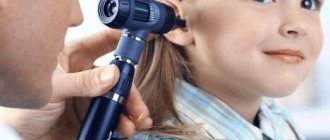
Otolaryngology (otorhinolaryngologia) is a branch of medicine specializing in pathologies of the ear, trachea, pharynx, larynx, nose and adjacent areas. The name comes from the Greek words:
- otos - ear,
- rhinos - nose,
- larynges - larynx,
- logos - teaching.
The conclusion suggests itself: the branch of medicine studies problems and diseases associated with these human organs. Who is this and what does an ENT doctor treat? He treats and monitors people with ear, nose and throat problems. He is also called an otorhinolaryngologist. They simply say ENT doctor, in the old fashioned way “ear, nose and throat.”
ENT doctor
Not everyone knows who an otolaryngologist is, but what an ear, nose and throat doctor does is not difficult to guess. These organs often bother people from infancy to old age. An otolaryngologist, ear, throat, nose doctor treats pathologies of the pharynx, trachea, larynx and all anatomical areas bordering them. This specialist knows everything about the prevention of ENT diseases.
The correct functioning of the ENT organs is very important for a person, because the larynx, throat, nose, ears are at the crossroads of the respiratory tract and digestive tract, therefore they are the first to respond to bacteria, viruses and other foreign agents. Inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs are the first sign of decreased immunity. In order to know which specialist to contact during an illness, it is better to already have information in advance, an otolaryngologist - who he is.
- The child’s nose cannot breathe - causes of congestion, diagnosis, treatment with medications and folk remedies
- The whole truth about the drug Helmifag - composition, instructions for use
- Medical examination of children in 2019: how is the medical examination carried out?
ENT office equipment
This doctor's office must have the following equipment:
- examination chair,
- chair for testing the vestibular apparatus,
- specialized tools,
- tuning forks,
- X-ray viewer (device for viewing X-ray images),
- endoscope.
In well-equipped clinics, the otolaryngologist’s office also contains other advanced equipment for the diagnosis and treatment of ENT diseases.
To facilitate the work of otolaryngologists and improve their skills, an ultra-modern ENT combine has appeared. This miracle device performs the following manipulations:
- Perform video endoscopy.
- Conducts examinations of the middle ear using a built-in microscope.
- Using a vacuum, it allows you to clean your tonsils and maxillary sinuses.
- Makes it possible to conduct cryotherapy of the tonsils and bacteriological studies of the nasopharynx.
ENT combine is a higher level in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the ear, nose and throat.
There are narrow specializations of otolaryngology:
- Audiology – deals with hearing problems and provides prosthetic hearing implants and devices.
- Phoniatrics – studies and treats problems with the vocal cords.
- Military otolaryngology is a very small specialty that helps with injuries to the ENT organs.
These areas are necessary for singers, artists, people whose activities are related to strengthening the functioning of the speech apparatus, for example, teachers, politicians. Therefore, if the patient falls into any of the listed categories, it is necessary to check their health status regularly.
What does an otolaryngologist do?
Inflammatory processes that cause pathologies of the ENT organs occur in both adults and children. Weak immunity allows infections that affect the nose, throat, and ears to pass through. If there is no adequate therapy, the virus penetrates further, sometimes causing irreversible consequences for the body. What does an otolaryngologist do? The specialist's competence includes surgical operations:
- Pharynx and larynx. Tonsillectomy, adenotomy and others are performed thanks to a set of special instruments of the otolaryngologist.
- Nasal cavities. An otolaryngologist surgeon performs puncture of the maxillary sinus, removal of polyps, correction of the nasal septum, and opening of abscesses.
- Ear. An otolaryngologist surgically removes hearing problems and also performs polypotomy, tympanotomy and other operations.
Who is an ENT
The incomplete name of the laryngootorhinologist specialty is ENT, and it is widely known among the people. ENT is considered a shortening of the word laryngootorhinologist.
- An otorhinolaryngologist who deals with diseases of the nose is called a rhinologist.
- An otolaryngologist who deals with ear diseases is called an otologist.
- A doctor who treats diseases of the larynx is called a laryngologist.
- Other otolaryngologists specialize in reconstructive surgery of the ears, nose and larynx.
An otolaryngologist is required to work in certain situations and as a therapist. He must continuously improve his knowledge of the economics of medicine.
There is also an otolaryngologist who specializes in operations. It is practiced in removing various formations in the neck, nose, ears, and correcting the nasal septum.
The main sciences studying the head and neck: audiology and speech anomaly, immunobiology, endocrinology and otorhinolaryngology.
What does ENT treat?
Otolaryngologist - who is he? An ENT doctor is trained to provide comprehensive treatment to patients with disorders and diseases affecting the ears, upper digestive and respiratory systems, and associated neck and head structures. An otolaryngologist may specialize in surgeries related to problems with the face, jaw, and respiratory tract. An ENT doctor can correct snoring, straighten the nasal septum, and remove a cyst. The competence of an otolaryngologist includes the treatment of pathologies such as:
- otitis;
- tonsillitis;
- throat diseases;
- pathologies of all ear parts;
- sulfur plugs;
- angina;
- sinusitis;
- allergic rhinitis;
- chronic and acute rhinitis;
- all diseases of the nasopharynx.
Unscheduled duties
An ENT doctor will solve completely unrelated problems for people with the following diseases:
- allergies – hay fever, allergic rhinitis, asthma,
- facial plastic surgery – cosmetic and reconstructive, correction of anomalies,
- throat disorders associated with difficulty swallowing and hoarseness,
- problem of snoring and apnea.
At the same time, the otolaryngologist treats with both surgical and conservative methods; unlike other doctors, he does not transfer his patients.
Throat diseases
As a result of drinking cold water, hypothermia, bacterial or viral infection, the larynx and throat are exposed to inflammatory diseases: tonsillitis, sore throat, pharyngitis, laryngitis. Sometimes pathologies such as scleroma, pharyngomycosis, and laryngospasm occur. In the absence of prevention, diseases of the throat and larynx can become chronic. There are other causes of pathologies of these organs that require consultation with an otolaryngologist:
- suffocation after inhaling chemical fumes;
- inhalation of smoke, dusty air, smoking;
- associated diseases: acute respiratory infections, influenza, whooping cough, scarlet fever;
- burns, injuries to the mucous membrane of the larynx or throat.
The most common cause of ENT diseases is an infection that causes inflammation in the larynx, tonsils, and nasopharynx. Pathogenic microorganisms enter the mucous membrane, causing its pathology. Bacteria can be in the human body and not manifest themselves in any way until immunity decreases. After hypothermia, overwork or stress, the pathogen begins to multiply, releasing harmful substances.
- What does an immunologist treat - what diseases. Treatment of adults and children by an immunologist
- Endocrinologist - who is he and what does he treat? An endocrinologist will help with diseases of the endocrine system
- Otitis - inflammation of the ear in adults and children
What diseases does an otolaryngologist treat?
All diseases of hearing and external respiratory organs come under the doctor's attention. An otolaryngologist deals with three parts of the body: the ear, nose and throat.
If these organs are unwell, you should first contact an ENT specialist. Let's find out what complaints you need to visit him with.
Throat
If you have a sore throat, pain when swallowing, or cough, go to the hospital. Often the cause is the following diseases:
- ARVI;
- flu;
- angina;
- laryngitis;
- pharyngitis;
- tumor formations;
- inflammation of the tonsils - tonsillitis.
With the onset of cold weather, cold season begins. ARVI, sore throat, flu - discomfort in the throat is the main symptom of the disease.
Ears
If you are bothered by tinnitus, itching, “tapping” pain, pressure, or any other discomfort, immediately go to an otolaryngologist. Unpleasant and painful sensations can be caused by:
- otitis;
- tympanosclerosis;
- mastiditis;
- labyrinitis;
- oncology;
- formation of sulfur plugs.
Ear diseases
In the practice of an otolaryngologist, ear diseases occupy an important place. They are of infectious, non-infectious origin or appear against the background of other pathologies. Diagnosis of ear diseases is difficult, because the human auricles have a complex structure. Ear diseases occur for various reasons, so the otolaryngologist must take them into account before prescribing a treatment regimen. The main factors for complications in the ear:
- decreased immunity;
- hypothermia;
- dental pathologies;
- strong physical activity;
- colds or viral diseases;
- mechanical damage;
- blockage of the ear canal;
- damage to the brain or disruption of blood circulation in it;
- neck pain as a result of osteochondrosis;
- tonsillitis;
- jaw pathologies;
- chronic or acute tonsillitis.
Pathologies of the nose and its appendages
If you have a disease of the nasal passages, this specialist will help you eliminate it. The doctor first examines the respiratory openings, after which he makes his verdict.
If the patient has a common runny nose caused by a cold, then the doctor prescribes general-spectrum medications, for example: Pinosol, Sialor, Protargol, and so on. The doctor may also detect dry mucous membranes during the examination. To treat this pathology, moisturizing sprinklers and drops are prescribed.
This group includes “Aquamaris”, “Saline solution”, “Aqualor” and others. For swelling and dilation of the vessels of the nasal passages, which are accompanied by deterioration in breathing, the doctor recommends using the following drugs: “Snoop”, “Vibrocil”, “Tizin”, “Nazivin” and so on. If during the examination a bacterial infection is detected, the doctor prescribes antimicrobial agents. This category includes Isofra, Albucid and many others.
As you can see, the doctor corrects all possible pathologies of the nasal passages. In some cases, the physician is forced to remove foreign objects from the respiratory tract. However, he can do this only when the foreign body has not yet left the nasal passages and has not descended below. Most often, young children encounter this pathology.
Another common disease in children is enlarged adenoids. These glands are similar to the tonsils, but are located closer to the nasal passage. Treatment of overgrown adenoids can be carried out medically or surgically. It all depends on the advanced stage of the disease and the age of the patient.
Diseases of the nose
Diseases of the nasal passages arise due to physical damage to the organ, infection, electrical, thermal, and chemical exposure. Main pathologies of the nose:
- Cavity atresia. Fusion of tissues within an organ, which is treated surgically. During the operation, the otolaryngologist removes the fused areas and creates a new lumen of the cavity.
- Deviated septum. It is characterized by changes in cartilaginous and bone structures, so the defect can only be corrected surgically by an otolaryngologist.
- Frontit. For inflammation of the frontal sinus, the basis of treatment is vasoconstrictor, antibacterial, and decongestant drugs.
- Ozena. Chronic foul runny nose is eliminated by rinsing the nose with saline solution.
- Sinusitis. Therapy for inflammation of the maxillary sinus is aimed at washing, warming and instilling the nose with antibacterial drugs.
- Rhinitis. Changes in the mucous membrane occur due to colds or allergies. The otolaryngologist prescribes local treatment with special sprays, turundas and rinsing with medicinal solutions.
How is an examination by an otolaryngologist performed?
The patient sits directly opposite the doctor; the doctor must perform the initial external examination in the following order:
- The doctor, using a frontal reflector and a bright light, examines the nasal and ear cavities.
- Performs palpation of the frontal sinuses, jaw and parotid lymph nodes.
- Using a spatula, examines the nasopharynx.
If the patient does not make any complaints and the doctor does not find any visible abnormalities, then the examination ends. Otherwise, the doctor performs additional procedures.
To establish an accurate diagnosis, the otorhinolaryngologist uses the following methods:
- Rhinoscopy is performed using a nasal speculum inserted into the nasal cavity.
- Rhinomanometry - allows you to see swelling in the nasal cavity.
- Mesopharyngoscopy - allows the doctor to see the tissues of the palate, swelling and hypertrophy of the tonsils, adhesions, and purulent plugs.
- Epipharyngoscopy - examination of the posterior wall of the larynx using a napkin, spatula and heated mirror.
When to contact the ENT
The condition of the ENT organs should be checked regularly for preventive purposes. To make an appointment with an otolaryngologist, you just need to call the nearest clinic and set a convenient time. To avoid serious complications in the future, contact your ENT doctor if you have the following symptoms:
- discomfort when talking, chewing, swallowing;
- speech and hearing disorder;
- elevated temperature for several days;
- sleep disorder;
- labored breathing;
- copious mucous discharge from the nose.
Otolaryngologist as a specialist
ENT (otorhinolaryngologist) is necessary for people suffering from various diseases of the respiratory system. This specialist is also contacted in case of medical examinations and commissions. The doctor also treats the hearing organ and olfactory system. What organs is this specialist responsible for?
- Ears and auditory receptors.
- Throat and tonsils.
- Nose and maxillary sinuses.
- Frontal sinuses.
- Vestibular apparatus.
- Bronchi and lungs (for some diseases).
If you have problems with the above organs, then you should visit a doctor called an otorhinolaryngologist (you already know who this is) as soon as possible.
There is an otorhinolaryngologist in every public clinic. In addition, the specialist is also present in the hospital, where patients stay around the clock. Also, private medical centers and clinics have recently become very popular. There is usually both a pediatric and adult ENT doctor there.
Sometimes an ENT specialist works in a highly specialized area such as:
- Audiologist. Treats various hearing disorders leading to partial or complete deafness. He is engaged in hearing care.
- Phoniatrician Treats diseases of the vocal cords. Such a specialist often works with singers, artists, teachers, politicians - people whose profession involves frequent use of the voice and its overexertion.
- Military otolaryngologist. Specializes in ENT injuries received in combat.
Treatment methods for ENT diseases
Modern otolaryngology uses many methods for treating ENT diseases. For each individual method, the doctor has to develop an individual scheme, but they can be divided into the following categories:
- Medicinal
e. The most extensive group, which includes various medicines, herbal decoctions and recipes for traditional medicine. Conventionally, they can be divided into local and systemic. So, for diseases of the nasopharynx and palatine tonsils, rinsing and washing with soothing and bactericidal solutions are actively used. At the same time, one cannot do without systemic therapy: antibacterial, antiviral, antihistamines, and so on. - Non-medicinal.
In the treatment of ENT diseases, various physical procedures are actively used: heating, electrophoresis, magnetic and ultrasound therapy, and so on. It is also important to normalize your lifestyle, for example, to get rid of allergens in case of allergic diseases and so on. - Surgical.
In some cases, surgical intervention is still necessary, for example, to remove the tonsils in severe forms of tonsillitis, open and drain the nasal sinuses during purulent processes, remove polyps, and so on.
The main difficulty lies in selecting the necessary treatment regimen. This often requires specialized education, work experience, and targeted diagnostics.
Causes
Common causes of nose, throat and ear diseases include:
- hypothermia of the body, both general (swimming in cold water, wearing shoes and clothes that are not suitable for the weather) and local (drinking cold drinks, especially in hot weather);
- a sharp change in temperature values;
- weak immune defense;
- lack of vitamins and microelements entering the body with food;
- stress, increased physical and mental stress;
- bad habits;
- viruses, infections.
Sinusitis
Sinusitis
Occurs when the maxillary sinuses become inflamed. The acute form develops against the background of infectious diseases, as a complication of rhinitis and in inflammatory diseases of the teeth.
The chronic form appears if negative factors are added to the acute stage (deviated septum, thickening of the mucosa, narrowing of the sinus openings).
Symptoms of acute sinusitis:
- temperature;
- pain radiating to the forehead, teeth, root of the nose;
- chills;
- lacrimation;
- purulent discharge;
- nasal congestion.
Chronic sinusitis is accompanied by pain in the sinuses and head, malaise, loss of smell and nasal congestion. Inflammation is treated with conservative, physiotherapeutic methods or through puncture, drainage and treatment of the nasal cavity. The main goal of therapy is to eliminate swelling and inflammation and improve the outflow of pus.
Frontit
Inflammation of the paranasal frontal sinuses occurs for reasons similar to sinusitis. Symptoms and treatment of nasal diseases depend on its shape. During an acute inflammatory process, swelling, changes in skin color, and an increase in body temperature occur. Sometimes phlegmon, purulent fistula, and abscess develop. Chronic sinusitis is accompanied by swelling of the mucous membrane or polyps form in the nasal passage. In case of necrosis of the posterior wall, meningitis and abscess develop.
Also does therapy mean?
- physiotherapeutic effects;
- taking Analgin and taking acetylsalicylic acid;
- carrying out inhalation or intramuscular administration of antibiotics.
Attention! Chronic frontal sinusitis is treated using traditional methods, but if there is no success, surgical intervention is performed.
Ethmoiditis
Develops during the inflammatory process of the mucous cells of the nose of the ethmoid labyrinth. Causes: infections, untreated frontal sinusitis or sinusitis, sepsis in newborns.
The disease is characterized by symptoms such as difficulty breathing, discomfort and a feeling of fullness in the nose, anosmia, and mucous secretion. Therapy involves the use of systemic antibiotics, antipyretics, painkillers and vasoconstrictors.
Sphenoiditis
Appears when the mucous layers of the sphenoid sinus become inflamed. Provoking factors are:
- dysfunction of the sphenoid sinus anastomosis;
- sinus defects (narrowness);
- penetration of foreign particles into the sinus;
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the respiratory organs (upper).
The leading symptom of sphenoiditis is headache of different localization. Sometimes ophthalmological problems develop (diplopia, decreased visual function). It is also possible to release purulent and mucous exudate and have a foul odor from the mouth.
Therapy consists of the use of vasoconstrictor, antibacterial and thinning drugs. The doctor also performs a procedure for enemizing the nasal cavity, which improves the outflow of secretions. The chronic form of the disease often requires surgical intervention.
Symptoms of diseases
Each otorhinolaryngic disease is accompanied by different symptoms, but in some cases the symptoms of one disease may be similar to another. The following signs of ENT diseases are characterized:
- pain, discomfort in the throat area (larynx, pharynx);
- difficulty breathing;
- inflammation of the ENT organs;
- hearing impairment;
- weakness of the body;
- headache;
- deterioration of sense of smell;
- bleeding (blood discharge from the ear or nose);
- discharge from affected organs, etc.
Sinusitis
One of the common nasal diseases accompanied by inflammation of the paranasal sinuses is sinusitis. During the illness, one or possibly several paranasal sinuses are affected, as a result of which breathing becomes difficult, discharge appears, headaches occur, and body temperature rises. Sinusitis is classified according to the nature, shape, and anatomical location of the inflammatory process. Types of sinusitis by localization (depending on the sinus that is affected):
- Frontitis is a lesion of the frontal sinus. It is more severely tolerated than other types of disease. Accompanied by severe pain in the forehead, hyperthermia, nasal congestion, difficulty breathing, etc.
- Sinusitis is inflammation of the maxillary paranasal sinuses. The patient exhibits breathing problems, copious mucopurulent discharge, high fever, and pain in the bridge of the nose.
- Sphenoiditis is inflammation of the sphenoid sinus. The disease causes headache, discharge from the sphenoid sinus, deterioration of vision and smell. It is one of the most common childhood diseases, ranking first among acute respiratory viral infections.
- Ethmoiditis is inflammation of the mucous membrane of the ethmoid sinus. Accompanied by difficulty breathing, pain in the upper part of the nose, forehead, between the eyebrows, and severe nasal discharge.
Sinusitis is a common disease and many try to cure it on their own, using well-known treatment methods. Advice for those with a runny nose:
- It is advisable to stay at home during illness and avoid going outside.
- For elevated temperatures, use antipyretic medications.
- It is recommended to drink plenty of fluids (warm tea with lemon or honey)
- Do inhalations, take warm baths.
- Take medications prescribed by your doctor. Possibly prescribing antibiotics.
Rhinitis
Inflammation in the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity, which often occurs during infectious diseases, is called rhinitis. There is nasal congestion, excessive nasal discharge, a burning or tickling sensation in the nose, and difficulty identifying odors. Rhinitis is treated with drops, nasal sprays, runny nose tablets, rinses, and inhalations. Rhinitis comes in different forms:
- Acute rhinitis. Lasts from 7 to 10 days and is caused by viruses and bacteria.
- Chronic rhinitis. It differs in the duration of the disease. For chronic rhinitis, a more complex approach to treatment is required.
- Catarrhal rhinitis. The disease proceeds more moderately and accompanies various ENT diseases.
- Atrophic rhinitis. Symptoms: dry nose, constriction, possible nosebleeds.
- Drug-induced rhinitis. Occurs with long-term use of medications (drops, nasal sprays).
- Vasomotor rhinitis. The disease as a result of impaired blood vessel tone is accompanied by a severe runny nose.
Ear otitis
Ear inflammation is otitis media, in which the middle, inner and outer ear can become inflamed. There are left-sided, right-sided and bilateral otitis media. Research has shown that this is one of the most diagnosed ear pathologies today. Symptoms of otitis media:
- noise, congestion in the ear;
- poor hearing;
- ear pain of varying degrees;
- purulent discharge;
- elevated body temperature.
During the treatment of otitis, nasal drops are prescribed for local instillation to reduce swelling of the mucous membrane, antiseptic solutions for the ear canal, drops for instillation for severe ear pain, and antibiotics. With chronic otitis media, treatment is more complex, so self-medication and traditional methods should be avoided. In children and adults, otitis media is treated in the same way, but it is better to consult a doctor for recommendations.
- Pus from the nose: causes and how to treat
- Use of the antibiotic Ciprofloxacin
- A child has a sore throat - possible causes and treatment
Pharyngitis
The inflammatory process in the mucous membrane of the pharynx is called pharyngitis. Mostly, the disease is considered infectious; it occurs when inhaling dirty air or under the influence of irritating factors (alcohol, cigarettes). Pharyngitis causes a sore throat, pain, discomfort, general weakness, etc. For treatment it is recommended:
- eliminate the factor that caused the illness;
- stop smoking;
- use medication prescribed by your doctor.
Ear diseases
Ear diseases in people are also quite varied. Let us consider in detail what ear diseases are, what are the symptoms and treatment of ear diseases.
Acute and chronic ear diseases are:
- sulfur plug;
- external, middle and internal otitis media;
- foreign bodies in the ear canal;
- ear disease tubootitis (eustachitis);
- injuries of the auricle, eardrum, inner ear;
- mastoiditis;
- Meniere's disease;
- labyrinthitis.
Symptoms of human ear disease are almost always associated with decreased hearing ability. Often, inflammatory processes in the ear are accompanied by fever and signs of general intoxication. Symptoms of ear disease in humans may also include fluid leaking from the opening of the ear and severe pain in the ear.
The symptoms and treatment of ear diseases can be studied more clearly if you look at images and photos of human ear diseases. More rare symptoms of ear diseases in humans are otogenic processes of the brain or cerebellum.
Symptoms of ear disease in adults may be more vague and subtle, making pathologies more difficult to identify. Signs of ear disease may be absent for a long time and sometimes appear only at the stage of manifestation of the disease.
Treatment of human ear disease includes drug therapy and physiological treatment. The most sustainable healing effect is achieved by hardware effects within the framework of physiotherapy. Treatment of ear diseases in humans also includes restoration or stimulation of the patient’s immune status.
Parents are interested in the question, what ear diseases occur in childhood? Answer: almost the same as in adults. However, in a child, pathologies are more acute, and therapy is longer.
How to cure laryngitis in a child? Recommendations in our article. Read about the treatment of pharyngitis in various ways, including traditional medicine methods.
Diagnostic methods
An otolaryngologist must be competent enough to use modern sophisticated diagnostic methods. The list of examinations includes:
- Audiometry and rhinoscopy . These examinations allow you to accurately determine the condition of the hearing organs and sinuses.
- Endoscopic method . It allows you to identify internal pathologies and take tissue samples for analysis. It is considered the most effective instrumental research method.
- An ultrasound prescribed by a doctor will allow you to make a more accurate diagnosis without causing harm to the body, using safe ultrasonic waves.
- MRI allows you to obtain a highly accurate diagnosis; the principle of operation is the use of electromagnetic waves.
- CT scan . Its use allows you to obtain a layer-by-layer image of organs, which eliminates the possibility of erroneous diagnosis.
Take your health seriously , do not spread infectious diseases. It is easier to cure the disease in the initial stage than to try to get rid of complications later. An experienced otolaryngologist will help you with this.
Source: LivePosts.ru
Operations in the ear, nose and throat clinic
The clinic performs a wide range of surgical operations, such as adenoid removal, tonsil removal, tympanoplasty, septoplasty, rhinoplasty, vasotomy, etc. We have an operating room and a hospital at our disposal, which are equipped with the most modern medical equipment. The team of surgeons is represented by a wide range of specialists in their field who have extensive experience in performing complex surgical operations using modern technologies for operating and rehabilitating patients.
Treatment
Diseases of the ENT organs and their treatment are something that is best left to an experienced specialist. To treat ENT organs, various methods are used depending on the severity of the disease:
- Therapeutic (physiotherapy, medication, inhalations)
- Surgical. This type of treatment is used for severe cases of acute inflammation.
Once your doctor diagnoses you, a treatment plan will be developed. Treatment methods will vary depending on the severity of the disease. The main methods of treating ENT diseases:
- The use of medications (for diseases of the nose, drops (sprays) are prescribed, for the throat - rinsing solutions, for the ears - antibacterial agents, etc.).
- Undergoing medical procedures (anemization, application (physiotherapeutic procedure), ultraviolet irradiation, laser treatment).
- Elimination of symptoms using physical methods (rinsing the nose, blowing out the ears, removing wax plugs)
- Folk remedies (massages, tinctures, herbs).
- Surgical methods. The most common surgeries are to remove tonsils and adenoids in the throat.
Tumors of the nose and paranasal sinuses
Cancer is a malignant growth in the nasal cavity and sinuses. The most common types are squamous cell carcinomas and basaloid carcinomas. The disease usually affects men over 50 years of age. Risk factors include smoking and the Epstein-Barr virus.
Signs of cancer are:
- voice change;
- nosebleeds;
- headache;
- hearing impairment.
These symptoms are nonspecific, so very often nasal cancer is detected at an advanced stage. To establish a diagnosis, an endoscope is used, as well as CT and MRI. As with other types of cancer, treatment involves surgery, radiation and chemotherapy.
Osteoma is a rare benign tumor. Most often, osteomas are found in the frontal sinuses. Risk factors are injuries and inflammatory processes. For a long time the disease is not accompanied by symptoms, but in advanced stages headaches, blurred vision, and strabismus begin.
What does an ENT specialist do during an appointment?
Initially, the doctor interviews and examines the patient, that is, he feels the lymph nodes, assesses the condition of the mucous membrane of the throat and other manipulations.
This helps him make a correct assessment of the situation and suggest what exactly caused the disorder and draw up an approximate list of pathologies that can manifest themselves with similar symptoms.
In the future, the doctor moves on to more detailed collection of information, that is, instrumental diagnostic methods.
The simplest are rhinoscopy and otoscopy,
during which the condition of the nasal passages and ear canals is examined using special funnels and dilators.
If deviations from the norm are detected, the specialist may recommend a number of additional laboratory and instrumental examinations.
Inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs
The cause of inflammation of the ear, throat or nose is most often a cold. These organs are attacked by viruses or bacteria and a painful reaction develops.
- During the cold season, people most often complain of a runny nose - rhinitis . This term refers to inflammation of the nasal mucosa. Most often, the disease begins acutely. In the sinuses of the nose, a burning sensation, tickling is felt, swelling occurs, and mucus begins to be secreted. This disease is not dangerous, but quite unpleasant. Nasal congestion interferes with eating and sleeping, leads to impaired sense of smell and loss of taste. Congestion also occurs in the ears, the voice changes its timbre to a rougher one.
- If a runny nose is not treated promptly, it leads to inflammation of the deeper sinuses. Diseases such as sinusitis and sinusitis . Swelling of the nasal mucosa can be caused by an increased level of estrogen in the body, an allergic reaction, foreign objects entering the nasal passages, and even improper functioning of the stomach and intestines. Sinusitis can be caused by the formation of wax plugs in the ear. The doctor’s task is to find the exact causes of the pathological condition and eliminate them.
- Otitis media is an inflammation of various parts of the ear. There are external, middle and inflammation of the inner ear. Most often, otitis media occurs as a complication of inflammation of the upper respiratory tract . A primary bacterial infection in the ear rarely develops. When you have a runny nose or cough, bacteria enter the middle ear through the auditory tube and begin to multiply rapidly. A symptom of otitis media is usually shooting pain in the ear. It is better not to delay treatment so that the infection does not penetrate deeper. After the examination, the doctor will prescribe adequate treatment. Particular attention should be paid to ear diseases in young children. A history of otitis media can cause hearing loss.
- Throat diseases are divided into pharyngitis and tonsillitis , depending on the location of the source of infection. With pharyngitis, inflammation covers the larynx. Tonsillitis is characterized by inflammation of the tonsils, it is also called tonsillitis. A sore throat appears, difficulty swallowing occurs, and the temperature may rise.
Diseases caused by injuries
Due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure, the nose is often subject to injury. Nasal injuries can be open or closed.
Symptoms:
- pain;
- bleeding;
- hematoma of the nasal septum;
- difficulty with nasal breathing;
- deformation of the nose.
Causes:
- mechanical;
- household;
- burn injuries.
In childhood, any injuries to the nose require special attention, even with a mild clinical picture of the pathology. It is recommended to take an x-ray of the facial bones, since swelling of the nose interferes with medical diagnosis, and it is easy to miss a displaced nasal septum and other pathological conditions.
Treatment:
- emergency care (cold, packing the nasal passages with gauze swabs soaked in hydrogen peroxide);
- in severe cases - surgical intervention.
Complications:
- nasal deformity;
- deviated septum;
- difficulty with nasal breathing.
Regardless of what types of nasal diseases there are, their treatment requires an individual approach to each patient. Treatment tactics should be selected taking into account age, characteristics of the body and the disease itself. Timely treatment of nasal diseases is an excellent prevention of possible complications.
Who is an ENT (otolaryngologist)
Every resident of our country has known Lore since childhood. What is the correct name of an ENT doctor? In fact, the correct name for this doctor’s specialty is otorhinolaryngologist (from the word “laryngo-otorhinologist”).
An otorhinolaryngologist is a specialist with a higher medical education who diagnoses and treats diseases of the ear, nose and throat. An ENT doctor has therapeutic skills and knowledge, often prescribing medication and hardware treatment, however, he must also have knowledge and skills in surgery, since simple surgical interventions are also performed by an otolaryngologist. However, performing more complex surgical interventions is the function of an otolaryngologist-surgeon. Working with young patients is the task of a pediatric otolaryngologist.
For ordinary people, a runny nose or sore throat is not something significant, however, this is a fundamentally wrong idea. Our body is inextricably linked, the nasal cavity is a kind of “gate” for infection, subsequently spreading through the nasopharynx. With prolonged sore throat, there is a high probability of developing severe consequences for the heart, kidneys, etc. This is because affected tonsils can pose a serious threat to the human body, since the infection can spread from one location to another.
Otolaryngologist: what kind of doctor? What diseases does it treat?
ENT, otolaryngologist - who is he? What does this doctor treat? People call a multidisciplinary doctor with a narrow specialty “ear, nose and throat”. An ENT doctor is involved in the diagnosis and treatment of these organs of the human body.
Who is an otolaryngologist? This is a qualified specialist who performs consultative and diagnostic work with patients and, if necessary, provides surgical care to children and adults. Otolaryngology is the field of activity of an ENT doctor.
The throat, nose and ears are the most vulnerable organs of people. With a runny nose, inflammation of the nasopharynx, hearing loss, headaches, tinnitus, nasal congestion and hoarseness, adults and children consult an otolaryngologist all year round. Traditional examination of ENT organs takes quite a lot of time. Who is doing this?
The otorhinolaryngologist prescribes laboratory tests. The level of hearing is determined using an audiological examination. Only this doctor can select a hearing aid for a patient.
Patients need to consult an ENT doctor.
All complex diagnostic and therapeutic manipulations for pathologies of the hearing aid, nasal cavity, and diseases of the larynx are performed by an otolaryngologist.
If a runny nose appears, an examination is carried out. Who is capable of performing it competently? The patient sits opposite the otolaryngologist, who uses a frontal reflector and a bright light source to examine the nasal cavity. The reflected beam passes through a hole in the reflector.
An external inspection is carried out. An important role in the diagnosis of sinusitis and rhinitis is played by external examination during palpation of the nose. Using gentle movements of the thumbs, a qualified doctor correctly examines the frontal sinuses. Normally, palpating these areas should be painless.
The method of examining the nose is rhinoscopy:
- First, the otolaryngologist, using a nasal speculum, examines the vestibule of the nose, lifting its tip with his thumb. By spreading the jaws of the mirror, the otorhinolaryngologist examines the nasal turbinates.
- In a healthy person, the nasal mucosa is moist, pale pink, and the surface of the turbinates is smooth and pink. On the midline of the cavity is the nasal septum. An ENT doctor uses rhinomanometry to assess the presence of edema and impairment of free nasal breathing.
Examination of the pharyngeal mucosa:
- If the patient has a sore throat or pharyngitis, the doctor conducts an external examination of the maxillary sinuses using circular movements of his hands. Using your fingertips, soft palpation of the submandibular and parotid lymph nodes is performed.
- The otorhinolaryngologist performs mesopharyngoscopy to assess the symmetry of the tissues of the palate, the degree of hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils, the presence of adhesive-scarring, the nature of the contents and deformation of lacunae, purulent plugs.
Normally, a person should breathe evenly and correctly. The doctor decides whether surgery to remove the tonsils is necessary.
How is posterior rhinoscopy - epipharyngoscopy performed:
- A spatula and a nasopharyngeal speculum are used, preheated slightly in hot water or on an alcohol lamp. The tongue is pressed down with a spatula. The ENT doctor examines the nasopharynx area and assesses its condition.
- If necessary, the doctor corrects the nasal septum surgically. Children may have hypertrophy of the nasopharyngeal tonsil.
Examination of the larynx:
- An ENT doctor performs it when symptoms of laryngitis appear. A napkin is wrapped around 2/3 of the tongue and the laryngeal mirror is inserted with its shiny surface downwards parallel to the tongue, without touching the back wall of the pharynx and tongue. The larynx is examined in 3 positions.
- The otorhinolaryngologist assesses the degree of symmetry of the closure of the folds. He examines whether this space, which is clearly visible when breathing freely, is functioning correctly.
Otolaryngologists today have a modern ENT combine at their disposal.
What does the multifunctional device treat? This is a modern multifunctional unit, which includes everything necessary for the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the ENT organs at a qualitatively different level than before.
Such equipment allows the otolaryngologist to perform video endoscopy. During the examination, an enlarged image of the processes that occur in the nose, throat or ear is displayed on the monitor.
This makes it possible to endoscopically visualize the condition of the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity and nasopharynx, identify additional neoplasms, the presence of polyps, hypertrophic changes in the mucous membrane, tumors, and assess the condition of the auditory tube.
ENT combine is not only a higher level of diagnostics. It allows you to quickly, efficiently, without any discomfort for the patient, carry out a lot of medical procedures and achieve excellent results.
The ENT unit is also equipped with a microscope, which is used to diagnose and treat diseases of the middle ear under control. A bacteriological study of the microflora of the pharynx and cryotherapy of the tonsils are carried out.
With the help of such modern effective equipment, doctors wash the lacunae of the tonsils in case of chronic tonsillitis. Inflamed tonsils can be cleaned with a vacuum using a special attachment.
In case of sinusitis, the device thoroughly rinses the maxillary sinuses.
In the practice of otolaryngology, not only therapeutic but also surgical treatment methods are used. Sometimes this is the most effective way to get rid of ENT pathologies. The use of endoscopic techniques makes operations minimally traumatic and minimally invasive. They are always much easier to tolerate. There is no need for a long time for rehabilitation in the postoperative period.
Endoscopic techniques are widely used in the surgical treatment of polyps, nasal cavity formations, cysts, and foreign bodies in the paranasal sinuses.
Surgical treatment of the nasal septum and chronic dacryocystitis - inflammation of the lacrimal sac - is carried out.
For a patient who comes to see an otolaryngologist with a problem, the doctor will always help to effectively get rid of various conditions and diseases associated with disruption of the ENT organs.
The patient can consult an experienced, qualified otolaryngologist. Adequate treatment will be prescribed under his supervision.
The name comes from the Greek word otorhinolaryngologia, composed of the words otos - ear, rhinos - nose, larynges - larynx, logos - teaching. Different readings have created several names for the same medical discipline - otorhinolaryngology, otolaryngology, laryngootorhinology.
A specialist who deals with ear, nose and throat therapy is called an otolaryngologist, otorhinolaryngologist, laryngootorhinologist, or ENT doctor.
An otolaryngologist treats diseases of closely related, complex organs - ear, nose and throat.
Each of these organs is a complex system that performs complex tasks in the body:
- the nose and sinuses are involved in the differentiation of odors and breathing;
- ears act as a receiver, transmitter, and sound analyzer;
- The pharynx is closely connected with the larynx, esophagus, and trachea.
Who is an ENT doctor
The abbreviated name of the profession of laryngootorhinologist is ENT. And an otolaryngologist is also an ENT doctor.
An otolaryngologist must possess the skills of a therapist and surgeon, and constantly improve his knowledge in branches of medicine that are closely related to the ENT organs.
What does an ENT doctor treat?
The ENT organs include the pharynx, larynx, ears, and nose.
People consult an otorhinolaryngologist for the following diseases:
- nose - sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, rhinitis, sinusitis, nasal polyps, adenoids;
- ear – otitis, eustachitis, tubo-otitis, tympanitis, furuncle of the auditory canal, cerumen plugs, ear injuries, hearing loss, tinnitus;
- pharynx, larynx - sore throat, pharyngitis, laryngitis, tonsillitis.
An otolaryngologist has to deal with the most pressing problems for people, for example, eliminating snoring.
Not everyone is aware of the danger of snoring, but it can cause respiratory arrest (apnea) and create a direct threat to life. Snoring (ronchopathy) is treated by ENT doctors using modern effective methods, including minimally invasive radiosurgery.
It is otolaryngologists who perform the most complex operations on the thyroid gland. The ENT doctor conducts complex therapy, prescribes physiotherapy and medication. All necessary medical procedures are carried out in his office.
Doctor's offices - "ear, nose and throat" are equipped with the most advanced medical equipment for diagnostics, physiotherapy, surgical and endoscopic manipulations.
The list of cabinet equipment includes:
- a special ENT chair for examining the patient;
- swivel chair to check the functioning of the vestibular apparatus;
- a set of specialized ENT instruments;
- tone audiometer;
- set of tuning forks;
- negatoscope;
- electrosurgical device;
- diagnostic ENT endoscopes;
- fibrinolaryngoscope.
Classification, types of hearing loss: symptoms and treatment
Don't know what to do if a wax plug has formed in your ear? Our article will tell you.
In addition to examination, prescription of medications and physiotherapeutic treatment, the otolaryngologist performs many therapeutic procedures every day.
He rinses the nasal cavities, treats the mucous membranes with antiseptics, removes foreign objects from the ear, removes wax plugs, toilets the ear, performs operations to treat otitis media, eliminates a deviated nasal septum, performs endoscopy of the nasopharynx, and punctures of the maxillary sinuses.
The equipment of the otolaryngologist's treatment room allows for complex operations such as prosthetics and restoration of the eardrum, and hearing-improving operations.
Ear surgery
- Hearing surgery;
- operations on the middle ear, eardrum.
- Septoplasty – correction of a deviated nasal septum;
- rhinoplasty – nose surgery;
- sinus treatment;
- removal of sinus tumors.
- Removal of adenoids;
- removal of tonsils;
- elimination of snoring;
- treatment of tumors of the throat and larynx;
- treatment of ligaments.
- Oncological diseases;
- plastic surgery of the neck;
- diseases of the thyroid and parathyroid glands.
- Endoscopic removal of salivary gland stones;
- Oncological diseases of the salivary glands.
Diseases of the nose
- otitis and all kinds of hearing pathologies (Meniere's disease, etc.);
- nasal congestion, including chronic vasomotor rhinitis, polyps and adenoids;
- sinusitis, sinusitis, frontal sinusitis;
- tonsillitis (acute and chronic);
- tracheitis;
- adenoiditis;
- allergic rhinitis;
- laryngitis;
- otomycosis;
- nasal polyps;
- naphthyzine addiction;
- rhinitis;
- pharyngitis;
- snore;
- hearing loss;
- deviated nasal septum;
- throat cancer (larynx cancer).