Inflammation of the middle ear is a pathology of the hearing organ of infectious etiology, affecting the structures of the tympanic cavity and characterized by rapid development. Otitis media is considered one of the most common otolaryngological diseases. Its cause is pathogenic microorganisms - bacteria, viruses, fungi. They enter the ear through the Eustachian tube or hematogenously from endogenous infectious foci.
The pathology primarily affects children's bodies. In adults, it is slightly less common. This is due to the structural features of the hearing organ in children and the imperfection of the immune system, which is not able to fully resist infection. The Eustachian tube in children is narrower. It is often compressed by enlarged adenoids. Children are more likely to get ARVI, cry and actively sniffle, which leads to infection spreading into the middle ear. According to modern statistics, sluggish otitis media is usually recorded in adults, and recurrent inflammation in children.
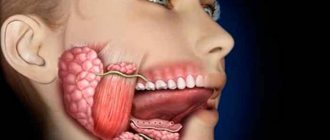
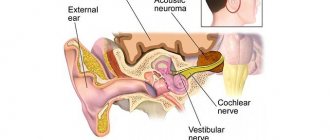
The ear is an organ with a complex structure that captures sound waves and converts them into electromagnetic waves that are perceived by the brain. The vestibular apparatus, which is responsible for the coordination of movements and orientation of a person in space, is located in the internal structures of the ear. The middle ear is filled with air and contains auditory ossicles designed to conduct sound vibrations. It is separated from the external environment by the eardrum. The middle ear cavity interacts with the cochlea, which perceives and recognizes mechanical waves.
ear structure
Otitis media is a polyetiological disease that develops mainly in people with immunodeficiency. Clinical manifestations of the pathology are: pain and hearing loss. Under the influence of microbes, signs of inflammation appear in the tympanic cavity - swelling, hyperemia, hyperthermia and other responses. Severe pain in the ear becomes shooting, piercing, unbearable when swallowing and chewing. Patients refuse to eat. They lie on their side and press the affected ear to the pillow. The pain syndrome is most pronounced in children. Acute inflammation is accompanied by intoxication - fever, weakness, aches throughout the body. Such signs require an urgent visit to the doctor.
Otitis media rarely occurs on its own. Usually it joins existing ear diseases and is a secondary, non-isolated pathology. The acute form of inflammation does not last long, is characterized by severe symptoms and often becomes chronic. Prolonged otitis media is manifested by signs of acute inflammation that do not stop for more than a month. The chronic process persists for more than three months. Patients periodically experience purulence from the ear, and hearing loss develops over time. There is a high risk of perforating the eardrum.
The disease has a favorable prognosis. In the early stages, it responds well to therapy and is rarely complicated by serious processes. Most modern medications are very effective for otitis media. The main thing is to start treatment as early as possible. If otitis media is ignored, the inflammation will progress and spread to neighboring organs. This can lead to the development of dangerous complications, including death.
Causes and symptoms of ear diseases in adults
Ear diseases in adults (symptoms and treatment require careful diagnosis to establish the exact cause of the pathology) are characterized by clinical signs, depending on the cause of the development of the disease processes.
| Name | What causes | Typical clinical picture |
| Otitis externa. | Infection of the skin in the ear area with bacteria or fungi. Provoking factors are hypothermia of the body, mechanical injuries, cleaning the hearing organs from sulfur, and the flow of contaminated water into the ear canal. | The outer part of the ear turns red and swells. A pain syndrome appears, which intensifies when pressing on the organ or when opening the mouth. The lymph nodes behind the ear are enlarged. Itching appears in the area of the ear canal. The ear is blocked, there is constant noise. |
| Diffuse external otitis. | Mechanical or chemical injury, thermal burn, infection. | The skin of the ear canal becomes swollen and red. It peels off and appears wet. Mucous or purulent contents are released. Sharp pain is replaced by severe itching and a feeling of stuffiness in the ear. |
| Limited external otitis. | The disease is most often a consequence of mechanical damage that occurs after cleaning the ear. | There is pain, noise and congestion in the ear. The temperature rises, headache occurs, and signs of intoxication appear. A boil forms in the area of the auricle. Limited external otitis is sometimes accompanied by purulent discharge from the auditory opening. |
| Otitis media | Occurs as a complication after external otitis. Infectious pathologies of the upper respiratory tract (tonsillitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis) also provoke inflammation. The same applies to ARVI (flu, measles, scarlet fever). | The disease is accompanied by pain. It intensifies if you press on the mastoid process. Hearing gets worse. There is a feeling of the presence of liquid inside. Purulent or watery contents are discharged from the ear. Body temperature rises. |
| Internal otitis. | The disease is provoked by viruses, bacteria, fungi and parasites, as well as ear injuries. | Dizziness occurs, accompanied by nausea and vomiting. Balance is disrupted and hearing deteriorates. Body temperature rises, tinnitus appears. |
| Meniere's disease. | The pathology is provoked by a large amount of endolymph in the inner ear. The cause is infection, vascular disease, ear damage or head trauma. | A rare disease characterized by dizziness, nausea, and vomiting. There is ringing and noise in the ears. Balance and coordination of movements are impaired. Sweating increases and hearing deteriorates. |
| Otosclerosis. | It is more often diagnosed in women during puberty, childbearing, menstruation, breastfeeding and menopause. | Hearing in one ear decreases, and after a while the second is affected. There is noise and dizziness. Pain and feeling of fullness in the ear. |
| Otomycosis. | They are provoked by mold and yeast fungi. Prolonged hydration, improper treatment with antibiotics and hormonal drugs. | The skin becomes inflamed, itching and pain occur. Yellow, dirty black or gray-green discharge appears. Depends on the type of mushroom. |
| Mastoiditis. | Occurs as a complication after acute otitis media. | Body temperature rises and headache occurs. Purulent discharge appears from the ear. The auricle protrudes, swells, and redness forms in the back of it. Pain in the ear of a pulsating nature when pressing on the mastoid process. |
| Otogenic sepsis. | It occurs as a result of otitis pathogens entering the bloodstream through large veins against the background of weak immunity. | Body temperature rises sharply (up to 40°C). Against the background of increased sweating due to heat, dehydration of the body is observed. The heart rate increases and blood pressure drops. Damage to the lining of the brain leads to severe pain, nausea and vomiting. |
| Bleeding from the ear. | A fracture of the bone part of the ear canal, rupture of the eardrum leads to bleeding. Acute chronic purulent otitis media, trauma, tumor of the middle ear or external auditory canal. | Moderate bleeding, accompanied by accompanying symptoms, depending on the cause of its occurrence. |
| Hearing loss. | The cause is chronic purulent otitis media, inflammation of the auditory tube and inner ear, sclerosis of the tympanic membrane. Obstruction of the auditory canal, anomaly of the middle ear. Senile hearing loss. Damage to the auditory nerve and the corresponding area of the cerebral cortex. | Pathological processes affect the sound-conducting apparatus, causing hearing deterioration. |
| Ear mite. | The parasite enters when a person is in close proximity to it. Animals are also carriers of ticks. Weak immunity provokes the occurrence of demodex. | Severe itching appears, hearing deteriorates, traffic jams form and wet discharge is observed. Allergic rashes appear on the body. There is a sensation of a foreign body in the ear. |
| Sulfur plug. | Accumulation of earwax in the area of the external auditory canal near the eardrum. | There is a hum, ringing, noise, pain in the ear. Hearing is getting worse. I feel dizzy and have a headache. |
| Neuritis. | Inflammatory process or atrophic changes. Infection, diseases of the heart, blood vessels and kidneys, impaired material metabolism. Long-term ear irritation. | Noise and buzzing in the ears. My head is spinning. Paroxysmal pain appears in the ears. Hearing and perception of high tones gradually decreases. |
Any pathology requires the intervention of an otolaryngologist (ENT). The specialist will conduct an examination and, if necessary, prescribe additional examination. Based on the results obtained, he will select the most effective and safe treatment.
Diagnostic process
Therapeutic and diagnostic measures for inflammation of the middle ear are carried out by an otolaryngologist. He consults patients, prescribes treatment and gives all necessary recommendations.
The doctor talks with the patient, listens to complaints, studies symptoms, and collects anamnestic data. Using special equipment, he examines the ear, nose and throat. To make a final diagnosis, the doctor needs the results of laboratory and instrumental studies.
- Hemogram - signs of inflammation: an increase in the number of neutrophil leukocytes, an increase in ESR.
- General urine analysis - signs of intoxication: traces of protein.
- Microbiological examination of ear discharge - identification of the causative agent of infection with a test for sensitivity to antibiotics.
- Otoscopy - examination of the tympanic cavity, identifying protrusion of the membrane outward, swelling and hyperemia.
- Audiometry – determining the degree of hearing impairment.
- Tympanometry - detection of infiltration in the middle ear or obstructions in the Eustachian tube.
- Radiography and tomography are performed in diagnostically difficult cases.
Based on the results of all the procedures performed, the doctor selects individual treatment for the patient.
Causes of congestion, noise, pain, shooting in the ear
Ear diseases in adults (symptoms and treatment are determined by an otolaryngologist) provoke serious problems if left without treatment.
| Name | Description |
| Inflammation of the auditory tube. | Ear congestion worries a person constantly. |
| Otitis externa. | There is a shooting pain. |
| Otitis media | A person complains of dull pain. |
| Stretched or damaged eardrum. | The reason is noise of varying intensity (acoustic, industrial). Not only pain occurs, but also lumbago. |
| Ear plug or foreign object. | Due to pressure on the eardrum, lumbago and pain occur. |
| Toothache (abscess). | The nerve endings in the head are closely connected to each other, so the pain syndrome is projected into the ear. |
Ear diseases: symptoms and treatment
In each case, diagnostics will be needed to determine the disease and select treatment.
Traumatic disorders
Traumatic ear diseases are classified into two types - mechanical and acoustic. There are also injuries to the outer, middle and inner ear.
External ear injuries
The outer ear is most susceptible to mechanical stress, but at the same time, its damage is the least dangerous, since it rarely leads to damage to the deep structures of the hearing organs.
Causes:
- gunshot wound;
- cuts;
- blows;
- falls;
- chemical and thermal burns;
- frostbite.
As a result of traumatic ear diseases, a person develops symptoms of a very diverse nature:
- wounds;
- hematomas;
- ruptures;
- tumors;
- pain;
- bleeding.
Wounds are treated with antiseptic solutions - Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, hydrogen peroxide, Furacilin solution. If necessary, apply a bandage with Levomekol ointment to prevent infection. In cases of ruptures and severe damage, plastic surgery may be necessary to return the ear to its normal shape.
Middle ear injuries
Middle ear injuries occur due to acoustic and mechanical damage. Acoustic ones are the result of a sharp drop in pressure in the ear canal, an airplane flight, and even strong kisses on the ear.
Causes of mechanical damage:
- strong blows;
- negligence during medical procedures;
- damage by foreign bodies.
Signs:
- sharp pain;
- bleeding;
- partial or complete hearing loss.
Therapy is carried out in a hospital setting, where the patient is examined and the extent of the damage is determined. In some cases, surgical treatment is required. But, in any case, antibiotics are prescribed - Azithromycin, Amoxiclav, Amoxicillin - to prevent the development of inflammation.
Medicines for the treatment of ear diseases
Therapy is carried out comprehensively, taking into account provoking factors, the degree of development of pathological processes and the patient’s condition. It is important not only to take medicine, but also to avoid stressful situations, maintain good hygiene, eat right, and drink vitamins to maintain immunity.
Antibacterial drugs
Ear diseases in adults (symptoms and treatment are considered individually by a doctor) can be eliminated with antibiotics. They kill and prevent the proliferation of pathogenic microflora. Broad-spectrum drugs are selected.
| Name | Application | Contraindications |
| "Amoxiclav". | The tablets are taken before meals. The course of treatment lasts 5-14 days. Patients are prescribed 250-500 mg every 8 hours. |
|
| "Cefalexin". | The medicine is prescribed at a dose of 250-500 mg every 6-12 hours. The duration of treatment is 1-2 weeks. |
|
To treat mild forms of disease or boils, antibacterial agents are used in the form of ointments and drops. Some drugs contain hormonal components that suppress the development of the inflammatory process.
Antihistamines
The drugs reduce the development of allergic processes. They are more used as symptomatic therapy, since they do not affect the underlying cause of the disease.
| Name | Application | Contraindications |
| "Suprastin". | The usual dosage is 75-100 mg 3-4 times. per day. |
|
| "Tavegil". | The daily dosage is a maximum of 6 tablets. The standard dose includes 1 tablet. 2 r. in a day. |
|
Medicines restore the patency of the auditory tube, and also relieve swelling of the mucous membrane and itching that accompanies many pathologies.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Medicines reduce pain and inflammation, eliminate high fever.
| Name | Application | Contraindications |
| "Ibuprofen." | 20-30 mg/kg every 6 hours. |
|
| "Paracetamol". | The standard dosage is 500-1000 mg, the time interval between doses is 4-6 hours. |
|
Ear diseases in adults, the symptoms and treatment of which are determined by an otolaryngologist, cause discomfort to a person and disrupt his usual way of life. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs alleviate the condition. Ear drops with an anesthetic (Otipax) have a positive effect. They have an anesthetic effect.
Glucocorticosteroid anti-inflammatory drugs
The drugs eliminate the cause of the inflammatory process and also have an antiallergic effect.
| Name | Application | Contraindications |
| "Dexamethasone." | 3 drops each. in each ear 3 r. per day. Treatment is carried out for 2-14 days. |
|
| "Prednisolone." | 4-5 drops. 3-4 r. in a day. |
|
During therapy, the otolaryngologist recommends that you adhere to strict hygiene in order to speed up the recovery process. Special antiseptics are used to rinse the ear canal.
Informative video: Otitis media
https://youtu.be/LZ0Ib9CL8uc
Inner ear injuries
Inner ear injuries are the most severe ear diseases in humans. They occur with traumatic brain injuries, strong blows, and gunshot wounds.
Clinical signs:
- severe pain;
- incoordination;
- dizziness;
- loss of consciousness;
- noises in the head;
- neurasthenic syndrome.
Injuries require long-term observation and careful examination. Treatment is aimed at preventing the development of cerebral edema and inflammatory processes in the meninges. In some cases, surgical removal of fragments and necrotic tissue is required.
https://youtu.be/pEw1lVLuKdY
Recipes for folk remedies for treating ears
Unconventional methods are used only for mild forms of ear disease and after consultation with a doctor. The components used may cause side effects or aggravate a person’s condition.
| Name | Recipe | Application and effectiveness |
| Ammonia and camphor. | Dissolve salt (1 tbsp) in warm water (1 liter). Mix camphor oil (10 g) and ammonia 100% (100 g). Combine all ingredients, stirring until the white flakes disappear. | Soak a cotton swab in the resulting solution, squeeze it well and apply it to your ear for a short time. The medicine reduces inflammation and pain. |
| Garlic oil. | Grind the garlic, add 150 mg of vegetable oil (60 mg). Leave in the refrigerator for 10 days. | The resulting solution is placed into the ear canal on a small piece of cotton wool. Treatment is carried out on days 14-16, 3 times a day. per day. |
| Lemon juice. | Squeeze out the juice, strain and use according to the recipe. | Drip 2-3 r. per day 3-4 drops. for 5 days |
https://youtu.be/GF5meGK7rSI
Propolis tincture has a regenerating and antimicrobial effect. A moistened cotton swab is placed in the external auditory canal. It should be changed 2-3 times. per day.
Otitis externa
Another common inflammatory ear disease is otitis externa (outer ear infection), which affects the outer structures of the ear. External otitis is of two types - limited and diffuse. Limited otitis media is characterized by the appearance of a boil in the external auditory canal, the inflammation is caused by Staphylococcus aureus and is accompanied by pain that increases with chewing. Diffuse external otitis is most often provoked by a streptococcal infection that covers the entire ear canal. With this type of disease, the characteristic symptoms are: pain, swelling and redness of the ear, external and internal discharge. Otitis externa can also be the result of an allergic reaction or inflammation that occurs when water gets into the ears. The presence of severe itching indicates a fungal infection of the ears caused by an infection that has penetrated the external auditory canal.
Physiotherapy
Ear diseases in adults are treated comprehensively. Not only medications and folk recipes are used.
If there are no contraindications, physiotherapeutic procedures will help eliminate unpleasant symptoms:
| Name | Description | Application and effectiveness |
| UHF. | An electromagnetic field of a certain frequency is applied. | The patient is prescribed 5-6 procedures of 5-7 minutes each. |
| Medicinal electrophoresis. | The medicine enters the site of inflammation with an electric current through the skin. | 7-10 procedures are prescribed, lasting from 10 to 20 minutes. |
| Microwave therapy. | The impact is carried out by an alternating electromagnetic field of ultrahigh frequency. | The duration of one session is 5 minutes. Biological reactions are activated and active substances are formed. |
Massage, ultrasound, laser treatment, and the use of infrared rays also help in the fight against various ear pathologies. Physiotherapy is carried out strictly after the acute period has subsided, in the absence of an active purulent process.
Meniere's disease
Meniere's disease is a non-inflammatory disease that affects the inner ear. The reasons for its development are unknown; there are only a few theories (viral, hereditary, nervous, trophic), which have not received either proper confirmation or complete refutation.
This pathology has 3 clinical forms:
- 1. Cochlear, which begins with hearing disorders.
- 2. Vestibular, starting with vestibular disorders.
- 3. Classic, combining the two previous ones.
The phases are divided into:
- Exacerbation.
- Remission.
By severity:
- Mild degree, characterized by short and frequently repeated attacks, alternating with long breaks: from several months to several years.
- Moderate degree, when frequent attacks are observed, lasting up to 5 hours, after which the person is unable to work for some time.
- Severe, when attacks last more than 5 hours, repeating from 1 time a day to 1 time a week, and the person’s ability to work is not restored.
By stages:
- The reversible stage, when there are light intervals between attacks and the disturbances are transient.
- An irreversible stage, when the frequency and duration of attacks increases, and the light intervals between them become rarer, until complete disappearance.
The main manifestation of Meniere's disease is an attack. It is expressed in the form of severe dizziness with nausea and vomiting, while the person is unable to stand or sit, and the condition worsens when moving. The ear is blocked, there may be a feeling of fullness or noise in the ear, coordination and balance are impaired, hearing decreases, shortness of breath and tachycardia appear, the face is pale, sweating is increased.
Attacks last from several minutes to several days. They are provoked by stress, overwork, poor nutrition, smoking, drinking alcohol, and increased body temperature. After the attack, hearing is reduced for some time, there is a feeling of heaviness in the head, minor disturbances in coordination of movements, instability of posture, changes in gait and general weakness.
Hearing impairment in this disease is progressive and ends in complete deafness, at the same time the attacks of dizziness cease.
Complications caused by ear diseases
The lack of correct and timely therapy leads to serious consequences. It is important to consult a doctor, undergo examination and begin treatment to prevent complications:
| Name | Description |
| Labyrinth (internal otitis). | The cause is an infection after otitis media that spreads to the inner ear. It also provokes a gradual deterioration of hearing until complete deafness. |
| Meningitis. | Complication after mastoiditis. The purulent contents end up on the lining of the brain. |
| Encephalitis. | Inflammation that affects the meninges, the causative agents of which are pathogenic microorganisms. |
| Abscess. | Microbes penetrate into the area of the temporal bone under the membrane of the brain or into its cells. Body temperature rises, the patient's condition worsens. Lethargy, severe headache and vomiting appear. |
Persistent hearing disorders and impaired functioning of the vestibular apparatus are also a consequence of the lack of proper therapy and neglect of the recommendations of the otolaryngologist. Otogenic intracranial complications lead to death.
Ear diseases in adults are not dangerous if you go to the hospital in time. Taking into account the symptoms, the doctor determines the source of the development of pathological processes. He will select treatment after diagnosis and monitor the condition until complete recovery.
https://youtu.be/83qSTcwsAl0
Dangerous complications
Complications of ear diseases depend on the type of disease. Inflammatory processes lead to infection of other ENT organs, resulting in the development of pathologies such as sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, pharyngitis, and tonsillitis.
Complications of otitis media and fungal infections:
- Myringitis is damage to the eardrum.
- Mastoiditis is inflammation of the mastoid process.
- Labyrinthitis is inflammation of the labyrinth.
- Facial nerve paralysis.
- Venous sinus thrombosis.
- Transition to chronic form.
- Relapses.
If ear diseases are treated incorrectly or untimely, the infection enters the bloodstream and infects internal organs. The greatest danger arises when the membranes of the brain become infected - the risk of developing encephalitis, meningitis or brain abscess increases. That is why any manifestations of ear diseases require an immediate visit to an otolaryngologist.
Diseases of the human auricle lead to inflammation of the cartilage tissue and the development of perichondritis. A long-term inflammatory process affecting the cartilage provokes necrotic changes, which can lead to deformation of the shell.
Some diseases of the human ear lead to partial or complete hearing loss, which can only be eliminated surgically - stapedoplasty or hearing aids. And not in all cases complete recovery is possible.
Routes of infection and diagnosis
Pathological microbes enter the inner ear in three ways:
- Otogenic - from the middle ear.
- Meningogenic - from the intracranial space. Infection can also occur due to inflamed meninges.
- Hematogenous - through the blood.
To accurately make a diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo the following types of examinations:
- take general urine and blood tests;
- otoscopy;
- audiometry;
- X-ray;
- tuning fork tests (to test the sensitivity of auditory receptors);
- sometimes an MRI is necessary.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment of middle ear inflammation is carried out on an outpatient basis. The doctor prescribes a set of measures aimed at fighting the infection, eliminating swelling and other signs of inflammation in the ear, and eliminating the unpleasant symptoms of the pathology. Patients with an acute form of infection are recommended complete rest, easily digestible food, and an optimal drinking regimen.
Medicines prescribed to patients with inflammation of the middle ear:
- Decongestants reduce swelling of the tissues of the nasopharynx and restore the patency of the auditory tube - “Nazivin”, “Rinonorm”, “Tizin”.
- Antimicrobial local agents in the form of ear drops - Ofloxacin, Neomycin, Otofa.
- Drops with an anti-inflammatory effect from the NSAID group – “Otinum”, “Otipax”.
- Combined hormonal drugs with corticosteroids, antibiotics and NSAIDs in the composition - Sofradex, Anauran, Polidexa.
- Antipyretic and painkillers - Ibuprofen, Paracetamol, Nimesulide.
- Immunomodulators for activating the immune system - “Imunorix”, “Ismigen”, “Immunal”.
- Antihistamines eliminate swelling and improve ventilation in the auditory tube - Suprastin, Zodak, Cetrin.
- Vitamin complexes – “Vitrum”, “.
- Adaptogens and biostimulants – “Actovegin”, “Eleutherococcus”, “Schisandra”.
Sinusitis
Sinusitis is not a disease of the ear specifically, but can cause pain in the ear. There are several types of sinusitis: sinusitis, frontal sinusitis and others. With this disease, the mucous membranes of the maxillary, frontal, ethmoid and sphenoid sinuses become inflamed.
With sinusitis, a runny nose, severe headache, a feeling of squeezing, pain and noise in the ears, blocked ears, and impaired sense of smell appear. If acute sinusitis starts, it can become chronic. This disease can also cause otitis media.
To correctly diagnose and identify inflamed sinuses, a number of studies are performed, including X-rays, MRI or CT.
Causes of the disease
Sinusitis occurs for various reasons.
- Colds.
- Allergic reactions.
- Abuse of nasal sprays in the treatment of a runny nose.
- Asthma.
- Fungus.
- Contaminated air.
- Bad habits such as smoking.
- Congenital anatomical features: structure of the nasal septum.
Most of the factors that provoke sinusitis can be influenced by the person himself.
Treatment
In case of acute sinusitis, you should immediately consult a doctor to prescribe therapy. Antibiotics are prescribed if sinusitis is microbial in nature, otherwise they will be useless.
- Nasal drops. They should not be used for a long time. The mildest effects are nasal drops based on essential oils - Pinosol, Sinuforte. If sinusitis is caused by allergies, then Vibrocil or Loratadine, Rhinopront are suitable.
- Antiseptic drugs. They will destroy the infection and prevent the spread of inflammation. Dioxidin, Miramistin, Furacillin are usually used.
- Means for rinsing the nose. For treatment at home, a solution is made from water and salt (one teaspoon of the substance is needed per glass of hot water), but special mixtures can be purchased in pharmacies: Aquamaris, Dolphin.
- Antibiotics. They are used if sinusitis is caused by bacteria. Depending on the degree of damage, the shape and variety are selected. The most commonly used are Amoxilav, Ampiksid, Fusafungin.
- Nonsteroidal painkillers. These include ibuprofen-based medications. Will help with pain in the head and ears.
Important! You cannot take antibiotics on your own. . Punctures are used in extreme cases when therapy does not help.
A properly performed operation will quickly bring relief, but it happens that it only provokes a chronic disease.
Punctures are used in extreme cases when therapy does not help. A properly performed operation will quickly bring relief, but it happens that it only provokes a chronic disease.
Preventing ear injuries
You can damage your ears in any conditions: at work, at home, in the gym, on a picnic. The following types of injuries are distinguished:
- chemical - a consequence of contact with a substance that irritates the skin on or inside the ear;
- thermal - the result of exposure to too low or high temperatures;
- mechanical – occur after an impact;
- acoustic - a consequence of long or short exposure to too loud a sound.
Self-medication or inaction for ear injuries can lead to hearing loss and other complications. After damage, you must urgently contact an otolaryngologist to prescribe the correct treatment.
To avoid various types of ear damage, you should adhere to the following rules:
- Prevention of acoustic ear injuries in people working in industries with high noise levels involves the use of special headphones.
- Production premises must have sound-absorbing walls and ceilings. It is impossible for high-frequency noise to exceed 85 background, mid-frequency - 90 background, low-frequency - 100 background.
- The volume of music, TV, computer should not exceed 40 decibels. To control, you can use a sound level meter; you can buy it or install it on any gadget.
- To avoid thermal damage, wear hats on cold and hot sunny days.
It is difficult to protect yourself from mechanical injury. The only way to reduce risk is to avoid situations in which they occur.
Ear diseases have different etiologies. They can cause hearing loss and other complications. Preventing ear diseases will help protect against health problems. If you experience discomfort, pain, hearing loss, or other signs of illness, you should contact an ENT doctor so as not to worsen the situation.
The main causes of ear diseases.
First of all, the causes of damage to the hearing aid include factors of an infectious nature. Here are the main ones: hemolytic streptococcus (causes erysipelas of the external ear), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (most often the cause of purulent perichondritis), staphylococcus (furuncle of the external ear, acute and chronic tubo-otitis), streptococcus (inflammation of the eustachian tube, otitis media), pneumococcus ( causes otitis media), molds (cause otomycosis), influenza virus (otitis) and many others, including Mycobacterium tuberculosis (ear tuberculosis) and treponema pallidum (ear syphilis).
These infections can themselves cause inflammatory lesions of the ear, or be complications of inflammatory processes in other organs - these include lesions of the sinuses (acute and chronic sinusitis, sinusitis), as a result of tonsillitis, scarlet fever, influenza and others.
Factors such as ear microtrauma, decreased local and general immunity, improper ear hygiene, and allergic reactions contribute to the infection. Also, these infectious lesions, in addition to inflammatory processes, can further cause complications and cause sensorineural hearing loss.
Among other causes of ear diseases, it should be noted that there is an increased function of the glands of the auditory canal, as a result of which, with improper hygiene, wax plugs can occur.
Some medications (antibiotics of the aminoglycosin group) have a toxic effect on the ear.
Ear injuries are also common: mechanical (bruise, blow, bite), thermal (high and low temperatures), chemical (acids, alkalis), acoustic (short-term or long-term exposure to strong sounds on the ear), vibration (due to exposure to vibration vibrations produced by various mechanisms), barotrauma (when atmospheric pressure changes). Also, the causes of ear lesions can be foreign bodies (most often in children, when they push buttons, balls, pebbles, peas, paper, etc. into themselves; less often in adults - fragments of matches, pieces of cotton wool, insects).
Other causes include genetic mutations, which result in congenital abnormalities in the development of the hearing system.
Ear research methods.
External examination and palpation of the ear. Normally, palpation of the ear is painless, but with inflammatory lesions pain appears.
Otoscopy is performed using an ear funnel; in inflammatory diseases, changes in the ear canal occur, you can see various discharge, crusts, scratches, and with various lesions, the eardrum also changes (normally it should be gray in color with a pearlescent tint).
Determination of the patency of the auditory tubes. This study is based on blowing and listening to the sound of air passing through the patient's auditory tube; 4 methods of blowing are performed sequentially to determine the degree of patency of the auditory tube.
The first method, Toynbee's method, allows you to determine the patency of the auditory tubes when making a swallowing movement performed with the mouth and nose closed.
The second method, the Valsalva method, takes a deep breath, and then intensifies inflation with the mouth and nose tightly closed; in case of diseases of the mucous membrane of the auditory tubes, this experiment is not successful.
The third method, the Politzer method, and the fourth method is blowing out the auditory tubes using catheterization; in addition to diagnostic methods, these methods are also used as therapeutic ones.
Study of the functions of the auditory analyzer. Speech hearing test. Study of whispered and spoken speech. The doctor pronounces the words in a whisper, first from a distance of 6 meters, if the patient does not hear, then the distance is reduced by one meter and so on, a study with spoken speech is carried out in a similar way.
Study with tuning forks; using tuning forks, air conduction and bone conduction are studied. Experiments with a tuning fork, Rinne's experiment, compare air and bone conductivity, a positive experience if air conductivity is 1.5 - 2 times higher than bone conductivity, negative on the contrary, positive should be normal, negative - in case of diseases of the sound-conducting apparatus.
Weber's experience, they place a sounding tuning fork in the middle of the head and normally the patient should hear the sound equally in both ears; with a unilateral disease of the sound-conducting apparatus, the sound is lateralized to the diseased ear; with a unilateral disease of the sound-receiving apparatus, the sound is lateralized to the healthy ear.
Jelle's experiment determines the presence of otosclerosis. Bing's experiment is carried out to determine the relative and absolute conductivity of sound through bone. Federici's experience: a normally hearing person perceives the sound of a tuning fork from the tragus longer than from the mastoid process; if sound conduction is impaired, the opposite picture is observed.
Hearing research using electroacoustic equipment; the main objective of this study is a comprehensive determination of hearing acuity, the nature and level of its damage in various diseases. They can be tonal, speech and noise.
Study of the function of the vestibular apparatus. Study of stability in the Romberg position, with disorders of the vestibular apparatus, the patient will fall. The study is in a straight line; in case of violations, the patient deviates to the side. An index test; if there is a violation, the patient will miss. To determine nystagmus (involuntary oscillatory movements of the eyes), the following tests are used: pneumatic, rotational, caloric.
To study the function of the otolithic apparatus, an otolith test is used.
Among other methods, the X-ray method is used to examine the ear. In particular, to identify traumatic injuries (fractures of the styloid process, mastoid process of the temporal bone), to identify various benign and malignant tumors of the auditory analyzer. For this purpose, both conventional radiography and computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are used.
You can also take discharge from the ear for research to determine the pathogen that caused a particular disease and subsequently determine its sensitivity to antibiotics for proper treatment.
A complete blood count also helps in diagnosing ear diseases. In cases of inflammatory damage to the ear, there will be leukocytosis in the blood, an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
Underdevelopment of the internal structure of the ear and neoplasms
This is a congenital pathology accompanied by impaired auditory perception. Sometimes it is possible to restore hearing through surgery. However, if there is no cochlea or organ of Corti in the ear, the problem cannot be solved at the moment.
Tumors, cysts, growths of epithelial tissue and malignant neoplasms can be localized in one of the areas of the inner ear.
Fungal infections
Ear diseases of fungal origin are called otomycosis. Most often, the fungus infects the outer and middle ear if hygiene rules are not followed and scratches and wounds are not treated.
Otomycosis
What causes otomycosis:
- mechanical skin lesions;
- sores in the ear (pimple, boil, insect bite);
- hyperhidrosis;
- dermatitis;
- diseases of the human ear;
- allergic reactions;
- diabetes;
- decreased immunity;
- poor hygiene.
Symptoms of fungal disease in the ears are expressed by itching, flaking, and redness of the skin. As otomycosis progresses, swelling develops, the ear canal narrows, noise in the ear appears and hearing decreases. If the fungus infects the eardrum, fungal myringitis is diagnosed, which has symptoms similar to otomycosis.
All fungal infections are treated with antifungal drugs:
- Tablets: Fluconazole, Terbinafine, Ketoconazole, Pimafucin.
- Solutions: Clotrimazole, Naftifine, Candibiotic, Candide.
To relieve itching and swelling, antihistamine tablets are prescribed: Loratadine, Suprastin, Zyrtec. To reduce fever and eliminate pain, anti-inflammatory drugs are needed: Ibuprofen, Paracetamol, Nimesulide. Be sure to follow a diet low in carbohydrates and fats.
Congenital pathologies
Congenital pathology of the hearing organs can affect the formation of a person both physically and psychoemotionally. Such disorders can be inherited. The formation of the problem often occurs during the intrauterine development of the fetus. It can be affected by the mother's lifestyle, illnesses, injuries, etc. Some children are traumatized during the birth process.
With congenital pathologies, any part of the auditory analyzer can be affected. A large number of diseases are hidden and are detected only in infancy or later. Only some diseases have pronounced external characteristics.
Congenital conditions can lead to increased episodes of ear infections, such as eustachian tube dysfunction or cleft palate. Also, some of them cause the development of hearing loss from an early age. The worst case is congenital deafness. It is very difficult to treat such anomalies; some cannot be treated and significantly complicate a person’s life.
Sensorineural hearing loss
Sensorineural hearing loss is a lesion of the organs responsible for the perception of sound. In this regard, the sound is received weakly and in a distorted form. The reasons may be:
- Meniere's disease;
- age-related changes;
- injuries to the temporal part of the head;
- neuritis of the auditory nerve.
If detected at an early stage, therapy is carried out with drugs, electrical stimulation, and physiotherapy. In other cases, it is necessary to resort to hearing aids.
Which doctor should I contact?
An otolaryngologist diagnoses and treats ear diseases. If necessary, consultation with a dermatologist, neurologist, or endocrinologist may be required.
An otologist performs operations on the hearing organs, and an audiologist eliminates hearing problems.
Diagnostic methods
An experienced specialist can diagnose most ear diseases by examining and interviewing the patient. But if the clinical picture is not completely clear to the doctor, he will prescribe other diagnostic methods. Instruments for examining the hearing organs can be seen in the photo.
Special tube for examining the ear canal
Methods for detecting ear diseases:
- otoscopy – examination of the ear canal and eardrum using a special tube;
- audiometry – measurement of hearing acuity, determination of auditory sensitivity to waves of different frequencies;
- tympanometry - a probe is inserted into the ear canal, after which the specialist measures the volume of the ear canal, periodically changing the pressure inside the ear;
- X-ray – allows you to assess the condition of the structure of all parts of the hearing organ;
- CT - this method allows you to see injuries, bone displacements, identify inflammatory and infectious pathologies, tumors, abscesses;
- Ultrasound – carried out to identify neoplasms, foci of infection, size and characteristics of the ear canal;
- bacterial culture to determine effective antibacterial drugs;
- clinical, biochemical and serological blood tests to detect infectious diseases.
All research methods are painless, special preparation is required only for blood tests - they must be taken on an empty stomach, the last meal should be 10-12 hours before the test.
Exercise, preventative measures and diet
Special exercises, dietary nutrition and preventive measures are of great importance in getting rid of the manifestations of Meniere's syndrome. If they are present in the patient’s life, then the risk of repeated attacks is minimal.
Exercises
The purpose of the exercises is to normalize the functioning of the vestibular apparatus. This is very important for Meniere's syndrome. Therefore, all patients should include them in therapy. Regular exercise will help get rid of most of the symptoms of the disease.
Effective exercises:
- Sit on a computer chair that can swivel. Straighten your back, rest your feet on the floor and look clearly at one object. The task is to slowly spin in a chair, keeping your gaze on that thing and without lifting your feet from the floor.
- Walk around the apartment with your eyes closed, trying to determine your location. It is advisable to perform with an assistant.
- Look at the wall, rise on your toes, slowly lower yourself. Repeat several times. At first with your eyes open, but after a few practices you should close them. You can also stand on only one leg or hold an unstable object (for example, a ball) in your hand.
It is possible to perform other exercises, but these will be enough to get started, because... they are simple and effective.
Prevention and diet
Regardless of whether a person suffers from Meniere-like syndrome or simply wants to avoid it, preventive measures should be taken regularly to reduce the risk of attacks and complications.
Most important:
- Quit alcoholic beverages and smoking;
- Eliminate stressful situations from life;
- Do not interact with anything that may cause allergies;
- Emphasize safety from injury;
- Avoid loud noise and vibrations;
- Visit a doctor at the first unpleasant symptoms and immediately treat all diseases;
- Monitor pressure and avoid changes (flight or dive);
- Spend time outside, play sports and special exercises.
Also one of the preventive measures is diet. It deserves special attention, because... in some cases, following it allows you to completely get rid of the symptoms of the disease. It consists of the following rules:
- Do not drink coffee, synthetic tea, alcohol;
- Eliminate fatty and smoked foods and spices from the diet;
- Limit the presence of salt in food;
- Drink no more than 2 liters of water per day.
Diet is especially important during attacks. The rest of the time it is advisory in nature. However, we should not forget about its effectiveness.
https://youtu.be/7Gg7lz2bMX4
Etiopathogenesis
The main cause of middle ear inflammation is infection. Bacteria, viruses or fungi penetrate organs and tissues from the external environment or internal foci. In people with strong immunity, foreign microorganisms bind to antibodies and die. Under the influence of endogenous or exogenous negative factors, immune defense is weakened, which leads to the development of an infectious process.
Bacterial otitis media is caused by streptococci, staphylococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa or Haemophilus influenzae, pneumococci, and moraxella.
- Inflammation of the middle ear often becomes a complication of viral diseases - respiratory and childhood infections.
- The causative agent of a fungal disease is usually candida. Recently, there has been an increase in the number of cases of otomycosis.
Otitis media is a secondary pathology that occurs after an infection enters the ear from neighboring parts and organs - the ear canal, tonsils, pharynx, larynx, nose, sinuses. When you sneeze and cough, particles of infected mucus and sputum are thrown into the ear through the auditory tube. Otitis media is often combined with eustachitis, which is preceded by laryngitis, sore throat, rhinitis and other diseases of the nasopharynx. When the lumen of the pipe narrows or is completely blocked due to edema, ventilation is disrupted and stagnation occurs. The accumulation of fluid in the ear leads to the development of the disease. Other, less common, methods of infection of the middle ear include: hematogenous, meningogenic, traumatic.
Factors that suppress immunity and contribute to the development of pathology:
- Ingress of dirty liquid into the hearing organ.
- Systemic or local hypothermia.
- Removing earwax, which protects the ear canal from drying out, water and pathogens.
- Excessive humidity and air temperature.
- Foreign bodies in the ear canal.
- Wearing a hearing aid.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Operations on the ear, pharynx, paranasal sinuses.
- Incorrect nose blowing.
Diseases, but against which otitis media may develop:
- Diseases of the throat and nose.
- Respiratory infections.
- Traumatic ear injury.
- Adenoids in children.
- Structural abnormalities of the auditory tube.
- Allergic reactions.
- HIV.
- Deformation of the nasal septum.
- Neoplasms of ENT organs.
- Meningitis.
- Damage to the auditory nerve.
- Cervical osteochondrosis and pathology of neck vessels.
The tympanic cavity is so small that any infectious inflammation can damage the auditory ossicles and disrupt the transmission of sound signals.
Pathogenetic links of the process:
- Narrowing or obstruction of the auditory tube,
- Vacuum formation in the tympanic cavity,
- Activation of mucous glands,
- Overproduction of inflammatory fluid,
- Increasing the viscosity and density of secreted secretions,
- Pain and hearing loss
- Reproduction of microbes in exudate,
- Development of purulent inflammation,
- Thinning and perforation of the eardrum,
- Discharge of pus outwards,
- Progression of degenerative processes,
- Hearing loss.
Traditional methods, homeopathy
You can also be treated using traditional methods or homeopathic remedies. However, such therapy cannot be considered basic and cannot be replaced with medication. Before using any additional products, you should consult your doctor.
Traditional methods
The use of folk remedies allows you to get rid of unpleasant symptoms and normalize your condition. Most of them can be easily prepared at home, without resorting to a complex search for certain components of the recipe.
The most effective means:
- Mix chamomile, St. John's wort, immortelle, birch buds, strawberry leaves (100 g each), then take a small amount of them (20 g) and pour boiling water (1.5 l). The drink should be infused for 10 hours. It should be consumed in the morning after meals, after straining through cheesecloth.
- Chop one onion and mix with honey (250 g). Take the mixture shortly before meals three times a day.
- Mix equal amounts of nettle, St. John's wort, bearberry, rose hips and plantain leaves. Pour a little mixture (15 g) with boiling water (0.6 l), boil for 5 minutes, then leave for one hour. Take small sips throughout the day.
Some products may have a specific taste. But adding other ingredients to them is not recommended.
Homeopathic remedies
The use of homeopathy may be justified if you want to complement the main treatment. Some remedies can have a positive effect, which will improve the patient's condition. However, you should discuss the idea with your doctor before using them.
Popular homeopathic medicines:
- "Amonium iodatum";
- "Causticum";
- "Chelidonium";
- "Cocclulus";
- "Glonoinum";
- "Ledum";
- "Theridion."
They should be taken in strict accordance with the instructions or recommendation of the attending physician.
It is not recommended to instill various products into the ears (herbal tinctures, hydrogen peroxide, boric acid, etc.), because this may have a negative impact on your hearing health.
Pathological processes in the vestibular apparatus
When infectious pathogens penetrate the vestibular apparatus, coordination problems occur. In addition, pathologies accompanied by positional vertigo are observed. This is due to dysfunction of the semicircular canals and their injury. Meniere's disease is one of the most common diseases in this group. This syndrome is caused by an increased content of endolymph in the inner ear.
The most serious consequence of these diseases of the inner ear is hearing impairment at the level of neural connections. The hair receptors of the ear are destroyed and do not have the ability to recover. When an inflammatory process of the serous type occurs, the receptor islands can be preserved and even provide the patient with hearing.
Diseases of the inner ear of a purulent nature are the most dangerous, since they cause tissue necrosis and decomposition. The cochlea and organ of Corti are affected. Sensory hairs die and irreversible deafness occurs.
Prevention of wax plugs in the ears
Every day, wax is formed in the ears, consisting of protein, sebum, and fat-like substances. It moisturizes the hearing organs from contaminants and pathogens due to its ability to capture and disinfect them. To prevent wax plugs from forming in the ear, prevention should include the following:
- Controlling blood cholesterol levels. Its increase can lead to thickening of sulfur.
- Avoid getting cold water into your ears; use special earplugs for diving.
- Sudden changes in pressure and temperature and dry air are undesirable. The recommended indoor humidity is 60-70%, temperature – 20-25 degrees.
- Use cotton swabs less often. Cotton pads are more suitable for cleaning ears.
- Frequent use of earphones is contraindicated.
It is advisable to wash your ears once a month:
- Take a syringe or syringe without a needle.
- Draw saline or warm water.
- Pull back and up.
- Pour the liquid along the upper wall of the ear canal in a stream of medium intensity.
Foreign bodies that enter the ear from the outside can be living (insects) or non-living (various small objects). Non-living ones most often get into the ears of young children. To prevent a foreign body in a child’s ear, you should remove all small objects out of reach and maintain hygiene. If this does happen, you should not try to remove the foreign body from the ear yourself . Due to inept actions, it can move even further along the ear canal.
Drops for ear prevention
If there is a tendency to form a wax plug, cleansing ear drops are used for preventive purposes. They are made on a water or oil basis.
Vaxol
Consists of pharmaceutical grade olive oil. Place 1-2 drops daily in each ear. Contraindicated in case of perforation of the eardrum and allergy to the product. Vaxol moisturizes and softens sulfur, eliminates infections.
Otipax
Has anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects. Can be used by children from 1 year. Contains lidocaine and phenazole. Used exclusively as prescribed by a doctor.
A-Cerumen
A gentle cleanser and moisturizer that does not cause allergies. Instill 1 ml into the ear 2 times a month.
Remo-Wax
The safest drug contains allantoin. For preventive purposes, use 3 or 4 times a month. Do not use for discharge, pain in the ear or damaged eardrum.
Aqua Maris Oto
Consists of specially prepared sea water. Contraindicated in case of inflammation in the ear or damaged eardrum.
Hydrogen peroxide 3%
Before use, the product is heated to 37 degrees. For prevention, drip 1-2 times a month.
Before using any drug, you should consult an otolaryngologist. If a rash or irritation appears, use of the product should be discontinued.
Symptoms
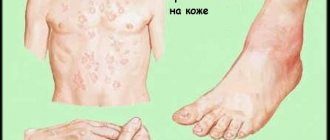
Ear diseases exhibit the following symptoms:
- Various discharge from the ears.
- Slight swelling, redness, pain and itching.
- Noise in ears.
- Autophony.
- Minor disturbances in orientation or balance.
- Deafness.
There may be a slight increase in temperature, headaches or malaise. In children, ear diseases can cause severe pain, poor sleep, prolonged crying and poor appetite.
The most common symptom of ear disease is pain, which can be tingling or severe. Usually, it radiates to the eye area, lower jaw or temple. When walking, swallowing or chewing, the pain may become stronger.
What is the inner ear
This part of the ear is a hollow bony formation, the part that includes the senses of hearing and balance. The system of communicating bone canals inside it is called the bony labyrinth; it contains the membranous labyrinth.
The outlines of the bony and membranous labyrinths completely coincide. The bony labyrinth is divided into three sections: the vestibule, semicircular canals and cochlea. The membranous labyrinth is divided into parts:
- semicircular canals;
- two vestibular sacs,
- vestibule water supply;
- snail;
- The cochlear canal, which is the only part of the inner ear that is a hearing organ.
This entire structure is immersed in fluid - endolymph and perilymph.