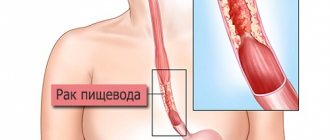
Stenosis, or narrowing of the esophagus, is a reduction in its diameter. It can have different etymologies. Stenosis, also called esophageal obstruction, is divided into several groups, which depend on the causes of the disease. This disease can develop as a result of trauma to the gastrointestinal tract. The pathology may be based on a tumor of the esophagus (benign or malignant). Surgical interventions can provoke the development of the disease, after which scars remain. In both adults and children, the esophagus can be affected. Narrowing of the esophagus often causes problems with swallowing function (dysphagia).
What is a narrowing of the esophagus
To understand what pathology is, you should consider the anatomical structure. What is a normal esophagus? Is narrowing of the esophagus always a pathology? Let's figure it out.
The esophagus is part of the digestive system. In the human body it performs the function of moving food from the mouth to the stomach. A healthy esophagus also necessarily has narrowings that do not interfere with the passage of food.
There are 3 anatomical narrowings:
- pharyngeal;
- diaphragmatic;
- bronchial
In addition, physiological narrowing of the esophagus is observed. They are caused by the tone of muscle tissue. When you relax, the constrictions disappear.
They are located:
- in the area of the junction of the esophagus and stomach;
- at the intersection of the aorta and esophagus.
Pathology is excessive narrowing that impedes the passage of food masses.
Sources of congenital disease
In such patients, the esophagus has been affected since birth. Narrowing of the esophagus is usually diagnosed in early childhood. Congenital stenosis occurs already during fetal development, before the birth of the child.
The main causes of this pathology are:
- The impact of harmful substances on the body of the expectant mother. Household chemicals, gasoline, dyes, when entering a woman’s body, affect the development of the fetus and can cause abnormalities.
- X-ray irradiation. Exposure to radiation also causes mutational abnormalities in the body. That is why X-ray examinations are strictly contraindicated for pregnant women.
- Various infections can also lead to deviations. These are viruses (for example, rubella), bacteria and protozoan microorganisms.
Are there effective preventive measures?
Unfortunately, there are no truly effective preventive measures. As for congenital forms, it is important for the mother to monitor her health. If there are risk factors (infection suffered during pregnancy, etc.), the examination should be carried out in the first days after the birth of the child in order to be able to adjust the diet and take safety measures in time.
In adulthood, the patient is recommended to monitor nutrition, as well as treat diseases of the digestive tract in a timely manner, preventing them from becoming more severe or chronic.
Causes of acquired disease
Pathology can develop both in childhood and in adulthood. Acquired stenosis can be due to a number of reasons. It can manifest itself in the most minor pathologies affecting the esophagus.
Narrowing of the esophagus often occurs as a result of ulcers. Subsequently, these erosions begin to heal. The areas where the scars form contract significantly less easily, resulting in food not being able to move freely. Such a process may underlie the pathology. In this case, cicatricial narrowing of the esophagus is diagnosed.
Ulcers can occur due to the following factors:
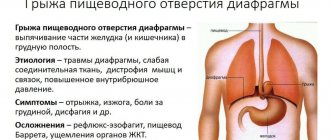
- axial hiatal hernia;
- chronic gastritis and stomach ulcers;
- toxicosis during pregnancy, which is accompanied by gag reflexes;
- gastroesophageal reflux disease;
- scar formation on the walls of the esophagus after surgery;
- mucosal disorder.
Stenosis can provoke inflammation of the esophagus caused by infection. Pathology can develop against the background of syphilis, scarlet fever, tuberculosis and diphtheria.
Injuries, such as chemical or thermal burns of the esophagus, damage to the walls with instruments or other objects, can also cause the disease. Disturbances can occur even with improper probing of the gastrointestinal tract. A burn of the esophagus requires adequate and timely treatment. Otherwise, it can lead to narrowing.
Much less frequently, factors influencing narrowing of the esophagus are:
- mycosis;
- radiation therapy;
- collagenosis;
- sclerotherapy for varicose veins.
The narrowing may be dictated by the appearance of tumors. Unfortunately, esophageal cancer is a fairly common pathology. However, it is extremely difficult to treat.
Pathologies also arise due to lesions and diseases that do not affect the esophagus. These are an aortic aneurysm, enlarged lymph nodes, mediastinal tumors, and abnormal arrangement of blood vessels.
Lifespan
Life expectancy is higher if adequate medical therapy is carried out. To avoid complications, a corrective diet was prescribed. Compliance with these measures guarantees the patient's condition improvement.
For a complete recovery, it is necessary to undergo appropriate treatment. Therefore, surgical intervention cannot be ruled out. With surgery there is improvement. The further course of the disease depends on the patient’s condition.
If esophageal stenosis is caused by a malignant pathology, then life expectancy is reduced. Since malignant pathology is characterized by systemic damage. However, in any case, you need to believe in your own recovery.
https://youtu.be/aYx2xQ683cc
Degrees of development
There are four stages of development of this disease:
- First degree of stenosis. It can be easily cured with timely consultation with a gastroenterologist. At this stage, the diameter of the esophagus decreases to 9 mm. Food masses pass, but with difficulty.
- Second degree - the esophagus narrows to 6 mm.
- In the third degree, the esophagus narrows to 3 mm.
- Fourth degree - narrowing of the esophagus to 1 mm makes the disease critical. At this stage of the disease, the food consumed is not digested by the body and stagnates in the intestines, as a result, feces accumulate, from which toxins are formed that affect the human body. Even when swallowing saliva, a person suffocates from spasms, suffocation and coughing attacks.
Possible complications
Without timely treatment, esophageal stenosis can be complicated by many other diseases.
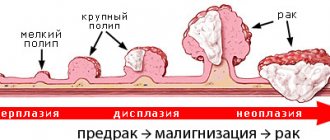
If the disease is caused by neoplasms, their nature may change (degenerate) into malignant ones. When eating hard, salty or spicy foods, it is easy to get injured in the esophagus: perforation, ulcers and even bleeding.
With a long course of the disease, due to frequent vomiting and the inability to eat, patients can reach an extreme degree of exhaustion.
To avoid such complications, at the first signs of illness you should immediately contact a specialist.
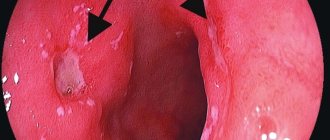
Esophageal erosion is a very dangerous disease, which, due to mild symptoms, cannot be immediately diagnosed. Therefore, with this pathology there is a high risk of developing dangerous consequences. These include:
- Bleeding in the esophagus, often accompanied by vomiting blood. One of the reasons for this condition is damage to a blood vessel in the organ.
- Peritonitis.
- Hyperplasia is an increase in cell growth. May provoke the development of malignant processes.
- Deep lesions and changes in the esophagus.
- Swallowing disorder.
- Shortening of the esophagus.
- Ulcerative lesions of the organ.
- Development of thrombosis and more.
Characteristic symptoms
A sign of stenosis is primarily a violation of the swallowing process.
Other indirect symptoms indicating narrowing of the esophagus:
- Regurgitation of uncurdled milk by newborns. If the milk does not curdle, it means that it could not enter the stomach. Congenital narrowing of the esophagus can already appear during the introduction of complementary foods containing solid particles. In this case, the baby refuses food, often burps, and has a gag reflex.
- In older adults, chest pain occurs due to tension in the muscles of the esophagus when trying to push food through the narrowing site, further into the stomach.
- Increased salivation (hypersalivation) is a reaction to food masses that accumulate in the esophagus, unable to pass further into the stomach.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Discharge of large amounts of mucus from the nose.
- Sudden weight loss caused by indigestion, the inability of food to pass through the esophagus and enter the stomach. With this condition, vitamin deficiency develops. In severe cases, cachexia (depletion of the body) may develop.
Stenosis can be complicated by pneumonia. Often with this pathology, pieces of food get into the respiratory tract. As a result of this disease, serious inflammation of the esophagus can develop and even rupture with bleeding. Such complications require urgent medical intervention.
Characteristics of the disease
The esophagus connects the pharynx to the stomach.
The main function of the organ is to deliver food to the digestive organs for further processing. It has 3 sections, is located along the neck, chest, and occupies part of the peritoneum. The length of the tube is 25-30 cm. Anatomically, the narrowing of the esophagus exists in three places, does not interfere with the movement of food, on the contrary, it promotes this process. In the presence of a constant inflammatory process, the reflux of acidic contents from a diseased stomach, the ingress of alkalis, erosions, thickening, and scarring appear on the esophageal mucosa. Their size may be such that the lumen of the organ narrows, making it difficult to transport food.
Initially, the symptoms are mild, the clinical picture is blurred, as it resembles diseases of other organs. Thus, the inflammatory process in the esophagus is transmitted to the pharynx and larynx. There is a painful sensation in the throat, pain during swallowing, which is often associated with a sore throat. As the disease progresses, which can take anywhere from a week to several months, symptoms become more severe. Unpleasant sensations arise precisely during eating, the first few hours after a meal.
With a slight narrowing, a person eats quite normally and does not feel much discomfort. This situation is often observed with congenital pathology. However, in the presence of concomitant diseases of the heart and gastrointestinal tract, the condition worsens. In severe cases, surgery is performed.
Stenosis is a serious condition that requires prompt medical intervention.
In addition to the trachea, the esophagus is interconnected with the aorta, bronchi, trunk of the vagus nerve and many other organs. That is why disruption of its functioning can be associated with a huge number of life-threatening complications.
In the international classification of diseases, esophageal stenosis is listed under number 22.2.
The appearance of esophageal tube stenosis can be caused by many reasons. Forms of this disease can be congenital, caused by impaired development of the embryo. As a result, various deviations may be observed.
Acquired causes are more varied:
- Damage to the esophageal mucosa due to frequent contact with acidic contents thrown from the stomach. This disorder often occurs with hiatal hernias, gastritis, ulcers and other gastrointestinal problems.
- No less often, stenosis or, in other words, stricture can occur as a result of various injuries. This can be burns with chemicals, damage to the wall by a solid foreign body, or puncture with diagnostic instruments when probing the stomach.
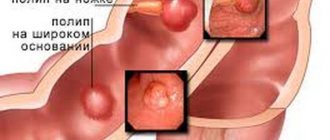
- Complete or partial narrowing of the lumen can occur as a result of benign or malignant formations.
- Damage to the wall of the esophageal tube can occur with infectious diseases such as scarlet fever, tuberculosis and many others. Also, such problems can occur against the background of bacterial or fungal infection.
- Sometimes narrowing of the esophagus occurs due to pathologies of the organs surrounding it. It may be compressed by malpositioned vessels or enlarged lymphatic ducts.
Diet food
At any stage of stenosis, you must follow a diet. You need to eat fractionally, often and in small portions. Eliminate from the diet all foods that may create difficulty swallowing and thereby cause choking.
You cannot eat hot food, it must be warm. The consistency of the dishes is liquid, semi-liquid or soft. At the same time, the body must receive all the necessary vitamins and minerals from the diet.
Traditional methods
Among the folk recipes for esophageal stenosis you can use:
- Cabbage juice with added sugar. For 1 liter of juice take 50 g of granulated sugar. Leave for 15 days. Drink 3 tbsp. spoons after each meal.
- Linden tea with May honey. It is recommended to dilute 1 drop of apple cider vinegar in it.
- Potato “tablets”. Squeeze the juice out of grated potatoes, make round “tablets” from the pulp, put them in a container and keep in the refrigerator for 7 days. Swallow 1-2 balls 10 minutes before meals, without chewing.
Treatment with folk remedies should not replace traditional therapy.
Before using prescriptions, you should consult your doctor, as self-medication may be counterproductive.
Treatment of pathology
What treatment methods are recommended for patients diagnosed with narrowing of the esophagus? Treatment of pathology is the expansion of the damaged area.
It is important not to forget about your diet. Until recovery occurs, you need to eat only liquid and semi-liquid foods.
If peptic stricture of the esophagus is observed, the patient is prescribed antacids and astringents.
However, conservative therapy rarely leads to complete recovery. Most often it is prescribed to prepare the patient for surgery.
Bougienage (artificial dilation using special devices) is used if a benign tumor of the esophagus is detected. During the treatment, the size of the bougie is gradually changed to a larger one.
If complications occur, a gastrostomy tube is placed to provide patients with normal nutrition.
Esophagoplasty is the transplantation of a section of the intestine or stomach into the esophagus.
In severe cases, when the body is very exhausted, or surgery is not possible, gastrostomy is performed. In this case, the body is able to feed enterally.
Classification of stenoses
Esophageal stenosis
By severity
The very first and most common symptom of acquired stricture of the esophageal tube is dysphagia - difficulty swallowing. In addition, the disease is accompanied by:
- belching;
- pain behind the sternum;
- vomiting after drinking water or food;
- sometimes bleeding;
- weight loss;
- increased salivation.
The choice of treatment for esophageal stenosis depends on the severity of anatomical changes in this organ, as well as on the clinical condition of the patient. Before starting treatment, a diagnostic examination of the esophageal tube is carried out, including:
- X-ray assessment of the condition of the organ, its peristalsis and the passage of food through the esophagus using a contrast agent.
- Esophagoscopy is an endoscopic examination that allows you to assess the condition and mobility of the walls of the esophagus.
- Cytological or histological examination to exclude malignant lesions.
In some cases, esophageal stricture is sufficient for pharmacological treatment, the main purpose of which is to reduce tension in the lower gastrointestinal tract, which reduces reflux and facilitates the movement of food to other parts of the digestive system. However, if the stenosis is fixed, this is due to anatomical changes and not due to muscle contraction, then it is necessary to dilate the esophagus endoscopically using special catheters.
Congenital stricture of the esophagus: a - membranous, b - hourglass, c - segmental
If attempts to widen the narrowed esophagus are unsuccessful, a more extensive surgical procedure may be necessary, including cutting the sphincter or making a prosthetic esophagus from a piece of the patient's intestine. Extensive surgical procedures may involve the temporary use of gastrostomy - feeding the patient through an artificial entrance to the stomach cavity.
Disease prevention
The effect of treating narrowing of the esophagus depends on therapeutic techniques. Esophageal resection and endoprosthetics are considered the best methods of treating this disease.
After bougienage and endoscopy, relapses may occur.
Prevention of stenosis involves timely treatment when the first symptoms of the disease occur.
It is imperative to combat diseases that can cause narrowing of the esophagus. Carefully avoid exposing your esophagus to chemicals and other harmful substances. Prevent foreign objects from entering the esophagus.
Diagnosis of pathological lesion
The standard examination program consists of:
- advanced blood test;
- urine analysis;
- coprograms;
- CT;
- MRI;
- esophagoscopy with biopsy;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- acidity measurements;
- X-ray of the esophagus with barium.
An important component of correct diagnosis is differentiation from other pathologies:
- diverticulosis;
- pharyngitis;
- stomatitis;
- hit by a foreign object.
Based on the research results, the specialist makes an accurate diagnosis and selects the correct treatment.