Diffuse changes in the parenchyma of the pancreas are a transformation of the organ tissue that arose during the disease process when the body was exposed to unfavorable factors or developed with age. It is detected by sonography. Such lesions of gland tissue do not always require special treatment.
Let's clarify the definitions
For better perception of information, it is necessary to clarify the terms that appear in the diagnosis.
The parenchyma in the pancreas is the main tissue. This entire internal organ consists of it. The parenchyma is divided into lobules by connective tissue. It is the parenchyma that secretes enzymes and hormones, that is, it performs the main function of this internal organ. As a result of various phenomena, changes occur in the parenchyma. They can be focal, that is, they occur only in a few places, or they can be diffuse. This means that the pathological process affects the entire organ; there are no longer areas with normal parenchyma.
Due to such diffuse mutations, the glandular tissue swells and becomes inflamed. In some metabolic diseases, pancreatic cells can be replaced by fatty or connective cells. Such changes lead to a decrease in the normal functioning of the organ, which negatively affects the digestion process.
Fibrosis and lipomatosis
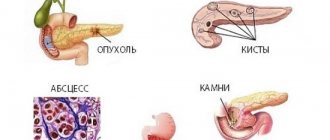
Diffuse changes in the structure of the pancreas most often indicate that partially glandular parenchyma cells have been replaced by connecting elements. Glandular structures are extremely sensitive and delicate by nature. They quickly die off under the influence of unfavorable factors: unhealthy diet, alcohol intake, nicotine, various pharmacological drugs, and serious illnesses.
In the place where there were once normal glandular elements, adipose tissue or fibrous formations appear. Diffuse processes affect all tissues of the pancreas. If the compactions are single, locally located and relatively large in size, we are talking about cystic neoplasms or tumor conglomerates of a malignant nature, but not about diffusion.
A special case
However, there is a situation when the phenomena of fibrosis or lipomatosis form certain foci without spreading throughout the parenchyma. If the organ has been subject to large-scale necrosis, the area where there is tissue deficiency is overgrown with fibrous or fatty cells.
Pathological changes
When examining with ultrasound, great attention is paid to echogenicity. This is an indicator of ultrasound reflection. The tissues of internal organs have different densities, and ultrasound is reflected from them differently. Dense tissue shows high echogenicity, and less dense tissue, on the contrary, has low echogenicity. With pathological changes, the organ tissue becomes denser.
Ultrasound also determines the radiation absorption coefficient. This indicator helps to identify the nature of neoplasms in the pancreatic parenchyma. Malignant tumors have a high coefficient in comparison with benign ones.
Fuzzy contours of the organ are considered signs of the beginning of transformations. The identified “blind” areas are signs of necrosis (death) of tissue areas. Dead cells are replaced by adipose tissue. If the disease develops rapidly, the fat cells can grow very strongly and put pressure on the parenchyma of the gland. This will lead to painful manifestations and severe disruption of the functioning of the organ.
Hemorrhages and fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity are also possible. With age, the size of the pancreas decreases, but echogenicity may remain within normal limits, which makes diagnosing the disease difficult.
What is pancreatic parenchyma?
Pathogenic changes in gland tissue are most often chronic in nature, and therefore there are no symptoms. But on ultrasound, with normal sizes, the gland has increased echogenicity. In elderly patients suffering from cardiovascular diseases and diabetes, healthy cells gradually die off and are replaced by connective or fatty tissue.
Also, similar transformations are observed when the blood supply to the enzyme-forming organ, the liver, is disrupted, when the functioning of the biliary tract is disrupted, or when endocrine and metabolic processes are disrupted. In what other cases do diffuse changes in the liver and pancreas occur?
Similar symptoms are observed with pancreatitis or dystrophic metabolic disorders. The diagnosis of pancreatitis may not be confirmed, and then treatment is not prescribed, and the patient is not recognized as having DIP. Typically, spreading changes occur in glandular tissue. In the chronic course of diseases, pathogenic changes in tissues are practically asymptomatic. These are moderate diffuse changes in the pancreas.
All organs can be divided into hollow and parenchymal. Parenchymal organs consist of the main tissue - parenchyma - and stroma, consisting of connective tissue. These organs include the liver and pancreas.
Its main structural component (i.e., its parenchyma) is glandular tissue, divided into lobules by connective tissue partitions and covered with a capsule. The parenchyma of this glandular organ is multifunctional and performs the following functions:
- Glandular tissue produces pancreatic juice, consisting of food-breaking enzymes such as amylase, lipase and trypsin;
- The islets of Langerhans produce the hormones insulin, lipocaine, and glucagon, which enter the blood and participate in the regulation of carbohydrate and fat metabolism.
Liver tissue is also represented by glandular tissue, which consists of lobules formed from bile-producing cells - hepatocytes.
Inside these parenchymal organs there are ducts - the pancreas and bile ducts. They form a common excretory duct, from which bile and pancreatic juice are excreted. That is why the functions of these organs are inextricably linked and if there is a disturbance in the functioning of one of them, pathological changes in the condition of the other are often observed.
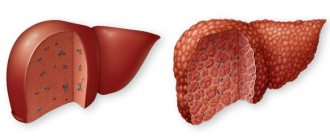
Normally, the structure of the parenchyma of the pancreas and liver is homogeneous, but with various inflammatory or metabolic-dystrophic diseases, the state of its glandular tissue changes - it becomes edematous or its cells are replaced by fatty or connective tissue.
The reasons for such changes are:
- Acute or chronic pancreatitis;
- Diabetes;
- Diseases of the biliary tract, gastrointestinal tract and liver;
- Benign or malignant tumors;
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system (provoking disturbances in the blood circulation of this organ).
Diffuse changes in the structure of the gland can also develop under the influence of the following predisposing factors:
- Unbalanced diet;
- Alcohol abuse and smoking;
- Chronic stressful situations;
- Irrational use of medications;
- Heredity;
- Elderly age.
That is why the term “changes in the parenchyma of the pancreas” is never considered as an independent diagnosis - such an ultrasound conclusion indicates the presence of pathological changes in the structure of the parenchymal tissue of the organ, i.e. it is a separate symptom of a particular disease.
If diffuse disorders are detected in the parenchymal tissues, the patient is prescribed a diet. Its choice depends on the nature of the pathology that led to the appearance of such changes.
If you have diabetes, it is recommended to completely eliminate sugar and sweet fruits from your diet. Alcohol, spicy, fatty, salty, fried and smoked foods, canned food, sausages, carbonated drinks, seasonings and packaged juices are excluded from the menu. The daily diet is allowed to include lean meat and fish, cereals, dairy products, vegetables and unsweetened fruits. Nutrition should be adjusted depending on glucose levels.
If diseases of the pancreas and gastrointestinal tract are detected, the patient is recommended to follow a diet that is indicated for the pathology of a particular organ. In such cases, dry food and overeating are strictly prohibited. Food should be steamed, boiled or baked and taken in small portions, 4-5 times a day.
Organs of various systems are divided according to their structure into hollow (stomach, intestines, gall and bladder) and parenchymal (liver, kidneys, spleen, thyroid gland). Parenchyma is the internal structure of an organ, consisting of active cells. Normally it is homogeneous.
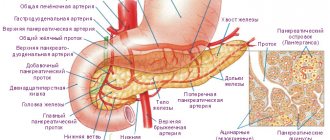
The pancreas is a parenchymal organ and is represented by the following tissues:
- glandular (parenchyma) - the main part of the organ,
- connective (stroma).
The pancreas performs a dual function in the body (digestive and endocrine) due to the structure of the parenchyma. It consists of various structures:
- lobules - the glandular part that produces pancreatic juice,
- The islets of Langerhans are clusters of cells of different structures that produce hormones.
The health of the pancreas is determined by echo signs on sonography. Changes in the picture obtained using ultrasound indicate how much the organ has changed. The pathology manifests itself with different echogenicity - its increase or decrease.
The more pronounced the echogenicity of the structures, the greater the diffuse parenchymal changes. Although in childhood and old age some minor or even moderate compactions are normal. They are represented by uniform or local deviations of echogenicity from the norm. All indicators are assessed in conjunction with the objective status, anamnesis, complaints and can express the degree of organ damage.
Similar symptoms are observed with pancreatitis or dystrophic metabolic disorders. The diagnosis of pancreatitis may not be confirmed, and then treatment is not prescribed, and the patient is not recognized as having DIP. Typically, spreading changes occur in glandular tissue. In the chronic course of diseases, pathogenic changes in tissues are practically asymptomatic. These are moderate diffuse changes in the pancreas.
Symptoms of pathology
Pronounced diffuse changes on sonography are visualized as uniform light, almost white, inclusions on a light gray background of the parenchyma. This indicates their high density and echogenicity. They are accompanied by symptoms of gland failure, which force the patient to see a doctor.
Depending on the duration of the process and the extent of damage to the parenchyma, dyspepsia, weight loss, anemia, and a violation of the general condition develop. With extensive changes in the parenchyma, the islets of Langerhans are involved in the pathological process with the development of type 1 diabetes mellitus. In such cases, a picture of diabetes develops: dry mouth, thirst, involvement of the nervous and cardiovascular systems in the process, and kidney damage. In the absence of diet and adequate treatment, the process progresses and becomes irreversible.
Symptoms of diffuse damage to the pancreas depend, first of all, on the underlying disease that caused the transformation of its tissues. Most often this is the result of developed pancreatitis. Pancreatic juice containing enzymes, during acute inflammation, stagnates in the ducts, not having access to the small intestine due to swelling of the pancreas. Enzymes under pressure enter the pancreas tissue, are activated not in the lumen of the small intestine, but in the parenchyma and increase inflammation: the process of autolysis occurs - self-digestion of organ tissue. This manifests itself in a pronounced clinical picture:
- pain of varying intensity and location,
- nausea,
- vomiting without feeling of relief,
- diarrhea,
- bloating.
Such symptoms of varying severity always accompany damage to pancreatic tissue. With chronic inflammation or other lesions, the manifestations are mild, but the main symptoms of dyspepsia are present. In severe cases, this is confirmed by pathological laboratory tests. In cases with moderate changes in the parenchyma, the main indicators may be within normal limits.
If the changes are caused by a neoplasm or infectious process, in addition to dyspepsia, signs of intoxication appear. Then there may be an increase in body temperature, headaches, dizziness, and poor sleep.
In all cases of changes during ultrasound, additional diagnostics are necessary. This is important for treatment tactics, which must be started as early as possible.
Additional examinations
Often diffuse tissue disorders occur as a result of diseases of other internal organs or systems. To find out the causes of pathologies, I prescribe additional examinations and tests. They examine the functioning of the liver and gall bladder; it is their inflammation that primarily affects the pancreas.
Be sure to conduct an examination of the biliary tract. They are connected by a duct to the gland. With some abnormalities, bile can enter the pancreas, irritate the parenchyma and even destroy it. In severe cases, organ cells die, which leads to death.
With additional examinations, it is necessary to determine how dangerous the pathological changes are to health; it is necessary to identify existing tumors and cysts. It is important to find the reasons for the changes and determine the extent of the damage.
Diffusion
The term diffusion is often used by chemists and physicists. In direct translation from Latin, the term means “spreading”, “merging”, “interaction”.
The essence of this phenomenon can be characterized differently as follows: atoms and molecules of one substance, due to certain circumstances, penetrate into the molecular formula of another substance. From the standpoint of physiology and anatomy of the human body, the diffusion process means a process when one type of cell is replaced by other cellular formations or cells, for some reason, penetrate the structure of other similar elements.
Diffuse changes in the pancreas are a clear example of pathological diffusion, when some healthy cells are replaced by pathologically altered structures. Such unwanted transformations can be both local and mixed in nature. All changes can be seen during an ultrasound examination of the organ.
Causes of changes in the structure of the pancreatic parenchyma
Diffuse changes in the pancreas are a reflection of pathological changes in organ tissue, although they also occur normally. An increase in echogenicity in a particular area is always a pathology.
The reasons for the development of changes in the diffuse nature of the pancreas are:
- Inflammation in the pancreas - pancreatitis. Fibrosis forms - normal cells are replaced by connective tissue. Sometimes this is the result of metabolic disorders.
- Pancreatic necrosis due to total cell death is manifested by increased echogenicity in the form of uniform changes in the parenchyma - morphologically this is also manifested by fibrosis. The size of the pancreas decreases.
- Diseases of the liver and biliary tract, pathology of the stomach and duodenum.
- Various neoplasms in the pancreas and neighboring organs.
- Lipomatosis is the replacement of gland cells with lipocytes (fat cells) that do not contain intracellular fluid - on sonography they appear as diffuse changes of increased echogenicity. The dimensions of the pancreas are not changed.
- Diabetes mellitus - due to the death of beta cells of the islets of Langerhans, which synthesize insulin.
- Vascular diseases that cause circulatory problems in the pancreas.
- Alcoholism, which causes massive destruction of pancreatic cells. Normal cells are replaced by connective tissue cells with the development of fibrosis.
Diffuse changes in the gland may be associated with the following reasons:
- biological aging of the body;
- prolonged inflammation;
- genetic predisposition;
- endocrine disruptions;
- metabolic problems;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- insufficient blood circulation;
- gland diseases: tumor, pancreatitis, cyst.
The above reasons can cause tissue necrosis and their replacement with fatty infiltrates and connective tissue. The process affects the functional part of the gland, which performs its main function. This is the danger of such cell transformations.
The following factors can provoke diffuse changes in the pancreas:
- prolonged stress;
- smoking, drug and alcohol addiction;
- poor nutrition;
- previous surgery on the pancreas;
- parasites.
A specialist can finally determine the disease and signs of diffuse changes in the pancreas by studying the objective results of tests and endoscopic examination of the digestive organs.
Disturbances in the functioning of the digestive organs affect the condition of the pancreas. Chronic diseases are especially difficult to bear because they are protracted. The gland is affected by both pathological processes and side effects of medications.
Causes of diffuse changes in the pancreatic parenchyma:
- Inflammatory processes in the body. For example, pancreatitis (acute and chronic).
- Metabolic diseases. For example, diabetes mellitus, cystic fibrosis.
- Long-term use of toxic medications.
- Diseases of the liver and bile ducts.
- Chronic pathologies of the heart and blood vessels.
- Infections of internal organs.
- Inflammatory processes in the digestive system.
- Abuse of alcohol, fatty foods.
- Smoking not only cigarettes, but also hookah.
Also, in older people, age-related changes in the tissues of this organ and a decrease in its functions occur.
Diagnostic procedures
Diagnosis of disorders in the pancreas begins with clarification of complaints, medical history and an objective examination of the patient. Because due to the location of the pancreas (retroperitoneal), it is rarely possible to palpate it. Functional studies initially include the simplest, most informative and accessible method - ultrasound. It is harmless, does not cause side effects or complications (examination using sonography is prescribed even for a child), and has good reviews from doctors of all specialties. In addition to the pancreas, it is imperative to assess the condition of the entire digestive system, therefore sonography of other digestive organs is performed: the liver, gall bladder and the spleen adjacent to the gland, kidneys and adrenal glands (left). Their size, location, clarity of boundaries, tissue condition - the presence of hyperechogenicity, heterogeneous compactions, organ structure, existing edema or pathological formations are determined.
To exclude pathology of the stomach and duodenum, EGD (esophagofibrogastroduodenoscopy) is performed. This diagnostic procedure makes it possible to assess the condition of the mucous membrane of the stomach, duodenum and esophagus. With peptic ulcer disease, reactive pancreatitis develops, which on ultrasound is manifested by diffuse disorders in the parenchyma.
At the same time, laboratory diagnostics are carried out. Defined:
- general clinical analysis of urine and blood,
- biochemistry indicators (blood and urine diastasis, bilirubin and total protein with their fractions),
- coprogram.
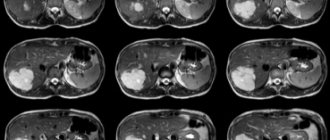
If the diagnosis remains unclear, an MRI or, if there are contraindications, a CT scan is performed.
Ultrasound reveals the presence of tumors, which can be local or diffuse. Even detected uniform parenchymal lesions can be localized only in the head, body or tail. With small tumors, the contours of the organ and its boundaries do not change. With sizes greater than 5−6 cm or more, some deformation of the pancreas may be detected. In such cases, additional examination methods are prescribed, and a biopsy is performed for morphological study.
The main signs of diffuse changes in the pancreas
As a rule, clinical symptoms depend on the severity and severity of the pathology in the parenchyma. Minimal transformation of the pancreatic parenchyma does not cause complaints and is not accompanied by manifestations of the disease: everything is asymptomatic. A person is not aware of changes in the gland; they are discovered by chance during an ultrasound for another reason.
As a rule, signs of DI are associated with the underlying disease. Most often, patients complain that they feel heaviness in the stomach, they are tormented by frequent diarrhea or, on the contrary, constipation. In acute pancreatitis, the pressure in the pancreatic duct often increases, which can cause its deformation. Due to a violation of enzymatic function, some of the digestive enzymes can pass through the cells of the pancreatic parenchyma and cause poisoning of the body.
The initial stage of chronic pancreatitis is accompanied by the appearance of edema and hemorrhages in the tissues of the gland. Then atrophy occurs, the gland decreases in size, connective tissue grows, and enzyme-forming cells stop producing digestive enzymes. Fibrosis is also accompanied by displacement of healthy pancreatic cells and their replacement with connective tissue.
Medicine interprets this as not a disease, but a fact observed on ultrasound. Where is the pancreas located in humans? It is located behind the stomach at the posterior wall of the abdominal cavity, partially in the left hypochondrium. The organ performs an exocrine function and synthesizes hormones. Diffuse changes in the gland are characterized by a decrease or increase in echogenicity - an indicator of ultrasound reflection at a certain density of the organ. In the early stages, the following are detected:
- diffusely heterogeneous structure;
- uneven edges;
- tortuosity of the duct.
Destroyed organ tissue can be replaced by scars and fat cells. Parenchyma is a collection of the main functioning elements of the gland, changes in which affect its density. Heredity can cause problems for a child. The cause of pancreatic disease lies in compaction of the organ. With such an echo sign, its function is impaired. Diffuse pathology is provoked by:
- careless eating;
- craving for salty, spicy, fatty foods;
- bad habits;
- stress, nervous breakdowns;
- age;
- chronic diseases.
In most cases, this pathology does not cause unpleasant symptoms and does not require therapy. It represents a uniform distribution of changes throughout the parenchyma. If there are complaints, the functioning of the pancreas, liver, gallbladder, and other digestive organs is checked. They are interconnected, and the symptoms of the disease for problems with these organs are similar.
By type of lipomatosis
The parenchyma of the organ can gradually be replaced by fat cells. As long as the replacement level remains at 30%, the patient feels almost no trouble. The growth of adipose tissue is associated with chronic inflammation, toxic lesions, and injuries. It is more often observed in older people and patients with diabetes. If the process progresses, this leads to disruptions in the functioning of the organ.
Manifestations of diffuse disorders
Vivid or unexpressed diffuse changes always manifest themselves as symptoms of the underlying disease. Frequent complaints with which a person turns to their doctor for acute pancreatitis include:
- feeling of heaviness in the epigastric region;
- changes in stool;
- painful sensations on the left behind the sternum;
- nausea, sometimes ending in vomiting;
- increased heart rate;
- decrease in blood pressure.
If these symptoms occur, the patient should be hospitalized for further treatment.
Chronic pancreatitis is initially characterized by the appearance of swelling of the organ and hemorrhages in its tissue. In the absence of medical intervention, dystrophy turns into atrophy, which is manifested by a decrease in the size of the gland.
At the same time, the parenchyma is replaced by connective tissue, and the production of digestive enzymes ceases.
With fibrosis, connective tissue grows and there is a lack of production of hormonal and enzymatic substances. The initial period of development of the pathology is manifested by minor symptoms that are similar to the onset of the inflammatory process. Ultrasound can reveal moderate diffuse changes in the pancreas.
Important information: Folk remedies for treating the pancreas at home: potatoes, oats, Izotov’s jelly, herbal medicine
Therapeutic measures
Modern medicine does not know methods for treating irreversible transformations of pancreatic tissue. The cause of this change must be treated to prevent even greater damage. If during examination there is a slight increase in echogenicity, then treatment is not required. Constant monitoring by a doctor and an ultrasound examination once a year are recommended in order to detect other manifestations of the disease in time.
Often changes in the pancreatic parenchyma are detected only during ultrasound, but symptoms will not appear. The patient does not feel pain, but the digestion process may be disrupted. This will mean that the production of enzymes in the pancreas is reduced due to a decrease in healthy cells.
Dying cells can cause intoxication of the body; in this case, special solutions and antibacterial agents will be prescribed. If the adipose tissue grows too much, it must be removed surgically. Competent treatment and a properly selected diet help reduce the rate of development of pathology and avoid complications.
The main cause of irreversible changes in pancreatic tissue is pancreatitis. It most often develops due to alcohol abuse. Fatty foods and toxic food additives also negatively affect this internal organ. The combination of alcohol and fatty foods is especially destructive.
As a preventative measure, every year after the age of 35 you should undergo an ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs. If signs of changes appear, you should consult a specialist. Sometimes it is enough to change some life habits to stop the onset of the disease.
The best preventative measures are to follow the principles of proper nutrition and avoid unhealthy habits. You can maintain the health of your digestive organs with the help of special mineral water and vitamin complexes.
If you are looking for a reliable cryptocurrency exchanger, then https://kassa.cc/ru/ has recently become a fairly popular service.
Treatment of DIP
Diffuse changes in the tissues of the pancreas do not require therapy, since they are not a disease, but only a consequence of any pathology of the pancreas or neighboring organs. They indicate natural processes in the body (found in older people and can be detected in a child) or past illnesses. In such cases, DIPH should not be a cause for concern, especially if you feel well and have no complaints. Therefore, treatment is prescribed only with a more precise diagnosis and can be either conservative or surgical.
Therapy is carried out for the underlying pathology, which is identified by clarifying complaints, anamnesis, objective examination and functional methods. It is impossible to cure already formed changes in the structure of organ tissue, since this is associated with the replacement of healthy pancreatic cells with connective or fatty tissue.
In case of mild exacerbation of pancreatitis, a therapeutic diet and physical therapy are prescribed to treat diffuse changes.
If the cause of DIPG is diabetes mellitus, it is necessary to maintain normal blood glucose levels: a diet and glucose-lowering medications are prescribed. To obtain the desired results, you must do everything that the doctor prescribes during the examination. Sometimes it is permissible to use traditional herbal recipes.
Treatment of diffuse changes in the pancreas in old age is not required. It is necessary to adhere to a diet, an active lifestyle, and give up bad habits.
Therefore, if DIPG is detected for the first time, it is necessary to find out the cause, eliminate it and prescribe restorative therapy. To normalize the condition, in many cases it is necessary to change your lifestyle.
https://youtu.be/JXPuL_Bhnjo
Structure changes
The structure of the parenchyma can be homogeneous and fine-grained. A slightly increased grain size is also not a big deviation. Taken together, an increase in granularity indicates existing inflammation and dystrophic changes in the gland associated with poor nutrition.
Healthy pancreatic parenchyma resembles the echostructure of the liver, being equally homogeneous and fine-grained. Age-related changes in the echogenicity of the gland structure indicate developing lipomatosis, which is often associated with the onset of diabetes. Signs of diffuse changes in the pancreas can be very informative.
Features of diet therapy
With diffuse changes in the pancreas, diet is of great importance. Its basic principles are as follows:
- exclusion of alcoholic beverages from the menu;
- introduction of fermented milk products, various cereals and vegetables;
- Dishes prohibited: smoked, high fat, with a lot of seasonings, salt;
- fractional meals, i.e. in small portions, but often (to exclude strong enzyme production);
- compliance with the calorie content of dishes, so it is better to boil or steam them;
- exclusion from the diet of tomatoes, citrus fruits, some berries (strawberries, raspberries, strawberries), garlic, acetic acid.
Important information: What you can and cannot eat if you have inflammation of the pancreas
In some cases, it is enough to follow the recommendations of nutritionists in order to alleviate the condition and restore the functioning of the gland. A diet for diffuse changes in the pancreas is prescribed by a doctor.
Fibrous DIPG
1) Metabolic disorders.
2) Alcohol poisoning.
3) Viral lesions.
4) Inflammatory processes.
Moreover, lesions caused by viruses affect the entire hepatobiliary system, and not just the pancreas. On ultrasound, diffuse changes in the pancreas are highly echogenic and dense. The presence of diffuse fibrous changes may indicate an existing benign tumor of the glandular tissue - fibroma, the growth of which can compress the gland and cause pain.
Depending on the location of the fibroid, different symptoms will be present. For example, when it is in the head of the pancreas, the ductal duct is compressed, and a symptom of jaundice occurs. If the tumor presses on the duodenum, nausea, vomiting and other symptoms occur that require differentiation from intestinal obstruction. What other echo signs of diffuse changes in the pancreas are there?
Moreover, lesions caused by viruses affect the entire hepatobiliary system, and not just the pancreas. On ultrasound, diffuse changes in the pancreas are highly echogenic and dense. The presence of diffuse fibrous changes may indicate an existing benign tumor of the glandular tissue - fibroma, the growth of which can compress the gland and cause pain.
Preventive measures
With the help of preventive measures, it is impossible to completely exclude the development of diffuse changes in the pancreas if they appear against the background of other diseases. But you can significantly reduce their severity or prevent transformations associated with aging or deterioration of the body. To do this, you must adhere to the following rules:
- Stop smoking and drinking alcohol.
- Follow a diet, do not overeat, eat little and often.
- Go to a proper, balanced and healthy diet, excluding the intake of harmful or heavy foods.
- Constantly use herbal infusions prepared according to the above traditional medicine recipes, using different mixtures.
- Treat all diseases, especially the digestive system, in a timely manner.
- Regularly undergo preventive examinations.
Even a completely healthy person should follow these recommendations in order to avoid most diseases. If there are lesions of the pancreas, they should become the norm of life.
Diffuse changes in the pancreas are often a natural process and may not cause any discomfort. But if they manifest themselves as pain or other negative symptoms, then they necessarily require identifying the causes with the help of competent diagnosis, as well as adequate further treatment. The prognosis depends on the timeliness of all measures, the degree of damage to the pancreas and the severity of the underlying disease against which they appeared. But most often it is positive and the functioning of the organ can be preserved.
Diagnostics
The main method for diagnosing the condition of the pancreas is ultrasound. The method reveals all changes in the ducts, tissue structure and organ size; determines the localization of neoplasms and compacted fragments.
Additional diagnostic methods are used:
- visual examination, palpation;
- anamnesis;
- carrying out general and biochemical analyzes of biomaterial;
- examination of the gland using an endoscope.
Often - in case of oncological diseases, cysts - additional examination is prescribed for differential diagnosis using modern high-precision diagnostic methods: magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP).
During the examination, a layer-by-layer scan of the gland is performed, the extent of the phenomenon’s spread and its exact localization are determined.
Doctors can name the correct diagnosis and correctly select treatment options using the entire range of diagnostic methods.
Ultrasound reveals the exact localization of the affected areas of the organ, the duration of the pathology, as well as various echo signs of diffuse changes in the pancreas:
- Pronounced echogenicity, unchanged size of the gland. Functional tissue is replaced by lipid tissue. If measures are not taken in time, fat can completely block the parenchyma.
- Decreased echo density, slight increase in organ size. Edema and diffuse changes in the pancreatic parenchyma are diagnosed; inflamed areas and self-digestion as a result of impaired enzyme excretion.
- Low level of echogenicity, unchanged organ size (typical symptoms of chronic pancreatitis).
- Echoscopic deficiencies, manifested in the displacement of healthy tissues by lipids, changes in the echo density of the organ. Signs point to diabetes mellitus.
- Sonographic pathologies: increased echo density, preservation (or slight reduction) of the size of the gland. Such changes confirm the development of fibrosis against the background of digestive disorders or inflammation.
- Dystrophic change that is irreversible. There are no pronounced symptoms of the disease, the pathology develops evenly.
- Increased echogenicity of the gland is evidence of pathology (abscess, pseudocyst).
- The heterogeneity of changes in the echostructure of an organ is a sign of mixing of its fragments.
Echo signs differ from each other, but are always a mandatory reason for a thorough examination.
During an examination of the pancreas using ultrasound, the doctor identifies the following signs:
- local - certain organ participants succumbed to high or low echogenicity;
- diffuse - without clearly defined boundaries of pathological areas.
Signs of diffuse changes are found in the parenchyma. When examining the organ, it is noticeable that it becomes heterogeneous. This symptom is often diagnosed with cholelithiasis, hepatitis or chronic gastroduodenitis.
To determine the disease, the treating doctor must conduct an ultrasound examination of all abdominal organs.
Ultrasound of the pancreas
If the doctor determines high or low echogenicity, then this is a serious indicator for further full examination. A high level of echogenicity manifests itself during inflammation with the formation of fibrosis, which develops on the basis of impaired metabolism, when healthy tissue in an organ changes to fat, during acute pancreatitis and its repeated inflammation.
Seals in the parenchyma can form under the influence of various diseases. As a rule, the patient notices certain symptoms that indicate pathological deviations from the norm. These include discomfort, weakness, weight loss. Changes in the parenchyma are also influenced by the diet and method of nutrition, the presence of cholelithiasis, cholecystitis and cystic fibrosis.
In a healthy state, iron has a homogeneous structure. During the examination, the doctor may detect unclear contours, incorrect position, increased or decreased parameters of the head and tail, and different tissue structures.
Heterogeneity of the pancreas is a manifestation of the formation of various pathologies. This indicator indicates pancreatitis and diabetes mellitus.
Moderate diffuse changes can also occur in children. In children, this manifestation occurs due to enzymatic deficiency of the gland.
Diet therapy and disease prevention
Prevention of the formation of diffuse changes consists of simple measures - following a diet in which foods will not irritate the mucous membrane and provoke the formation of various ailments, as well as timely diagnosis and treatment of gastrointestinal pathologies.
1) It is necessary to completely give up alcohol.
2) Follow a diet, take food in small portions, but often.
3) Minimize the consumption of fatty foods.
In case of diffuse changes detected during sonography of the pancreas, one of the main points of complex therapy is diet. Any pathology involving the pancreas requires dietary restrictions. It is recommended to avoid fatty, fried foods, smoked, salty foods, seasonings that promote increased secretion of gastric and pancreatic juice, and reduce the consumption of sweets.
In addition to giving up junk food, you need to stop drinking alcohol, which is one of the main factors that provokes the development of pancreatitis. Alcohol-containing drinks are perceived differently by the human body. Sometimes a few sips are enough to cause the development of pancreatic necrosis.
Smoking, lack of proper rest, and constant stress can increase the risk of pathological disorders. To prevent pancreatic diseases, it is necessary to change lifestyle, include dosed physical activity, and avoid psychological trauma. By following your doctor's advice and adhering to a healthy lifestyle, you can avoid severe irreversible conditions of the pancreas and maintain its normal condition for many years.
Bibliography
- Mitkov V.V. Doppler ultrasonography of celiac blood flow is normal. Ultrasound and functional diagnostics 2001 No. 1 pp. 53–61
- Sidu P.S., Chong W.K. Ultrasound measurements. Practical guide. Medical literature Moscow, 2012
- Ultrasound diagnostics: standards, materials and guidelines. Edited by S.A. Balter. M. Interprax, 1990
- Drobakha I.V., Yakusheva L.V., Malysheva T.F., Chavgun L.B. Ultrasound examinations in the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis. Congress of the Association of Ultrasound Diagnostics in Medicine, abstracts. M., 1995, p. 82.
Diseases that cause the pancreas to become dense reduce its function. Most often, lipomatosis and fibrosis cause pancreatitis, which can be caused by bad habits.
To prevent the development of pancreatitis and its consequences, you should stop smoking and drinking alcohol, and review your diet. The digestive organs react negatively to:
- abundance of food additives;
- a large number of spices;
- canned foods and juices;
- carbonated drinks;
- irregular eating and overeating.
The gland is especially affected by the simultaneous consumption of alcohol and fatty foods. The daily routine should be optimized so that there is time for rest and proper sleep; reduce the number of stressful situations.
If pain and unpleasant symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor.
Signs and symptoms
Changes detected during ultrasound are not always accompanied by symptoms. They become a confirmation of a pathological condition that was in the anamnesis and does not bother the patient today.
Clinical signs of DIPG depend on the disease present at the time of the study, of which they are a manifestation. Moreover, based on the picture obtained using ultrasound, it is possible to verify the diagnosis or conduct a differential diagnosis of suspected diseases.
Signs of DIP include:
- loss of appetite,
- bowel disorder (diarrhea or constipation),
- heaviness or pain in the stomach and hypochondrium,
- nausea and vomiting.
The patient's appearance is characteristic: he is pale, emaciated, with dry skin and underdeveloped muscles.
Symptoms of pathology
The symptoms that accompany diffuse changes in the pancreas obtained on ultrasound are not always a manifestation of pancreatitis. The pancreas is anatomically and physiologically in close connection with the adjacent organs of the digestive system. Therefore, their diseases cause structural transformation in pancreatic tissues.
The clinical picture depends on the existing underlying pathology at the time of the study:
- When a duodenal ulcer is detected, hunger and night pain in the epigastric region, belching, and heartburn are disturbed. At the same time, this may manifest itself as heaviness or pain in the left hypochondrium, unstable stools, and dry mouth.
- With cholecystitis, especially calculous, in addition to pain in the right hypochondrium, bitterness in the mouth and other manifestations of dyspepsia are disturbing. At the same time, the pancreas is disturbing: appetite disappears, discomfort under the ribs on the left with irradiation to the back, the atrium region is disturbing.
- Hepatitis of any etiology also occurs with the involvement of pancreatic tissue in the pathological process. Its symptoms consist of signs of liver damage: pain or heaviness in the right hypochondrium, a feeling of bitterness in the mouth, asthenic syndrome, changes in the blood, and in severe cases - hepatomegaly, jaundice, itching, skin manifestations. But it may also include individual manifestations from the gland itself.
Treatment with folk remedies
Disseminated pathology does not pose a threat to life, but is also not treatable. Only a small fragment of the organ can be removed. In other cases, the doctor prescribes a diet for diseases of the pancreas, medications to treat symptoms of the disease, and replacement therapy (including enzymes). Traditional medicine has its own remedies - alleviating the disease and gradually healing.
Oatmeal jelly is a product in which it is important to first prepare the base. Fill a 3-liter jar 1/3 full with crushed ripe oat grains and pour settled water under the neck. Then:
- As a starter, use 0.5 cups of kefir or a crust of rye bread.
- The preparation is allowed to ferment for 3-4 days.
- Strain, leave for 12 hours, drain the liquid, and put the grounds in the refrigerator.
- Kissel – 8 tbsp. l. sediment with 2 glasses of water - simmer for 5 minutes over low heat.
- Eat before breakfast. It is allowed to add milk and cream.
Herbal decoction with oats is prepared differently. Grind and mix the ingredients: 4 parts purple sedum, 5 parts fennel root, 4 parts centaury, 1 part lemon wormwood, 6 parts milky oats. How to prepare and eat:
- For incomplete st. l of plants take 0.5 l of boiling water.
- Simmer for 2 minutes over low heat. Then leave for 1 hour.
- Drink 50 ml before breakfast, lunch and dinner.
It’s easy to prepare an infusion with sage:
- Mix 3 tsp. calendula, 2 tsp. sage, 1 tsp. iron ore.
- Pour the mixture with a glass of boiling water.
- They insist and filter. Drink in portions of up to 0.5 glasses twice a day.
Find out what diffuse changes in the liver parenchyma are.
Many people with signs of diffuse changes are concerned about how to treat the disease. Medicine has not yet found ways to stop this process. Today, this process cannot be cured. Doctors prescribe therapy aimed at eliminating the source of the disease, which caused the formation of changes in the parenchyma and reducing symptoms.
If the patient is diagnosed with a slight increase in echogenicity, then the patient does not need treatment. Most likely, these changes were discovered during a routine abdominal examination. And if pronounced changes are detected, the patient urgently needs treatment.
A gentle diet is prescribed that will not irritate the gastrointestinal mucosa. You need to eat meals three to four times a day.
The patient must eliminate all bad habits.
Drug treatment is prescribed to the patient if it is necessary to combat the symptoms.
You can use traditional medicine only after consulting a doctor. The doctor may prescribe the patient to drink tea and tinctures of milk thistle, dandelion root, and rose hips.
Treatment of diffuse changes in the pancreas begins with eliminating the factors that caused its pathological condition.
Timely treatment begins greatly reduces the risk of tumors. In this case, a mandatory condition: how to treat, the doctor must decide. He may prescribe medications, physical therapy, diet, or folk remedies under the supervision of specialists.
Complex treatment includes the prescription of vitamins, drugs to improve metabolism, microelements, some hormones and amino acids.
The choice of additional means depends on the disease that provoked the pathology.
- When diabetes is diagnosed, medications are prescribed to stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Pancreatitis is treated in a hospital with medications that relieve pain and spasms, and enzyme preparations.
- For cholecystitis, antibiotics are prescribed; anti-inflammatory, choleretic and antispasmodic agents.
- To treat inflammation of the duodenum, antibiotics and medications that reduce the acidity of gastric juice are used.
The drugs are prescribed when minor diffuse changes in the gland are detected and there are no contraindications.
Treatment
Diffuse changes in the pancreas are not a diagnosis, so treatment is not always required. Minor or moderate transformations of the parenchyma are rarely accompanied by complaints or objective symptoms, so therapy is not prescribed. But in such cases, it is necessary to carry out certain examinations over time and avoid harmful effects on the pancreas, so as not to aggravate the changes and cause progression of the process.
If the condition worsens, complex therapy for the underlying pathology that caused the changes is prescribed. It includes:
- lifestyle modification,
- diet,
- medications,
- physiotherapeutic procedures.
All methods are specified by a doctor and carried out under his supervision. It is not recommended to take certain medications on your own due to possible complications.
It is impossible to cure the morphological changes existing in the parenchyma, especially if a significant part of the organ is affected by them - this is an irreversible process. But it is possible to ensure that they do not increase or progress.
Drug treatment
The most common cause of objective manifestations of pathology in the pancreatic parenchyma is pancreatitis. This is a serious disease that requires drug treatment. The volume of therapy depends on the severity of the manifestations: in some cases, treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis; in case of severe disorders, the patient may be admitted to the intensive care unit or surgical department.
The main groups of drugs that are prescribed for pancreatitis of any severity:
- antispasmodics, anticholinergics, painkillers - they relieve pain well if pancreatic necrosis has not developed (in severe cases, narcotic painkillers are used in the intensive care unit),
- anti-enzyme drugs (also prescribed for progressive necrosis, when it is necessary to stop autolysis - self-digestion of the pancreas with its own enzymes) - have recently been used less frequently due to the fact that the risk of complications outweighs the therapeutic effect,
- drugs for the purpose of detoxification and detoxification (in a hospital setting for acute inflammation or severe exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis),
- enzymes as replacement therapy,
- drugs that reduce the secretion of gastric juice (it provokes excessive formation of pancreatic juice with increased production of enzymes),
- hypoglycemic agents for incipient or already developed diabetes mellitus.
If the changes are caused by a gastric or duodenal ulcer, the underlying disease is treated. Added to therapy:
- antibiotics for detected H. pylori (a microorganism that causes peptic ulcers),
- antisecretory agents,
- hypoacid drugs,
- bismuth derivatives.
Pathology of the liver and biliary tract requires the following:
- hepatoprotectors,
- choleretic drugs (in the absence of stones and small calcifications).
Specific drugs are prescribed by a gastroenterologist or therapist taking into account the general condition, identified changes, contraindications, and their tolerability by the patient.
Phytotherapy
Herbal medicine in the case of pancreatitis can cause allergic reactions and become a factor that provokes an exacerbation of the process. This occurs with minor or moderate diffusion changes in the parenchyma, when there are no complaints and the inflammatory process is in remission. Decoctions of some medicinal herbs (rose hips, dandelion root) are acceptable; bran can be added to the diet to improve intestinal function if there is no peptic ulcer. All decoctions or infusions must be agreed with your doctor.
With pronounced fibrotic changes, traditional methods of treatment are not used, as they can cause progression of the process.