Ear wax is a very common situation. For a long time, until this conglomerate, consisting of a secretion product of special ear glands, blocks the ear canal, a person does not even know about it. He begins to notice it when the accumulation of sulfur increases either on its own, blocking the passage for air and sounds, or when water gets into the ear, causing the conglomerate to swell. Then the person notices that he has difficulty hearing in one ear, feeling congestion in it, his own voice takes on a sound “like coming out of a barrel,” and dizziness and nausea may appear.
In this case, trying to clean the ear with dense instruments is a bad idea: in this way you can only push the conglomerate further, where the diameter of the passage is even narrower. Removing wax plugs at home is only possible by dissolving it with means such as 3% hydrogen peroxide or the like. It is better for the child not to risk removing the accumulation of sulfur on his own, but to visit an ENT doctor, since in childhood the reasons for the formation of such conglomerates are different, and under the plug there may well be otitis media and even perforation of the eardrum.
After washing out the compressed sulfur with a warm solution of sodium chloride, furacillin, dioxidine or warm boiled water (if the washing was done at home), the hearing will not immediately return to normal. There will be a temporary feeling of stuffiness after this procedure, which will go away later.
Ear structure
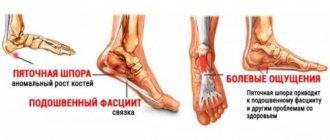
The external auditory canal is a “tube” that is a “conductor” of sounds from the external environment to the area of the eardrum. Its initial section is framed by the ear cartilage, which serves as a kind of “locator” that collects and conducts sound waves. Closer to the eardrum, the auditory canal already lies inside the temporal bone, so this part of it is called the bony part. Here, sound vibrations are transmitted to the eardrum, it vibrates and transmits this to the bones, and their swaying sets in motion a special fluid that is located in the inner ear, in the so-called “cochlea”.
Since the main part of the ear is located in the cranial cavity, not far from the brain, and is an almost open structure (only the eardrum separates it from the external environment), the body tried to protect the ear canal as much as possible from the possible entry of microbes. For this purpose, in addition to the sebaceous and sweat glands, there are special glands - sulfur glands; there are about 2 thousand of them in each ear. Their secretion, being viscous, ensures that microorganisms, dust or accidentally flying small insects stick to it. After immobilizing potentially harmful substances, earwax treats them with antimicrobial substances, and then it must be gradually removed from the ear during jaw movement (when we chew or talk).
The sulfur glands have the same feature as the sebaceous glands: if you constantly cleanse the skin of the products they produce, it will “tell” the nervous system that there is not enough secretion, and the latter will stimulate the glands to work even harder. Normally, only 15-20 mg of sulfur is produced per month and it is removed on its own: a person only needs to periodically wash his ears and blot them with a napkin.
Effective folk methods
Traditional methods for removing wax plugs can be quite effective, but they should be used with extreme caution. They are designed to quickly remove wax, but not to treat various ear diseases.
For prolonged pain in the ear, severe headaches, bloody and purulent discharge, any traditional methods can be used only after consulting a specialist.
Folk remedies:
- Almond oil. An effective remedy that helps painlessly break through even significant accumulations of sulfur. Natural almond oil will help to effectively moisturize the ear mucosa, soften and dissolve even large plugs. A small amount of oil needs to be warmed up a little and dripped into the ear while warm, 5-7 drops each, then insert a cotton swab. This procedure can be carried out 3 times a day. If it does not help, you can carry out the washing procedure after 2-3 days.
- Wax funnel. The principle of operation of this method is the same as that of candles for removing plugs. A piece of wax-impregnated tissue folded into a funnel is inserted into the sore ear and set on fire. Candles bought in a store have a protective stop; when using funnels, you need to be careful not to let the wax drip. When exposed to wax and heat, the sulfur plug softens and stretches. This procedure can be carried out several times.
- Soda solution. This method is not used for ear drops, but for rinsing. To do this, you need to draw a weak soda solution into a rubber bulb or syringe (without a needle). When washing the ear, the water pressure should not be directed at the eardrum, but should flow only along the wall of the ear canal.
What is earwax made of?
Before we tell you how to remove wax plug, here are a few more interesting features about it. So, it consists of:
- fats, primarily cholesterol;
- proteins;
- desquamated skin cells;
- enzymes;
- hyaluronic acid (a substance that attracts water and retains it);
- immunoglobulins and lysozyme - structures that protect against viruses and bacteria.
After the onset of puberty, the secretion of the sulfur glands of men and women begins to differ in content. In women, it should be such that it would provide her sulfur with a more acidic pH. Also, the composition of this secretion will differ among representatives of different nationalities.
What is not recommended to do
The presence of wax plugs can cause quite serious complications.
In addition to frequent headaches and hearing impairment, this condition significantly increases the risk of developing various inflammatory processes. Their treatment involves fairly long-term therapy.
Complications and negative consequences can only be avoided if this problem is addressed in a timely manner.
What is not recommended to do if there is wax in the ear canal:
- Ignore the appearance of wax plugs;
- Clean your ears, remove wax with cotton swabs and other objects;
- If there are first signs of complications, postpone a visit to the otolaryngologist.
Why do sulfur plugs form?
It is not enough to simply clean the wax plug: if the conditions that provoke its occurrence are not removed, it will form again, which will affect the quality of life. So, the following factors provoke compression of the secretion of the sebaceous glands and blockage of the ear canal:
- Poor ear hygiene. This is the most common cause of wax buildup, especially in children. Improper hygiene means:
- frequent irritation of the skin of the ear canal with an ear stick or hard improvised means, which further increases sulfur formation;
- pushing wax deep into the ear canal with cotton swabs, matches, rods, pins;
- You need to clean your ears no more than 2 times a week and you should do this by simply blotting your ear, which has been washed under water, with a clean napkin or towel.
- Genetic predisposition. It may consist of one of the following factors:
- the more viscous composition of the secretion of the sulfur glands, inherited, will accelerate the process of clogging of the ear canal;
- genetically programmed narrowness or excessive tortuosity of the ear canal will also contribute to the accumulation of sulfur;
- the growth of a large amount of hair in the ear canal is not always a sign of atherosclerosis; sometimes it is inherited;
- if sulfur is formed of normal consistency, but a lot of it is secreted, it can also be compressed into a conglomerate - sulfur plug.
- High humidity or frequent exposure to water (for example, among divers or swimmers) in the ears leads to swelling of the volume of wax that the body has prepared to come out. If you recognize yours in this situation, you need to take care to remove the sulfur plug as soon as possible: conditions of high humidity are created between the eardrum and the conglomerate, in which microbes that enter with water quickly multiply. Antimicrobial molecules from sulfur are unable to resist this.
- Being in an area with changes in atmospheric pressure also contributes to the formation of traffic jams. This is due to vibrations of the eardrum, which, either retracting inward (if the pressure decreases) or bulging outward (if it increases), helps to compact the sulfur secretion.
- Elderly age. Sulfur plugs are formed due to a combination of three reasons:
- deterioration of ear hygiene;
- hair growth in the ear canal;
- more viscous secretion.
- Frequent inflammatory diseases of the ears, which change the viscosity and pH of earwax, are the second main cause of ear plugs in children. This is why you should not remove wax plugs for a child at home: inflammation may be “hidden” under it.
- Working in a dusty factory. Earwax is a viscous substance, so dust particles easily stick to it, forming a dense conglomerate. In addition, when the existing sulfur is quickly covered with dust, the body “gives the command” to form even more sulfur, which further increases the sulfur conglomerate.
- The use of headphones, frequent conversations on the phone, especially through the Blue mechanism. In this case, a person deliberately “disconnects” the auricle from participating in sound transformation; in addition, the device increases the humidity in the ear canal.
- Increased blood cholesterol levels. This both causes excess hair growth in the ears (the mechanism is unclear) and increases the amount of wax produced.
- Skin diseases (eczema, psoriasis, dermatitis), which, affecting the area of the ear cartilage or the cartilaginous part of the ear canal, complicate the removal of wax from the ears.
How to properly remove wax from the ear
Often the cause of plug formation is the inability to properly clean the ears. In order not to harm your own body, you must observe the following measures:
- Wax can only be removed from the outside of the ear.
- Do not put objects into the ear canal.
- If there is an ear plug and it is not possible to remove it at home, you should consult a doctor.
- Never clean your ears with sharp objects.
- Dress appropriately for the weather to prevent hypothermia.
Types of sulfur plugs
These conglomerates may be:
- pasty: soft, light or dark yellow;
- plasticine-like: their color is brown, and their viscosity is like plasticine;
- solid: they contain practically no water, and the color can vary from dark brown to black;
- epidermal. This is a special phenomenon, the origin of which is not clear. This plug consists of sulfur, particles of the upper layer of skin (epidermis), has a gray color, stony density and often causes inflammation of the middle ear. Scientists believe that these formations occur either in people with congenital syphilis, or in those who have other general biological changes in the body (deformations of nails, teeth). Often such masses form on both sides and are capable of growing towards the eardrum, destroying it.
When an ENT doctor examines the ear, he evaluates which plug is present in this particular case. So he decides whether the sulfur conglomerate can be washed out, or whether it will have to be removed using a dry method.
<Symptoms in children and adults
Now we need to consider the symptoms that occur with congestion. Until the plug completely blocks the passage, no symptoms will occur. If water gets into the ear, the plug can close the passage, and then the problem will make itself felt.
- You will feel an unpleasant sensation, as if something is bothering your ear.
- Hearing decreases sharply.
- If the plug is very hard, it puts pressure on the ear. As a result, headaches, nausea, dizziness, otitis media, and neuritis occur.
- If the plug is not removed for a long time, inflammation of the middle ear may occur.
- Atrophy - when you hear your own voice in the ear.
If the plug occurs in children, they may periodically complain of pain that occurs in the ear, ringing and noise. Babies may also scratch their ears frequently. But it is worth noting that if a child often asks again, does not hear the call of his parents, or may flinch when someone appears nearby, then you need to pay attention to this. If a child constantly touches his ears, this also indicates the presence of plugs. Therefore, you need to carefully examine your ear. It is better to take the child to an otolaryngologist.
How is atrophic pharyngitis treated?
Find out if you can walk with your child with a runny nose.
Causes of dry cough in the morning in an adult: .
How does wax plug manifest itself?
Signs of wax plugs in the ear usually do not appear until the conglomerate fills the entire lumen of the ear canal. They usually appear after swimming or washing your hair, when water gets into the ear and causes the wax to swell. This:
- loss or significant decrease in hearing in one ear;
- noise in the ear;
- feeling of ear fullness;
- obsessive feeling of removing a foreign body from the ear canal;
- a person begins to hear the echo of his own voice in his ear.
Symptoms of a condition where wax plugs in the ears have developed directly near the eardrum and put pressure on it are as follows:
- dizziness;
- yawn;
- cough;
- nausea (as with motion sickness in transport);
- lack of coordination;
- headache;
- There may even be a disturbance in cardiac activity, since the work of the heart is reflexively connected with the nerve endings approaching the ear.
If the accumulation of sulfur exists for a long time, or it was able to create conditions in the ear for the development of microbes, inflammation of the middle ear develops, manifested by pain in it, a feeling of “transfusion” or “gurgling”, the appearance of discharge (sometimes purulent) and an increase in temperature.
If, based on all the symptoms, you see that the child has sulfur plugs, what should you do? The only possible solution is to visit an ENT doctor; fortunately, for this you do not have to wait in line at the clinic, but you can make an appointment (for the same day) with an otolaryngologist at a private clinic. This doctor will conduct a diagnosis, quickly and competently remove the formation, after which he will re-examine the ear for otitis media and prescribe appropriate treatment. Remember: otitis media is a disease that is dangerous due to its complications, especially those that can develop in the cranial cavity. Therefore, self-medication, especially in children, is unacceptable.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of accumulation of excess sulfur in the ear canal is the same in adults and children. The main symptom is stuffy ears. Hearing is lost partially or completely, which is determined by how tightly the infiltrate has closed the ear canal. Against this background, a person may feel rustling. In addition to hearing loss, the following signs of wax plugs in the ear stand out:
- headache, tinnitus;
- cough, dizziness, nausea, heart rhythm disturbances - observed with deep penetration of sulfur and involvement of the eardrum in the process;
- autophony - your own voice is heard like a ringing in your head.
Diagnostics
Determining that a child or adult has a plug in the ear is very simple. An ENT doctor may suspect this diagnosis based on complaints alone, and then confirms it with an otoscopy examination. This is an examination of the ear using a funnel or a special light device that does not touch the ear. If the doctor needs to examine the ear without removing wax yet, he can enter it with a special button probe.
No other studies (ultrasound, x-ray or others) will help make this diagnosis.
Hydrogen peroxide
You can remove ear plugs at home using hydrogen peroxide. The solution should be 3% to avoid burning the ear canal.
It is necessary to fill the pipette with peroxide and take a lying position. Apply drops to the ear and cover with a cotton swab; do not push the swab deep into the ear.
Immediately after instillation, a hissing sound and a slight tingling sensation may appear in the ear. This is a reaction of hydrogen peroxide, if there is no pain, there is no need to worry.
It is necessary to drip into the ear for a week. The cork will dissolve and come out on its own.
Treatment
To get rid of the conglomerate formed by the “efforts” of the sulfur glands, it must be removed. The doctor can do this using two methods – “wet” or “dry”.
"Wet method"
This way you can wash out the wax plug. The method is painless, but unpleasant. It consists of the following:
- the patient sits on a couch or chair, turns to the doctor with the sore ear;
- an oilcloth is laid on his shoulder, on which a metal kidney-shaped tray is placed;
- the doctor fills a large syringe (Zhanet) without a needle with a warm sterile solution;
- inserting its tip into the ear, injects a stream of solution along the upper wall of the auditory canal.
In some cases, this procedure does not immediately clear the accumulation of sulfur, which requires repeating it two or three times. Between procedures, the ENT specialist may recommend dropping drops into the ear:
- 3% hydrogen peroxide 2-3 drops 3-4 times a day. The solution should remain in the ear for 2-3 minutes, after which it is drained;
- A-Cerumen: 1 ml in each ear (1 bottle will be used immediately for 1 instillation) twice a day. A-Cerumen is not used in children under 2.5 years of age;
- “homemade” or prescription (ordered in special pharmacies with a prescription department) drops consisting of 1 g of soda mixed with 20 ml of glycerin and 20 ml of boiled water.
"Dry method"
Sometimes the doctor has to pull out the wax plug. This is done in case of dry formations, only by an ENT doctor, under visual control. The doctor inserts a special ear hook into the ear, with the help of which the conglomerate is removed piece by piece.
Apple cider vinegar and rubbing alcohol
Some experts say that rinsing your ear with a combination of rubbing alcohol and apple cider vinegar is the most effective DIY ear plug removal remedy. Apple cider vinegar will help get rid of the infection as it has antibacterial properties. When combined with alcohol, it helps remove the ear plug.
To use this solution you will need:
- pipette;
- two tablespoons of apple cider vinegar;
- two tablespoons of medical alcohol;
- cotton balls;
- small towel.
- Combine rubbing alcohol and apple cider vinegar in a small cup.
- Pipette the solution.
- Lie down with the affected ear facing up. Drop in the solution.
- Place a cotton ball in your ear for a few minutes.
- Remove the cotton balls and then apply a towel to your ear.
- Tilt your head and remain in this position, allowing the liquid to flow out.
- Repeat as often as needed for relief.
What can you do at home?
You can try to get rid of wax plugs at home if:
- the ear does not hurt, but is blocked, and it appeared after water procedures;
- We are talking about an adult;
- when pressing on the cartilage of the auricle (tragus) sticking forward (closest to the face), it does not hurt;
- body temperature is normal.
For this purpose you can:
- For 1-2 days, drip the ear with peroxide, A-Cerumen or a soda solution (can be done without glycerin), as described above;
- find a ballpoint pen from which you can make a tube by removing the rod and those parts that hold the rod inside;
- get into the bath;
- adjust the water so that it is 37 degrees and the pressure is not strong;
- unscrew the shower head and place a straw from the handle in its place;
- carefully, tilting your head so that your ear “looks” down, pour water into your ear for about 3 minutes, holding the shower with one hand and the tube with the other, and the second end of the tube should be loosely leaning against the entrance to the ear canal;
- There should be no pain, you can also see how the plug comes out. You can “help” her by inserting the tip of your little finger moistened with water into the ear canal;
- even if this does not happen, do not try again immediately, it is better to re-drip the ear with 3% peroxide;
- if the plug comes out, you need to drip the ear with Ciprofloxacin, dioxidin from an ampoule, Okomistin or other antiseptic drops.
You can also buy a solution of furacillin or make it from tablets (you can use a physiological solution of sodium chloride, put it in a “bulb” syringe No. 14, place it in warm water so that it warms up to 37 degrees and rinse the ear with a gentle stream, without pain. At the same time, the second hand pulls the auricle back and up so that the stroke is smooth and the stream is not very strong.
Special herbal candles are officially approved for removing traffic jams at home and must be used with an assistant. They are hollow tubes with essential oils applied to the inner surface. One part of the tube has a tip and foil: it is inserted into the ear after lighting the upper section of the phytocandle. The candle must be removed and the flame must be extinguished when it reaches the mark on the candle body. The effectiveness of this method is 30-40%. It works by creating negative pressure in the tube during its combustion, which draws out the sulfur.
We do not recommend continuing any manipulations with your own ears at home if they were unsuccessful the first or second time or were accompanied by minimal pain. Otolaryngologists are accepted in many private centers, which are quite easy to get into after work and without any referral.
How to remove an ear plug
To avoid complications and injury, it is strictly not recommended to remove wax from the ear canal using hard and sharp objects. If the problem has arisen for the first time and there is no confidence in your own abilities, it is better to seek help from an otolaryngologist.
There are three main methods of cleansing:
- Rinse with water and antiseptic solutions.
- Dissolution of sulfur deposits with special preparations.
- Hardware dry cleaning techniques.
For a successful result, it is important to know how to properly remove wax plugs from the ear at home, so as not to harm yourself. Let's look at each method in more detail.
Washing
The easiest way to clear ear plugs is to wash them with water or medicinal liquid. In clinics, they are washed with a special Janet syringe with a rubber tube. At home, a disposable large syringe for injections without a needle is suitable.
How to rinse your ear with a syringe yourself:
- Stand near the bathroom sink or grab a basin.
- Fill a syringe full of boiled warm water or furatsilin solution at room temperature.
- Lean over the container with your affected ear. Pull the earlobe slightly up and back, inject the liquid into the ear canal under pressure.
- Rinse this yourself several times in a row.
- Dry with a towel and insert a shallow cotton swab for 10 minutes to dry the mucous membrane.
If the plug is small, it will pop out quickly and relief will come immediately. If necessary, the procedure for rinsing the ears from wax plugs is repeated several times throughout the day. If such manipulations do not help or cause pain, you should stop them and make an appointment with a doctor.
Home rinsing can also be done for children, but with extreme caution. Their ear canal is narrow, and the water inside causes some discomfort - the child can reflexively twitch and damage the mucous membrane. To avoid such a situation, it is better to contact a specialist.
Dissolving the cork
Removing ear plugs using dissolution involves the use of special drugs, called cerumenolytics in official medicine. Their action is due to the softening, crushing and dissolution of the sulfur mass inside the ear. Among the most popular are: Glycerin, Otinum, Vaxol, Debrox, A-Cerumen. They are sold in pharmacies without a prescription, but are used strictly according to the instructions.
Ordinary peroxide can provide home help for ear congestion. It also serves as a good solvent for uncomplicated conditions. The procedure is simple:
- put 5-6 drops of a 3% hydrogen peroxide solution into a pipette or any dispenser;
- lie on your side with your painful ear facing up;
- drop the liquid into the ear and lie there for 10-15 minutes, the feeling of hissing and stuffiness at this time is considered normal - this is how the medicine dissolves the sulfur;
- Apply cotton wool and carefully turn over to the other side so that the contents spill out.
Don't despair if the plug doesn't come out the first time. You can repeat the procedure 2-3 times a day. The main condition is that there is no severe burning or discomfort. For greater effect, dissolution is recommended to be used in combination with rinsing.
Dry removal
How can you break through an ear plug if popular methods are not suitable or do not help? There is an alternative option - the so-called dry removal. The following procedures are widely used in ENT practice:
- Vacuum aspiration is the suction of accumulated secretions using a special tube with negative pressure. The process is painless, the only negative is the loud sound during operation of the device. Indispensable for violations of the tympanic septum.
- Curettage - penetration into the auricle with a special curette to remove the plug mechanically. The procedure is unpleasant, so it is prescribed mainly when the sulfur has a hard consistency.
- Phytosuppositories – extraction of sulfur deposits using the vacuum principle. Cleansing is carried out using a funnel made of beeswax and essential oil. In a supine position, the ear is lubricated with moisturizing cream and covered with a napkin with a slit for the ear canal. The upper end of the candle is set on fire, and the lower end is placed against the passage. It remains in this position until it burns out to the mark, approximately 2/3 of the way. The ear is wiped and covered with a cotton swab for 15 minutes. The mechanism of action is to warm up and soften the cork, which makes it easier to come out. Additionally, phytocandles relieve excess pressure in the ear and improve well-being.
The first two procedures are available only in a clinical office. They require special tools and medical supervision. Phytofunnels are easy to use at home. You can prepare them yourself or buy them at any pharmacy.
Preventing traffic jams
Take the following steps:
- There is no need to clean the ear canal more often than once every 7-10 days. Do this with a cotton swab with a limiter, which is only slightly inserted inside the ear and rotated left and right, and not back and forth.
- Control your cholesterol levels.
- People working in dusty environments should protect their ears.
- Those who have to dive, use hearing aids, headphones, or be in conditions of high humidity periodically (once a month) need to use A-Cerumen drops or similar preparations.
- Get eczema, dermatitis or psoriasis treated promptly by qualified dermatologists.
Author:
Krivega Maria Salavatovna resuscitator
How to tell if you have a plug in your ear
There are not many symptoms of wax plug:
- hearing loss in the ear where the plug has formed;
- feeling of stuffiness;
- slight itching;
- perhaps ringing or noise in the ear;
- Sometimes there is pain that goes away fairly quickly.
These signs suggest that there is a plug in the ear, and not some other, more unpleasant process.
Please note: if you observe other symptoms - for example, fever, or acute pain that lasts for hours, or severe dizziness, or nausea - this is a direct indication for a visit to the otolaryngologist. Such symptoms may indicate otitis media or inflammatory processes in the nasopharynx. To avoid complications, including hearing loss, such diseases must be treated under the supervision of a doctor.
Possible complications of wax plug and prevention
Earwax is easier to prevent than to treat!
Wax plug is not inherently dangerous, but if it is not removed in time, it can lead to unpleasant consequences. It should be remembered that it is not so much the wax plug itself that leads to complications, but rather its incorrect and careless removal.
Complications of wax plug:
- Hearing loss. In some cases, the plug can cause inflammation of the ear canal, leading to partial or complete hearing loss. Hearing restoration is possible with long-term treatment.
- Neuralgia. If the plug is large and deep, it can put pressure on the auditory nerve. This leads to headache, dizziness, nausea, sometimes vomiting, and reflex cough.
- Inflammation. In some cases, aggressive washing can lead to an inflammatory process, which in turn can lead to hearing loss or otitis media. Inflammation is accompanied by pain in the ear canal and hearing loss.
- Perforation of the eardrum. Damage to the membrane can result from improper rinsing with strong water pressure, as well as attempts to remove the plug with tools and cotton swabs.
To prevent wax plugs from forming, you need to follow simple prevention methods. To begin with, you should not use hairpins or pins to clean your ears. They injure the ear.
Important! You can use cotton swabs, but the cleansing procedure is carried out only on the outside of the ear canal and auricle.
When swimming in ponds, rivers, or swimming pools, your ears should be protected from water. This contributes not only to the formation of sulfur plugs, but also to the penetration of infection.
You need to wear swimming caps or insert cotton swabs into your ears. If the work involves dust or industrial noise, you need to use earplugs or hearing protection.
Differential diagnosis
Differential (distinctive) diagnosis of wax plug is often carried out with such diseases and pathological conditions of the ear as:
epidermal plug - a formation that is formed from exfoliated skin cells lining the external auditory canal;
- foreign body - a foreign object in the lumen of the ear canal;
- ear tumors - benign and malignant (including metastatic - formed during the transfer of groups of cells from primary tumors, which can be located in any organs and tissues);
- cholesteatoma is a formation in the form of a tumor, which consists of a capsule surrounding a cavity filled with dead epithelial cells and some organic substances (keratin, cholesterol crystals stuck together into a single conglomerate).
Removal
Removal of wax plug must be carried out only by a specialist, because any incorrect actions can increase the risk of complications. The method of extracting the sulfur clot is chosen by the doctor based on the type of formation. For soft plugs, standard rinsing of the auricle using a syringe without a needle is used. A strong stream of warm water is applied through the instrument directly into the outer ear canal, after which the plug comes out on its own.
If the sulfur mass is too hard, then the clot is first softened with a-cerumen or hydrogen peroxide. There are cases when the formation cannot be softened or pierced using the usual method, then the plug is removed with a medical instrument - a probe hook or an electric suction device. This method is indicated for damage to the eardrum and is called “dry”, since a lump of wax is scraped off from the walls of the ear canal manually.
Normally, the ear should get rid of wax on its own, but situations arise when this substance begins to accumulate in the ear canal, and over time the lumen is completely blocked.
The person experiences severe discomfort.
1. When diving under water, a kind of pressure is generated, which affects the occurrence of a traffic jam.
2. Excessive cleanliness. The more often you remove wax from the ear canal, the faster it will accumulate again.
4. You are working in an area where there is a lot of dust.
5. Staying in a room with dry air for a long time.
6. Blood cholesterol levels are greatly elevated. Oddly enough, this also affects the formation of a traffic jam.
7. Anatomical features of the auditory canal - it is excessively tortuous.
8. Structure of the auricle.
9. Be sure to find out if any of your relatives have had problems with traffic jams.
10. Intensive work of the sebaceous glands, which are responsible for the development of sulfur. In this case, the auricle cannot clean itself, as a result, a cerumen plug is created.
There will be noise in the ears, and the head will periodically feel dizzy. The appearance of a reflex cough is possible.
You can even detect the presence of a plug visually; pull back your ear and look inside. If the cavity is clean, then there is no cause for concern, but when lumps are visible, you need to contact an ENT specialist as soon as possible.
There are a lot of products on the pharmaceutical market that are used to remove wax plugs. Under their influence, the sulfur plug dissolves, while doctors simply soften it. Among the majority of medicines, two drugs have proven themselves well - Remo-Vax and A-Cerumen.
Remo-Vax is produced on the basis of allantoin. It dissolves the plug well and also helps keep the ear canal clean. It is recommended for people with increased sulfur production.
The main advantage of this product is that it does not contain antibiotics, which means it can be used at any age.
Drops A-Cerumen (Nycomed) - removes wax well. After the drug gets inside, it will dissolve the plug, preventing it from swelling. The main advantage of the drug is its pre-calculated dosage. One bottle is designed to be dropped into the ear canal. The drops are completely safe; they do not cause irritation to the mucous membrane. They can be used by children starting from 2.5 years old.
The only contraindication is otitis media, as well as increased sensitivity.
You can also use special candles to remove the plug; they are sold at any pharmacy. Their peculiarity is that they are made on the basis of propolis.
Before looking for ways to remove a traffic jam at home, you need to carefully study all the available methods, as well as the sequence of their implementation. Many of them can be used at home. If you cannot perform any actions yourself, you can ask a family member to help.
Getting rid of wax plugs by rinsing
This procedure is quite simple. For ease of use, it is recommended to use a syringe without a needle, or a small bulb.
1. Stand in front of a sink or bathtub and lower your head with your affected ear over it.
2. Prepare a container of water in advance and fill it with a syringe. Use gentle pressure to release the air. Start pouring water along the walls of the ear canal.
Folk remedies
1. Take one small onion and grate it. Place the pulp in cheesecloth, squeeze out the juice well, then dilute it in warm water in a 1:1 ratio. After this, take the resulting product into a pipette and drop a few drops into the ear; you are allowed to do this no more than three times a day.
2. It is also recommended to dilute the resulting juice with vodka; if it is not available, then with boric alcohol, the dilution ratio is 1:4.
3. Pour sunflower oil into a spoon and melt it over the fire. Place a few drops into the sore ear for two or three days.
Hydrogen peroxide against wax plug
• Take a few drops of hydroperite into a pipette. Lie on your side with your healthy side down. Drop the resulting solution into your ear and place a cotton swab in it. It is better if you do these steps in the evening, before going to bed. The course of treatment is about one week.
• Rinse your ear.
• Wash the plug with a shower. Remove the watering can from the hose, turn on warm water and point it directly at your ear. Many people claim that after this the plug will come out immediately.
Phytocandles
Phytosuppositories can be purchased at any pharmacy or you can make them yourself at home. To do this you will need propolis, essential oil, beeswax and medicinal herbs.
Thanks to the effect of such suppositories, the hardened ear plug dissolves, inflammation and pain are relieved.
A positive effect can be achieved by heating the ear canal, as well as creating a vacuum that occurs when a candle burns.
• using baby cream, massage the outer ear canal;
• with the healthy side you need to lie on your side, cover your head with a napkin with a hole for the ear;
• insert the edge of the candle with the narrow side into the ear and set fire to its second part;
• wait until a little more than half of the candle burns out, then take it out and dip it in the prepared water so that it goes out;
• remove the remaining wax from the candle from the ear with a cotton swab;
• in order to retain heat, you need to insert a tampon into your ear and lie in this position for another 10-15 minutes. If you have pain in both ears, then at this time you can carry out the same procedure with the second.
• do not use candles under any circumstances if you have problems with the external auditory canal;
• pus has formed in the ear;
• the outer ear is injured;
• allergies may occur to bee products;
• the eardrum is damaged.
Self-blowing of the nose
If, after you have tried to soften the plug or performed the rinsing procedure, the wax plug still does not disappear, you can try self-blowing your nose.
To do this, you need to take a strong breath and pinch the wings of your nose with your fingers. After this, exhale as much as possible, the sulfur should come out.
But keep in mind that this procedure should be carried out with extreme caution; if you suddenly feel severe pain, consult a doctor as soon as possible.
In fact, getting rid of wax at home is quite simple, but think about whether you will cause even more harm. If you are not confident in your abilities, it is better to contact a specialist so that he can rid the ear of the plug with a special means.
• Remove earwax only from the auricle.
• The ear canal can only be cleaned from the outside.
• Once you suspect the presence of cerumen, you should definitely visit a specialist.
• Never use sharp objects to clean the ear.
• Avoid hypothermia.
The doctor should look at your ear canal and determine whether there is excess wax or not. If the suspected diagnosis is confirmed, the specialist will carry out professional cleaning.
Often, sulfur plugs form due to an inflammatory process, which is why it is necessary to carry out treatment in a timely manner. One of the preventative measures is the treatment of eczema and dermatitis. Get your blood tested once every few months to monitor your cholesterol levels.
If you remove earwax at home, be extremely careful not to damage the eardrum. Once the problem is resolved, follow preventive measures to prevent the blockage from forming again.
Drops for removing wax plugs in the ears
If a child has wax plugs and he is restless, then the doctor may prescribe drops into the sore ears that will dissolve the plugs. A-Cerumen is most often used.
Causes and symptoms of wax plug
Earwax is a collection of hardened earwax in the ear canal.
A certain amount of sulfur is constantly formed in the auditory canal. It gradually accumulates, dries out, particles of dust and microbes settle on it, and then this sulfur flakes off and comes out on its own. The removal of sulfur is also facilitated by cartilage, which moves during chewing and speaking; sulfur begins to be pushed out at this moment.
To understand how to remove wax plugs at home, you must first identify the reasons for its formation. In some cases, the reasons are related to improper ear hygiene, and all previous attempts to remove the plug will lead to even greater compaction.
Causes of wax plug:
- Cotton buds. The habit of cleaning your ears with cotton swabs leads to the fact that earwax is compacted and compacted even deeper, which leads to the formation of a plug. Attempts to remove the cork in the same way will not lead to a positive effect.
- Too active hygiene. Even if sulfur is removed carefully, but too often, the consequences will be negative. Frequent cleansing of the ear canal leads to stimulation of the glands, and more and more sulfur is released after each cleaning.
- High cholesterol. Improper metabolism and impaired cholesterol production can also lead to increased earwax production. In this case, traffic jams will form quite often.
- Unfavourable conditions. Ear plugs often form in people whose work involves dust or loud noise. Unfavorable factors activate the defense system, and sulfur is released in large quantities.
- Exposure to humidity. Earwax is more actively released and accumulates under the influence of moisture, for example, in swimmers who spend a lot of time in the pool, or simply when the air humidity is high.
Useful video - How to remove wax plug at home:
The formation of sulfur plugs is accompanied by characteristic symptoms. While the plug is small, no symptoms appear, but as soon as it blocks more than 50% of the ear canal, a feeling of stuffiness occurs and hearing decreases.
A person hears the resonance of his voice in his head, while extraneous sounds seem muffled. If the plug is large enough, headaches and dizziness may occur.
Candles
Special suppositories from the pharmacy help get rid of sulfur plugs. The product helps soften the seal and eliminate the inflammatory process. During the procedure, the inner ear is warmed up and immersed in a vacuum due to the burning of a candle.
To get rid of sulfur compaction, you must additionally prepare baby cream, cotton swabs and swabs, matches, a napkin and water. Next, the following actions are performed:
- Before removing the plug, the outer ear is massaged with cream.
- The person lies on his side, and the open ear is covered with a napkin with a cutout for the auricle.
- The lower edge of the candle is inserted into the ear, and the upper edge is lit with a match.
- A small part of the candle should burn down to the mark, after which it is removed from the ear canal and extinguished with water.
- Remove the remains of the candle from the surface of the organ with a cotton swab. To preserve heat, cover the ear with a tampon for 10 minutes.
Washing methods
There are different methods that help you both get rid of ear plugs that are interfering with the normal functioning of your hearing aid, as well as warm the ear as a whole.
Flushing with a syringe
Take an ordinary syringe without a needle and warm water. The syringe is filled with water and does not plunge too deeply into the ear canal. Next, the water pressure is released. Afterwards, the head tilts to the side, due to which the water flows out of the ear, washing out the plug along with it. The end of the procedure will be thoroughly wiping the ear with a soft cloth.
The procedure is daily, its course is one week. During this time, the cork is completely washed out by the liquid.
Washing with enema
To carry out the procedure, you will need a medium-sized hydrogen peroxide enema. The first step is for the person who has a plug in his ear to lie on his side for comfort. Next - instill 3 drops of peroxide into the clogged ear. Peroxide that gets into the ear dilutes the accumulation of wax. You should wait 5 minutes without changing your body position to achieve the maximum softening effect. Five minutes later, warm water is drawn into the enema.
The enema does not go deep into the ear (it rests against the ear canal - no further).
It must be squeezed as hard as possible to create a powerful pressure.
Particles of the plug during this action will be removed from the auricle along with the infused water.
If at the end of the procedure a person still feels discomfort, and his hearing has not fully recovered, the plug has not been completely removed. In this case, washing is carried out several more times until the unpleasant symptoms cease to bother you.
Rinsing with a shower hose
If you were unable to get rid of the blockages yourself using the previous methods, it means that the ear canal is too clogged.
In this case, rinsing with a shower hose without a spray nozzle will help quickly remove wax.
In order not to cause mechanical damage to the eardrum, it is important not to overdo it with increasing pressure.
The hose is placed close to the ear, and warm water is turned on. The pressure gradually increases. The procedure is highly effective, allowing you to remove wax blockage at home in one go. Immediately after the procedure, hearing is restored and unpleasant symptoms disappear.
Prevention
The following measures are the basis for preventing the occurrence of wax plug:
- prevention of damage to the external auditory canal, which provokes increased production of earwax - namely dermatitis, eczema, chronic external otitis. If they have already developed, their timely diagnosis and adequate treatment are necessary;
- proper ear cleaning;
- prevention and proper treatment of extranasal (extranasal) pathologies that can provoke increased production of earwax - endocrine disruptions, metabolic disorders, damage to the ear glands;
- preventing dehydration;
- in people with increased hairiness in the external auditory canal - timely removal (cutting) of hairs;
- choosing the right hearing aid;
- avoiding frequent use of headphones and earplugs;
- avoiding employment in areas that involve working in a dusty atmosphere;
- preventive examinations by an otolaryngologist even in the absence of complaints.
Despite the fact that cleaning the external auditory canal from wax is a fairly simple procedure, it should be carried out according to certain rules:
- earwax is removed only from the surface of the auricle and the area around the opening of the ear canal;
- If earwax accumulates in other places, it should be removed by a medical professional.
To prevent the problem from occurring, it is recommended to follow a few simple advice from doctors. It is very important to maintain proper hygiene by washing the ear with soap and water twice a week. Sticks should be used only to cleanse the external auditory canal, without pushing the accumulation of wax deeper into the ear canal.
Preventive actions
When it comes to what an ear plug looks like, prevention plays an important role. To avoid the formation of a sulfur clot, you should follow simple rules. First of all, it is necessary to carry out proper hygiene, which means washing your ears twice a week with soap. As for cotton swabs, they should be used to clean the outer part of the ear canal without going deeper.
In addition, you should spend as little time as possible in places where the climatic conditions are unfavorable (dry air, high humidity levels). And, most importantly, if you have any suspicious signs, consult a doctor.
Forecast
The prognosis for sulfur plugs is favorable. Any complications occur quite rarely, but there are cases of complications (in particular, intracranial ones) that require intensive care.
Kovtonyuk Oksana Vladimirovna, medical observer, surgeon, consultant doctor
7, total, today
( 47 votes, average: 4.60 out of 5)
Cyclamen juice for the treatment of sinusitis: how to prepare the medicine
Nose burn: causes, symptoms, treatment
Related Posts
Washing a child's ears
Irrigation is not easy for small patients because they cannot sit still. This procedure will require at least two people, the second one is needed to secure the baby. The adult sits the child on his lap and pinches his legs with his legs. One hand holds the child’s hands tightly, and the other holds the head in a certain position. Such measures are simply necessary, because if the baby twitches during the procedure, even a non-sharp syringe tip can damage the septum.
For young children, the same compositions are used when washing the ears, with the exception of the concentration and dose of the infused liquid. Children in the first years of life are often prescribed a solution of furatsilin.
Total information
Sulfur plug is not actually made of sulfur as a chemical element on the periodic table. Earwax is a mixture of secretions from glands that are found in the thickness of the skin lining the external auditory canal. The sulfur glands are located deep in the ear canal; their pure, unmixed secretion is similar to a milky substance and has a slightly creamy tint. In addition to sulfur, in the external auditory canal there are:
- superficial sebaceous glands, which produce so-called sebum;
- Apocrine sweat glands, which produce sweat.
The secretions of these glands are mixed with the secretion of the sulfur glands, as well as with keratinized particles of the skin epithelium that covers the external auditory canal. The end result is the characteristic yellowish discharge that millions of people around the globe patiently extract from their ear canals every day throughout their lives.
Normally, earwax performs a protective function - it prevents such negative changes in the external auditory canal as:
damage;
- drying of the skin;
- maceration – wet erosion of tissues;
- damage by pathogenic bacteria and fungi, as well as viruses, which can lead to the development of external otitis. Prevented by the fact that earwax is acidic;
- clogging of the external auditory canal with dirt, dust particles, and small foreign objects. Such blockage is prevented by the following: during chewing, talking or yawning, movements occur in the mandibular joint, located close to the external auditory canal, due to this, earwax moves outward along with small particles.
If a sulfur plug forms, it causes a failure in the described protective mechanisms.
Complications
Among the negative consequences are the following conditions:
- allergic manifestations in the form of a rash, itching of the skin, intolerance to the components of the sulfur solvent occurs;
- infection of the middle organ of hearing, with undetected perforation of the ear membrane;
- ear canal injury.
Unremoved serous blockage of the ear is fraught with the following complications:
- chronic otitis;
- increased sweating;
- headaches;
- throbbing pain in the ear;
- itching, burning in the area of the auditory organ;
- stenosis.
An incorrect rinsing method, as well as delayed treatment of wax plugs, can lead to the development of complications and worsen the patient's condition. For this reason, providing therapeutic assistance at home is not recommended. Most people are not aware of the likely consequences of developing a pathological process in the ear canal. The most common complications are:
- otitis;
- deafness;
- inflammation of the cartilage of the middle ear;
- tachycardia;
- burns;
- perforation of the eardrum;
- heart failure.
How to remove wax plug from the ear at home: medications
How to remove a plug from the ear correctly is written in the instructions for pharmacological drugs specifically designed for this. These agents are called cerumenolytic, and the process of removing the plug is called cerumenolysis.
Liquid medicine dropped into the ears should be warmed by holding it in your hands for 10 minutes or in a water bath. The optimal temperature of the product used for the procedure is 32-36°C.
Medicines containing oil components are used to remove and soften plugs during constant hygiene of the external auditory canal; they are not suitable for old plugs.
Remo-Wax. Instructions for use
The drug is used until the wax plug is completely removed. Depending on the density of the sulfur plug, it can be used in the morning and evening or up to 5 times daily. For prevention, Remo-Vax is used 2 times a month. The products are available in 10 ml bottles with a dispenser.
Main components: phenylethanol, sorbic acid, allantoin. Also contains lanolin, oils that soften sulfur plugs.
Instructions for using drops:
- The head is placed on its side and the ear is pulled down and backward by the lobe to “straighten” the ear canal.
- Place so many drops along the back wall to fill the entire ear canal, up to the borders of the auricle. It is impossible to instill the medicine in the center of the ear canal, as an air plug will form.
- You need to wait 20-60 minutes, then turn your head so that the solution can flow out of the ear onto the napkin. Wait for 1 minute until all the solution has flowed out.
Coloring of the solution after its removal is a normal process and is determined by the color of the earwax, i.e. it can be yellow to brown in color.
Drops A-Cerumen. Instructions for use
The contents of the dropper bottle contain surfactants. Once opened, the packaging should be used within 24 hours. Its volume is 2 ml.
The product is used both to remove a plug from the ear and for the prevention and hygiene of the ear canal. The medicine is not used for individual intolerance to the components or ENT diseases. Contraindications include children under 2.5 years of age.
Instructions for using the dropper:
- The head is placed on its side and the earlobe is pulled down and backward, 1 ml of solution is poured along the back wall of the ear canal and left for 1 minute.
- The head is turned on its side and the contents are allowed to drain from the ear, washed with saline or water, and the discharged contents are wiped with cotton wool.
The procedure must be carried out twice a day for 3 to 4 days. For hygiene and prevention 2 times a month.
Klin-Irs. Instructions for use
The medicine contains olive oil and surfactants and is used to remove traffic jams and prevent their formation. Klin-Irs are Israeli ear drops and are used for several days until the wax plug is completely removed. The method of application is the same as for the above mentioned products.
Blowing
You can get rid of sulfur plugs yourself using a mechanical method - blowing. He is approached quite rarely, since not everyone is familiar with the intricacies of the procedure.
The principle of blowing is to penetrate the ear with a stream of air through the Eustachian tube. The Eustachian tube is a canal connecting the nasopharynx and the tympanic region. There are more than 10 blowing techniques: the Lowry technique, the Edmonds maneuver and others.
The simplest method is the Valsalva maneuver. To carry out blowing, take a deep breath, and then exhale through the nose while pinching the nostrils with your fingers. Do not exhale sharply, as this may damage the inner ear.
Air is forced into the nasopharynx, from where it is directed into the auditory canal. This entails an increase in the gap in the Eustachian tube. Before the procedure, the nasal mucosa is cleaned and disinfected with a saline solution. This will help prevent pathogenic flora from entering the ear.
Attention! If pain occurs during blowing, the procedure should be stopped immediately and consult a doctor.
Contraindications and complications
Incorrect or untimely rinsing procedure for wax impaction can lead to unpleasant consequences.
The ear rinsing procedure has virtually no contraindications. When performed correctly, it is safe and painless. You can rinse your ears for otitis media to remove pus and disinfection, for wax plugs and dust accumulation in the ear canal, as well as for a foreign body in the ear.
It is not recommended to rinse the ear if you suspect a perforated eardrum, as water can get on the auditory nerve and cause hearing impairment.
In case of microcracks, damage and sores in the ear, rinsing can lead to infection, so it is not recommended to carry out the procedure without a doctor’s recommendation.
Ear rinsing and possible complications:
- Otitis. Otitis is an inflammation of the middle ear. It can occur when pathogenic microbes enter the ear canal. This is possible both when cleaning the ear with ear sticks, and when washing it improperly or using unsterile syringes. Otitis is accompanied by pain in the ear and head, often with purulent processes. Treatment is carried out using antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drops.
- Burns. Burns to the mucous membrane often occur not during the washing procedure itself, but when using folk remedies and preparations to soften the sulfur plug. If the ear mucosa is inflamed and damaged, peroxide can also cause a burn.
- Hearing loss. One of the most unpleasant consequences. Hearing loss can occur when water or droplets come in contact with the auditory nerve. The reversibility or irreversibility of deafness depends on the degree of complications.
- Stenosis of the external canal. This is often a consequence of the cork itself, and not of rinsing. Stenosis of the external auditory canal is accompanied by pathological narrowing of the canal, noise in the ear occurs, and hearing is significantly reduced.
To avoid undesirable consequences, you need to consult a doctor for examination. Only after examining the ear can you begin the rinsing procedure.
It is important to follow the rules of the procedure and not use drugs not recommended by your doctor.
Causes
Cleaning an ear plug is a simple task, but preventing such problems in the future is much more difficult. Since several factors can provoke the development of a conglomerate, it is best to familiarize yourself with them in advance. The most common cause of this disease is improper hygiene, which affects every third child.
Constantly cleaning the ear canal is harmful to the normal functioning of the ear canal, because special sticks or any other hard objects stimulate the production of even more wax. Many patients have a genetic predisposition to the formation of clots, which manifests itself in the form of a viscous consistency of the secretion of the cerumen glands, a narrow ear canal, or a large amount of hair in the auricle. Medicine also knows other factors that influence the appearance of traffic jams:
- autophony (increased perception of the sound of one’s own voice);
- high humidity;
- changes in atmospheric pressure;
- frequent entry of water into the ears;
- inflammatory diseases;
- elderly age;
- increased blood cholesterol levels;
- regular use of headphones or other headset;
- some skin ailments.
The child has
The appearance of a jelly-like infiltrate in a child is not a pleasant phenomenon, since the neoplasm brings concern not only to the child, but also to his parents. A baby's sulfur plug will be no different from the same clot in adults, but since it is much more difficult for children to endure discomfort, household members will have to take action as soon as possible. A sick child with an ear conglomerate requires urgent medical attention, so it is necessary to bring the little patient to the doctor.
The reasons for the formation of wax plugs in the ears can be very different.
Earwax can form in the ears for the following reasons:
- There is a lot of wax in the ears
- Accumulation of sulfur due to poor release
- Diligently cleaning out wax every day with ear sticks, respectively, wax for its intended purpose - protecting the ear canal is not enough, and its production increases
- Various skin diseases
- Inflammatory diseases of the ears
The accumulation of wax in the ear canal can be:
- Due to the narrow passage
- Due to pushing deep into the wax with ear sticks, when cleaning the ear canal
- Foreign object in the ear
- High dust content in the air
- Because of the hearing aid
- Due to wearing small headphones that are inserted inside the ears
Fixing a problem at home
Dear readers, I would like to point out right away that the process of removing earwax is quite unpleasant. If you do not know exactly how to do this, or are not sure of the favorable consequences, it is better to seek help from an ENT specialist. You can wash the cork at home under the following conditions:
- you really feel like you have a plug in your ears;
- you have not had otitis media or other ear infections;
- you do not have diabetes;
- the eardrum is not damaged.
I would like to offer you two options for washing ear plugs at home.
Cleaning ear plugs with hydrogen peroxide
I did this procedure at home, but I must tell you that the process is quite labor-intensive. I would recommend that you have this done by a specialist. But for those who are not afraid, here is a step-by-step method:
- At the first stage, earwax needs to be softened. This is best done in the evening so that the cork softens a little overnight. This step is usually carried out with hydrogen peroxide, but you can also use saline solution heated to 37 degrees. Glycerin or vegetable oil are also suitable.
- Take a few drops of the solution with a pipette and sit down so that the sore ear is on top.
- Pull the auricle with your hand: this is necessary to straighten the ear canal.
- Pour the product from a pipette into the ear and cover with a cotton swab.
- Leave the tampon on overnight.
- In the morning, draw hydrogen peroxide into a 20 ml syringe.
- Lie on your side and inject liquid from a syringe into your ear.
- Lie down for a quarter of an hour in this position.
- To clean the ear plug, you can lie in the bathtub and plunge your head into the water. Sera will come out on her own. Another way is to direct the shower stream into the ear canal until the shower touches the auricle.
Medications
To solve the problem of how to remove wax plug from the ear of a small child who cannot sit through long standard procedures, products from the pharmacy help. They can also help out in cases where the sulfur plug is quite dense and the symptoms do not disappear from exposure to water, hydrogen peroxide and other liquids.
Aqua Maris Oto
An effective nasal remedy that is used to rinse the auditory organ and soften plugs. It is absolutely safe as it is made from sea water. Suitable for children and pregnant women. Use is contraindicated if the eardrum is damaged and there is inflammation in the auditory organ.
Otipax
The drug has anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects. The active ingredients are lidocaine and phenazole. Treatment is carried out as prescribed by the doctor, he will indicate the required dosage. Indicated for children from one year of age and pregnant and lactating women.
Otipax relieves pain in the ears and stops the production of prostaglandins.
Remo-Wax
Gently and carefully removes sulfur accumulations and prevents the recurrence of compactions. The composition contains penetrants that eliminate dead particles and soften sulfur. Remo-Vax contains moisture-retaining components that push the plug out and moisturize the ear canal. It is allowed to periodically use the product to prevent the occurrence of sulfur seals. Contraindications are the presence of ear pain and deformation of the eardrum.
Vaxol
The product consists entirely of olive oil. It not only removes wax plugs at home and protects against new formations, but also softens and moisturizes the ear canal. Treatment is as follows: the drug is instilled once a day for 5 days. One bottle is enough for 200 uses. It is not recommended for use by persons allergic to olive oil or with damaged eardrums.
A-cerumen
Allowed to be used by children from the first days of life. The surfactants included in the preparation dissolve sulfur accumulations and bring them to the surface. The drops do not cause irritation and can gently clean the ear canal. An excellent remedy for preventing the occurrence of sulfur seals.
Main reasons
The following categories of people are exposed to increased secretion of sulfur:
- people whose work involves increased dust generation;
- those who frequently use headphones or hearing aids;
- poorly performing hygiene procedures;
- people with certain features of the physiological structure of the ear.
In human ears, wax formation occurs constantly. This is a secret that performs a protective function against the entry of various microorganisms and fine dust into the ear opening. For necessary hygienic cleaning of the ear, so-called ear sticks are often used. This is extremely incorrect, and here’s why: wax should come out of the ear canal on its own, so cleaning the ears should be done with a soft swab twisted from a piece of cotton wool, and only from the outer part located near the ear opening. When cleaning the ears with a stick, some of the wax is still removed, but the main part penetrates deep into the ear, becomes denser and gradually forms a wax plug, which subsequently causes a lot of trouble.
Reasons for the formation of sulfur plugs
There are several reasons why sulfur plugs form. This phenomenon is usually caused by increased secretion of earwax. The body does not have time to naturally remove it from the ear canal, as a result of which a cerumen plug forms. Increased sulfur secretion can also occur for various reasons. Most often this happens due to mechanical damage to the ear cavity or chronic otitis media. Let's consider some more factors that provoke increased secretion of earwax:
- Concomitant pathology of the ear canal. These include psoriasis or eczema;
- Working conditions. Wax is essential to prevent viruses or infections from entering the ear cavity. If a person works in a polluted room with a huge amount of dust, the body naturally tries to protect itself and produces doubly sulfur;
- People over 50 years of age are more susceptible to ear plugs. This is due to the fact that with age, all processes in the body slow down. Including the process of self-purification of sulfur;
- The presence of a foreign body in the ear cavity. The body again tries to protect itself by producing an increased amount of sulfur. Hearing aids or frequent wearing of headphones can serve as a foreign body;
- High cholesterol levels can affect earwax production.
Help: Increased secretion of earwax can be normal, and in some cases - pathology. To find out the cause, be sure to undergo an otoscopic diagnosis from an otolaryngologist.