Enlarge In modern gynecology, laparoscopic operations are very common. This is due to the fact that this type of surgical procedure is the safest of all those existing on the female genital organs. Due to this, many doctors prescribe this type of intervention to their patients. This reduces the risk of damage to healthy tissue and significantly reduces the period of postoperative rehabilitation. However, preparation for laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst is also required before it is performed.
What is an ovarian cyst
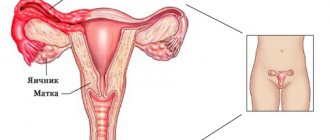
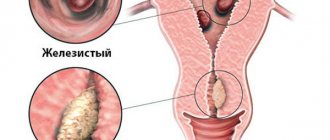
A cyst is a round, hollow formation on the surface of the ovary or in its thickness, resembling a bubble. Its contents and wall structure depend on its origin. Although it is a benign tumor, some types of cysts can degenerate into cancerous cells. This process is called malignancy.
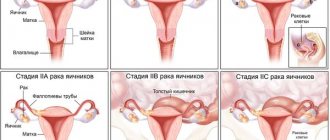
Sometimes a similar formation occurs in ovarian cancer, when, due to central disintegration, an uneven cavity is formed inside the tumor. During examination, women may also be diagnosed with paraovarian cysts. The fallopian tubes take part in their formation, but the ovarian tissue remains unchanged.
Possible types of ovarian cysts:
- follicular, which is formed from a follicle that did not rupture during the ovulatory period; streaks of blood are sometimes found in the fluid inside such a cyst;
- luteal, which occurs at the site of the ovulated follicle (in the corpus luteum), contains serous fluid and sometimes an admixture of blood from destroyed small vessels;
- endometriotic, which develops when endometrial cells multiply outside the uterine mucosa, undergoes cyclic changes in accordance with the menstrual cycle and contains a dark, thick liquid;
- a dermoid cyst (or mature teratoma) may contain germinal tissue or even partially formed formations (teeth, hair), is formed at the site of an egg that has begun to develop independently and is often congenital;
- mucinous - is multi-chambered and contains mucus, can grow up to 40 cm in diameter.
Follicular cysts can be multiple, in which case they speak of polycystic ovaries. In each cycle, the egg does not ovulate; the follicle continues to grow and turns into a cavity under the outer membrane of the ovary. Other types of cysts are usually solitary.
Ovarian cyst
Laparoscopic versus laparotomic approach: which is better? (the view of a gynecologist)
One of the most frequently asked questions from patients is the choice of surgical approach.
Of course, laparoscopic operations have many significant advantages:
- Early activation of the patient;
- The postoperative period is easier;
- Less pain after surgery;
- Postoperative adhesions develop less frequently;
- There is no risk of developing hernias;
- Less anesthesia load (as a rule, laparoscopic operations are performed faster than open ones).
But it is important to know that this method cannot be used in absolutely all patients, as it has a number of serious contraindications.
- Pronounced adhesions in the abdominal cavity;
- The presence of concomitant pathological formations that also need to be removed (for example, large uterine fibroids);
- Widespread endometriosis involving the intestines, peritoneum, and bladder;
- The patient has grade 4 obesity;
- The woman has diseases of the cardiopulmonary system in the stage of decompensation;
- Rupture of an ovarian cyst with large blood loss;
- Biopsy-confirmed malignant ovarian tumor.
Thus, when studying this issue in detail, it becomes obvious that these methods do not “compete” with each other, but simply complement. Where laparoscopic surgery cannot be performed, an open method of cyst removal comes to the rescue.
Simply put, the operating doctor should not be a supporter of one method or another; on the contrary, he should be fluent in all techniques. And the choice of surgical approach should be carried out individually in accordance with the indications, as well as data from additional studies.
When does pathology require treatment?
Follicular and luteal cysts are hormonal-dependent and can gradually resolve. But if they reach large sizes and do not undergo reverse development, they must be removed. When endometrioid formations are detected, conservative therapy is first prescribed. If it is ineffective and there are large formations, a decision is made on surgery. All other types of cysts require only surgical treatment. In case of infertility, the doctor may recommend removing even small tumors, after which hormonal therapy is most often prescribed.
The purpose of the operation is to completely remove the pathological formation. In women of reproductive age, they try to preserve ovarian tissue as much as possible, performing only resection. And in postmenopause, when sex hormones are practically no longer produced, the entire organ can be removed without consequences for the woman’s health.
The operation is performed using the classical method (through an incision on the anterior abdominal wall) or laparoscopic removal of the ovarian cyst is performed. In both cases, the woman goes to the hospital, most often such hospitalization is planned.
Laparotomy
Laparotomy is a surgical intervention in which the surgeon performs all manipulations through an incision in the anterior abdominal wall.
This type of operation requires a fairly large incision, but is often preferred if the cyst is too large. Indications for this type of intervention are as follows:
- the cystic formation is large;
- the cystic formation is affected by a purulent process;
- the cyst affects the deep layers of the ovary, due to which its functional activity is significantly reduced;
- the pelvic organs are susceptible to adhesions;
- additional neoplasms with oncological characteristics were identified in the uterine appendages.
Features of surgery
Laparotomy is a more complex surgical procedure compared to laparoscopy. It is also considered more invasive, since the surgeon performs all manipulations through a fairly large incision.
Despite all the features, laparotomy has a number of significant advantages, which include:
- it becomes possible to examine and assess the condition of internal organs and lymph nodes located near the cystic formation, which helps in the timely detection of cancer metastases or in case of cyst rupture;
- with the help of laparotomy, it is possible to remove large cystic formations filled with liquid secretion, and there is no fear of the cyst rupturing and its contents entering the abdominal cavity;
- Laparotomy helps get rid of ovarian tumors without significant blood loss.
A DOCTOR, CHOOSING LAPAROTOMY AS A SURGICAL INTERVENTION, USUALLY DOES THIS IN COMPLEX CASES WHEN REMOVAL OF THE CYST THROUGH A SMALL INCISION IS PROBLEMATIC.
Preparation for surgery (laparotomy)
Laparotomy does not require particularly serious preparation. All a woman needs is to follow the doctor’s recommendations.
- Before the intervention, women are not recommended to drink water or eat food. A ban on this is usually imposed from 19-20 pm on the preoperative day if the intervention is scheduled for the morning.
- An additional element of preparation is evening and morning enemas. Their task is to cleanse the intestines of feces.
Progress of the intervention
The surgery is performed on the woman under general anesthesia. The course of laparotomy is basically always the same.
- First of all, the skin at the incision site is treated with an antiseptic to prevent bacteria from entering the body. After antiseptic treatment, the first incision is made on the skin.
- The incision can be made in two main ways: in the first case, the surgeon runs the scalpel parallel to the bikini line, and in the second case, the incision is made vertically. In a vertical incision, the midline of the abdomen serves as a reference point.
After making an incision and detecting a cystic formation, the surgeon must examine the surrounding tissue. Such an examination helps to identify metastases or other unfavorable changes in the female pelvic area.
Depending on the location of the cyst or cysts, the ovary is either completely removed, or the detected tumor is removed from it. After removal, the surgical wound is sutured using a cosmetic suture, which leaves virtually no traces if the healing processes proceed without complications.
The removed tissues are sent to a histology laboratory. There, the origin of the neoplasm is confirmed, and signs of malignant tissue degeneration, if any, are detected. Histology is an important element of diagnosis; it allows you not to miss oncology.
Contraindications
Laparotomy is an invasive intervention that has a number of serious contraindications that impose restrictions on its use. For example, intervention is not carried out in the following cases:
- the woman has chronic diseases of the respiratory or cardiovascular system in the acute stage;
- the woman suffers from an active infectious process (in this case, the infection is first treated, and then surgery is performed);
- the patient has hemophilia or other diseases that interfere with blood clotting processes;
- the patient suffers from frequent episodes of high blood pressure;
- The woman was previously diagnosed with diabetes of any type.
It is important to remember that laparotomy is an abdominal operation that requires a set of mandatory tests that help assess the woman’s health status and whether she will tolerate the intervention. The doctor has the right to refuse intervention if he does not have accurate data on the woman’s health condition.
Possible complications
Laparotomy is a serious intervention associated with the risk of complications. Doctors usually give a number of recommendations that help minimize risks, but still no one is immune from them. Possible complications include the following conditions:
- development of active adhesions in the abdominal cavity;
- the appearance of painful sensations in the suture area, which are not so easy to get rid of, even when the wound has already healed;
- infectious lesion of a postoperative suture, which requires careful medical care of the wound to prevent purulent complications and sepsis;
- an unsuccessful operation during which the intestines or other nearby organs were injured.
Unfortunately, there is no 100% insurance against complications. Careful selection of the operating surgeon helps to significantly reduce risks. Compliance with all medical recommendations in the preoperative and postoperative periods also plays an important role.
Recovery period after surgery
Although laparotomy is an abdominal operation, it is rarely associated with a long recovery period unless it is accompanied by complications. So, for example, after the intervention, a woman will have to stay in the clinic for a maximum of 4 days, and only if any difficulties arose during the operation. If the operation went without problems, the woman will be discharged home on the second day.
- It is important to remember that full recovery will not occur earlier than in 4-6 weeks (the specific period depends on individual characteristics). Until this happens, the woman will have to follow a number of rules that will prevent the development of complications.
- If in the first days after the intervention a woman experiences pain in the area of the postoperative wound or abdominal discomfort, doctors will select painkillers for her. Thanks to the use of medications, unpleasant phenomena can be stopped quickly and easily.
After discharge from the hospital, the woman will have to limit her physical activity for a while. This is necessary so that the seam on the abdomen does not come apart and the wound does not open again. She also needs to remember that for at least a month after the intervention, a complete ban on alcohol consumption is imposed.
Laparotomy is generally well tolerated by patients. During the operation, women of childbearing age are trying to preserve tissues that have functional activity as much as possible so that the patient does not lose fertility and can conceive and give birth to a child.
If the intervention is carried out for a postmenopausal woman, then the ovary affected by the cyst is basically completely removed. This is done to prevent relapses and prevent the degeneration of a benign neoplasm into a malignant one.
You might be interested in:
menstruation with an ovarian cyst can a cyst resolve on its own contraindications for an ovarian cyst
What is an ovarian cyst and does it need to be removed?
https://youtu.be/XkNm8thZYvU
Benefits of laparoscopy
Removal of an ovarian cyst by laparoscopy is a gentle intervention. All manipulations are performed through 3 punctures of the abdominal wall. In this case, the abdominal muscles are not dissected, the thin inner serous lining of the abdominal cavity (peritoneum) is minimally injured, and there is no need to manually move the internal organs away from the surgical site.
All this determines the main advantages of the laparoscopic method over classical surgery:
- lower risk of developing adhesive disease in the future;
- low probability of a postoperative hernia, which may occur due to incompetence of the dissected muscles of the anterior abdominal wall;
- small volume of surgical wounds, their rapid healing;
- gentle effect on neighboring organs during surgery, which reduces the risk of postoperative intestinal hypotension;
- fewer restrictions in the postoperative period, earlier discharge from the hospital;
- no deforming postoperative scars; puncture marks can be hidden with underwear.
The laparoscopic treatment method allows a woman to quickly return to normal life, without being embarrassed by her appearance and without worrying about the possible development of long-term consequences after surgery.
Postoperative manifestations requiring referral to a specialist
And in conclusion, it should be clarified which symptoms and health problems after treatment and discharge from the hospital require a woman to immediately contact her doctor:
- Intense pain in the lower abdomen. Pain in the ovary after laparoscopy is only acceptable for 12-18 hours.
Sharp abdominal pain after a recent laparoscopic procedure is a reason to seek medical help
- Pain, severe redness of the skin or suppuration at the puncture sites.
- White, yellow, or green vaginal discharge.
- The occurrence of persistent nausea. Vomiting that lasts for several hours.
- A rise in body temperature above 38 degrees, which does not subside and lasts more than 24 hours.
- Confusion, presyncope, persistent severe weakness.
Seeking help quickly reduces the likelihood of complications, and therefore increases the chances of a successful pregnancy in the future. In general, you should be observed by a gynecologist for 12 months after surgery.
Preparation
Before laparoscopic surgery to remove an ovarian cyst, a woman must undergo an examination, which is usually performed on an outpatient basis. It includes a general and biochemical blood test, urine test, blood collection for screening for hepatitis, syphilis and HIV, ultrasound of the pelvic organs, fluorography of the lungs, determination of blood group and Rh factor, and a vaginal smear for purity. In some cases, it may also be necessary to do an ECG, examine the state of the blood coagulation system, determine the hormonal status, and obtain a physician’s opinion on the absence of contraindications to surgery. The scope of research is determined by the doctor based on the overall clinical picture.
Before performing planned laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, reliable methods of contraception are used. If you suspect pregnancy, you must inform your doctor in advance.
A few days before surgery, you need to exclude cabbage, legumes, carbonated drinks, brown bread and other foods that increase gas formation in the digestive tract from your diet. If you are predisposed to flatulence, the doctor may recommend taking sorbents and carminatives; cleansing the lower intestines is often prescribed. On the eve of the intervention, the last meal should be no later than 18:00, you can drink until 10:00 pm. On the day of the operation, it is forbidden to drink or eat; if you are very thirsty, you can rinse your mouth and moisten your lips with water.
Immediately before laparoscopy, pubic and perineal hair is shaved and a hygienic shower is taken. After this, you should not apply lotions, creams or other care products to the skin of the abdomen.
Test results or what may be grounds for canceling the operation
Since there are numerous contraindications for the operation, the doctor during preparation pays attention to the following signs of changes in the body:
- An increase in leukocytes in the blood and urine, the presence of cylindrical bodies and protein in the urine, which occur in the presence of an inflammatory process in the body. In this case, the operation is postponed to a later date, and the necessary treatment is carried out.
- A decrease in hemoglobin and red blood cells indicates anemia, which can cause complications after surgery. If such violations are present, the operation is postponed and therapy is carried out.
- The presence of infections in smears and a positive Wasserman reaction are direct contraindications to laparoscopy. Surgery is possible after a full course of treatment and rehabilitation.
- A decrease or increase in blood clotting is a relative contraindication. If the pathology cannot be treated, the possibility of intervention with the introduction of anticoagulants or drugs that prevent bleeding is considered.
- If pathological cells are detected in the test results before laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes (smear for cyto-oncology), it is necessary to undergo a more detailed examination on CT or MRI, as well as other tests (biopsy, repeat cyto-oncology, tumor markers).
If the deviations are minor, as, for example, happens during pregnancy, hormonal imbalance or diseases that are not direct contraindications to laparoscopy, the operation will not be canceled. However, the doctor will take into account existing concomitant diseases and take measures to prevent possible negative consequences.
How is laparoscopy performed?
Laparoscopy for removal of an ovarian cyst is performed under general anesthesia (anesthesia). On the day of the operation, the woman is consulted by a resuscitator to identify possible contraindications and make a final decision on the type of anesthesia. Most often, tracheal intubation is used, which allows you to control breathing and maintain the required depth of immersion in anesthesia. Before this, premedication is carried out, when a sedative with a hypnotic effect is administered intravenously; tranquilizers are usually used for this. Instead of such an injection, you can use mask anesthesia.
The operating table is tilted with the head end down by 30º so that the intestine moves towards the diaphragm and opens access to the ovaries. After processing the surgical field, a puncture is made in the navel, through which the abdominal cavity is filled with carbon dioxide. This allows you to increase the distance between organs and creates space for the necessary manipulations. A laparoscope, a special instrument with a camera and a light source, is inserted into the same hole. It is advanced to the pelvis, where the ovaries are located. Under the control of a video camera, 2 more punctures are made in the lateral sections of the abdomen, closer to the groin, which are necessary for introducing manipulators with instruments.
After a thorough examination of the ovaries and cysts, a decision is made to continue laparoscopy or whether wide access to the abdominal cavity is necessary (which is quite rare). In the latter case, all instruments are removed and the classic operation begins.
During laparoscopy, the doctor can perform enucleation of the cyst, wedge-shaped resection (excision) of a fragment of the ovary with a cyst, or removal of the entire ovary. The extent of surgical intervention is determined by the type of cyst and the condition of the tissues surrounding it. At the end of the operation, a check is made for the absence of bleeding, the instruments are removed, and carbon dioxide is sucked out. External sutures and sterile dressings are applied to the puncture sites.
After removing the endotracheal tube, the anesthesiologist checks the patient’s breathing and her condition, and gives permission to transfer to the ward. In most cases, the patient does not need to be admitted to the intensive care unit, since vital organs are not disrupted and massive blood loss does not occur.
https://youtu.be/_xLucPXFZpI
Laparoscopic cyst removal
Today, the vast majority of such operations are performed using laparoscopic techniques.
The operation is carried out as follows:
The woman is placed on the operating table in a supine position.
- Anesthesia is then performed. For such operations, general anesthesia is usually performed, but spinal types of anesthesia are also not contraindicated.
- The surgical field - the abdominal area - is treated three times with antiseptic solutions (96% alcohol, iodine).
- A scalpel is used to make a micro-incision in the skin in the navel area (most often from above).
- Then, using a special clamp, the skin above the navel is fixed and raised. This allows you to safely insert the conductor into the abdominal cavity without touching the internal organs.
- Through the first puncture, carbon dioxide is injected into the abdominal cavity.
- When the carbon dioxide pressure reaches the required values, a laparoscope is inserted. This instrument is a complex optical system equipped with lighting and a high-resolution camera. The resulting image is displayed on a large monitor located opposite the operating surgeons. This allows doctors to fully operate on the abdominal organs.
- Two additional abdominal punctures are made in the right and left iliac regions. The necessary surgical instruments (manipulators, clamps, aspirators, etc.) are passed through them, with the help of which the operation to remove the ovarian cyst is performed.
- Using a clamp, the assistant fixes the cystic ovary.
- The surgeon uses a bipolar electrode to cut off the cyst. During this stage of the operation, it is very important to ensure that the cyst is completely removed (along with the capsule).
- Then a thorough stop of bleeding from the ovary is carried out. It is important to remember that ovarian tissue is very well supplied with blood from two arterial sources (from the ovarian artery and from the branches of the uterine artery). It is for this reason that it is very important that hemostasis is performed carefully and thoroughly;
- In some cases, it is not possible to remove only the cyst (if the entire ovarian tissue is affected). In such a situation, an oophorectomy is performed - removal of the ovary. And in case of severe adhesions or damage to the fallopian tube by a pathological process, sometimes it is necessary to remove the appendages (ovary and tube).
- The removed tissue is fixed with a clamp and folded into a special reservoir, which is carefully removed through an opening in the abdominal wall. If the cyst is large, the cut tissue can be removed in small parts.
- After removing the cyst and stopping the bleeding, it is imperative to rinse the abdominal cavity with sterile saline and examine the organs. Only after you are completely sure that the bleeding has stopped can you complete the operation.
- All instruments are removed from the abdominal cavity, carbon dioxide is removed through a guidewire, and the skin incisions are closed with separate sutures.
Video: laparoscopic removal of an ovarian cyst
https://youtu.be/U6D5MnfpYgg
Postoperative period
After laparoscopy, getting out of bed early is recommended. After just a few hours, with stable blood pressure, it is advisable for the woman to sit down, stand up, and carefully move around the ward. A gentle diet is prescribed, including fermented milk products, stewed vegetables and meat, soups, fish, without products with gas-forming properties.
Sutures are treated daily and body temperature is monitored. Discharge is made 3-5 days after surgery, but sometimes already in the evening of the first day. Sutures are removed on an outpatient basis for 7-10 days. Full restoration of working capacity usually occurs by the 14th day, but if the woman is in good condition, the certificate of incapacity for work can be closed earlier.
Sutures after laparoscopy
Removal laparoscopically
Laparoscopy, the purpose of which is diagnosis and simultaneous treatment, is performed under general anesthesia. Laparoscopy requires special equipment and skill from the surgeon.
First, the abdominal cavity is filled with gas, usually carbon dioxide. To carry out the entire operation, four incisions of no more than two centimeters are made. Through one, a gas supply is introduced - the gas filling the abdominal cavity will lift the wall and make the organs more accessible for examination and removal of the ovarian cyst.
Through the second puncture, a video camera is inserted to examine the condition of the organs - the image from the camera is fed to a monitor near the operating chair.
For surgical actions, instruments are inserted into the remaining two punctures. The instrument is not inserted directly but requires a metal tube to prevent the instruments from touching the skin.
After the surgeon detects the cyst, its surface is punctured and emptied. Once the contents of the cyst are released, it can be easily removed.
Possibility of pregnancy
Until the end of the current menstrual cycle, it is advisable to exclude intimate contacts; if this recommendation is not followed, contraception must be used. Pregnancy after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst can occur in the next cycle. Therefore, you should definitely check with your doctor when you can stop using contraception. With functional cysts (luteal and follicular) and polycystic ovary syndrome, conception is most often allowed after the first menstruation, if the operation and recovery period were without complications. But after removal of endometrioid cysts, a stage of drug treatment often follows.
How to understand that surgery is needed?
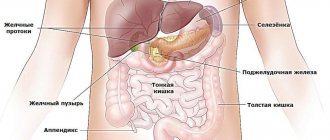
When identifying pathology of the left or right ovary, it is necessary to determine the type of formation and find out whether there are indications for surgical intervention. To do this, a woman must undergo a full examination, which includes:
- Blood test for tumor markers CA-125, CA 19-9, HE4. An increase in the level of these indicators speaks in favor of a malignant tumor and requires careful differential diagnosis. In modern gynecology, to clarify the type of formation, the definition of the ROMA index is used;
- Ultrasonography. On ultrasound, benign cysts are usually hypoechoic, single-chamber, without inclusions (except for the dermoid). With cancer, a large number of chambers appear, as well as pathological inclusions;
- Doppler. Detection of atypical blood flow indicates a probable malignancy;
- Magnetic resonance imaging. MRI allows you to see structures invisible on ultrasound and clarify the type of formation.
If these methods do not make a diagnosis, diagnostic laparoscopy is performed. During the operation, the doctor may detect additional symptoms indicating ovarian cancer (peritoneal carcinomatosis, changes in lymph nodes). Endoscopic intervention also helps to distinguish an ovarian cyst from salpingo-oophoritis, ectopic pregnancy and other pathologies.
This is what an ovarian cyst looks like during diagnostic laparoscopy.
It is also useful to read: Effective diet for polycystic ovary syndrome
Possible complications
The most common complication after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst is pain. Moreover, unpleasant sensations are noted not in the area of the operation or punctures, but in the area of the right side and right shoulder. This is due to the accumulation of carbon dioxide residues near the liver, which irritates the phrenic nerve. Muscle pain and mild swelling of the lower extremities may also be noted.
In the first days after laparoscopy, subcutaneous emphysema may be observed, that is, an accumulation of gas in the upper layers of fatty tissue. This is a consequence of a violation of the surgical technique and does not pose any health hazard. Emphysema resolves on its own.
In the long-term postoperative period, adhesive disease occasionally develops, although the risk of its occurrence after laparoscopy is much lower than after classical surgery.
Contraindications for surgery
There are no absolute contraindications for surgery. If the cyst needs to be removed, the doctor will perform all the necessary manipulations. The operation can only be postponed in certain situations:
- Acute infection: influenza, intestinal infection, respiratory tract diseases, etc.;
- Exacerbation of chronic pathology;
- Neuropsychic disorders;
- Skin diseases in the incision area.
Surgical treatment is carried out after recovery or stabilization of the woman’s condition.
When laparoscopy is not performed
Despite the woman’s wishes, the doctor may refuse to perform laparoscopic surgery in the following cases:
- severe obesity (grade 3-4);
- detection of stroke or myocardial infarction, decompensation of existing chronic diseases;
- severe disturbances of hemostasis due to blood coagulation pathology;
- abdominal surgery less than 6 months ago;
- suspicion of a malignant tumor (cyst) of the ovary;
- diffuse peritonitis or severe hematoperitoneum (accumulation of blood and abdominal cavity);
- the woman’s state of shock, increasing severe blood loss;
- pronounced changes in the anterior abdominal wall with fistulas or purulent skin lesions.
Removal of an ovarian cyst laparoscopically is a modern and gentle method of surgical intervention. But the operation should take place after a preliminary thorough examination of the woman in the absence of contraindications to it. It must be remembered that some cysts can form again if predisposing factors are not eliminated. Therefore, in case of functional cysts, a dynamic study of hormonal status and correction of identified disorders are required.
How is abdominal surgery to remove an ovarian cyst performed?
Open abdominal surgery is performed by layer-by-layer dissection of the anterior abdominal wall. After this, the cystic formation is removed, and adhesions are dissected if necessary. If the cyst is endometrioid, then the vesicouterine fold, omentum, intestines and peritoneum are visible for the presence of foci. After the operation, the layers of the abdominal wall are sutured in the reverse order.
Rehabilitation after laparotomy
The patient stays in the hospital for 4-5 days, and fully returns to active life after 1-1.5 months. For women who are planning a pregnancy, doctors try to preserve the uterus and ovaries so that they can become pregnant later. During menopause, the patient has two ovaries removed so that there are no unnecessary consequences, and the woman can safely continue to be sexually active. Possible complications after laparotomy:
- infectious processes;
- damage to internal organs;
- pain syndrome;
- formation of adhesions.
How long does the operation take?
Laparoscopy is performed, depending on the experience of the surgeon and the type of intervention, from 20 minutes to 1.5 hours. With laparotomy, the duration of the operation can be up to 2 hours. If there is a suspicion of a malignant cystic formation, then removal of the fallopian tube is included, so the doctor may need more time. The surgeon selects the surgical tactics individually each time.
Features of menstrual cycle restoration after laparoscopy
Despite the fact that laparoscopy is a minimally invasive method in which, instead of an open operation, only three small punctures of the abdominal wall are performed, each body perceives it differently. And also surgical intervention on various organs of the female genital area can manifest itself in various variations.
One of the most important signs of normalization of the reproductive function of the female body is timely and normal periods. Based on the type and nature of menstruation after laparoscopy, it is easy for specialists to draw conclusions about the woman’s health condition and the need for further treatment.
.
Cyclicity must be stable
Features of laparoscopy
It is important for many girls and women to know on what day of the cycle a laparoscopy is performed, how it goes, how long the operation to remove an ovarian cyst lasts, and whether anesthesia is used during it.
Doctors believe that the most optimal time for performing laparoscopy surgery for an ovarian cyst is the first phase of the menstrual cycle, preferably 6–7 days after the end of bleeding.
If the surgeon does not encounter complications or oncology, then the average duration of surgery is from 40 to 90 minutes. The duration is related to the size of the cyst to be removed, the volume of ovarian tissue excised, and existing diseases.
Laparoscopy of ovarian cysts is performed using 2 micro-incisions made to insert very small medical instruments into them. The third incision is for a laparoscope equipped with a tiny camera and LED. At the initial stage of surgery, a small volume of carbon dioxide is injected into the abdominal cavity to lift the peritoneal wall above the internal organs in the pelvis. In an enlarged operating space, it is easier for the doctor to monitor the removal process and easier to manipulate the instruments.
The volume of excised tissue depends on the degree of development of the cyst, its germination into the ovarian capsule, the number of endometrioid foci, detected oncology and other features.
During diagnostic laparoscopy, a specialist will examine the internal organs. If nodular structures are detected, the doctor will be able to remove them immediately. After the excision procedure, the surgeon will stop the bleeding, remove inserted instruments and carbon dioxide, and apply stitches and dressings.
In young patients, if no cancerous changes are detected in the cells, they try to affect the gonads to a minimal extent, preserving their functions for further pregnancy. For women over 47 - 50 years old, it is often recommended to remove the ovary with excision of the cyst in order to maximally protect the patient from malignancy (cancerous transformation of cells) of the gonad, the risk of which increases during this period. This also helps prevent the recurrence of new cystic structures and tumors from developing.
The scope of surgical intervention is often determined by the doctor at the time of the procedure:
- Cystectomy (husking out the cystic lump). This operation is performed in the absence of signs of cancerous cell degeneration and with intact ovarian tissue. Doctors recommend cystectomy for women of reproductive age and teenage girls.
- Partial resection of the ovary (removal of part of the organ along with neoplasm). Wedge resection is performed when the ovary partially preserves its functions. Such an operation in Moscow costs from 18 to 25 thousand rubles.
- Ovariectomy (removal of the ovary along with the cyst). This procedure is indicated for necrosis and replacement of healthy organ structures with connective tissue. Ovariectomy is often performed during menopause. The cost varies from 15 to 20 thousand rubles.
- Adnexectomy (removal of the cystic capsule, ovary, fallopian tube). Such removal is carried out when cancer is detected, the pathology is complicated, or it has spread to nearby organs.
Removing one of the ovaries does not interfere with conception, since the second one remains. Thanks to this, a woman gets the opportunity to maintain reproductive health and bear a healthy baby.
Laparoscopy of a cyst of the left and right ovary is carried out according to the same scheme.
The following complications may occur after laparoscopy:
- heavy bleeding;
- infectious lesion and further inflammation, suppuration;
- seam divergence;
- injury to the pelvic organs.
Restrictions and contraindications
Contraindications to surgery are rare. These include viral diseases, heart disease, blood clotting disorders and others similar to the standard ones.
There are restrictions that will have to be adhered to until full recovery, that is, the next month.
A sample list of what not to do:
- Due to the fact that the body takes a long time to completely heal damage, you should not engage in sports, for example, doing abs.
- Sexual life also falls under the definition of “sport,” since when having sex, the abs tense, which can cause seams to separate and cause severe pain.
- This also explains why weight should not be applied - there is a high risk of sutures coming apart and opening internal wounds. The maximum permissible weight is 4 kilograms, so entry into the gym and bathhouse is prohibited, as are gymnastics.
- It is worth limiting yourself in exposure to high temperatures. This means that you should not take a bath, although you can wash in the shower.
- The bathhouse is also prohibited. After surgery, a high temperature may persist, at which additional heating of the body is very harmful. What is dangerous about high temperature is that it can have a bad effect on the healing of organs. You should refrain from relaxing at sea and swimming.
One of the most common questions that arise in connection with this operation is whether it is possible to get pregnant after such operations? Yes, this is possible, although if we are talking about removing one of the ovaries, it will be more difficult. If the operation involved simple removal of a cyst, then the chances of this are reduced very slightly.
If we talk about timing, then you should wait 2-3 months before trying to get pregnant. This is necessary for the hormonal levels to return to normal, and for the doctors to make sure that the recovery is completed successfully.
Menstrual cycle after surgery and pregnancy planning
Restoration of the menstrual cycle and normalization of hormonal levels occurs within 1-2 months after removal of the ovarian cyst. In the normal course of the postoperative period, ovulation occurs already in the first cycle and is observed 2-3 weeks after surgery.
. After another 2 weeks, the first menstruation arrives.
According to reviews of women who have undergone surgery, the first periods can be heavy, prolonged and painful. This picture persists for up to 2-3 months, after which the cycle returns to normal.
. Menstruation lasts up to 6-7 days and may be accompanied by a deterioration in overall health. If your period turns into bleeding, you should consult a doctor and rule out the development of complications.
Delayed menstruation is a common occurrence after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst. The reproductive system does not recover immediately, and sometimes it takes time for ovulation to start. The delay usually does not exceed two weeks
.
Less often, periods do not come within 60 days after surgery
. This situation requires consultation with a gynecologist.
On a note
If your periods 3 months after laparoscopy are irregular and/or accompanied by severe pain, you need to be examined by a doctor. The development of complications is possible.
You can plan a pregnancy after endoscopic removal of an ovarian cyst after 3-6 months.
After surgery, pregnancy should be planned no earlier than 3 months later.
Before conceiving a child, you should visit a doctor and undergo diagnostics:
- Gynecological examination;
- General clinical blood and urine tests;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
This approach will eliminate the development of postoperative complications and increase the chances of a favorable pregnancy outcome.
Particular attention should be paid to the results of histological examination of the removed cyst. Knowing what kind of formation was in the ovary, you can decide on the woman’s further management and prevent relapse of the disease.
According to reviews, most women manage to get pregnant within 6-12 months after removal of an ovarian cyst using laparoscopic access. If it is not possible to conceive a child naturally, IVF is possible.
Indications for surgery
Surgeons gain access to the location of the cyst using the following techniques:
- Laparotomy or classic (cavitary, open) surgery to remove an ovarian cyst. This surgery is performed through a wide incision in the abdominal wall. This is the most traumatic removal method, after which a long recovery period is required. Large and giant cystic neoplasms are removed in this way.
- Laparoscopy. With this minimally invasive removal surgery, access to the lesion is made through small holes. Surgeons insert the necessary instruments and a microcamera through the punctures, which transmits the image to the monitor.
- Transvaginal access (through the vagina), which is carried out using a hysteroscope.
What are the criteria for choosing the type of surgical treatment for ovarian cysts - laparotomy or laparoscopy?
Laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst has basically the same indications as abdominal surgery; it differs only in the method of access to the affected ovaries. Although there are certain restrictions.
Indications for elective laparoscopic surgery are:
- ineffectiveness of therapeutic methods in the treatment of retention cysts (follicular, luteal);
- dermoid, paraovarian cyst, endometrioid and mucinous formation (since these neoplasms are not treated with medications and do not resolve on their own);
- large size of the cystic structure and its rapid progression (growth);
- signs indicating a high probability of suppuration, necrosis, rupture of the capsule, twisting of the leg;
- purulent-inflammatory process, ovarian deformation;
- infertility due to disease;
- displacement of the uterus, compression of the fallopian tubes, ureters, intestines, bladder;
- risk of malignant cell degeneration (malignancy).
What determines the normalization of the menstrual cycle during surgery?
In most cases, your period will return to normal after the first two to three months, and this may depend on several important factors. These include:
- hormonal status;
- general health status of the patient;
- age and physiological characteristics;
- professionalism of the surgeon performing the procedures.
If necessary, a number of drugs are selected to solve the problem
Practice shows that many operated patients have their periods on time and there are no cycle disturbances. Only in certain cases do menstruation not return to normal or come, but much later. This is often due to a weakened immune system or due to stress.
If for some reason the menstrual cycle does not improve after laparoscopy or hysteroscopy and the procedures do not bring the expected result, do not despair. First, you should visit your doctor, listen to his recommendations and follow the instructions exactly.
Most likely, a specialist will prescribe conservative treatment based on taking hormonal medications to stabilize the functions of the endocrine system, which will help smooth out the menstrual cycle and restore the reproductive capacity of the female body.
https://youtu.be/6NN7v5ykQAI
Laparoscopic surgery is considered the gold standard in the treatment of ovarian cysts. Manipulations are carried out through neat incisions in the abdominal wall and do not involve major tissue damage
. In modern gynecology, such tactics are successfully used for functional and organic formations, polycystic disease and many other diseases of the uterine appendages.
Recovery after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst lasts 2-4 weeks. Rehabilitation begins in the hospital in the first hours after surgery and continues at home. It is important to follow all the doctor’s recommendations in order to prevent the development of complications and prevent relapse of the pathology.
Let's look at the important nuances of the postoperative period and figure out what to expect after removal of an ovarian cyst.
Consequences and complications
Consequences and common symptoms after surgery include:
- Itching,
- Hematoma,
- Temperature increase,
- Colds,
- Cystitis,
- Thrush and other viral diseases,
- Bloating, diarrhea, or missing stools
- Scanty periods or their delay,
- Gas, slight pain in the lower abdomen,
- Swelling of the pubis,
- Swollen breasts
- Sore throat.
Symptoms for which you should consult a doctor:
- Bloody issues,
- Brown discharge,
- White discharge.
Medication support during the rehabilitation period
After removal of an ovarian cyst, the following are prescribed:
- Antibacterial drugs. Broad-spectrum antibiotics are selected that affect the maximum possible number of infectious agents. Taking antibacterial agents reduces the risk of developing inflammatory processes after surgery;
- Probiotics. Prescribed as a second step after taking antibiotics. Help restore the microflora of the intestines and vagina and avoid the development of dysbacteriosis;
- Painkillers. Used in the early postoperative period, then according to indications;
- Antispasmodics. Serve to relieve pain, including during the first menstruation after surgery;
- Enzyme preparations. They prevent the formation of adhesions and are prescribed to all women in the postoperative period for a course of 10-20 days;
- Vitamins. Serve to strengthen the immune system and keep the body in good shape.
Treatment after surgery often involves taking hormonal medications in tablets. Priority is given to combined oral contraceptives (COCs) - Janine, Marvelon, Regulon, Klaira, Yarina, etc. The purpose of such therapy is not only to normalize hormonal levels and avoid the recurrence of the cyst
.
COCs do not allow a woman to become pregnant before the time allowed by the doctor and enable the body to prepare for conceiving a child. In late reproductive age and premenopause, gestagens can be prescribed instead of COCs.
The rehabilitation period involves the use of combined oral contraceptives to restore hormonal imbalance.
In addition to medications, physical procedures are indicated after surgery: electrophoresis, ultrasound, magnetic therapy. Physiotherapy prevents the development of adhesions, normalizes hormonal levels and promotes tissue regeneration.
Surgery during menstruation
Many who have encountered problems associated with the ovaries, uterus or diseases of the female sphere at an early stage are wondering whether it is possible to perform laparoscopy during menstruation . It’s worth saying right away that surgical intervention in the body is not performed during menstruation.
.
During the period of heavy discharge, processes occur in the uterus that do not allow intervention in the body. During this period, even blood clotting indicators change
. Therefore, it is unlikely that a doctor who does not have a full range of information about the patient will undertake surgery on him.
Restoring menstruation is a purely individual process and it is safe to say that after a month or two, everything will be restored. The main thing is to follow the recommendations of doctors and take care of your health.
https://youtu.be/uOYoA1juuJU
Video
https://youtu.be/abdoKDT1yJI
Rehabilitation after laparoscopy is many times faster and easier than after strip surgery. The modern minimally invasive method of endoscopic surgery can significantly reduce the time required for regeneration of tissues and organs. Thus, discomfort after laparoscopy is minimized. However, recovery after laparoscopy is still necessary. Its duration depends on the type and complexity of the operation, and the individual characteristics of the patient. Some people feel good after a few hours, while for others the process lasts for a couple of weeks.
When can you plan a pregnancy after laparoscopy?
It is advisable to implement your plans to become pregnant six months after laparoscopic surgery, when the body has recovered. It is necessary to take some measures to guarantee pregnancy:
- drink folic acid for three months;
- both partners should stop smoking and drinking alcohol;
- avoid stress;
- eat healthy food with vitamins;
- move a lot;
- see a gynecologist;
- get tested;
- exclude sexually transmitted infections;
- be examined by ultrasound;
- undergo genetic counseling;
- plan conception on the days of ovulation.