When treating infants and children under three years of age, any self-medication is strictly contraindicated, and if symptoms are detected, you should immediately call a doctor at home.
In the presence of other diseases of infectious etiology, urgent hospitalization is required.
Recommendations for the treatment of laryngitis at the first manifestations of the disease
At the first manifestations of the disease, it is recommended to immediately contact a pediatrician (call a doctor at home). Quick implementation of appropriate measures and the appointment of adequate treatment prevent the occurrence of severe laryngeal edema and, as a consequence, acute stenotic laryngotracheitis, and also accelerate recovery and ensure a rapid improvement in the child’s well-being.
If symptoms characteristic of acute laryngitis appear, you should organize bed rest, reduce physical and mental stress, and create comfortable conditions for rest. You should also adhere to the following recommendations:
- Minimizing the load on the vocal apparatus. Neglecting this measure may cause the development of irreversible voice defects.
- Drink plenty of fluids. It is necessary to drink mineral water, sweetened fruit drinks (made from fruits and berries that do not irritate the mucous membrane of the throat), dried fruit compotes, and boiled drinking water. Drinks should be warm (36 - 45 degrees). Due to the large amount of fluid entering the body, the resulting sputum is diluted and the frequency and intensity of coughing attacks is reduced, and the elimination of pathogenic microorganisms and toxins from the body is accelerated.
- Creation of optimal microclimate parameters in the room. It is necessary to ventilate the children's room daily and use a humidifier.
- Application of traditional medicine methods. The use of foot baths, inhalations, mustard plasters, and gargles has an effective therapeutic effect on the child’s body at the initial stage of laryngitis.
- Eliminating the allergen. Used in cases of allergic laryngitis.
- Rational balanced nutrition. All foods that irritate the oropharynx should be excluded from the diet. The temperature of food eaten should be between 32 and 42 degrees.
The effectiveness of the activities is influenced by the presence of a calm, comfortable environment and the absence of stressful situations. An integrated approach to the treatment of acute laryngitis in children ensures an uncomplicated course of the disease and prevents the development of a chronic form of the disease.
What to do during an attack of false croup
- Call an ambulance.
- Provide the child with a flow of fresh air, but not cold.
- Sit him down, free him from tight clothes.
- Take a hot foot bath.
— Of the medications, only inhalations with a nebulizer are permissible, preferably with mineral water or saline solution. Any medications can cause allergies and laryngeal spasms.
— The air that the child breathes must be humidified. You can place a basin of hot water near him, hang a wet towel, or take your baby to the bathroom more often and turn on the hot water.
- You can let the child breathe over a hot soda solution.
- It is undesirable to eat or drink during an attack, as swelling of the larynx can cause food to enter the respiratory tract.
How to speed up treatment of the disease
Inflammation of the larynx is a disease that often develops in babies under one year of age. When choosing how to treat laryngitis in children, you should understand that not every drug is suitable for treating such a small child.
- The inflammatory process occurring in the throat is characterized by difficulty breathing, so the child should breathe freely through his nose. If your baby's sinuses are blocked, you should use vasoconstrictor drops recommended by your doctor. In addition, diseases of the upper respiratory tract, which are accompanied by a runny nose, can themselves be the cause of laryngitis, so a runny nose must be treated promptly.
- A child whose vocal cords and larynx are inflamed must maintain vocal rest for several days. You cannot ask a sick person to talk in a whisper. Such a load on the vocal apparatus will only worsen the situation. If a hoarse baby needs to say something, it is better to do it without trying to make his voice quieter. Often children with laryngitis are too young to understand why they need to be silent, so parents should think about how to do this in a playful way.
- An important part of recovery is drinking plenty of fluids. You should not give hot milk or broth to a baby suffering from laryngitis. To avoid exacerbation of the disease, food and drink should be warm. It is best if the sick person drinks through a straw. This measure allows you to avoid burning your throat while eating.
- A sick child should not be fed salty, sour, or even spicy foods. In addition, the inflamed larynx is irritated by seasonings and spices added to dishes.
- It is best if the patient remains at home during the recovery process. If it is not possible to maintain bed rest and you have to go outside (especially in winter), you should try to cover the baby’s mouth and nose with a warm scarf. A patient with laryngitis should under no circumstances talk in the cold, since inhaling cold air is fraught with exacerbation of the disease and the appearance of complications.
- If you notice that your child's body temperature has increased, you can use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Drugs containing ibuprofen and paracetamol are used as an antipyretic for laryngitis. It is not advisable to take such medications if the scale on the thermometer has not reached 38. If the baby has a hard time withstanding the rise in temperature and has previously experienced convulsions, the medication can be given already at 37.5 °C.
- The most important factor in recovery is the humidified air that a small patient should breathe. Parents are required to ensure that the room maintains high humidity (preferably at least 70%). To do this, you need to reduce the power of the heating device (if possible), place a container of water in the room, cover the radiator with a damp towel, or purchase an air humidifier, etc.
It is best to give the sick person warm raspberry tea with honey or give alkaline mineral water, for example, Borjomi.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis of laryngitis in children, an objective examination of the patient and data obtained from collecting complaints and anamnesis may be sufficient. Otorhinolaryngological examination for suspected laryngitis in children includes oto-, rhino-, pharyngoscopy, indirect laryngoscopy, as well as palpation of the cervical lymph nodes. In this case, hyperemia, edema, petechial hemorrhages and/or increased vascular pattern of the laryngeal mucosa, incomplete closure and thickening of the vocal cords during phonation are detected.
In acute laryngitis, bed rest and drinking plenty of fluids are indicated.
During a general blood test, an increase in the number of leukocytes and an increase in ESR are determined. Identification of the pathogen in laryngitis in children can be done through bacteriological and virological examination of swabs from the upper respiratory tract, and polymerase chain reaction.
In case of long-term voice disorders, the patient is referred for consultation to a phonologist and speech therapist, and a study of voice function is carried out.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with foreign bodies of the larynx, diphtheria, retropharyngeal abscess, congenital stridor, laryngeal papillomatosis, epiglottitis, laryngospasm caused by spasmophilia, as well as tuberculosis, laryngeal cancer, ectopic thyroid gland.
How to understand that a child has laryngitis
The development of the inflammatory process in the larynx in children manifests itself more often in an acute form and, as a rule, suddenly. Parents, first of all, may notice in the child some changes in the timbre of his voice, hoarseness, loss of appetite due to pain when swallowing, dry cough, rapid or, conversely, difficulty breathing. At night and in the morning, the frequency of coughing increases, until attacks of suffocation occur.
Laryngitis can also cause the following symptoms:
- the appearance of a runny nose;
- redness and swelling of the mucous membrane of the throat;
- presence of bloody discharge in the area of inflammation;
- possible loss of voice, hoarseness;
- difficulty breathing due to spasm of the larynx, its swelling
- feeling of sore throat, dry mouth;
- a child has a strong barking cough, dry at first, then scanty sputum gradually appears;
- slight increase in body temperature, less often high fever, headaches.
- see also causes of dry cough without fever, or why dry cough does not go away or
Causes of the disease
Most often, children attending children's institutions are susceptible to the disease. Constant contact with a large number of people who may be infected with viruses, as well as nervous stress due to separation from the mother, make the child vulnerable. Laryngitis in a 2-year-old child is a fairly common disease, but children over 5 years old suffer from it very rarely. What reasons cause it?
— Viruses, most often ARVI or influenza, but laryngitis can also develop when infected with whooping cough, diphtheria or scarlet fever.
— Allergens: tobacco smoke, the smell of paint or perfume, dust, animal hair or food. Help for laryngitis in children prone to allergies should be provided immediately so as not to lead to laryngospasm and stenosis.
- Some medications, especially in spray form, the spray of which can cause spasm of the larynx.
— Features of the baby’s development. Some children develop lymphatic-hypoplastic diathesis from birth. They are prone to frequent colds and swelling.
- Very hot drinks or spicy foods.
— Severe stress or psychological trauma can also cause laryngitis in children.
Treatment of laryngitis in children
Before treating laryngitis in children, you must visit your treating pediatrician so that he can make the correct diagnosis and determine the severity of the disease. Following these rules will help cure laryngitis as quickly as possible:
- proper dietary nutrition that does not contain any irritating foods. All food and drink should be warm, drinks not carbonated. Taking vitamins is indicated;
- reducing the load on the vocal cords. It is advisable for the smallest patients to remain completely silent so as not to deform the inflamed vocal cords, which are in the growth stage;
- Bed rest is required. Children can only “walk” on the balcony to get some fresh air, but provided that it is summer outside, and such a “walk” will be stopped at the first sign of fatigue;
- strict control of the air condition, which consists of regular humidification and ventilation. Optimally, if the room has an air purifier and humidifier, the ionization function will be very useful;
- a large amount of liquid is required. If the throat hurts very badly, then the child should be given milk, broths, cream soups so that solid food does not injure the throat and cause pain. Drinking plenty of fluids will help avoid intoxication and quickly relieve dry cough.
Drug treatment
Before taking medications, you should consult your doctor, especially if the child is still very young.
If your baby has a cough that makes it difficult to fall asleep, then an antitussive medication is needed. Children one to two years old can be given Stoptusin (from 6 months), children over two years old can be given Gerbion, and children over three years old can be given Libexin. Also shown are chest packs, marshmallow, and ambroxol.
Important! Follow the indicated dosage so that the treatment does not cause harm to the child!
medications are also needed for swelling of the larynx. For children under two years of age, products in the form of drops and syrup are suitable: Zyrtec, Fenistil, Cetrin, Clarisens; for older children - in tablets: Clarotadine, Claritin, etc.
If a child has a fever, then it is necessary to take antipyretic and anti-inflammatory drugs, such as Ibufen, Paracetamol, Panadol, etc.
As soon as the first symptoms of the disease appear, we treat the child by gargling with Furacilin or any other remedy for laryngitis. Lozenges should not be used if the child has a dry cough, as there is a risk of choking.
Antibiotics for laryngitis in children are rarely prescribed; they should be taken only on the recommendation of a doctor.
Inhalation treatment
Inhalations for laryngitis can quickly improve the child’s condition, ease breathing, and relieve swelling. They also have antimicrobial, antibacterial and soothing effects. Both traditional medicine and Doctor Komarovsky advise doing inhalations, especially since they are indicated at the first symptoms of the disease. Unlike medications, inhalations can be preventive. Both modern nebulizer inhalers and conventional steam inhalers are used. Inhalations will be useful and harmless if you adhere to the following rules:
- steam inhalation is acceptable for children over 5 years old, as younger children can get burns to their mucous membranes;
- half an hour before and after the procedure you can neither eat nor drink;
- inhalations are done 2 times a day, during the procedure and after it the child should not speak for 30 minutes;
- During inhalation, you need to inhale through your mouth and exhale through your nose.
Inhalations for laryngitis
- Inhalations are one of the prerequisites for successful treatment. A special device is ideal for this - a nebulizer, which can be easily found in a pharmacy. The main advantages of the device are convenience and possibility of use at any age.
- When treating the disease, inhalation solutions should be used:
- soda solution;
- mineral water (Borjomi or Essentuki);
- medications (Lazolvan, Rotokan, Sinupret, Tolzingon);
- herbal infusions (chamomile, sage, mint).
Inhalations are carried out up to 3 times a day, mainly a couple of hours before bedtime and 30 minutes after eating, and in the evening always before 19.00. An hour after the procedure, it is recommended to give the child cough syrup.
Inhalations are contraindicated:
- at high temperature
- breathing and cardiovascular problems
- tendency to bleed from the nose
Features of laryngitis in children
Acute laryngitis is called inflammation of the mucous membrane of the larynx. A wide variety of viruses and bacteria cause the development of the disease. Laryngitis begins with an increase in temperature, the child becomes apathetic and refuses to eat. Soon, parents notice that the child has a strong barking cough and hoarseness. The baby himself may complain to his parents about a sore throat.
A barking cough is evidence that the inflammation has spread to the vocal cords.
Young children cannot complain about unpleasant symptoms themselves, so parents need to be vigilant. Laryngitis in infants is supported by changes in behavior (the baby becomes lethargic or, on the contrary, restless, whiny), wheezing during crying, whistling when breathing, and coughing.
In young children, the lumen of the larynx is narrow. And inflammation of the mucous membrane of the larynx immediately leads to its swelling and, accordingly, a significant narrowing of the lumen. Doctors call this pathological condition stenosing laryngotracheitis or.
Important! Stenosis (narrowing) of the larynx in young children can lead to a complete cessation of air supply to the lungs with the development of suffocation.
Croup often occurs at night. The child cannot take a normal breath, as if something is bothering him. In this case, breathing is accompanied by wheezing and bubbling sounds. Due to insufficient oxygen supply, cyanosis of the skin appears. This is a dangerous condition for a child that requires qualified medical care.
What kind of disease is this?
Laryngitis is an infectious inflammation of the mucous membrane of the larynx and vocal cords. Most often, infants and preschoolers are exposed to it. Under the age of 2 years, in 1/3 of cases, laryngitis occurs together with ARVI.
- The disease can also develop in combination with bronchitis, tracheitis, measles, tonsillitis and other infectious pathologies.
The disease is often accompanied by obstruction, that is, obstruction, of the upper respiratory tract, which is a dangerous condition and requires immediate medical attention.
Therefore, if the larynx is inflamed, it is necessary to carefully monitor the baby’s condition. This will allow timely assistance to a child with laryngitis with significant swelling of the mucous membrane in the throat.
Unlike viruses, bacteria cause laryngitis in a child less often (about 10% of cases), but the disease in this case is more severe. The provoking disease may be pneumonia, scarlet fever, whooping cough, or hemophilus influenzae infection.
Predisposing factors for the development of laryngitis in children:
- In infants and children from 1 to 5 years old, the larynx is narrow and lined with looser mucous membrane, which increases the risk of viruses or bacteria multiplying on it;
- Allergic reactions, in particular lymphatic-hypoplastic diathesis;
- Dry air and living in regions with a polluted atmosphere;
- Hypothermia;
- Vitamin deficiency, poor nutrition;
- Passive smoking;
- Decreased immune strength;
- Frequent crying (for example, during colic), singing, loud screaming and other mechanical factors.
The spread of infection to the larynx and throat mucosa in children can occur even with a normal runny nose, if left unattended. Therefore, any infectious disease requires timely and effective treatment.
The nature of laryngitis in children under one year and from 1 to 5 years is associated with the anatomy of the respiratory tract:
- The narrow lumen of the larynx and its funnel-shaped shape;
- Loose mucous and connective tissue;
- Not fully developed respiratory muscles;
- Features of innervation of the larynx.
Because of this, children with laryngitis are at high risk of developing swelling of the mucous membrane and obstruction of the upper respiratory tract. In addition, the lumen of the larynx can become clogged with inflammatory discharge, and the situation is complicated by a reflex muscle spasm.
The disease can occur in a child in a chronic or acute form.
Prognosis and prevention
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, the prognosis is favorable. The disease subsides 7-10 days after the start of therapy. If you ignore the doctor’s recommendations, acute laryngitis may develop into a latent form. Treatment of chronic inflammation is more difficult and takes about 3-4 weeks.
Primary prevention of laryngitis plays an important role. Its goal is to prevent the development of inflammation. It includes the following measures:
- adherence to daily routine;
- balanced diet with sufficient vitamins and minerals;
- strengthening the immune system - hardening, taking immunostimulating drugs during the season of exacerbation of colds;
- washing hands after visiting the toilet and places with large crowds of people;
- doing morning exercises.
Secondary prevention is aimed at excluding relapses of laryngitis. Her tasks include:
- regular preventive examination by a pediatrician;
- lubricating the nose with ointment with oxoline (for seasonal exacerbations of diseases);
- rinsing the nasal sinuses with sea water;
- taking antiviral drugs.
Medicines
1. An important medicine for laryngitis for children is some kind of antihistamine.
“Zyrtec”, “Zodak”, “Claritin”, “Suprastin” and others are good at relieving swelling, even if it is not caused by an allergic reaction. 2. Doctors often prescribe sprays to relieve inflammation of the larynx or lozenges. But it should be borne in mind that most of them cannot be used by children under 5 years of age. The safest drugs are: IRS 19, Hexoral, Grammidin, Stopangin and some others.
3. A severe cough often occurs when a child has laryngitis. To help him fall asleep, the doctor may recommend antitussive drugs: Libexin, Stoptussin, Sinekod and others. And when the cough becomes wet, you need to take expectorants: “ACC”, marshmallow or thermopsis syrup, “Bronchosan”, “Lazolvan” and others.
4. If the temperature rises strongly, the child should be given an antipyretic: Ibuprofen, Paracetamol or Panadol.
5. An important means of preventing spasm of the larynx and relieving swelling of the mucous membrane are antispasmodic and diuretic drugs, for example, No-Shpa and Furosemide.
6. In very rare cases, if a bacterial infection is associated with the disease, antibiotics are prescribed: Amoxiclav, Cefix, Clarithromycin and others.
Drug treatment
Medicines for laryngitis in children are prescribed to relieve the patient's symptoms. The drugs are selected by the doctor after diagnosis. Treatment is carried out using several groups of medications.
Antihistamines
Antiallergic drugs are used to eliminate swelling of the nasopharynx during illness. For children 1-5 years old, it is customary to use medicines in the form of syrups and drops. Children from 3 to 6 years old can be given tablets if they have learned to swallow them. Among the antihistamines used for laryngitis are:
- Zyrtec;
- Loratadine;
- Fenistil;
- Suprastin;
- Cetrin;
- Claritin;
- Zodak and others.
How and in what dosage to take this or that medicine is decided by a specialist when examining the patient.
Homeopathic medicines
Experts who are supporters of homeopathic treatment of laryngitis speak positively about the following drugs:
- Homeovox;
- Belladonna;
- Spongia;
- Aconite.
The choice of one remedy or another should be based on the patient’s symptoms and his individual characteristics.
Cough remedies
For a dry, irritating cough during laryngitis, the following is used in medical practice:
- Sinecode;
- Libexin;
- Erespal;
- Gedelix;
- Gerbion;
- Omnitus and others.
At the stage when a dry cough turns into a wet one, the following drugs are prescribed:
- Ascoril;
- ACC;
- Fluditek;
- Bronholitin;
- Stoptussin;
- Alteyka;
- Lazolvan.
Patients with bronchial asthma and allergic rhinitis are often prescribed Singulair and Eufillin.
Preparations for resorption
For laryngitis, a child can be given lozenges to relieve a sore throat.
The following tools have proven themselves well:
- Faringosept;
- Lysobacter;
- Stopangin;
- Grammidin;
- Strepsils.
Many of them have side effects, so treatment is recommended to be carried out strictly under medical supervision.
Solutions for inhalation
Inhalation for laryngitis is a reliable and safe method that can be used even by one-year-old children. It is better to be treated in this way through a nebulizer. The device allows you to spray the medicine into small particles and deliver it directly to the affected area.
Popular drugs for inhalation:
- Berodual;
- Pulmicort;
- Adrenalin;
- Ambrobene;
- Ventolina;
- Lazolvan.
Inhalation is carried out according to the instructions for use of the drug as prescribed by a doctor.
Antibiotics
Antibacterial drugs are prescribed to children if the causative agent of laryngitis is bacteria. The following means can be used:
- Suprax;
- Amoxiclav;
- Flemoxin;
- Amoxicillin;
- Chemomycin;
- Macropen;
- Ecomed and others.
Antibiotics are quite serious drugs that often cause side effects. Self-medication with their help is not allowed.
Antiseptics
Antiseptic solutions help cope with the infection and eliminate the symptoms of laryngitis. Among them are used:
- Tonzilong;
- Lugol's solution;
- Mirmistin;
- Furacilin;
- Rotokan.
Antiseptics are produced mainly in the form of solutions for external application or gargling.
Relieving swelling
In emergency situations, drugs such as Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone, Dexamethasone and other medications are used to quickly relieve swelling and spasm of the larynx.
Hormonal drugs are prescribed to the child under the strict supervision of a doctor. They often cause side effects, so self-medication with them is not allowed. No-Shpa also helps relieve mild spasms.
Medicines
Self-medication of young children is excluded . Only a pediatrician or an infectious disease specialist can prescribe how to treat a baby and adequate therapy. Any heating, pads, rubbing with ointments, fats are contraindicated.
Traditional recipes, especially when treating babies under one year old, are prohibited. Also, when treating children under 3 years of age, it is not recommended to use drugs in aerosol form , unless otherwise recommended by the attending physician.
Drug therapy includes taking the following groups of drugs:
- antihistamines – have anti-edematous and anti-inflammatory properties, effectiveness increases when used at night (Suprastin, Cetrin, Claritin);
- antitussives and expectorants (Gerbion, Stoptussin phyto), for wet coughs (Alteyka, Thermopsis), sprays Lugol, Miramistin, Stopangin;
- antipyretics – (Paracetamol, Ibuprofen).
Antibiotics are prescribed in the following cases:
- bacterial inflammation identified after diagnosis;
- intoxication of the body.
Sometimes antibiotics can be prescribed by a doctor for reinsurance, in order to avoid consequences (as a rule, in a hospital setting, antibiotics are prescribed in 90% of cases).
Laryngitis is of a bacterial nature in rare cases; more often the causative agent is of a viral nature . In the latter case, antibacterial drugs are not used. For the fungal form, antimycotic drugs are prescribed.
Antibiotics that may be prescribed to treat laryngitis are:
- penicillins (Flemoclav, Augmentin);
- cephalosporins in the form of syrups (Cefadox, Suprax), in injection form (Fortum);
- azithromycin - for severe disease (Sumamed, Azitrox) and other macrolides (Macropen).
When treating laryngitis in children, inhalers can be used; nebulizers are recommended for administering drugs. Their use in infants and children over one year of age must be previously agreed with a doctor.
Compresses against laryngitis
Compresses give positive results when treating children. A variety of drugs can be used as medicines for compresses. It is better to leave their choice to the doctor
This is extremely important, because if used correctly, compresses can be very helpful, but if used incorrectly, they can cause serious harm.
Wet compresses
Wet compresses have a warming property, and the following products can be used as a basis:
Compress with Dimexide for coughs in children:
- ethanol;
- oil solutions;
- wine;
- tincture of calendula, etc.
If vodka or alcohol is used as a base, then it is important to dilute it in equal proportions with water. The gauze is moistened with the product and wrung out. Next, the napkin is applied to the throat or chest, covered with a plastic bag and tied with a woolen scarf.
Dry compresses
Dry compresses are applied in the morning using a sterile napkin, which can be purchased at the pharmacy. This procedure has a slight warming effect, so it is used in the initial stages of the pathological process.
Dexamethasone has anti-inflammatory and antiallergic effects.
Dexamethasone for laryngitis in children is used in the form of inhalation procedures. This type of drug delivery allows dexamethasone to be converted into tiny particles that settle on the bronchioles of the bronchial tree and have a localized effect.
Contraindications to the use of the drug are:
- increased sensitivity;
- weakened immune system;
- heat;
- purulent sputum.
Dexamethasone is diluted with saline and inserted into a nebulizer. It is important to explain to the child that he breathes as usual, and should not take deep breaths. This can lead to bronchospasm and increased coughing.
Inhalations will help achieve the following results:
- relieve dry cough attacks for a long time;
- significant improvement and acceleration of sputum formation;
- ensuring the release of sputum from the bronchi;
- pronounced therapeutic effect in the form of an anti-inflammatory effect.
Inhalations based on dexamethasone do not harm the general condition of the child.
Features of inhalation procedures are the following:
- The duration of the procedure is from five to ten minutes;
- at least one hour must pass after eating;
- when treating small children, the mask can be worn while sleeping;
- dilution of the drug should be done immediately before the procedure.
Home treatment recipes
Home treatment recipes are no less effective than medications, so it is easier to defeat the disease with a comprehensive fight against laryngitis.
These include:
- foot baths with mustard;
- warm compresses in the neck area;
- mustard plasters are applied to the back;
- steam inhalation over potatoes for 10 minutes (unpeeled vegetables are boiled, laid out on a eucalyptus, mint or chamomile leaf);
- gargling with medicinal plants with antiseptic, anti-inflammatory and expectorant properties (3 times a day with boiled beet juice or an infusion of a glass of boiling water with 1 teaspoon of honey boiled for a minute).
It is useful for laryngitis to give your baby an infusion of herbs and honey. Suitable herbs:
- plantain;
- coltsfoot leaf;
- tricolor violet.
To prepare the solution, take 1 tsp. each herb, everything is poured with a glass of boiling water. Let the liquid cool until it cools and strain. Give the baby 1 tsp. 4 times a day (for ages 2-3 years), 1 tbsp. l. 4 times a day (for children over 3 years old). The course of treatment is 3 days.
The following recipe will help in treatment: 1 tbsp. l. sea buckthorn is poured with 2 cups of boiling water and boiled for 2 minutes, covered with a lid and left for 1 hour. The child should be allowed to drink 1 tablespoon per day up to 6 times or gargle up to 3 times a day.
Carrot juice with honey in a 1:1 ratio will have a beneficial effect on laryngitis. The medicinal product is used by the child 4 times a day, 1 tsp.
An onion compress will provide excellent relief. To prepare it, you need to finely chop 1 onion, place it in a cloth bag and place it over water in a saucepan while boiling. After heating the bag, place it on the baby's neck. Make sure it is not too hot so as not to burn your baby.
Symptoms of laryngitis
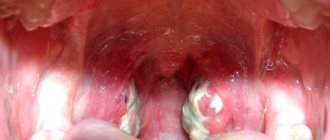
The first and most striking manifestation of laryngitis in children is hoarseness. In addition, the initial stage of development of the disease is accompanied by a dry cough, painful sensations when swallowing and difficulty breathing.
The following symptoms also indicate the development of laryngitis:
- red throat and swelling;
- a cough that sounds acoustically like a dog barking;
- temperature rise to 37.5-38 degrees;
- feeling of dryness and tickling in the mouth;
- spasms of the laryngeal muscles.
In principle, the symptoms of laryngitis are quite similar to the development of other infectious diseases. But voice problems and a barking cough are the distinctive features that will help almost accurately determine the development of laryngitis.
Symptoms of laryngitis in newborns and infants
If older children themselves may complain of discomfort in the throat, pain symptoms and other causes of illness, then with the youngest it is more difficult. They cannot express their problems verbally. Therefore, in infants, signs of laryngitis should be looked for visually. Parents should be alert to the child's moodiness, restlessness and general lethargy, wheezing during his cry and difficulty breathing, accompanied by whistling and noise, as well as coughing and profuse nasal discharge. All this is a reason to consult a doctor in order to accurately diagnose and prevent the development of complications.
Symptoms of the development of croup with laryngitis
Speaking about laryngitis, one cannot fail to mention such a complication as croup. This term refers to respiratory pathology in children, which develops due to a significant narrowing of the lumen of the larynx. In most cases, croup occurs at night and the attack looks quite scary. The child complains of difficulty breathing, the sound of which is accompanied by many unusual sounds. In some cases, cyanosis may appear on the body, which indicates insufficient oxygen saturation of the blood.
The reason for this is the development of inflammation of the larynx. In the narrowest place of this organ, the subglottic space, the lumen becomes so small that it begins to complicate the breathing process. It is at night that this happens due to the fact that the accumulating mucus flows into this particular place, drying out there due to insufficiently humid air in the room and a sufficiently high temperature. According to statistics, croup, as a consequence of laryngitis, occurs in every second child. Therefore, having heard from a pediatrician a diagnosis of laryngitis, you need to be prepared for the fact that the child will begin to develop respiratory pathology the very next night.
The first and surest step in such a development of laryngitis will be to immediately call an ambulance and hospitalize the child. You can overcome croup on your own by abundantly humidifying the air and cooling the temperature in the room where the patient is located to 18 degrees. Ideally, the child should be taken to the bathroom and open a cold water tap. After this, the symptoms of croup quickly begin to subside.
Doctors note that croup, despite its visual complexity and problems, does not pose a serious danger. The absence of panic among parents and simple, correct actions in most cases make it possible to overcome this complication even before the doctors arrive.
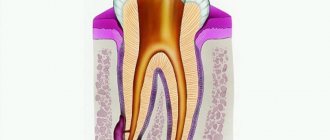
What is laryngitis
The disease laryngitis develops in the larynx, approximately in the place where our vocal cords are located. In fact, inflammation of the larynx is classic laryngitis, one of the most common and common forms of ARVI in children.
Especially often, laryngitis in children takes a form in which the larynx not only becomes inflamed, but also narrows, causing difficulty breathing, discomfort and pain, especially when talking or swallowing. Sometimes the walls of the larynx narrow so much that the baby cannot even drink, let alone eat or talk.
This form of laryngitis appears in the medical lexicon as “stenotic laryngitis” (stenosis is a narrowing of an organ). And naturally, it is most dangerous for children, especially the smallest ones, because it can cause sudden suffocation.
Stenotic laryngitis in children can be caused by various reasons - for example, an allergy attack, a rapidly developing infectious disease, a burn of the respiratory tract, etc. Stenosing laryngitis, caused by infection, often develops into the so-called false croup in children.
The main reasons for the development of the disease are:
• hypothermia, • infections, complications after infectious diseases, • oral infections, • drinking hot or cold drinks, • after screaming, singing, etc. That is, as a result of overstrain of the vocal cords. • allergy, • psycho-emotional factor.
Swelling of the larynx and severe redness may cause suspicion to the doctor. After examining the larynx and if inflammation of the vocal cords is detected, the doctor will diagnose laryngitis. Parents may suspect the early development of the disease based on the following symptoms:
• altered timbre of voice or its complete absence, • burning sensation and dryness in the throat, • barking dry cough, • runny nose, • weakness, • enlarged lymph nodes, • shortness of breath, • chills.
It should be noted that temperature with laryngitis is not a mandatory symptom. In some cases, body temperature can rise to 39°C.
Disease prevention
An important method in the prevention of laryngitis will be hardening.
Physical activity, sports and walks in the fresh air will also have a beneficial strengthening effect. The child needs to be provided with adequate nutrition. If necessary, the therapist may recommend a vitamin-mineral complex to replenish missing minerals and vitamins.
Classification
Depending on the course of inflammation, acute and chronic laryngitis are distinguished.
According to the prevalence of the inflammatory process, acute laryngitis can be:
- diffuse, or diffuse;
- limited.
Forms of pathology according to the nature of the course:
- catarrhal;
- stenosing;
- hyperplastic, or hypertrophic;
- atrophic;
- hemorrhagic;
- phlegmonous;
- diphtheria.
Before you start taking any medications, especially antibacterial ones, you must consult a doctor and select a treatment regimen depending on the etiological agent that caused the inflammation.
Depending on the etiology, laryngitis can be:
- viral;
- bacterial;
- fungal, or laryngomycosis;
- traumatic;
- allergic.
Infection of the larynx most often occurs in a descending manner when inhaling contaminated air, inflammation of the nasopharynx, paranasal sinuses or tonsils. An ascending path is also possible - with tracheitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, tuberculosis.
Acute laryngitis can be a manifestation of many infectious diseases (influenza, measles, scarlet fever, etc.).
If treatment is untimely or inadequate, a chronic form of the disease may develop.
The first signs of laryngitis
Children over 3 years old can already talk about pain and feelings, so it is possible to provide the treatment they need in a timely manner. However, it is better to determine a bad condition yourself at the very beginning of the development of the disease. If you notice that the body temperature rises above 38 degrees, then we can conclude that he has a cold. But what if he exhibits other signs:
- children have difficulty breathing at night;
- cyanosis appears on the lips;
- the voice settles and becomes hoarse;
- a barking cough appears;
- nervous behavior;
- When you breathe, you have to tense your muscles a lot.
In children under one year old
In younger children (under 3 years old), laryngitis is more severe. He is very dangerous - parents may simply not notice changes in breathing, his restless behavior or other signs. If rapid breathing and anxiety, which appears from the very beginning, are not noticed in time, the inflammatory process can go lower, which can even lead to the death of the child. Signs in children under one year of age are as follows:
- restless sleep;
- difficulty breathing at night;
- blue discoloration appears around the lips;
- there is retraction of the skin between the ribs;
- high body temperature (up to 39 and above);
- barking cough.
How is the fourth stage of laryngitis treated?
If in the first three stages of the development of the disease the main task of parents and doctors is to quickly relieve symptoms and improve the child’s condition, then in the fourth we are talking about saving the baby’s life. The patient is immediately hospitalized and placed in the intensive care unit. There, the baby is constantly under the supervision of doctors who know how to treat laryngitis in children 4 years old.
In addition, the conditions of resuscitation in cases of deterioration of the child’s condition make it possible to perform a tracheostomy. This surgical intervention, which is necessary when the glottis is completely blocked, is practically the only option for saving the baby. A breathing tube is inserted through an incision in the neck.
How to measure temperature
Measuring this indicator will help determine whether you need to take antipyretics. In addition, a decrease in temperature during laryngitis is one of the indicators of the effectiveness of the treatment.
There are different places to measure: forehead, armpits, rectum, mouth, ears. Depending on the place where it is measured and the device used, the value of this indicator may vary by 0.2-0.8 °C.
For an adult
The classic method of measuring this parameter is using electronic thermometers, which have almost completely replaced the previously used mercury thermometers.
The method of using them is very simple. The device is placed in the armpit and wait for a sound signal. They can also measure the temperature in the mouth or rectally.
Important! Rectal temperature is considered the most reliable, but in case of laryngitis, measurements in the armpit will be sufficient to assess the degree of the inflammatory process.
To kid
It is more difficult to measure this indicator in a small child using an electronic thermometer. The baby cannot lie down quietly for 3-4 minutes to get a reliable result. Other types of thermometers come to the mother’s aid, which allow you to quickly and painlessly find out this parameter:
- Infrared thermometer. There are contactless and ear-based. Measures temperature in 5-10 seconds. Disadvantages: high price, there is an error in measurements. Can be used to measure temperature over time.
- Disposable thermometers. This test strip is applied to the skin or pushed under the tongue for a minute. Does not measure values accurately, but is convenient for travel use.
- Electronic in the form of a pacifier. Suitable for children who love pacifiers.
See also
How and with what to treat coughs and colds with the flu in adults and children, how long does it last
Read
In childhood, temperature is measured rectally, in the armpit, on the skin of the forehead or in the mouth. It is important to remember that normal values for infants are up to 37.2-37.3 °C. During feeding and in the evening it tends to increase, and in the morning in a calm state its lowest values are observed.
Traditional medicine recipes
Of course, no one can prohibit parents from using “grandmother’s” methods to treat their children. But, unfortunately, these recipes can not only be ineffective, but also harm the baby’s health. Healthy foods such as honey or lemon can cause an allergic reaction and severe swelling. And the child’s body can react ambiguously to herbal preparations.
Of course, we will not categorically state that infusions or decoctions should not be used for respiratory diseases in children. But before treating laryngitis in children 2 years of age or smaller ones with folk remedies, be sure to consult with your doctor. Perhaps he will supplement the treatment regimen with auxiliary procedures based on traditional medicine recipes.
Just in case, here are a couple of recipes.
- Pour boiling water (1 tbsp) over dill seeds (1 tsp) and leave for 40 minutes. Strain and drink a little daily.
- A good remedy is an infusion of plantain leaves. To prepare it, pour boiling water over 2-3 teaspoons of dry leaves and leave for half an hour. Take 0.5 cups 20 minutes before meals three times a day.
Milk and honey is a classic of the genre. But! Please note that honey is a strong allergen. Dissolve a teaspoon of honey in a glass of warm, not hot (!) milk. Take three times a day.
So, it's time to take stock. Laryngitis is a rather serious disease, in some cases causing attacks of suffocation. A severe dry cough causes severe discomfort. Attacks most often occur at night and can last a couple of hours. Doctors recommend sitting the baby higher, placing pillows under the back. How to treat laryngitis in children - folk remedies or medications - is up to you. However, in any case, consultation with a pediatrician is necessary!
Concept of disease
Laryngitis is characterized by inflammation of the mucous membranes of a child's larynx. The frequent occurrence of this disease at an early age is explained by the physiology of the walls of the larynx, which until 2-3 years of age has a loose structure and is more susceptible to external irritants. Laryngitis is rarely an independent disease. Much more often it appears as a supplement for viral infections and influenza. It may bother the child along with tracheitis and bronchitis, or develop into one of these diseases in the absence of proper treatment. Laryngitis in children is a fairly common occurrence and experienced parents already have a solid first aid kit, both traditional and folk methods of combating the disease. However, it is the prerogative of the attending physician to engage in therapy. Self-medication can lead to the development of complications due to laryngitis.
Causes
Laryngitis is an inflammatory disease of the vocal cords with an acute or chronic course. The most common factor in the development of the disease is hypothermia. Wet and cold weather weakens the child's body and opens the door to infection. The causes of laryngitis are as follows:
- Colds - adenoviral infection, flu.
- The microclimate in which the child spends the most time is hot, dry air, a smoky room, exposure to exhaust gases that the child breathes.
- An allergic reaction to inhalation of dust, pollen, and chemicals with oxygen.
- Long and loud conversation, shouting, singing.
- Injury to the larynx or vocal cords.
- Reflux disease is accompanied by the reflux of acidic contents from the stomach cavity into the respiratory tract.
- Entry of foreign bodies blocking the entrance to the larynx.
The risk group for childhood laryngitis includes those who have chronic respiratory diseases that lead to difficulty in the passage of air flow.
In some cases, tracheal damage occurs. This becomes one of the predisposing factors for the appearance of acute stenotic laryngotracheitis. Gradually, the process can become chronic.
Causes and mechanism of development of laryngitis
When studying the causes and mechanism of development of laryngitis, it is necessary to take into account the age-related anatomical and physiological features of the development of the larynx in children:
- the larynx in young children is located high, in boys and girls under 3 years old it has the same length;
- intensive growth of the larynx, vocal and vestibular folds, and epiglottis begins at 4 years of age;
- the funnel-shaped shape of the larynx begins to change to cylindrical from the age of 5;
- an abundance of lymphatic slits and vessels in the larynx, a large number of thin-walled blood vessels, mucous glands, extensive accumulation of lymphoid tissue is typical for children of all ages;
- the tendency of the larynx to convulsions and spasms when irritated is explained by the lability of the nervous system in children, mainly of an early age;
- the inflammatory process in the nasopharynx in young children very quickly spreads to the larynx, which is associated with the small distance from the oral cavity to the glottis with a high larynx;
- the lumen of the larynx in children is narrow, and the vocal folds are short, so even a slight inflammation of the mucous membrane can lead to stenosis, significantly aggravating the child’s condition;
- vocal folds in children under one year of age are more susceptible to inflammatory and traumatic damage due to anatomical and physiological immaturity.
The development of pathology is promoted by prolonged screaming or crying
The cause of inflammation of the larynx can be:
- viral, bacterial or fungal infection;
- acute and chronic inflammatory diseases of the upper and lower respiratory tract;
- domestic injuries;
- presence of a foreign body;
- surgical interventions;
- burns: chemical, thermal, electrical, radiation;
- allergy;
- inhalation of cold air;
- overstrain of the vocal apparatus;
- difficult nasal breathing, in which the child begins to breathe through the mouth;
- drinking cold drinks;
- metabolic disease;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- vegetative neuroses.
Under the influence of an exogenous or endogenous irritant, inflammation of the mucous membrane of the larynx occurs: hyperemia, pinpoint infiltration, and serous permeation of the tissues appear. Increased penetration of leukocytes through the interepithelial spaces and increased work of the mucous glands contribute to ruptures, desquamation and partial rejection of the columnar epithelium of the larynx.
Drugs for the treatment of acute laryngitis
If acute laryngitis is diagnosed, treatment in children is complex and is aimed at combating the bacterial environment, increasing immunity, and eliminating factors that cause coughing attacks.
Recommended medications, the action of which is aimed at the complete and high-quality recovery of the baby, are:
- Antihistamines. They help relieve swelling of the mucous membrane and have a calming effect on the baby. Usually the doctor prescribes Clarisens (for infants), Zyrtec (from 6 months), Clarotadine (from 2 years), Cetrin (in syrup from 1 year), Parlazin (from 6 years).
- Antitussives and expectorants. From a large variety of medications available on the pharmaceutical market, the doctor selects the most optimal ones that can help the baby at the current stage of the disease. For paroxysmal cough, the attending physician may prescribe "Gerbion" (from 2 years), "Sinekod", "Libexin", "Erespal". When the cough enters the wet stage, expectorants such as Bronchosan, Ambrobene, Lazolvan, ACC, and Fluimucil help well.
- Antipyretics (Panadol, Paracetomol, Ibuprofen). Prescribed at high (more than 38 oC) temperatures.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. For example, Ibufen.
Acute laryngitis in a child is not recommended to be treated with aerosols and lozenges: against the background of a dry cough, the baby may choke on the tablets, and sprays can cause laryngospasm - an allergic reaction that can worsen the child’s condition.
Treatment
Treatment of acute laryngitis in children involves the integrated use of three basic approaches to therapy:
- Mode.
- Drug intervention.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures.
Depending on the age of the child, treatment may vary.
Up to a year
Therapy for children under one year of age involves maximum limitation of various irritants. The child should cry and scream minimally. Parents monitor his feeding and regular diaper changes to prevent unnecessary irritation.
Cool and moist air in the room is required, which helps reduce swelling. Among the medications used in infants, antihistamines are used to combat swelling. Representatives: Suprastin, Diazolin, Tavegil.
If the temperature rises, additionally use ibuprofen or paracetamol. Other groups of medications should be used with caution in young children and only after consulting a doctor.
After a year
In children over two years old, acute laryngitis can be treated with the additional inclusion of expectorants - Alteyka, Lazolvan and a variety of lozenges to relieve throat discomfort - Strepsils, Doctor Mom and the like.
Effective physiotherapeutic procedures:
The selection of therapy is carried out by a doctor.
Treatment of the viral form of the disease
As for the general recommendations regarding the treatment of the disease, they are all aimed at stabilizing the psycho-emotional state of the baby, as well as moisturizing the respiratory tract.
In other words, if your baby has a hoarse voice, is irritated and constantly coughs and cries, do not panic. After all, a child can feel the anxiety of adults and get scared. The first thing you need to do, of course, is go to an appointment with a pediatrician, he already knows how to treat laryngitis in children 3 years old. If you can’t make it to the clinic on this day, you can try calling a specialist to your home. And at this time you need to calm the baby down and try to convince him that he doesn’t need to cry or talk. After this, the main task of parents is to humidify the room in which their child is located. To do this, you need to hang wet towels on the radiators and the backs of chairs, and place a large container of water near the patient. During this difficult period of illness for the baby, it is strictly forbidden to turn on various heaters in the room, as they dry out the air very much. If adults have previously encountered the disease and know how to treat laryngitis in children at home, there is no need to waste time, it is better to immediately call an ambulance. In the meantime, the specialists are on their way, the baby needs to be inhaled with saline - the medicine will moisten the airways and improve the condition slightly. A few minutes later, specialists will examine the little patient and, if necessary, hospitalize him.
Complications
Hyperplastic laryngitis increases the size of the mucous membranes of the vocal cords and the lining of the larynx, thickens them over the entire area. Nodules or bumps that are firm and white may appear on the larynx. Rubbing or swallowing causes erosion or contact ulcers. With hypertrophic laryngitis, hoarseness in the voice is observed, and the larynx is irritated. Complications include laryngeal stenosis.
Catarrhal laryngitis and its symptoms are common. The first signs are similar to those observed with viral diseases or bacterial infections. The disease is similar to forms of sore throat or flu. This laryngitis descends only to the trachea, and if complicated, inflammation of the lungs or bronchi may occur. The complication can greatly affect the baby’s immunity. With severe inflammation, spasms of the larynx, breathing becomes difficult, narrowing of the larynx and narrowing of the airways can lead to death. At the first suspicion, you need to call an ambulance.
Symptoms
The main thing in making a diagnosis is to recognize the first signs of the disease. Symptoms of laryngitis in children vary and depend on the degree of the disease. The baby may suffer from an acute or chronic illness. The manifestations of ARVI are much milder compared to inflammation of the larynx. It is very important to determine the type of disease at the initial stage and begin its treatment in a timely manner. Next, you will read a list of characteristic symptoms for the acute and chronic stages of the disease in infants and older children.
Acute laryngitis in children
Signs of acute laryngitis can appear either suddenly or gradually. It all starts with a fever and a hoarse voice. Temperatures can rise to 39 degrees. The normal voice becomes hoarse and rough, the inflammatory process descends on the vocal cords, which are located in the larynx. The main symptom is irritation of the respiratory tract. Additional list of symptoms:
- barking cough;
- inhalation lasts longer than exhalation;
- agitation and anxiety;
- attacks of false croup;
- noisy breathing
Chronic
If the acute form is easy to cure by eliminating the source of inflammation, then chronic laryngitis cannot be cured. This form of the disease evolves from acute, but is considered a complication. If this disease is not cured in the initial stages, the child will suffer from laryngitis all his life. Symptoms by which the disease can be identified:
- dry cough;
- dry or sore throat;
- sputum is released in the throat, which freezes in place, forming crusts; if you detach them, a small amount of bloody discharge will occur;
- weakness appears and performance decreases.
Chronic laryngitis and its manifestations
Depending on the form of the chronic process, catarrhal, hypertrophic and atrophic laryngitis are distinguished. The first, in addition to severe hoarseness, is characterized by sputum production when coughing and rapid fatigue.
With the hypertrophic course of the disease, the patient develops severe hoarseness, which can later develop into a complete loss of voice. The cough is absent and appears only during exacerbation. Quite often, against the background of such symptoms, parents assume that their child has a sore throat or a cold. They don’t even know about the true cause of the baby’s illness and don’t think about how to treat laryngitis in children until they turn to a pediatrician for help.
The atrophic form of the disease, in addition to pronounced hoarseness, is characterized by a strong dry cough with a small amount of sputum. When you expectorate, you may notice spots or streaks of blood in the mucus.
If parents ignore the symptoms described above and are not interested in how to treat laryngitis in children, the consequences can be very serious. Due to lack of oxygen, babies may experience hypoxia and even suffocation.
Clinical manifestations of the disease and hospitalization of the patient
In the classic course of the disease, the baby initially develops a slight runny nose and a dry cough. In such situations, even the most attentive parents do not think about how to treat laryngitis in children. The medications they immediately give to their little ones, suspecting a common cold, only “lubricate” the main symptoms. But later, when the child’s voice becomes hoarse and sometimes disappears altogether, breathing becomes impaired and attacks of suffocation appear, it is not advisable to talk about a simple respiratory disease. It is urgent to call an ambulance. Professionals will provide the baby with the right medical care and, most likely, will insist on hospitalization of the patient. And you shouldn’t refuse this, since the hospital knows exactly how to treat laryngitis in children.
Symptoms of the disease may become even more pronounced during hospitalization. This is explained by the fact that the nervous overexcitation of the baby, who is worried and afraid to go to the hospital, is directly related to respiratory function. Therefore, before taking your baby to the hospital, you should calm him down.
Pediatric laryngitis
The anatomical features of the larynx in children, as well as the high incidence rate in childhood, contribute to the frequent development of laryngitis, laryngopharyngitis, laryngotracheitis and other pathologies of the vocal apparatus.
Since any disease in children develops much faster than in adults and there is a high risk of complications, it is necessary to provide children with timely help with laryngitis.