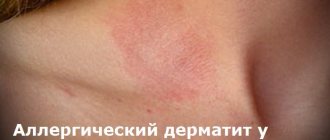
Simple irritant dermatitis forms on the skin after direct, single contact with a provoking factor.
Signs of the disease are irritation, redness of the skin, blisters, microcracks, unbearable itching, peeling. Your doctor will tell you how to treat dermatitis.
Contact dermatitis is a skin disease that occurs due to direct exposure to irritating factors. Simple irritant dermatitis should be treated immediately.
Effective treatment of simple contact dermatitis
Irritant contact dermatitis is an inflammation of the dermis that occurs in response to direct exposure to various substances: detergents, alkalis, solvents, acids. The symptoms of the disease depend on the nature and strength of the influence of provoking factors. The disease can be expressed in dryness, redness, swelling of the skin, blisters, scabs.
Simple contact dermatitis is diagnosed by identifying the etiology of the disease with direct exposure to various chemicals on the dermis. Therapy for the disease consists of eliminating the cause, local use of anti-inflammatory, glucocorticoid, antibacterial and healing drugs.
What provokes it?
Simple contact dermatitis occurs when there is contact with substances that irritate the skin of any person. Such irritant substances are called obligate substances. Obligate type stimuli include:
- caustic chemicals, for example, sulfuric acid;
- physical type actions - ultraviolet or radiation irradiation, exposure to high or low temperature;
- mechanical type action - squeezing, friction;
- biological substances - plant juice or pollen.
Advice! An example of the effect of a biological factor on the skin is contact with nettles. Upon contact with this plant, redness of the skin and the appearance of small rashes or blisters are noted.
Simple irritant contact dermatitis has no incubation period; the skin reaction occurs almost immediately after adverse exposure. The disease can occur in any person, regardless of gender and age.
Causes of skin disease
There are several types of illness:
- simple irritant contact dermatitis - develops in the presence of provoking
factors: alkalis, acids, various chemistry;
- contact allergic form of skin inflammation - reaction of the dermis to cosmetics, various metals, plants, dyes;
- contact phototoxic dermatitis is a disease that occurs through exposure to ultraviolet radiation on the dermis (diagnosis of this form of the disease is difficult, since the symptoms of the disease occur directly upon contact with the irritant);
Skin reactions can occur in response to exposure to various substances. In the development of the disease, the decisive factor is determined not by the nature of the provoking factor, but by the individual reaction.
Substances that cause contact irritant dermatitis:
- nickel is a material used in the manufacture of buckles, coins, various jewelry,
dentures for teeth and utensils;
- latex – used in the manufacture of gloves, condoms, pacifiers, pacifiers, toys;
- medications: ointments, creams containing hormones, antibiotics;
- cosmetics intended for the care of the dermis (decorative products);
- household products intended for home care;
- synthetics, used to make various clothes;
- substances such as ink, paint, glue.
Diagnostics
To establish a diagnosis, special application tests (patch tests) are used, which involve applying the allergen to a particular area of the skin. At the same time, during the diagnostic examination, a clinical and biochemical analysis of blood and urine is prescribed. If there are indications, blood tests are performed for hormones, a coprogram, tests for dysbacteriosis are taken, and an ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs is performed (in order not to miss concomitant pathologies).
During the study, it is mandatory to carry out a differential diagnosis of contact dermatitis with various forms of eczema and atopic dermatitis.
Signs of skin disease
Simple contact dermatitis is formed due to the influence of external factors on the skin. Mediators begin to be released in the dermis. Swelling and inflammation appear, thereby triggering the main inflammatory process.
General signs of the disease:
- The acute course of dermatitis is accompanied by an inflammatory reaction (after direct contact with the provocateur) - redness, with angular, clear edges.
- The localization of the lesion depends on the duration, strength of exposure and type of irritant, and the depth of infection.
- Simple contact dermatitis occurs in several stages:
- erythematous: swelling, redness;
- vesiculobullous: vesicles with clear liquid form against the background of inflammation, bursting, exposing the erosive surface;
- necrotic-ulcerative stage: the appearance of ulcerations, scabs, scar formation.
- The patient begins to be bothered by a burning sensation, unbearable itching, and pain in the affected area.
- With simple chronic dermatitis, keratinization and thickening of the dermis, increased skin pattern, and peeling may be observed. Such signs appear with repeated and constant contact with the irritant.
Contact dermatitis: symptoms
We said above that the disease can occur in acute and chronic forms.
Acute contact dermatitis is characterized by a severe inflammatory process. The affected area becomes red and swollen. In addition, in the acute phase of the disease, small blisters and nodules appear on the patient’s skin. If the acute phase is severe, diaper rash and crusts on the skin may occur.
Often the acute phase of contact dermatitis affects large areas. Therefore, the vesicles and nodules formed on the epidermis are necrotic in nature. This in turn leads to additional symptoms.
The patient experiences:
- Itching.
- Severe burning sensation.
- Feeling hot.
- In rare cases, pain occurs.
- Contact dermatitis is a very insidious disease, and if not treated in a timely manner, the disease becomes chronic.
The cause of the chronic form of the disease can be frequent friction and pressure. The clinical picture is characterized by thickening of the upper skin layer, so the patient may experience infiltration or lichenification. To be clear, lichenification is a secondary element of the rash. It is characterized by a sharp thickening of the skin and an intensification of the pattern. Often this symptom causes a pigmentation disorder.
If left untreated, contact dermatitis in the chronic phase can lead to hyperkeratosis.
It should be noted that the disease can manifest itself in the form of erythema or bullous reaction. Therefore, the skin is swollen and pronounced hyperemia is observed. This course without treatment leads to atrophy of the skin.
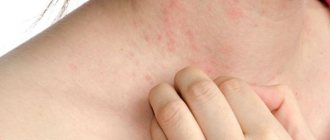
With allergic contact dermatitis, the following symptoms occur: severe itching, redness of the skin at the site of contact with the allergen. Small blisters filled with clear liquid begin to appear on the skin. The surface of the skin begins to ache, and a person with allergic contact dermatitis feels weak.
Simple contact dermatitis in a baby
Allergic skin diseases are quite often associated with the use of various cosmetic hygiene and dermal care products. The disease can also form as a reaction to contact with metal, latex toys and objects, under the influence of the sun or cold.
Simple dermatitis can appear as a result of systematic pressure, friction of clothing or shoes, or interaction of the skin with chemicals (for example, when washing things with aggressive detergent powders). An allergic reaction in newborns is often caused by the use of low-quality (cheap) diapers, as well as powders or creams for the buttocks and groin area.
At the first signs of simple dermatitis in a baby, you need to consult a specialist to identify the etiology of the disease, and also eliminate the irritating factor.
Chronic dermatitis
If we talk about the chronic form of contact dermatitis, it can develop with constant exposure to even a mild irritant. Very often the skin of the hands can be affected. Typically, this disease is directly related to constant contact of skin and detergents or any other household chemicals. Characteristic manifestations of chronic dermatitis can be dry skin, congestive hyperemia, infiltration and more. In special cases, an atrophic process occurring on the skin may be observed. If we talk about subjective sensations, they are weakly expressed.
Complications and consequences of the disease
Simple irritant dermatitis generally does not cause serious problems and goes away when the provoking factor is neutralized. Sometimes small areas of scar tissue or hypopigmentation remain on the dermis, which is caused by damage to the deeper layers of the skin.
Prolonged exposure to X-rays can lead to the formation of non-healing small ulcers and their malignancy.
The main complication that the disease can cause is chronic eczema. Scratching the affected areas often causes the appearance of pyoderma and microbial eczema. Through microtraumas, viral and fungal pathogens penetrate the skin - lichen, HPV, herpes.
Complications
In addition to chronicity, contact dermatitis can be accompanied by other possible complications.
For any form, there is a high probability of infection in those places where the integrity of the skin is damaged, for example, in the area of scratching:
- Scars can also form at the site of injury;
- pigment spots remain after inflammation;
- the allergic type can develop into eczema.
Typically, the occurrence of complications is associated with self-treatment at home and failure to consult a doctor in a timely manner to make a correct diagnosis and prescribe therapy.
Preventative measures against the disease
Treatment of dermatitis is a comprehensive long-term therapy aimed at eliminating the symptoms of the disease. To prevent allergic reactions in children and adults, you need to follow a number of recommendations:
- when working with
when dealing with chemicals, it is worth using protective special gloves to prevent the development of simple acute contact dermatitis;
- in direct contact with water or soil, it is better to use protective creams;
- Allergic reactions on the face can be prevented with the help of special cosmetics;
- For the safety of children, it is necessary to limit contact with chlorine-containing substances and dyes;
- In addition, it is important to adhere to general medical recommendations: bathe babies thoroughly with soap and shampoo every day, and systematically change diapers.
Classification
According to the mechanism of skin reaction, contact dermatitis is divided into simple and allergic.
Allergies on the arms and hands
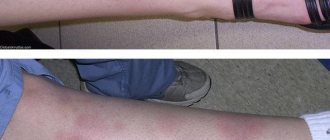
In the area of the palms and forearms, allergic dermatitis appears most often due to contact with various chemicals, due to profession or at home.
Itchy redness on a swollen base appears on the skin of the outer surface of the palms or wrists immediately or several days after exposure to the irritant. Against the background of erythema, small bubbles with a yellowish liquid are visible, which open to form erosions. This picture is typical for new-onset acute dermatitis.
In repeated cases, cracks often form instead of blisters, the skin becomes dry, thickened with a pronounced pattern due to its chronic course.
The lesion affects not only the skin directly exposed to contact, but also at a distance, and with frequent exacerbations and improper treatment, it can spread throughout the body (erythroderma).
What does irritant look like on the fingers?
Manifestations of irritant dermatitis depend on the concentration of the irritant.
Dryness and small cracks on the fingers arise from constant contact with water and soap, exposure to the cold without gloves. The skin acquires a waxy sheen, becomes inflamed in areas of cracking, and movements become painful.
Exposure to a concentrated irritant leads to skin burns with severe inflammation, burning, blistering, and even necrosis.
Irritant dermatitis can affect both the entire surface of the fingers and only their tips. The skin near the nails cracks, peels, and touching it is painful.
Causes of simple irritant dermatitis on the face
Simple irritant contact dermatitis on the face can be caused by:
- Decorative cosmetics, which is most common among women.
- Contact with metals when wearing piercings or earrings.
- Physical factors such as low temperatures (chapping), solar radiation, ultraviolet solarium lamps.
- Medicines for the local treatment of facial skin diseases.
- Use of essential oils undiluted.
- Cosmetic procedures (peeling, laser, mesotherapy).
- Contact with poisonous plants or flora to which the skin is hypersensitive.
Effective therapy for skin diseases
Treatment of simple contact dermatitis involves a comprehensive approach. Often, allergic reactions are associated with inflammation of a specific area of the dermis. When bubbles and blisters filled with serous fluid form, a dermatologist may recommend antihistamines. With the help of such drugs, unbearable itching can be eliminated, preventing the spread of various infections.
Among the effective medicines we can highlight Diazolin; it is affordable and easy to use. According to the instructions, it must be used 3 times a day, one tablet at a time. In addition to antihistamines, local treatment is prescribed, for example, Flucinar ointment. The medicine contains glucocorticosteroids that have a certain effect:
- neutralizes infiltration;
- restores damaged cells;
- eliminates swelling.
For mechanical impact, zinc-containing ointment is recommended. Regarding the choice of drugs, recommendations should be obtained from a doctor who, after identifying the etiology of the disease, will help prescribe appropriate therapy.
In complex therapy of contact allergies, the following are used:
- solutions of aniline natural dyes;
- local antihistamines: “Fenistil”, “Psilo-balm”;
- medicines containing zinc for drying small wet areas: “Zinocap”, “Skin-Cap”;
- creams and ointments to accelerate the recovery process of the dermis, eliminate dryness: “Propolis”, “Menthol ointment”, “Bepanten”, “D-panthenol”;
- baths with celandine, string and natural oak bark;
- antibacterial drugs for damage to the dermis by pathogens: “Lincomycin”, “Erythromycin” ointments.
During therapy, as well as to prevent relapses of allergies, you should adhere to a special diet that excludes certain foods - food allergens, carbohydrates.
Causes
Simple contact dermatitis can occur either due to the direct influence of an allergen or as a result of a complex reaction of the immune system. For the formation of the disease, a secondary or prolonged effect of the irritant on the skin is necessary. When the allergen first comes into contact with the skin, a process called sensitization occurs. This is the activation of the immune system, the development of a unique reaction to the pathogen. In appearance it is not expressed at all. With secondary exposure to an allergen, it is recognized and a pronounced immune response occurs, manifested by specific inflammation. An infectious disease, usually enterobacterial, occurs again.
Treating dermatitis at home
For mild forms of simple dermatitis, folk remedies will help overcome the disease:
- Potato. Finely grate the vegetable, mix with honey (tbsp), apply the resulting mixture to the affected areas, leave under film overnight.
- Baths with an infusion of medicinal valerian, chamomile, oregano and stinging nettle (in equal proportions) will help quickly eliminate the disease. Add 2 tablespoons of herbal mixture per liter of liquid.
- It is useful to apply herbs soaked in boiling water (melissa, burdock, calendula) to the surface of the skin. After the plant has completely softened, grind it and apply it to the problem area as a compress, leaving for several hours.
- For unbearable itching, it is recommended to rub fresh cucumber juice.
- Dill. Infuse 100 grams of the plant into 400 ml of sunflower oil. Leave in a dark place for
for 3 weeks, wipe the skin if there is severe itching.
- Crush the nut leaves well. Pour a tablespoon of the plant with plain water (200 ml). Place on fire, bring to a boil, leave for several hours, filter. Use as compresses.
- Birch buds. Prepare a decoction: 2 tbsp. l. for 300 ml of plain water. Wipe the skin with the resulting infusion, and also use it as a compress.
- It is recommended to rinse items several times after washing and use only high-quality hygiene products and cosmetics.
Preventing dermatitis is much easier than treating it. It is recommended to buy clothes for your baby and for yourself made from natural fabrics, of the appropriate size, without hard parts. Adhere to personal hygiene rules and avoid direct contact with provoking factors. In addition, you should not self-medicate.
What is the difference between allergic dermatitis and contact dermatitis?
Allergic contact dermatitis develops under the influence of facultative irritants, which most often are haptens in nature. What does this mean? A hapten is a small particle of a substance that, when combined with skin proteins, triggers an allergic reaction. Symptoms of allergic dermatitis do not develop immediately, but within several hours after contact. As a rule, they are represented by severe swelling, pronounced hyperemia, and a rash like urticaria. Small bubbles filled with liquid appear on the inflamed skin, after opening which a weeping surface remains. Healing of the damaged area occurs through the formation of crusts; a purple or bluish spot remains at the site of hyperemia for a long time.
The difference between contact dermatitis and allergic dermatitis is the extent of the lesion. Simple irritant dermatitis clearly corresponds to the area of contact with the damaging factor and appears in the first hours after damage.
The severity of inflammation symptoms directly depends on the time of contact and the concentration of the irritant. Allergies can spread much more widely. For example, after contact with a detergent, hyperemia and swelling occurs on the hands, and a urticaria-type rash occurs on the forearms and shoulders. It does not always develop immediately; a latent period of up to 15 days is possible. The time of contact and the concentration of the irritant do not affect the severity of the inflammatory process; it depends only on the strength of the immune response.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
To reduce itching and soothe inflamed skin, try these self-help methods:
- Apply anti-itch cream or calamine lotion to the affected area. An over-the-counter cream containing at least 1% hydrocortisone may temporarily relieve your itching.
- Avoid contact with irritants or allergens. If this concerns jewelry, then you can simply refuse to wear it.
- Apply a cool, damp compress. Soak a soft cloth in cold water and apply it to the affected area for 15 to 30 minutes to soothe your skin. Repeat this procedure several times a day.
- Take anti-itch medication. Over-the-counter antihistamines, such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl, etc.), may be helpful if you suffer from severe itching.
- Take cold baths and immerse the affected areas of the skin (arms and legs) in them. You can also spray the affected skin with cold water and baking soda.
- Avoid scratching. Trim your nails. If you can't stop scratching the itchy area, cover it with a bandage and bandage.
- Protect your hands with moisturizers and gloves. Apply moisturizers to your skin throughout the day. If you get a rash on your hands, wear protective rubber gloves.
- Use cream soap without dyes or fragrances. Wash the rash areas thoroughly, then pat the skin dry and apply moisturizer.
An important rule is to purchase clothes only from natural fabrics, as well as appropriate size, with no hard parts.
What is cutaneous dermatitis?
Dermatitis comprises a huge group of skin diseases. They can be triggered by both external and internal reasons.
The disease may be accompanied by:
- decreased functional characteristics of the skin;
- disturbances in homeostasis;
- various pathological processes.
ICD 10 code
According to the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision, dermatitis and eczema are coded L20-L30 . Moreover, the terms “dermatitis” and “eczema” refer to one block of diseases.
This classification also includes types of skin dermatitis under an individual code:
- L 20 - Atopic dermatitis.
- L 21 - Seborrheic dermatitis.
- L 22 - Diaper dermatitis.
- L 23 - Allergic contact dermatitis.
- L 24 - Contact dermatitis.
- L 25 - Contact dermatitis, unspecified.
Stages of atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is characterized by the presence of two stages:
Acute stage. It is expressed by severe redness of the skin, itching, dryness, swelling, the appearance of wounds and blisters.
Chronic stage - the spots take on clear outlines, the skin thickens, and cracks may appear. The itching becomes very severe.
Scratching the inflamed areas can lead to the appearance of pustular rashes due to dirt getting into the wounds.
Folk remedies in the treatment of dermatitis symptoms
In addition to drug treatment, you can add folk remedies. Decoctions from some plants will help relieve inflammation, remove redness and itching, these include: string, celandine, geranium, Japanese Sophora and periwinkle.
Healthy diet
When treating a disease, you must adhere to proper nutrition and exclude foods that cause allergies, namely:
- sweets: honey, chocolate, caramel, marmalade;
- plant origin: citrus fruits, tropical fruits, mushrooms, pickled beans, sauerkraut, raisins, nuts, dried apricots, berries, dates;
- protein: fatty meat, fish, chicken eggs, whole milk, caviar, stewed meat, seafood;
- Preservatives, sauces, mayonnaise;
- Seasonings, semi-finished products.
It is advisable to consume low-allergenic foods:
- veal;
- cod;
- sea bass;
- oatmeal;
- semolina;
- liver;
- skim cheese;
- fresh cabbage;
- rice;
- cucumbers;
- pears;
- gooseberry;
- white currants;
- cherries;
- spinach;
- zucchini;
- still water;
- compotes;
- fermented milk;
- prunes.
All food should be quickly and easily digested. Without proper nutrition, curing dermatitis will be difficult and will take twice as long.
Causes of dermatitis
Dermatitis can be obligate (conditional), which includes external irritants, and facultative (unconditional), which affects people with severe sensitivity.
The nature of the disease can be physical, mechanical, medicinal, biological or chemical.
- Biological irritants - flowers, grass, animal hair, insects, pollen, fish scales, honey, etc.
- Physical – burns, reaction to sunlight or cold, insect bites, consequences of electrical injuries.
- Chemical - the effect of acids and alkalis, synthetics, detergents, paints, perfumes, varnishes, dyes, polymers and other chemicals.
- Mechanical – diaper rash, abrasions.
- Medicinal - reaction to novocaine, lidocaine, sulfur, acids, and other drugs.
Video about the causes of dermatitis
nginx
Pruritic dermatitis and its symptoms
Severe stress or nervous tension causes itchy dermatitis. Its occurrence is provoked by poor hygiene and various allergens.
Symptoms of the disease:
- purulent, vesicular, confluent or papular rash;
- decreased sensitivity in localized areas;
- increased body temperature;
- itching
It is rare in children. The manifestation of dermatitis in adults is observed in different parts of the body. The skin is very itchy, as a result of which the skin is scratched until wounds form.
Allergic dermatitis - symptoms in adults and children
All types of allergic dermatitis have a similar clinical picture. Adults and children may have the following symptoms:
- erythema - redness of the skin, which is accompanied by swelling and increased local temperature;
- hives;
- itching, burning;
- blistering rashes;
- wet crusts;
- eroded areas of skin.
The above signs do not appear all at once. The development of the acute stage of the disease occurs in several stages:
- The first signs are erythema (erythematous dermatitis) or blistering rashes (vesicular) on non-inflamed skin;
- The second stage is the formation of eroded areas;
- The necrotic stage of advanced allergies is the formation of non-healing ulcers with tissue death.
Article on the topic: Dexamethasone (tablets, injections in ampoules, spray and eye drops) - instructions for use
The localization of allergic manifestations depends on the type of dermatitis and the characteristics of the patient’s body. The atopic form appears as blistering rashes between the fingers, on the fingers themselves, on the inside of the palm.
Blistering rashes on hands
Less commonly, it spreads to the backs of the hands and higher up the arm. Severe nervous shocks suffered by an adult can cause acute neurodermatitis on the face, neck, décolleté, and arms to the elbow in a couple of days.
Blistering rashes develop into eroded lesions. Treatment requires systemic and local medications, often hormonal in a hospital setting.
Contact dermatitis in children (diaper dermatitis) is localized in the genital area, buttocks, perineum, and on the inside of the thigh. Poor hygiene causes similar inflammatory symptoms, but the manifestations of allergic dermatitis require different treatment methods.
Food dermatoses in children are manifested by inflammation on the face, neck, behind the ears, on the arms, stomach, back, and head. In older children, toxic allergic dermatitis is localized on the inside of the elbows, under the knees.
Note! Dermatoallergoses in children affect a larger area of skin than that which is in direct contact with the irritating factor.
Food dermatoses on the body in adults
Local treatment
Several methods are used for local treatment of dermatitis:
- Ointments. They are made from fats or fat-like substances. They have softening, warming and nourishing properties.
- Crema. The preparations are made on a water basis and contain a smaller amount of the active ingredient.
- Gels. They have a cooling effect, which is based on improved absorption of medicinal components.
- Pastas. These products consist of half ointment and powder. They have an anti-exudative effect.
- Lotions. It has drying properties and absorbs exudate from the affected areas.
- Chatterboxes. It is a mixture of vegetable oils and aqueous-alcohol solution. They have an antipruritic and anti-inflammatory effect on inflamed areas.
- Plasters. Used to treat chronic dermatitis. They are a mixture of wax, polymers and resins.
The best option for treating dermatitis remains hormonal and non-hormonal ointments.
Hormonal ointments for skin dermatitis
Topical hormonal drugs have a whole range of contraindications:
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Application is possible only in short courses.
- The manifestation of side effects may be delayed.
- Skin atrophy.
- Sometimes adrenal insufficiency may develop.
- The patient's age is up to 2 years.
For skin dermatitis, ointments based on hormones are most effective:
- Celestoderm. Used in the treatment of seborrheic, atopic, solar, contact dermatitis. On average, the price ranges from 220-350 rubles per tube.
- Advantan. It is a hormonal, fatty ointment. Prescribed for all types of skin dermatitis. The cost ranges from 350-400 rubles per package.
- Flucinar. The ointment is effective for seborrheic and atopic dermatitis. If ointment bases are poorly tolerated, you can use a gel. Not suitable for use by children under 2 years of age. The price ranges from 170 to 200 rubles.
- Fucicort. Hormonal cream effectively fights not only all manifestations of dermatitis, but also additional infections. The price is within 380 rubles.
- Akriderm. The product is used both for skin dermatitis and for any allergic reactions of the skin to irritants. The ointment is also effective against psoriasis, eczema and neurodermatitis. The price does not exceed 120 rubles.
Here you can read in more detail the instructions for using Akriderm ointment and what it is for.
Non-hormonal ointments
Non-hormonal ointments are quite effective in the fight against dermatitis:
- Eplan. Used for psoriasis, ulcers and cracks. Used to relieve swelling and itching in dermatoses. Can be used as a prophylactic drug to protect against chemical irritants. The price ranges from 140 to 160 rubles.
- Skin Cap. It has antifungal, antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects on inflamed areas of the skin. The drug is effective for seborrheic and atopic dermatitis. Can be used by children from 1 year of age. The price ranges from 15 to 650 rubles.
- Exoderil. An antifungal cream that can be used even with unknown provoking factors. The price is within 350 rubles.
- Radevit. The ointment effectively fights all dermatitis. Has anti-inflammatory, antipruritic, softening effect. The average price is 320 rubles.
- Elidel. Prescribed to combat atopic dermatitis. The working component is pimecrolimus. The cost is about 950 rubles.
Treatment of skin dermatitis
Each type of dermatitis has its own specific therapy.
Depending on the manifestations of skin inflammation, there are several methods for treating dermatitis:
- Taking antihistamines.
- Diet food.
- Use of hormonal and non-hormonal drugs.
- Taking an antifungal complex of medications.
- Antibiotic therapy.
- The use of drugs to normalize digestive processes.
- Psychotherapy.
- Phototherapy.
- The use of baths or lotions based on medicinal herbs.
Symptoms
In the process of development of skin dermatitis, it is customary to distinguish two types of its course:
- acute form;
- chronic form.
This disease may be accompanied by mandatory or additional symptoms .
The first one is itching. In the acute form, the skin shows signs of swelling and redness with unclear edges. If the disease has become chronic, the skin may retain its usual color. The most commonly affected areas of the body where rashes occur are:
- groin area;
- sides of the body;
- scalp;
- face and skin on joints.
If the disease occurs in a chronic form, then it is necessarily accompanied by lichenification . It refers to a condition characterized by thickening of areas of the skin that take on a rough pattern. In addition, the skin may scratch itself and become covered with cracks. If skin dermatitis has an acute form, then the skin will have exudative inflammation. Patients also experience peeling caused by decreased activity of the sebaceous glands and dehydration of the skin.
The type and nature of additional symptoms becomes particularly important for the physician, who uses them as the basis for making a differential diagnosis for a specific dermatitis. For this purpose, functional tests are taken, laboratory tests, visual examination and patient interviews are carried out.