What is bronchoscopy and why is it needed?
Lung bronchoscopy is a pulmonological method for studying the bronchial tree, showing even minimal problems that threaten the patient’s health.
This medical procedure is needed to:
- assess the internal condition of the bronchi and trachea;
- take a sample of a suspicious area of tissue for histological examination;
- remove a foreign body from the trachea.
Indications for use
Indications for the procedure:
- detection of tumors that are benign;
- diagnosis of bronchial cancer;
- identification of stagnant processes in the respiratory organs (sanitation bronchoscopy is required);
- suspicion of infection and inflammation;
- establishing the causes of bloody discharge when coughing;
- a feeling of shortness of breath, incomplete inhalation and exhalation (when heart disease and asthma are excluded);
- excessive production of mucus that has an unpleasant odor;
- pronounced symptoms of chronic cough.
Contraindications
Contraindications for the study:
- narrowing of a pathological nature, in which the endoscope is unable to penetrate the trachea and bronchi;
- the patient has asthma or diseases of the vascular or cardiac system;
- mental problems;
- respiratory failure;
- hypertension (high blood pressure);
- pregnancy.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages and disadvantages of the procedure:
| pros | Minuses |
| The method allows the operation to be performed without incisions, only thanks to several punctures | Possibility to examine only the mucous surface |
| During the examination, it is possible to obtain a cell for subsequent examination (biopsy) | Insertion of the bronchoscope is unpleasant for the patient |
| Allows for simultaneous treatment | Irritation of the mucous membrane after manipulation |
Does it hurt or not?
Bronchoscopy of the lungs does not cause pain, but the insertion of the device is accompanied by:
- numbness of the palate;
- lump in throat;
- difficulty swallowing.
Bronchoscopy can be unpleasant at the initial stage of the procedure, but then the negative sensations disappear.
What does it reveal?
This examination method reveals:
- neoplasms of various etiologies;
- bronchial deformities;
- tuberculosis;
- stenosis of the branches of the windpipe;
- decreased tone of large bronchi.
The Health-Saving Channel briefly describes what bronchoscopy shows and determines.
Contraindications to bronchoscopy
In some cases, bronchoscopy is dangerous for the patient. Absolute contraindications are:
- allergy to painkillers administered to the patient before the study;
- acute cerebrovascular accident;
- myocardial infarction suffered in the last 6 months;
- severe arrhythmias;
- severe heart or pulmonary failure;
- severe essential arterial hypertension;
- stenosis of the trachea and/or larynx of the 2nd–3rd degree;
- exacerbation of bronchial asthma;
- acute stomach;
- some diseases of the neuropsychic sphere - consequences of a traumatic brain injury, epilepsy, schizophrenia, etc.;
- oral diseases;
- pathological process in the cervical spine;
- ankylosis (lack of mobility) of the temporomandibular joint;
- aortic aneurysm.
The last 4 pathologies are contraindications only for rigid bronchoscopy, and fiber-optic bronchoscopy is acceptable in these cases.
In some conditions, bronchoscopy is not contraindicated, but it should be temporarily postponed until the pathological process resolves or clinical and laboratory parameters stabilize. So, relative contraindications are:
- 2nd and 3rd (especially 3rd) trimesters of pregnancy;
- period of menstruation in women;
- diabetes mellitus with high blood sugar levels;
- IHD;
- alcoholism;
- 3rd degree enlargement of the thyroid gland.
Types of research
Types of bronchoscopy differ depending on the type of device used, as well as the purpose of the procedure.
Depending on the device
Depending on the bronchoscope, there are:
Fiberglass bronchoscopy (FBS) is a study using a flexible endoscope and is used when there are no direct indications for using another type of instrument. The thin tubes of the device make it easy to move into the lower parts of the bronchi.
Bronchoscopy of the lungs using a rigid device has another name - rigid. It is used to examine large bronchi and is widely used for resuscitation purposes.
Depending on the purpose of the event
Depending on the purpose of bronchoscopy, there are:
- diagnostic;
- medicinal;
- virtual.
Diagnostic bronchoscopy
The purpose of the procedure is to examine the respiratory organs to identify certain lesions that can confirm the doctor’s preliminary diagnosis.
Diagnostic bronchoscopy is:
- Fluorescent. It involves administering a special acid to the patient, after which the light system of the device can determine the red zone (indicating the presence of a tumor).
- Autofluorescent. Also used to detect various tumors. A special light system causes a green glow of the bronchus (its submucosal layer).
Therapeutic bronchoscopy
The need for therapeutic bronchoscopy may arise when:
- rinsing of the airways to remove blood clots or sputum is required;
- the patient suffers from a severe form of pneumonia, in which it is recommended to administer an antibiotic to a specific bronchus;
- you have to stop bleeding in the lungs;
- it is necessary to get rid of pus if the accumulation is located near the bronchus.
Virtual bronchoscopy
Features of virtual bronchoscopy:
- represents an alternative study - CT scan of the bronchi;
- X-ray sections and a special program allow you to see the smallest details and pathologies;
- This method does not involve external intervention.
Bronchoscopy of the lungs in children: to do or not
For some indications, bronchoscopy is also performed on children. Here are the most common reasons for performing bronchoscopy of the lungs in children:
Entry into the respiratory tract of a foreign body that makes breathing difficult
Most often children swallow:
- Spikelets, blades of grass;
- Small parts of toys;
- Buttons, coins, cogs, beads, screws and so on.
It is very dangerous when parents do not notice that their baby has swallowed something, and only dense metal objects are visible on the x-ray, and the child’s condition often resembles severe pneumonia. It is with the help of bronchoscopy that a foreign body can be detected and removed.
If a foreign body is not removed from the respiratory tract in time, complications such as suffocation, bronchial inflammation, pneumonia, and sepsis may occur.
Preparation for the procedure
Preparation for bronchoscopy includes:
- preliminary analyses;
- consultation with a doctor;
- diet and taking sedatives.
What research needs to be done?
Before the procedure you need to do:
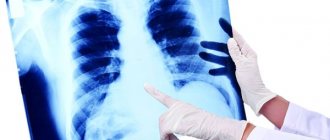
- radiography;
- electrocardiography;
- take blood tests: general and biochemical, coagulation tests;
- determine the level of gases in the blood.
Consultation with a doctor
With the results obtained, you should consult your physician. He will tell you whether additional examinations are required from specialized specialists, and will also answer all questions about the procedure. If no contraindications are found, the specialist will refer the patient to undergo pulmonary bronchoscopy.
Proper diet and sedatives
The following rules will help the patient prevent negative consequences:
- You should eat eight hours before the procedure. It is important not to eat heavy foods or those that cause bloating. You also need to limit yourself in fluid intake.
- So that the patient can fully rest, the specialist will prescribe sedatives and sleeping pills.
What should you do immediately before bronchoscopy?
Immediately before the procedure you need to:
- calm down and set yourself in a positive mood;
- empty your bladder;
- take a towel for examination - after completion of the examination, a short cough with blood discharge is likely to occur;
- refrain from smoking;
- in the morning, before visiting the clinic, cleanse the intestines (using an enema or replacing with glycerin suppositories).
What to do after?
After bronchoscopy, you must remain under the supervision of medical personnel. In the postoperative period, slight hemoptysis may be observed; this is considered normal. Patients with bronchial asthma may have an attack, so it is necessary to have an inhaler with them. Mild pressing pain in the heart may occur if the patient suffers from diseases of the cardiovascular system.
After local anesthesia, speech, swallowing and sensitivity problems persist and may last for 2-3 hours after surgery. Until these residual effects pass, it is not recommended to eat or drink water - this can lead to food particles getting into the respiratory tract. Sedatives used during bronchoscopy slow down the reaction, so for 8 hours you should not drive or do any work associated with a risk to life and health that requires concentration and increased attention. You should also refrain from smoking for 24 hours.
If bronchoscopy was performed under general anesthesia, then after removing the patient from this state, he must remain in the hospital for at least a day to avoid the negative consequences of anesthesia - a sudden drop in blood pressure, an asthmatic attack and other manifestations. If the patient’s condition allows, he is discharged from the hospital the next day. However, orthostatic hypotension, dizziness and weakness may still occur and last for several days. It is advisable at this time to refrain from any activity associated with a risk to life.
If one or more of the following symptoms occur after bronchoscopy, you should immediately call an ambulance:
- hemoptysis after bronchoscopy lasts more than 5 hours, does not weaken or intensifies;
- chest pain is felt;
- wheezing appeared, breathing was difficult;
- nausea, vomiting;
- After the procedure, the temperature increased and chills began.
The symptoms listed above are signs of infection or bleeding in the bronchi. It is necessary to consult a doctor in time so that these complications do not become life-threatening.
How is bronchoscopy done?
If the manipulation takes place without the use of general anesthesia, the procedure involves the following algorithm of actions:
- The patient undresses to the waist and lies down on the couch, or remains in a sitting position on a chair; the rules of behavior during the procedure and how it goes are explained to him.
- An injection with a special drug is injected into the shoulder area, which has a suppressive effect on salivation.
- A sedative is administered.
- Drugs are sprayed into the mouth area to dilate the bronchi.
- Local anesthesia is given to the root of the tongue and the device itself (its outer part) is treated with the same solution.
- The bronchoscope tube is passed through the mouth or nose while the patient takes a deep breath and begins to look at the respiratory organs.
- An endoscopy is performed strictly according to the scheme, first examining the glottis and larynx. When there is a need for a biopsy, material is collected for research.
After completing the bronchoscopy, the patient is given a protocol of the completed examination with photographs.
General or local anesthesia?
Most bronchoscopy cases require only local anesthesia.
The need to use general anesthesia may be due to the peculiarities of the patient’s mental state or his age. This type of anesthesiology is used to examine children and patients in stress and shock.
How long does the procedure take?
Bronchoscopy of the lungs takes no more than half an hour. The duration depends on the purpose of its implementation, but as practice shows, this is a fairly quick study.
What's next?
- After the study is completed, the patient is recommended to remain under the supervision of medical personnel for at least an hour.
- He should not eat or smoke for 2 hours - this can cause bleeding.
- If the patient took sedatives before bronchoscopy, he should not drive a vehicle for 8 hours after taking them. This is due to the fact that the above drugs often cause drowsiness and reduce reaction speed, which means that the risk of an accident increases sharply.
Decoding the results
The results of the study may be as follows:
| Disease | Endoscopic picture |
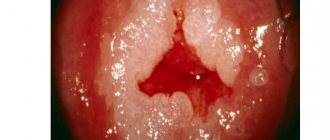
| Polyp on vocal cords | A neoplasm that prevents the ligaments from closing completely. Has different lengths. |
| Tuberculosis | Sputum of cloudy and viscous consistency on the walls of the bronchi. The mucous membrane is thickened and inflamed. |
| Foreign body present | Visualized at the level of the junction of the pharynx and esophagus. These can be pieces of food, small toys (for children). |
| Malignant formation | Narrowing of the lumen, proliferation of the bronchus on the mucous membrane, some blood clots. The tumor has an irregular shape |
| Bronchitis (chronic) | In the lumen there is a small amount of mucus with a thick consistency. |
Contraindications
There are strict contraindications to bronchoscopy. Bronchoscopy is not recommended if:
- There is a focus of active inflammation in the body. For example, if a child has a runny nose, fever, and all the signs of a current acute respiratory infection, it is better to wait for recovery and then do a bronchoscopy. However, these recommendations are not absolute; in some cases, the study must be carried out immediately; the final decision is made by the attending doctor.
- The child is in serious general condition and has decompensated somatic pathology.
- There are disorders of the blood coagulation system. In this case, the risk of developing difficult to stop pulmonary hemorrhage increases.
SOURCES: https://zdravotvet.ru/bronxoskopiya-podgotovka-kak-delayut-pokazaniya-rezultaty-posledstviya-posle-procedury/ https://proskopiyu.ru/bronhoskopiya/bronhoskopiya-detyam.html https://diagnostinfo.ru /skopiya/vidy/bronhoskopiya-detyam.html
What is the price?
The average cost by region looks like this:
| Region | Price | Firm |
| Moscow | from 4500 rub. | "Miracle Doctor" |
| Saratov | from 1420 rub. | "SarNIITO" |
| Saint Petersburg | from 2400 rub. | "Consultative and Diagnostic Center of the Military Medical Academy" |
| Ufa | from 860 rub. | "BSMU" |
| Novosibirsk | from 1050 rub. | "Diagnostic Center of the Research Institute of Tuberculosis" |
Carrying out bronchoscopy
Many patients ask how to prepare for an examination? In order to get the most accurate result and avoid complications, you must follow all the doctor’s recommendations. One of the stages of preliminary actions is the choice of anesthesia. Most often, endoscopy and biopsy are performed under local anesthesia. A solution of Lidocaine is used.
The diagnostic algorithm is simple:
- The patient inhales special drugs that dilate the bronchi.
- The procedure is performed through the nose or mouth.
- Studies are performed on a patient who is in a sitting or lying position.
At the end of the examination, you are allowed to drink some water in small sips or suck on an ice cube.
Photo gallery
The principle of bronchoscopy
Bronchoscope
Closer view
Close-up
Foreign body removal during bronchoscopy
In the photo - conventional bronchoscopy (left) and fluorescent (right)
Are there any complications?
In some cases, complications arise during bronchoscopy. The lion's share of them consists of bleeding (the result of injury to the mucous membrane) or an infectious process (due to non-compliance with the rules of asepsis and antisepsis). Their main clinical manifestations are as follows:
- incessant hemoptysis;
- high body temperature, chills;
- chest pain;
- wheezing heard at a distance;
- nausea, vomiting.
If at least one of these symptoms occurs, you should not waste time; it is important to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Also complications of bronchoscopy are pneumothorax, mediastinal emphysema (if a lung biopsy was performed through the bronchus), cardiac arrhythmias, hypoxia (in people with insufficient heart and lung function), bronchospasm (in patients suffering from bronchial asthma). These conditions do not develop in a delayed manner, but are noticeable immediately and require emergency medical care for the patient.
Condition after the procedure
It usually takes some time to come off the sedative. Sedatives leave a feeling of calm and drowsiness. General anesthesia requires a longer recovery time.
Do not eat or drink for 2 hours after the test due to numbness in the throat and difficulty swallowing. The patient may experience dry mouth, hoarseness, cough and muscle pain.
After the biopsy, you may regurgitate a small amount of blood.
Bronchoscopy is generally a safe and very effective test of the condition of the airways and early diagnosis of malignant tumors.
Types of lung biopsy
Cough and respiratory symptoms of unknown origin can occur against the background of damage to lung tissue of different locations. Depending on the location of the suspected pathological area, different manipulation techniques may be required. Biopsy is a collective concept that refers to the process of taking tissue for further study.
This diagnostic procedure is divided into the following types:
- Biopsy during bronchoscopy. When examining the tracheobronchial tree, the doctor, using an elastic tube with a video camera at the end, takes for examination a section of the lung parenchyma located as close as possible to the bronchi;
- Needle biopsy. A long needle is used to puncture the skin of the front or back wall of the chest to obtain tissue for analysis. The technique is relevant only for superficial pathological processes in the lung, accompanied by cough;
- Transthoracic (open) lung biopsy. The technique involves excision of tissue during surgery. The patient's chest is opened with direct access to the pathological area by the doctor. Performing the corresponding manipulation is possible only if surgery on these organs is necessary. They don’t open the chest just like that;
- Video thoracoscopic biopsy. The essence of the procedure is to insert a thoracoscope into the chest. Under the visual supervision of a doctor, a piece of the pathological area of the lungs is removed for further study.
Fact! The choice of the appropriate technique is made by the doctor depending on the results of the initial tests. Preliminary X-ray diagnosis of the disease remains mandatory for more accurate localization of the pathological process.
How to prepare for the procedure?
Before starting the study, the doctor will notify you of some rules for its conduct:
- It is not advisable to eat or drink for 6-12 hours;
- remove all things that interfere with the free access of the device or may create interference (glasses, contact lenses, cosmetics, jewelry);
- empty your bladder;
- remove most of your clothes, leaving only your underwear;
- To help you relax, you will be given a sedative through an IV or orally. In this case, the patient remains conscious, but in a sleepy state.
In most cases, both before and after bronchoscopy you need to take a chest x-ray.
What is this?
Bronchoscopy (FBS) is an instrumental study that involves visual examination of the mucous layer of the tracheobronchial tree with a special device. This device looks like a flexible probe that is equipped with a microscopic video camera. The bronchoscope is also equipped with various attachments for performing various manipulations - taking samples for biopsy, administering medications locally, expanding the lumens of the bronchi, etc.
During the procedure, the doctor can view the condition of the mucous membrane on the monitor. It is performed under general or local anesthesia.
If the doctor knows which lung is affected, then the healthy organ is examined first, and then the sick one. This is the case if the pathological process is unilateral.
Bronchoscopy is performed on all infected people, since this method relates to differential diagnosis. It does not matter what form and stage of the pathology, because it is necessary to assess the condition of the mucous membranes of the lungs throughout the entire treatment therapy.
Using fluorography, the presence of pathology can be determined, and the degree of its development can be determined by bronchoscopy. Additionally, by visually examining the lungs, the doctor can assess how effective the surgery was. This is also due to the fact that with the help of the device it is possible to remove pus and mucus from the lumen of the bronchi.
Bronchoscopy as a treatment method
Like many types of modern endoscopic examinations, bronchoscopy allows, simultaneously with diagnosis, to take tissue samples for biopsy, take washings, carry out sanitation or completely remove tumors. This approach minimizes the invasiveness of surgery while demonstrating the highest efficiency. Bronchoscopy is also used to wash the bronchi and introduce medications into them.
Using the online form on the clinic’s website, or by calling us, the patient can sign up for an endoscopic examination of the respiratory tract at the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences. You can also find out over the phone the cost of the procedure, whether preparation is needed and other information.
Taking medications
If the patient is taking certain medications, the doctor should be informed in advance. He will tell you whether you can take this or that drug on the day of the test or not. If a person has allergic reactions to medications, then the medical staff should also be informed about this in advance. If the patient develops allergy symptoms during the administration of anesthesia, this can lead to extremely negative consequences.
The algorithm for preparing for bronchoscopy is based on the fact that you must come to the procedure with an empty stomach, that is, on an empty stomach. Despite the fact that during this diagnostic procedure it is not the digestive system that is examined, but the respiratory organs, there should be no food in the stomach. This is necessary in order to reduce the severity of the urge to vomit, and, if it develops, to prevent the person from choking on the vomit.
To prepare the patient for bronchoscopy, the last meal before the examination can be taken seven to eight hours before the examination. If the procedure is scheduled for the morning, then the last meal should be taken in the evening, and if bronchoscopy is scheduled for the afternoon, then it is necessary to calculate whether it is possible to have a snack in the morning or not. Three days before the proposed test, it is not recommended to eat heavy foods, drink alcoholic beverages or smoke, as this can lead to erroneous diagnostic results.
What does preparing a patient for bronchoscopy include? The algorithm for performing the procedure involves several more rules.
Differential diagnosis for tuberculosis
Almost any patient knows how to check for tuberculosis using fluorography. This diagnostic method is accessible to everyone and simple, however, it is not informative enough. The X-ray picture of tuberculosis is often similar to other lung pathologies. Focal changes in the images are characteristic of bronchopneumonia. Shadows of various shapes are noted during X-ray examination after inflammatory diseases, which result in limited tissue fibrosis. Lobar and segmental darkening may be a sign of endobronchial lung cancer. Globular shadows are formed during the development of many benign tumors of the bronchi and lungs. X-ray signs of disseminated lesions may indicate the progressive development of pneumosclerosis or emphysema.
Often the clinical picture of diseases such as sarcoidosis, idiomatic alveolitis, and interstitial pneumonia is similar to tuberculosis. In addition, the cause of similar radiological signs may be exposure to toxic substances and a reaction to certain medications. Each of the listed diseases and conditions requires timely treatment; a diagnostic error can be fatal. This is why differential diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis is so important: it allows timely selection of effective treatment for a dangerous pathology.
Open lung biopsy:
An open lung biopsy is an operation in which a small piece of tissue is removed from the lungs through an incision in the lung area. The sample is then tested for cancer, infections and lung diseases. This method is used when a large portion of lung tissue is needed for diagnosis. This procedure can also help diagnose a number of different diseases, such as: – Rheumatoid pulmonary diseases – Sarcoidosis – Wegener’s granulomatosis. An open lung biopsy is performed in a hospital operating room under general anesthesia, i.e. you sleep and don't feel pain. A tube is placed through the mouth into the airway, which leads to the lungs. After cleaning the skin, the surgeon makes an incision between the ribs in the chest area and removes a small piece of lung tissue. A chest tube may be left in the incision area for 1-2 days to prevent the lungs from collapsing. It is removed when the drainage stops, the sutures are removed after 7 to 14 days. Stitches are placed on the wound. The entire procedure usually takes about an hour, after which the patient is left in the recovery room for approximately 1-2 hours.
Bronchoscopy for lung cancer
A comprehensive examination for suspected lung cancer includes bronchoscopy, during which it is necessary to collect material for histological examination. A biopsy can confirm the diagnosis of the disease and determine the stage of the cancer. Thus, bronchoscopy and lung biopsy for cancer play a big role in making a diagnosis.
Testing for lung cancer may involve inserting catheters into the small bronchi to collect material. This procedure is performed for peripherally located tumors. During the study, the bronchial wall is punctured and a smear is taken from the lymph nodes. This manipulation is called catheterization, and is performed under general anesthesia more often to diagnose peripheral cancer. To conduct a more detailed examination of lung cancer, general anesthesia is required.
Thus, bronchoscopy for lung cancer is performed not only to clarify and confirm the diagnosis, but also to establish the extent and operability of the lesion. There are direct signs of cancer, characterizing the growth of a tumor in the lumen of the bronchus, its penetration with signs of tumor growth into the organ cavity, and indirect signs associated with external growth and damage to the lymph nodes (inelasticity of the walls of the bronchus, their compression).
The tumor is not operated on if there is deformation and flattening of part of the trachea, especially if, when taking a puncture, cellular elements of cancer are determined, the transition of the tumor from the bronchus to the tracheal wall.
Rules for taking a biopsy
To obtain a reliable result of analyzing the tissue being examined in order to identify the causes of cough, shortness of breath and other symptoms, there are rules for taking a biopsy:
- material should be taken from the center of the pathological zone and from the edges at the point where the affected area transitions into normal tissue;
- the thickness of the sample should be no more than 5 mm;
- the resulting sample cannot be divided into parts;
- after excision of the parenchyma, it must immediately be placed in a bottle with a fixative (formalin);
- After packaging the material, the containers are marked for sending to the pathology department.
Compliance with these rules provides the opportunity for laboratory technicians to qualitatively study a sample of pathological tissues and formulate an appropriate conclusion.
How is bronchoscopy performed in adults and children?
If it is necessary to use bronchoscopy for children, then the procedure must be performed under general anesthesia and the probe is different, it is thinner and more flexible. To prevent complications from occurring, a ventilator should be available at all times.
Before bronchoscopy, both adults and children need to inhale Oxprenoline aerosol using an individual dispenser. An analogue may be Salbutamol. These drugs help expand the bronchopulmonary tree. After this, anesthesia is administered. Local anesthesia can reduce the gag and cough reflex and discomfort in the nasopharynx.
The probe is inserted directly when the patient takes a semi-sitting position or lying on his back. The doctor begins the examination with the larynx, trachea and then the bronchi. During bronchoscopy, the doctor can record all the information received on video or take pictures of specific areas. This allows you to then carefully examine them with magnification.
=
Research results and specialist consultation
The results of endoscopy of the lungs and bronchi are presented in graphic and text material, which the patient receives in printed and electronic form. Our clinic’s specialists will immediately interpret the information received, make a diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment. Diagnostic bronchoscopy is an affordable service that anyone can use if they suspect problems in the bronchopulmonary system.