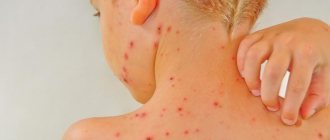
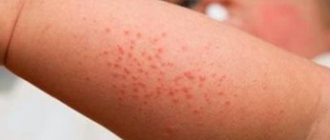
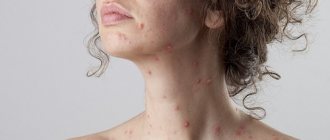
Skin problems are quite common in modern society and bring trouble and trouble to people. Rashes, redness, itching - these symptoms, in addition to worsening your health, also affect your appearance. Among skin diseases, cutaneous dermatitis is common, photos of the symptoms of which can be seen below. The development of the disease is associated with inflammation of the skin. Symptoms of dermatitis at an early stage are limited to itching, redness, and swelling. The disease does not pose a threat to human life, but if ignored, it can cause a lot of discomfort to the patient.
Causes
The skin disease dermatitis can be caused by a number of unrelated reasons. All of them can be divided into distant (acquired and genetic) and close (provoked).
The first group includes causes whose main characteristic is an individual predisposition (genetic or acquired). In almost 50% of infants, skin dermatitis occurs due to the fact that this disease was previously suffered by someone from their parents. Acquired predisposition occurs against the background of infectious, invasive diseases (especially in chronic form), unfavorable living conditions, mental anxiety, physical ill health, and weak immunity.
The second group includes pathogenic causes that caused the development of dermatitis in the body, which theoretically had no predisposition to this disease. These include stress, physical factors (frost, heat, solar energy), chemical substances, protein allergens.
Not all people develop skin dermatitis when exposed to pathogenic pathogens. Reasons in connection with individual stability are divided into mandatory and optional. Mandatory ones are those that cause dermatitis, regardless of the resistance of the human body. These include aggressive liquids, low or high temperatures (from 60 degrees Celsius), strong radiation (radiation, quartz, sun), strong allergens. Facultative factors affect people with individual hypersensitivity. This is a temperature of +4 degrees, some allergens (insect bites, cosmetics, oils and liquids, medicines, food, pollen).
Treatment methods for chronic dermatitis
Chronic dermatitis occurs with periods of exacerbation and remission. Treatment of the disease should be carried out both in the presence of symptoms and in its absence. Therapy outside of exacerbation consists of applying moisturizing creams, taking vitamin complexes, following a diet, and spa treatment. During an exacerbation, the doctor selects an individual set of drugs that will act on a specific type and subtype of dermatitis.
Diet for chronic dermatitis is of primary importance. Proper nutrition with the exception of highly allergenic foods will improve the patient's condition. With correctly selected therapy, periods of remission of chronic dermatitis are lengthened, and during exacerbation the pathology does not progress. Also, treatment of chronic dermatitis should include sanitation of foci of chronic infection: cystitis, pyelonephritis, caries.
Skin pathology usually occurs due to problems with internal organs, in particular the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, when chronic dermatitis is detected, it is necessary to be examined for diseases of the stomach and intestines, and if they are detected, appropriate therapy is carried out.
Treatment of eczema
Eczematous dermatitis is accompanied by weeping, therefore, local treatment begins with drying the lesions. To do this, the leather is treated with aniline dyes, and lotions are applied with resorcinol, delaskine or 2% boric acid. Lotions draw water from the source of pathology and have an astringent effect.
Also, when treating chronic seborrheic dermatitis, you can make lotions with tannin. To do this, brew strong tea and cool it to room temperature. Afterwards, moisten gauze folded in 5-6 layers in tea, squeeze well and apply to the site of inflammation. Every 5-10 minutes the gauze needs to be soaked in the solution again. Such lotions need to be carried out for 1-1.5 hours 2 times a day. Usually after this there is a significant improvement and the eczema becomes dry.
Lotions with other solutions are carried out in the same way. The procedure should not be performed longer than the specified time, otherwise the skin will lose a large amount of water, which will aggravate the severity of chronic dermatitis.
After the eczema lesions have dried, creams and ointments are applied to them. Considering that chronic inflammation is often accompanied by pathogenic microflora, it is recommended to use three-component ointments: Triderm, Triakutan, Trimistin, Pimafukort. They consist of topical corticosteroids, antibiotics and antifungals.
For the systemic treatment of eczema the following are used:
- antihistamines in tablets (it is better to use levocetirizine preparations);
- injections of antihistamines (Tavegil, Suprastin);
- for microbial eczema (which is more common than true eczema) - broad-spectrum antibiotics;
- for hyposensitization of the body - calcium gluconate (intravenously or intramuscularly) or sodium thiosulfate (intravenously).
All of the above treatments should not be used without consulting a doctor, especially drugs for systemic use.
Eczema
Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis
Therapy for chronic seborrheic dermatitis is mainly carried out using local remedies. Systemic treatment consists of taking antifungal tablets - Itraconazole, Fluconazole. They are prescribed for severe chronic dermatitis that does not respond to local therapy.
Local treatment for chronic seborrheic dermatitis is as follows:
- The use of antiseborrheic shampoos, which is aimed at destroying fungus on the scalp.
- Three-component creams should be applied to the face (ointments for the treatment of facial dermatitis are not recommended). Pimafucort cream has a good effect against seborrheic dermatitis.
- Lesions on the chest also need to be treated with three-component products (Pimafukort cream or ointment).
With seborrhea, it is especially important to find the pathology of the internal organs and carry out treatment. Seborrheic dermatitis is usually caused by diseases of the digestive system, so it is advisable to use probiotics during therapy.
Chronic seborrheic dermatitis
Symptoms
The skin disease dermatitis can occur in acute and chronic forms. Its symptoms are divided into mandatory (regardless of the reasons) and additional (depending on the reasons). A mandatory symptom is itching. The acute form is characterized by swelling and redness with unclear edges. In the chronic course of the disease, redness may be absent. Rashes (eczema) appear on the most mobile parts of the body (groin area, sides of the body, scalp, face, skin on joints).
Obligatory symptoms in the chronic form include lichenification - a condition when areas of the skin thicken and a rough pattern appears on them. Self-scratching and cracks on the surface of the skin may also be observed. In the acute form of dermatitis, exudative inflammation may occur. In addition, the patient develops peeling due to insufficient functioning of the sebaceous glands and dehydration of the skin.
The presence and nature of additional symptoms is important for the differential diagnosis of specific dermatitis. They are identified as a result of functional tests, laboratory tests, examination and questioning of the patient.
Treatment options
Dermatitis is treated with medications and physiotherapeutic procedures, but there is no universal method. In each specific case, the treatment regimen is selected individually, but there are several general principles:
- Accurate diagnosis – traditional and latest methods of skin examination are used to determine the causes of the disease.
- A complex effect on symptoms in order to eliminate all irritating factors and increase immunity.
- Continuity – treatment is carried out until the skin is completely regenerated.
Conservative therapy
The acute form of the disease is treated with local drugs, but chronic dermatitis requires an integrated approach. Skin rashes are treated with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs, which are available in different forms - ointments, solutions, creams, etc. Antifungal ointments successfully cope with seborrheic dermatitis. Treatment of a chronic disease involves taking corticosteroids. Severe ulcerative lesions can only be cured in a hospital setting.
General therapy includes taking antihistamines and immunomodulators, which are selected taking into account all the factors that provoked the onset of the disease. It is also important to eliminate all sources of chronic infection.
Diet and proper nutrition
If a patient is diagnosed with allergic dermatitis, diet and healthy eating are an integral part of treatment.
This is the only way to protect the body from receiving new doses of the allergen. In case of pathology, it is recommended to consume low-allergenic foods:
- protein - butter, lean meat and cottage cheese, fish;
- vegetable - zucchini, spinach, cucumbers, pears, cereals;
- drinks - fermented milk without dyes, green tea, still mineral water, apple compotes;
- desserts - dried fruits.
To correctly correct the daily menu, you can undergo examination using special markers. If this is not possible, new foods should be introduced into the diet in stages, at intervals of two weeks.
Folk remedies
As an addition to the main therapy and with the permission of a doctor, alternative medicine recipes can be used for treatment:
- Celandine - squeeze out the juice and dilute it with water, then apply to problem areas of the skin. During the period of remission, honey can be added to the product.
- Periwinkle - brew the leaves, leave and leave on low heat for ten minutes. Cool the broth, strain and add to bathing water. Squeezed periwinkle is suitable for a compress.
- Cornflower - pour boiling water, leave, cool and take twenty minutes before meals.
- The sequence is to brew, steep, moisten a gauze bandage and apply to problem areas. Perform the procedure several times a day.
- Grate potatoes, wrap in gauze and apply to the inflamed area, change the bandage after two hours.
- Aloe – grind and leave for twelve days. Then add castor oil and red wine, mix thoroughly. Apply the prepared mixture to the skin for twenty minutes.
Kinds
Depending on the nature and causes of the disease, skin dermatitis is divided into several types. The following are considered the main ones: contact (allergic and simple), seborrheic, toxic-allergic and atopic. Each of these types has its own symptoms, diagnostic and treatment features.
Depending on the influencing factor, such types of dermatitis are distinguished as perianal, actinic, keychain, infectious, bullous, polymorphic, caterpillar, symmetrical dysmenorrheic, perioral, golden. In addition, radiation, solar, purpuric, follicular, and cercarial dermatitis are distinguished. In early childhood, diaper dermatitis and exfoliative dermatitis of newborns are the most common.
All these types of skin diseases differ from each other, but they all invariably bring discomfort and trouble to the patient. In order for the treatment of the disease to be as effective as possible, it is necessary to establish the cause and then the type of skin dermatitis. If you start to counteract the disease in time, then there is a chance to prevent its development and protect yourself from unpleasant problems.
Prevention of dermatitis
Before you begin treatment for dermatitis, you first need to know how chronic dermatitis manifests itself. Treatment in this case can be of a very different nature. Therefore, it is best to go to a doctor, because treatment still needs to be carried out under the supervision of a specialist.
The doctor prescribes treatment depending on the type of dermatitis, as well as the severity of the disease. And it includes prevention and treatment. Sometimes simple prevention is enough to get rid of the disease. But most often the doctor prescribes a whole treatment complex:
- proper nutrition or diet, which is prescribed when the cause of dermatitis is allergic reactions to certain types of foods;
- drug treatment includes tablets, as well as ointments, solutions and creams (it all depends on the type of disease);
- physiotherapy - massages, water treatments, therapeutic exercises and other types of treatment to improve tone;
- anti-stress medications and antidepressants are used if the cause of the disease is stressful situations;
- travel to places where the climate is best suited for the patient;
- surgical intervention for acute forms of dermatitis.
The diet includes not only proper nutrition, but also the selection of things to which the patient will not be allergic. And these are things, cosmetics, and also a daily routine. Some allergy sufferers, for example, may suffer during certain seasons. For example, when poplar fluff flies around the city or when ragweed blooms. In some particularly severe cases of chronic dermatitis, the patient is prescribed a special antibacterial soap, which must be used to treat the affected areas.
Creams and ointments are used to treat lesions such as fungal parasites. But the main thing is to ensure that the patient does not have an allergic reaction to any component of the drug.
It is not recommended to use harsh soap and washcloth while showering. It is better to limit yourself to gauze or a special soft washcloth. Buy soap in liquid form. And you need to wipe your body carefully so as not to damage the skin.
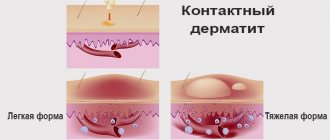
Contact skin dermatitis (simple)
Contact dermatitis can be simple or allergic. The causes of the first type of disease are the effects of biological, mechanical, physical and chemical factors.
Simple dermatitis can occur in acute or chronic form. Acute skin dermatitis (photos of the skin condition with it can be seen in our article) have pronounced symptoms. First of all, swelling and bright redness of the skin occur. Then small bubbles and nodules form. In some cases, crusts and scales are observed. The patient's condition is characterized by pain, itching, burning, and a feeling of heat.
The occurrence of a chronic form of simple dermatitis is associated with constant friction and low pressure. Infiltration, lichenification and thickening of the skin occur due to thickening of the hyperkeratosis and epidermis. For example, the development of radiation dermatitis in chronic or acute form is facilitated by ionizing radiation. The radiation type of the disease can manifest itself as a bullous reaction, hair loss, and erythema. Its further progression leads to skin atrophy, pigmentation disorders, persistent alopecia, and the development of a necrotic reaction with the formation of ulcers and erosions that are difficult to heal.
Simple skin dermatitis can appear on the face, arms, legs, and torso. The disease caused by exposure to a chemical factor is particularly acute: scabs form on the surface of the skin, in place of which ulcers remain. Ignoring the disease can cause it to spread throughout the body, making it very difficult to get rid of it.
Course of the disease in childhood
The most common types of dermatitis in children are:
CONTACT. It may appear as a result of the use of poor-quality hygiene products and external irritants (rough seams on clothing, poor-quality ointments and creams for treating the skin), which cause skin disorders, especially in infants (pictured). As a rule, in children, contact dermatitis may disappear after cessation of interaction with the provoking factor. Symptoms of contact dermatitis occur in three stages: erythematous, vesicular and necrotic.
NAPPY. This form of the disease develops in infants when the rules of care are violated. External irritation most often appears on the gluteal region, as well as on the thighs. Its manifestations are expressed by redness of the skin, rashes and peeling.
The baby's behavior becomes restless, he may refuse to eat, try to remove the diaper, sleep restlessly and often cries. Sometimes a baby may develop intestinal dysbiosis. In all cases, the child must be shown to a pediatrician, who will examine the baby and conduct a conversation about the rules of caring for the child’s skin. Based on the symptoms, the doctor may prescribe treatment using special creams or ointments with the addition of lanolin. Diaper dermatitis in infants should be treated with drug therapy only as a last resort. It is necessary to observe preventive measures (after bathing the baby, lubricate the skin with moisturizing creams; do not wrap the baby tightly, preventing normal air exchange).
ATOPIC FORM. Allergic dermatitis is characterized by skin redness (especially on the face) and peeling. In addition, the atopic variant of the development of the disease can have a chronic course, therefore, to prevent exacerbations, it is necessary to diagnose symptoms in a timely manner, and then carry out appropriate therapy. The symptoms of atopic dermatitis occur with slight differences in children of different age categories.
Most often, pathological symptoms on the face and entire body occur in children 5-6 months old and are expressed by a hyperemic rash in the buttocks, face and neck. In a child, allergic dermatitis is accompanied by severe itching and the child may scratch the area, which can lead to infection. In this case, the child may experience a rise in temperature and restless behavior.
Atopic dermatitis in an older child can be localized in the groin area, popliteal and elbow. In addition, skin dermatitis at this age often occurs in the palms and soles. The skin in the affected area thickens and becomes swollen. During the lull of atopic dermatitis, the child's skin may be dry, so it is recommended to use moisturizing ointments.
Dermatitis can quite often provoke the development of intestinal disorders. The reasons for this manifestation are explained by the fact that atopic dermatitis in children occurs due to violations of feeding conditions and non-compliance with hygiene measures.
If children experience skin changes and restless behavior, it is necessary to seek advice from a specialist, since atopic dermatitis must be treated at the initial stage. If an atopic type of disease is diagnosed, it is necessary to review the diet (especially in infants). In addition, it is recommended to use only hypoallergenic products and detergents. Antihistamines and other drugs are prescribed for atopic dermatitis only when absolutely necessary.
SEBORRHEA FORM. Occurs when mycotic activity increases with disturbances of opportunistic microflora. In children, the pathological process is often localized in the head and face (redness, thickening of the skin, hair loss on the head and other characteristic symptoms). The appearance of white patches on the head is accompanied by minor itching and pemphigus.
Atopic dermatitis and seborrheic form are characterized by periodic remissions and exacerbations. In the initial form, a medical examination and further treatment are necessary.
Atopic dermatitis and seborrheic form are characterized by periodic remissions and exacerbations. In the initial form, a medical examination and further treatment are necessary.
Allergic dermatitis
Allergic skin dermatitis occurs as a result of direct exposure to an allergen. The development of the disease can be caused by pathogens of chemical origin (washing powder, cosmetics, perfumes, paints and varnishes, synthetic materials), medications, plants, and animals. The course of the disease largely depends on the degree of exposure of the allergen to the skin, on the condition of the body and the patient’s immune system.
Acute allergic contact dermatitis causes changes in the area of skin that came into direct contact with the allergen. The area of influence may expand slightly depending on the nature of the pathogen. With allergic dermatitis, clear contours of the affected area appear. Symptoms appear gradually. First, swelling of the tissues and redness of the skin are observed, then fluid-filled blisters are noted, which form areas with erosion after opening. Healing begins with crusting the skin and ends with peeling. Allergic skin dermatitis is accompanied by constant itching. The chronic form develops as a result of prolonged exposure to the allergen on the skin after the allergic reaction has appeared. As a result of severe itching, external damage to the skin surface occurs, its thickening, peeling and dryness.
Symptoms and types
Chronic forms of dermatitis can manifest as individual symptoms (itching, redness, peeling) or be a whole disease. Then skin lesions are the main symptoms (seborrheic, atopic dermatitis, etc.)
Chronic contact dermatitis
The main symptoms are stagnant, constant redness of the skin, swelling, thickening of the outer surface of the skin, the appearance of cracks, peeling. The lesion corresponds to the size and shape of the irritating factor.
Itching may develop. Usually it does not appear outside of contact with the irritant and exists at first only when interacting with the cause, disappearing when it is eliminated.
The clinical picture of the disease can be varied - it all depends on how strong the irritant affected the skin, how long this effect lasted, what immunity the body has and others.
In the future, inflammation persists even without interaction with the irritant, but at the same time significantly weakens.
Allergic dermatitis
It also develops upon contact with an irritant. It differs from chronic contact in more extensive lesions that spread beyond the site of interaction with the allergen.
The symptoms are simple and include itching and redness on a certain part of the skin. The situation is also accompanied by the appearance of bubbles with erosion.
The first signs appear after 5-10 days, sometimes after several weeks. Signs of chronic allergic dermatitis are redness, itching or burning, and swelling. Often bubbles, nodules appear, crusts appear, and weeping.
Eczema
Chronic, often relapsing disease. Manifested by rashes and inflammation.
There are several main forms of eczema:
- True. During periods of exacerbation, it manifests itself as swelling, redness of the skin, rashes of small blisters and nodules. The bubbles burst, forming erosions from which liquid exudate oozes. When drying, the exudate turns into gray-yellow crusts. Due to the wave-like nature of the rash (rashes appear in “portions”), crusts, blisters, and erosions are simultaneously present on the skin. It starts from the hands or feet and is symmetrical in nature. Patients are bothered by severe itching. As the exacerbation subsides, eczema becomes more calm and manifests itself as peeling, cracks in the skin, and areas of dryness.
- Pruriginous eczema differs from true eczema in the nature of the rash. Instead of blisters, severely itchy papules appear (bubbles without a cavity or liquid inside) 1-2 mm in diameter.
- With dyshidrotic eczema, small blisters and papules appear, up to 1 mm in diameter. They are located on the lateral surfaces of the fingers, soles of the feet and skin of the palms. It has a relatively “calm” course, but can sometimes be accompanied by severe itching.
Atopic dermatitis
Genetic, chronic, often recurrent skin disease. The current may be:
- paroxysmal (episodes of exacerbations alternate with periods of calm);
- permanently manifesting (symptoms are always present, only their intensity changes);
- asymptomatic with the appearance of signs only during contact with the allergen and their persistence for a short time.
Atopic dermatitis usually manifests itself as itchy skin, which persists even after the rash disappears.
The allergen can be plant pollen, house dust, animal hair, various food products, household chemicals, etc. There are airborne, contact and food routes of allergen penetration into the body.
Itching intensifies in the evening and at night, preventing patients from sleeping. The skin is dry, inflamed, reddened, and the following are found on its surface:
- papules;
- small (up to 1 mm) bubbles filled with exudate;
- peeling, scales;
- signs of scratching (scratches, abrasions, desquamation of the surface epithelium in the form of erosions and abrasions).
In the erythematous-squamous form, dry skin, itching, fine flaking, and scaliness predominate. Flat and round papules, up to 0.5-1 mm in size, are found on the skin. The lesions are located on the inner surface of the elbow joints, hands, and behind the knee.
The lichenoid form of chronic atopic dermatitis is accompanied by severe dry skin against the background of its swelling and inflammation. Large, few papules covered with scales are found in the lesions. Along with extensive skin damage, separate areas of peeling are found in the upper third of the chest, on the back and neck. Natural folds contain abrasions, scratches, erosions and cracks.
The pruriginous form is characterized by large individual papules of dense consistency, spherical in shape in the upper third of the body, on the arms and face.
The eczematous form of chronic atopic dermatitis is manifested by small papular rashes against a background of crusts, cracks and peeling. The surface is inflamed, but slightly changed in color. The lesions are located on the hands.
Seborrheic dermatitis
An inflammatory chronic disease of the skin that occurs due to the activation of opportunistic fungi. Appears due to increased function of the sebaceous glands of the face, torso, neck, and scalp. The result is redness and peeling of the lesions. The main location of foci of chronic seborrheic dermatitis is the scalp, which contains a large number of sebaceous glands. Often the process spreads to other hair-containing areas of the body: mustache, beard, pubis, perineum and anus. In severe cases, the disease may spread to hair-free skin of the body.
The human body can control the growth of fungi. However, due to weakened immune defenses, frequent stressful situations, endocrine disorders, and nervous diseases, this natural ability is lost. Yeast-like fungi begin to grow and multiply.
The lesions appear as itchy areas with peeling and redness. The skin is swollen, a huge number of scales are visible on its surface. Even before pronounced inflammatory-edematous symptoms, seborrhea is manifested by increased formation of dandruff, which cannot be treated, and itching that appears during psycho-emotional stress, after acute respiratory viral infection, and when working in polluted conditions.
Atopic dermatitis
Cutaneous atopic dermatitis is an inflammation of the skin of an allergic nature. This chronic disease is genetically determined. There are a lot of factors that may be involved in the development of the disease: allergens entering the patient’s body through the respiratory (by inhaling dust, pollen), contact, and food routes. Most often, the disease develops at an early age and can remain for life if it is not treated in time. In most cases, atopic skin dermatitis first appears on the hands (photo attached in our article). A hereditary predisposition to allergic reactions increases the risk of developing the disease.
The occurrence of atopic dermatitis is associated with internal problems in the body and problems in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. The body cannot cope with some substances that enter it: the intestines do not digest them, the liver does not neutralize them and the kidneys do not remove them, after which they become antigens, to combat which antibodies are produced. Antigens, together with antibodies, are the cause of the rash.
Symptoms of the disease
All symptoms of the disease are divided into mandatory and additional. Obligatory ones occur in all types of dermatitis.
- Redness of the skin. The capillaries are intensively filled with blood. Erythema does not always appear during the chronic course of the disease.
- Skin rashes, eczema. The rash occurs on any part of the body.
- All stages of the disease are accompanied by itching. Its intensity increases as the disease progresses.
- Formation of blisters with clear or purulent exudate. Localized mainly on the legs.
- Peeling of the skin. The epidermis becomes dry, peels, and cracks.
- In the later stages of the disease, fever, general weakness, and headache are noted.
Additional symptoms include:
- anxiety, depression, sleep disturbance;
- failure of the digestive system;
- disturbance of intestinal microflora;
- thinning of the walls of blood vessels;
- disruption of the nervous system.
Chronic dermatosis is localized in different parts of the body.
- On hands. The skin between the fingers and on the outer surface dries out, turns red, and cracks. Severe itching, burning, and rarely a rash occur. Dermatitis on the hands is caused by food allergies, contact with household chemicals, cosmetic products and external factors.
- On the face. Dermatitis affects the hairline, forehead, ears, and wings of the nose. The main causative agent is a fungal infection and an allergic reaction.
- On foot. Localization in the leg area is most common. Dermatitis is caused by a fungal infection, external factors, or an allergic reaction. Manifests itself in the form of itching, burning, and rashes on the skin. Tight and poor-quality shoes can provoke the disease. A type of disease on the legs is varicose dermatitis. In the later stages of the disease, trophic ulcers form. Difficult to treat.
Dermatitis in children
Skin dermatitis is very common in children. Its appearance may be associated with the state of immunity, the mother’s lifestyle during pregnancy, and the immaturity of the baby’s body. There are chances that the child will “outgrow” his allergy, but parents need to take immediate action when the first signs of the disease appear. It is worth paying attention to manifestations that may precede the development of skin dermatitis. These include disturbances in the functioning of the intestines, peeling and increased dryness of the skin, hyperemia of a certain area of the skin, burning and itching of the inflamed area, nervousness, irritability, and insomnia.
In children, skin dermatitis most often occurs on the arms, legs and face. The disease is caused by the penetration of allergens into the body. There are three ways of getting into them: through breathing, exposure to the skin and ingestion. It is worth remembering that skin dermatitis in a child can cause complications and affect his future life activities, so it is recommended to take preventive measures. So, the baby needs to be breastfed for as long as possible, and the mother must follow the correct diet during lactation. At the first symptoms of intestinal disorder, appropriate treatment should be carried out. It is important to correctly create a child’s menu so that it does not contain products that could cause allergies.
Causes of dermatitis
As a rule, all types of dermatitis have individual causes for the development of the pathological process. For example, toxidermia provokes food allergens or medications (antibiotics, sulfonamides, etc.). The likelihood of skin dermatitis increases sharply in patients with a mental history and gastrointestinal diseases. In addition, it can develop with unregulated use of oral contraceptives. The reasons for this are hormonal imbalances, which leads to endocrine changes.
Exogenous reasons:
- irritation of the skin with buttons, buckles, paws, etc.;
- use of synthetic fabrics;
- use of low-quality household chemicals;
- exposure to low temperatures on the skin;
- use of low-quality decorative cosmetics on the face;
- contact with certain plants;
- perfumery products;
- hygiene products (most often shampoo for washing hair on the head);
- chemicals, etc.
Directly allergic dermatitis is possible not only to unknown allergens, but also to well-known products that have not previously caused symptoms of dermatitis. This reaction can especially often occur in a child.
Diagnostics
As a rule, the diagnosis of simple dermatitis does not require special studies. An experienced doctor can determine by sight the presence or absence of a disease, its type, and degree. A superficial examination of the affected areas of the skin may not be sufficient if allergic dermatitis occurs. Then the dermatologist may prescribe a general blood test or take a scrape from the affected surface of the skin.
Diagnosis of the disease depends on its type. The first thing the doctor needs to determine is whether it really is dermatitis, because some forms of the disease may have symptoms similar to psoriasis or some other skin disease.
Areas affected by dermatitis
Symptoms of chronic dermatitis can appear throughout the body, but most often specific areas of the body are affected.
- Hands, area between fingers. The skin in these areas dries out, turns red and cracks, while the patient feels very itchy, and the skin may become covered with small pimples. This can be caused either by an allergic reaction to some product, or by interaction with household chemicals, hygiene products and cosmetics.
- Face. In particular, the affected area is limited to the roots of the hair, the forehead, ears and sides of the nose. In this case, the cause of dermatitis can be either a fungal infection or an allergic reaction.
- Legs. These are the most common areas affected by the disease. At the same time, the patient wants to itch constantly. Either small pustules or redness appear on the legs. This is due to a variety of reasons: fungal infection, allergies, a wide variety of external influences. For example, one of the reasons is heat rash, which appears when the leg does not “breathe” for a long time and is constantly in a humid environment.
Traditional medicine
If a person is faced with this disease, then the question arises: “how to treat skin dermatitis?” It is recommended to immediately consult a doctor who can find out the causes, type, and degree of the disease, and then prescribe effective medications.
An important step on the path to recovery is to rid the patient of exposure to the irritating factor. Any type of skin dermatitis can be improved with a hypoallergenic diet. Antihistamines (Telfast, Claritinide, Claritin, Tavegil) will help reduce swelling and infiltration and eliminate itching. Skin dermatitis, the treatment of which must be carried out comprehensively, in the later stages can cause a number of problems for the patient. To neutralize allergens from the inside, detoxification therapy is prescribed (sodium thiosulfate, Polypefan, activated carbon).
For local treatment, hormonal ointments are prescribed (Akriderm, Diprosalik, Sinaflan). Weeping dermatitis should be treated with tinctures of oak bark, chamomile, and antiseptics. To prevent neurological disorders that arise due to burning and itching of the skin, mild sedatives of plant origin are prescribed (tincture of peony, valerian, motherwort, Novo-Passit, Persen). If the cause of dermatitis is stomach upset, then it is necessary to take medications to restore normal intestinal microflora (Mezim, Linex).
Ointments for dermatitis and skin diseases in adults
Dermatitis has several varieties:
- contact - occurs when an irritant directly affects the skin;
- atopic - exposure to allergens;
- seborrhea - fungal infection;
- infectious - bacterial damage (eczema, herpes, acne, acne).
In turn, these types of dermatitis are divided into types:
dry dermatitis - peeling, itching, crusting, possible cracks;
- weeping - on the reddened skin, hills with bubbles on the top may appear, which subsequently burst;
- itchy - the appearance of irritation on the skin, which brings an unpleasant sensation that causes particular discomfort; a person constantly wants to itch.
Modern medicine allows humanity to recover from this disease and offers different approaches to treatment.
Treatment of dermatitis should not be delayed, otherwise it will complicate the situation. The disease must be treated from the inside and outside. Thus, it is unacceptable to use only local effects on inflamed areas, since this will only have a cosmetic effect and will not get rid of the problem itself.
There are several ways to treat skin dermatitis - drug treatment and treatment using folk remedies. It should be remembered that when choosing the right treatment approach, one must not forget about the doctor’s recommendations. Only a doctor can prescribe effective treatment specifically for your case.
note
In the field of pharmaceutical services, a great variety of treatment options can be offered, but each of them has its own contraindications and side effects, so self-medication is not recommended.
Medicines for dermatitis come in different forms, such as tablets, even injections, drops, syrups, creams, ointments, shampoos, etc. are possible. Having found out the cause of the occurrence, it is worth removing this inflammatory pathogen. For allergic dermatitis, it is necessary to remove the source using antihistamines (drops, tablets, gels, ointments). They also prescribe drugs that remove toxins from the body (activated carbon or other sorbents).
Fungal dermatitis is treated with topical preparations that contain zinc and salicylic acid. For dry dermatitis, ointments and gels are used to moisturize the skin; if it is accompanied by itching, they also relieve this symptom. If the affected area becomes wet, then local antiseptic drugs are used.
Any of the drugs should be used with caution, and if any of them for any reason has a negative effect, then you need to replace it by contacting a doctor. If a child requires treatment, then it is definitely impossible to do without the help of a specialist. The child's body is still so delicate and susceptible to all external influences that one should be wary of the occurrence of adverse reactions when using medications.
Treatment with folk remedies
Not only traditional, but also folk medicine has recipes that help overcome skin dermatitis. Treatment with plants in some cases can be even more effective than taking medications. To improve the condition, traditional healers use the properties of plants that have anti-inflammatory, antiseptic, antiallergic, and mild sedative effects. Skin dermatitis requires a comprehensive approach to therapy, so traditional medicine can be both auxiliary and alternative.
To eliminate irritation, eczema, and itching, use a decoction of birch buds. For skin diseases in Tibetan medicine, decoctions and infusions of grape leaves are used externally. A decoction is prepared from oak bark for compresses and washes. St. John's wort juice is applied to areas of skin affected by dermatitis for disinfection. Purulent wounds, burns, eczema will heal faster under the influence of raw grated potatoes. For purulent focal inflammation, sweating, and skin itching, an ointment prepared from petroleum jelly and fresh cranberry juice is used externally.
Among other plants whose properties are used in the treatment of skin dermatitis, the following also stand out: chamomile, plantain, dandelion, linden, celery, yarrow, burnet, thyme, pine, black currant. They all have their own sphere of influence. Some are intended for external use, others for internal use. And if you have any of the listed plants on hand, then simply make a decoction, soak the affected areas with it and your skin will immediately feel better. If you use diet therapy, medications and traditional medicine in combination when treating dermatitis, you can very soon forget about this unpleasant problem.
Dermatitis - treatment
It is quite possible to completely cure dermatitis - symptoms and treatment, which depend on the type. To do this, you need to take adequate therapy, change your diet and give up bad habits. Treatment of dermatitis includes eliminating the irritant, destroying harmful microorganisms, taking sorbents, eliminating sucrose, using special ointments and other measures.
- Dermatitis on the legs of a child or adult - types, symptoms and treatment
- What are autoimmune skin diseases - causes, symptoms and treatment
- Types of dermatitis in children and adults
In children
The main therapy is eliminating the connection with the allergen, using medications, and preventive measures. Medicinal shampoos, creams, and preparations based on dexpanthenol (Bepanten, Desetin) are used. The child additionally needs vitamin therapy to strengthen the immune system. Treatment of dermatitis in children is also carried out using traditional methods.
In adults
Traditional therapeutic methods include identifying the cause of the disease, observing personal hygiene rules, and taking anti-inflammatory and antihistamine drugs. If the symptoms are pronounced, then hormonal therapy with corticosteroids (Dexamethasone, Prednisolone) is added to the main treatment of dermatitis in adults. In case of a simple contact form of the disease, the lesions are treated with hydrogen peroxide, a solution of potassium permanganate (weak) or alcohol.
Dermatitis treatments
Local therapy is carried out using disinfectant lotions, powders, photoprotective agents, corticosteroid aerosols, and ointments. Common medications for the treatment of dermatitis include ascorbic acid, diuretics, enterosorbents, potassium orotate, calcium pangamate, calcium pantothenate, and in severe cases, neohemodesis and corticosteroids.
Folk remedies
How to treat dermatitis using natural ingredients? You can independently prepare an ointment to eliminate pathology, which is mixed with glycerin and St. John's wort juice (1:1) or with petroleum jelly and cranberry juice (4:1). Treatment of dermatitis with folk remedies is carried out at night. The ointment should be applied to the affected areas and covered with gauze. Lotions with tincture of birch buds (1 tablespoon per glass of boiling water) are effective. The products must be used daily until the problem is completely eliminated.
Prognosis and complications
The general prognosis for recovery from dermatoses is favorable. But for this, one important condition must be met - timely treatment at an early stage of the pathology. Otherwise, complications are possible in 30% of cases during the patient’s life. With atopic dermatitis in children under 3 years of age, critical periods of exacerbation occur, regardless of the type of therapy. Re-formation of skin rashes is possible during puberty - from 12 to 17 years (puberty).
Dermatoses manifest themselves in the form of clinical wave-like flows. According to statistics, in only 60% of patients the symptoms of the disease completely disappear. 40% experience relapses throughout their lives.
Prevention
Prevention of dermatitis consists in prolonging the recovery period and in the absence of exacerbation of the pathology after a course of treatment. In particular, in case of contact skin lesions, it is necessary to exclude direct contact with the allergen; read more about the treatment of contact dermatitis here. In case of an atopic reaction of the epidermis, the underlying disease is prevented - this is usually the gastrointestinal tract or nervous system. The patient is advised to adhere to a strict diet that excludes allergenic foods: red fruits, citrus fruits, chocolate, foods with chemical dyes.
Allergic dermatitis occurs after being in a dusty room, contact with animals, plants. To prevent exacerbation of the skin immune reaction, it is recommended to take antihistamines.
With seborrheic dermatitis, it is necessary to strengthen the protective functions, since fungal microorganisms multiply in a weakened body. Drugs for the treatment of seborrhea are described here.
Please note that it is not recommended to expose the affected skin to hot water or use aggressive detergents. In order to prevent exacerbation of skin itching and redness, it is recommended to adhere to a diet, avoid stressful situations, and normalize the water balance in the body. For patients with dermatological problems, sanitary spa treatment is indicated.
In conclusion, we repeat that chronic dermatitis, in its clinical symptoms, is not a separate disease. Acute skin disease, if left untreated, becomes severe chronic. If itching, redness of the epidermis, burning, swelling and pain occur, you should contact a dermatologist. The prolonged course of the disease leads to scars on the skin, atrophy of the dermis, loss of sensitivity, trophic ulcers and erosions. Dermatitis is treated with antihistamines, hormonal ointments, and detox medications.
Treatment
The basic principle of treating pathology is to eliminate the effect of the allergen on the epidermis. The patient is prescribed a strict hypoallergenic diet, which helps reduce the symptoms of itching. If the cause of the disease is internal disorders in the body - diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, genital organs, endocrine and nervous systems, then emphasis should be placed on treating the root cause.
For adults
An adult with dermatological problems is prescribed complex treatment:
- Antihistamines – Clemastine, Citrine, Loratadine;
- Detox therapy aimed at removing toxins - activated carbon, Smecta, sodium thiosulfate injections in severe clinical cases;
- Non-hormonal ointments - Elidel, Naftaderm, Destim, Aisida;
- Treatment of affected areas with herbal decoctions;
- The use of antibacterial ointments – Tetracycline, Lincomycin;
- Sedatives – Novopassit, Glycine, motherwort tincture.
Weeping, erosive areas of the epidermis are cleaned with tar soap, treated with chlorhexidine, and a drying zinc ointment or regular baby powder is applied.
For children
Treatment of dermatosis in a child should be gentle. Dry erosive areas are treated with cream with Panthenol - Bepanten, Dexpanthenol. For deep lesions of the epidermis, hormonal glucocorticosteroids are prescribed in the form of an ointment - Advantan, Elokom. When using hormonal products, it is recommended to mix them in a 1:1 ratio with baby cream. To relieve inflammatory processes, use zinc ointment, lanolin, and a decoction of medicinal herbs.
As maintenance antihistamine therapy, children are given Tavegil, Suprastin, as well as calcium gluconate in combination with vitamin D to improve the absorption of medications.
Traditional methods
In addition to drug treatment prescribed by a doctor, you can use traditional methods. Before using traditional medicine in the treatment of dermatoses, you need to consult a doctor, as adverse reactions and complications after self-medication are possible.
An effective remedy for dermatitis is celandine juice. It should be applied in its pure form to the affected areas of the epidermis. It is not recommended to treat open wounds and ulcers with celandine.
Persons with dermatological diseases are recommended to take medicinal baths with a decoction of string, chamomile, and oak bark. Areas of redness and itching are treated with tar soap, which can be purchased at any store. Inflamed areas of the skin are spot-treated with tea tree and grape seed essential oils (ratio of 5 drops of essential oil per 10 ml of base oil). For trophic ulcers, compresses made from raw grated potatoes are used.
Diagnostic methods
The latest methods for diagnosing the disease
To accurately diagnose a disease that occurs at any age, you need to seek help from a specialist. Determining the disease itself is a simple procedure; based on the symptoms and location of the rash, you can determine its type. But in order to identify the true irritants that cause the disease, patients need to undergo a series of tests:
- You will need to take a general urine test;
- Blood, biochemical analysis reveals the amount of immunoglobulins contained in the blood;
- Examination of the secreted fluid from the formed foci of inflammation, thus revealing the presence of bacteria and fungi;
- The so-called fluid culture tank allows you to determine the patient’s response to various types of antibiotics in case they are needed;
- Immunogram - this type of study will allow you to assess the condition and performance of the immune system;
- When contact dermatitis is diagnosed, skin samples are tested.
These are not all studies that can be prescribed to a patient; the list depends on the stage and type of disease; in addition, ultrasound examinations (ultrasound) are sometimes prescribed.
What causes skin dermatitis?
For different people, the causes of this disease can be completely different, since the pathological process is individual for everyone. You can see what skin dermatitis looks like in the photo on the Internet. But it is better to remember the reasons for its appearance.
So, toxicerma, as a rule, is caused by drugs that contain antibiotics or sulfonamides. Skin dermatitis can also develop due to taking oral contraceptives.
Exogenous dermatitis can be caused by:
- Household x
name
- Cheap shampoo and wash (foam or shower gel)
- Non-natural fabrics
- Poor quality perfume products
- Some (especially poisonous) plants
- Skin irritation (for example, collar or button rubs)
- Poor quality cosmetic products
- Low ambient temperatures
As you can see, there are more than enough reasons for the appearance of dermatitis. It can also be caused by certain foods.
Types of dermatitis
There is a complex classification of types of disease, according to which types of dermatitis are divided according to several symptoms. Almost all names have a couple of synonyms. The types of dermatitis in adults and children are the same. For the latter, the causes of the disease are slightly different factors (reactions to diapers, foods, dysfunction of the body). Types of dermatitis in children and adults are classified according to factors:
- By localization: contact, atopic.
- According to reactions: allergic, inflammatory, infectious, fungal.
- By nature of manifestation: acute, chronic.
- By name of the rash: bullous, vesicular, scaly.
- According to the main symptoms: dry, itchy, exudative.
Dry
In cold weather, older people or people with extremely dry skin experience dry dermatitis. The cause of its manifestation is a genetic predisposition to allergies, cold dry air, and heredity. The dry appearance is localized on the feet, less often on other areas of the skin. It manifests itself as severe dry skin, cracks, itching, inflammation, redness, and filling of cracks with exudate. The disease can weaken the immune system. Symptoms occur when:
- disruption of the functioning of the sweat and sebaceous glands;
- deficiency of amino acids and microelements;
- dehydration.
Infectious
Infectious dermatitis occurs in the superficial and deep layers of the skin, the causes of which are a history of chickenpox, measles, scarlet fever, injury, postoperative complications and the penetration of microorganisms into the skin. Development factors include staphylococci and streptococci. The infectious form in the patient manifests itself in vague pustules, abscesses in the subcutaneous tissue. Sometimes boils, boils, carbuncles, and phlegmons appear - these are inflammations:
- hair follicles;
- sweat glands;
- surrounding tissue.
Atopic
Diffuse neurodermatitis, or atopic dermatitis, is considered a chronic skin disease associated with allergies. The main symptoms are inflammation, severe itching, dry skin, and the appearance of red spots and plaques. When scratching, the skin becomes covered with erosions. Localization of symptoms: joint bends, neck, forehead, temples, wrists, hands and feet. The causes of the manifestation are hereditary predisposition, age under 12 years, and the body’s rapid response to allergens. In the absence of therapy, the disease becomes chronic, with remissions and complications.
- Infectious dermatitis in children and adults - symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
- Dermatitis on the legs of a child or adult - types, symptoms and treatment
- Symptoms and treatment of seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp with ointments, preparations and shampoos
Contact
The collective term is the concept of contact dermatitis, which characterizes the appearance of acute or chronic diseases when the skin is exposed to irritants in the form of chemicals. The type can be called a delayed allergic reaction; everyone has a predisposition to it. There are several types:
- simple – the cause is irritation from chemicals (acids, alkalis);
- allergic – reaction to metals, cosmetics, oils, dyes, plants;
- phototoxic - occurs due to the action of ultraviolet radiation.
Symptoms appear on areas of the skin exposed to irritants. The first signs appear immediately, but sometimes the appearance time takes several days. The contact type is characterized by redness, swelling, itching, and the appearance of blisters with clear liquid. They pass, but erosion and pain occur at the site of the rash. If you get rid of the acute process, a yellow crust will remain.
Allergic
A type of contact dermatitis is allergic dermatitis, which is a disease that is the body's response to exposure to an irritant through contact with the skin. Causes of occurrence: washing powders, metals, medications, cosmetics, food products, latex. Clinical manifestations resemble eczema, which is acute in nature - red spots, small blisters, they burst and leave a weeping surface. Scales and crusts may appear in large quantities, swelling may develop, the skin will turn red, and the itching will intensify.
Seborrheic
Seborrheic dermatitis or seborrheic eczema is considered one of the types of inflammatory processes of the skin. It affects people under 40 years of age and is a common disease in men. Symptoms develop on the scalp and face. The cause is excessive proliferation of the fungus in the sebaceous glands of the head, nose, forehead, chest and interscapular area. Due to the development of the parasite:
- the sebaceous glands stop functioning normally;
- irritation and itching occurs;
- pores become clogged.
Symptoms of seborrheic type include itching, irritation, redness of the skin, white or yellowish scales, and peeling. Acne is visible on the face, the skin is painful and especially sensitive. Under the scales there are wet areas, eyebrows, nasolabial folds, and lips are affected. When touching the scalp, a “seborrheic crown” is visible - a clear border along the forehead with a matte red tint and greasy scales. The skin behind the ears, cheeks, and chin may be affected. During therapy you should follow a diet.
Oral
Perioral, perioral or rosacea-like is also the name for oral dermatitis, which is rarely encountered in medical practice. It affects only 1% of people, most often women under 40 years of age. Small papules, pimples, and redness appear on the skin near the mouth and chin. Over time, the rash leads to irritation and the growth of papules over a large area. Pimples may have a head with clear liquid, which over time develops into an abscess. Gradually, the rash creates colonies, the skin becomes covered with transparent scales.
The reasons are a decrease in local immunity, climate change, and prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation. A rash can be caused by hypersensitivity to bacteria, the use of local corticosteroids, or a predisposition to allergies. If your facial skin is too sensitive, using too much cosmetics or hormonal imbalance, unpleasant symptoms also appear. They can be provoked by products containing paraffin, petroleum jelly, and cinnamon flavorings. Treatment should begin with consultation with a specialist.
- Fungal dermatitis in children and adults - causes, symptoms, diagnosis and drugs for treatment
- Types of dermatitis in children under one year of age - causes, symptoms, treatment and nutrition at home
- What are autoimmune skin diseases - causes, symptoms and treatment
Fungal
Fungal dermatitis is characterized by peculiar mycids rashes. It is an allergic rash in the form of primary papules and pustules and secondary crusts. The reasons for the development of a colony of fungi are disorders of the immune, endocrine systems, resistance of the skin and body to pathogens, and high humidity. The doctor prescribes treatment for the patient and suggests the necessary measures to the child’s parents. You can consider folk remedies.
Ear
Ear dermatitis manifests itself in acute and chronic types. The disease is accompanied by severe itching. The acute form is characterized by flat redness, swelling, urticaria, papules and blisters. The prolonged type brings peeling, weeping crusts, erosion, and ear congestion. The causes include scratching the shell, skin irritation, fungal growth in the ear canal, and skin damage from chemicals or mechanical actions. In the absence of full-fledged treatment methods, the disease penetrates into the middle and inner ear, and the pathology proceeds stubbornly.
Itchy
The body's response to irritation of nerve endings in the skin is itchy dermatitis, accompanied by scratching and nervousness in a child or adult. There are types:
- Widespread – the reaction occurs throughout the body. The causes are atopic, allergic dermatitis, diabetes mellitus, kidney and liver diseases. Occurs due to disorders of the brain, sebaceous glands, allergies to wool, insects, and worms.
- Local – local. Appears for reasons such as insect bites, contact exposure, and the initial stage of allergies. It can be diagnosed on moving parts of the body, delicate skin, and open parts of the body. It can appear on the buttocks, thighs and perineum against the background of venereal, gynecological, and andrological diseases. Local itching develops due to parasites and fungi on the scalp. Ointments and creams come to the rescue.
Bullous
The formation of a primary bulla rash is characterized by bullous dermatitis. It is characterized by the appearance of bubbles half a centimeter in diameter, which ripen, burst and form erosion. The bottom of the bullae lies in the dermis, the cavity is filled with exudate. Blisters are localized on the scalp, back and chest in men, mucous membranes of the mouth, and the red border of the lips. The rash is accompanied by itching and loss of sensitivity under the burst bullae. If the disease affects the mouth and lungs with a mass of blisters, death is inevitable.
Red
Red dermatitis is considered an unpleasant disease, characterized by severe itching and the formation of nodular red papules with a purple tint. A distinctive feature of the species is the depressed tip of the pimples, which grow, merging into plaques. As the formations grow, they become gray-red, thicken, and after elimination they leave brown hyperpigmented spots. The red type is localized to the joints of the arms, sides, oral mucosa, and genitals.
Exfoliative
Exfoliative dermatitis is considered an inflammatory skin disease, characterized by severe redness and peeling of 90% of the skin surface. Men suffer from it after 40 years of age. Doctors say the reasons are complications of psoriasis, seborrheic, atopic, and contact dermatitis. In a third of cases, the cause cannot be determined. The type manifests itself as a high temperature, a feeling of cold, red thickened spots with scales and crusts. The exfoliative type is characterized by enlarged lymph nodes, release of fluid through inflammation, and severe itching.
Diagnosis of dermatitis
When it comes to contact dermatitis provoked by external causes, it is enough for a specialist to examine the skin to make a diagnosis. In cases where the cause of dermatitis is not clear, blood tests and allergy tests are performed. If the patient’s dermatitis is itself a symptom of a disease, then clarification of the internal causes of dermatitis comes to the fore, and for this it is necessary to conduct an examination, including with a therapist, allergist, gastroenterologist (it is possible that with other specialists).
When diagnosing dermatitis, a microscopic examination and culture of the material is carried out in order to detect pathogenic fungi, and tests are also carried out to exclude toxicoderma and erythroderma, which have similar symptoms, the treatment of which requires emergency measures.
Types of seborrheic dermatitis
If the violation of the sebum secretion of the skin consists mainly in the increased production of excessive amounts of secretion by the sebaceous glands, then this is oily seborrheic dermatitis.
At the same time, the skin becomes oily, shiny with fat and enlarged pores. Even a few hours after washing with degreasing products, the skin turns red and takes on a dirty, greasy appearance.
Dry seborrheic dermatitis. With this type of dermatitis, dysfunction of the sebaceous glands leads to only a moderate increase in the separation of fat, but it becomes thick and clogs the excretory ducts of the glands. The skin of patients with dermatitis becomes rough, dry, flaky and horny.
What you can eat and what you can’t eat
If a person has suspicions about the products and that they may cause an allergic reaction, then you can contact the clinic. The attending physician will tell you everything in detail. But, most likely, you will first need to undergo tests.
What can cause an allergy? Here is a list of the most allergenic foods:
- Meat: fatty beef and pork
- Caviar
- Smoked products
- Chicken eggs
- Milk
- Canned foods
What you can consume without fear of skin dermatitis:
- Cottage cheese
- Cod, perch (or other sea fish)
- Butter
- Beef and chicken by-products
- Lamb, horse meat, beef without fat
- Cottage cheese and sour cream
- White currants and gooseberries
- Corn
- Spinach
- Pearl barley
- Barley grits
- Apple
- Pear
- Vegetable or olive oil
- Cucumber
- Zucchini
- Rice
- Cabbage (white cabbage, broccoli, cauliflower)
You can also consume all dried fruits and dried fruits (for example, bananas) without restriction. You can treat skin dermatitis with a diet of the above products.
Symptoms of dermatitis
There are three stages of dermatitis with different symptoms:
- acute stage - red spots, papules and vesicles appear on the skin;
- subacute stage - the skin peels off, crusts form in place of the opened vesicles;
- chronic stage - the skin in the affected areas thickens, becoming red-violet.
The main symptoms of dermatitis of any stage are: redness of the skin, the appearance of a rash and swelling of the tissues; in addition, itching, heat and burning are almost always felt in the affected area.
What is the difference from simple dermatitis?
The difference between the chronic form of dermatitis and the simple one is that it is preceded by 2 stages - acute and subacute. The first two forms of inflammation of the epidermis occur with pronounced symptoms: the skin itches, burns, becomes bright red, and swells. The lesion is characterized by an increase in local temperature.
Acute and subacute stages can be treated with medication, and the prognosis for recovery is favorable. In the absence of timely treatment for dermatitis, inflammation of the epidermis becomes more extensive. The skin thickens, becomes covered with scales and dark red spots. The most unfavorable outcome is epidermal atrophy.
With chronic dermatitis in an adult, the skin may become covered with multiple ulcers and erosive lesions. Later treatment of skin inflammation leads to the formation of pigmentation on the skin, scars, and the occurrence of dyschromia. It is extremely rare that the chronic form of the pathology ends with healing without visible damage to the skin.