A cyst is a benign formation that often forms in the tissues of the reproductive system, in particular in the area of the cervical canal and the vaginal part of the cervix. Many women of reproductive age face a similar problem. Naturally, patients in the gynecology department are interested in any available information about the disease.
What are the causes of cysts on the cervix? What danger is associated with the appearance of such a neoplasm? What symptoms should you pay attention to? What treatment methods can modern medicine offer? The answers to these questions are of interest to many women.
What is a cyst?
According to statistics, approximately 10-20% of women of reproductive age are faced with a problem such as a cyst on the cervix. Causes, treatment, symptoms - this is, of course, important information. But first, it’s worth considering the general data.
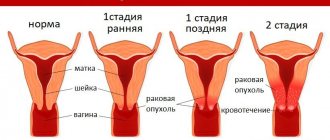
A cyst is a kind of tumor that forms as a result of blockage of the gland duct. Mucus and secretions begin to accumulate inside the cavity, causing the gland to increase in size. Such neoplasms can have different sizes. As a rule, they are located in the tissues of the vaginal part of the cervix or cervical canal.
Types of cystic formations of the cervix
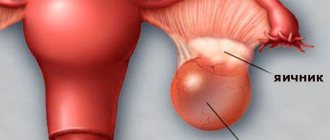
The cervix can become the site of the formation of two types of cysts, namely retention (nabothian) and endometrioid. The structure of a retention cyst is an enlarged cervical gland, the duct of which is blocked, and a mucous secretion accumulates inside. Nabothian cysts are quite common - they are diagnosed in 10-15% of patients of reproductive age, more often in those who have already given birth.
Short neck during pregnancy: causes and consequences
Endometrioid cysts form as a result of the progression of endometriosis, which has affected the vaginal portion of the cervix. Cystic formations of this kind are combined with heterotopias located in other locations.
Cysts are also classified according to the site of formation. According to this criterion, paracervical (location is the vaginal portion of the cervix) and endocervical (location is the cervical canal itself) cysts are distinguished. In addition, single and multiple cystic formations are distinguished. The size of the cavities most often does not exceed 1 cm, but there are also larger ones - 3 cm or more.
According to the method of formation and etiology, cystic formations are:
- traumatic;
- tumor;
- parasitic;
- inflammatory;
- dysontogenetic;
- retention.
Cyst on the cervix: causes, photo
As mentioned, this is a fairly common problem. The reasons for the formation of cysts on the cervix can be very different. It's worth checking out their list.
- Mechanical injuries of the cervix. The causes of a cyst on the cervix may lie in injuries received during childbirth or an incorrect abortion. Tissue damage is often accompanied by blockage of the glandular ducts, which subsequently leads to the formation and growth of cysts.
- Menopause and other hormonal changes. Fluctuations in hormonal levels affect the condition and functioning of the tissues of the reproductive system. For example, during menopause the mucous membrane becomes thinner. The glands are more vulnerable and produce more mucus in response to any, even the slightest, irritation. An increase in the amount of secretion increases the risk of cyst formation.
- Infectious diseases. Almost any infection that affects the organs of the reproductive system (including sexually transmitted infections) can provoke the appearance of such a neoplasm. Against the background of the inflammatory process, the secretion secreted by the glands becomes more viscous, which contributes to blockage.
Based on the reasons, risk factors include the introduction of an intrauterine device, diagnostic gynecological curettage, metabolic disorders, diseases of the endocrine system, and any inflammation of the pelvic organs.
What to do if cystic lesions are detected in the cervix
Methods for correcting this pathology involve both conservative and surgical treatment. Conservative measures are necessary for the treatment of infectious and inflammatory processes that provoke the formation of cysts, as well as for the correction of hormonal disorders.
The tactics of drug therapy depend on the characteristics of a particular clinical case and are prescribed by a doctor after carrying out all the necessary diagnostic procedures: determining hormonal abnormalities, identifying the causative agent of an infectious pathology, colposcopy, ultrasound examination.
As for surgical correction in the presence of cystic formations, the issue is somewhat controversial. The opinions of gynecologists regarding the need to treat retention cysts are divided: some doctors do not see the need to correct asymptomatic formations and recommend monitoring them over time, while other specialists see the cyst as a potential source of infection and consider it advisable to remove it.
Prolapse and prolapse of the cervix: causes and methods of treatment
Large cysts must be removed, as they cause severe clinical symptoms and interfere with the process of conception. If cystic formations provoke suppuration and do not allow assessing the condition of the cervix, then they must also be removed.
During surgery, the cystic cavity is first opened using a puncture. Next, it is emptied. Then the cyst bed is treated using electrocoagulation, laser exposure, radio wave therapy, and cryotherapy.
In some cases, more radical intervention is necessary. It involves cone-shaped amputation of the cervix.
Classification of neoplasms, depending on the cause of occurrence
Today, there are a huge number of ways to classify such pathology as cervical cyst. The reasons for the appearance are also taken into account. Based on this, such neoplasms are divided into several groups:
- traumatic - such cysts are formed as a result of tissue damage and displacement;
- tumor - neoplasms are the result of progression of tumor processes;
- parasitic - cysts that appear as a result of the activity of various parasites;
- dysontogenetic - the development of neoplasms in this case is associated with the presence of congenital anomalies or anatomical disorders in the patient;
- retention - this group includes cysts that are formed as a result of an increase in the volume of secretion produced by the gland.
What it is?
Cysts are voids that form in various tissues. There are two types of cervical cysts:
- Nabothian cysts of the cervix are formed as a result of pathological changes in the Nabothian glands and epithelial tissue of the cervix.
- Endometrioid. Endometrial cells lining the inner surface of the uterus, entering the cervix, can grow to it, forming a cyst filled with blood. Endometrial penetration into the cervix can occur, for example, during childbirth, abortion, or installation of a uterine device. Endometrioid cysts usually form in women 30-40 years old. There is often a genetic predisposition to the occurrence of such a disease.
The cervix is covered with several layers of epithelium. There are two types of epithelial cells. The first ones are flat or scaly. They cover the outer part of the cervix, which extends into the vagina. Designed for mechanical protection of this part of the uterus.
The second ones are cylindrical. Through them, mucus produced in the nabothian glands of the cervix is excreted. The purpose of the mucus is to create a protective plug that prevents bacteria from entering the uterus. Mucus is discharged through the cylindrical epithelium into the cervical canal (inner area of the cervix).
Nabothian cysts of the cervix are formed due to blockage of the glands in which this mucus is produced. Having no way out, it accumulates, the glands swell, forming voids. The causes of cyst formation are:
- Pseudo-erosion (cervical ectopia). In some cases, squamous epithelial tissue begins to grow, spreads to the area of columnar epithelium, and blocks the exits from the glands.
- Changes occurring in the glands themselves that produce mucus. Sometimes it thickens spontaneously, blocking the exit from the gland.
Such pathologies usually arise as a result of hormonal disorders in the body or inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system.
Natobian cysts of the cervix: causes
Unfortunately, young women quite often face such a problem as neoplasms appearing on the genitals. And in some cases, patients leave the doctor's office with a diagnosis of Nabothian cysts on the cervix. Causes, treatment, photos - these are the points that are interesting to many women.
As you know, the tissues of the cervix contain glandular cells that produce a specific secretion. In some cases, there is a blockage of the ducts of these cells. Secretions begin to accumulate inside them, resulting in the formation of small but dense, round structures of white-yellow color. By the way, this phenomenon was first described by researcher Nabotov.
Why do these small cysts appear on the cervix? Unfortunately, it is not always possible to find out the reasons. Today there is information that such neoplasms often appear as a result of chronic inflammatory processes in the pelvic area. Risk factors also include changes in hormonal levels, erosive processes in the tissues of the uterus, and genital infections.
Nabothian cysts, as a rule, are small in size and have virtually no effect on the functioning of the reproductive organs. There are often no symptoms - the pathology is diagnosed accidentally during a routine gynecological examination. Of course, such a problem requires a more thorough diagnosis. However, in most cases, specific therapy is not necessary. Patients are recommended to undergo periodic gynecological examinations so that the doctor can promptly notice any changes in the patient’s condition.
If the cyst quickly increases in size and compresses nearby structures, including blood vessels and nerve endings, the doctor may decide to surgically remove it.
Why are uterine cysts dangerous?
Is it dangerous when a cyst forms in the uterus? And is it necessary to have surgery to remove such a formation?
As long as the nodes are painless and small, they do not affect the woman’s condition. But there are conditions under which such a pseudotumor can cause negative consequences.
In what cases can it be dangerous?
If the node and surrounding tissues become infected with microbes and viruses, inflammation begins. If this process is often repeated, chronic diseases of the reproductive organs occur: cervicitis in the cervix, colpitis in the vagina, salpingitis, adnexitis, oophoritis in the fallopian tubes and ovaries. In addition to the fact that these diseases themselves are dangerous for the female body, many of them can cause inability to conceive.
Often small nodules cover a significant part of the cervical canal or grow over the entire internal surface. If the entire internal lumen of the cervix becomes overgrown with such nodes, it will close, which can complicate conception and gestation. Large nodes also narrow the internal canal, being a mechanical factor in menstrual dysfunction, menstrual pain and infertility. This is why it is necessary to treat cervical cysts.
Can a uterine cyst burst?
Such cases in gynecology are recorded very rarely. But rupture can occur if a large node (more than 20 mm) with a thin wall is damaged during rough intimate contact. Sometimes this happens during childbirth if the tumor is located in the area of a cervical rupture or an artificial incision made surgically to facilitate the baby's exit from the uterus.
What symptoms accompany the pathology?
Many young women face such a problem as a cyst on the cervix. Causes, treatment, possible complications are important questions. But it is worth familiarizing yourself with the characteristics of the symptoms.
In this case, the number and size of neoplasms are of great importance. A single small cyst is unlikely to cause any serious deterioration in health - they are often discovered by chance during a medical examination.
If we are talking about large tumors, then unpleasant, nagging pain in the lower abdomen may appear. Some patients complain of pain and discomfort during sexual intercourse. Symptoms include the appearance of uncharacteristic vaginal discharge (if an infection occurs, it may acquire a yellowish or greenish tint, as well as an extremely unpleasant odor). In some cases, the growth of the cyst is accompanied by the appearance of bloody discharge.
Types and symptoms of cervical cysts
There are single and multiple cervical cysts. Single cysts are formed when there is a small defect and disruption of the outflow of secretions from one gland. Multiple retention cysts of the cervix are more common, since in most cases the outflow of secretions from several glands is blocked at once. Such cysts can be located throughout the cervix or be concentrated in one place.
Cysts on the cervix - is it dangerous? The danger of cervical cysts is that they are often asymptomatic and are diagnosed only when complications occur. Small cysts of the endocervix of the cervix are detected during a preventive gynecological examination or during an ultrasound examination, which is performed for another pathology. Since nabothian cysts of the cervix are not proliferative, they do not disrupt the normal ovario-menstrual cycle and do not affect the general condition of the woman.
Symptoms of the disease appear in the presence of multiple or large cysts. The first signs of a cervical cyst may be discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse, as well as the discharge of bloody or purulent contents from the vagina when the cysts become infected. These signs are not always expressed. They depend on the size and number of tumors. When a cyst ruptures, light-colored discharge may appear, which women usually do not pay attention to.
If the integrity of the epithelium is violated and an infectious process is added, the following symptoms are added to the clinical picture of the disease:
- Severe pain in the lower abdomen;
- Purulent vaginal discharge;
- Systemic reactions in the form of a rise in temperature and severe intoxication syndrome.
If a cyst is detected on the cervix, why is it dangerous? Sometimes cervical cysts are diagnosed during pregnancy. Then postpartum septic complications may occur due to infection of the cyst. Therefore, when a nabothian cyst is diagnosed in a pregnant woman, it is removed using minimally invasive methods. Gynecologists at the Yusupov Hospital individually select a treatment method that has minimal impact on the condition of the fetus and the birth canal. When a cervical cyst develops in older women, further metaplasia of the cervical epithelium may develop as functional changes in the columnar epithelium occur. For this reason, when a cervical cyst is detected, gynecologists recommend removing it without waiting for complications.
List of possible complications
Many women are interested in the causes of cysts on the cervix, as well as possible complications that develop with this pathology. In fact, a neoplasm rarely poses a serious threat. However, patients should monitor their health status.
There is no risk of malignant tissue degeneration. But the possibility of tissue infection cannot be ruled out. The appearance and growth of cysts are often associated with infectious and inflammatory diseases of the cervix, endometrium, etc.
It is worth talking about reproductive function. A small cyst by itself cannot prevent fertilization or the successful completion of pregnancy. However, a large tumor is often associated with infections, endometriosis and inflammatory diseases - together these factors can lead to infertility. In addition, due to the growth of the cyst, the cervix may become deformed, which can lead to complications during pregnancy and childbirth.
Diagnosis of cystic formations
Hysteroscopy is an option for diagnosing diseases of the cervix.
Cysts of the cervical canal are detected during an examination of the cervix by a gynecologist in the speculum. Visually, retention cystic cavities look like whitish or yellowish formations, and endometriotic cavities look like dark red or purple lesions that release blood when touched.
Small cysts are determined during colposcopy, and formations localized endocervically - during hysteroscopy and transvaginal ultrasound.
If cystic formations are detected, the doctor prescribes a test for infections to identify the possible etiological factor of the pathology. The patient undergoes a smear analysis for flora, as well as cervical secretion for examination using polymerase chain reaction (PCR). To exclude oncopathology, the gynecologist prescribes a cytology analysis of the cervix scraping, as well as a targeted biopsy followed by a histology study.
Diagnostic measures
As already mentioned, most often the doctor accidentally discovers a cervical cyst during a gynecological examination. The causes of occurrence and treatment for such pathology are closely related. That is why in the diagnostic process it is important not only to confirm the presence of formations, but also to understand their causes.
Colposcopy is informative in this case - during the procedure, the doctor can carefully examine the tissues of the vagina and cervix. A microflora examination of smears is required. It is important to determine the presence of bacterial infections, including chlamydia, trichomoniasis, etc. You need to donate blood - a general analysis will make it possible to notice inflammation. Since cyst growth is sometimes associated with hormonal disorders, it is important to conduct a blood test for hormones.
Examination of patients with cervical cysts
Nabothian cysts of the cervix are most often discovered accidentally or when complications occur. A simple consultation with a gynecologist with a speculum examination of the cervix does not always make it possible to establish a diagnosis, but changes in the cervix often suggest the development of cystic formations. Then, to confirm the diagnosis, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital conduct additional research methods.
Ultrasound examination using cavity sensors - cervical cysts are defined as anechoic inclusions of a round or ovoid shape. They can be either single or multiple. Most often, cystic formations are located in the endocervix, but cervical stromal cysts are also found. The internal structure of cysts is often homogeneous and anechoic, but sometimes heterogeneous finely dispersed or hyperechoic contents with uneven contours are found. This is due to the fact that cysts occur when the outflow of secretions from glands located not only in the mucous membrane of the cervical canal, but also in the muscle layer is disrupted. When the cyst is located cervically, the internal contents of the cysts do not contain vessels. There is no enhancement of the vascular pattern in the adjacent stroma.
Colposcopy is an examination of the cervix with a special device that has a magnifying power of several tens of times. This examination allows you to examine the cervix and see any changes in the epithelium. The columnar epithelium looks like a network of cells with pronounced glands, having the appearance of a papillary structure. If the outflow of gland secretions is disrupted, blockage of these glands and areas of their expansion can be seen. If there is concomitant erosion or other damage, they are also detected during colposcopy.
A smear of the cervical canal can exclude inflammatory diseases and metaplasia of the cervical epithelium. Histological examination of the smear shows the expansion of the gland and its deformation with the accumulation of secretions. In general clinical analysis of blood, urine and bacterial culture from the vagina, there are no characteristic changes.
Gynecologists at the Yusupov Hospital carry out a differential diagnosis of Nabotian cyst with diseases that are accompanied by damage to the epithelium of the cervix. Externally, cysts may resemble polyps, but upon ultrasound examination, the polyp has a dense structure, in contrast to the cavity of the cyst. Differential diagnosis of nabothian cyst with endometrioid heteropias is carried out on the basis of visual differences and histological examination of the material.
Ultrasound for diagnosing cysts
Ultrasound examination is a mandatory procedure if a cyst is suspected. This is a simple but really informative method. During the examination, the doctor can examine the body and cervix, assess the quality of the blood supply, notice any changes in the structure of the organ, see the neoplasm, record its exact size, etc.
The examination is carried out in a standard way - the cervix can be seen using a transabdominal or transvaginal ultrasound probe. The procedure is safe and painless. The results obtained often help doctors not only detect the presence of tumors, but also determine the possible causes of a cyst on the cervix.
Diagnostic search
Examination scheme:
- Gynecological examination in mirrors. Upon visual examination, cysts located on the vaginal part of the cervix are clearly visible - yellowish, round, protruding above the surface of the mucous membrane. There may be signs of chronic cervicitis and erosion. Endocervix formations are not visible upon examination;
- Oncocytology test. Allows you to identify changes in the cervix, including precancerous conditions and cancer;
- Survey stroke. Detects gonorrhea, bacterial vaginosis and candidiasis. In a smear of a cyst against the background of cervicitis, an increase in the number of leukocytes is determined;
One of the diagnostic methods in gynecology is a smear for microflora.
- Bacteriological culture from the cervical canal. Makes it possible to identify the causative agent of the disease and select treatment taking into account its sensitivity to antibiotics and antifungals;
- Examination for other infections: human papillomavirus, herpes virus and cytomegalovirus, chlamydia, mycoplasma, ureaplasma, etc.;
- Colposcopy. The main method for diagnosing cervical pathology. Detects nabothian cysts and other changes in the mucous membrane;
- Ultrasound of the cervix. Detects endocervical formations hidden from the doctor during examination and colposcopy;
- Biopsy. Tissue collection for examination is carried out after colposcopy. The microspecimen is sent to the laboratory. Based on the results, an accurate diagnosis is made;
- Hysteroscopy. It is carried out to assess the patency of the cervical canal and identify concomitant pathologies.
It is also useful to read: Endocervical cysts and their treatment
The photo shows Nabothian cysts when examined in a gynecological speculum. There are signs of an inflammatory process on the cervix:
Surgical methods of treatment
It is immediately worth noting that the doctor makes the decision to perform surgical intervention only if the neoplasm is large and/or prone to rapid growth.
The operation is performed using endoscopic equipment. The doctor makes small punctures in the abdominal wall, through which a special instrument is inserted. The cyst is punctured, and then the mucous/purulent secretion is removed from its cavity.
Then the cyst cavity is treated with a special antiseptic solution - this prevents possible complications and re-accumulation of pus inside the tumor. The operation does not require long-term rehabilitation - after a few days the patient can return to her usual lifestyle.
Nabothian cysts: causes of occurrence
Cysts in the nabothian glands occur when the ducts are blocked; the latter process, in turn, is influenced by factors such as:
- Hormonal disorder. An excess or deficiency of hormones directly affects the consistency of cervical mucus, and the secretion of too viscous and thick secretion leads to disruption of the glands and blockage of the ducts.
- Diseases of the reproductive system. Pseudo-erosion can lead to the appearance of cystic cavities, during which cylindrical epithelial cells are detached, enter the acidic environment of the vagina and are subsequently destroyed.
- Natural birth. During the process of recovery of the body after childbirth, a Nabothian cyst may form, which is caused by increased secretion of cervical mucus.
- History of termination of pregnancy.
- Cleaning the uterine cavity.
- Surgical intervention in the tissue of the cervix.
- Incorrect actions by the doctor when installing an intrauterine device.
- Failure to maintain intimate hygiene.
So, all the causes of nabothian cysts of the cervix can be divided into 3 categories:
- Hormonal imbalance, disturbance of estrogen concentration, when taking hormonal drugs, after pregnancy and with diseases of the reproductive system or thyroid gland.
- Mechanical damage to the epithelial tissues of the cervix during surgical interventions.
- The course of inflammatory processes and infectious diseases in the pelvic organs. The fact is that during such diseases, the nabothian glands begin to produce much more mucus in order to remove all pathological microorganisms from the cervix.
To date, research aimed at studying nabothian cysts of the cervix and the causes of their appearance has not been completed, so the above list is not exhaustive.
Methods for removing a cyst
During endoscopic surgery, the doctor can clean out the cyst cavity. But the wall of the tumor must be removed. For this, different techniques are used.
- Cauterization. For this purpose, aggressive chemical substances and special medications are used.
- Radio wave therapy. The cyst is removed by destroying its tissue with high-frequency radio waves. This is a gentle treatment method that is often prescribed to young women at the stage of planning pregnancy.
- Cryotherapy, or freezing. Neoplasm tissues are destroyed by exposing them to ultra-low temperatures (liquid nitrogen).
- Laser removal. This is a relatively new but expensive procedure that allows you to remove cyst tissue using a laser beam without contacting the mucous membrane of the cervix.
Treatment of cervical cysts
Gynecologists at the Yusupov Hospital take an individual approach to the choice of management tactics for patients with nabothian cysts. If a cyst is found in a woman under 45 years of age, surgical intervention is required. If there is an asymptomatic cervical cyst measuring less than one centimeter in diameter, a wait-and-see approach is followed. Such cysts do not transform into a malignant tumor, do not grow and do not cause discomfort.
To relieve swelling, pain and other signs of inflammation, patients are prescribed Dicloberl vaginal suppositories. Sometimes treatment is carried out with ichthyol ointment. This method has been used for a long time, but it is not always effective. Tampons are moistened in ichthyol ointment and placed in the vagina for 10-20 minutes. They have anti-inflammatory and anti-edematous effects. In the presence of accompanying microflora, ichthyol destroys microorganisms and prevents septic complications. Conservative treatment methods are used as symptomatic therapy, which affects the development of the cyst. If a cervical cyst is accompanied by severe symptoms, gynecologists at the Yusupov Hospital perform surgery with removal of the lesion and further symptomatic therapy.
The following methods of surgical treatment of cervical cysts are used:
- Surgery;
- Electrocoagulation;
- Cryocoagulation;
- Laser vaporization;
- Radio wave therapy.
Surgery involves puncturing the cyst with a needle and aspirating the contents. The operation in the presence of large cysts is performed under ultrasound guidance. This is a fairly simple method, but when used there is a risk of developing infectious complications. Electrocoagulation, cryocoagulation, laser vaporization, radio wave therapy are methods in which doctors use the physical properties of electric current, liquid nitrogen, laser and radio waves to remove the cyst. These methods are less invasive than puncture, but technically more complex. The presence of special equipment and work experience allows doctors at the Yusupov Hospital to widely use them in clinical practice.
Diathermocoagulation. The method has long been used in gynecological practice and has 2 main methods of administration:
- Contact - in this case, the device has direct contact with the neoplasm tissue, or the nozzle is embedded into the thickness of the tissue;
- Non-contact – involves the presence of a micro-arc, which cauterizes the cyst at a certain distance and does not require contact with the tissue.
The advantage of this method is the ability to study the pathological focus, as well as complete excision of pathological tissue.
Unfortunately, the risk of recurrence of a cervical cyst when removed using diathermocoagulation is quite high.
Chemical removal. Removing a cervical cyst using a chemical method involves using a special solution. In our country, the most prominent representative is solkovagin. It contains a set of strong acids: nitric and acetic.
To carry out the procedure, the vagina and cervix are wiped with a tampon soaked in saline solution. Then the mucous membrane is anesthetized with local anesthetics and a tampon soaked in the vagina is applied. Leave for a certain period of time, and then wipe with a clean swab.
The disadvantage of this method is that it cauterizes the entire surface of the vaginal part of the cervix, and not just benign neoplasms.
Cryodestruction. This method is part of the chemical effect. But it has long been separated into a separate technique. In this case, a special gun with liquid nitrogen is used. It freezes modified tissues, which promotes their death. This happens because sudden exposure to cold temperature provokes a stoppage of blood circulation in the cyst with the formation of ice crystals in the capillaries and vessels. They destroy the tissue from the inside.
Removal of a uterine cyst (on the vaginal part of the cervix) does not require additional pain relief, since liquid nitrogen also blocks the conductivity of nerve receptors, which ensures a complete absence of pain.
Laser therapy. This is a relatively new method of combating benign tumors, which is one of the most optimal at the moment.
Laser treatment is permitted for young patients who have not yet given birth. When the indication for other methods is a history of childbirth.
The technique is quite painful, so before the procedure, the vagina and cervix are treated with a local anesthetic, and conduction anesthesia is also administered.
In this case, the risk of bleeding is reduced to zero, since laser radiation coagulates damaged vessels during cauterization.
The development of nabothian cysts on cervical erosion is common. Therefore, similar cauterization methods can be used simultaneously for erosion and cervical cysts.
Cauterization of the cervix usually precedes surgery, but what to do first is up to the attending physician.
The presence of special equipment and work experience allows doctors at the Yusupov Hospital to widely use them in clinical practice.
Further treatment tactics
Drug therapy largely depends on the causes of the cyst and the presence of concomitant diseases. If there is a sexually transmitted infection, then appropriate therapy is carried out (for both partners).
If the cause of the appearance of tumors is hormonal fluctuations, then doctors recommend taking progestins and combined oral contraceptives. Additionally, anti-inflammatory drugs can be used. The treatment regimen sometimes includes various physiotherapeutic procedures.
Nabothian cysts: treatment
Experts have different opinions about the treatment of nabothian cysts of the cervix: some believe that this disease does not harm a woman’s health and does not require treatment, while others, on the contrary, insist on the use of medications or surgical intervention. In any case, therapeutic methods are prescribed individually, taking into account all the characteristics of the female body.
Treatment of nabothian cyst involves the use of the following methods:
- Conservative. Treatment of neoplasms with medications.
- Alternative. Treatment of the disease through traditional medicine.
- Surgical. Removal of cystic cavities through surgery.
Single or small multiple neoplasms do not require treatment - many experts share this opinion, but make a reservation:
- Cysts in the nabothian glands, however, should not cause pain or discomfort.
- Based on the results of the tests, no deviations in hormone levels from the norm were found.
- The examination did not reveal any diseases in the woman’s reproductive system.
- According to the results of the studies, no inflammatory or infectious processes occurring in the pelvic organs were identified.
In such cases, the woman visits the doctor at least once every 6 months, and if there are no changes in the number and size of the follicle, Nabothian cysts on the cervix are not treated.
Treatment with folk remedies: how effective is it?
Now you already know about how and why cysts appear on the cervix (reasons). Traditional methods of treatment exist, although they can only be used as aids.
Decoctions of chamomile flowers, sea buckthorn leaves, nettle, sage, plantain, string, and rose hips are considered effective. To prepare decoctions, these components can be mixed or used separately. Such home remedies are suitable for both oral administration and douching. Herbs help improve tissue trophism, relieve inflammation and irritation, and strengthen local immunity.
Of course, doing anything without the doctor’s knowledge is strictly prohibited. Despite the fact that a cyst on the cervix rarely poses a serious threat, you should not self-medicate.
Nabothian cyst: symptoms
Small cavities are revealed only upon examination, and larger formations or penetration of infection into the cyst cavity can lead to the following symptoms:
- Pain in the lower abdomen. Sharp or nagging pain can occur both with multiple cysts blocking the cervical canal and with infection of single follicles. The narrowing of the canal prevents the release of menstrual bleeding, and its accumulation in the uterine cavity leads to pain.
- Changing the color of the discharge. Inflammatory processes occurring in the cervical canal lead to changes in the consistency and color of the secreted secretion.
- A sharp, specific smell of discharge. The presence of purulent-inflammatory processes is reflected in the smell of cervical mucus.
- Pain during sexual intercourse. This is how a cyst located on the vaginal part of the cervix, an endocervical nabothian cyst, may manifest symptoms; treatment involves slightly different symptoms.
- Headache. Purulent inflammation leads to intoxication in the body and a general deterioration in the woman’s well-being; in addition, the acute course of the disease can lead to an increase in body temperature.
- Violation of the vaginal microflora and scarcity of cervical mucus discharge. In the case when the ducts of the gland are blocked by tissue cells or thick secretions, the secretion of cervical mucus is significantly reduced, which leads to discomfort during sexual intercourse.
- Cervical cysts can cause changes in how a woman feels. Often, the resulting cavities feel like a foreign body and cause pain during sexual intercourse.
Diagnosis of the disease is rarely based on the symptoms of nabothian cysts, since all of the above signs can accompany other diseases of the genitourinary system:
- Polyps accompanied by bleeding between menstruation, pain during sexual intercourse, nagging pain in the lower back and lower abdomen.
- Erosion, the symptoms of which are menstrual irregularities, heavy discharge, discomfort during sexual intercourse and bloody discharge after it.
- Endometriosis, manifested by spotting, pain in the lower abdomen, and pain during intimacy.
Symptoms of a nabothian cyst on the cervix appear quite rarely; in most cases, detection of the disease is based on functional diagnostics, which involves several types of studies
Useful video
Watch this video about the causes, symptoms and treatment of cervical cysts:
Similar articles
- Chronic cervicitis: options - moderate, focal...
Chronic cervicitis is quite unpleasant and dangerous for women's health. It can be moderate, focal, active and inactive, viral, with metaplasia. Unfortunately, pregnancy before his treatment is almost impossible. Read more - Nabothian cysts of the cervix
Nabothian cysts of the cervix occur in women 25-35 years of age. These are benign formations. A woman may not know about them until a certain moment. Removal is not always required. Read more
- Tumor in the vagina: symptoms, inside, on the walls...
If a tumor is detected in the vagina, do not immediately panic, since they can be benign or malignant. By location they are inside on the walls, at the entrance, on the stump, near the vagina. There are no symptoms for small sizes. Treatment involves removal. Read more
- Is it possible to confuse a cyst with pregnancy?
Some gynecologist patients doubt whether a cyst can be confused with pregnancy. However, in practice the symptoms are really similar. Tests and ultrasound will help make a diagnosis. Read more
What are the types of ultrasound of uterine cysts?
Transvaginal
When diagnosing a uterine cyst, a special transducer shaped like a vagina is used. When preparing a patient for this ultrasound method, it is necessary to find out whether there is an allergic reaction to latex. It is also important not to drink liquids for 4 hours before the diagnosis, the bladder should be empty.
Transabdominal
Prescribed for examination of the pelvic organs, if necessary, to examine virgins and as a supporting diagnostic method for transvaginal ultrasound. It is carried out through the abdominal wall, the bladder must be full. The patient should be warned about the need to drink large amounts of water several hours before the test.
A little anatomy
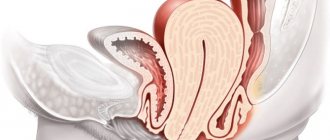
The cervix is a tubular organ connecting the vagina to the uterus. The inside of this “canal” is lined with columnar epithelium, which contains special Nabothian glands that secrete a special secretion. This secret destroys bacteria, and on the other hand, depending on the phase of the cycle, changes its consistency. So in the middle of the cycle (at ovulation), the secretion becomes transparent and liquid, which facilitates the penetration of sperm into the uterine cavity and fallopian tubes, where further fertilization occurs.
On other days of the menstrual cycle, the cervical secretion is more viscous, which protects the uterus from the entry of microorganisms and sperm into its cavity. That's how wise nature is!
Outside, the cervix is covered with multilayered squamous epithelium, which is not capable of producing secretions; there is also a junction zone between the cylindrical and squamous epithelium - otherwise called the transformation zone. This is where various pathological processes can occur.
What is the threat to women's health?
Nabothian cysts never develop malignant growth. But they can provoke chronic inflammation in the cervix and become inflamed on their own with the appearance of a vivid clinical picture:
- Painful sensations in the lower abdomen;
- Unpleasant discharge.
Large retention cysts can interfere with fertilization if they act as a barrier to the advancement of sperm.
Expert opinion
Daria Shirochina (obstetrician-gynecologist)
Nabothian cysts, which are small in size, do not cause any problems and do not require any treatment. In such cases, observation by a gynecologist and regular testing for atypical cells in the cervical canal are sufficient.
Symptoms and treatment
Even with harmless, at first glance, small nabothian cysts that do not manifest themselves in any way, observation of a specialist over the cervix is necessary. Colposcopy is considered effective. This method will allow you to timely identify emerging negative changes and prevent dangerous consequences.
What happens if you ignore the advice of specialists and, when there is a cyst on the cervix, postpone treatment “for later”? Although infrequent, the following consequences are observed:
- Deformation of the cervix occurs due to the growth of neoplasms or due to their significant number, which further complicates the course of pregnancy and childbirth.
- In the clogged gland, suppuration occurs, leading to an abscess.
- Predisposition to one of the types of infertility. As the glands grow, they block the cervical cavity.
- There is a potential risk of miscarriage. Being in the cervical canal, a large cyst or many small ones constantly irritate the cervix.
The decision on how to treat is made by the doctor in each individual case. For example, a large single retention cyst is eliminated because its contents can provoke inflammation and further infection of the genital organs. When choosing between regular monitoring, medication or surgical help, the doctor first identifies the causes of cyst growth. Limited to dynamic observation when:
- no infection was detected,
- hormonal balance is fine,
- colposcopy did not show ectopia of the cervix and other pathological changes,
- cysts do not increase in volume.
When there is inflammation of an infectious nature, antibacterial therapy is used. It is carried out in stages:
- Stage I - introduction of antibacterial agents. Locally (suppositories, gels, creams) - for vaginal infections, orally (tablets) - for damage to the pelvic organs and intrauterine infections.
- Stage II – reconstruction of the vaginal microflora using pro- and eubiotics.
The presence of ectopia along with a cyst on the cervix indicates the need to eliminate the latter. During the treatment of pseudo-erosion, it is possible to cure Nabothian cysts (opened using an instrument).
If a hormonal cause for the formation of cysts is identified, medications are prescribed to restore the balance of hormones. There may be endometriotic areas on the cervix that provoke the development of neoplasms. To eliminate them, you need to cure endometriosis. If this is not done, but only the cyst (endometrioid) is mechanically removed, there will be no positive result. By treating the disease that caused the formation of cysts, it is possible to prevent their recurrence.
Kinds
While undergoing another preventive appointment with a female doctor, or turning to him about, for example, pain in the lower abdomen, unexpectedly during the examination you can hear: “Cysts on the cervix.” What does it mean and why is it dangerous?
We are talking about a benign cavity formation with liquid contents. The cervix is not a separate organ from the uterus. It resembles a hollow tube containing the cervical canal. The uterine end of the tube narrows - this is the internal os. The other, external, is located at the base of the cervix in the vagina, and cysts most often appear in this place.
Nabotovs, they are retentionists
Retention cysts of the cervix appear due to disruption of the functioning of the glands. They become blocked, which is why formations grow. Nabothian cysts occur predominantly against the background of inflammatory processes and in the presence of a transformation zone (altered epithelium) on the cervix.
In appearance, they resemble a scattering of small white-yellow hemispheres. Often, it is Nabothian cysts of the cervix that the gynecologist means when using the expression “cysts on the cervix.” They were named Nabotov in honor of the scientist who discovered them.
For modern specialists, it is not difficult to diagnose formations. They are detected during examination on a chair, and a colposcope is used to confirm the disease. Cysts are often accompanied by an inflammatory process or pseudo-erosion. To determine the composition of the vaginal microflora, laboratory testing is used (PCR study, smear, bacterial culture). This will allow you to accurately determine the type (source) of infection and fight it in the future. Ultrasound examination (US) is also used to identify endocervical cysts, which allows them to be detected in places that are difficult to reach for visual inspection.
In most cases, small multiple retention (Nabothian) cysts do not pose a danger, and the gynecologist does not prescribe their treatment, much less removal. Numerous Nabothian cysts occur regularly throughout a woman’s life and often go away on their own. An exception is the presence of cervicitis. If there is one large uncomplicated cyst in an accessible location, the question of its removal is raised. This procedure can be performed on an outpatient basis using one of the methods chosen together with the attending physician.
Endometrioid cyst
There are neoplasms of a different origin caused by pathology in the uterine mucosa - endometrioid cysts of the cervix. These are a piece of the endometrium of the uterus, which has “taken root” in the thickness of the cervix. Such cysts often go along with endometriosis of other localization (including on the vaginal wall, in the uterine cavity, on the ovaries, fallopian tubes and other pelvic organs).
Surgery
Treatment of cysts includes several stages, mandatory of which is the elimination of the original cause that influenced its formation:
- In most cases, this is anti-inflammatory therapy with the possible exclusion of specific infections.
- In case of erosion or dysplasia, therapy aimed at removing the pathological focus is recommended.
- For leukoplakia or dyshormonal disorders, hormonal correction is required.
Traditional medicine methods:
- Decoction of boron uterus. This herbal remedy is widely used in the treatment of various gynecological pathologies. This is due to the mechanism of action of the plant on the reproductive system. The main one is the provision of an anti-inflammatory effect, as well as the restoration of hormonal imbalance. In order to prepare the resulting decoction, you need to pour the dry grass of the boron uterus into hot water. You need to prepare it from the ratio of 15 grams of grass with 200 ml of water. This mixture can be left in a mug or put in a thermos and left until it cools down; if stored in a thermos, you need to keep it for 2-3 hours. It should be consumed 30 ml three times a day. The course of therapy should be long, on average it takes 3-4 weeks. But taking boron uterus has its own characteristics, since a few days before and after menstruation you should stop taking it. There are almost no contraindications for use.
- Golden mustache tincture. This plant is widely used as a traditional medicine, including gynecology. To prepare, you should take the branches of the golden mustache and first clean them, cut them into fragments 3-4 cm long. The stems are placed in a jar of various sizes, and they should not lie too tightly in relation to each other. Next, they are filled with an alcohol solution, it can be either vodka or ethyl alcohol at a concentration of 70%. The mixture is covered with a plastic lid and left in a cool, dark place for three weeks so that the solution can infuse with the juice contained in the stems. After the allotted time has passed, the solution can be consumed. Before you start taking it, be sure to strain the mixture; you can leave them for further infusion. If it is not completely consumed, you can add a small amount of alcohol. Use the tincture in a volume of 30 drops twice a day. The course of therapy can be 1-2 weeks. Sometimes, it can be repeated after some time. The method has restrictions on its use due to the presence of alcohol in the composition. When infused with a water base, it will contain much less useful substances.
- A mixture of yarrow, marigold, and oak bark has a positive effect in the treatment of cervical cysts. A mixture is prepared from the obtained ingredients. To do this, you need to mix these plant components in equal proportions, with an average of 15 grams or one tablespoon of each of them. The mixture is poured with hot water and left to infuse. The volume of water must be at least one liter. If necessary, the mixture can be heated over a fire until it comes to a boil. After this, it should be cooled and strained at room temperature. Use the resulting solution throughout the day; it can be divided into several meals or consumed throughout the day in a small volume. The average course of therapy is 30 days; if necessary, it can be repeated after a month's break.
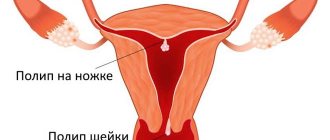
Nabothian cysts are a type of retention cyst and are formed in the cervix due to blockage of the glandular ducts. These neoplasms are benign in nature and are most often diagnosed in women of reproductive age who have gone through childbirth.
The vaginal part of the uterine cervix contains a large accumulation of glandular cells that form a mucous secretion. Under the influence of various factors, these cells can become clogged with epithelial cells. Unable to get out, the secretion stagnates and stretches the gland - this is how a cystic formation is formed.
Nabothian cysts can be either single or multiple. Often, when small tumors are detected, doctors advise not to take any measures to remove them, but to constantly monitor them.
Large cysts are recommended to be removed, since, contrary to popular belief, neoplasms cannot resolve on their own, and their accumulation and large size contribute to deformation of the cervical canal, which is especially dangerous during childbirth.
In addition, the presence of one or more nabothian cysts significantly increases the risk of developing inflammatory and infectious processes in the genital organs.
The exact reasons for the formation of nabothian cysts have not yet been established, but medical scientists have been able to identify a risk group for developing this disease. The likelihood of developing nabothian cysts increases if:
- you have suffered one or more episodes of inflammatory diseases of the genital organs;
- the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix was injured due to surgical manipulations, aggressive sexual intercourse or under other circumstances;
- there are hormonal disorders;
- you have a history of cervical erosion or ectopia.
Conservative treatment of cervical pathology
Treatment tactics will differ depending on the type of cyst. The choice of treatment method is also influenced by the woman’s age and concomitant pathology.
In the presence of an endometrioid cyst
Hormonal drugs are used in the treatment of cervical endometriosis. They influence the cause of the disease. Medicines reduce the level of your own estrogens and normalize hormonal levels. They lead to a decrease in size of the lesion up to complete regression. The effect is temporary - after discontinuation of the drug, heterotopias reappear.
Recommended hormonal agents:
- Combined oral contraceptives (Klaira, Yarina, Jess, Regulon, Marvelon, Novinet, Zhanin, Belara, etc.). Prescribed for 3-6 months according to the standard contraceptive regimen. If a woman is not planning a pregnancy, she can continue taking COCs for a year or more;
Combined oral contraceptives prescribed for the treatment of endometrioid cysts.
- Gestagens (Duphaston, Utrozhestan, Norkolut, Visanne). Progesterone-based drugs are prescribed from the 5th to the 25th day of the cycle or continuously. Course of therapy – 3-6 months;
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists (Lukrin, Buserelin, etc.). Used in a short course. They lead to rapid regression of the lesion, but have a large number of side effects. Prescribed in combination with other foci of endometriosis - in the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries.
On a note
Homeopathic medicines are used as an adjuvant in the treatment of cervical cysts. Their effectiveness has not been proven. It is impossible to say unambiguously how homeopathy affects the course of the disease, and whether there is any point in using it.
In case of retention cyst
In the conservative treatment of nabothian cysts, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial agents are used. Such drugs act on the presumed cause of the disease - a chronic inflammatory process on the cervix. They destroy pathogens and remove the source of inflammation. Priority is given to topical products – vaginal tablets and suppositories.
Treatment options:
- Antiseptic and antibacterial drugs (Hexicon, Betadine, Fluomizin). Prescribed for bacterial infection;
Antibacterial drugs used in the treatment of nabothian cysts against the background of an inflammatory process.
- Antifungal agents (Zalain, Pimafucin). Indicated for isolated fungal infection;
- Broad-spectrum drugs (Polygynax, Klion D-100, Neo-penotran forte, Macmiror complex). Used for mixed bacterial and fungal infections;
- Products with an anti-inflammatory component (Terzhinan). Indicated for mixed infections with severe clinical symptoms.
The choice of a specific drug is determined by the causative agent of cervicitis. Treatment is prescribed after a complete examination. It is important to take into account the sensitivity of the identified microorganisms to medications - the development of drug resistance is possible.
Taking antibiotics and antifungals is only the first stage of therapy. It is necessary not only to get rid of pathogens, but also to restore the natural flora of the vagina. Normally, lactobacilli should predominate, and the number of opportunistic microorganisms should not exceed 104. There should be no pathogenic flora. To achieve the desired effect, after completing a course of antibiotics and antifungal agents, probiotics (Lactagel, Gynoflor E, Vagilak) are prescribed. They normalize the balance of microflora and prevent relapse of the disease.
For the entire period of treatment it is recommended:
- Maintain intimate hygiene. You need to wash yourself twice a day or more often as needed;
- Avoid using soap. Washing with soap dries out the mucous membrane of the genital tract and changes the microbial landscape. It is better to use intimate hygiene products (Lactacid, Epigen gel, Saugella) or regular running water;
Intimate hygiene products recommended for use during the treatment of cervical cysts.
- Change panty liners regularly or stop using them altogether. Wipes create a favorable environment for the proliferation of pathogenic flora.
After completion of therapy, a control study is carried out - a bacteriological culture is taken from the cervical canal. If there is no effect, treatment tactics change.
It is also useful to read: Retention cysts of the cervix and modern approaches to their treatment
Chronic cervicitis caused by intracellular microorganisms requires a different approach to therapy. If chlamydia, mycoplasma or ureaplasma are detected (in high titres), antibiotics from the macrolide group are prescribed orally (in tablets). The course of treatment is up to 10 days.
Viral infection is a reason for prescribing special medications. In case of confirmed HPV infection or activation of the herpes simplex virus, treatment is selected taking into account the identified pathogen. Additionally, immune stimulating agents are used.
On a note
The cost of conservative treatment depends on the price of the drug and the duration of therapy. Getting rid of cervicitis will cost 300-1500 rubles. Treatment of endometriosis is expensive. The cost of COCs and gestagens reaches 500-1000 rubles per package, GnRH agonists - up to 9 thousand rubles per injection.
Traditional therapy can be supplemented with traditional methods. Douching with herbal decoctions, administration of herbal tampons, and treatment with honey and salt are practiced. The effectiveness of such techniques has not been proven, their effect on the body has not been studied. You should not get carried away with alternative medicine recipes to the detriment of your doctor’s prescriptions.
Treatment of nabothian cysts
By themselves, these formations do not resolve or disappear, so nabothian cysts, especially large ones, are removed, getting rid of the source of infection in the genital tract. In addition, with this pathology, an intrauterine device cannot be installed.
It is pointless to treat Nabothian cysts with folk remedies. On the contrary, the introduction of tampons into the vagina and uncontrolled douching lead to the growth of old and the appearance of “fresh” tumors.
Before removing Nabothian cysts, the cervix is punctured to allow the contents to drain out. Residues are removed using laser or radio wave coagulation (sealing of blood vessels), which does not cause pain, severe tissue trauma or bleeding.
Such cellular formations are removed using modern methods:
- electrocoagulation (electric current);
- cryocoagulation (cooling with liquid nitrogen);
- laser excision;
- endoscopic method (microinstruments equipped with a microscope and illumination);
- radio wave therapy is the latest technique.
The gynecologist decides how exactly to remove the nabothian cyst. The doctor selects the method individually, taking into account the size of the formation and the characteristics of the body. If you have a choice, it is better to prefer a radio knife, since there are no bleeding or complications after it. The technique is suitable even for nulliparous women.
Since the cervix does not contain nerve endings, the procedure is painless. A small number of patients with sensitivity in the cervical area are given local anesthesia or general anesthesia.
The procedure is carried out after the end of the next menstruation. The epithelium is restored before the next menstrual cycle.
After surgery, you need to take medications: antibiotics, antiseptics, vitamins and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Causes and mechanism of development
The mechanism of formation of nabothian cysts may involve two factors. Either a mechanical blockage of the excretory duct of the gland occurs and it begins to “swell” or the mucus secreted by the endocervical glands thickens.
In the first case, the cause of the formation of such formations is a violation of the integrity of the tissues of the cervix. During the process of regeneration (healing), a new layer of epithelium grows, which can block the excretory duct of the nabothian gland. Another option for mechanical blockage of the duct is the process of transition of true erosion (open ulcer) into pseudo-erosion or ectopia of the cervix.
Pseudo-erosion is a section of columnar epithelium that normally covers the cervical canal, located on the vaginal part of the cervix (it, in turn, is lined with stratified squamous epithelium). During the formation of pseudo-erosion, the cylindrical epithelium “descends” from the cervical canal, trying to close the cervical ulcer and blocks the excretory ducts of the glands.
In the second case, hormonal disruptions occur in the body, due to which the mucus secreted by the glands becomes viscous and thick, which makes it difficult to empty the gland and leads to the formation of its cyst.
It should be noted that there is a third factor in the mechanism of formation of nabothian cysts – the inflammatory process. Local inflammatory process occurs as a result of pathological microorganisms entering the cervix. As a result, the cervical epithelium is loosened, and infectious agents penetrate into the cavity of the glands.
In response to the introduction of infection, the glands begin to intensively produce mucus in order to wash away the “invaders” from the surface of the cervix. But as a result of inflammation, the mucus itself becomes infected, it becomes thick and purulent. When the healing of the outer surface of the cervix begins, inflammation inside the glands still remains.
Causes
The main reasons for the formation of nabothian gland cysts are:
- Mechanical injury to the cervix:
- artificial termination of pregnancy;
- cervical ruptures during childbirth;
- diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity;
- installation/removal of the IUD;
- hysteroscopy;
- surgical interventions on the neck.
- Hormonal disorders:
- changes associated with age (perimenopause);
- endocrine pathology;
- pregnancy;
- taking hormonal medications;
- bad habits (smoking, alcohol, drug use);
- various gynecological hormonal pathologies (tumors of the uterus and ovaries, cycle disorders, polycystic ovaries, endometriosis, etc.).
- Inflammatory processes:
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the internal genital organs (adnexitis, endometritis);
- cervicitis (endo- and exo-);
- colpitis;
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- neglect of the rules of intimate hygiene;
- background diseases of the cervix (pseudoerosion, leukoplakia);
- cervical dysplasia (precancer);
- endometriosis of the cervix.
Diagnostic scheme
The following methods help make a diagnosis:
- Gynecological examination. Nabothian cysts are clearly visible in the mirrors. These are dense round formations of white or yellowish color, located around the opening of the cervical canal. Multiple lesions are more common. Endometrioid cysts stand out on the mucous membrane due to their bright red color. They are especially noticeable before menstruation;
- Colposcopy. Examination of the organ under magnification allows you to determine the type of formation, identify concomitant pathology: cervicitis, erosion, etc.;
- Smear for oncocytology. Allows you to assess the condition of the epithelium, determine the inflammatory process, detect changes in the cervix;
- Screening for vaginal infections. A survey smear, bacteriological culture, PCR and ELISA help to identify the causative agent of cervicitis and determine its sensitivity to drugs. An examination for HPV, herpes simplex virus, chlamydia, mycoplasma, ureaplasma, gardnerella, trichomonas, gonococci and opportunistic flora is indicated. Based on the data obtained, drugs for the treatment of cervicitis are selected;
- Biopsy. It is carried out when the colposcopic picture is unsatisfactory. Allows you to determine the type of education. The resulting material is sent for histological examination;
- Ultrasound. Indicated for determining the size and location of cystic cavities. The cyst is visible as a thickening or hardening of the cervical canal;
- Hysteroscopy. Indicated for lesions of the cervical canal. Allows you to evaluate its patency, identify formations and other changes.
A minimally invasive method of visual inspection of the cervical canal using a hysteroscope allows you to thoroughly assess its condition.
Based on the data obtained, a diagnosis is made and a treatment regimen is selected.
It is also useful to read: Endocervical cysts and their treatment
Postoperative period
After removal of a cervical cyst, the following symptoms may occur, which are considered normal:
- nagging pain of low intensity for up to 4 days;
- yellowish and brownish discharge for up to 7-10 days.
10 days after surgery, patients are prescribed anti-inflammatory suppositories. But it is also recommended to avoid complications within 20-45 days after surgery:
- exclude physical activity;
- refuse sexual intercourse;
- do not take hot baths;
- do not swim in ponds and pools;
- maintain hygiene.
Do I need to treat a cervical cyst?
For cystic formations of the cervix, expectant management is often acceptable. A small cyst (up to 5 mm) without severe symptoms may not be treated. This does not mean that you need to let the situation take its course and forget about the problem. You should regularly visit a gynecologist to monitor the growth of the cyst and the condition of the cervix.
Observation scheme:
- Control examination by a gynecologist – once every 6 months;
- Smear for oncocytology – once a year.
If changes are detected in the cervix, a colposcopy is performed. If necessary, the patient's management tactics change.
Colposcopy during dynamic observation of cervical cysts allows timely detection of dangerous changes.
It is important to know
If bloody or other pathological discharge, itching, burning, or pain in the lower abdomen appears, you should consult a doctor outside of the schedule.
Single and multiple cervical cysts can regress on their own:
- Nabothian cysts disappear after the inflammatory process subsides. They decrease in size and are not detected during examination. If, after getting rid of cervicitis, the pathology progresses, you need to change the treatment tactics;
- Cervical endometriosis goes away during menopause. With the onset of menopause, hormonal levels change, and the lesions regress. If cysts remain postmenopausal or even continue to grow, their removal is indicated.
Indications for prescribing therapy:
- Pregnancy planning. Before conception, you need to get rid of pathologies that can interfere with the development of the fetus;
- Infertility. Cervical cysts are rarely the only cause of this condition. It is necessary to look for other diseases, but cervical pathology cannot be ignored. Success is achieved after complex treatment;
- Miscarriage. If the cyst has caused a miscarriage or premature birth in the past, the lesion must be removed before another pregnancy;
- Chronic recurrent cervicitis. Nabothian cysts support inflammation in the genital tract and interfere with the restoration of vaginal microflora;
- Bloody discharge from the genital tract. Frequent bleeding from the vagina creates some discomfort and interferes with a full sexual life;
- Combination with pathology requiring mandatory treatment. If the cyst occurs along with erosion or another disease, the indications for conservative therapy or cauterization of the lesion expand;
Cysts requiring treatment. The photo shows a large cystic cavity that deforms the entrance to the cervical canal.
- Suspicion of precancerous conditions or cervical cancer. Against the background of large or numerous cysts, it is impossible to conduct a full diagnosis and treatment.
It is also useful to read: Paracervical cysts on the cervix and methods of treating this pathology
Refusal of therapy when indicated risks the development of complications:
- Narrowing of the cervical canal. Endocervix cysts block the lumen of the organ, preventing the release of menstrual blood and the conception of a child;
- Deformation of the cervix. Multiple formations change the structure of the organ and interfere with its normal functioning;
- Inflammation of the pelvic organs. Cysts support chronic cervicitis. Ascending infection threatens the development of endometritis and salpingoophoritis.
The development of complications is caused not only by refusal of treatment, but also by inadequately prescribed therapy. In some cases, cysts can be treated using conservative methods. But if drug treatment is ineffective, surgery should not be postponed. In the early stages, the disease is easier to cope with and you can do without radical measures.
Nabothian cysts are not dangerous in terms of malignancy. They are not capable of cell division and do not develop into cancer. There is no clear opinion regarding endometrioid cysts. By default, they are considered benign formations.
Prognosis and complications
Detection of a nabothian cyst is not fatal. This is not a harbinger of cancer. But if no measures are taken, the cyst becomes the cause of serious diseases, including anemia and sepsis. One of the consequences of a ruptured cyst may be infertility or difficulty in conceiving. A significant decrease in the lumen of the cervical canal often causes blood stagnation during menstruation, and painful sensations intensify.
Knowing the mechanism of occurrence of the pathology, it is possible to provide preventive measures: eliminate the factors contributing to the formation of the cyst. For women of childbearing age, it is very important to maintain good hygiene. Use contraception during sexual intercourse, avoid frequent changes of partner, monitor changes in hormonal levels and conduct examinations with a gynecologist at least 2 times a year.
Obstetrician-gynecologist, endoscopic surgeon
More articles
Signs
Symptoms of the pathology depend on its type and single or multiple nature. It is known that Nabothian cysts, unlike endometrioid cysts, are rarely accompanied by a clinical picture.
Retention view
In particular, small single brushes do not have a clinical picture and are usually discovered accidentally during an examination by a gynecologist. The appearance of symptoms with the addition of infection, growth or multiple forms of neoplasm.
Signs of pathology are quite subjective. Some women experience discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse. This is due to a decrease in mucus and vaginal dryness. If the blockage of the ducts is caused by ectopia, abundant mucous discharge is noted. When an infection occurs, the discharge becomes purulent and is often accompanied by an unpleasant odor.
Endometrioid form
As a rule, cysts resulting from endometriosis are accompanied by acyclic bleeding. In addition, a week before and after menstruation, spotting in small quantities may be observed. After sexual intercourse, contact discharge is noted.
Also, the consequences of endometriosis are characterized by the occurrence of:
- pain in the lower abdomen, intensifying during menstruation;
- dyspareunia.
The signs are due to the fact that endometrioid heterotopias slightly increase in size before menstruation. It is noteworthy that they can open on their own and then empty themselves. After the cessation of menstruation, heterotopias decrease.
The pathology is not considered dangerous, does not negatively affect reproductive function in women, and does not cause complications during childbirth. However, the presence of cystic formations may indicate chronic cervicitis or endometriosis. In addition, pathology may indirectly indicate possible causes of infertility or ectopic pregnancy.
If the neoplasms are large or multiple in nature, deformation and hypertrophy of the cervix may develop over time. These complications negatively affect natural childbirth.
The pathology is not dangerous from the point of view of the development of cervical cancer.
Dangerous consequences of pathology
It is important to know:
- A cervical cyst does not affect hormonal levels. It does not change the course of the menstrual cycle. If menstruation is delayed and amenorrhea, you need to look for another reason for this condition;
- Retention formation extremely rarely leads to infertility. If a woman cannot conceive a child, she needs to look for another concomitant pathology. With endometriotic formation, the cause of infertility is often foci of other localization (including in the ovaries);
- The cyst is not associated with the development of fibroids, endometrial hyperplasia, pathology of the ovaries and fallopian tubes, but can appear simultaneously with these diseases;
- Cystic formations of the cervix, ovary, and fallopian tubes develop in isolation from each other and have different causes;
- A cervical cyst does not develop into cancer. This is an exclusively benign pathology;
- Retention cysts often go along with erosion;
- Pathology does not prevent a woman from leading her usual lifestyle. It is allowed to take a bath, sunbathe, visit the solarium, sauna, and the beach.
Nabothian cysts usually accompany cervical erosion.
All of the above does not mean that cervical cysts are not dangerous. However, without treatment, the pathology can lead to the development of undesirable consequences. :
- Chronic cervicitis. An ovarian retention cyst is a site of accumulation of viruses and bacteria. With a decrease in local immunity, an inflammatory process develops. The infection can spread to the lining of the uterus and lead to endometritis. Damage to the fallopian tubes and ovaries is possible - salpingoophoritis;
- Discomfort during menstruation. Endometrioid cysts increase the duration of menstrual flow and lead to pain during menstruation;
- Sexual disorders. Bloody discharge, long-term inflammatory process, pain in the vagina during sexual intercourse - all this interferes with a full intimate life.
Timely detection and treatment of pathology helps to avoid the development of complications.
Possible complications
Cervical cysts cause adverse consequences for a woman’s reproductive system and her health in general:
- Infertility. Caused by the proliferation of endocervical glands, subsequent deformation or complete blockage of the cervical cavity.
- Deformation of the cervix. The reason is the presence of multiple small nodes or one, but large in size.
- An abscess at the site of a blocked nabothian gland. The reason is the suppuration of its contents.
- Rejection of the fertilized egg. The reason is irritation of the cervix by the resulting nodes, which causes contraction of the reproductive organ and the development of a miscarriage.
To minimize the risk of complications, you need to follow all the recommendations of your doctor. If a specialist prescribes hospitalization (for example, if there is a high risk of miscarriage), you should not refuse the advice of a qualified doctor.
Explanation of results, norms and pathologies
norm
Is it possible to independently understand the doctor’s conclusion? Yes, but before diagnosing yourself, you need to carefully familiarize yourself with the norms of ultrasound examination.
First, let's look at what the size of the cervix should be. In normal proportions, the cervix is up to 35 mm. Some women, especially those who have given birth, have a slightly larger cervix. In this case, up to 45 mm is considered normal.
The uterine pharynx is considered normally no more than 5 mm. Please pay special attention that a normal indicator is when there is good patency of the cervical canal itself.
When the cervix dilates, no additional indicators, such as an echo signal, should be observed. If echoes are present, this means that the woman has an ectopic cervical pregnancy, a polyp, or a submucosal myomatous node.
The examined organ has a clear structure, and during the examination the cervix will be without deformations.
There should be no plus or minus tissue symptoms present. If this symptom is detected in a woman, then the ultrasound report will indicate cervical cancer, because such signs are characteristic only of malignant tumors.
In addition, the doctor must take into account the location of neighboring organs. All of the above indicators are considered normal ultrasound.
Pathological changes
It is not difficult for an experienced doctor to make the correct diagnosis. With the help of such an examination, many diseases can be identified. Let's look at the most common pathologies.
You can see cervical erosion and other gynecological diseases on an ultrasound. In women, this unpleasant disease occurs quite often. Erosion is a background pathology, and if treatment is not started on time, there is a risk of an oncological process. But, before you diagnose cervical erosion by ultrasound, you need to know how to smooth out pseudo-erosion.
So, pseudo-erosion is a defect directly in the mucous membrane of the cervix. This problem occurs more often in girls, especially at the age of 25. Pseudo-erosion occurs due to the action of hubbub.
Erosion is already presented as a true defect; it occurs against the background of trauma, as well as under the influence of microorganisms.
Is the extent of erosion visible? Yes, on ultrasound you can see the nature of the erosion. Therefore, the monitor will show during erosion a shallow surface defect that extends deep into the tissue.
A transvaginal ultrasound will help determine the degree of damage, because the doctor does not just insert a sensor into the uterine cavity, but carefully makes rotational movements.
What to do if an ultrasound shows cancer?
Let us immediately note that cancer is a pathology that requires early diagnosis. Therefore, if you suspect cervical cancer, you should urgently undergo an ultrasound examination. After all, this diagnostic method will help establish the localization of the pathological process. In addition, you can find out the extent of the damage, whether the tumor is spreading to neighboring organs, and also carefully examine the condition of the lymph nodes.
How to smooth out cervical cancer with an ultrasound? At the beginning of the article, we told you that if a woman had a “plus-tissue” symptom, then this would mean only one thing: you had a malignant tumor.
In addition, the cancer has an unclear structure; ultrasound will show heterogeneous echogenicity.
Note that malignant formations can fill the entire cavity; we are talking specifically about the cervical canal. There have been cases when a malignant tumor was also located in the uterus itself, here it is necessary to take radical treatment measures, most often surgical intervention is used.
Remember, if you are diagnosed with cancer, you must immediately undergo a full course of treatment, including surgery.
Cervical cyst on ultrasound
Cervical cysts also require careful diagnosis. In medical practice, a cyst means a non-proliferative formation. Such growths on the cervix are most often benign.
A cervical cyst on ultrasound: detecting it is quite simple, because if a round formation is shown on the monitor, this is a cyst. In this case, the cervical cyst will have a homogeneous composition inside.
Carcinoma
Ultrasound examination also shows malignant formations, for example, carcinoma; adenocarcinoma is often discovered during examination. Formations develop from glandular tissue, in particular development occurs from the epithelial layer.
On the monitor you can see that the carcinoma has the appearance of a fuzzy formation, while the pathology penetrates into the thickness of the cervix. Carcinoma is also characterized by heterogeneity.
Treatment
Nabothian cysts do not require treatment. It is only necessary to visit a gynecologist regularly, at least once a year. You should not believe the stories that the cyst needs to be removed surgically, otherwise it may burst, its contents will fall onto the entire cervix, filling the canal - they are not true.
Retention cystic formations do not cause harm: small ones regress on their own, large ones very rarely deform the neck. In this case, they can be subjected to electro- or laser coagulation, performed on an outpatient basis. But what really requires observation and treatment are the pathological processes that accompany complicated ectopic CE: viral, bacterial infections, hormonal, immune abnormalities.
The choice of treatment method for endometriotic lesions is made taking into account the size of the inclusions, severity of complaints, age and reproductive plans of the woman. For small-sized formations and the absence of clinical manifestations and complications, it is sufficient to observe the patients (examination once every 6 months). Volumetric heterotopias, accompanied by bloody discharge and pain, require the prescription of hormonal drugs and immunocorrectors. The ineffectiveness of conservative therapy forces one to resort to electro- or laser coagulation.
Taking into account the location, size and concomitant pathologies, the most optimal method of treating cervical cysts is selected.
Usually, easily accessible formations are opened, freed from contents and treated with antiseptic drugs. If purulent impurities are detected in the secretion contents, antibacterial drugs are prescribed, a sample is taken to identify the suspected pathogen and determine its sensitivity to antibiotics.
In the surgical treatment of cervical cysts, various removal methods are used:
- 1) Cauterization – cystic cavities are removed by cauterization with chemicals.
- 2) Diathermocoagulation method – exposure of the neoplasm to high temperatures.
- 3) Removal of cysts with electric current - electrocoagulation method.
- 4) Laser destruction - allows you to remove the cavity in a non-contact way, controlling the depth of penetration of the laser beam.
- 5) Removal by cryodestruction occurs using exposure to cold - liquid nitrogen.
- 6) The use of the radio wave method is the most optimal today. After it, no scars remain on the tissues, and complications are not typical.
Simple preventive measures can help prevent the development of cystic neoplasms on the cervix. To do this you need:
- regular examinations by a gynecologist;
- be periodically examined using ultrasound;
- for the purpose of prevention, undergo endoscopic examination;
- timely treatment of inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system.
There are quite a few “homegrown” methods for treating cystic formations, but before using them, consult your doctor. Trust yourself to a professional.
If, after reading this article, you think that you have symptoms characteristic of this disease, then you should
Due to the high risk of suppuration of the contents of retention cysts, gynecologists recommend removing these growths. Especially if they:
- Prevents pregnancy
- Disturbs the menstrual cycle
- Causes pain
- Cause uterine bleeding
- Excludes the possibility of sexual activity
- Causes vaginal discharge (purulent, with accompanying itching and unpleasant odor)
There are 3 types of treatment for cysts formed on the cervix - conservative, minimally invasive and surgical. In the first case, hormonal and antibacterial therapy is used. Together, they stop the growth of tumors and eliminate inflammation of the genital organs, which creates favorable conditions for the development of cysts.
Minimally invasive methods are shown in the table
| Cervical cyst removal method | Features of the method |
| Diathermocoagulation | Cauterization of the tumor with high-frequency alternating current. The patient is first given anesthesia. The day before and for about 2 months after the intervention, you should not have intimacy. Currently, the method is practically not used in gynecological practice. The reason is the high risk of side effects. |
| Chemical cauterization | It involves the use of a special chemical solution - “Solkovagina”. Almost all patients tolerate this drug well. Control of the application and distribution of the substance over the problem area is carried out using colposcopy. No preliminary anesthesia is required. |
| Laser vaporization | Upon completion of the manipulation, a thin protective crust is formed on the treated surface. It comes off on its own within a few days. It is not recommended to try to remove it yourself - this will cause bleeding and inflammation. The advantage of the method is that only the area of the cervix where the neoplasms are localized is subject to treatment. |
| Cryodestruction | The main contraindication for the procedure is the presence of fibroids. Throughout the recovery period, the patient experiences watery vaginal discharge. They do not have a bloody consistency, but cause discomfort. |
| Radio wave technique | The procedure is absolutely painless. During treatment, the doctor does not touch healthy tissue. Contraindication: the presence of an implanted pacemaker. The likelihood of bleeding is excluded, since the blood vessels that lie near the growths are sealed with high temperature. |
Diathermocoagulation
After cauterization, a characteristic scab is formed on the tissues - a crust, which is torn off approximately by the 12th day of the recovery period. But complete healing of the area occurs within 2 months. Minor bleeding is observed until complete scarring occurs. During tissue epithelization, you cannot use hygienic tampons to minimize the risk of developing inflammatory processes.
The drug is applied to the cervical cysts using a regular cotton swab and tweezers. Pre-problem fabrics should be dried. The duration of the procedure is no more than 3 minutes, the treatment is painless. The method is effective if it is completed in a course - a single exposure is not enough to remove cervical growths.
It is the evaporation of emerging nodes using a high-energy beam. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. Complete tissue restoration occurs after 1 month. It is not always possible to eliminate neoplasms in one treatment - a second visit to a specialist is possible. The risk of infection or bleeding is excluded.