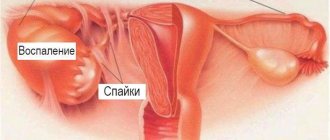
What is Bartholinitis Bartholin glands
The content of the article
Bartholinitis is an acute or chronic inflammation of the Bartholin glands.
The Bartholin gland (large vestibular gland) secretes a thick, viscous secretion that moisturizes the mucous membranes of the vagina and acts as a natural lubricant during sexual intercourse. The ducts through which fluid flows are located inside the labia minora. Bartholin's glands are only about 2 cm in size.
Microorganisms enter the gland tissue from the urethra, genital tract, through the blood or lymph flow. Inflammation leads to blockage and accumulation of fluid inside. Treatment of bartholinitis requires the mandatory intervention of specialists. But first of all, it is necessary to determine the cause of the inflammation, otherwise, without proper treatment, suppuration will begin.
Symptoms of a Bartholin gland cyst
At the beginning of this disease, the cyst has a small diameter (up to 2 mm), it is painless and does not cause any unpleasant sensations of discomfort. This pathological process can occur over a long period of time.
Routine medical examinations help identify this cystic change. Or when its growth becomes noticeable, and its size may exceed 10 centimeters in diameter.
During the development of a Bartholin gland cyst, a clinical picture develops, which is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Dryness of the mucous walls of the vagina, accompanied by unbearable vaginal itching.
- Throbbing pain that intensifies as a result of sudden movements or when walking quickly.
- Rapid fatigue, a feeling of weakness, and daytime drowsiness appear.
- The psycho-emotional state is disturbed, there is a sharp change in mood.
- Sometimes symptoms of hyperthermia (up to 39 degrees) are observed.
- The digestive system can react to this disease with the appearance of nausea and uncontrollable vomiting, and the development of symptoms of anorexia.
If no therapeutic action has been taken for this disease, the cyst may fester, which leads to the development of an abscess.
This condition is accompanied by:
- A sharp rise in temperature, to critical numbers.
- Severe symptoms of general intoxication of the body (nausea, vomiting, defecation disorder, diarrhea or constipation).
The cyst can open on its own, and its contents penetrate into the bloodstream. This leads to the development of sepsis, and is an alarming sign and a reason for urgently contacting a doctor.
Common causes of bartholinitis
Inflammation of the Bartholin glands and their ducts is caused by:
- Infection with streptococci, staphylococci and other pathogenic microbes - they can enter the genitals not only through sexual contact, but also when the infection spreads from other organs or due to poor personal hygiene.
- Protozoal and fungal infections, sexually transmitted - trichomoniasis, chlamydia, candidiasis (thrush).
- Hypothermia, decreased immunity.
- Wearing synthetic underwear in hot weather.
- Microtraumas caused by sexual intercourse with insufficient vaginal hydration.
- Traumatic medical procedures.
As a result of inflammation, the outflow of secretions becomes difficult. Its accumulation leads to the formation of a false abscess. If the disease is not treated, suppuration will begin (a real abscess).
Causes
There is a widespread belief that the causes of bartholinitis are sexually transmitted diseases. However, this is only one way of infection, which is quite rare. The causative agents can indeed be bacteria characteristic of STDs - gonococci, trichomonas and others, but the routes of infection are quite diverse.
Hypothermia is one of the main causes of bartholinitis
Among them are:
- Lack of personal hygiene. From the moment of puberty, girls are recommended to carry out hygiene procedures in the genital area at least twice a day, morning and evening. It is necessary to change your underwear at least once a day, twice in the summer. The most common route of infection with bartholinitis is household, associated with violation of hygiene rules.
- Cosmetology services for hair removal in the intimate area can cause infection. You can become infected both in the salon and at home.
- Decreased immunity. The vagina is a self-cleaning organ; usually opportunistic microflora does not survive in it due to a rather aggressive acidic environment. However, if a woman’s immunity is compromised, this protective ability deteriorates, and therefore the risk of developing an infection increases, even with a small amount of microflora.
- Hypothermia. It is also one of the common causes of the disease and is also typical for young girls who wear inappropriate clothes in the autumn-winter period.
- Complications of surgical operations, abortions. The most dangerous types of bartholinitis are associated with the ingestion of Staphylococcus aureus, which is a specific hospital infection. Infection is associated with non-compliance with hygiene rules by doctors or nurses.
Sometimes inflammation occurs due to a source of infection in another organ, usually also located in the pelvis. In this case, you should pay attention to other symptoms, because there is a whole list of diseases that often accompany chronic bartholinitis.
Among them are the following:
- colpitis - inflammation of the vaginal mucosa and vulvitis - vulva;
- endometritis and its complications - parametritis, endocervicitis, pelvioperitonitis;
- adnexitis and also associated salpingitis, salpingoophoritis;
- cystitis and urocystitis.
All these diseases affect the genitourinary system - vagina, fallopian tubes, ovaries, uterus. As a rule, they accompany each other, since the organs are located close to each other. Sometimes the source of the disease is pathology of the rectum in combination with a violation of hygiene rules: in this case, bacteria from the intestine enter the vagina and begin to actively develop in it. Therefore, the symptoms and treatment of bartholinitis in women are closely related to other possible diseases.
Symptoms of bartholinitis
There are several forms of the disease:
- Acute
, in which inflammation, swelling and redness are pronounced at the location of the excretory duct of the gland. Inflammation is accompanied by fever and pain that increases with movement. When examining the labia, a tumor the size of a bean (or smaller) is felt. Without treatment, the inguinal lymph nodes may become inflamed - in this case, a new disease will appear - lymphadenitis. - Subacute
, in this case the symptoms are mild. Slight pain is observed only during movement and sexual intercourse. The temperature is not elevated, there is no pronounced edema. This form of bartholinitis can become acute or go away on its own. - Recurrent
when the disease recurs. Hypothermia and wearing tight synthetic underwear contribute to the return of the disease. - Chronic,
characterized by the constant presence of inflammation and swelling. The temperature is kept within 37.1-37.5 degrees, no acute pain is noted. Chronic bartholinitis is very dangerous - it can lead to vaginal cysts.
Signs
Signs of an external cyst are associated with the stage of an abnormal process, which can occur without inflammation and suppuration of the Bartholin gland, being limited to the excretory canal, or reaching the glandular tissue.
The following stages are distinguished:
- Inflammation limited to the excretory canal (canaliculitis).
The walls of the duct swell, the lumen narrows, but the outflow of mucus is not impaired. The course is not severe, and the cyst on the labia has not yet formed. Pathology attracts attention:
- swollen labia (usually on one side);
- slight pain when palpated;
- unpleasant sensations during sexual intercourse, walking, sitting.
- A false abscess, in which the walls of the excretory canal stick together, blocking the outflow of mucus, but the gland itself functions normally. Microorganisms invade the walls of the glandular duct, causing inflammatory changes in the form of edema, which further narrows the lumen of the excretory canal, aggravating the pathological process. The unpleasant symptoms of the first stage intensify.
- A true abscess (acute suppuration, purulent bartholinitis) is a severe stage of a cyst that occurs when an infectious-inflammatory process passes to the gland and its tissues are destroyed by pathogenic organisms.
Symptoms of the acute stage:
- the vulvar cyst swells, fills with pus, increases in size to the size of a chicken egg, bulges in the form of a round formation;
- the labia is swollen, hot, dense, purple;
- the pain becomes pulsating, acute pain occurs with the slightest pressure on the swelling on the labia;
- temperature rises to 38.5 - 40C;
- symptoms of intoxication appear (headache, chills, severe weakness, nausea) due to the absorption of microbial poisons and toxins from cell decay into the blood;
- the inguinal lymph nodes enlarge.
Acute bartholinitis
The disease begins with the formation of a false abscess - a swelling in the area of the labia minora caused by accumulated fluid. A woman complains of pain in the groin area and increased temperature. As the disease progresses, a purulent (true) abscess occurs. A woman complains of severe pain in the labia area, swelling and enlargement of the inguinal lymph nodes. The temperature rises to 39-40 degrees. An abscess can be felt inside the gland.
When an abscess is opened independently, the contents leak out and the woman’s health temporarily improves, but then the hole closes and inflammation resumes. Sometimes the abscess breaks not outward, but inward. This often occurs when a woman tries to squeeze out an abscess on her own. Extensive suppuration of the surrounding tissues forms, which can lead to sepsis (blood poisoning).
The disease is provoked by:
- Failure to comply with hygiene rules. Wearing tight synthetic underwear in hot weather, which interferes with the natural ventilation of the skin. Dense tissues cause stagnation in the gland and interfere with the outflow of lubricant.
- STIs (gonorrhea, chlamydia, ureaplasmosis) and other genital infections.
- Diseases of the mucous membrane, accompanied by itching and scratching (leukoplakia, kraurosis). Through superficial damage, microbes from the vagina and urinary tract easily enter the gland.
- Gynecological operations and abortions performed with violation of sterility during the intervention or in the postoperative period.
- Hypothermia.
- Decreased immunity and vitamin deficiencies. A weakened body is less resistant to infections and microbes begin to multiply rapidly.
- Thrush, causing disturbances in the flora and dysbacteriosis of the vagina.
- Chronic infections in the body outside the genital tract. Microbes from there can enter the Bartholin gland with blood and lymph.
Treatment methods
Treatment methods depend on the severity of the inflammatory process:
- In the absence of an abscess, therapy is carried out on an outpatient basis with the help of medications.
- When an abscess forms, urgent hospitalization and autopsy are indicated.
- A vaginal gland cyst that causes discomfort must be surgically removed as planned.
- If the cyst is asymptomatic, there is no need for surgical correction.
For bartholinitis, local and general methods of therapy are used. During treatment it is necessary to abstain from intimate life.
Local therapy
Locally prescribed:
- applying anti-inflammatory ointments with an antibacterial component (Levomekol, Vishnevsky ointment, Metronidazole), antiseptic solutions (Miramistin, Betadine), which fight bacteria directly at the source of infection;
Levomekol ointment has anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects
- applying an ice pack to reduce pain;
- physiotherapeutic procedures.
Antibacterial drugs (Terzhinan, Trichopolum, etc.) should not be administered into the vagina without a doctor’s recommendation. This can lead to the spread of infection from the external genitalia to the internal ones.
With early treatment at the very beginning of the disease, local physiotherapy can be prescribed:
- UHF is a physiotherapeutic treatment method that uses ultra-high frequency electromagnetic fields, a kind of heat treatment that, with the help of special equipment, penetrates human tissues and organs;
- ultraphonophoresis on the area of projection of the inflamed gland is a method based on the combined action of ultrasound in combination with medicinal substances.
Physiotherapy has the following effects:
- improves blood circulation in the area of inflammation;
- increases the number of immune system cells that destroy pathogens;
- relieves swelling;
- stimulates rapid resorption of infiltrate;
- prevents suppuration.
Recipes for preparing antiseptic decoctions, infusions, solutions for compresses and baths
Instead of pharmaceutical antiseptics, you can use herbal preparations (decoctions of chamomile, sage, etc.) for lotions and baths, and saline solution for applying compresses.
Preparation of sage decoction:
- Take 2 tablespoons of dry sage leaves and place them in an enamel bowl.
- Pour in 200 ml of hot water.
- Place in a water bath and keep for 15 minutes.
- Strain the resulting broth and squeeze the leaves through cheesecloth.
- Bring the volume of the decoction to 200 ml by adding clean boiled water.
- Cool to room temperature and use 2 times a day as a lotion.
Chamomile decoction is prepared in the same way. The ingredients are taken in the same proportions.
Chamomile decoction for bartholinitis relieves inflammation
Preparation of infusion from nettle leaves, blackberries and yarrow flowers:
- Take 1 tablespoon of the listed plants.
- Pour 700 ml of boiling water over the leaf mixture.
- Leave for 1.5 hours, then strain the cooled infusion.
- The prepared infusion is used as a lotion on the external genitalia twice a day.
In addition to lotions, baths based on medicinal herbs are used. To prepare a bath that has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect, you will need:
- Take 1 tablespoon each of eucalyptus leaves, chamomile flowers and dried oak bark.
- Pour 1 liter of water over the leaves.
- Boil the mixture for 10 minutes.
- The resulting broth must cool to room temperature, after which it must be strained.
- Immerse the external genitalia in the resulting decoction for 15–20 minutes 1–2 times a day.
Instead of decoctions and infusions, you can use baths with potassium permanganate. To do this, you need to fill a basin with water (preferably boiled) and add a few crystals of potassium permanganate (the solution is prepared by eye). It is necessary to immerse the external genitalia in a basin with the solution for 10–15 minutes. Potassium permanganate is a strong antiseptic and effectively fights the causative agent of the disease. The resulting solution should have a pale pink tint. The bright pink solution is too concentrated. Its use can lead to a chemical burn to the mucous membrane.
Saline compress:
- Take 3 heaped tablespoons of table salt (90 grams).
- Pour them into 1 liter of warm boiled water.
- Stir until completely dissolved (a solution with a salt concentration of 10% is obtained).
- Apply multi-layer gauze dressings with saline solution to the swollen labia, changing them as they dry.
- Before changing the dressings, rinse the genitals with clean boiled water.
- Under no circumstances should the compress be covered with airtight materials (oilcloth, cellophane).
A hypertonic salt solution attracts water from soft tissues, thereby reducing their swelling and severity of pain. In addition, a high salt concentration contributes to the death of harmful microorganisms in the area of inflammation.
Self-applying warm compresses to the area of the inflamed gland can lead to the spread of infection.
In case of recurrent inflammation, immunomodulatory therapy (Genferon, Viferon suppositories for insertion into the vagina) can be prescribed. These drugs are intended to increase local immunity of the external genitalia and to improve the body's overall resistance to infections. Immunomodulators should be used during the period of remission (after the elimination of inflammation).
Doctors argue about the effectiveness of immunomodulators
There have been no serious medical studies confirming the effectiveness of immunomodulators, so many doctors do not recommend the use of these drugs, considering them useless.
Methods of systemic influence
Common treatments include:
- antibiotic therapy;
- taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Bartholinitis is a bacterial disease, the causative agent of which is fought with antibiotics. Their appointment is necessary when the pathology is accompanied by an increase in body temperature. Antibiotics of various groups (for example, Amoxiclav, Ceftriaxone, Levofloxacin, Metronidazole, Clarithromycin, etc.) can be prescribed orally or by injection (intramuscular or intravenous). After the analysis is ready to determine the sensitivity of bacteria, the drugs are replaced if necessary.
You should not neglect antibiotics for bartholinitis and try to cure it yourself only with folk remedies (baths, lotions, saline solution). This can lead to the formation of an abscess.
In case of high fever (temperature more than 38.5 °C), as well as to relieve pain, NSAIDs (Nurofen, Ketonal, etc.) are prescribed.
Nurofen is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, it relieves pain, relieves inflammation and reduces temperature during fever
Treatment of vaginal gland abscess
When an abscess forms, hospitalization in a gynecological hospital and opening of the abscess is required:
- An incision is made in the skin near the labia minora, the abscess cavity is emptied, and it is washed with a solution of hydrogen peroxide.
If an abscess forms, urgent surgical treatment is indicated.
- Then an operation called marsupialization is performed - sewing the edges of the mucous membrane lining the gland to the skin of the vagina. This procedure facilitates the drainage of purulent masses from the abscess cavity.
- After the operation is completed, drainage in the form of a gauze turunda with a concentrated salt solution is installed into the hole from the abscess, which is replaced daily. After cleansing the abscess cavity, cotton-gauze turundas with Levomekol or Vishnevsky ointment are introduced into it.
After surgery, antibiotic therapy is indicated. Inpatient therapy lasts about 7 days. The woman is then discharged for home treatment. You cannot sit for 4–5 weeks and you must abstain from sexual activity. Recovery after surgery is usually uneventful.
If the incision is made correctly, the skin and mucous membrane around the vagina heal without pronounced scars and discomfort does not occur in the future during sexual intercourse.
Sometimes, if not addressed in a timely manner, the opening of the abscess occurs spontaneously. Usually after this the severity of the pain syndrome decreases and overall well-being improves. In case of spontaneous opening of an abscess, in order to avoid possible complications, hospitalization is required, which includes professional wound care and antibiotic therapy. Therefore, it is necessary to consult a doctor immediately.
Video: how to treat inflammation of the Bartholin glands
Chronic bartholinitis
The untreated acute form of the disease becomes chronic. Mild inflammation of the gland occurs with constant exacerbations after menstruation, hypothermia, during heat. In the chronic course of the disease, there is constant swelling in the labia area and the formation of a cyst filled with liquid contents. The formation periodically breaks through with the release of pus. A woman complains of a dull pain in the labia area that gets worse when sitting and walking. Sometimes discomfort occurs during sexual intercourse. When pregnancy occurs, the symptoms of the disease intensify and an exacerbation occurs.
Causes of cysts on the labia
Among the causes of Bartholin gland cysts, experts identify the leading one - an infectious process of the external reproductive organs, accompanied by inflammation.
However, many bacteria are constantly present in the area of a woman's external genitalia, without causing the formation of a Bartholin cyst. Therefore, there are certain provoking factors that create the conditions for its development:
- reduced immunity;
- hypothermia of the external genital area;
- dysbacteriosis of the vaginal mucosa;
- failure to observe basic hygiene of the genital organs, especially during menstrual bleeding, rare changes of sanitary pads and tampons;
- sexual relations with more than one partner;
- injury to the epidermis during abortion, medical procedures, sexual intercourse, hair removal;
- genital infections, inflammation of the mucous membrane (vulvaginitis, colpitis, endometritis, cervicitis, adnexitis, salpingoophoritis;
- chronic diseases, diabetes, prolonged or severe stress;
- synthetic underwear;
- rubbing the skin of the perineum with tight underwear;
- the use of synthetic lubricants during intimacy.
Sometimes a Bartholin gland cyst can form due to the proliferation of connective tissue.
Is it necessary to treat bartholinitis?
Bartholinitis always occurs as a reaction to the presence of an infectious pathogen in the gland duct, which means that without treatment one can expect not only severe inflammation that will last for an unknown amount of time, but also the formation of an abscess.
Most often, patients who are faced with such a problem and, having read advice from the Internet, do not consult a doctor for a long time, waiting for the disease to resolve itself. And after some time, the symptoms actually become less pronounced and acute - this occurs as a result of the fact that the abscess opens on its own, removing the pus.
If you are ready to wait for the suppuration to burst, endure swelling and pain, then, of course, you don’t have to go to the gynecologist. But keep in mind that the danger of such an outcome is that the opening does not always occur externally - the infection can spread internally. And then you will also have to treat the consequences of bartholinitis.
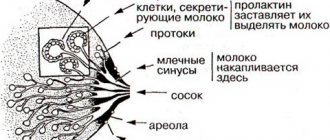
What is the Bartholin gland and where is it located?
A parenchymal paired organ that performs the function of external secretion, located in the subcutaneous fatty tissue of the labia majora and opening through the excretory duct into the vestibule of the vagina, is called the Bartholin gland.
The gland produces a secretion that enters the vagina through the outlet and moistens it. During sexual arousal, more secretion is released, which ensures stretching of the vaginal walls for free passage of the penis. Iron performs the same function during childbirth, protecting, if possible, from ruptures.
The activity of the Bartholin gland is under the control of sex hormones, in particular estrogens, so during menopause the gland begins to cope poorly with its task, and menopausal women experience dryness and discomfort in the external genitalia as a result. Under certain conditions, microorganisms that enter or inhabit the vagina can freely penetrate the gland and cause inflammation.
Is it possible to cure inflammation of the Bartholin gland on your own?
Bartholinitis can be caused by completely different pathogens, occur with different severity and in different forms. In addition, each patient may have associated problems that require additional treatment. For example, bartholinitis is often accompanied by reduced immunity, thrush; during an examination, a gynecologist may detect genital herpes or another disease.
After making a final diagnosis, only a doctor can prescribe treatment that will be aimed at eliminating exactly those infections and problems that are detected.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of bartholinitis includes a consultation with a gynecologist, who will suspect the pathology based on characteristic complaints, as well as upon examination of the external genitalia in a gynecological chair.
To diagnose bartholinitis, an examination by a gynecologist is necessary, during which you need to take the correct position on the chair
Additionally, for bartholinitis, the following studies are prescribed:
- general blood test - it is expected to increase the number of leukocytes and ESR, which is a sign of an inflammatory process;
- examination of a vaginal smear under a microscope is a method that allows you to quickly determine the causative agent of the disease, but it is not always accurate, therefore it is used only for preliminary diagnosis;
- sowing the contents of the gland on a nutrient medium to determine the sensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics is a labor-intensive, but the most accurate method for determining the causative agent of the disease and its sensitivity to antibiotics, which is very important due to the increasing number of cases of bacterial infections that are resistant to the most commonly used antibacterial drugs (Amoxiclav , Ceftriaxone, etc.).
The result of sowing is usually known no earlier than 3 days after collecting the material.
When an abscess forms, the gynecologist, when examining the external genitalia, will see a rounded formation and pronounced swelling, spreading to the labia majora and minora.
Unlike an abscess, a Bartholin gland cyst has an elastic consistency to the touch and is absolutely painless. The skin in the projection of the cyst is not changed in any way, the general well-being of the patient is not disturbed.
Sometimes Bartholin gland cysts reach large sizes, which leads to unpleasant sensations in the genital area and worsens the quality of intimate life.
Treatment of bartholinitis
Antibiotics are prescribed to treat bartholinitis, but there are no universal tablets that act immediately against gonorrhea, chlamydia, streptococcus, staphylococcus, herpes, etc.! Each pathogen requires its own medicine, so “standard regimens from the Internet” do not work.
Treatment measures depend on the form of the disease:
- Acute bartholinitis
. The doctor prescribes antibiotics and painkillers. The resulting abscess is opened and a duct is formed through which purulent fluid will drain. This operation is called marsupialization. - Subacute bartholinitis
can be treated without the intervention of a surgeon, which is why it is so important to consult a gynecologist in a timely manner. The doctor will find out the cause of the disease and prescribe antimicrobial or antiprotozoal medications; warm baths with herbs, physiotherapy, etc. will complement the treatment. - Treatment of recurrent and chronic bartholinitis is complex
. Existing cysts and ulcers are removed. The woman is prescribed antibiotics, sulfonamides, drugs that enhance immunity, and vitamins. Ultrasound treatment and magnetic therapy are recommended. In severe cases and in the presence of frequent relapses, extirpation (removal) of the Bartholin gland is performed.
To resolve the swelling, warm sitz baths with a slightly pink solution of potassium permanganate and physiotherapeutic procedures are used. Painkillers and antipruritics, vitamins, and immune stimulants are prescribed.
Surgery
Treatment of Bartholin gland cyst by surgery is indicated:
- with increasing formation and severe pain;
- if the cyst is accompanied by suppuration (abscess) of the Bartholin gland;
- with frequent exacerbations of pathology.
The purpose of the operation is to remove the formation, restore the patency of the ducts, the function of the gland, prevent an abscess and the spread of the inflammatory-purulent process to neighboring tissues.
Removal of a Bartholin gland cyst is performed in several ways, one of which is chosen by the doctor, taking into account the stage of the disease and complications.
Types of operations:
- Marsupialization of a cyst is a method in which a surgeon, under local anesthesia, opens the capsule and treats the cavity with antiseptics. In this case, a special temporary incision is surgically created to drain the exudate until the wound is completely cleansed. Marsupialization of a Bartholin gland cyst is prescribed for frequent exacerbations.
- Vaporization (evaporation) of a cyst with a laser. A soft method in which the cyst is removed with a narrow laser beam, evaporating the thick contents of the capsule. Adjacent healthy tissues remain undamaged, there is no bleeding or pain, and the likelihood of relapse is very low.
- Husking of a Bartholin gland cyst, in which the cystic capsule is removed under general anesthesia along with the membrane, separated from adjacent tissues. The method eliminates relapses, but is considered quite difficult due to the risk of bleeding and subsequent scarring of the wound. Healing 3 – 4 weeks.
- Extirpation (resection) or radical excision of the cyst with simultaneous removal of the Bartholin gland. Prescribed for frequent blockages of the excretory ducts, severe suppuration of the gland, and the failure of more gentle methods. The operation provides a complete cure, but complicates sexual life.
Recovery period
During the healing period of damage after surgery to remove a Bartholin gland cyst in women, it is recommended:
- Treat the damaged area with an antiseptic 2–4 times a day to prevent infection;
- follow the postoperative treatment prescribed by the doctor, including physiotherapy, antibiotics, wound healing ointments;
- To avoid infection and bleeding, exclude intimate contacts, physical activity, hot baths, saunas, steam baths, and swimming pools for 30–40 days.
Features of the treatment of bartholinitis
In the treatment regimen for bartholinitis, local therapy plays an important role - ice compresses, salt lotions, absorbable ointments and gels. These treatment methods provide maximum relief for a sick woman’s condition and have a symptomatic effect, relieving pain, relieving swelling and irritation. Related methods are also prescribed individually.
If the patient’s condition is accompanied by very high body temperature, chills, and severe pain, the gynecologist will prescribe additional medications that reduce fever and pain, including injections.
Causes and formation of bartholinitis
It is known that the vagina is not sterile; it is populated by various microorganisms that maintain the pH of its environment (bacillus, cocci, etc.). Natural inhabitants during a woman’s sexual life are often joined by foreign microorganisms that have the ability, under favorable conditions, to cause inflammatory processes, or viruses and infections that themselves provide these conditions. The causes of inflammation in the Bartholin gland or in its outlet duct (canaliculitis) can be:
- disturbances in the immune system, which not only allow the infection that has penetrated from the outside to “clear up,” but also do not “notice” when the vagina’s own microorganisms acquire a pathogenic form;
- infectious agents that come through sexual contact, where the leaders are gonococcus and trichomonas. Chlamydia, ureaplasma and the human papillomavirus, which has an extremely bad reputation, may also not pass by the small exit hole, which is not an obstacle for them, since they are even smaller;
- failure to comply with the rules of personal hygiene, when other organisms that are not typical for it (staphylococcus, streptococcus, E. coli) can enter the vagina and can penetrate the Bartholin gland and cause its inflammation - bartholinitis.
Inflammation in the excretory duct without damage to the gland tissue
When the infection is stuck in the excretory duct, they talk about canaliculitis or false bartholinitis (pseudobartholinitis). Local swelling of the outlet, the resulting pus that flows out when pressed, clog the duct, and purulent fluid begins to accumulate in the gland, stretching it.
The symptoms of pseudobartholinitis are not particularly bright and are expressed by a slight increase in body temperature to subfebrile, pain, although sharp, but tolerable, aggravated by walking, running and sexual intercourse. However, the developing inflammatory process in the exit duct of the gland can easily lead to pseudo-abscess of the gland, characterized by increased symptoms and a clear deterioration of the condition.
It is important to consult a doctor at such a moment, otherwise the “well-being” that occurs in a few days will turn into a chronic form and, from time to time, will remind itself.
True bartholinitis
If the pathogenic microorganism has entered the gland itself, then we will talk about true bartholinitis, which is accompanied not only by inflammation and the formation of a large amount of pus, but also by melting of the parenchyma of the gland itself. The symptoms of true bartholinitis are pronounced:
- severe “pulsating” pain in the swollen and hyperemic labia;
- enlarged regional (in this case inguinal) lymph nodes;
- temperature that has jumped above 38 degrees and the accompanying condition – chills, malaise, weakness and sweating;
- an increase in the number of leukocytes and an increase in ESR in a general blood test.
Rapid events in such cases indicate the development of a Bartholin gland abscess.
It is important not to self-medicate. It happens that acute inflammation under the influence of folk remedies and self-prescribed antibiotics can “die out,” which does not give reason for complacency. Most likely, the inflammatory process has become chronic.
As for the abscess, it must be opened surgically in compliance with all the rules of asepsis and antisepsis. Cases of spontaneous opening of an abscess sometimes occur, but this will be followed by almost 100% chronicity with the formation of a Bartholin gland cyst.
Is surgery always necessary?
Surgical treatment of this disease may be required in cases of manifestations of an abscess (purulent process) of the Bartholin gland. In this case, the operation consists of opening the purulent focus, removing all the contents and placing a special drainage tube for 5-6 days. During this time, the remaining purulent particles are removed from the gland cavity.
At the same time, the operation does not cancel the classical therapeutic regimen described above - antibiotic therapy, local techniques, strengthening the immune system, which means that you will have to take the pills anyway.
You can refuse the operation, but this is not recommended, since the abscess will still open on its own. In this case, everything will be much more painful, the infection can get into the vagina and spread to the internal genital organs, and everything will take a very long time to heal.
In severe cases, the gland must be removed.
Complications and consequences
The cyst itself does not pose an immediate threat to a woman’s health. The development of complications is dangerous, the most common of which is suppuration and abscess formation. If an abscess is not treated promptly, the bacterial infection can spread further, leading to sepsis (blood poisoning) in severe cases.
Other complications may also develop:
- fistula formation;
- relapse of the disease;
- vulvitis, vagnit, urethritis, cervicitis.
With an uncomplicated course, the outcome of the disease is favorable. In some cases, the cystic formation resolves on its own, without external intervention.
What to do if bartholinitis worsens?
If the disease recurs, it is necessary to determine the cause of the relapse: perhaps the pathogen remains in the body. In this case, treatment will be aimed at eliminating the infection and strengthening the immune system.
As for frequently recurring periods of exacerbation, surgical intervention may be necessary for effective treatment, and chronic bartholinitis requires an operation different from that performed in the acute form.
In the chronic form of bartholinitis, simply removing the contents of the abscess is ineffective, since the tissues quickly stick together, again blocking the gland duct. To solve this problem, surgeons have developed two methods of performing surgery for chronic bartholinitis:
- The first surgical technique was called marsupialization and represents the formation of a new drainage canal of the gland, which does not undergo adhesion and removes the secretions and contents of the vaginal vestibule without causing suppuration. It is possible to achieve the formation of such a channel through an incision in the suppurated cavity, followed by washing it and installing a catheter, which is left for 4-5 weeks. During this time, a stable duct is formed for the discharge of glandular secretions, which reduces the risk of exacerbation by almost 90%.
- The second surgical technique is aimed at completely removing the Bartholin gland. It is only used in cases of multiple failed attempts at marsupialization. Unfortunately, the absence of the Bartholin gland leads to excessive dryness and irritability of the tissues and mucous membranes of the vagina, so patients have to use special moisturizers - these are prescribed by the doctor.
Complications
Without timely treatment, suppuration in the vestibule of the vagina can lead to the spread of infection to other organs of the reproductive system.
There is a risk of spontaneous opening of the abscess inside with the subsequent spread of purulent inflammation to other tissues and organs, up to sepsis.
When the abscess is opened, relief comes out, but the disease without appropriate treatment becomes chronic; in some cases, a fistula forms at the site of the abscess breakthrough.
The following complications are possible with bartholinitis:
- Formation of a true abscess from a false abscess, in which the infection spreads to the external genital organs and vaginal mucosa, that is, vulvovaginitis develops;
- The appearance of a cyst, after which inflammation becomes a sluggish process;
- Transfer of infection to neighboring organs (urethritis, colpitis);
- Constant relapses;
- The large size of the formation can cause awkwardness when walking and discomfort during sexual intercourse;
Prevention
To prevent bartholinitis you need:
- Get tested regularly for STDs and, if infections are detected, treat them immediately;
- Avoid wearing thick synthetic underwear, especially in hot weather;
- Avoid hypothermia of the lower half of the body;
- Do not use aggressive soaps or antibacterial agents (unless prescribed by a doctor). These drugs disrupt the natural balance of microflora, contributing to the occurrence of dysbiosis (development of pathogenic flora) and candidiasis - a fungal infection;
- Use pH-neutral intimate hygiene products.
Bartholinitis is easy to prevent; if you follow preventive measures, the risk of the disease is greatly reduced.
Prevention of Bartholin gland cysts
Preventing the development of this pathological process is the main goal of preventive measures.
To do this, every woman needs to follow simple rules:
- Daily use of personal hygiene items.
- Avoidance of casual sex.
- Use condoms during sexual intercourse.
- Treat acute infectious diseases in a timely manner and prevent them from developing into a chronic, protracted form.
- Do not postpone visits to the antenatal clinic. Visit a gynecologist at least twice a year.
- Eliminate bad habits and lead a healthy lifestyle.
- Do therapeutic exercises and hardening.
- In the autumn-winter period, use medications (multivitamins) that help raise and strengthen the immune system.
- During an epidemic of influenza and ARVI, carry out all preventive measures to prevent the development of these diseases.
Where to cure inflammation of the Bartholin glands in St. Petersburg
Every woman faced with such a serious condition needs to promptly contact an experienced gynecologist. Such doctors work in St. Petersburg at the Diana Medical Center. Specialists use only proven effective treatment methods, so you will get rid of an unpleasant disease without complications. An appointment with a gynecologist costs 1000 rubles.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Consequences of removal of the Bartholin gland
A hospital stay, general anesthesia and the likelihood of postoperative hematoma formation are not the worst consequences of removing the Bartholin gland. These manifestations relate to the postoperative period and eventually disappear. But the absence of a gland will also lead to a lack of lubrication, which will be accompanied by constant discomfort, and especially during sexual intercourse. This fact will be felt by both the woman herself and her partner, who will also not enjoy such contact.
Scars left after stitches can deform the labia, interfere with movement, and cause pain.
The disease does not seem to be fatal, which can also be argued, because a rapidly developing abscess can sometimes end in sepsis. The cyst suppurates rapidly and requires immediate surgical intervention, so it turns out that the size of the organ is small, the gland itself is located on the surface in an accessible place, but it requires an attentive and careful attitude towards oneself. After all, the Bartholin gland is accessible not only to the skillful hands of a surgeon, but also to dangerous microorganisms invisible to the eye, which the woman herself must put a barrier to.
Recommended Articles
Paraovarian ovarian cyst
“Chocolate” or endometrioid ovarian cyst
“Harmless” cyst of the corpus luteum of the ovary
Symptoms
The symptoms of bartholinitis are individual. Its manifestation depends on the type and extent of inflammation.
In mild forms of the disease, it causes only slight discomfort in the vaginal area, women hardly notice it.
In more severe forms of bartholinitis, the formation enlarges and thickens and can be palpated.
Inflammation of the Bartholin gland in the form of a true abscess has more clearly defined symptoms:
- Body temperature rises to 39 degrees;
- It is painful for a woman to sit and walk;
- Heat in the labia, throbbing pain, feeling of fullness;
- State of weakness, weakness;
- Headache.
If a true abscess is diagnosed, the formation enlarges, thickens, and bulges above the labia. The skin over the gland takes on a reddish tint.
The temperature of the gland increases. In the chronic course of the disease, the formation transforms into a cyst. It can reach the size of a chicken egg.
Sometimes an abscess can open involuntarily. Then the pus pours out. It looks like a yellow-green thick liquid with an unpleasant odor.
If the abscess does not open outward, but into the thickness of the labia, this causes another inflammation. In such a situation, the pain will sharply intensify and nearby tissues will swell.
Reasons for the development of bartholinitis
Bartholinitis is an infectious disease caused by the presence of pathogenic microbes.
There are only two ways of infection:
- reduced immunity provokes the development of its own opportunistic microflora (streptococci; staphylococci; Escherichia coli; Klebsiella);
- infection with microorganisms from the external environment (Trichomonas, gonococci, chlamydia).
A potential pathogen in the body can be activated in the presence of certain factors:
- decreased general immunity;
- external violations of the integrity of the integument of the groin area;
- failure to comply with the rules of personal intimate hygiene;
- frequently changing intimate partners;
- the presence of chronic inflammation in the body;
- other sexually transmitted infections and urinary tract infections;
- the period of menstruation and the second half of the cycle are favorable for the development of the disease;
- violation of sterility standards during intravaginal manipulations;
- tight underwear.
External infection most often occurs through sexual intercourse. Infection through household contact is rare.
Factors that increase the likelihood of infection include:
- diabetes. Against the background of diabetes, immunity is reduced, glucose is an additional nutrient medium for the proliferation of microorganisms;
- congenital or acquired immunodeficiency;
- changes in the normal microflora of the vagina, dysbiosis, which is caused by poor personal hygiene;
- promiscuity.
There are 2 stages:
- bartholinitis itself (catarrhal stage) - inflammation inside the gland;
- damage to other tissues with the appearance of purulent formation. When the gland is blocked, a cavity of pus forms and a cyst forms.
Mechanism of disease development
The Bartholin gland belongs to the exocrine glands, that is, it secretes its secretion out through the excretory duct. Functionally, it can be divided into:
- The producing part is pea-shaped, lined from the inside with secretory epithelium, which produces a liquid secretion. This is where fluid accumulates before it is released.
- The excretory tract is a thin tube 1.5-2 cm long that opens between the labia minora and the entrance to the vagina. Through it, the secretion is released onto the surface of the mucous membrane.
The duct of the Bartholin gland is relatively wide and various microorganisms easily penetrate through it. With a decrease in local immune defense or general resistance of the body, even opportunistic microflora that populate the skin and rectum can cause inflammation - bartholinitis.
The main causes of the disease are:
- Streptococci;
- Staphylococcus;
- Escherichia coli;
- Proteus;
- Klebsiella.
Nonspecific microflora can penetrate into the gland not only through the duct from the outside, but also through the blood or lymph flow from internal foci of chronic infection (tonsillitis, carious cavities, inflammatory diseases of the internal genital organs). In this case, bartholinitis is secondary and recurrent in nature if the underlying cause of the disease is not cured.
Among the causative agents of STDs, damage to the Bartholin gland is caused by:
- Gonococcus;
- Trichomonas;
- Chlamydia.
Microorganisms attach to the surface of the epithelium, penetrate deep into it, where they multiply intensively and release toxic metabolic products. Under their influence, epithelial cells die, an inflammatory reaction develops: a rush of blood to the site of the lesion, swelling, and the release of leukocytes into the tissue. Due to swelling of the walls, the gland duct narrows or becomes completely impassable, its secretion accumulates inside, stretching the capsule - a cyst is formed. The purulent process inside it leads to the formation of an abscess - a limited cavity filled with pus. In the latter case, the gland is filled with dead leukocytes, microorganisms and remnants of epithelial cells. Partial breakdown products are absorbed into the blood with manifestations of a systemic reaction: body temperature rises, general health worsens.
in the photo: Bartholin gland cyst
Without treatment, the perineal tissue surrounding the gland sometimes undergoes purulent melting. As a result of this development of the disease, rough, disfiguring scars are formed at the site of inflammation, which interfere with sexual activity. In some cases, the abscess opens out, but complete emptying rarely occurs and the remaining pus causes new exacerbations of bartholinitis. The inflammatory process in the gland duct often leads to the formation of a cyst, which gradually increases in size and blocks the entrance to the vagina.
Diagnosis of bartholinitis
Gynecological examination of the patient to diagnose bartholinitis
Diagnosing bartholinitis is not difficult. During a gynecological examination, a doctor can easily identify this disease by characteristic abscesses with swelling and redness of the glands.
To confirm the diagnosis, they take a smear on the flora, a bacterial culture (to determine the sensitivity of the pathogen to antibiotics), a bacteriological examination of the pus of the affected gland, a general analysis of urine, blood, an analysis for syphilis and HIV.
Acute bartholinitis can be of both venereal and non-venereal nature. In order to understand what its nature is, the gynecologist examines smears taken during the examination.
A woman can independently suspect this illness when the symptoms are clearly expressed - severe pain and a purulent process. You should not expect that the symptoms of bartholinitis will go away on their own; on the contrary, the inflammation will progress.
Forms of bartholinitis
Either one or both glands can become inflamed. Bartholinitis can take an acute form - with this course of the disease, its symptoms are clearly expressed. The duration of the acute course of the disease is up to eight weeks.
When it becomes chronic, the disease has a wave-like course - a relatively stable state is replaced by a sudden exacerbation of the disease. In this case, the external symptoms of the disease are not clearly expressed, and gland cysts form.
When inflammation of the Bartholin gland cannot be cured for more than two months, its chronic form is diagnosed. With this course, the disease worsens 1-2 times a year.
There are three types of inflammation of the Bartholin gland:
- Kanakulit. Inflammation of the excretory duct of the gland. At the same time, its walls swell, but do not close. The outflow of secretions continues.
- False abscess. With this diagnosis, the gland duct closes and the outflow of secretions is impossible. Due to the filling of the formation with mucus, it turns into a cyst.
- True abscess. With it, the gland tissue is destroyed. It fills with pus and enlarges. Substances secreted by microbes and cell breakdown products poison the body, and the patient’s temperature rises.
A recurrent cyst caused by inflammation of the glands is treated by completely removing the formation.
Popular recipes for external use
The most effective treatment for bartholinitis is to use external agents - baths, ointments, lotions and compresses. They can be prepared from various natural ingredients.
The use of external folk remedies in treatment is most effective when combined with antibacterial drugs.
Yarrow, nettle and blackberry leaves
To prepare lotions for the genitals, you will need to take a tablespoon of nettle, yarrow and blackberry leaves and pour 700 ml of boiling water. After 90 minutes, the broth must be filtered. Use the prepared infusion as a lotion on the genitals in the morning and before bed. To carry out the procedure, the decoction must be warm. It is recommended to prepare a fresh decoction daily.
Treatment with St. John's wort
One of the most effective means to combat bartholinitis is to use a decoction and ointment based on St. John's wort.
To prepare the decoction, you will need to pour a tablespoon of dry St. John's wort into 0.5 liters of water and boil for 20 minutes. To make the ointment, you will need 50 ml of goose or rabbit fat, 5 ml of beeswax and a tablespoon of crushed St. John's wort flowers. Mix the ingredients and heat until the fat is completely dissolved. The finished ointment should be stored in a cool place.
Treatment of bartholinitis with St. John's wort occurs in two stages: first, the external genital organs should be rinsed with a decoction of St. John's wort, and then an ointment based on it should be applied to the inflamed area.
Bath based on oak bark, chamomile and eucalyptus
An important stage in the treatment of bartholinitis is the daily use of baths based on medicinal herbs. To prepare an anti-inflammatory and wound-healing bath, you will need to take a tablespoon of eucalyptus, chamomile and oak bark and add a liter of water. Boil for 10 minutes.
The broth should be cooled until warm, and then make baths for the inflamed area. The exposure time is 15-20 minutes.
Compress with onions
The onion must be baked together with the peel in the oven. Then chop it up and wrap it in a bandage. Apply to the vaginal opening for 4-5 hours or overnight.
Elena Malysheva will tell you more about inflammation of the Bartholin glands.
Cabbage compress
An effective folk remedy is treatment with cabbage leaves. You need to take a thick sheet and pour boiling water over it. Apply it to the inflamed area overnight. It is most effective to combine such treatment with the use of antibacterial therapy.
Features of treatment at different stages
In some cases, an unauthorized opening of the abscess occurs, which entails an improvement in the general condition. But this does not mean that you do not need to visit a doctor, because the neoplasm sometimes opens not outward, but inward, thereby melting the tissue, and this will require other specific therapy.
At the initial stage of development of the disease, the patient will need to adhere to bed rest and limit physical activity. Local procedures using cold compresses and taking antibacterial drugs are also required.
The disease, which occurs at stage 2, is also treated on an outpatient basis. If there is a serious inflammatory process that occurs with severe intoxication syndrome, the woman may be sent to a hospital. At stage 2, antibiotic therapy and local treatment with ointments are prescribed. If necessary, the affected gland is opened on an outpatient basis.
At the third stage of bartholinitis, hospital treatment is required. The abscess is opened surgically and an artificial excretory duct is created.
Bartholinitis, treatment at home with medications
Let us repeat once again - bartholinitis is a serious infectious disease of the genitourinary system, requiring mandatory examination by a specialized doctor with subsequent treatment. But if the illness takes you by surprise or a trip to the hospital is postponed for a couple of days for reasons beyond your control, you can use medications that each of us probably has in our home medicine cabinet.
Treatment of bartholinitis with ointments
To disinfect and relieve inflammation during bartholinitis, three main ointments are used:
- Vishnevsky liniment;
- Ichthyol ointment;
- Levomekol ointment.
It is not enough to simply lubricate the affected area; you need to apply a gauze swab soaked with a medicinal agent to the swelling. Repeat the procedure three times a day.
Important! Use the first two ointments alternately to treat bartholinitis in the initial stage, and apply Levomekol in case of spontaneous opening of the abscess to speed up the healing process of the wound.
Most alternative medicine methods are unable to overcome pathogenic microorganisms that cause inflammation. Moreover, if the disease is a consequence of STDs (sexually transmitted diseases), then you first need to completely get rid of this problem, because otherwise the treatment of bartholinitis will be ineffective. Without determining the type of infection, it is impossible to achieve good results, so only supportive and preventive procedures can be carried out at home. The main therapy should be prescribed by your gynecologist.
Is it possible to cure bartholinitis at home?
What is bartholinitis? Is treatment at home possible, or is it necessary to stay in a hospital? What kind of disease is it, how does it progress? What studies are used to diagnose, what tests are required to be taken in order for adequate therapy to be prescribed? Such questions are asked by those who have had to deal with the disease.
If the disease becomes chronic, it will be quite difficult to get rid of it.
In most cases, chronic bartholinitis is treated with surgery, during which the gland must be completely removed.
Causes of the disease
The main root causes of bartholinitis are a variety of infections. Harmful microorganisms enter a woman’s body due to a decrease in the immune system. However, more often infection occurs through sexual contact. Typically, the disease is caused by the following microorganisms:
- Trichomonas;
- streptococcus;
- gonococcus;
- Klebsiella;
- coli;
- staphylococcus
Bartholinitis in women develops against the background of other diseases that significantly reduce the level of immunity. The risk of infection increases if the patient has been diagnosed with the following concomitant pathologies:
- Diabetes mellitus leads to deterioration of the immune system;
- IDS (immunodeficiency states) can be primary or secondary - against the background of various diseases;
- non-compliance with the rules of intimate feminine hygiene, which provokes the development of vaginal dysbiosis;
- unprotected sexual intercourse, since many microorganisms that cause bartholinitis are transmitted sexually.
Important! The disease can develop in a healthy woman who has one sexual partner. The infection appears from hypothermia, lack of vitamins, or stress.
Operational assistance
Chronic bartholinitis can be cured only through surgery. This is especially necessary if the pathology occurs in combination with a formed cyst. Conservative therapy in such cases does not bring a positive result. Surgery is the only way to recovery.
The operation is performed only in cases of chronic and advanced pathology.
Surgery is performed only after excluding concomitant chronic pathologies. To do this, before its appointment, the woman undergoes a gynecological examination, takes a smear and other tests for the presence of infections. If the latter are present, treatment begins, and only after the infection is eliminated, surgery is performed.
Today, there are 3 methods of surgical treatment of bartholinitis: excision of the abscess, excision of the gland as a whole, excision of the abscess with restoration of the duct. The first technique (abscess excision) is the least traumatic among the others. In this case, only the neoplasm is removed, preserving the Bartholin gland. The only negative is the long formation of a new duct for the gland.
The most radical method of surgical intervention is complete excision of the Bartholin gland. In this case, the risk of relapse can be completely eliminated. The main negative consequence of the operation is the cessation of secretion production necessary to moisturize the vagina. It is for this reason that this method of therapy is used extremely rarely.
Excision of the abscess with restoration of the duct involves preserving the gland and creating a new duct that will facilitate secretion. For this, a special mechanism is used - a catheter, which is inserted into the tissue of the labia minora, which allows the creation of an artificial duct. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. A catheter is inserted for up to 1.5 months. During this period, a natural new duct is formed.
After surgery, a person will need to take antibiotics to prevent the development of secondary infections, and apply applications and compresses with ointments prescribed by the attending physician. In addition, physiotherapeutic procedures are often prescribed in the postoperative period, for example, magnetic therapy, phonophoresis, UHF, etc.
Traditional methods for bartholinitis
Traditional methods can be used only at an early stage and exclusively in combination with a treatment regimen from a doctor. The following remedies will help you recover:
- Grind aloe leaves to obtain about 200 g of raw material. Add 350 g of honey and 300 ml of red wine. Boil the mixture for about 1 hour in a water bath. Strain, take 1 tbsp half an hour before meals. l. Repeat the procedure throughout the official treatment.
- Mash half a piece of black bread without crust, add 1 tsp. honey and chopped garlic clove. Using a gauze swab, apply the mixture to the inflammation, secure with a band-aid, and leave overnight. Continue until the abscess comes out.
Prevention of bartholinitis
It is always better to prevent a disease than to fight it later. To protect yourself from inflammation of the Bartholin gland, treatment following diagnosis of the disease, you need to follow the recommendations given below.
Only cotton underwear should be worn. If there are diseases of the genital organs, you need to treat them without delay.
Monitor your health and promptly stop outbreaks of chronic infections - caries, tonsillitis and sinusitis. Eat well - this way your body will receive a sufficient amount of vitamins and microminerals, which will help avoid inflammation.
Do not weaken your body with alcohol and smoking, including passive smoking. Temper it by playing sports. This will strengthen your immunity and protect the body.
Conservative way
Drug treatment of the disease is considered effective if you consult a doctor in a timely manner. To avoid possible complications, you should contact a gynecologist if a small lump occurs in the labia or at the entrance to the vagina.
Bartholinitis is treated in a hospital setting. Drug therapy is aimed at:
- reduction of pain syndrome;
- reduction of the inflammatory process;
- preventing intoxication of the body.
Timely treatment of bartholinitis allows you to avoid the formation of a Bartholin gland cyst and abscess. Vishnevsky ointment and Levomekol are effective as local treatment. The ointment should be applied to the inflamed area in the form of a lotion. To do this, apply a thin layer of the product onto gauze folded several times. Keep the ointment for 20-30 minutes.
Chlorhexidine, Miramistin and Chlorophyllipt have an antibacterial effect. These solutions should treat the source of inflammation 2 times a day.
For bartholinitis, doctors prescribe drugs from the cephalosporin group, namely Ceftriaxone, Cefuroxime and Cefotaxime. These agents have a bactericidal effect and prevent the proliferation of bacteria. The dosage and course of treatment are prescribed by the doctor depending on the scale of the inflammation. In case of overdose, side effects are possible: increased body temperature, digestive upset and allergies.
Treatment with antibiotics shows good results, so drug therapy includes taking fluoroquinolone antibiotics. This group includes Ofloxacin, Levofloxacin and Ciprofloxacin. The drugs have an antimicrobial effect due to the destruction of the cytoplasm and membrane of bacteria. Taking medications is contraindicated during pregnancy and while breastfeeding.
In addition to antibacterial therapy for bartholinitis, desensitizing treatment is prescribed with drugs such as Suprastin, Diphenhydramine, Diazolin and Claritin. For severe pain, doctors recommend taking Spazmalgon or Analgin.
Phytoset, Novopassit and valerian tincture are prescribed as sedatives. Conservative treatment also includes taking immunomodulatory drugs: Timalin, Viferon and Taktivin.
Tactics for prescribing antibacterial drugs
There are about ten groups of antimicrobial drugs, differing in their spectrum of activity, toxicity, list of contraindications and side effects. The ability of pathogenic bacteria to develop resistance to the effects of medications is of great importance. Ideally, antibiotics for bartholinitis are prescribed as follows:
- The gynecologist takes a smear of the vaginal mucosa or purulent discharge from the gland if the duct is patent.
- In the laboratory, the material is sown on dishes with a nutrient medium and antibiotic solutions.
- Depending on the degree of growth of colonies of microorganisms, conclusions are drawn about the activity of the drugs.
It should be noted that this process takes about 3 – 5 days. With the acute development of bartholinitis with high fever (up to 39°), intense pain, an increase in the size of the gland and symptoms of general intoxication, delay is fraught with serious complications. Therefore, it is necessary to decide which antibiotics to treat based on the most likely causative agent of the bacterial infection. Before starting therapy, pay attention to the following factors:
Features of the treatment of acute bartholinitis Metronidazole (Trichopol, Flagyl) is taken 250 mg twice a day for 7 - 10 days. Tablets are not recommended in the first trimester of pregnancy, in case of chronic renal and liver failure. According to doctors, if there are such contraindications, suppositories or cream applications should be used on the area of the inflamed gland. The most common side effects are disturbances of the vaginal microflora and allergic reactions.
Inflammation during pregnancy
If there is any hint of inflammatory processes in the Bartholin gland, women carrying a child should consult a doctor as soon as possible. A disease such as bartholinitis has the same symptoms during pregnancy as in the normal state, so it will not be difficult to recognize the disease. It is very important to do this, since this disease, which developed between the fifth day from the moment of conception and the thirteenth week, can lead to fetal death.
Regarding the issue of treating bartholinitis in pregnant women, an individual approach is required in each case. If it so happens that during the period of inflammation the impact of other vaginal infections is discovered, there is reason to think about surgery.
Traditional medicine
Bartholinitis is a dangerous disease, so its treatment should be supervised by a specialist. Treatment of bartholinitis depends on its form, as well as the general condition of the patient.
In acute forms of the disease it is recommended:
- The use of drugs with anti-putrefactive action and lotions with antiseptics;
- Taking antimicrobial drugs that are prescribed after identifying the causative agent of the infection;
- Physiotherapy. Microwaves and UHF are most often prescribed. It is recommended only at normal body temperature, as well as during the period of subsidence of inflammation;
- Taking painkillers;
- Surgical treatment and rinsing with antiseptic solutions.
To treat the chronic form of the disease, it is recommended to use the following methods:
- Physiotherapeutic procedures including paraffin, ozokerite and infrared laser;
- Baths based on natural herbs and anti-inflammatory agents;
- When a cyst forms, surgical restoration of gland function is recommended;
- Treatment of concomitant diseases of the genitourinary system;
- Taking general strengthening and immunostimulating drugs.
Treatment of the disease should be carried out only after a thorough diagnosis, as well as under the supervision of an experienced specialist.
The essence of the disease, according to an obstetrician-gynecologist, is described in this video.
Bartholinitis during pregnancy
Usually the disease develops against the background of infections that have a detrimental effect on the unborn child. With this disease, the protective systems of the expectant mother will not always be able to fully work and prevent pathogenic effects on the fetus. Infection of the baby can occur in utero.
Important! At the first symptoms of pathology, a woman should urgently consult a doctor.
Preventive measures
Perhaps some ordinary people will be interested in how bartholinitis manifests itself in men. The symptoms of this disease, it is worth noting, are not characteristic of the male part of the population. The fact is that representatives of the stronger sex do not have Bartholin's gland, which means they are not threatened with bartholinitis. But in men, the bulbourethral glands can become inflamed, although this happens extremely rarely.
As part of the prevention of bartholinitis in women, the following measures will be relevant:
- rejection of bad habits;
- good nutrition and strengthening the immune system;
- examination by a gynecologist on an ongoing basis;
- immediately visit a doctor if you suspect infection;
- a thorough approach to personal hygiene;
- use of products that protect against sexually transmitted infections.
Clinical picture
Symptoms of bartholinitis are expressed to varying degrees, depending on the intensity of the inflammatory process. They appear acutely, often after hypothermia, menstruation, childbirth, abortion or unprotected sexual intercourse. First, a woman feels tingling, pain, heat, heaviness in the labia, which intensifies with movement and makes sexual intercourse painful or impossible. Along with this, general health worsens: body temperature rises to 38 degrees C, appetite disappears, headaches, and general weakness occur. Gradually, the pain in the perineum increases, becomes pulsating, the woman finds it difficult to walk and sit, and night sleep is disturbed.
Acute bartholinitis in most cases develops on one side. The labia majora at the site of the gland swells, increases in size, and its skin turns red. In the thickness of the lip, a painful lump ranging in size from one to several centimeters is felt - the gland itself. If the inflammatory process does not involve the surrounding tissues, then the skin above it is mobile and easily moves. When subcutaneous fat is involved, the epidermis becomes fused with it and loses its mobility. Often the inguinal lymph nodes react to inflammation; they increase in size and become visible in the form of round, dense formations under the skin. After some time from the formation of an abscess, it may burst outward with the flow of yellow-green pus.
After acute inflammation subsides, the disease enters the chronic stage. At first, the symptoms completely disappear and the woman feels healthy. This period of calm lasts from several months to several years, but any decrease in immune defense leads to an exacerbation of bartholinitis. Pain and swelling in the labia area, discomfort when walking, sitting, and sexual intercourse reappear. The temperature does not always rise and does not reach high values. As a rule, general health does not suffer.
Sometimes the inflammation is mild and occurs unnoticed by the woman or with minimal symptoms that are easy to miss. If, as a result of the disease, the patency of the gland duct is disrupted, then the gradual formation of a cyst begins. In the thickness of the labia majora, at its base, a subcutaneous volumetric formation of a round shape appears, painless to the touch, not fused with the surrounding tissues. It bulges outward, partially covering the entrance to the vagina. If both Bartholin glands are affected, the vestibule can be completely blocked, and sexual intercourse becomes painful due to the dryness of the external genitalia.
Etiology and risk factors
Inflammation of the Bartholin gland is caused by various microorganisms. The inflammatory process can be caused by:
- 1Sexual infections (gonococci, trichomonas, chlamydia, mycoplasma, ureaplasma, and so on).
- 2 Opportunistic microorganisms, components of normal microflora (staphylococci, streptococci, E. coli).
- 3Polymicrobial associations (mixed infection, the most common option).
Not all women suffer from bartholinitis; predisposing factors are necessary for the disease to occur.
These include:
- 1Microtraumas in the area of the vaginal opening, labia majora. They can form due to unsuccessful shaving, hair removal, itching in the perineum (scratching), sexual intercourse without preliminary preparation of the woman and sufficient moistening of the vaginal opening.
- 2Wearing uncomfortable, tight underwear made of synthetic fabrics.
- 3 Neglect of the principles of intimate hygiene, especially during menstruation.
- 4Inflammatory diseases of the urogenital tract (vulvitis, vaginitis), copious discharge facilitates the penetration of infection into the lumen of the gland duct.
- 5Chronic foci of infection in the body.
- 6Decreased immune strength of the body (diabetes mellitus, long-term hormonal or antibacterial therapy, taking cytostatics, radiation therapy and other causes of immunodeficiency).
- 7 Failure to comply with the rules of asepsis and antisepsis when performing gynecological and/or urological surgical interventions.
When an infection penetrates the ducts of the Bartholin gland, an inflammatory reaction develops with all its inherent manifestations (hyperemia, swelling, pain, local increase in temperature, development of an adhesive process). The glandular epithelium “tries” to get rid of foreign microorganisms through increased secretion. The secreted secretion contains living and dead microbial bodies and a large number of leukocytes.
With further spread of infection, the surrounding tissue is involved in the inflammatory process. To delimit the pathological focus, the body forms a capsule with purulent contents - an abscess. The increase in edema and gradual thinning of the capsule lead to the opening of the abscess and the removal of pus to the outside.
After this, 3 outcomes are possible: 1) cure and recovery, 2) chronicity of the process, 3) spread of infection to surrounding tissues.
Treatment of Bartholin's gland with folk remedies
If there is an inflammatory process, you should not self-medicate.
All recipes for folk remedies must be agreed with a gynecologist. Medicines containing natural ingredients are an addition to the main course of treatment for bartholinitis.
At home, you can use the following methods:
- sitz baths;
- products for internal use;
- compresses;
- lotions.
Baths
To relieve symptoms of inflammation, eliminate pain, and antiseptically treat the Bartholin gland area, sitz baths are used. Important requirements for treatment at home:
- procedure time – 15 minutes;
- application – daily;
- composition temperature – 37 degrees;
- Duration of the course is until symptoms are eliminated.
You can make a decoction for baths using the following recipes:
| Action | Cooking method |
| Wound healing, soothing, analgesic |
|
| Disinfectant | Dissolve potassium permanganate granules in warm water to obtain a pale pink composition |
| Anti-inflammatory |
|
Lotions
Using products with natural ingredients in the treatment of bartholinitis helps relieve pain, relieve swelling, and draw out pus. The lotions are applied 4 times a day and kept for 30 minutes. You can make a hypertonic solution - dissolve 3 tablespoons of salt in a liter of water. Recipe for lotions for home treatment:
- Mix equal parts of plantain, walnut, sweet clover, and chamomile flowers.
- Pour a spoonful of the mixture into a glass of boiling water.
- Leave for an hour.
- Strain.
Oral preparations
| Preparation of the composition | Application | |
| Herbal collection | 1. Mix herbs:
2. Take 2 spoons of the mixture. 3. Add half a liter of water. 4.Cook for 15 minutes. 5. Leave for an hour, strain. |
|
| Aloe decoction in wine |
|
|
Videos on the topic
Bartholinitis is an infectious disease in which the gland near the entrance to the vagina becomes inflamed. The causative agent of the disease is E. coli, streptococci, staphylococci and other types of infections.
Bartholinitis can occur at any age, but is most often observed in women of childbearing age. At the first signs of the disease, it is recommended to visit a gynecologist. After a thorough diagnosis, antibacterial treatment is prescribed.
It is effective to use not only pharmaceutical drugs in treatment, but also effective home recipes.