Author: A. Olesya Valerievna, candidate of medical sciences, practicing physician, teacher at a medical university
Each of us has experienced the feeling of a pounding heart at least once in our lives. This symptom can be quite frightening and make you immediately rush to the doctor, but most often it goes away quickly and on its own, and those who experience it try to independently find the cause of the stabbing sensation in the heart.
Not only older people with a number of diseases of both the heart and other organs can complain of tingling in the heart. Often the symptom worries young people, both female and male, teenagers and even children. It can be difficult to understand its origin only on the basis of a description of sensations, since not every patient is able to describe in detail and as accurately as possible exactly how it hurts or stings.
At the same time, a detailed questioning can lead the doctor to the cause of the complaints, and a simple examination can confirm it. In some cases, additional examinations are required to establish an accurate diagnosis, but if they are prescribed by a specialist, then there is still no need to panic. An in-depth examination does not always mean the presence of severe pathology.
In some cases, tingling in the heart area is not at all associated with the activity of its muscles, the level of blood supply, the presence or absence of inflammation and other pathological changes. The symptom can be functional in nature, have a psychogenic mechanism, or occur with pathology of other organs.
Elderly patients, when they experience stabbing sensations or pain in the heart, grab validol or nitroglycerin; young people, who have never encountered such symptoms, are lost and do not know where to run or what to do.
In all cases of unexplained pain or tingling in the heart area, first of all, you should visit a doctor. You can start with a therapist who will refer you for an ECG and, if necessary, a cardiologist. It is clear that a short-term tingling that lasts a few seconds and goes away on its own is not a reason to panic, but if the discomfort recurs, the tingling lasts for several minutes or more, and the usual medications in the form of validol, corvalol or nitroglycerin do not bring any effect, you should consult a doctor .
Cardiac reasons
Relatively few in number. According to medical statistics, only 12% of clinically recorded situations are determined by problems with the heart and blood vessels themselves.
Usually these are relatively dangerous pathologies that threaten life and health.
Cardiac ischemia
It develops independently, but more often becomes the result of some third-party condition, cardiac or other.
The essence of the process is insufficient blood circulation in the myocardium. This results in a decrease in the efficiency of blood ejection and hemodynamic deviations.
Stitching pain in the heart is the result of gradual degeneration and death of cardiomyocyte cells. But this symptom is not always observed, in approximately 15% of clinical cases. Other situations pass without discomfort.
Myocardial infarction
If the heart hurts, intensely, pain radiates to the left arm, shoulder blade, stomach and epigastric region, pressure, shortness of breath occurs, this is a direct indication of acute necrosis of muscle tissue.
The process is accompanied by severe changes in the functioning of the heart, hence a possible fatal outcome in the short term.
It all ends with cardiosclerosis, that is, the replacement of functional tissues with connective tissues that are not capable of maintaining activity and contractility. Over the course of 1-6 months, a relapse is likely, potentially more lethal than the first case.
Cardiomyopathies
A group of heterogeneous pathologies accompanied by anatomical changes in the myocardium.
The process is rarely accompanied by pain; if it is present, it is only in the later stages, as part of third-party syndromes and processes. Rarely does cardiomyopathy occur in isolation; more often it is combined with other diagnoses of the same kind.
Angina pectoris
Strictly speaking, this is not really a disease. More like a symptom complex. As part of the phenomenon, the discomfort is sharp and extremely intense, occurs suddenly, and is characterized by additional symptoms.
Congenital and acquired heart defects
What kind needs to be clarified through objective research. At a minimum, a physical assessment, electrocardiography and ECHO-CG are performed. If there are suspicions of processes, the presence of such, but in a poorly developed stage, regularly, in dynamics. Every six months to a year.
Atherosclerosis of the aorta and its branches
Formation of lipid plaques on the walls of blood vessels. Pain appears in the late clinical period, when the nature of circulatory disorders is such that blood pressure rises to critical levels.
Arrhythmias of various kinds
Paroxysmal tachycardia, extrasystole, fibrillation. If these processes are prolonged, pain occurs. In other cases, they are rarely found, in no more than 10% of situations.
Endocarditis and similar inflammatory processes
Infectious or autoimmune type. An exceptional option when pain is constantly present.
Cardiac causes are relatively few in number, but pose a significant danger to life or, at least, health.
On the other hand, it’s good that there is discomfort. The patient manages to seek help in a timely manner and is aware of problems in the body.
What should you do if your heart hurts?
It is clear that when the heart is stabbing, it is difficult to maintain peace of mind, and most patients begin to panic, call an ambulance or rush to the clinic for a diagnosis, imagining conclusions about a heart attack and other serious diseases. However, despite all the unpleasantness of the symptom, most often it is not caused by a serious pathology, so first of all you need to calm down.
If your heart is stabbing, it is advisable to try to assess the pain - how acute it is, what its duration is, what other symptoms have appeared. At the moment of pain, you can hold your breath, try to move your torso, palpate the intercostal space to assess the relationship of stabbing pain with movement, breathing, and palpation. When contacting a doctor, this information will speed up and facilitate diagnosis, especially if the pain has subsided or gone away completely by that time.
A child may have a stabbing sensation in the heart area for the same reasons as adults, but diagnosis will be much more difficult, because not even every adult can correctly describe their sensations, and the child will be completely confused or scared. In such cases, it is better for parents not to search for answers on their own, which is why their children’s hearts are hurting, but the right thing to do is contact a pediatrician or cardiologist.
It is better not to get carried away with self-medication of any pain in the heart, because you can waste time or miss a serious illness, but some measures can be taken. For example, patients with an already established diagnosis of angina or arrhythmia can take the medications prescribed to them - nitroglycerin with validol, cordarone, anaprilin. Many people simultaneously use Corvalol, Valocordin and other “heart drops”, which have a sedative effect.
If the heart is stabbing against the background of a surge in pressure in a hypertensive patient, then it is quite advisable to independently use antihypertensive drugs - captopril under the tongue, the same nitroglycerin, if there is concomitant coronary heart disease, intramuscular magnesium, a diuretic. As a rule, after the pressure normalizes, the heart “relaxes.”
For tingling in the heart area against the background of neurosis, panic attack, autonomic dysfunction in young people who do not have heart disease, sedatives give a good and quick effect. You can drink tinctures of valerian or motherwort, hawthorn, Corvalol in accordance with the doses recommended for age and condition.
In case of inflammatory processes - myositis, neuralgia, herpes zoster - it is better to immediately consult a doctor who will prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics, antiviral drugs, and also recommend physiotherapeutic treatment.
Particular vigilance must be exercised if the heart is stabbing and shortness of breath appears, blood pressure drops, nausea with vomiting occurs, stabbing pain develops into a stabbing or burning pain, and the pulse is disturbed. These symptoms indicate a serious pathology that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment.
In the case when the heart is stabbing in the midst of complete health, and the symptom is short-term and goes away on its own, you can simply calm down, breathe deeply and calmly, take a horizontal position, loosen the collar of your shirt or tie. If the tingling sensations recur, then you should visit a therapist.
Extracardiac factors
Much more diverse.
Diaphragmatic hernia
Protrusion of anatomical structures into the lumen of the abdominal cavity. Occurs at any age, usually against the background of intense physical activity, overeating, and anatomical abnormalities during fetal development.
A relatively common phenomenon, it occurs in every thousand people on the planet. Almost does not make itself known, until a certain moment.
Chest pain is weak, aching, stabbing. Discomfort increases when eating or mechanical activity.
Inflammation of the pleura
This is the membrane lining the lungs. Rarely acts as an isolated process. More often accompanied by pneumonia or, at a minimum, bronchitis.
The complex phenomenon requires urgent medical care under the supervision of a pulmonologist. If there is colitis in the heart (presumably), you need to take a couple of deep breaths.
Problems with the pulmonary system will reveal themselves at one point. Against the background of movements, discomfort increases significantly, which does not happen with pathologies of cardiac structures. This method can be used independently to determine the cause early.
Intercostal neuralgia
One of the most common factors of pain syndrome. With intercostal neuralgia, it always seems that the heart is pounding when inhaling.
Discomfort is localized in the chest. In fact, special nerve fibers and muscle structures become inflamed.
Pathology can only be delimited objectively, based on the results of ECG, ECHO and other techniques. You can suspect something is wrong by again taking a deep breath. The pain will intensify. This does not happen with cardiac pathologies.
Fractures, bruises of ribs, cracks
They arise against the background of certain phenomena, the connection with which the patient can trace himself. Again, heart damage is also possible. Diagnostic measures put an end to the issue.
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
Inflammatory, degenerative diseases of the musculoskeletal system. It is extremely difficult to distinguish it from cardiac pathologies.
Radiography is used as the main method of verification and differential diagnosis.
Stomach problems
Like gastritis, ulcers of the mucous membrane. The tingling sensation becomes stronger when eating food, taking anti-inflammatory medications, and others.
Self-diagnosis
Doctors place great importance on pain. Pain syndrome has a pathogenic and signaling function. If there is a threat of damage in the body, it immediately reports this to the brain using pain impulses. Pain is divided into two types:
- Spicy. It is characterized by short duration and a pronounced connection with the area of damage.
- Chronic. A nagging pain that occurs constantly during the recovery period.
Types of heart pain
Cardiac discomfort causes many reasons for concern, because its consequences are potentially life-threatening. Stitching pain impulses in the area of the heart are accompanied by sweating, pressure surges and a feeling of lack of air. They are characterized by the following types:
Anginous. Soreness manifests itself during emotional disturbances or physical exertion. As a result of short-term stress on the muscles and psyche, the heart organ does not receive enough nutrients and oxygen at this time. In this case, the person feels a shooting pain radiating to the lower jaw area and under the scapula.
Heart attack. A piercing sensation in the area of the heart. This pain is characterized by increasing intensity and is accompanied by severe sweating (sweat is sticky and cold). The patient's skin turns pale, and it is difficult for him to even take a faint breath.
Cardialgia. A person feels stabbing pain in the area of the heart, which increases with any body movements. This group includes a type of pain signal that indicates various heart diseases:
- Arrhythmia.
- Myocarditis.
- Pericarditis.
- Angina pectoris.
- Cardiomyopathy.
- Intercostal neuralgia.
- Mitral valve prolapse.
- Cardiopsychoneurosis.
Cardialgia in its manifestation is divided into three types:
Simple. A form of painful syndromes observed in 95% of cases of neurocirculatory dystonia. The pain impulse appears spontaneously and is felt from 3-5 minutes to 1.5-2 hours. The pain is aching, prickly or pinching in nature, it spreads to the entire cardiac region or affects its apex.
Simple cardialgia has a subtype - angioedema cardialgia. In her case, a person experiences paroxysmal, pressing, squeezing pain. The attacks are short, but always strong.
Cardiac spasms of cardialgia and its subtypes go away on their own. Nitroglycerin and validol are used to relieve an attack. It is recommended to visit a neurologist.
Vegetative crisis. Exacerbation of neurocirculatory dystonia. Doctors call this pain “prolonged wave-like cardialgia.” The pain impulse is sharp, pressing in nature and does not disappear even after taking a cardiac. Symptoms of an attack include:
- Dyspnea.
- Body trembling.
- Lethargic state.
- High pressure.
- Increased heart rate.
Attacks of pain are controlled by taking medications that lower blood pressure and sedatives.
Sympathalgic. Painful impulses are burning, sharp in nature, a burning sensation is felt in the left side under the ribs. If you feel the intercostal spaces during an attack, the pain intensifies. The pain is not relieved by conventional means (validol, nitroglycerin).
The only thing that helps relieve discomfort is warming with mustard plasters and acupuncture. The causes of such pain are excitement and irritation of the nerve endings responsible for stress manifestations in the body.
In the nervous system of the human body, everything is interconnected; the nerves have a common origin and arise from a single trunk. Therefore, any affected organ is capable of transmitting a pain signal to a healthy part of the body. If there is frequent pain in the sternum area, this is not evidence of heart pathologies. Painful impulses are also caused by other reasons:
- Herpes (shingles) provokes a sharp stabbing painful syndrome in the cardiac zone.
- Damage to the ribs/pinched nerves in this area cause nagging pain that increases with palpation.
- Osteochondrosis of the neck and chest provokes the appearance of burning acute pain in the left zone of the chest. It radiates to the scapular area and arms.
- Heartburn causes a piercing pain impulse. The painful syndrome varies in duration and is accompanied by a feeling of unbearable acidity in the mouth.
- Pleurisy and pneumonia go away with acute prickly pain in the area of the heart, which increases with sneezing and coughing (the patient feels that the heart is suffering when inhaling).
- Problems in the peripheral nervous system respond with aching, needle-like soreness in the upper region of the sternum. Doctors call this syndrome “cardioneurosis”; it occurs after severe nervous shock.
How to distinguish cardiac from extracardiac causes?
Differential diagnosis is carried out by objective methods, under the supervision of a group of specialists.
Primary measures fall on the shoulders of the therapist. Common sense rules suggest when there are cardiac problems:
- If you feel a stabbing pain in the area of the heart, there is already reason to exclude cardiac pathologies. More often, against the background of serious illnesses, they are cutting, burning or pressing. They radiate (radiate) to the back, left arm (it seems that the discomfort is traveling through the veins). The potentially dangerous process is accompanied by shortness of breath, weakness, and sweating. The only exception is angina pectoris.
- If possible, you should try to find a body position that will be more comfortable. Usually this is the left side. In such a situation, there is also no need to talk about cardiac problems.
- You need to take a deep breath several times, bend over, move your arms, legs, back, and chest. When pain increases, we are not talking about heart problems. Either the lungs are to blame, or neuralgia. An extreme option is osteochondrosis of the spinal column. As a rule, it is neglected, especially if the discomfort practically does not go away.
- When taking drugs based on organic nitrates or phenobarbital (Valocordin), only heart pain is eliminated. In the absence of an effect, a different etiology of the process is possible, but this is not an axiom.
- If discomfort develops progressively, there is a high probability of cardiac pathologies. When the pain periodically shoots through and disappears, it is again impossible to talk about problems of the muscle organ.
Doctors are guided by the same points when collecting anamnesis and identifying complaints. As the condition is assessed, certain studies are prescribed.
So, why does the heart hurt? The distribution of processes is approximately this:
- Cardiac problems - 12% of cases.
- Gastroenterological diseases - 20%.
- Intercostal neuralgia - 40%.
- Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine - 20%
- Other factors not listed above - 8% of situations.
It’s better to figure it out in a hospital, especially if there are suspicions of cardiac pathologies.
What is the danger?
Most diseases accompanied by this symptom should not be ignored:
- intercostal neuralgia can lead to insomnia, hypertensive crises and impaired blood supply to tissues;
- if the cause of unpleasant symptoms is the herpes virus, then it must be constantly suppressed so that complications do not arise;
- if the cause of the stabbing pain is myositis, then at some point the inflammation can lead to difficulty moving;
- neurosis, in addition to physical manifestations, can greatly influence a person’s character, changing him beyond recognition, and the consequences of neurosis can affect any organ or system;
- complications of lung diseases can include difficulty breathing, cough, pain, high fever, and even death;
- osteochondrosis in an advanced stage can lead to loss of mobility and disability;
- neurocirculatory dystonia speaks of vegetative-vascular diseases, and those in a neglected state greatly interfere with life: thermoregulation is disrupted, convulsions and fainting appear;
- a heart attack, if not intervened in time, causes death of the heart and leads to death;
- angina, in turn, leads to a heart attack;
- hypertrophic cardiomyopathy can lead to a decrease in cerebral blood flow, the development of atrial arrhythmias, and sometimes provokes ventricular fibrillation - a condition when they contract unevenly, which interferes with the normal functioning of the heart and can lead to myocardial ischemia;
- Coronary spasm also increases the risk of heart attack, as it is a narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels, which increases the likelihood of blockage.
What can you do at home?
It is difficult to relieve an attack of pain because it is not known what causes it. As part of home emergency care, you should resort to the following algorithm:
- Measure blood pressure and heart rate. This is necessary to understand the nature of the process and define it as cardiac.
- Take a deep breath. If the discomfort does not intensify with a deep breath, it makes sense to look for the cause in the heart.
- When the tests are positive, take a Nitroglycerin tablet, drink a phenobarbital-based drug (Valocordin or Corvalol), it is better not to exceed the dosage.
Next you need to lie down and wait for the effect. Failure to act is grounds for calling an ambulance.
- If the tests are initially negative, you should take an anti-inflammatory tablet and then a pain reliever. Which ones exactly need to be decided. Diclofenac, Ketorolac, Nise are suitable as NSAIDs. Analgesic - Pentalgin. Older generations should not be used; these are dangerous drugs that affect the circulatory system and the rheological properties of liquid connective tissue.
- If there is no action, you should again call an ambulance. Just in case, since it’s not clear what’s going on here.
Be sure to open a window or window to ensure a flow of fresh air into the room.
What not to do: take baths, contrast showers, use unfamiliar drugs that could be harmful, exercise physical activity. At a minimum, this will lead to a worsening of the condition. Maximum - fatal.
Causes of stabbing chest pain not related to cardiovascular diseases
Traditionally, any pain in the chest, especially on the left side, is attributed to heart disease. Although this is sometimes true, similar symptoms occur in a number of other diseases. Among them:
- intercostal neuralgia;
- myositis;
- neurosis;
- lung diseases;
- osteochondrosis.
Intercostal neuralgia
This disease is a pinched or inflamed intercostal nerve. There are many reasons: from sleeping in an uncomfortable position to infections, such as herpes.
Other symptoms:
- burning;
- tingling in the affected area;
- muscle twitching;
- increased pain when coughing or sudden movement.
When you touch the ribs or the space between them, the pain intensifies. This is one of the main distinguishing signs: if the cause of the pain is heart problems, the pain does not intensify when coughing, touching, or trying to turn around.
Myositis
This is an inflammatory process that affects skeletal muscles. People say “it was blown”, “there was a draft”, although this is not the only possible reason.
Painful sensations intensify in the cold and when palpated, sometimes swelling and redness of the skin appears.
Neurosis
A neurotic excited state that has physical manifestations: a lump in the throat that interferes with swallowing and speaking, twitching of the facial muscles. At the same time, sometimes a person is extremely excited, describing his condition in all colors, and in other cases it is difficult for him to believe that he has a neurosis: he feels calm, and all experiences occur in the “background”, having only physical manifestations.
Lung diseases
Bronchitis, tuberculosis, inflammation of connective tissue can cause acute pain, which intensifies with deep breathing. In addition, the temperature usually rises and a cough appears.
Osteochondrosis
This disease includes the following manifestations:
- numbness of hands;
- dizziness;
- muscle weakness.
Osteochondrosis can be confused with heart disease; it provokes increased blood pressure.
Symptoms that require you to see a doctor
Any discomfort that worries the patient is considered grounds for visiting a specialist. An approximate list of manifestations (can be used as a guide) is as follows:
- Chest discomfort. Any character, not only stabbing, but also aching, cutting, pulling, pressing. Moreover, if there are other signs of the process. Typically, for cardiac causes, the pain is of moderate intensity and intensifies with physical activity, work, and stress.
- Dyspnea. Violation of blood oxygen saturation leads to general hypoxia. The body does not receive enough substances. Fasting ends in tissue atrophy, this is dangerous because the heart itself is under attack. Everything can end in a heart attack, stroke and severe disability. And that's the best case scenario.
- Headache for no apparent reason. Caused by insufficient nutrition of the brain. The phenomenon occurs in approximately 15% of cases. Against the background of heart problems, this is an alarming sign.
- Vertigo. To the point of inability to feel the ground under your feet and complete disorientation in space. The functioning of the cerebellum is disrupted.
- Sweating or hyperhidrosis.
- Paleness of the skin.
- Cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle. The last two manifestations are 100% likely to indicate cardiac problems.
- Weakness, drowsiness, general symptoms. Most often found in cardiac pathologies. Complications are likely.
These are grounds for routine visits to doctors.
Causes of heart problems
People get scared when they feel pain in the heart area, immediately thinking that a myocardial infarction is impending. But, as already mentioned, not every pain syndrome indicates cardiac pathology. Especially considering that not every person knows exactly where the heart is located and is not able to sensibly assess the discomfort of the sternal area.
When most people talk about heart pain, they mean the area of the left chest. But the heart is not there! Place your fist exactly in the middle of your sternum so that the bottom of your hand touches your stomach. This is where the heart organ is located!
Speaking about cardiac discomfort, you should pay attention not only to the area of the left pectoral muscle, but also to the condition of the diaphragm and the rib area, whether there is a stabbing pain in the heart there.
Not heart problems
There are several diseases whose symptoms include the presence of prickly painful syndromes reflected in the heart area, but not affecting the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
A snag in the spine. Stitching, paroxysmal pain radiating to the sternum area is observed with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. The painful impulse is reflected in the interscapular area. Radicular syndrome (pinched nerves due to pathological conditions of the intervertebral discs) affects the condition of the skin. The epidermis, changing sensitivity, causes a person to feel tingling and numbness.
Pain in the heart area that appears at night also indicates osteochondrosis. At night, the spinal column shortens slightly due to its own weight and puts pressure on the nerves and blood vessels.
Heart pain in spinal osteochondrosis is diverse. It can be long-lasting, lasting for hours, or instantaneous (there is a piercing sensation of a rough prick). The pain intensifies when moving your arms or turning your body. An accurate diagnosis is made by a doctor based on MRI and radiography of the spine. In addition to problems with the spinal system, heart pain is also caused by other bone-related diseases:
- Thoracic radiculitis. Or intercostal neuralgia. In this case, the pain impulse is localized in the intercostal space of the sternum and intensifies with pressure. The causes of the disease are rib injuries (fractures, bruises) and pinched nerve endings.
- Tietze syndrome. Inflammatory processes of the cartilaginous segments of the ribs at the points of their connection with the sternum. The pain syndrome resembles cardialgia. An attack of pain begins suddenly with burning jabs, intensifying with pressure on the sternum.
Lung problems. When it stings in the area of the heart, what is it? One of the common causes of stabbing paroxysmal pain in the area of the heart organ is pleurisy (inflammation of the pulmonary serous membranes). In this case, patients feel a sharp shooting pain in the area of the heart, which intensifies with inhalation and exhalation. In addition to pleurisy, stabbing pain syndrome is caused by other problems of the pulmonary system:
- Pulmonary hypertension. A pathological condition in which the intravascular pressure of the pulmonary artery sharply increases. Shooting pain in the sternum occurs against a background of shortness of breath and faintness.
- Pneumothorax. Accumulation of air in the pleural area. This condition occurs spontaneously in both healthy people and people suffering from pulmonary diseases. A person feels a sharp stabbing pain in the chest while inhaling.
- Pulmonary artery embolism. Blockage of the pulmonary artery by a blood clot or air bubble, amniotic fluid. The life-threatening condition blocks blood flow to the heart, causing stabbing pain that increases with breathing and coughing.
- Bronchial asthma. Inflammatory disease of the pulmonary tract of immunoallergic nature. During an exacerbation of the disease, attacks of the disease, it is difficult to breathe, and the pressure of the chest wall increases. The heart rhythm is disturbed, causing the appearance of acute sharp pain in the sternum.
- Pneumonia. Stitching, aching pain on the left side of the chest appears with left-sided inflammation of the lung. They are paroxysmal and very similar to cardiac ones. The following symptoms should alert you: lethargy, shortness of breath, high fever and dry cough.
The reason is in the gastrointestinal tract. When gases accumulate, intestinal bloating begins, which creates pressure on the body's organs. As a result, the functioning of the cardiovascular system is disrupted, and discomfort in the lower sternum space appears. Swallowing disorders (dysphagia) are the cause of pulsating, prickly pain in the left hypochondrium, which intensifies with swallowing. Some stomach diseases lead to chest pain:
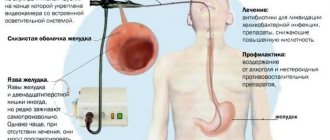
- Gastritis, ulcer. Such ailments are accompanied by attacks of heartburn, reminiscent of a burning sensation in the chest area. The pain is nagging in nature and intensifies after eating, combined with a pronounced sour taste in the mouth.
- Diaphragmatic hernia. This hernia is dangerous because the stomach or intestines penetrating through the hole in the diaphragm compresses the internal organs and prevents the lungs and heart from functioning normally. Sharp throbbing pain in the cardiac region appears in a lying position after eating.
- Esophageal spasm. A disease that grows from destabilization of the muscles of the esophagus. Attacks of the disease make themselves felt by burning chest pain and difficulty swallowing.
- Gastroesophageal reflux. It is associated with 45-50% of painful symptoms appearing on the left side of the chest. During an exacerbation, hydrochloric gastric acid ends up in the stomach and causes painful discomfort. The pain is located in the left side of the sternum and radiates to the arm, under the jaw, neck and rib.
Influence of the nervous system. Depression can take a person out of the usual rut of life for a long time. The destabilization of mental balance that occurs due to negative events also worsens a person’s physical condition, causing an exacerbation of chronic diseases.
Against an alarming background, pressing pain impulses appear in the area of the ribs. Spreading along the left side of the sternum, the pain is localized in the neck-shoulder girdle and is characterized by a sharp tingling and aching character.
- Panic attacks. Succumbing to uncontrollable outbursts of fear, a person simultaneously feels profuse sweating and severe arrhythmia along with throbbing pain in the sternum.
- Neuroses. In neurotic conditions, the patient experiences aching pain that torments him for 3-4 hours, tingling in the sternum area. The painful impulse of the heart in neuroses is concentrated in a small area, but it is difficult for the patient to describe his condition due to mixed symptoms.
- Neurocirculatory dystonia (VSD). A functional disorder of the nervous system that negatively affects the functioning of internal organs, affecting the heart. It is characterized by a sharp pulsating pain impulse in the retrosternal space.
Hormones are acting up. Hormonal changes of any nature negatively affect the functioning of the cardiovascular system and are the culprits of discomfort in the heart area. Symptoms, when stabbing pain can radiate to the left arm, are caused by problems with the adrenal glands and thyroid gland.
Excessive amounts of adrenaline (a hormone actively produced by an adrenal tumor) causes convulsive contractions of the myocardium and shooting pain in the heart. If adequate treatment is not carried out, this condition risks developing into a stroke or heart attack.
Muscle spasms. The culprit of pain in the left zone of the sternum is inflammation occurring in the intercostal muscles. With muscle inflammation, the pain is constant and wave-like attacks (a feeling of injections appears). The pain intensifies with breathing, turning and bending the body, and with fast walking.
The location of the pain impulse corresponds to the intercostal space and is concentrated at three points:
- At the sternum.
- In the armpit area.
- In the area of the spine.
Viral diseases. When infected with pathogenic microflora and the introduction of viruses and bacteria into the cells of the human body, ARVI, influenza, and acute respiratory infections develop. Microorganisms enter humans through the mucous membranes of the respiratory system. Having occupied the respiratory tract, viruses quickly spread throughout the body, poisoning it.
If, with a respiratory disease, a person feels pain in the cardiac region, this is a consequence of the penetration of toxins into the tissue of the heart. It is strictly forbidden to self-medicate in such situations - contact a doctor immediately!
The herpes virus, dormant peacefully in the body with a strong immune system, “wakes up” when the body weakens and begins destructive activity, causing shingles. This disease is characterized by severe acute pain in the sternum, high fever and skin rashes.
Attention! If, with pain in the area where the heart is located, a person experiences the following symptoms, emergency help should be called immediately:
- Dyspnea.
- Fainting.
- Hemoptysis.
- Dizziness.
- Numbness of the limbs.
- Increased sweating.
- Semi-fainting states.
- Nausea leading to vomiting.
Heart diseases
A group of reasons that cause sharp pain in the sternum. The cause of discomfort is damage to the heart organ itself, caused by inflammatory, pathological changes in the tissues of the heart organ. Insufficient supply of blood and oxygen to the heart, an increase in the load on the muscle occurs due to blood pressure.
The main, main signs of pathological heart problems are:
- Severe fatigue, weakness.
- Hoarseness of voice, dry cough.
- Disturbances in normal heart rhythm.
- Tachycardia (increased heart rate).
- Hyperthermia (increased temperature).
- Dizziness to the point of loss of consciousness.
- A feeling of lack of oxygen (the person is suffocating).
- Nocturia (involuntary urination at night).
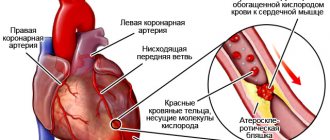
Angina pectoris. The most common heart disease that causes burning attacks of pain. Every 4th person over 45 years of age is familiar with the disease. The mechanism for the formation of a pain impulse is simple - the culprits are cholesterol plaques. They block the coronary arteries, which are responsible for supplying the heart with oxygen.
As a result, a narrowing of the myocardium (the middle muscle layer of the heart organ) occurs. As a result, the heart muscles accumulate lactic acid, which leads to the appearance of a painful syndrome. Painful impulses are relieved by taking heart medications. Patients suffering from angina pectoris are under medical supervision and undergo regular outpatient treatment.
Attention! Sometimes heart pain similar to angina attacks is caused by vegetative-vascular dystonia. Painful impulses are also compressive and stabbing in nature. In stressful situations, discomfort increases.
The cause of pain is an inadequate response of the myocardium to increased load. It is necessary to be able to distinguish angina from VSD. The patient must undergo an examination to make an accurate diagnosis and receive treatment.
Myocardial infarction. Complicated stage of angina. The appearance of a pain impulse is influenced by a sharp narrowing of the coronary arteries and a complete cessation of blood flow to the heart muscle (myocardium) and its death. In addition to unbearable stabbing pain that cannot be stopped, other symptoms are also observed:
- Nausea.
- Feverish condition.
- Feeling of fear of death.
- Pallor of the skin.
- Appearance of sticky cold sweat.
- A drop in blood pressure leading to a person fainting.
The painful syndrome during a heart attack is very strong, doctors relieve pain with narcotics. In this case, the timely arrival of the ambulance and competent actions of doctors are important. The ECG gives a clear picture of the disease, the patient is immediately placed in the intensive care unit for treatment, otherwise the condition leads to death.
Ischemia. Ischemic disease becomes the culprit of insufficient oxygen supply to the heart organ. The reason is blockage of the coronary heart vessels by cholesterol plaques. Doctors divide ischemia into five groups, depending on the clinical picture of the disease:
- Asymptomatic. The disease proceeds unnoticed, without causing discomfort to the patient. Doctors call this type of disease “silent ischemia.”
- Unstable ischemia. It is characterized by wave-like attacks, each of which is more severe and acquires new symptoms. Often this form of the disease warns of the possible development of a heart attack.
- Tension ischemia. Chronic disease. Characterized by pain in the intercostal space, shortness of breath. Discomfort increases with muscle strain and anxiety.
- Arrhythmic. The disease is recognized by pronounced heart rhythm disturbances. Without treatment, the disease develops into chronic ischemia.
- Cardiac arrest or heart attack. Severe stages of ischemic disease. They arise as a result of a decrease in the supply of oxygen and blood to the heart.
Ischemia is more common among men; in women of reproductive age, the body produces hormones that prevent the formation of vascular atherosclerosis. But during menopause (due to hormonal changes), the risk of ischemia is also high among the female part of the population.
Arterial hypertension. Significant increase in blood pressure (from 80 and 120 mmHg). The heart, experiencing colossal loads, forces the muscles of the cardiac organ to work with triple load. The myocardium, not receiving enough oxygen, reacts with acute pain, which intensifies with deep inspiration.
The culprit of hypertension is atherosclerosis. Plaques block the heart arteries, preventing the tissues and muscles of the heart from receiving oxygen normally. Loads increase and provoke discomfort, expressed in piercing heart pain and the following symptoms:
- Migraine.
- Noise/ringing in the ears.
- "Floaters" before the eyes.
- Unsteady gait.
- Apathy, lethargy, drowsiness.
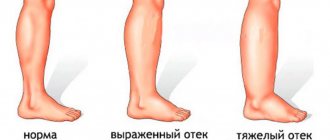
- Swelling of the limbs in the evening.
- Feeling of heat and redness of the skin.
A person experiences painful impulses especially often during a hypertensive crisis (a rapid increase in blood pressure to extremely high levels). Heart pain appears in the third stage of the disease, when high blood pressure and impaired blood supply to internal organs affect the heart muscle.
Myocarditis. Inflammation of the heart muscle. The myocardium contains receptors that respond to inflammatory processes with acute throbbing pain. The cause of myocarditis is the penetration of pathogenic microflora (viruses, bacteria) into the body. Microorganisms cause inflammatory processes and provoke the appearance of paroxysmal acute heart pain.
Painful impulses do not depend on loads, stress and are not relieved by taking heart medications. The ECG also does not reveal pathologies. In addition to heart pain, myocarditis has the following symptoms:
- Weakness, fatigue.
- Shortness of breath even at rest.
- Low-grade fever (+37-37.5⁰С).
Pericarditis. An inflammatory disease affecting the outer lining of the heart (pericardium). There are also numerous nerve endings that respond to inflammation. With pericarditis, painful impulses differ in some features:
- Cutting nature of the pain.
- The pain intensifies with breathing.
- Discomfort covers the right side of the chest, affecting the limb.
- The pain is especially felt on the left and in the lower region of the sternum (apex of the heart).
- The pain syndrome does not increase with exercise, but depends on the position of the torso.
Pericarditis is accompanied by weakness, dry cough, hemoptysis and fever. Treatment is based on relieving the main problem of pericarditis - relieving the inflammatory syndrome. They use antibiotics, anti-inflammatory, antiviral and antifungal agents.
Cardiomyopathy. This disease refers to pathological conditions of the heart associated with and arising from a lack of oxygen to the cardiac organ. In most cases, metabolic disorders are the culprits of cardiomyopathy. In such conditions, a person is bothered by heart pain of various types. They can:
- Be localized in one place or cover large areas.
- Be permanent or occur spontaneously due to stress or anxiety.
- Have a sharp, burning, stabbing character or become aching and prolonged.
Menopausal cardiomyopathy develops due to a lack of sex hormones. This pathology is typical in women during menopause and in teenage girls. At this time, the female half suffers from functional ovarian disorders. Sometimes menopausal cardiopathy becomes a consequence of pathologies of the endocrine system (thyrotoxicosis).
Heart defects. Heart defects are congenital or acquired, but regardless of their origin, they are accompanied by acute pain discomfort. With defects, the structure of the valve of the heart chamber is disrupted. As a result, some parts of the heart become overfilled with blood, while others receive less oxygen.
An overloaded myocardium contracts stronger and more often, experiencing a high need for blood supply. But its resource is not unlimited; there comes a time when the muscle begins to work inadequately, which becomes the cause of a painful cardiac impulse.
Pain due to heart defects has a variety of manifestations; they are accompanied by swelling of the limbs and high blood pressure. Stitching, sharp and piercing pain impulses occur with the following heart defects:
- Aortic stenosis. A sharp narrowing of the cardiac aorta in the area of its branch from the ventricle.
- Valve prolapse. Dysfunction of the organ located between the atrium and the left ventricle.
- Rheumatic heart defects. Appear as a result of chronic rheumatism.
According to statistics, the valves of the left heart are most often susceptible to defects. They account for 35% of disease cases.
Arrhythmia. A disease that affects normal heartbeat. Doctors have identified 4 types of cardiac arrhythmias, all of which are accompanied by pulsating, sharp, prickly pain:
- Disturbances of the intracardiac impulse (atrial fibrillation and sinus arrhythmia, sinus tachycardia and bradycardia).
- Impaired excitability of atrial contractions (paroxysmal tachycardia, extrasystole).
- Impaired impulse conduction (atrioventricular and intraatrial blockade).
- Mixed (ventricular fibrillation, atrial fibrillation).
Pain syndrome occurs directly during attacks. An attack of atrial fibrillation is especially common. According to statistics, 6% of people over 60 have already encountered it. Exacerbations of conditions are accompanied by dizziness and weakness. The patient's heart beats frequently and strongly. Sometimes the heart apparatus cannot cope with the load and the person loses consciousness. The causes of cardiac arrhythmias include the following factors:
- Brain diseases.
- Menopause.
- Alcoholism, long-term smoking.
- Infectious (viral) diseases.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Problems with the adrenal glands and thyroid gland.
- Disorders of sodium, calcium and potassium metabolism.
- Long-term use of certain medications.
Any pain in the heart area should raise suspicion. What to do in case of cardiac discomfort, run to the doctor or try to relieve the pain on your own?
Symptoms requiring an ambulance call
- Facial distortions.
- Inability to speak normally. Speech is impaired completely or partially.
- Intense headache.
- Dysfunctions of vision, hearing, and other sensory organs.
- Paralysis, paresis, or a feeling of goosebumps running all over the body.
These are all signs of a heart attack or stroke. They are potentially fatal. The earlier help is started, the higher the chances of survival and the absence of neurological deficits (irreversible changes in cerebral structures are likely).
How to help with severe tingling in the heart
Although pain in the chest area is nonspecific, its severity must be managed. This is not always possible on your own; there are a number of symptoms that require calling an ambulance or a scheduled visit to the doctor.
When you definitely need a doctor
Symptoms that require urgent calling an ambulance:
- facial asymmetry;
- speech disorders;
- migraine;
- impaired vision, hearing, loss of sensitivity;
- paresis, goosebumps running all over the body.
These are signs of a deadly heart attack or stroke.
Any other cardiac discomfort that is accompanied by:
- shortness of breath;
- sudden headache;
- disorientation in space;
- increased sweating;
- acrocyanosis;
- general weakness.
This is a reason for a routine examination by a doctor.
At home
Before the ambulance arrives or with unexpressed tingling in the chest on the left, a person can:
- open a window or go outside, but you should not make active movements;
- find a comfortable position (sitting, lying down), ensuring yourself peace;
- loosen tight clothing;
- strong tingling means taking painkillers: Ketanov, Nimesil, Ibuprom;
- the presumed cardiac etiology allows the use of: Validol, Corvalol, Persen;
- regularly measure blood pressure and heart rate;
- You shouldn’t take Nitroglycerin, it won’t help.
The main thing is not to be nervous and calmly wait for the ambulance to arrive.
Features of treatment
Pain therapy is directly correlated with the cause of the pathology.
| Cause of the problem | Corrective drugs |
| Gastrointestinal pathology | Proton pump inhibitors (Acrilanz, Lancid, Epicurus), antacids (Phospholugel, Almagel), balanced diet |
| Osteochondrosis | They use anti-inflammatory drugs (Nurofen, Voltaren), hormones (Prednisolone), massage, physiotherapy, surgery |
| Cardiovascular diseases | Cardiac glycosides (Digoxin, Celanide), ACE inhibitors (Captopril, Enalapril, Lisinopril), beta blockers (Anaprilin, Betalok, Obzidan), antihypertensives (Renitek, Concor, Norvasc), antiarrhythmics (Novocainamide) are used, surgery is possible if indicated |
When drawing up a treatment regimen, the principles of rationality and expediency are observed (gastritis is not treated with gastric resection).
What examinations need to be completed
Approximate diagnostic tactics are determined by a cardiologist. The initial appointment and routine methods are carried out by a therapist. Among the ways to identify the etiology of the process and make a diagnosis:
- Oral questioning of the patient regarding complaints. Already at this stage you can roughly understand what doctors are dealing with.
- Anamnesis collection. Family history, previous diseases, current somatic and other pathologies, treatment, if any, its duration, specific names of drugs. The vector of further examination is determined by these two methods.
- Listening to heart sounds. With cardiac problems, changes will always occur. Their absence is grounds for revising the probable diagnosis, although there are complex clinical cases.
- Measurement of blood pressure and heart rate.
- For the purpose of dynamic assessment, 24-hour monitoring is used using an automatic Holter programmable tonometer.
- Electrocardiography. Functional impairment, even minimal, will be noticeable. The main problem is the need for highly qualified diagnosticians and cardiologists.
- Echocardiography. Ultrasound technique. All organic disorders are visually determined.
- MRI or CT. If neoplastic or other pathologies are suspected.
- Angiography.
As necessary, under the supervision of other specialists, the following studies are prescribed: FGDS, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, general blood test, biochemistry, etc. The list is incomplete. The issue is resolved on the spot.
Diagnostics
The algorithm for examining a person is standard: taking an anamnesis, physical examination, pulsometry, tonometry. Further:
- UAC, OAM, biochemistry;
- ECG, EchoCG, Holter;
- X-ray examination: general X-ray of the chest, CT, MSCT;
- MRI;
Usually the doctor prescribes consultations with specialists. Prescribing the correct treatment depends on strict adherence to the recommendations, so every person who cares about their health should help the doctor in making the correct diagnosis.
Approximate treatment tactics
The complaint of colitis in the heart area is not very informative. Diagnostics shows the process itself, it is possible to determine its etiology.
Therapy directly depends on the nature of the phenomenon, its duration, and neglect. Both medications and surgical solutions are used.
You can answer as follows:
- Gastric problems are corrected by taking proton pump inhibitors and antacids. Diet and proper nutrition play the biggest role. It is better to discuss the issue with a gastroenterologist.
- Osteochondrosis cannot be treated as such; it can be put into remission. For this purpose, anti-inflammatory drugs of non-steroidal and steroidal origin are used. After the acute period is over, massage and physiotherapy are indicated. Hernias are eliminated surgically, but only beyond the possibility of conservative care.
- Cardiac processes themselves are treated through a group of medications, depending on the nature of the phenomenon. From glycosides to ACE inhibitors, antiarrhythmic drugs. Surgical therapy is possible, but this is a last resort.
When selecting a course and, in general, ways to correct the condition, the principle of expediency is observed. There is no need to treat gastritis through gastrectomy, this is an exaggerated example, but this is how it is in practice.
What to do when your heart hurts
How to relieve heart pain? First of all, you should consult a doctor. If a person has previously experienced heart pain and knows his diagnosis, take urgent measures before doctors arrive:
- Neuroses and neuralgia. Valerian and fresh air help with cardiac discomfort. In such conditions, it is especially harmful to worry and be nervous. Try to calm down, and after stopping the attack, take a course of a mild herbal sedative.
- Angina pectoris. If angina is complicated, access to fresh cool air and a nitroglycerin tablet under the tongue is necessary. The dose of Nitromint spray also helps to stop an attack.
- Signs of a heart attack. Before the doctors arrive, sit the patient down and lower his legs into a basin, where you dissolve 2-3 tablespoons of mustard powder in hot water. In this case, a person cannot lie down! Place a validol tablet under your tongue. In its absence, you can give up to 40 drops of Corvalol or Valocordin.
- Arterial hypertension. Before the doctors arrive, take medicine that lowers blood pressure (Capoten, Teveten, Corinfar, Micardis). Usually a person has in his medicine cabinet medications prescribed by a doctor and suitable for him.
Nitroglycerin is a universal remedy for heart pain. It dilates the coronary heart vessels, improving myocardial function. If nitroglycerin was unable to relieve pain, its ineffectiveness indicates an incipient myocardial infarction. This medicine does not help with rheumatic heart diseases. In this case, aspirin or analgin helps relieve attacks.
What to do if your heart suddenly starts acting up for the first time? Don't be scared and don't panic! Excess stress and worry will only make the situation worse. Instead of panic, comb through your first aid kit in search of suitable products:
- Validol (tablet under the tongue).
- Aspirin or analgin (take 1 tablet).
- Corvalol or Valocordin (40 drops per ¼ glass of water).
If you don’t have any of the above at home, try this method: take a sip of alcohol (vodka or cognac). Don't swallow! Hold the alcohol in your mouth for a while, then spit it out. After 15-20 minutes, assess the condition. If the pain does not subside, call an ambulance.
Attention! If you know that you do not suffer from any heart disease, using nitroglycerin is not recommended. This aggressive drug is intended for cardiac patients. And for hypotensive people, nitroglycerin is also dangerous - the medicine dilates blood vessels and further lowers blood pressure.
Massage rubbing with ointments based on bee venom (Virapin, Apizartron, Apitrin) also helps relieve pain in the sternum area.
Pressing pain
In cases where the heart is overloaded, pressure or dull pain may be felt on the heart.
- This type of pain can also occur in healthy people, for example, with excessive physical exertion or playing wind instruments, which increases pressure in the pulmonary circulation.
- With arterial hypertension, the heart has to pump blood against a pressure gradient, which impairs its blood supply and increases the load.
- Thyrotoxicosis leads to increased heart rate and overloads the heart with volume.
- Cardiac tamponade is a consequence of wounds and compression of the heart by blood. Also, the heart can compress the effusion during pericarditis of various origins (tuberculosis, tumor).
- With myocarditis of an infectious or allergic nature, mild pressing pain is accompanied by shortness of breath, rhythm disturbances, and heart failure.
- Myocardiopathy, myocardial dystrophy, cardiac tumors also give pressing sensations without a clear connection with the load, long-term or episodic.
- Pressing pain behind the sternum imitates foreign bodies of the esophagus or esophagitis.
- Intoxications of various natures (medicinal, narcotic, alcoholic), as well as poisoning with organophosphorus substances, ether, chloroform, and neurotoxic plant poisons, cause severe pressure on the heart, are combined with arrhythmias and heart failure, and are fraught with sudden cardiac arrest.
- Purulent pathologies of soft tissues, mastopathy. Breast cancer will also cause excess pressure in the projection of the heart.
- High ulcers in the cardiac part of the stomach also lead to a situation where pressing pain imitates cardiac pathologies.
In order not to fall into the situation of Tom Sawyer, who was not good at anatomy and hid the gifted flower closer to either the heart or the stomach, you can use a comparative table to distinguish stomach pain from heart pain.
Heart pain due to ischemic heart disease | Pain in the stomach due to a cardiac ulcer | |
| arise | During loading, less often at rest | On an empty stomach or in the first half hour after eating |
| Night pain | Uncharacteristic. Rarely - in the early morning hours | Characteristic |
| Nature of pain | Compressive | Pressing or sucking |
| Duration | From a few minutes to half an hour | Long-term |
| How are they eliminated? | Nitroglycerin. Sydnofarm | Gastrocepin, Omeprazole, Metacin |
How to quickly relieve an attack?
Naturally, if an attack of heart pain occurs, it is best to consult a doctor for medical help. However, every person should know what to do at home if an attack occurs at night and there is no way to go to the hospital, since no one is one hundred percent insured against such a situation.
In order to relieve pain, you should do the following:
- Try to take a comfortable position that will reduce discomfort from the heart. Try to breathe evenly and not intensely, alternating deep and long inhalations and exhalations, eliminate physical and emotional stress, and try to calm down.
- Take Nitroglycerin. If the cause of the pain is cardiac in nature, the pain syndrome will disappear within a few minutes. You can take sedatives such as valerian or motherwort tincture.
- If there is no positive result after previous procedures, you can try to reduce the pain by taking an anesthetic drug. The pain will go away if its cause is problems with the digestive tract, respiratory system or musculoskeletal system.
Nitroglycerine
It is worth remembering that if the heart is stabbing, and at the same time symptoms of an aggravating nature appear, which are expressed by paleness of the skin, changes in blood pressure and pulse, and a fainting state of the patient, then calling an ambulance is the first priority procedure. Doctors do not rule out the possibility of taking a Nitroglycerin tablet or a sedative before their arrival, however, they do not recommend taking other medications on your own.
Diagnostics and therapy
The heart is an organ that absolutely does not tolerate a permissive attitude towards its condition, since the quality of life depends on its functionality. Any uncomfortable signals from the heart should cause an immediate trip to the doctor, even if these “alarm bells” are not too intense to bother the patient. The most irrational approach to treatment when your heart hurts is to decide for yourself what to take, which pills are best to take.
When the heart tingles, only a qualified specialist should decide what to take, based on special examinations of the body, after making an accurate diagnosis. The treatment and diagnosis of heart disease in medicine is carried out by a cardiologist, who is the patient’s first point of reference for diagnosing the problem. The cardiologist will make primary conclusions about the condition of the heart based on examination of the patient, analysis of his complaints, as well as after listening to the organ and its percussion, or in simple words, tapping. Further diagnostics is multi-stage and includes the following procedures:
- Determination of the regularity of the heart rhythm, the frequency of its contractions and the specific functioning of the muscles of the organ using an electrocardiogram, which can be done in any clinic under the direction of a cardiologist.
- The Holter diagnostic method is a study of the functionality of an organ using special sensors for three days. The essence of the method is to analyze the work of the heart in different conditions, while the patient leads a normal lifestyle throughout the entire period and is not hospitalized.
- The doctor may prescribe the patient to undergo a Treadmill test for a detailed diagnosis of the functioning of the organ in load mode. The procedure is very similar to an ECG, but differs in location, namely, it is performed on a treadmill. The test helps determine the criteria for an organ’s tolerance to physical activity and analyze its performance in difficult conditions.
- The most comprehensive results are obtained by examining the heart using ultrasound. Ultrasound allows you to determine the thickness of the walls of the organ, the parameters and condition of the chambers and valves, identify the presence of defects, tumors, the development of ischemia, and much more. At the same time, with the help of ultrasound, a specialist will be able to assess the ability of the heart to pump blood normally and analyze the condition of the large vessels of the organ.
Often the described diagnostic measures are enough to put together a complete picture of the disease, establish a diagnosis, determine the reason why the heart tingles, and also prescribe specific therapeutic procedures.
If the primary source of pain is indeed a cardiological problem, the specialist, in accordance with the diagnosis, will prescribe treatment, which may include the following areas:
- If there are cardiac pathologies, drugs such as Valocordin, Corvalol, Nitroglycerin and other drugs are prescribed to suppress discomfort. Often, the doctor recommends drinking these medications only when necessary, excluding their regular use.
- Beta blockers are prescribed to normalize blood pressure, treat arrhythmia and reduce stress on the muscles of the organ. In modern medical practice, such drugs as Metoprolol, Atenolol or Bisoprolol are used for this purpose.
Bisoprolol
- Treatment of inflammatory processes in the heart most often cannot be done without drugs such as Markofen, Spazmalgon or Toradol. At the same time, these drugs help eliminate pain.
If pain occurs due to stress or strong feelings, drink valerian or any other sedative that will help calm you down and normalize the functioning of your nervous system.
In the absence of cardiac problems, the patient will be referred for additional examination, which involves diagnosing the primary source of stabbing pain in the heart, followed by comprehensive treatment.
What exactly needs to be taken for heart pain should be determined by a specialist, since by taking the “wrong” medicine prescribed to oneself, the patient may not only not improve the situation, but also complicate the illness, provoking its relapse with all the ensuing consequences.
How to get rid of pain at the beginning of anxiety?
What to do if stabbing pains appear in the heart? If you are already aware of your illness and know that the cause of the pain lies in a heart disease, then the doctor probably had a conversation with you and told you what to do during stabbing heart pain. Take the necessary medicine and carry out the necessary procedures to alleviate the condition. If your heart hasn’t pounded like this before, then you should probably just rest and take one of the following medications: Valocardin, Corvalol, Valoserdin.
In such situations, it is also necessary to provide fresh air. If a person is registered with a cardiologist, then at the moment of pain you should not wait for the condition to improve; it is better to immediately call an ambulance. While you are waiting for the doctors, ask your household to prepare a basin of warm water for you to make a foot bath and take a Valocardin tablet.
How to cope with pain in the first minutes?
If you do not know why, in some cases, pain occurs in the heart area, and every day its intensity only intensifies, then it is likely that this is a sign of the onset of myocardial infarction.
This disease is extremely serious and is characterized by blockage of one of the coronary arteries. During a myocardial attack, the sensation of pain becomes much stronger than during angina pectoris, and may include a number of atypical symptoms.
In any case, whether it is myocardial disease or angina pectoris, the patient is recommended to undergo a clinical examination to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
heart disease makes it difficult to breathe
What to do if your heart hurts | Alexander Drozhennikov
Why does my heart hurt for no reason?
Most often, stabbing pain occurs due to inflamed nerves (intercostal neuralgia). Discomfort comes from the chest and intensifies during periods of psycho-emotional tension (stress). Often the patient’s left arm goes numb - this is a characteristic sign of the disease.
Another common cause of stabbing pain is shingles. This disease cannot be confused with anything, since its main symptom is a characteristic rash.
Shingles causes heart pain
Other causes of stabbing discomfort:
- Myositis. Unpleasant sensations are localized on the left side of the chest. Myositis appears as a result of injuries, inflammatory processes and intoxication of the body. The most common causes: muscle damage, hypothermia.
- Cardiac neurosis or neurocirculatory dystonia. With this pathology, pain occurs after physical activity that is unusual for a particular person.
- Infectious and inflammatory cardiac pathologies (myocarditis, pericarditis). Unpleasant sensations arise sharply and are felt very strongly. Discomfort occurs against the background of a bacterial, or less commonly, viral infection.
- Lung diseases (pneumonia, tuberculosis, cancer). A sharp stabbing pain occurs when coughing and taking deep breaths. Discomfort is accompanied by a burning sensation in the chest.
- Aortic dissection. Unpleasant sensations are localized in the left side or near the heart, spreading to the shoulder blades. Patients experience acute stabbing pain, which experts rate as 10 out of 10.
- Osteochondrosis (thoracic and cervical). This pathology torments the patient constantly: discomfort can last from 2-3 days to several months. Osteochondrosis is characterized not only by stabbing pain, but also by spasms.
- Myocardial infarction. The discomfort increases every day, at some point it becomes unbearable. The disease is accompanied by arrhythmia, and the patient often experiences abdominal cramps. The disease most often develops in women during menopause, pensioners and people suffering from obesity.
Increasing pain in the heart may indicate myocardial infarction
Why does a child experience stabbing pain? Infants and children under 8 years of age rarely experience cardiac discomfort. Naturally, if your baby experiences severe pain, you should consult a doctor. Most often they are associated with pathologies of the heart itself, physical or psycho-emotional stress, and the development of early osteochondrosis.
If your child often has heart pain, you should see a doctor.
Cardiac discomfort is typical for adolescents over 14 years of age. Often, painful sensations are not dangerous, as they are associated with the growth of the body or an unfavorable emotional background. Discomfort may also occur after physical exercise.
Recommendations on what is strictly prohibited to do
Often, a slight tingling sensation in the heart area is not perceived by a person as a serious symptom, however, even minor pain from the organ should become an alarming signal, which requires certain actions on the part of the patient.
Doctors warn that minor discomfort in the heart area can signal both simple fatigue and the beginning of the progression of a serious pathology, therefore such a symptom should not be ignored by the patient.
The following actions are dangerous for the patient in this situation:
- uncontrolled use of medications to relieve painful symptoms;
- intense movement or physical activity;
- performing breathing exercises that provoke thromboembolism, which is often followed by a heart attack;
- the use of massages, which, like intense breathing, can provoke a blood clot;
- activity accompanied by panic or nervous agitation.
Prevention
As effective methods of prevention, one should adhere to general recommendations regarding a healthy lifestyle, eat properly and in a timely manner, and provide oneself with a healthy psycho-emotional environment. In addition, you need to periodically undergo a medical examination for preventive purposes.
The heart is an organ responsible for the vital functions of the entire organism. Tingling in this area may indicate either the presence of a certain disease or simple fatigue. The heart reacts to our mood and experiences. Let's figure out what causes cardiac colic.
Drug treatment
To cope with stabbing sensations in the heart, the following medications are used:
- "Validol" - this remedy has a sedative effect. It is applied sublingually and dissolved until the tablet is completely dissolved. The patient's condition returns to normal within 5-15 minutes. It is especially useful to take the substance in a state of stress or when discomfort rarely occurs.
- "Corvalol" - the drug is produced in the form of tablets and alcohol tincture. The substance has a pronounced calming effect. The alcohol base calms the nerves. The disadvantage of the drug is considered to be a negative effect on the liver.
- “Valocordin” is produced in the form of an alcohol tincture, which promotes vasodilation. The number of drops taken should correspond to the patient's age.
- "Nitroglycerin" - this substance has a quick effect. It has calming properties and belongs to the category of effective antispasmodics. You should take the medicine if you suspect a heart attack. It also quickly relieves severe pain. However, it is recommended to use the product only in case of severe pain or on the recommendation of a doctor. The tablets are dissolved in the mouth until dissolved.
- "Cardiomagnyl" is an effective analgesic that helps provide first aid and relieve pain.
- Aspirin helps relieve pain. In a critical condition, the substance is combined with Analgin, while calling an ambulance.
- “Sedalgin”, “Spazmalgon”, “Ketanov” are effective analgesics that have a wide spectrum of action.
Stitching pain in children
Read more: Causes of dull aching pain in the heart
You need to pay special attention to the complaints of children. They experience periodic stabbing pain in the heart for other reasons, unlike adults. In this case, the child must be carefully examined. The following pathologies may be detected:
- congenital heart defects;
- pericarditis;
- rheumatic carditis after tonsillitis;
- myocardial dystrophy;
- coronary circulation disorders;
- neurosis.
How can your heart hurt?
To help understand the causes of pain and periodic tingling in the heart, a thorough questioning is intended, during which the patient will clarify the location, duration and nature of his sensations. As practice shows, describing pain in detail and accurately is not an easy task, and in order to cope with it, it is advisable to know what sensations generally exist in the heart area and what you should pay attention to when they occur.
Tingling in the area of the heart can be safely classified as a type of pain, which can be acute and short-term or chronic, long-term, nagging in nature. When the heart is stabbing, the patient may also feel a lack of air, a rush of cold sweat, a sudden headache or dizziness and a host of other symptoms, which it is also advisable to check with the doctor.
DETAILS: Heart defect 3 degrees what is it
It is customary to distinguish several types of pain in the heart area:
- Anginal - more often occurs with pathology of the myocardium and cardiac arteries, intensifies with stress, stress, is of a pressing nature, usually relieved by nitroglycerin (angina);
- Infarction - sharp, dagger-like, stabbing, burning, almost always very intense, accompanied by cold sweat, fear of death, respiratory distress, swelling of the veins of the neck and other symptoms accompanying necrotic processes in the myocardium (infarction);
- Cardialgia is associated with both cardiac and non-cardiac pathology, is most often stabbing and short-term in nature, and can intensify with inhalation and body movements.
This classification is largely arbitrary, because pain and tingling are very subjective sensations, and each patient evaluates their intensity in his own way. By nature, the pain can be stabbing, pressing, burning, and in some cases these symptoms are combined, and it is extremely difficult for the patient to both localize and characterize his sensations.
- Connection with breathing, chest movements;
- Changes in the nature of sensations when palpating the chest, intercostal spaces;
- Weakening of tingling sensations when taking medications or lack of effect from them;
- Duration of negative sensations, intensity, spread to the arm, shoulder blade, epigastrium, etc.
The risk of such pathologies should not be excluded:
- Intercostal neuralgia. A very popular cause of stabbing pain in the heart. Neuralgia is usually understood as inflamed plexuses or nerve endings that manifest themselves as aching or acute pain. The root cause in this case may be osteochondrosis. It is this that often manifests itself as stabbing pain in the heart area.
- Pericarditis. This is an inflammation of the pericardium, the outer lining of the heart. Stitching pain occurs in the early stages of the development of the disease, and often it is the first symptom that helps diagnose the presence of pericarditis.
- Myocarditis. This is focal or widespread inflammation that affects the heart muscle. Myocarditis can occur due to infections in the body, taking certain medications, or deterioration of the immune system. It manifests itself not only with stabbing sensations in the chest, but also with shortness of breath and increased body temperature. In the case of myocarditis, the heart may continue to pound for a long time, even if the person does not undergo any physical activity.
- Neurosis. These are functional disorders of the nervous system that are a consequence of certain psychotraumatic factors. In addition to heart pain, the patient may experience headaches, feel constant tiredness and fatigue.
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia (vegetative dysfunction). In this case, it makes sense to talk about a complex of disorders of the autonomic nervous system, which is responsible for the functioning of all organs of the body as a single system. Dystonia often affects a person after prolonged depression. In this case, the heart may hurt even with complete rest, the heart rate increases, and blood pressure may increase.
There are also other possible reasons that need to be noted:
- Embolism. This is a pathological process that develops due to limited access to the heart muscle of blood. In most cases, the cause is a blood clot inside the pulmonary artery that blocks blood from reaching the heart. With an embolism, a slight tingling sensation is felt in the heart, for example, when a person takes a deep breath.
- Aortic rupture (dissection). In this case, the inner, middle and outer lining of the aorta become dissected due to blood that penetrates through cracks in the inner lining. The pain in this case will be quite severe. They may spread as the dissection changes its location.
- One of the most dangerous causes of stabbing sensations in the heart area is a blood clot. A thrombus is a blood clot that blocks proper blood circulation. As a result, a heart attack is possible. The symptoms of a blood clot are very similar to pericarditis, but the former is much more dangerous.
- Angina pectoris. This form of ischemic disease is quite common. It manifests itself as painful discomfort in the heart, as well as shortness of breath. Angina pectoris is popularly known as “angina pectoris.”
- Cold. The heart may also tingle with a common cold, in which case the pain is usually a reaction to toxins.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. One of the symptoms of diseases such as ulcers, gastritis or cholecystitis is also aching or stabbing pain in the heart area.
- Rib injuries. If the ribs are damaged, the pain resulting from bruises and fractures, combined with difficulty breathing, can be mistaken for pain in the heart area. With proper treatment, these symptoms go away.
- Congenital heart defect. A very serious disease in which pain in the heart and thoracic region is an important indicator that there are quite dangerous problems in the functioning of this organ.
- Physical activity. In the case of high physical activity, stabbing sensations in the chest and heart area are the result of increased work of the body. These symptoms usually disappear upon returning to a resting state.
There are a lot of reasons why the heart can pound, and not all of them are so harmless. Therefore, to determine the nature of the pain, you need to contact a cardiologist, who will prescribe the necessary examinations, and then appropriate treatment measures, which will be individual in each case.
DETAILS: How to take Concor for high blood pressure
How is diagnostics carried out?
The diagnosis of cardiac tingling is made sequentially:
- ECG
. Such a study will help the cardiologist see if there is a disturbance in the heart rhythm or in the heart muscle. In principle, all common heart diseases are diagnosed based on electrocardiography. - Blood tests
- as a result, the presence of inflammatory processes and the level of certain enzymes in the body are determined. - ECHO CG is prescribed - echocardiography
. Using ultrasonic waves, you can see the overall picture of the “motor” operation. - CRT – electron beam tomography
. Helps to diagnose the appearance of coronary disease in advance to eliminate its first symptoms. - Myocardial scintigraphy
. The essence of the method is due to the introduction of a small amount of radioactive substance into the blood to test the coronary arteries. Using special cameras, the movement of this substance through the bloodstream through the lungs and heart is monitored. - Angiography
. A contrast agent is injected into the arteries of the heart through a catheter. X-rays can be used to see the condition of the heart arteries for any obstructions.
Such studies are carried out to determine heart diseases. If none are identified, then you will have to visit other specialists:
- Pulmonologist.
- Therapist.
- Gastroenterologist.
- Traumatologist.
- Surgeon.
Experts prescribe a set of measures to identify the causes of tingling in the heart.
The difference between cardiac pain and non-cardiac pain
The following signs may indicate a non-cardiological origin:
- They are permanent, while an attack of angina pectoris lasts no more than 10-15 minutes.
- Usually shooting or piercing. As for the heart, they can be pressing, burning, squeezing.
- Acute stabbing pain occurs with sudden movements, deep breaths, and coughing. Cardiac problems are usually associated with psycho-emotional and physical stress.
- Painful sensations of non-coronary origin, as a rule, do not radiate to the left arm, neck, shoulder blade, jaw, as can be the case with heart diseases.
Let's sum it up
Stitching heart pain is an ambiguous symptom, which can be both a sign of the presence of problems of the cardiological category, and a concomitant indicator of other pathologies in the human body. It is almost impossible to independently determine the cause of painful manifestations of the heart, therefore it is most prudent to contact a medical institution and undergo a comprehensive examination if such pain occurs.
It is more than unreasonable to ignore such a manifestation of the body, even if it is symptomatic, since the performance of the entire organism directly depends on the correct functionality of the heart.
Aching pain in the heart area
The more intense the rhythm of modern life becomes, the greater the number of patients complaining of pain in the heart in the cardioneurosis program. In such patients there are absolutely no organic changes in the organ or the vessels that feed it, or they are insignificant.
- there is only a high degree of neuroticism
- depression
- anxiety disorder
- Cardioneurosis often develops as part of somatized depression.
Dissatisfaction with oneself and the world around us, which does not come out in behavioral characteristics, breaks out in the form of pain in the heart. At the same time, patients are haunted by many unpleasant sensations: pressure on the heart, freezing when breathing, aching pain and anxiety for their health.
Often, fixation on a non-existent cardiac pathology forces a person to undergo multiple examinations, change specialists and clinics, significantly complicating his life. At the same time, an experienced psychotherapist or group correction could solve the problem in a short time.
Nature of pain in the heart area
The description of suffering by the patient himself is very important at the first stage of diagnosis. It is the detailed description of pain that allows the doctor to navigate in the direction of the search and reduce additional examination methods to the necessary minimum.
When questioning the patient, the following are taken into account:
- conditions for the occurrence of pain (during or after exercise, at rest, association with food, at night or during the day)
- the nature of the sensations (pricks, squeezes, aches, cuts, presses, constantly or periodically)
- duration of pain
- after which they stop.
Why does my heart pound when I inhale?
Usually the heart stabs when inhaling when respiratory problems occur. This sign is often caused by the occurrence of pneumothorax. The disease occurs against the background of complications of pathologies of the respiratory organs.
As a result, a kind of cushion is formed between the chest and lung tissues. This causes a feeling of tightness and acute pain when a person inhales air.
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW! No more shortness of breath, headaches, pressure surges and other symptoms of HYPERTENSION! Find out the method our readers use to treat blood pressure. Learn the method.
The development of pneumothorax is observed against the background of inflammation and chronic pathologies of lung tissue, tuberculosis. Other diseases can also cause it.
When blood clots form in the pulmonary vessels, there is a risk of developing embolism. This disease is characterized by an acute pain syndrome of a stabbing nature. It increases with strong breaths. This condition is characterized by rapid heartbeat and shortness of breath.
Important: The appearance of pain in the heart with the listed anomalies is observed in the center of the chest. Usually the symptom is present in a calm state.
The provoking factors of the disease also include non-cardiological factors. If pain is observed when inhaling, inaccurate movements, coughing and sneezing, this indicates intercostal neuralgia.
Acute pain syndrome indicates precordial syndrome. With strong inhalations, discomfort increases and can be present for up to 3 minutes. Also, provoking factors include traumatic injuries to the chest, diseases of the esophagus, and the development of osteochondrosis.
Symptoms
If tingling in the heart is a clinical manifestation of a cardiogenic disease, then the following symptoms will be present:
- acute pain on the left, which manifests itself periodically at rest or during certain actions (physical activity, emotions, physical activity);
- shortness of breath, frequent and shallow breathing; when trying to take a deep breath, the tingling sensation may intensify;
- rapid pulse;
- dizziness;
- high blood pressure;
- increased sweating, in some cases especially intense at night;
- fatigue, decreased performance even after a long rest.
The nature of the duration of pain will depend on the underlying factor. So, with angina pectoris, tingling in the heart and pain are observed from 5 to 30 minutes, can radiate to the left arm, are easily relieved by an attack, and occur only after physical exertion or emotional shock.
An identical nature of tingling and pain in the heart will be observed with myocardial infarction, however, the distinguishing feature will be that with such a pathology, the pain is not eliminated by nitroglycerin, and a panic state, fear of death, and severe shortness of breath are added to the general clinical picture.
Regardless of the nature of the manifestation of this clinical sign, you should immediately seek medical help. In some diseases, delay threatens not with complications, but with death.
With excessive physical exertion, the manifestation of such a symptom may be due to a lack of oxygen. This is due to the fact that the vessels simply cannot cope with physical activity. That is why this symptom often manifests itself in those who, without the proper level of physical fitness, sharply load the body during training.
The cause of tingling in the heart may be a gastroenterological disease. In this case, the symptom will be reflective in nature, and the additional clinical picture will be characterized as follows:
- abdominal pain, which can radiate to the chest area and back;
- heartburn, belching of sour or air, depending on the provoking factor;
- unstable stool;
- nausea and vomiting, which most often occurs after eating fatty foods that are difficult for the affected intestines;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- a foul, pungent odor may emanate from the mouth;
- weight loss;
- deterioration or, on the contrary, increase in appetite;
- general malaise, weakness, decreased performance.
This clinical picture is typical for many gastroenterological diseases, so self-medication in the presence of such symptoms is strongly not recommended. All therapeutic measures should be carried out only after an accurate diagnosis.
Tingling in the area of the heart may be due to intercostal neuralgia, which will be accompanied by a typical clinical picture for this disease:
- spontaneously occurring pain and tingling in the heart, which can persist for quite a long time;
- at the site of localization of the pathological process, swelling of the skin may be observed;
- when you try to change your body position, cough or take a deep breath, the pain and tingling become more intense.
A similar clinical picture may be present with osteochondrosis, but the following additions take place:
In case of pathologies of the lung or both organs, tingling in the heart can be supplemented by the following clinical manifestations:
- shortness of breath that does not go away even with complete rest;
- pain in the chest area, feeling of tightness, heaviness;
- increased sweating;
- labored breathing;
- tachycardia;
- dizziness;
- cyanosis of the skin;
- nausea, vomiting that does not bring relief;
- abdominal ascites with pulmonary hypertension.
Tingling in the heart is no exception as a sign of infectious diseases. In such clinical cases, the above symptom will be supplemented by the following symptom complex:
For any symptoms, you need to seek qualified help, that is, a doctor. Only a doctor can determine the true cause of this symptom and prescribe effective treatment.
How to identify heart pain
To determine the reasons why your heart is stabbing and understand what to do in such a situation, you need to assess the nature of the discomfort. To do this, pay attention to the following features:
- Localization of pain and the circumstances under which it appears - with lesions of the heart muscle, discomfort is not associated with movement or change in body position.
- Changes in the nature of pain over time - if the severity of discomfort increases and then ends abruptly, this indicates the cardiac nature of the disease. In other cases, discomfort may persist for several hours or even days.
- Reaction to the use of Nitroglycerin and similar drugs - such drugs help with coronary artery disease. If with the help of nitrates it is possible to stop or weaken the attack, a cardiac origin of the discomfort can be suspected.
If the severity of symptoms changes when changing body position, it is worth feeling the pectoral muscles and the spaces between the ribs. If there is spasm of the pectoral muscle or the development of intercostal neuralgia, it is possible to identify painful areas.
To establish the causes of a symptom, you should evaluate the strength and nature of the pain:
- If a person has severe pain and describes in detail all the details of his condition, non-cardiac factors are most likely the cause. In such a situation, emergency measures are not needed.
- When true symptoms appear, people describe their condition rather sparingly, but accurately. There are no unnecessary details.
The following manifestations indicate cardiac disorders:
- increased heart rate;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- dizziness;
- dyspnea;
- fainting conditions;
- vomit;
- pale or blue complexion;
- frequency of pain;
- increased sweating.
Possible causes of the symptom
The appearance of stabbing pain is a symptom of functional or organic diseases of the stomach or nearby organs. The stomach is an organ with significant innervation, closely connected with the human central nervous system. The slightest errors in nutrition, disruption of the usual diet, side effects of medications on it and nearby gastrointestinal organs can disrupt its condition.
Possible causes of stabbing pain:
- Poor diet, overeating;
- Stress, psycho-emotional tension;
- Physical overload;
- Introduction of pathogenic bacteria, infections;
- Action of toxins;
- Abdominal injuries;
- Congenital pathologies of the stomach and intestines;
- Allergy.
It is possible that such a sensitive organ as the stomach can receive pain experienced by other organs, even those not related to the digestive system. A striking example is myocardial infarction, manifested by stabbing pain not in the heart, but in the stomach, radiating to the arm.
What to do: first aid, treatment
First of all, you need to determine why the tingling in the heart occurs. If it is difficult for a person to determine the area where pain is located, the following must be done:
- first of all, stop physical activity and eliminate the influence of stress;
- provide the patient with peace;
- unfasten the buttons on your shirt and the belt on your trousers;
- give the patient 1 tablet of “Nitroglycerin”;
- give the patient 300 mg of Aspirin;
- if angina discomfort is present for more than 5 minutes, you need to give the patient 1 more tablet;
- if symptoms still persist, you should call an ambulance.
If there is a sharp pain in the chest that lasts more than 5 minutes, a heart attack can be suspected. In such a situation, you need to act quickly. If acute and burning pain occurs, which is characterized by a feeling of heaviness and lack of air, you need to do the following:
- call an ambulance;
- free a person from oppressive objects;
- measure pressure;
- with high or normal blood pressure, you can give the patient a Nitroglycerin tablet - the substance is taken sublingually;
- if systolic pressure is less than 100 mmHg. Art., the use of “Nitroglycerin” is prohibited - the drug can cause a decrease in blood pressure, which will aggravate the person’s condition;
- give 300 mg of Aspirin - the patient must chew the drug.
Important: If a person loses consciousness and stops breathing, first aid should include cardiac massage and artificial respiration. If the patient's condition is stable and there is burning pain in the chest, he should not be left alone until the doctor arrives. Usually the patient is given an ECG and hospitalized in the cardiology department.
Organ pathologies - the cause of stomach colic
Stomach colic accompanied by pain are symptoms of damage to the stomach or other nearby organs:
- Gastritis – long-term pain is felt after digesting sour or rough foods, additionally accompanied by a feeling of heaviness, weakness and irritability.
- Stomach ulcer – in a third of patients, mild pain may occur after eating; relapses of this disease are replaced by seasonal exacerbations.
- Duodenitis – projects pain from the small intestine to the stomach. In addition to stabbing pain, intestinal inflammation is accompanied by hyperthermia, weakness, vomiting and nausea.
- Appendicitis - an attack begins with the appearance of stabbing pains in the projection of the stomach, they later move to the iliac region on the right. Symptoms: slight vomiting, slight increase in temperature.
- Coronary heart disease (CHD) - a violation of the blood supply to the myocardium occasionally radiates to the stomach. Additional symptoms are shortness of breath, tachycardia, weakness.
Treatment
In this case, treatment can be carried out with both conservative and radical treatment methods. Treatment tactics will depend entirely on the provoking factor.
When treated with conservative methods, the following drugs may be prescribed:
- antibiotics;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- to stabilize blood pressure;
- painkillers;
- diuretics;
- calcium antagonists;
- ACE inhibitors;
- anticoagulants of direct and indirect action;
- nitrates;
- sedatives and antidepressants.
Any drug should be taken only in strict accordance with the doctor’s prescription.
In addition to taking medications, such patients are advised to adhere to bed rest for a certain time, avoid stress and nervous experiences, and adhere to an optimal diet and proper diet.
If such a clinical manifestation is observed in a child, then in addition to general treatment, physical activity, including physical education lessons in an educational institution, is excluded.
Causes of pain in the heart area
| Heart diseases: | Diseases of the stomach and esophagus: | Toxic effects: |
|
|
|
| Heart overload: | Pulmonary pathologies: | Pathologies of large vessels: |
|
|
|
| Mediastinal diseases: | Lesions of nerve trunks: | Bone lesions: |
|
|
|
| Muscle damage: | Skin lesions: | Pathologies of the mammary glands: |
|
|
|
Consequences, what is the danger?
Complications and adverse effects of stabbing pain depend on the factors that caused it:
- Some diseases have a favorable course , for example, neuro-circulatory dystonia (the state of the central nervous system is disturbed) or osteochondrosis (intervertebral discs are destroyed and nearby nerves are compressed).
- Other ailments, when not detected in a timely manner, significantly reduce the quality of life and shorten its duration. For example: neoplasms of the mediastinum and lungs cause difficulty breathing and bleeding in the chest area;
- myocarditis (inflammatory processes in the myocardium) leads to heart rhythm dysfunction and heart failure;
- A stomach ulcer (defects in the gastric walls are formed) is complicated by ulcerative bleeding or malignancy (transformation into cancer).
If severe acute pain in the heart is not cardiac
Pain in the left side of the chest can occur due to diseases of the stomach, lungs, musculoskeletal, and nervous system. The most common reasons are:
- peptic ulcer complicated by bleeding, perforation of the ulcer;
- burns and injuries to the esophagus or stomach;
- acute pancreatitis and cholecystitis;
- pneumonia, pleurisy;
- tumor processes;
- neuralgia;
- neurocirculatory dystonia of the cardiac type;
- osteochondrosis.
Distinctive features of stomach pains are their connection with food, pulmonary pains occur during breathing, joint and muscle pains occur when turning or bending. Cardialgia in vegetative-vascular dystonia is not associated with physical activity, develops after fatigue or emotional stress, is not alleviated by Nitroglycerin, and is reduced by sedatives.