.
If the cause of deviation from the norm in creatinine is kidney disease, then specialists should take care of the therapy.
Diagnostics
If your blood test shows that you have high creatinine levels, you may have the following tests:
- Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) Test – This test checks your kidney function by measuring the amount of urea nitrogen in your blood. Too much or too little urea nitrogen often hints at kidney problems.
- A basic metabolic test (BMP) is a combination of tests that evaluate the functioning of the body's major functions.
- Comprehensive Metabolic Test (CMP) - This test is a series of 14 tests that gives your doctor important information about the health of your kidneys, liver, electrolyte and acid-base balance, etc.
Laboratory diagnostic methods
To identify the real level of creatinine in the body, various laboratory diagnostic methods are used, which help to make a correct assessment of the functional characteristics of many organs and systems, to determine the nature of changes in the general condition of the human body using capillary or venous blood.
This:
- Comprehensive diagnostics biochemistry .
- Hemorenal tests (Rehberg-Tareev) - determination of the level of endogenous substances according to GFR.
- Azotemia is the standard for early diagnosis of renal pathologies (protein/creatinine ratio).
To eliminate errors in laboratory test readings, two days before the examination you should avoid strength training.
24 hours before donating blood, exclude protein and meat foods, especially beef, from your diet. Drinking plenty of fluids is helpful, but on the eve of blood sampling you should not drink strong tea or coffee.
Based on the results of each of these tests, one can judge the patient's health status.
How to Reduce Creatinine Levels Naturally
Apple vinegar
Ingredients
- 1 tablespoon apple cider vinegar
- 1 glass of warm water
- Honey
Recipe
- Add a tablespoon of apple cider vinegar to a glass of warm water and stir well.
- Add some honey to this solution and consume daily.
Causes of low creatinine specific to a particular gender
The female body differs from the male body in the presence of estrogens, a more fragile constitution, and slower absorption of proteins. In addition, women are usually less active than men and do less hard work. Therefore, their blood creatinine is lower more often. Specific factors that lead to this include:
- First trimester (first three months) of pregnancy. It happens that it decreases in the second trimester.
- Severe cases of anorexia, when a woman loses more than 30% of her normal body weight.
In men, low creatinine is less common than in women, which is due to better muscle development, faster absorption of proteins, the presence of the male hormone testosterone, and most importantly, greater physical activity. Typically, creatinine in men falls due to:
- chronic severe liver diseases (cirrhosis, hepatitis, atrophic processes);
- problems with blood flow in the liver;
- problems with blood supply to the kidneys;
- obstruction of the urinary canal (stones, neoplasms);
- Duchenne and Becker diseases, which cause muscular dystrophy. These diseases are usually not caused by lifestyle or poor environment and are transmitted exclusively by inheritance.
Expert answers to readers' questions
What does it mean if I have hypothyroidism and high creatinine?
Hypothyroidism causes an increase in blood creatinine levels, likely due to a decrease in glomerular filtration rate (GFR). However, these changes develop quickly and in most cases are reversible.
How can I increase hemoglobin in case of high creatinine (female)?
In some cases, high creatinine levels can cause low hemoglobin levels. This occurs mainly due to decreased production of erythropoietin in the kidneys. You can increase your intake of vitamins B6, B12, B9 and C to increase your hemoglobin levels. You can also increase your iron intake through diet or supplements and purchase additional chitosan supplements to improve hemoglobin production in the body.
Symptoms and treatment
Associated symptoms with elevated creatinine:
- myalgia (lower limbs and back in the kidney area);
- increased blood pressure;
- swelling (face, legs);
- decreased ability to work, fatigue;
- pale skin.
Often, an increase in creatinine is accompanied by dysuria, manifested both in rare urination (up to anuria) and in polyuria of more than 2 liters of daily urine. It may be cloudy due to protein admixtures and may also contain blood (hematuria). All clinical manifestations are associated not with changes in metabolite content, but with the underlying disease that caused its fluctuations. Tests will help you understand the symptoms. The interpretation of the analysis should be done only by the attending physician who fully knows the medical history.
Important! The results of creatinine tests done one day apart may vary by up to 15%.
Treatment with folk remedies
To reduce creatinine and improve kidney function, infusions, decoctions and other herbal remedies from medicinal plants are used.
Mint infusion
An infusion is made from dried peppermint (2 tbsp) and 500 ml of boiled water: the leaves are poured into a thermos, the container is closed for 2 hours. Drink the strained infusion in small portions throughout the day.
Infusion of nettle leaves
Take 2 tbsp for a glass of boiling water. l. dry nettle and leave for an hour, wrapped. Strained nettle infusion is taken half a glass after and before bedtime.
Lingonberry leaves
1 tbsp. l. Pour a glass of boiling water over dried lingonberry leaves and cook for half an hour in a water bath. Drink the strained broth three times a day, one-third of a glass.
Sage-based collection
Sage (4 tbsp) is mixed with dandelion leaves, birch bark and burdock root (3 tbsp each). Pour the mixture into 1 liter of boiling water and keep in a thermos for 3 hours. Take the strained infusion at night, 3 tbsp. l. It is not recommended to drink for pregnant women.
Dandelion root decoction
For 1 tbsp. l. root 2 cups of water, cook over low heat until boiling, after 5 minutes remove from heat and cool. Drink 2 tbsp. l. half an hour before meals 3-4 times a day.
Ways to Normalize Content
Depending on the reason for the increase, different methods should be used. If there is a slight increase in the amount of creatinine, when at the end of a more serious examination no pathologies were found, it is enough to use these tips:
- Watch your diet. An adult should eat only half a kilogram of meat per week, dividing it into several servings. The best option is 3 days, 150 grams each. At the same time, you need to monitor the quality of the meat - it should not be too fatty and high in calories. Rabbit, veal, chicken, turkey are suitable options. It is better to fill the basic daily protein requirement with food of plant origin. It's better to take care of your intestines and eat more fiber-rich foods. First of all, this is bran bread and porridge.
- Monitor the amount of water you drink to prevent dehydration. The norm for an adult is more than two liters. A person who drinks little will find it difficult to get used to it. In this case, you can keep a notebook and write down all the liquid you drink, and also take water with you to work. You must remember to drink one glass on an empty stomach. The liquid you take can be fruit drinks and herbal teas. But if a person is afraid of consuming too much sugar or suddenly discovering an allergy to some plant, then he can simply drink pure water.
- Regulate physical activity. If a person does not play sports at a serious level, then he will simply take a short break. But even professional athletes are better off refusing to participate in the competitive season for the sake of their own health. This time is enough for the complete restoration of kidney function.
If serious pathologies are detected, mandatory treatment is required. Medical procedures to correct urinary and kidney problems are determined by your doctor. Doctors usually prescribe medications necessary to bring protein breakdown processes back to normal. Trying to independently regulate creatinine levels with medication is strictly prohibited - this is dangerous to health.
For what purpose and when is a blood test done to determine creatinine levels in men?
The occurrence of general malaise, lower back pain, and increased blood pressure may be signs of kidney disease. Correct data obtained from the analysis are key in determining the disease and prescribing a course of treatment.
An increase in creatinine in the blood has the following symptoms:
- Clouding of consciousness;
- Chronic feeling of fatigue;
- Labored breathing;
- Heaviness, mild pain in the lumbar region.
Such symptoms can be short-term, that is, during a walk, when a person quickens his pace, a slight dizziness may occur, which will quickly pass, but after a while it will repeat with increasing load.
Preparation for the analysis does not require any diets or special diet. You just need to follow these instructions:
- For two days before the analysis, it is necessary to avoid any physical activity;
- For 24 hours before the analysis, refrain from eating alcoholic beverages, meat, coffee, and foods with a high protein content;
- You should not eat food for 10-12 hours before the medical test;
- Immediately before the analysis, you should sit quietly and try to relax;
- The analysis is taken before meals.
By following simple instructions, the analysis will be reliable.
The analysis is carried out on the basis of taken samples of capillary and venous blood, this determines the principles and methods of taking the analysis.
Capillary blood is taken from a finger. Venous blood is taken using a syringe from a vein in the bend of the elbow.
Blood collection
After treating the elbow area with alcohol, the nurse will apply a pressure tourniquet to the shoulder in order to stop the flow of blood through the veins and increase the pressure in the vessels. Then, using a sterile needle and syringe, the nurse will puncture a vein in the elbow area and take a few milliliters of blood. After that, a patch with sterile cotton wool moistened with a disinfectant solution is glued to the injection area.
Collection of a 24-hour (daily) urine sample
- Urine collection begins in the first half of the day. After you wake up, you need to urinate, but you do not need to collect this urine. All subsequent portions of urine will need to be collected in a sterile container with a volume of 4-5 liters. You cannot separate urine into different containers. You should also avoid touching the inner surface with your hands. This container should be kept in a dark, cool place, the ideal place for this is the refrigerator
- Store the container of collected urine in the refrigerator for 24 hours;
- It is necessary to empty the bladder for the last time exactly 24 hours after the first urination, that is, the last portion of urine should be the morning portion of urine the next day;
- The collected urine should not contain foreign objects or substances, for example: toilet paper, pubic hair, feces, menstrual blood, etc.
Normal creatinine values may vary among laboratories depending on the reagents used. More precisely, it is not the parameters that vary, but the units of measurement.
| Creatinine and creatinine clearance | |
| Blood creatinine | Men: 0.6-1.2 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or 71-106 micromoles per liter (µmol/L) Women: 0.4-1.0 mg/dL or 36-90 µmol/L |
| Creatinine clearance | Men (up to 40 years): 107-139 milliliters per minute (ml/min) or 1.8-2.3 ml per second (ml/sec) Women (up to 40 years): 87-107 ml/min or 1.5-1.8 ml/sec Creatinine clearance values typically decline with aging (normal values decrease by 6.5 ml/min for every 10 years after age 20) |
| Nitrogen to creatinine ratio | |
| Norm | 10:1 to 20:1 |
The test is simple, like any other BAC (biochemical blood test). They come to the laboratory in the morning on an empty stomach, wait in line, provide a vein in the elbow and wait a little (until the mosquito bites), the rest will be done by specialists who have studied for this. The result will be ready on the same day (creatinine testing begins immediately, it does not like to sit idle).
As for the urine test, the patient receives instructions on how to collect it (per day, two, three...). Usually urine is collected 24 hours in advance, the diet is normal, unless the person is a great meat eater, a workaholic or an Olympic champion (lots of meat, physical activity - high creatinine).
It is unlikely that the experts on our site can recommend any specific folk remedy or medicine that is sold in a pharmacy. It is necessary to find and eliminate the cause, then the increased creatinine will go away on its own. Probably, from the article we can conclude that this component is an indicator of serious disorders in the body (with the exception of active work and addiction to meat products), including the development of kidney failure.
Diet with elevated creatinine
If creatinine is elevated, a diet must be prescribed. First of all, it is necessary to limit the amount of meat in the daily menu. However, you should not completely exclude it from your diet. The amount of meat products should be reduced to 200g per week. It is better to completely avoid fatty varieties. They should be replaced:
- chicken;
- veal;
- rabbit
At the same time, the body must receive its daily protein intake. It is better to replenish it by eating eggs, nuts, dairy products and fish. The menu should be varied. It is recommended to include a large amount of vegetables and fruits. With elevated creatinine, the following can have a beneficial effect:
- pomegranate;
- porridge cooked in water;
- citrus;
- tomatoes;
- pumpkins.
Buckwheat porridge is especially beneficial. Eating yeast-free bread with bran is also beneficial. Such a diet will reduce the production of creatinine and its entry into the blood.
You also need to pay attention to your diet. Every day you need to drink at least 1 liter of clean water. The action is recommended to be performed in the morning on an empty stomach or between meals. It is highly not recommended to wash down your food. Reducing physical and mental stress can also normalize the amount of the substance in the blood.
How to increase?
Therapeutic measures depend on the reasons that influenced the decrease in its indicators. You can quickly normalize creatinine concentration using folk remedies:
- grind flax seeds and comfrey roots in a coffee grinder, add honey in a 3:1 ratio, mix well and take 3 times a day after meals with tea;
- 1 tsp. dissolve pollen in 200 ml of boiled water, take 2 times 1 tbsp. l.;
- Prepare an infusion from barberry berries (you can buy them in the pharmacy chain) and take 80 ml of it 2 times before meals.
A balanced diet plays a significant role - the daily menu should contain foods that contain protein:
- meat and fish;
- buckwheat, rice and semolina;
- mushrooms;
- walnuts and peanuts;
- dried apricots;
- bananas;
- potato;
- kiwi;
- pork liver;
- chicken eggs;
- premium pasta;
- legumes and seafood.
Particular attention should be paid to treating the underlying pathological process, increasing physical activity to build muscle mass, maintaining a sleep schedule, drinking enough fluid (at least 1.5 liters per day) and taking vitamin and mineral complexes.
In conclusion of all of the above, I would like to emphasize once again that creatinine is considered an important parameter for examining a patient, which is a harbinger of various serious pathological processes. Establishing the reasons for its change is a matter for qualified specialists! Timely diagnosis of diseases and appropriate treatment and preventive measures will help avoid serious complications.
How to recognize violations
Creatinine is a low-toxic substance. Symptoms of poisoning can only occur at excessively high concentrations, which is noted in life-threatening conditions. Even a significant increase in the indicator above the norm in case of illness is not capable of influencing overall well-being. Hypercreatinemia does not have its own symptoms and can manifest itself as signs of the disease that caused the abnormalities, for example:
- for nephropathies - dysuria (small or large amounts of urine, difficult, painful emptying of the bladder), lower back pain, swelling, impurities of pus, mucus, flakes in urine;
- with muscle damage - muscle pain, weakness, fatigue, bruises;
- for liver diseases - weakness, apathy, jaundice, digestive disorders;
- for gastrointestinal dysfunctions - stool disorders, nausea, vomiting, flatulence, abdominal pain;
- with internal bleeding - vomiting blood, melena (black tarry stool), red urine or with clots;
- endocrinopathies - changes in body weight, polyuria (large daily amount of urine), tachycardia, etc.
Heart disease can be indicated by chest pain, swelling, heart rhythm disturbances, high or low blood pressure.
Additional tests
Useful information: Urobilinogen in urine is increased: what does this mean, reasons, norms for adults and children.
What is the danger of the condition? If there are deviations in the results of a biochemical blood test, you should contact a general practitioner (general practitioner). The specialist will evaluate the abnormalities, review other test results, interview the patient, and possibly make an immediate diagnosis. If the disease cannot be quickly identified, additional diagnostic methods are prescribed or a referral to a specialized specialist (endocrinologist, nephrologist, gastroenterologist, cardiologist, hepatologist, hematologist) is issued. The localization of the problem can be assumed based on combinations of analysis deviations:
- elevated creatinine, ESR, leukocytes may indicate an infectious disease, a chronic source of inflammation;
- high creatinine and urea indicate disorders of nitrogen metabolism and nephropathy;
- creatinine and high bilirubin, ALT may indicate liver pathology;
- creatinine and elevated AST occur in heart disease, myocardial infarction;
- with a parallel increase in cholesterol levels, complications of atherosclerosis (blockage of blood vessels with circulatory disorders) are possible;
- an increase in creatinine and amylase indicates diseases of the digestive system (pancreatitis, cholelithiasis);
- with high alkaline phosphatase, damage to the kidneys, liver, and musculoskeletal system is suspected.
As a further examination, tests for creatinine in urine, clearance, general blood test, and glucose measurement will be required. If damage to internal organs is suspected, ultrasound or MRI, endoscopic examinations may be performed.
Preparation and conduct of the study
Patient preparation is required for reliable results.
Donating blood for testing is required on an empty stomach. The last meal should be at least 8 hours before sampling. Before donating blood, you can only drink clean water.
For maximum accuracy of the analysis, you should not consume a large amount of protein food in the last 24 hours or subject the body to significant physical activity. If you are taking medications for a long time, you must first notify your doctor.
Symptoms
In fact, the problem of hypercreatinemia is quite common. Since it does not cause undue problems, many people do not give it any importance. Changes in concentration, and especially growth, are the result of various pathologies present in the body. It is worth noting that the condition itself does not manifest itself; it requires a reason and it is predominantly pathological in nature.
Symptoms of elevated creatinine
People encounter signs of hypercreatinemia every day, and it is worth noting that they do not always associate them with kidney diseases.
If there is an excess of the substance, the following symptoms are observed:
- muscle pain;
- tissue swelling;
- muscle hypotonicity;
- pain in the back, lower back;
- hypertension;
- decrease in the volume of urine excreted or increase;
- pathological indicators in urine tests (high protein, red blood cells, white blood cells).
Symptoms of elevated creatinine fit the description of many diseases.
Symptoms of low creatinine
Signs of low levels may vary. They are affected by the primary disease. They often manifest themselves more clearly with low muscle mass, liver disease, and addiction to strict diets.
Symptoms of decreased performance:
- prostration;
- pain in the upper abdomen;
- attacks of nausea;
- fainting state;
- weight loss.
The symptoms that appear with low creatinine are also quite applicable to other pathologies and usually do not cause much concern.
What could be the consequences?
Typically, a decrease in creatinine in itself does not entail negative consequences for the human body and is the body’s reaction to some subjective factors. Therefore, it is enough to change your lifestyle or diet, and this indicator will return to normal.
However, if the decrease is associated with serious pathologies or serious illnesses, then you should undergo a course of treatment. And only in case of complete recovery can we hope that creatinine will return to normal.
When creatinine values are too low
As we have seen, a physiological decrease in the concentration of creatinine in the blood is observed in children and during pregnancy. In the first case, due to slow metabolism, in the second case, due to an increase in blood volume and thinning of the blood.
Other reasons may be a vegetarian lifestyle, which involves avoiding animal proteins, or old age, when muscle mass decreases.
However, in some cases, a decrease in creatinine levels is pathological.
Low creatinine – tumors and muscle atrophy
Most often, a decrease in creatinine levels occurs in the following pathologies:
- Tumors: Some cancers, such as leukemia and prostate tumors, are characterized by decreased creatinine levels. The mechanism of this process is not yet well understood, but it is likely that cancer cells cause damage throughout the body.
- Muscle wasting: and generally all diseases that cause problems for the muscles, such as myasthenia gravis or muscular dystrophy, determine a decrease in creatinine values due to the fact that it comes from the conversion of creatine phosphate in the muscles. If this transformation does not occur because the muscles are not healthy, then you will have a decrease in creatinine levels.
Although these diseases are so serious that they are in an advanced stage before getting to this point, a proper diet can give us valuable help.
What is creatinine, and why is its level important?
Creatinine is the final link in the complex process of converting amino acid-protein compounds, accompanied by the release of the required amount of energy. The energy obtained as a result of successive reactions is consumed by muscle tissue, which ensures its constant contractile activity. Since muscles are one of the main structures of the body, having significant mass, a large amount of resources is required for their functioning.
At the same time, muscle structures are designed in such a way that they need powerful energy carriers that, if necessary, can provide the body’s emergency needs for energy resources. The main supplier of this type of nutrition for muscle structures is creatine phosphate - creatine phosphoric acid.
Upon completion of the synthesis carried out in liver cells, it is transported to the muscles, where the dephospholation process is started, for which the enzyme creatinine kinase, or as it is also called, creatine phosphokinase, is responsible. As a result, energy and creatinine are released. Energy is consumed by the muscles, and creatinine enters the urine and, after being filtered, is excreted by the kidneys.
Reference! Creatinine, after the completion of all biochemical reactions, is of no value to the body - it no longer participates in any metabolic processes. At the same time, it is a rather harmful compound, and should be removed from the human body as much as possible. In addition, it should be noted that failures in the creatinine chain of reactions can occur at any of the stages - entry, exchange and output.
The process of converting creatine into creatinine
How to take a creatinine test?
The research can be carried out in a state or private laboratory. Proper preparation is the key to accurate results.
Important: if red blood cells are destroyed during blood collection (the color of the blood in the test tube becomes dark brown), the analysis is canceled. Obtaining reliable laboratory analysis data in this case is impossible.
In order to reduce the risk of hemolysis (decomposition of red blood cells), the patient is recommended to drink large amounts of unsweetened water 2 to 3 hours before the visit to the laboratory. The study must be carried out on an empty stomach. Any sports are excluded 12 hours before, and smoking 30 minutes before.
Read further: How to reduce creatinine in the blood - treatment and diet
- About
- Latest Posts
Yulia Martynovich (Peshkova)
Certified specialist, in 2019 she graduated with honors from the Orenburg State University with a degree in microbiologist. Graduate of the graduate school of the Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education Orenburg State Agrarian University. In 2015 At the Institute of Cellular and Intracellular Symbiosis of the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, she completed advanced training in the additional professional program “Bacteriology”. Laureate of the All-Russian competition for the best scientific work in the category “Biological Sciences” 2019. Author of many scientific publications. More details
Deviations in creatinine levels from normal
The following factors influence the level of the substance in women:
Article on the topic:
What is urolithiasis? Symptoms and treatment in women
- Pregnancy (creatinine decreases in the first semester).
- Exercising, especially strength sports, increases the level of the substance.
- Eating large amounts of protein foods. Meat contains protein breakdown products, so with a protein diet, blood creatinine increases slightly.
- Using sports supplements (Creatine) to gain muscle mass.
- Taking certain medications (antibiotics, antipyretics, NSAIDs).
- Heavy physical work increases creatinine.
- A sharp decrease in creatinine occurs with strict diets, rapid weight loss, and severe toxicosis of pregnant women.
In all of the above cases, the deviation from the norm is physiological and does not require adjustment. After eliminating the provoking factors, for example, normalizing nutrition, rest, stopping medications, everything returns to normal.