Computed tomography (CT) is a relatively new examination method, first used in 1972.
During a non-invasive examination, the doctor receives a three-dimensional image of organs and tissues, which makes it easy to establish or confirm the suspected diagnosis. Using CT, you can examine any organs and systems, including the abdominal cavity.
Abdominal CT (ABC) is prescribed to diagnose diseases of the stomach and intestines, pancreas, liver, spleen, and gall bladder. Also during the study, the doctor analyzes the condition of the structures and organs of the retroperitoneal space: kidneys, the entire urinary system, lymphoid tissue, blood vessels.
Unlike X-rays, in which the image of internal organs has shadows and looks as if “superimposed” on each other, the results of computed tomography provide clear layer-by-layer images of all structures. Like any other method, computed tomography of the ABP has its indications and contraindications and requires certain preparation of the patient.
Indications for the procedure
Indications for CT scan of the abdominal cavity (with and without contrast):
- assessment of PD organs before surgical treatment and observation after surgery;
- confirmation of the diagnosis after ultrasound or gastroscopy;
- primary diagnosis of diseases when other methods are not possible;
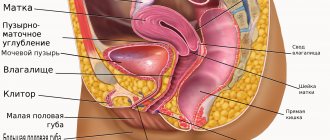
- examination of the pelvic organs, urinary tract and kidneys to identify stones and stones (CT urography of the kidneys);
- identifying the causes of jaundice and weight loss;
- suspicion of benign or malignant formations, cancer and metastases;
- determining the extent of gastric cancer spread;
- examination of lymph nodes for generalized lymphadenitis or oncology;
- monitoring the patient's condition during conservative and surgical treatment.
Contraindications to the procedure with contrast
To avoid complications, abdominal CT is not performed in patients with:
- allergy to iodine;
- severe renal failure with elevated creatinine levels in the blood (creatinine testing is included in the services of our diagnostic center);
- hyperthyroidism and other thyroid diseases.
Children over 12 years of age have their internal organs checked with contrast only according to indications with a doctor’s referral.
For women breastfeeding, the procedure is not prohibited. Radiation exposure does not affect milk, but the dye partially penetrates into it. Therefore, you will have to give up at least two consecutive feedings. Before the study, the woman must express and store the milk. After CT or MSCT with contrast, you must wait until the drug leaves the body and after two pumpings, feed the baby as usual.
Any questions you may have and the price for contrast examinations can be clarified with the administrator.
Contraindications to CT scan of the abdomen
Due to the presence of harm from x-ray radiation, the procedure has some contraindications and risks. This technique is prescribed when preliminary diagnostics using ultrasound, gastroscopy and other options for examining OBP showed the presence of a pathological process, but did not allow an accurate determination of the extent of the disease.
Abdominal CT with contrast is contraindicated in the event of an adverse reaction to taking intraurografin before CT. The method is not the main option for examining a child; childhood will be a relative contraindication; it is performed in case of emergency (replaced by MRI).
Absolute contraindications to CT of the PD organs, pelvis and retroperitoneum:
- first trimester of pregnancy;
- contrast agent intolerance;
- hyperkinesis (inability to maintain body stillness);
- mentally unbalanced state;
- body weight more than 120 kg (when it is not possible to use an open tomograph).
Relative contraindications to CT and MSCT of the abdominal cavity with contrast:
- age up to 14 years;
- severe endocrine pathologies, myeloma, diabetes mellitus;
- hepatosis, severe liver dysfunction;
- recent gastric contrast bolus;
- renal failure.
What is tomography and what are its advantages?
Computed tomography of the abdominal cavity is today one of the most reliable and detailed methods for examining a patient. Diseases detected with its help can not only significantly undermine a person’s health, but sometimes even cost him his life. Therefore, it is important not only to detect them in time, but also to conduct a detailed analysis of the patient’s condition in order to choose the most optimal treatment therapy.
IMPORTANT!!! Computed tomography of the peritoneal organs allows you to perform a detailed diagnosis of the condition and functioning of all organs of the peritoneum and retroperitoneal space in just one procedure, lasting several minutes.
Based on the results of the images obtained during the study, the specialist receives information about how the peritoneal and retroperitoneal parts of the body work, whether there are pathologies in the organs located here, and whether they correspond to healthy standards. The images show in detail pathologies such as:
- inflammatory processes;
- malignant tumors;
- metastases of oncological tumors;
- cysts;
- manifestations of infectious diseases;
- abscesses.
Such common diseases of the circulatory system as aneurysms of the vessels of the abdominal organs, pathologies in the work of lymphatic vessels and nodes will not be left without attention. Traces of internal bleeding, as well as foreign objects that have entered the patient’s body, are clearly visible in the photographs.
But, like any diagnosis, CT has a number of disadvantages, as well as contraindications, under which its implementation is undesirable or completely impossible. Who is the procedure indicated for, how to prepare for a CT scan of the abdominal organs, and why is it dangerous?
What does the examination show?
Computed tomography of the PD and retroperitoneal space shows a number of pathologies. During a CT scan, the device takes pictures from different angles; all organs of the thyroid gland, the intestines, the urinary and urinary system, the prostate gland in men and the uterus in women are subject to scanning.
What the doctor can see in the image:
- vascular abnormalities, including atherosclerosis;
- urolithiasis, calcifications and stones in the ureters;
- cirrhosis and hepatitis of various origins;
- malignant cancer and benign neoplasms of varying degrees;
- metastases in lymph nodes and surrounding tissues;
- acute, life-threatening soft tissue diseases;
- foreign bodies in the stomach or intestines;
- violation of the outflow of bile.
Examination of the gallbladder may reveal sclerosing cholangitis, strictures and choledocholithiasis. A scan of the adrenal glands will show congenital and acquired anomalies, tissue degeneration and oncological processes.
A CT scan of the liver will reveal hemangioma, adenoma, cancer, areas of metastasis, and the degree of cirrhosis. An examination of the stomach will determine ulcerative lesions, diaphragmatic hernia, esophagospasm, congenital anomalies, and neoplasms.
Scanning of the spleen is prescribed to identify the inflammatory process, tissue degeneration, and malformations of the organ. When analyzing an image of the pancreas, you can see the formation of cysts and the development of chronic pancreatitis.
Alternative diagnostic methods
Ultrasound is an affordable and harmless technique for examining organs in this area. Ultrasound allows for a detailed assessment of the location of structures and tissues, detecting foci of infection, developmental anomalies, cholelithiasis, hepatitis and other processes. Due to the physical characteristics of the technique, not all organs of the abdominal cavity can be reliably examined using ultrasound; for example, hollow organs are difficult to access for this type of diagnosis due to the gas content in them. It is also often difficult to conduct a qualitative examination of the pancreas, since it can be blocked by gases localized in the stomach or intestines. The kidneys and adrenal glands are also difficult to examine using ultrasound due to the peculiarities of their structure, location and ambiguous interpretation of the results of ultrasound diagnostics.
The question of which method to examine a particular organ of the abdominal cavity, ultrasound or CT, should be decided only by the attending physician.
One of the effective methods for diagnosing the abdominal cavity is MRI, which does not use X-rays and is excellent for examining organs during pregnancy, as well as in young children. MRI contrast does not contain iodine and can be administered to patients with diabetes, thyroid diseases, allergies to iodine, etc.
The main advantage of MRI is its informativeness in the diagnosis of neoplasms and pathologies of soft tissue structures. Using this technique, liver cirrhosis, hepatitis, pancreatitis, areas of inflammation and other disorders are detected. One of the disadvantages of MRI is poor visualization of hollow organs, as well as the presence of contraindications for persons with metal and ferromagnetic objects in the body.
Using Contrast
A contrast scan is performed to assess the degree of malignancy of tumors and examine blood vessels (CT angiography). Before the procedure, the patient takes a contrast agent orally; double contrast can also be performed, in which case the drug is additionally administered intravenously during the scanning process.
The contrast agent allows you to view the focus of the pathological process in more detail and monitor the blood flow. The patient first undergoes a regular scan, then pictures are taken during and after the contrast is administered. Thanks to this, the doctor can see clear boundaries of the organ and identify weak areas with impaired tissue density.
Preparation
Preparation for a computed tomography scan of the abdominal organs begins the day before the main study.
From the evening before the start of CT diagnostics, the patient should exclude gas-forming foods and drinks from the diet (cabbage, legumes, fermented milk and fermented products, apples, yeast products), and under no circumstances drink alcohol. The procedure itself is carried out on an empty stomach, since active intestinal motility, which appears after eating food, can interfere with computer images. CT can be performed on an outpatient basis, without hospitalization of the patient.
When performing a computed tomography scan of the abdominal organs, contrast enhancement is used according to a special medical scheme. A contrast agent is an iodine-based substance that is used to visualize in detail the areas of interest. The iodinated drug is injected intravenously through a special catheter (Venflon) into the cubital vein and is carried by the blood, staining the vessels, with subsequent accumulation in organs and systems, improving their visualization on images.
Contrast penetrates especially well into pathological areas that are abundantly supplied with blood (areas of inflammation, tumor growths, etc.).
For each patient, a different volume of the substance may be needed to undergo a computed tomography scan with contrast of the abdominal cavity, which is individually selected depending on the person’s weight category. After the examination, the drug is completely eliminated from the body within 24 hours.
If there is an indication for scanning a specific parenchymal organ, oral forms of radiopaque contrast agent are used. The patient must drink several glasses of liquid within a certain amount of time. This method is indicated for studying the work and condition of parenchymal organs:
- liver;
- kidney;
- pancreas.
In rare cases, the patient will need contrast administration in the form of an enema.
Then the whole procedure takes place directly on the table. Before the scan itself, the patient lies down on the table. He must not move so that the data obtained is reliable. According to the protocol, the X-ray specialist asks the patient to hold his breath for a couple of seconds. The entire scanning process takes from 15 minutes, in the case of contrast injection - 25 minutes. During the entire diagnostic process, the patient will be under the supervision of qualified medical personnel. After the study is completed, the intravenous catheter is removed. To speed up the removal of the contrast agent from the body, all patients are recommended to drink plenty of fluids.
How to prepare for an abdominal CT scan
A few days before the procedure, a diet is prescribed that eliminates constipation and bloating. On the day of the study, the patient skips breakfast; the last meal should be at least 12 hours before the CT scan. Dinner should be light, avoiding the consumption of fermented milk products, fresh vegetables, fruits, yeast products and carbonated drinks. A week before the procedure, it is better to completely avoid alcoholic beverages. On the day of the study you need to stop smoking.
If cases of allergy to contrast have previously been recorded, contrast is not performed.
Preparation for CT scan of the abdomen with contrast:
- collecting anamnesis of the disease, excluding contraindications;
- questioning the patient about previous studies using contrast;
- informing the patient about possible temporary adverse reactions after administration of a contrast agent.
Proper preparation for a computed tomography scan of the abdominal cavity affects the quality of the resulting images. To avoid having to carry out additional procedures, it is important to follow all the rules and recommendations of the doctor.
Additional methods of preparation for tomography
In addition to a gentle diet, it is recommended to perform additional preparation methods:
- CT scans are performed on an empty stomach, so the last meal should be no later than 8-9 hours before the examination
- Be sure to do a cleansing enema and take a laxative in the evening and morning before the procedure
- You must wear loose clothing for the examination.
- Metal objects are also excluded. These include: dentures, jewelry, metal “wires” in a bra, watches, glasses, piercings, etc. Pacemakers, hearing aids, and cell phones are also prohibited.
- Depending on the area of study, your doctor may prescribe drinking water. They start drinking water 2-3 hours before the start of the examination, the approximate volume is 2 liters.
If the patient, in addition to the main treatment, takes additional medications, this must be reported in advance before the CT scan.
The attending physician may prescribe medications to improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract:
- Lactofiltrum, Smecta, activated carbon to reduce gas formation;
- for spastic pain or high gastric motility, No-shpu is prescribed;
- mild laxatives for effective bowel movements.
You cannot prescribe or cancel recommended medications on your own! If radiography was performed before the CT scan, the time interval between the two procedures should be at least 5 days.
How the research is carried out
The patient comes to the diagnostic room with a referral from the doctor and the results of other tests, which became the reason for a computed tomography scan of the abdominal cavity. Before the study, you must sign a consent to carry out medical manipulation with the introduction of a contrast agent. The specialist may need the results of a biochemical blood test for urea.
The procedure is completely painless, no anesthesia is required. If there is fear of the test and severe anxiety, the doctor may give a sedative.
The patient lies down on a mobile table around which the tomograph will rotate. During the scanning process, it is important to maintain a stationary position, so you need to take care of comfortable clothes in advance that will not interfere and cause skin irritation. To reduce the noise level from the operation of the device, headphones with pleasant music or earplugs are offered.
How long does the procedure take?
An enhanced computed tomography scan of the abdomen lasts from 1.5 to 2 hours. CT scan with contrast continues for half an hour. A standard computed tomography scan without contrast or enhancement lasts from 15 to 30 minutes.
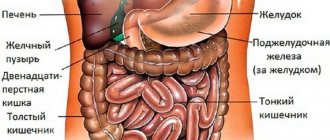
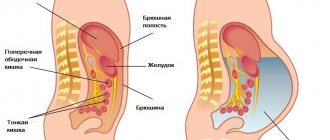
What organs are checked during an abdominal CT scan?
The following BP bodies are subject to examination:
• liver with ducts; • gallbladder with ducts; • stomach and pancreas; • spleen, intestines; • kidneys and adrenal glands; • urinary tract; • blood vessels and lymphoid tissue.
What will the procedure tell you?
The study of the abdominal organs includes the assessment of many internal organs, vessels, their supply, as well as components of the musculoskeletal system located in this part of the body (lumbosacral spine and lower thoracic).
When tomography of the abdominal organs, the state of all systems functioning in this part of the human body, their sizes, shapes and density, and the presence of pathologies in them are assessed. It is important for a specialist not only to examine all systems, but also to assess their performance, the degree of their wear and tear, and suggest the development of possible diseases.
During the diagnostic process, the following systems are studied:
- all parts of the intestine (large, small, rectum);
- liver and pancreas;
- liver, gall bladder and its ducts;
- spleen;
- organs of the urinary system.
A significant addition to diagnosis is the use of contrast fluid: it is injected into the circulatory system, and it is distributed through the bloodstream through the vessels of these organs. Thanks to this, all pathologies of blood and lymphatic vessels in the patient’s abdominal cavity become clearly visible.
IMPORTANT!!! The procedure using contrast is called an angiography (scan). It is not prescribed for every diagnosis and also has a number of limitations and contraindications.
Interpretation of CT diagnostic results
The following data indicates the norm:
- correct anatomical location;
- shape and size within the age norm;
- no neoplasms, no signs of inflammation;
- foreign bodies, areas of fluid accumulation and bleeding are not detected;
- the vessels have normal filling;
- the density of the lymph nodes is not affected.
In case of pathology, CT interpretation includes a description of the following disorders:
- tumor formation or cyst, signs of inflammation;
- areas of altered tissue density and loss of integrity;
- obstruction of the intestines or bile ducts;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- abnormal size and shape of organs;
- stones and calcifications in the gallbladder and ducts;
- foreign body.
1% of patients experience severe complications following the administration of iodine-containing drugs.
Computed tomography of the abdominal cavity: preparation for the study
Firstly, before this examination, the patient is often sent for a preliminary biochemical blood test. Two days before the examination, you will need to follow a diet that excludes the consumption of foods that contribute to bloating - carbonated drinks, dairy products, bread and other confectionery products, vegetables and fruits. The study is performed on an empty stomach. Computed tomography of the abdominal cavity with a contrast agent is performed to enhance the visibility of the organs being examined. To do this, the patient is injected with an iodine-containing drug that stains the tissues and organs being examined, which allows for an accurate diagnosis of tumors and vascular pathologies. Contrast agents are given intravenously, sometimes orally or rectally.
How much does a scan cost?
Average cost of an abdominal CT scan in Moscow clinics:
- CT scan of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneum – 5,000 rubles;
- intravenous contrast – 3500 rubles;
- bolus contrast enhancement – 5000 rubles;
- MSCT OBP – 5500 rubles;
- MSCT of the abdominal aorta – 4500 rubles;
- MSCT of the pelvic organs – 3600 rubles.
Possible side effects after the procedure
The risks of CT scanning are associated with the use of contrast agents. The radiation exposure during scanning is minimal, the consequences of its harm can only be observed with frequent CT scans, which no doctor would allow.
If the skin is hypersensitive, redness and slight swelling may appear in the area where the contrast is administered. After oral administration of the drug, an unpleasant taste in the mouth is noted. These symptoms are not considered dangerous and go away on their own without any consequences. A normal reaction to the use of contrast is a feeling of heat or cold as the substance is introduced into the blood and spreads through the blood vessels.
What is an abdominal CT scan with contrast?
Contrast agents are used to increase the accuracy of the data obtained. This is done by administering contrast agents inside in an amount proportional to the person’s weight. The contrast agent enters the examined organs and tissues through the blood and increases their brightness and clarity in the images.
The contrast agent is introduced into the body of the patient being examined in different ways:
- intravenously
- orally
- rectally.
The specific method of administering the substance is related to the area being studied:
- a method of drinking a special liquid is used to contrast the upper gastrointestinal tract
- administering an enema with a contrast agent - these are the lower sections (large intestine)
- in order to visualize the liver, spleen, pancreas, kidneys, and blood vessels, the drug is administered intravenously (bolus method).
Contrast agents are eliminated from the body within two days and do not harm the patient’s health. If contrast is used to examine nursing mothers, then doctors necessarily recommend not breastfeeding for two days and replacing breastfeeding with artificial feeding.
In CT scans, a drug containing iodine is used as a contrast agent. These drugs, entering the blood, accumulate in the tissues and stain them. Thanks to this ability, the visibility of organs and tissues, as well as the quality of their images, are increased. Areas with inflammation and organ pathologies are very clearly visible, since the blood flow in them is more intense. Contrast agents do not have a negative effect on the body and are eliminated within two days. To increase the speed of contrast removal, it is recommended to drink a lot of water. The amount of contrast administered depends on the patient's weight.