Category: Published 04/27/2016 · Comments: · Reading time: 5 min · Views: 5,190
Furosemide, what do these tablets help with? The drug is well known for its diuretic properties, which help relieve swelling. The diuretic "Furosemide" instructions for use prescribes taking it for edema, heart failure, hypertension.
Release form
A loop diuretic can be purchased in the form of tablets and solution for intravenous administration (in rare cases, intramuscular injection).
Pills
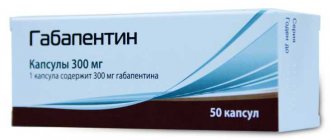
The package contains 50 tablets. Each tablet contains 40 mg of active ingredient.
Solution
The package contains 5, 10 or 25 ampoules with a 1% solution of 2 ml. There is a 5% solution that is used in veterinary medicine.
Furosemide can be purchased in the form of tablets and solution for intravenous administration (in rare cases, intramuscular injection).
Is it possible to lose weight with Furosemide?
Before studying the question of how to take Furosemide for weight loss, you need to find out how effective the drug is. The tablets, in addition to the main component, contain: potato starch, magnesium stearate and milk sugar. A diuretic (a group of diuretics) increases urine production. This process helps draw additional fluid from the tissues, so the medicine is prescribed to people suffering from kidney disease, liver disease, cardiovascular pathologies, and not from excess weight.
A side effect of Furosemide treatment is weight loss, but this is only a temporary effect. Fat deposits remain in place, only water leaves, which will return again after stopping the diuretic. For this reason, you should not rely only on Furosemide if you want to get rid of some excess weight. The drug will only help for a short period of time, so it is better to use it as an express method, but first you must consult a specialist.
Pharmacological properties
In the instructions you can learn about the pharmacological properties of this drug.
Pharmacodynamics
The drug blocks the reabsorption of sodium ions. After administration, the blood pH level increases. Phosphates, calcium, chlorine, sodium, potassium and magnesium are intensively removed from the body. The drug dilates peripheral blood vessels and reduces the load on the heart.
Pharmacokinetics
Completely absorbed and 95% protein bound. Metabolized in the liver. Excreted in urine and bile. The half-life is 50-60 minutes.
Description of Furosemide
The drug Furosemide is a substance with a diuretic effect on the body. It is also called loop therapy, due to the fact that the main action is on the loops of Henle, which stimulate strong but short-term diuresis (urine excretion).
Prevents the absorption of sodium and chloride ions that occur in the kidney tubules. Therefore, it is believed that the drug acts on the body as a diuretic, removing sodium and chlorine. Due to the loss of essential beneficial elements, the kidneys increase the excretion of moisture and increase the production of potassium ions. At this stage, calcium and magnesium are removed from the body. Such rearrangements begin to affect renal blood flow, redirecting it to calcium secretion.
Indications for use
The drug helps reduce blood pressure in arterial hypertension and eliminate swelling that is caused by:
- nephrotic syndrome;
- heart failure;
- liver diseases;
- renal failure (including burns and pregnancy).
The solution is used for the acute course of these diseases. Injections are carried out for pulmonary and cerebral edema, eclampsia, cardiac asthma, hypertensive crisis and chemical poisoning. The drug may be prescribed for ascites in the form of tablets or solution.
Furosemide for edema
Furosemide helps with edema because it stimulates the kidneys to remove salt and fluid from the body. Unfortunately, this medicine does not eliminate the causes of edema, and sometimes even worsens them. As a rule, edema is caused by heart failure, kidney or liver disease, and also problems with blood vessels in the legs. It is necessary to take measures to eliminate the cause of edema, and not just muffle their symptoms with furosemide. Unauthorizedly taking diuretics for edema, you can get yourself into trouble. Furosemide is a powerful medicine that causes serious side effects. There is a possibility that it will permanently damage the kidneys.
If you regularly experience swelling, do not ignore it, but consult a doctor as soon as possible. Get a medical examination to determine the cause. The diseases listed above respond well to treatment in the early stages. Potent diuretic drugs are prescribed as symptomatic treatment in severe cases, when time has been lost and the underlying disease can no longer be affected. Furosemide for edema sometimes helps even patients for whom it is no longer useful to take thiazide diuretics (Hypothiazide and its analogues).
How to take Furosemide
You need to take the tablets in the morning before meals. For arterial hypertension, 1-2 tablets per day are prescribed. If necessary, other drugs are used in combination to lower blood pressure. In other cases, the dosage is selected taking into account the indications. For children, the recommended dosage is 1-2 mg/kg. It is better to administer the solution intravenously if it is not possible to take pills. An IV should be placed in cases of severe nephrotic syndrome or in an emergency situation. Dosage - 1 or 2 ampoules.
Furosemide should be taken in the morning before meals.
For renal failure
Take 1-2 tablets (40-80 mg) per day. If possible, the dosage is divided into 2 doses.
With sand in the kidneys
Daily dosage is from 20 to 80 mg.
For glomerulonephritis
Prescribe half a tablet once a day. The dose can be increased to 2 tablets per day.
For renal colic
You need to take 20-40 mg per day.
For pyelonephritis
The daily dosage for pyelonephritis is half a tablet. The dose may be increased to 40 mg.
For urolithiasis
In the presence of phosphate and calcium stones, 1 tablet per day is prescribed.
In the presence of phosphate and calcium stones in the kidneys, 1 tablet per day is prescribed.
For cystitis
The minimum dosage is prescribed. The tablet is taken 1 time per day. The interval between doses should be at least 6 hours.
For nephrotic syndrome
The standard dosage is 1 tablet per day. You can take 2 tablets. As your condition improves, you can take 1 tablet every 2-3 days.
Dose selection
It is worth remembering that the dose and frequency of administration are determined only by the attending physician, and he takes into account:
- severity of imbalance of water and electrolytes;
- the amount of filtration of the kidney glomeruli;
- severity of the patient's condition.
It makes sense to administer furosemide intravenously if other routes of administration have proven ineffective. In this case, it is necessary to switch to oral use of this drug as quickly as possible.
The maximum daily dose for an adult patient is 1.5 grams. The dose for a child is calculated as 1 mg/kg body weight.
Swelling due to chronic cardiac dysfunction begins to be treated with the administration of 20-50 mg of the drug per day, divided into 2-3 doses. Treatment of edema in acute cardiac dysfunction involves the use of 20-40 mg of the drug for bolus injection.
Before starting the administration of furosemide in the presence of acute renal failure, it is necessary to compensate for hypovolemia, low blood pressure and a significant imbalance between electrolytes and acids with alkalis. The initial dose is 40 mg, which is administered intravenously.
A hypertensive crisis is treated with a dose of furosemide of 20-40 milligrams in the form of a bolus injection, and the dose is adjusted depending on how the patient’s body reacts.
Special Tips
When using furosemide in injections, it is worth considering certain features:
- the intravenous injection is given slowly at a rate of 4 milligrams of the substance per minute;
- in the presence of severe liver dysfunction, it is recommended to reduce the rate of administration to 2.5 milligrams of the drug per minute;
- furosemide injections are given on the condition that intravenous and oral use is inappropriate;
- It is prohibited to administer the drug in case of pulmonary edema;
- This drug should not be mixed in the same syringe with other drugs.
How many days to take Furosemide
The duration of treatment depends on the indications and the patient’s condition during therapy.
How long does it take to work?
The tablets begin to act 30-60 minutes after administration, and the injections - after 10 minutes.
Furosemide tablets begin to act 30-60 minutes after administration, and injections - after 10 minutes.
How long does it last?
The product is effective for 3-6 hours.
Instructions for use
| pharmachologic effect | Furosemide stimulates the kidneys to excrete more fluid and salt in the urine. This is called a diuretic (diuretic) and natriuretic effect. Thanks to it, swelling in patients decreases. Unfortunately, along with excess water and salt, the body also loses valuable electrolytes - potassium and magnesium. This may cause side effects, which are detailed below. The diuretic effect of furosemide is pronounced, and the larger the dose of medication the patient takes, the stronger it is. The kidneys are made up of filtering elements called nephrons. Furosemide acts on a part of the nephron called the loop of Henle. Therefore, it is classified as a loop diuretic. It is more powerful than thiazide and thiazide-like diuretics - Hypothiazide and Indapamide (Arifon). |
| Pharmacokinetics | After taking a furosemide tablet, the diuretic effect begins within 60 minutes. The injection of this medicine begins to act within 5 minutes. Each dose of furosemide lasts 3-6 hours. The diuretic effect wears off quickly and is considered a disadvantage compared to the newer diuretic drug torasemide (Diuver). Furosemide and its metabolites are excreted 88% by the kidneys and 12% by the liver, with bile. The more severe the kidney or liver failure, the slower furosemide is eliminated from the body and the higher the risk of side effects. Also, the excretion of furosemide slows down in patients with heart failure due to weakened renal function. |
| Indications for use | Furosemide can be prescribed for edema caused by heart and kidney failure, and liver diseases. Arterial hypertension is also included in the list of indications for use. Sometimes people voluntarily take furosemide for edema and for weight loss. This is discussed in detail below. Diuver (torasemide) is a medication that replaces furosemide in the treatment of heart failure. Torsemide acts more smoothly and causes less side effects. For hypertension, competent doctors try not to prescribe furosemide for daily use due to frequent side effects. It is sometimes used to provide emergency care during a hypertensive crisis. Furosemide remains a popular treatment for ascites caused by cirrhosis of the liver. It is prescribed together with spironolactone; read the article “Veroshpiron” for more details. |
| Contraindications | Kidney disease in which urine production stops. Allergy to furosemide, sulfonamides or sulfonylurea diabetes medications. Significant deficiency of potassium or sodium in the body. Dehydration. Acute glomerulonephritis. Decompensated mitral or aortic stenosis. Severe liver failure, threat of hepatic coma. Furosemide can harm patients who have high levels of uric acid in the blood or gout, impaired glucose tolerance or diabetes, low blood pressure, acute heart attack, pancreatitis, impaired urinary flow, systemic lupus erythematosus, diarrhea (diarrhea). |
| special instructions | Furosemide can cause weakness and fatigue, which increases the risk of getting into an accident. Refrain from driving vehicles and dangerous machinery for at least the first 5-7 days, until the body gets used to the new medicine. It may make sense to take Asparkam, Panangin tablets or salt substitutes rich in potassium along with a diuretic drug. Discuss this with your doctor and do not take potassium supplements on your own. Also discuss with your doctor how much and what kind of liquid you can drink. Be wary of gastrointestinal illnesses that involve vomiting or diarrhea because they can cause dehydration, a dangerous deficiency of potassium and magnesium in the body. Try not to overheat in the sun; it is not advisable to visit a solarium. |
| Dosage | The doctor selects the dosage of the drug furosemide individually, depending on the indications for use, the severity of the disease, the patient’s age and other factors. Adults take furosemide tablets 20-80 mg once or several times a day. Intravenous or intramuscular injections - 20-240 mg. Sometimes higher doses than those indicated above are prescribed. The initial dose of furosemide for children is 1-2 mg per 1 kg of body weight. Maximum - up to 6 mg per 1 kg of body weight. The initial dosage of the diuretic medication is often increased or decreased later. This depends on whether urine formation has increased, the dynamics of the patient’s condition and test results. |
| Side effects | Furosemide often causes unpleasant and even dangerous side effects. Therefore, it should not be taken for self-medication. Symptoms of dehydration, potassium and magnesium deficiency include muscle cramps, weakness, confusion, drowsiness, dizziness, fainting, dry mouth, thirst, nausea, vomiting, fast or irregular heartbeat, unusual decrease in urine output. If you are concerned about serious side effects, consult your doctor immediately. To reduce dizziness, stand up smoothly rather than abruptly from a sitting or lying position. An allergy to furosemide may cause skin rash, itching, and difficulty breathing. Older age and kidney and liver disease are factors that increase the risk of side effects. |
| Pregnancy and breastfeeding | Furosemide crosses the placental barrier and affects the fetus. During pregnancy, it is occasionally prescribed only for severe illnesses, usually threatening the life of the mother. At the same time, carefully monitor the condition of the fetus. Do not take furosemide during pregnancy without permission! Studies on laboratory animals have shown that furosemide in high doses has a negative effect on pregnancy. No studies have been conducted on humans. Furosemide should not be taken while breastfeeding. This medicine passes into breast milk and may affect the baby. It also suppresses the production of breast milk in the mother's body. |
| Interaction with other drugs | Furosemide interacts negatively with many other medications. Because of this, patients often experience dangerous side effects. To reduce your risk, tell your doctor about all the medications, herbs, and dietary supplements you use before you are prescribed furosemide. Use caution when taking this diuretic medication with hormone medications, antibiotics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), constipation medications, insulin, and diabetes pills. Furosemide enhances the effect of high blood pressure pills, which can cause hypotension, dizziness, and even fainting. The list of furosemide drug interactions given above is not complete. Discuss the details with your doctor without hiding any of the medications you take. |
| Overdose | An overdose of the drug furosemide causes the symptoms listed above in the “Side Effects” section. Significantly low blood pressure, a state of shock, delirium or apathy, and manifestations of blockage of blood vessels by blood clots may also be observed. It is likely that urine output will stop due to dehydration. Treatment is carried out in the hospital in the intensive care unit. Before emergency help arrives, it is recommended to pour a lot of liquid into the patient’s stomach, then induce vomiting, and give activated charcoal. Next, doctors will take measures to eliminate dehydration and acid-base balance disorders. To replenish the loss of fluid and electrolytes, droppers with saline, potassium and magnesium are used. For hypotension - dopamine or norepinephrine. Treatment is stopped when symptoms of overdose cease to be observed for 6 consecutive hours. |
Together with the drug Furosemide they are looking for:
- Lasix
- Veroshpiron
- Asparkam
- Hypothiazide
Contraindications
There are some contraindications to the use of this product:
- allergy to the components of the drug;
- lack of urine in the presence of renal failure;
- precoma and hepatic encephalopathy;
- hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy;
- dehydration of the body;
- low blood pressure due to a decrease in circulating blood volume;
- disturbance of urine outflow;
- increased level of uric acid in the blood;
- glomerulonephritis in the acute stage;
- asymptomatic form of aortic stenosis;
- decompensated aortic or mitral stenosis;
- poisoning with cardiac glycosides.
Tablets are not prescribed to children under 3 years of age.
Side effects
We list what adverse reactions from the body may occur, as well as their symptoms:
- Hypokalemia is a life-threatening condition for the patient, characterized by low potassium levels in the body. Can become a catalyst for life-threatening arrhythmia. This is especially true for patients who have suffered a heart attack, who are taking glycosides for the heart muscle, and for people who have previously suffered from arrhythmia. Symptoms: weakness, muscle pain, pins and needles, cramps, constipation, rapid heartbeat, irregular heart rhythm, low blood pressure.
- Lack of magnesium increases neuromuscular excitability, resulting in convulsions, arrhythmia, and atrial fibrillation.
- Hyponatremia is a decrease in the concentration of sodium ions in the blood. Symptoms: migraine, feeling of depression (overexcitement), cramps, fatigue, lethargy, vomiting and nausea. This symptomatology is usually associated with swelling of the cells of the nervous system.
- Chronic loss of fluid , manifested by loss of strength, feeling of weakness, craving for sleep, severe decrease in blood pressure, frequent dizziness.
- Attacks of gout due to uric acid retention.
- Metabolic alkalosis as a result of loss of sodium, potassium, chlorine. Symptomatic picture: muscle cramps, low blood pressure, constipation, weakness.
- Glomerulonephritis due to long-term toxic effects on renal cells can occur (rarely).
- Increased ototoxicity of aminoglycosides (negatively affects the hearing aid) and nephrotoxicity of cephalosporins (damage to kidney tissue).
Furosemide is a dangerous drug that can cause serious problems in the human body. For this reason, the drug should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor and the dosage should be adjusted as necessary.
Side effects and harm
The drug can harm the body if taken for a long time.
Along with the fluid, electrolytes are excreted, which support the normal functioning of muscles, nerves and the entire body. During therapy, side effects from various organs and systems may occur:
- The cardiovascular system. Blood pressure decreases, heart rhythm is disturbed, and the number of platelets, red blood cells and leukocytes in the blood decreases.
- Nervous system. Migraines, dizziness, fatigue, muscle weakness often occur, and hearing and visual functions deteriorate. With prolonged use, convulsions and confusion may occur.
- Digestive system. Appetite may decrease. Sometimes thirst and nausea are felt, and defecation is delayed. In rare cases, diarrhea appears and pancreatitis worsens.
- Genitourinary system. The formation and excretion of urine slows down, potency decreases, and blood appears in the urine.
- Allergies. The skin becomes sensitive to ultraviolet rays, urticaria, skin itching, and dermatitis appear. In rare cases, anaphylactic shock occurs.
- Water-electrolyte metabolism. The levels of electrolytes in the blood may decrease and cholesterol and blood glucose levels may increase. Deterioration of the condition leads to dehydration.
If side effects occur, treatment should be stopped.
Side effects
The drug "Furosemide", reviews and instructions confirm this, can cause negative reactions in the body. Side effects include:
- tachycardia, dizziness, hearing impairment;
- anorexia, oliguria, exfoliative dermatitis;
- aplastic anemia, dehydration, thrombophlebitis;
- orthostatic hypotension, muscle weakness;
- blurred vision, dry mouth;
- interstitial nephritis, urticaria;
- thrombocytopenia, metabolic acidosis;
- kidney calcification (in newborns);
- arrhythmia, headache, cholestatic jaundice;
- hematuria, skin itching, hypochloremia;
- low blood pressure, tetany, stool disorders;
- urinary retention, purpura, leukopenia;
- hyponatremia, collapse, apathy;
- nausea or vomiting, lethargy, impotence;
- necrotizing angiitis, agranulocytosis;
- hypovolemia, confusion;
- exacerbation of pancreatitis, vasculitis;
- anaphylactic shock, adynamia, drowsiness, erythema.
By
Overdose
In case of an overdose, blood pressure decreases, the volume of circulating blood decreases, the heart rhythm is disturbed, drowsiness and confusion appear, blood clots appear, electrolytes are washed out of the body and the water-electrolyte balance is disturbed.
With an overdose of furosemide, blood pressure decreases, the volume of circulating blood decreases, and the heart rhythm is disturbed.
How does Furosemide work on excess weight?
According to the instructions for use, Furosemide diuretic tablets are not used for weight loss. However, reviews of people losing weight about this drug claim that its periodic use allows you to control your weight and maintain a normal figure. Just one tablet of Furosemide after a stormy feast helps to avoid swollen legs and a swollen face in the morning, which means you can appear slim and fresh at work. But don’t think that this medicine is a panacea for weight loss. Furosemide is a very powerful drug that should be used as prescribed by a doctor.
The main advantage of Furosemide is its ability to instantly start the removal of water. Within two hours after taking the tablet, excess fluid begins to be released from the body. However, useful substances also leave with it: vitamins, microelements, especially calcium, iron, sodium, magnesium, potassium. The result of such weight loss can be disastrous for health. The heart suffers first, as its work becomes difficult due to a lack of potassium and magnesium, then the muscles lose tone. It may take several weeks to restore normal functioning of the body after taking Furosemide for weight loss.
special instructions
During therapy, you need to regularly measure blood pressure, monitor the levels of electrolytes, sugar and uric acid. If no urination occurs within 24 hours after administration, discontinue use.
It is better to limit intake in case of diabetes mellitus, decreased protein levels in the blood plasma, low blood pressure, acute myocardial infarction, gout, systemic lupus erythematosus, pancreatitis and ventricular arrhythmia. It is not recommended to use it in combination with ACE inhibitors (it is better to maintain an interval of several days).
Hypokalemia can be prevented by alternating diuretic therapy with potassium-sparing diuretics. It is necessary to eat foods that contain potassium during therapy.
During pregnancy and lactation
During pregnancy, taking the drug should not be long-term.
The active ingredient passes into breast milk, so breastfeeding must be stopped before starting therapy.
Can Furosemide be used for children?
Therapy with this drug is contraindicated for children under 3 years of age. In other cases, only a doctor should prescribe treatment.
Alcohol compatibility
The drug should not be taken with alcohol. If taken simultaneously, adverse reactions may increase. It is better not to use if you have a hangover.
Furosemide should not be taken with alcohol, because Adverse reactions may increase.
Special rules
During the course of treatment with furosemide, it is important to ensure a constant flow of urine, especially for patients who have partial obstruction.
It is also important to monitor the health of patients while using this drug. This especially applies to the following categories of patients:
- who have a history of arterial hypotension;
- having latent or severe form of diabetes mellitus;
- with gout;
- with functional disorders of the kidneys and liver;
- premature babies.
During furosemide therapy, doctors often recommend monitoring the levels of creatinine, potassium and sodium in the blood. This applies most of all to patients who have had dyspeptic symptoms for a long time. Any changes in balance should be corrected, and in some cases diuretic therapy should be discontinued.
While using this medication, it is necessary to enrich your diet with foods with high levels of potassium, which will help reduce the need to compensate for the deficiency of this element.
The combination of risperidone and furosemide increases the mortality rate in patients who have senile dementia.
It is important to consider all risk factors when taking it concomitantly with other diuretics, as this can lead to dehydration.
Furosemide and alcohol
It is important to avoid the combination of furosemide and alcohol of any strength.
Use by pregnant women
Furosemide is used to treat women during pregnancy solely for vital signs, while constant monitoring of the condition of the fetus is carried out.
If therapy with this drug is necessary during lactation, doctors recommend stopping breastfeeding the baby for a while.
Effect on reaction speed
The instructions describe that during therapy with this drug there is a risk of developing severe hypotension, which can provoke an emergency situation on the road. For this reason, it is necessary to refrain from controlling mechanisms during treatment with furosemide.
Prescription for children
When prescribing furosemide in pediatrics, it is necessary to take into account the child’s weight, because, based on its figure, the required dose of the drug is calculated.
Drug interactions
Use with Cephalosporins, Aminoglycosides, Chloramphenicol, salicylates, Ethacrynic acid, Cisplatin, Amphotericin B leads to a deterioration in the condition of the kidneys and the functioning of the vestibular apparatus. Increases the effect of taking the drug Dioxide and Theophylline, but reduces the effect of Allopurinol and drugs for hyperglycemia. The concentration of the active substance in the blood increases if drugs that block tubular secretion are used simultaneously.
Hypokalemia can occur while taking corticosteroids, cardiac glycosides, and the drug Amphotericin B. Lithium excretion from the body is reduced and the risk of intoxication increases. After taking NSAIDs, the diuretic effect may not occur immediately. The effect of the drug is enhanced by antihypertensive drugs and Succinylcholine.
Is it possible to lose weight
Like other diuretics, Furosemide does not affect fat cells, so the weight loss process starts only if there is a tendency to swelling.
The drug is available in three dosage forms: in addition to tablets, granules are available (prescribed for children for medical reasons) and liquid for injection (20 mg of active substance). The unique pharmaceutical properties of the active substance help to get rid of two to four kilograms in one use. A longer period helps in achieving optimal figure parameters.
The main advantage of the drug is its almost instantaneous effect. A few hours after ingestion, the liquid begins to leave the body naturally. About three kilograms of water comes out per day, since the urge to urinate occurs every 15-20 minutes.
Important! Diuretics “relax” the body. With long-term use, all systems and organs cease to function fully. Over time, addiction occurs: withdrawal from Furosemide results in the inability to urinate on your own.
Reviews from those who have lost weight
Ilona, 32 years old
The product has a sharp diuretic effect. You can lose up to 1 kg per day if you don’t eat a lot of sweets and fatty foods. The product helps remove fluid from the body, but fat deposits do not disappear. I think there is no point in taking the drug. Excess weight returns after stopping use.
Marina, 28 years old
A good product for weight loss. I use it only in special cases. The drug allows you to quickly lose 3-4 kg. You should not take it constantly because there are side effects. After losing weight, you need to lead an active lifestyle and eat right. Otherwise, excess weight will appear again.
Reviews from patients and doctors
Today, many people take Furosemide tablets. Indications for use: swelling, increased blood pressure and fluid retention, which, you see, are quite common problems. Reviews from doctors about the drug are positive - it really provides a quick effect.
Patients also leave mostly positive reviews. After just a few days of therapy, blood pressure normalizes and swelling decreases. An undoubted advantage is the low cost, thanks to which the product will be affordable for everyone.
On the other hand, it is worth understanding that you cannot arbitrarily use a drug such as Furosemide. You don't need a prescription to buy it, but that doesn't mean it's completely safe. The list of side effects is impressive, and incorrect use of tablets increases the risk of their development. In recent years, a lot of information has appeared that this medicine is used as a means of losing weight. In fact, such use is strictly contraindicated. Furosemide is a diuretic that is not intended to combat excess weight. Taking the drug incorrectly will affect the functioning of the excretory, cardiovascular and nervous systems, so you should not risk your own health.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Inside the kidney, loops are formed from small afferent blood vessels. Together with the membrane and specialized cells (podocytes), a kidney filter is formed, which is surrounded by a capsule. This filter acts like a sieve and allows fluid to pass back into the bloodstream. The kidneys filter 150-200 liters of water during the day. The filter is followed by a tubular system, the task of which is to accumulate primary urine up to 1.5-2 liters per day through the reabsorption of water and substances.
In addition, these cells are also capable of secreting certain substances into the urine. For these purposes, the cells of this system have many different channels and transporters. After passing through this system, the so-called secondary or final urine passes through the ureter, accumulates in the bladder and can be excreted through the urethra.
Furosemide inhibits the transport protein for sodium, potassium and chloride, which is located in the thick section of the loop of Henle. As a result of transporter inhibition, water reabsorption slows down. Thus, an increased amount of water enters the bladder.
If furosemide is taken in tablet form, only half of the substance appears in the blood. Thus, bioavailability is 50, sometimes up to 70%.
In the kidneys, the largest portion is filtered and partially released through the kidney cells. Degradation of the substance in the blood occurs relatively quickly. From 30 minutes to 2 hours, only half the concentration of substances is present in the blood (plasma half-life 0.5-2 hours).
The diuretic effect begins after 30-60 minutes and reaches a maximum after 1-2 hours. After about 6 hours the effect disappears completely. If furosemide is administered intravenously through an infusion, the effect begins within 15 minutes and lasts up to 2 hours.
Many people ask whether furosemide lowers or increases blood pressure. Loop diuretics help lower blood pressure and reduce both preload and afterload on the heart. However, using the drug during a hypertensive crisis is highly discouraged.
Treatment for furosemide-dependent kidney
To prevent hypokalemia, it is recommended to increase the content of potassium-rich foods in food (dried apricots, nuts, raisins, peas and legumes, potatoes, especially baked in their skins, seaweed). The use of drugs with potassium, such as asparkam, is also indicated.
Magnesium deficiency is corrected by using magnesium gluconate or chloride. When treating hyponatremia with sodium chloride, you must be extremely careful, since salt causes water retention in the body.
When furosemide is discontinued, swelling may worsen. This may be either a consequence of the disease for which you were prescribed furosemide, or a manifestation of dependence on furosemide (usually in cases where the diuretic was used for weight loss). In the first case, you cannot do without consulting a doctor and adjusting the treatment of your disease. In the second, you can try to “get off furosemide” by limiting the amount of fluid consumed while taking mineral supplements of potassium and magnesium. Use medicinal herbs as diuretics during this period. Take any liquids no later than 3-4 pm. The last meal is no later than 6 pm. The process of getting rid of addiction is long and will take at least a month, be patient.
Furosemide is prohibited for use in athletes by the World Anti-Doping Agency. It itself is not a dope, but as a drug that can lead to the removal of traces of other prohibited drugs by increasing the amount of urine and as a means for rapid weight loss, it is unacceptable in the sports world.
General practitioner, nephrologist Sirotkina E.V.
Diuretics are a common group of medications. They should only be prescribed by doctors. But due to the availability of drugs, people prescribe them to themselves as treatment or for weight loss
. One of these drugs is Furosemide, an overdose of which leads to serious disorders in the human body.
Why can an overdose happen?
Diuretics are prescribed strictly according to indications.
A drug overdose has never been detected in a hospital. After all, in a hospital, the staff is responsible for treating the patient and administering or taking medication. For home treatment, each person is prescribed an individual dose. Throughout the entire period, the status of the biochemical level will be shown. This will help eliminate problems with water and electrolyte balance. Along with a diuretic, the doctor may prescribe potassium supplements, which will reduce the likelihood of side effects.
Or, as an alternative, a diet is prescribed. That is, together with your doctor, you create a special diet for every day, which will contain foods rich in potassium. If the patient himself does not exceed the prescribed dose, then an overdose will not occur.
A sane person cannot take many pills at once. However, diuretic overdose still had to be observed. There is only one explanation for this phenomenon, or rather there are two. Either the person deliberately decided to take a large number of diuretic tablets, or it is all a matter of poor memory. The second reason is especially noticeable in older people. Therefore, it is simply necessary to have someone nearby with older people.
It is strictly forbidden to take medicine with alcohol. This combination will lead to an overdose.
Someone is trying to lose weight with Furosemide, so they exceed the dose. But this has a negative impact on health. True, the drug really struggles with weight loss. Many athletes take it, as the tablets remove doping from the body.
Contraindications for use
The medicine has many contraindications that must be taken into account before you start using Furosemide. You should not use the drug for the following conditions and diseases:
- anuria;
- renal failure in the acute stage;
- stones in the kidneys or ureters;
- anuria;
- glomerulonephritis in the acute stage;
- stenosis of the mitral valve or aorta;
- heart failure in the stage of decompensation;
- cardiomyopathy;
- disturbed water-electrolyte balance;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- lactose intolerance.
With caution and under the strict supervision of a doctor, the use of the medicine is allowed for the following conditions:
- heart attack;
- cardiogenic shock;
- diabetes;
- pancreatitis;
- inflammation of the prostate gland in men;
- hydronephrosis.
In old age, it is recommended to take the medicine only in the minimum dosage. The drug should be used with extreme caution if you have an allergic reaction to the components of the product.
Signs of acute drug overdose
To answer the question of whether Furosemide is harmful, consider its effect on the body at high doses.
One of the first symptoms of an overdose is a decrease in blood pressure
. This is expressed in the following signs:
- General weakness, lethargy, apathy, malaise, weakness;
- Pain in the occipital region of the head;
- Feeling of lack of air, shortness of breath;
- Increased sweating;
- Dizziness when changing position;
- Nausea.
With a progressive decrease in pressure, collapse occurs. Its symptoms are associated with hypoxia (oxygen starvation of the brain):
- A sharp deterioration in health;
- Darkening of the eyes, noise in the ears;
- Dizziness, severe headache;
- Pale skin, cold sweat;
- Decreased body temperature, chills;
- Frequent and shallow breathing;
- Cramps.
In case of an overdose of the drug, hypovolemia develops ─ a decrease in circulating blood volume (CBV). Diastolic pressure (lower reading) decreases inadequately. This reduces the amount of blood pumped out by the heart, resulting in decreased blood supply to the organs. A decrease in blood volume provokes damage to the kidneys, brain, and leads to death.
Taking large doses of Furosemide creates a risk of developing dehydration ─ dehydration of the body
. The person experiences severe thirst, weakness and fatigue. The kidneys do not produce urine in the required quantity, it becomes dark in color. With severe dehydration, decreased blood pressure, weak pulse, blue skin, and clouding of consciousness are observed.
Hemoconcentration ─ blood thickening. Blood microcirculation is disrupted, which is manifested by tingling and numbness of the limbs. Serious consequences include thrombosis, which leads to heart attack and stroke, and intracerebral hemorrhage.
Among the functional disorders of internal organs, the following develop:
- Arrhythmia ─ disturbance of heartbeat rhythms;
- Ventricular fibrillation ─ uncoordinated muscle contractions of the heart;
- Heart block due to impaired conduction of impulses from the atria to the ventricles;
- Acute renal failure.
Interaction with other drugs
When taking furosemide and other drugs simultaneously, various toxic reactions may occur. Furosemide interacts with the following medications:
- Glucocorticoids, carbenoxolone, laxatives (increased potassium loss),
- Anti-inflammatory drugs (for example, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as indomethacin and acetylsalicylic acid),
- Probenecid, methotrexate (an antirheumatic drug),
- Phenytoin (for cramps and special forms of pain),
- Sucralfate (stomach medicine),
- Cardiac glycosides (possible cardiac arrhythmia, ECG changes),
- Salicylates (increase side effects),
- Antibiotics (for example, aminoglycosides, cephalosporins, polymyxins),
- Aminoglycosides (some antibiotics),
- Cisplatin (increased risk of kidney and hearing damage),
- Lithium (increased risk of heart and nerve damage),
- Antihypertensive drugs (too rapid decrease in blood pressure with pronounced consequences),
- Theophylline (asthma medicine) and curare-like drugs (muscle relaxants),
- Antidiabetic drugs,
- Hypertensive drugs (eg, epinephrine, norepinephrine),
- Licorice (food).
When is a diuretic prescribed?
If you don't know, Furosemide is a diuretic drug that has a therapeutic effect. Moreover, the effect occurs very quickly. When administered intravenously, the effect on the genitourinary system begins to develop in a matter of minutes. The diuretic drug is available in the form of tablets and solutions for injection. Moreover, medicinal formulations can be administered not only intravenously, but also intramuscularly.
In most cases, the doctor prescribes this medication to prevent edema in heart disease, ascites, liver and lung diseases. A diuretic is used for intoxication with chemical components. Sometimes a diuretic drug is prescribed to lower blood pressure in hypertension.
If, when taking Furosemide, the volume of urinary fluid increases, then our body begins to lose useful microelements. If all prescribed dosages are followed, the drug does not have a negative effect. But if a diuretic is used for other purposes, serious signs of overdose may appear.
What does the diuretic composition combine with and what does it not interact with?
Before you start taking pills, you need to find out if you have any of the components included in the medication. You can ask your doctor for a list of ingredients
It is also very important to tell your doctor if you plan to take vitamins, supplements, or other medications at the same time.
Don't forget to tell your doctor if you are taking medications.
This is very important, since Furosemide does not interact with some drugs. This list includes:
This list includes:
- Gentamicin, Tobramycin;
- Benazepril, Captopril, Fosinopril, Quinapril and all drugs ending in – adj;
- Candesartan, Irbesartan and all drugs ending with - rotan;
- Phenobarbital, Secobarbital;
- Betamethasone, Cortisone, Hydrocortisone and all drugs ending in -zone;
- Cyclosporine, Cisplatin.
Your testimony will help the doctor prescribe the correct treatment regimen and carefully monitor side effects. If you miss a dose, you do not need to take a double dose next time. Just continue to follow all instructions.
Furosemide is considered the most powerful diuretic. It is mainly prescribed in case of emergency. After oral administration, the effect occurs within half an hour and lasts about 6 hours. In case of severe intoxication, as already mentioned, it is necessary to rinse the stomach. How to do this correctly?
- First you need to drink a liter or one and a half warm water. But for a better effect, it is worth diluting it with manganese. The main thing is not to overdo it, otherwise you won’t be able to drink the solution. The water should turn out slightly pinkish. Then use the back of a small spoon to press down on the root of your tongue. These manipulations will help provoke vomiting. If you make the solution too dark, vomiting may occur without outside intervention. But this is bad, since we need to disinfect the stomach. This will not happen unless the solution gets inside.
- After which a saline laxative is taken. Magnesium sulfate is most often used.
- Next you should take enterosorbent. Activated carbon is very popular here. The dosage is calculated as follows: 1 tablet per 10 kg of the victim’s body weight.
If severe intoxication with a diuretic drug occurs, call an ambulance. They will take the victim to the hospital, where they will perform certain manipulations:
- replenish the volume of incoming blood (Ringer, sodium chloride solution, Poliglyukin are suitable for these purposes);
- perform artificial ventilation;
- special solutions are administered intravenously;
- Prescribe medications for proper heart function.
Useful information: Remember that medications and alcoholic drinks cannot be mixed. Every year in our country up to 900 thousand people die from the effects of alcohol. Moreover, many died due to the simultaneous use of medications and alcoholic beverages.
Furosemide has several analogues, but their effects are inferior to the diuretic. The doctor prescribes a treatment regimen with tablets depending on the patient’s age, weight and individual characteristics. Abuse of the drug is extremely dangerous, as it has side effects.
Compound
The composition of the drug "Furosemide" includes:
- Furosemide 40 mg.
Excipients:
- Starch,
- Milk sugar,
- Povidone,
- Gelatin,
- Microcrystalline cellulose, etc.
Doctors' opinion about the drug
Doctors say that powerful diuretics, such as Furosemide, are prescribed exclusively for pathologies of the liver, kidneys or heart to get rid of painful swelling. The instructions for use of the drug do not say anything about losing weight, so using the drug for these purposes is not only useless, but also dangerous.
In case of an overdose, all systems can be affected. The consequences of taking Furosemide can lead to symptoms of diseases of the nervous, digestive, genitourinary and cardiovascular systems. For men, such weight loss can result in impotence. Furosemide should be taken strictly under the supervision of the attending physician.
Reviews: is it possible to lose weight if you take medicine?
Avdeeva. I take diuretics extremely rarely - at the moment only when necessary. But three years ago, I could take a couple of pills “for prevention” to lose weight. Yes, I understood that only excess water was leaving (and not only excess!), and my fat remained with me, but this difference of 1 kg on the scales made me very happy and gave me strength to lose weight further! I didn’t really think about it then , what such a bad habit can lead to. I took furosemide for weight loss for a short time - literally for a couple of months. But what did they cost me? Loss of strength, cramps, tics, swelling began to visit me more often, because when a lot of fluid is removed from the body, then when drinking water, the body in a panic tries to store this fluid in the tissues, again leading to swelling. This is such a vicious circle!
Kozhevnikova. Who needs to urgently lose a couple of kilos for some important event or in general - DRINK. BUT not every day)) the other day I took 1 tablet at night and during the night minus 2kg 700g, my stomach, which was sticking out, was noticeably deflated. Not very pleasant: dry mouth (but after drinking some water everything became normal), slight weakness (after drinking tea with candied fruits everything went away)
Antonina 2013. I tried many ways to lose weight. One of the dumbest ones was taking a diuretic. Of course, I didn’t quite understand that it was impossible to lose weight from it. So I bought this product and thought that I would take it before going out somewhere so that it would remove excess water. In the end, I only took it once. I decided to go to the club. Before this I took Furosemide, and when I was already at my destination I felt very bad. I thought I was going to faint. Thank God this didn’t happen to me. It was a lesson for me. When I arrived home, I threw this product away. So girls, learn from other people's mistakes!! To be honest, I'm very ashamed of this. After all, I'm not a stupid person.
Features of the drug and its effect on the human body
A diuretic has a number of positive effects on the body.
- Furosemide causes a diuretic effect that occurs quickly. After oral administration, the drug begins to act after half an hour and lasts for 6 hours. Of course, with intravenous administration, the effect will occur within a couple of minutes and last about 2 hours. During the process, the output of sodium ions increases, but at the end of the process, everything returns to its place.
- When the drug is administered intravenously, the veins dilate. The medication acts on the heart, which reduces its level of stress. Furosemide also reduces left ventricular blockage pressure.
- When the incoming blood levels decrease, a hypotensive effect occurs. Accordingly, sodium ions increase.
- As a result, edema and congestion in the lungs go away and a slight pulmonary resistance occurs.
- The drug will be beneficial if the filtration rate is low in people with liver problems.
Overdose and interaction
If the drug is taken uncontrolled or for too long, the patient may experience pronounced side effects and symptoms of overdose. The most common symptoms are respiratory depression and paralysis. But with very high doses of the drug, coma and acute renal failure are possible.
Overdose therapy will involve restoring the body’s water and electrolyte balance by injecting a sodium chloride solution intravenously. The patient also needs gastric lavage and the use of enterosorbents. If necessary, symptomatic treatment is selected.
Most often, Furosemide is prescribed as an additional drug in the treatment of many diseases. Therefore, its compatibility with certain products should be taken into account. Thus, when used simultaneously with Phenobarbital, the diuretic effect is significantly reduced. Therefore, it is important to take this point into account and adjust the dosage.
When taking a diuretic and cephalosporins at the same time, there is a risk of side effects from antibiotics. Therefore, you need to be careful when using them together.
When combined with aminoglycosides, the removal of the latter from the body is significantly slowed down. This can cause nephrotoxicity of the drugs and lead to serious health consequences.
Furosemide significantly reduces the effect of hypoglycemic drugs. Therefore, during therapy with diuretics, the dosage of insulin should be adjusted.
With simultaneous treatment with a diuretic and glucocorticosteroids, the risk of developing hypokalemia increases. And this, in turn, leads to serious complications from the cardiovascular system.
Particular caution should be taken when taking Furosemide with antihypertensive drugs: this can lead to a sharp decrease in blood pressure. Often, under the influence of uncontrolled use of these drugs together, the patient experiences collapse and acute heart failure.
If a patient is prescribed the simultaneous use of a diuretic drug with ACE inhibitors, acute renal failure may develop. Furosemide can be used only 3 days after stopping the inhibitors.
When using the drug together with radiopaque agents, kidney function may be impaired. Therefore, you should either discontinue Furosemide for the duration of the studies or carry out treatment in a hospital setting under the strict supervision of a doctor.
Furosemide price
In Moscow pharmacies, the average price of Furosemide is 25 rubles.
The site provides reference information for informational purposes only. Diagnosis and treatment of diseases must be carried out under the supervision of a specialist. All drugs have contraindications. Consultation with a specialist is required!
Furosemide is not a new drug and has been used in medicine for a long time. But when taking a furosemide tablet, few people think about how much this drug affects the condition of the body as a whole. If you want to learn more about furosemide, as well as about the scandals in which this drug was involved, read this article, and the medical board of tiensmed.ru (www.tiensmed.ru) will tell you about all this.
Furosemide is a very strong drug. No doctor will argue about this. Perhaps there is no such diuretic that would begin to act in a matter of minutes. Yes, yes, in a matter of minutes. Within fifteen minutes after the administration of furosemide intravenously, the drug begins to act. Sometimes such a rush is really simply necessary, for example, during cerebral edema or during a hypertensive crisis.
Recommendations for long-term treatment
If it is necessary to treat arterial hypertension with furosemide, it is necessary to exclude from the patient all conditions and diseases included in the list of contraindications. Patients taking the medicine for a long time should be regularly monitored by a doctor. In this case, it is necessary to constantly monitor blood pressure levels and periodically measure blood electrolytes, evaluate liver and kidney functions.
When used in the treatment of hypertension, furosemide does not require reducing salt intake. On the contrary, a lack of sodium can trigger the development of side effects. Patients with diabetes mellitus during treatment with furosemide should regularly monitor their blood glucose levels.
The drug can affect concentration, so during long-term treatment they should stop driving and not engage in work that requires increased attention.
You can purchase the drug at any pharmacy with a doctor's prescription. Its cost is small. There are analogues, for example, Lasix.
In what cases should Furosemide not be taken?
It is necessary to find an alternative to this drug in the following pathological conditions:
- renal failure (severe, acute);
- acute glomerulonephritis;
- urolithiasis in severe manifestations (stone obstruction);
- hypertrophic stenosis;
- increased venous pressure;
- precomatose state;
- aortic stenosis;
- digitalis intoxication;
- imbalance of water and electrolyte metabolism;
- various forms of arterial hypertension;
- acute form of myocardial infarction;
- lupus erythematosus;
- urethral stenosis;
- pancreatitis;
- mitral stenosis;
- renal coma.
Particular care should be taken when treating with Furosemide if you have the following diseases:
- prostatic hyperplasia (benign);
- atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels;
- hypoproteinemia;
- hypotension (if there is a risk of ischemia due to insufficient blood flow);
- diabetes;
- hepatorenal syndrome.
Insufficient effectiveness of Furosemide and the manifestation of undesirable effects are observed when the patient has hypoproteinemia against the background of nephrotic syndrome.
In the presence of natremia, it is necessary to analyze the sodium level before starting treatment, with subsequent monitoring during therapy. Treatment with diuretics may cause the development of hyponatremia. Low sodium levels at the very beginning have no characteristic manifestations. Therefore, monitoring of its concentration should be carried out in patients at risk, namely the elderly, patients with liver cirrhosis and extreme exhaustion of the body (cachexia).
Loop diuretics can reduce potassium levels, causing hypokalemia. Therefore, patients who are at risk need to be constantly monitored. These patients include the elderly, those with ascites or cirrhosis, and those with heart failure.
When taking Furosemide, patients with a high potential for electrolyte disturbances (vomiting, diarrhea, sweating) should be under close medical supervision.
Use of the drug during pregnancy and lactation
In the 1st trimester of pregnancy, Furosemide tablets are not prescribed to women, since at this stage the internal organs of the fetus are formed and the effect of medicinal substances on the maternal body is undesirable.
In the 2nd and 3rd trimesters of pregnancy, Furosemide can be prescribed to patients only if there are serious indications. The doctor carefully evaluates the possible risks to the fetus versus the benefits to the mother. The drug easily penetrates the placental barrier, however, during clinical trials, no teratogenic or embryotoxic effect of Furosemide on the child was revealed.
The drug is excreted in breast milk and can enter the baby's body. If therapy with Furosemide is necessary, a nursing mother should stop lactation so as not to harm the baby.
Chronic drug overdose
With systematic use of tablets, thrombophlebitis develops - inflammation of the veins with the formation of blood clots. More common in older people.
The following symptoms are observed from the gastrointestinal tract:
- Nausea, vomiting;
- constipation or diarrhea;
- Pancreatitis ─ inflammation of the pancreas;
- Stagnation of bile.
Symptoms of chronic damage to the nervous system:
- Hearing loss due to damage to the inner ear;
- Fog in the eyes;
- Confusion, nervousness;
- Dizziness, migraines;
- Anorexia.
Allergic manifestations: exfoliative dermatitis, itching, urticaria, photosensitivity (sensitivity to light).
The maximum permissible dose of the drug is 600 mg per day. In medical practice, in some cases, for example, with ascites (fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity), the dose is increased to 900 mg per day. The lethal dose of Furosemide has not been established
, critical daily dose 1500 mg.
How to drink: warnings
For pressure that progresses against the background of chronic renal failure, the use of Furosemide is allowed if thiazide diuretics are contraindicated for the patient. Patients with gout are at risk of exacerbation, since taking the drug reduces the outflow of uric acid. Diabetics need to monitor the level of sugar concentration in the blood plasma and urine. There is an opinion that Furosemide helps to lose weight and in the fight against obesity, but the drug serves as an ordinary diuretic that has nothing to do with diet, as a result, weight is reduced exactly by the amount of fluid removed. When taking Furosemide, you must stop driving and operating machines.
Features of the treatment of hypertension with furosemide
Furosemide for hypertension is included in the treatment regimen when there is a persistent increase in blood pressure that is not corrected by monotherapy, that is, by taking any one drug.
Furosemide is combined with various drugs for high blood pressure: beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, sartans.
If such treatment does not give the required effect, it is permissible to add another diuretic from another group. All doses of drugs during treatment with furosemide are reduced by half from the original dose used in monotherapy.
The dosage of furosemide is selected individually for each patient according to the degree of hypertension, the presence of concomitant diseases, taking into account the characteristics of the body. They usually start with a minimum dose, gently increasing to an amount that will have the desired effect.
Indications
Furosemide is widely used for high blood pressure and other health problems. Quite often, the medication is prescribed for edema syndrome that occurs against the background of diseases and conditions such as:
The drug should be taken by women with eclampsia.
- hypercalcemia;
- heart failure (grade 2-3, chronic form);
- severe hypertension;
- pulmonary edema;
- eclampsia during pregnancy;
- nephrotic syndrome (complex therapy);
- renal failure with normal urine outflow (chronic form);
- swelling of the brain due to tumor formation or injury;
- swelling in cirrhosis.