Every woman needs to be examined annually by a mammologist to prevent the development of cancer in the mammary glands. After all, only at the initial stage can cancer be successfully cured. Today it is no longer a secret to anyone that the earlier a woman’s tumor is detected, the greater the chances of a long life expectancy. Early detection increases breast cancer survival rate by up to 90%.
Statistics are such that age becomes critical after 35 years, when X-ray procedures should become mandatory and permanent, at least once a year. After all, only under such conditions will it be possible to prevent the development of cancer and take radical measures to eradicate the tumor in full.
Not only in women, but also in men, breast cancer is not uncommon due to a number of negative factors: poor environment, bad habits, employment in hazardous chemical production.
Of course, women of childbearing age, during lactation during pregnancy, as well as older women during menopause due to hormonal imbalance are most at risk of getting a tumor. However, the chances of survival for a 10-year period are high if the tumor is immobile and is not yet growing or metastasizing. Of no small importance is the place of its localization, shape, size, and the effectiveness of timely prescribed therapy.
The most amenable to treatment and without further relapses is a tumor at stages 1-2 of development. But at stages 3-4, treating breast cancer becomes problematic. If at stages 0-1 doctors give a prognosis for survival in almost 90% of cases, then already at stages 3-4 - no more than 10%, mortality from cancer is high for 2 years.
Breast cancer - causes:
- excess weight is a major risk factor for the development of malignant breast tumors;
- Smoking and excessive drinking:
- late menopause;
- hormonal dependence;
- genetic predisposition;
- absence of children;
- endocrine disorders;
- nonspecific carcinogenic factors;
- fibrocystic mastopathy.
Each patient has a different medical history. For example, cancers detected in the early stages are treated more successfully. If the disease is advanced, the results can be disastrous.
It is important to know! To minimize the risk of disease, oncologists recommend avoiding abortion. On the contrary, frequent childbirth and a long period of breastfeeding reduce the existing risk of developing a tumor in the breast.
Reasons for getting a breast exam are related to early signs of breast cancer. Often the manifestation of certain symptoms gives a woman a reason to be wary and immediately consult a doctor.
Symptoms of breast cancer at stage 1 of the oncological process:
- change in contour, shape, decrease or increase in breast size;
- discharge from the nipple for no apparent reason;
- redness of the skin of the nipple or the entire mammary gland;
- peeling of the skin;
- the appearance of compaction;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- pain in the chest and axillary area;
- increased body temperature;
- sudden weight loss, loss of appetite, fatigue and general malaise are common symptoms of breast cancer.
If you notice at least one of the symptoms, do not be careless. Diagnosis of breast cancer must be carried out regularly to detect oncology in the early stages of its development.
Causes
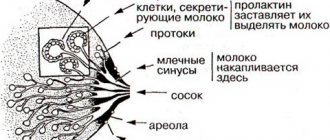
The mammary gland, according to many experts, is the most hormone-dependent organ. And the hormonal status can be influenced by various negative factors, increasing the likelihood of developing pathological processes.
Genetic predisposition
Heredity causes the disease in 10% of registered cases. The risk of cancer increases if you have close relatives who have been diagnosed not only with a breast tumor, but also with an intestinal tract or ovarian tumor.
Features of reproductive function
Special attention should be paid to the connection between breast blastoma and the influence of hormones. The risk of tumor formation increases when the body is exposed to estrogens. These steroidal female sex hormones provoke cell division. If overactive, some will be atypical and therefore potentially malignant.
The following are considered particularly dangerous:
- the appearance of menstrual cycles before the age of 9 years;
- late menopause;
- abortion after the first pregnancy;
- absence of own children or infertility;
- first birth over 30 years of age;
- refusal to breastfeed .
Accompanying illnesses
Benign breast formations, such as fibroids or mastopathy, can develop into cancer over time.
In addition, obesity, diabetes mellitus, pathology of the pancreas and liver, low level of immunity, and problems with the cardiovascular system often lead to the disease.
Lifestyle
Here we should note smoking and drinking alcohol, exposure to chemicals on the body, poor diet, exposure to radioactive radiation, and working in hazardous industries. Even minor injuries to the chest of any nature can lead to the formation of a tumor after a long time.
Also, according to experts, the risk of cancer increases when wearing tight, tight-fitting bras. They limit the free flow of lymph, which entails a worsening of the removal of waste and toxins.
Breast cancer - classification by stages
Oncologists distinguish 4 main stages of breast cancer. Thanks to classification, it is much easier for specialists to determine the current state of the tumor and how intensively it is progressing. Based on the results already obtained, any predictions should be made and specific treatment should be selected. After all, the method of treating breast cancer depends on what stage of development of the cancer is detected. Medicine distinguishes 4 stages of breast cancer, including stage 0 or precancer stage.
In turn, stages 2 and 3 are divided into:
- Stage 2 breast cancer with substages A, B;
- Stage 3 breast cancer with substages A, B, C.
Prognosis and life expectancy
The malignant tumor at stage 2 progresses, but the prognosis for survival is favorable. If the pathology is detected at substage 2A and the tumor is no more than 2 cm, about 95% of patients live for 5 years; with a tumor size of up to 4 cm, the number decreases to 85%. The lifespan when type 2B is formed is reduced. According to statistics, the 5-year survival rate for breast cancer is 60%.
The success of treatment and life expectancy after surgery are determined by accurate and quick diagnosis. Whether the disease was completely cured depends on the occurrence of relapse after treatment. A stage 2 breast tumor is not life-threatening and can be cured. But without appropriate therapy, it can quickly develop into stage 3 breast cancer, and cancer cells spread through the blood and lymph throughout the body.
https://youtu.be/PDfF32VNxz0
Breast cancer stage 2
What to consider when determining the stage of breast cancer?
The classification of breast cancer by stages is based on:
- tumor size;
- prevalence of the process and germination into surrounding tissues;
- the presence of metastases in regional (axillary, supra- and subclavian) lymph nodes;
- the presence of distant metastases of internal organs and tissues (liver, lungs, brain, skeletal and spinal bones, etc.).
A diagnosis such as cancer, of course, makes most women fall into despair and give up. After such news, I don’t want to do anything, just look for any miraculous remedies from different healers. Many women, out of ignorance and despair, engage in “healing” fasting, which does not have an optimistic effect on the course of the disease, leading the body to a state of weakening and exhaustion.
If we refer to statistics, then about 80% of women triumph over cancer, but only if it is detected at an early stage. Of course, simply identifying is not enough. It is very important that all breast cancer treatment is comprehensive and not interrupted.
What is stage 2 breast cancer and what is the prognosis?
Stage 2 tumor
Stage 2 breast cancer is considered an early stage of this type of disease. However, this is already a malignant tumor, the size of which reaches 5 cm. Also at the second stage, the lymph nodes in the armpit area are affected. The lesion is characterized by the fact that the lymph nodes do not have adhesions between themselves and other tissues. If there are adhesions, then this indicates inflammation of the tumor focus, which is caused by the spread of the tumor itself to other organs. The presence of adhesions is the first sign that stage 2 breast cancer is progressing to stage 3.
Among all stages of cancer, only the second and third are divided into subtypes. This is necessary in order to distinguish between patients according to the volume of surgical intervention required, type of chemotherapy, and radiation treatment.
Signs and types of stage 2 breast cancer:
- 2A substage. The size of the tumor exceeds 2 cm. The tumor spreads to the lymph nodes. If the tumor size is up to 5 cm, and the nodes are not affected, in 81% of cases this type ends in recovery of the patients. These statistics are provided by the American Cancer Society;
- 2B substage. It is characterized by a tumor diameter of 5 cm or more, with further spread to several nodes.
How to recognize the disease?
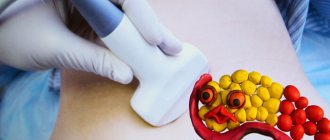
To begin with, to detect breast cancer, you need to carefully monitor the condition of your breasts, feel and examine them every day. If hardened nodules, compactions or an uneven surface become noticeable, this should alert you and be a reason for immediate contact with oncologists. Next, you should monitor for nipple discharge, sudden changes in breast shape or nipple color. The ideal option is to visit a doctor once a year to diagnose the glands, undergo an ultrasound, and be examined by a mammologist.
Diagnosis of stage 2 breast cancer
Tumors that are regarded as stage 2 breast cancer have fairly clear symptoms, which makes it possible to determine the disease quite simply. All that is required is sufficient attention to your body and the changes that occur in it.
Palpation and examination of the mammary glands is a simple diagnostic procedure, during which nodular formations are detected in the thickness of the mammary gland, which in turn becomes the main reason for women to see a doctor. This is why stage 2 breast cancer most often occurs when the initial diagnosis is made.
At the second stage, cancerous tumors can reach quite large sizes; therefore, they can be diagnosed without the use of additional research methods.
Detailed diagnostics are carried out using the following methods:
- Ultrasound for patients under 40 years of age;
- mammography of older women;
- MRI to determine the presence of metastases;
- tumor markers for breast cancer;
- biopsy followed by histological examination of the material;
- examination of lymph nodes is carried out as an additional examination for the presence of metastases;
- scintigraphy;
- Abdominal CT scan;
- general blood and urine tests.
It is important to know! A histological examination of the suspicious area is carried out in order to determine the nature of the tumor, namely, whether stage 2 of breast cancer is confirmed, or whether the tumor is at a different stage of development.
Treatment of stage 2 breast cancer
Depending on the size of the tumor, a course of chemotherapy may be prescribed, both before and after surgery.
It is worth noting! Treatment for stage 2 breast cancer is similar to treatment for stage 1 breast cancer.
Positive treatment results can be achieved by using the following therapy methods:
- Surgery
Breast cancer stage 2: treatment involves radical surgery, the extent of which can only be determined by the attending physician. This can be either a mastectomy or an organ-preserving type of surgery (sectoral resection, quadrantectomy of the breast). If the lymph nodes are affected, they are also surgically removed.
- Chemotherapy
Cancer cells are destroyed using powerful modern drugs. Chemotherapy is used to treat any type of cancer. Treatment regimens and course duration may vary depending on the individual characteristics of the cancer.
- Radiation therapy
This type of therapy does not always take place. It is used in combination with surgical treatment or is part of a comprehensive treatment program.
Life expectancy for stage 2 breast cancer
Breast cancer at the second stage is a relatively favorable form of the disease, despite the fact that it belongs to the group of malignant tumors; more than 80% of patients overcome the 5-year survival line. After this period, patients are not monitored, since it is believed that the disease can no longer recur. Stage 2 breast cancer with properly selected treatment is characterized by a favorable outcome and survival rate is 80-85%.
Diagnostic methods
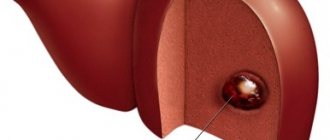
Breast cancer on an x-ray
The patient is sent for a consultation with an oncologist or mammologist. The doctor will perform an initial examination. Conclusions will be drawn regarding changes in breast shape, skin color, nipple discharge, and the presence of lumps. To make an accurate diagnosis, a woman will need to undergo a series of examinations and a diagnostic method chosen by the doctor.
Diagnostic tests:
- Blood test for tumor markers. Detects the formation of a malignant tumor.
- General blood analysis. The composition of the blood is studied, which helps to notice deviations in certain processes in the body.
- Mammography. Diagnostics allows the doctor to see changes in the breast tissue. New growths and tumor size will be visible. You can also determine the stage.
- CT or MRI. Provides visibility of the tumor. It becomes possible to consider the form and boundaries of education.
- Biopsy. A thin needle is used to remove a microscopic piece of tissue from the affected part of the breast. This method helps to make the most accurate diagnosis, determine the aggressiveness of the tumor and its nature.
Breast cancer stage 3
Very often, oncologists classify inflammatory breast cancer as stage 3 and position it as one of the most serious forms of the disease, occurring in 10% of patients. It manifests itself primarily as redness of the skin on the chest. As a rule, it is warm and often covered with orange peel or pimples. Induration may also be observed, but do not confuse ordinary mastitis induration with inflammatory cancer. Very often, not a simple compaction is formed, but a clear knot. This indicates the spread of “other” cells into the tissue, which leads to their adhesion. Such a tumor does not have a contour and is often accompanied by a change in the shape of the mammary gland.
Stage 3 breast cancer is more serious and dangerous to a woman’s life and health. It also has three substages: 3A, 3B, 3C. The third stage can be characterized by the active movement of cells to nearby tissue areas. The main symptoms of the disease begin to appear. In addition to lumps in the areas of the chest and armpit, clear or bloody discharge may begin, complete deformation of the breast and a change in the structure and color of the skin may occur.
The third stage can be roughly divided into types:
- 3A substage. The tumor may be larger or smaller than 5 cm. In the first case, the tumor begins to spread to the lymph nodes in the chest areas. The second option is about the same, only on the side of the cancer process itself;
- 3B substage. The tumor has already reached the walls of the chest, or has touched the skin. In this case, the cancer has spread to the lymph, as well as to nodes in the sternum. Inflammatory cancer can also be attributed to this stage, when the breast becomes red and swollen;
- 3C substage. The tumor can be of any size. The disease rapidly metastasizes to all groups of lymph nodes (axillary, supraclavicular, cervical).
Stage III-A
Stage III-B
Treatment of stage 3 breast cancer
The main method of treating stage 3 breast cancer is a complex attack on the tumor, which includes chemotherapy and hormone therapy. And only after the treatment measures have been carried out, a decision is made on surgical intervention. If the result is positive, the surgeons consolidate the treatment process with a course of chemotherapy or targeted ionized radiation.
However, in case of tumor necrosis, bleeding or abscess formation, treatment begins with surgery (palliative radical mastectomy). And subsequently, after the operation, chemotherapy and radiation therapy are used.
Chemotherapy is carried out using cytostatic drugs that destroy the mechanism of division of cancer cells and thereby destroy them.
Such drugs include:
- platinum preparations (Cytoplastin, Cisplatin, Carboplatin, Triplatin, etc.);
- drugs from a group of taxa (Paclitaxel, Taxan, Paclitax, Paxen, etc.);
- drugs from the vinca alkaloid group (Vincristine, Vinorelbine, Vinblastine, Maverex);
- oxazaphosphorine derivatives (Endoxan, Mafosfamide, Trofosfamide, etc.);
- fluoropyrimidine carbamate derivatives (Capecitabine, Xeloda), etc.
Chemotherapy for breast cancer can be carried out as the only method of treatment, as well as to reduce the size of the tumor before surgical removal and stop the formation of metastases after surgery.
Surgical intervention consists of removing the tumor and part of the surrounding tissue (lumpectomy). Mastectomy - performed in most clinical cases of breast cancer - removal of the entire mammary gland.
Radiation therapy for breast cancer, like other methods of therapy, destroys cancer cells under the influence of radioactive radiation. Radiation therapy can complement chemotherapy and surgical removal of a breast tumor.
Hormone therapy is carried out only for patients with hormone-dependent tumors, that is, if cancer cells have receptors for estrogen and progesterone. Aromatase inhibitor drugs are prescribed, which include Anastrozole, Letrozole or Exemestane.
Combined treatment of stages of breast cancer involves individual selection and simultaneous or alternate use of all methods and therapy.
Life expectancy for stage 3 breast cancer
Already at stage 3, cancer is considered incurable. However, it is quite possible to extend life for more than a dozen years, especially if this is only the initial 3rd degree of development.
It has already been mentioned that at the third stage, cells begin to actively divide and take over the free space of neighboring tissues. Statistics for stage 3 breast cancer indicate that the prognosis for successful treatment can be observed in only 30% of patients. However, it is too early to be afraid. If you organize treatment correctly and follow the recommendations of your oncologist, you can defeat cancer.
Stage 4 breast cancer
The most serious problem in oncology is the advanced stage of the oncological process, that is, stage 3 or 4. The presence of such forms of neoplasms is alarming, since modern diagnostic conditions are set at a fairly high level. This is explained by the fact that most patients neglect their health and do not react carefully enough to the presence of signs of the disease.
Stage 4 breast cancer is usually incurable. This is due to the development of the oncological process not only within the mammary glands; the axillary region, nodes and main organs, including the brain, are also affected. Cancer cells (metastases) spread throughout the body and penetrate into the lungs, liver, bones and other organs. Without a doubt, stage 4 cancer is the most severe form of breast cancer.
What kind of cancer is this and what is the likelihood of survival?
IV stage
What do you mean by stage 4 breast cancer?
- The presence of cancer in one or both mammary glands. The tumor can grow throughout the thickness of the mammary gland and extend beyond its limits. The neoplasm reaches very large sizes and spreads to: bones, muscles, intrathoracic lymph nodes and lymphatic collectors of the axillary region.
- Tumor of any size with distant metastases in internal organs.
- Breast cancer is accompanied by the disintegration of the neoplasm.
Reasons for late diagnosis of breast cancer:
- late seeking medical help;
- old age (60-80 years;
- rapid and rapid progression of cancer;
- cancer recurrence and disease progression after radical treatment. This part of stage 4 cancers has a significant place in the overall structure of advanced breast cancers. Most often, this is possible in the treatment of women with stage 3 cancer, when the tumor has spread beyond the breast or has given large metastases to the axillary lymph nodes.
Diagnosing stage 4 breast cancer is not difficult. You don't need to be a great specialist to identify an obvious tumor in the breast or in the area of the armpit, which is caused by enlarged lymph nodes.
At this stage of development of breast cancer, symptoms such as:
- change in the shape of the mammary gland;
- change in size (breast enlargement or reduction);
- purulent and bloody discharge from the nipple with an unpleasant odor;
- redness, peeling of the breast;
- severe pain;
- yellowness of the skin with metastatic liver disease;
- headaches, bone pain.
Treatment of stage 4 metastatic breast cancer
Unfortunately, at this stage, it is difficult to fight breast cancer, and this fight does not give positive results, since at stage 4, it is possible to talk only about prolonging life and making it easier.
There are many types and types of breast cancer, and each differs in the degree of aggressiveness and spread of cancer cells. Some rapidly metastasize, while others, being at stage 4, have single metastases. The effectiveness of treatment depends on this. Metastatic breast cancer must be treated comprehensively.
The main method of treating such an advanced disease remains combination drug therapy, which should include the use of powerful chemotherapy drugs,, if necessary, hormone therapy, and targeted therapy drugs (of course, only in individuals sensitive to such treatment).
If the tumor is not large and there are single metastases in the lungs and liver, a combined surgical intervention is possible, followed by a course of chemotherapy, hormone therapy and radiation therapy if necessary. The operation is performed to remove one or both mammary glands, as well as resection of segments of the liver or lungs affected by metastases.
Also, surgery to remove the mammary gland is performed to relieve symptoms that are caused by the disintegration of the tumor. Before and after surgery, courses of chemotherapy and radiation therapy are prescribed.
There are patients for whom surgery is not appropriate. They are given painkillers that help reduce pain and improve well-being.
Breast cancer stage 4, what is the prognosis and life expectancy?
It is worth noting that survival prognoses for stage 4 breast cancer are quite modest. And if in the initial stages of development of a malignant neoplasm of the breast, the 5th survival rate is about 85% or even 90% of patients, then with the 4th degree of damage to the female body, with a diagnosis of breast cancer, the percentage of five-year survival is negligible and amounts to no more than 10%. .
In any case, even with such a scary diagnosis, sitting with arms folded is not a way out. Many women at this stage of the disease managed to extend their lives by many years with the help of chemotherapy and hormone therapy. The main thing is not to give up!
Diagnosis of blastoma: prognosis for cure
28 Feb
Every year, about five million people die around the world whose organs and systems in their bodies have been affected by malignant tumors. The diagnosis of blastoma (malignant tumor) sounds like a death sentence for many. However, blastomas, depending on the location and type of tumor, can be easily eliminated if detected and treated in a timely manner. The type of blastoma plays a key role in the patient’s prognosis for recovery.
What is blastoma? In oncology, under the general name blastoma, it is customary to combine any neoplasms and tumors. Their occurrence is caused by pathological excessive growth of tissues, which consist of altered cells of the body, the functions and shape of which have been changed under the influence of certain factors. Blastomas continue to grow even after the influence of the factors that triggered the start of their growth ceases.
Blastomas are divided into two types: Benign tumors (their growth is slow, they do not grow into neighboring tissues, but only push them away or squeeze them). Malignant tumors (their growth is invasive (infiltrative), that is, they grow into surrounding tissues, destroying them, damaging blood vessels, which then spread deadly cells throughout the body, thus causing the development of metastases). If the nature of the detected tumor is benign, it is not considered an oncological disease (blastoma, the prognosis of which is the most favorable of all), however, unfortunately, benign forms occupy only one percent of the total number of neoplasms. In addition, even a benign tumor can be dangerous if it is located in a dangerous place where it can put pressure on organs that are responsible for performing vital functions of the body. Another danger of benign tumors is that they can, under certain circumstances, develop into malignant tumors.
Malignant tumors with metastases affect vital organs, lead to anemia, intoxication of the body with decay products of degenerated tissues, metabolic disorders, dysfunction of the body's regulatory systems and immunity. The inevitable consequence of all these processes is complete exhaustion of the body, in which conservative treatment of blastoma is no longer effective, and the prognosis is completely unfavorable.
Blastomas are divided into main types (depending on the affected organ): Glioblastoma (brain tumor) Medulloblastoma (cerebellar tumor) Neuroblastoma (tumor affecting the nervous system) Retinoblastoma (eye tumor) Nephroblastoma (kidney tumor) Hepatoblastoma (liver tumor) Pleuropulmonary blastoma ( lung tumor) Breast blastoma Uterine blastoma Gastric blastoma Treatment methods for a patient diagnosed with blastoma and the prognosis depend on the type of tumor, the stage of its development and location.
The further a tumor develops, the more independent its growth becomes from the body's regulatory systems. In the absence of medical intervention, metastasis follows, which significantly complicates (sometimes makes it impossible) further treatment of blastoma, and the prognosis for recovery is reduced to a minimum.
Causes of blastoma The main reason is genetic mutations that can occur even before a person is born (hereditary predisposition to cancer is known). Genetic changes (that is, mutations) are provoked by carcinogens affecting the DNA molecule in a cell gene. Under normal conditions, protection against cancer in the body is carried out by antioncogenes, but under conditions of mutations the level of protection drops to a critical level.
Oncogenic viruses that create a high risk for the human body of developing malignant tumors include:
hepatitis types B, C (provokes the development of hepatoblastoma - liver cancer); human papillomavirus of certain types (increases the risk for women of developing cervical and genital cancer - the latter is also true for men); herpes virus type 8 and Epstein-Barr virus (provoke the occurrence of sarcoma and lymphoma); HIV status (not directly related to cell transformation, but creates immunodeficiency in the body, under conditions of which it is easier for blastomas of any type to develop). A hereditary predisposition to cancer has been proven. Therefore, people whose close relatives are familiar firsthand with the terrible medical phrase “blastoma prognosis” are recommended to regularly (once every six months to a year) undergo preventive medical examinations and examinations.
When it comes to female forms of cancer (for example, breast blastoma), serious problems with the hormonal levels in the body may be possible reasons that triggered the growth of malignant cells.
Among other reasons that indirectly affect the development of malignant formations in the body, scientists name bad habits (smoking, alcohol abuse), poor quality nutrition (excess calories, an abundance of animal fats, nitrates, preservatives, vitamin deficiency) and weak immunity, suppressed by uncontrolled intake relevant medications.
A healthy lifestyle is an excellent prevention for any person who does not want to ever type the query “blastoma forecast” into an Internet search engine.
Symptoms of blastoma In the initial stages of cancer, there is no pain, fever or other symptoms that force a person to immediately seek medical help. Therefore, many patients who neglect preventive examinations by doctors are subsequently forced to undergo treatment in the final stages of blastoma development, when doctors’ forecasts are no longer accurate.
However, in oncology there are a number of so-called minor signs, which in combination should make a person wary and turn to doctors for tests and a comprehensive examination. These include decreased ability to work, rapid fatigue, general weakness, loss of appetite, food rejection (including nausea and vomiting), sudden significant loss of body weight, unnatural discharge (mucus or blood).
It is also worth focusing on the syndrome of unsuccessful treatment. It is characterized by a persistent disruption in the functioning of any organ or system of the body - and the detected disease cannot be cured by classical methods.
The growth of a space-occupying formation is possible, which can be detected by palpation of the sore spot. Particular attention should be paid to the lymph nodes. When palpated, the affected nodes may be enlarged, lumpy, and dense.
All of the above signs serve as a signal to immediately consult a doctor if a person does not want to risk getting to know blastoma and its prognosis in the future.
Diagnosis of blastoma Detection of tumors in modern medicine is carried out using x-ray examinations and morphological studies:
Traditional X-ray Computed tomography Magnetic resonance imaging Ultrasound Laboratory analysis for oncological markers Biopsy of affected tissue The more complete diagnosis is carried out, the more accurate the diagnosis the oncologist will be able to establish, significantly increasing the prognosis for curing blastoma.
Treatment of blastoma Treatment methods depend on the type of tumor, its location, stage of development of the disease, physical condition and age of the patient, etc. The further prognosis depends on the correctly selected and successfully applied treatment method for a specific type of blastoma.
Traditional methods of treatment: Surgery Chemotherapy Radiation therapy Palliative therapy Most often, oncologists recommend surgery to remove the tumor in order to prevent subsequent metastasis. However, this type of radical treatment is ineffective in the case of metastases. Also, surgery is not always possible due to the dangerous location of the tumor (if there is a risk of damaging neighboring vital organs). Otherwise, radical surgical excision today has the highest chance of giving a patient diagnosed with blastoma a prognosis for a further full and healthy life.
Other methods of treating malignant neoplasms are used both separately and in combination treatment.
Unfortunately, modern medicine can offer patients at the last, 4th stage of cancer only palliative treatment (short-term prolongation of life and improvement of its quality). Therefore, the best treatment is prevention in the form of regular medical examinations and traditional examinations, which significantly improve the prognosis for preventing the development of blastoma in the body.
Blastoma prognosis The prognosis for recovery, as well as the survival of patients, mainly depends on the type of blastoma.
Different types of blastomas have different prognoses:
Lung blastoma has an extremely poor prognosis due to the aggressive type of tumor. With timely treatment, the five-year survival rate of patients is about 15-30% (depending on the stage at which treatment was started and the type of tumor). If detected early and surgically removed, there is an 80% chance of cure. However, the prevalence of relapses of biphasic lung blastoma and the occurrence of metastases is 30-40%, which significantly worsens the prognosis.
Uterine blastoma in women has a more favorable prognosis. A favorable prognosis depends on the stage at which treatment of the disease began. In the CIS countries, the five-year survival rate is about 90%, provided that uterine cancer is detected at an early stage. According to other sources, this figure is about 80%, which is still a favorable forecast. In the second stage of the disease, survival is 50-60%, in the third - about 30%, and the fourth stage is characterized by low survival - 7-9% of patients.
Prostate tumors in men also have a fairly high prognosis for healing - in the case of radical prostatectomy in the early stages, the five-year survival rate is 80-90%. And even at stage 3, when the tumor has spread beyond the prostate but has not yet metastasized, doctors manage to remove the source of malignant cells in 50% of cases.
Nephroblastoma (Wilms tumor - kidney damage), with high-precision diagnosis and the use of combination therapy in the early stages, gives a very high chance of recovery - about 80-90% of patients return to normal life. The prognosis for brain blastoma may vary depending on the stage of the disease, the type of tumor and its location. However, it is not so high due to the danger of damage to the most important organ that controls the entire human body. Thus, glioblastoma is considered the most malignant - an inoperable tumor that leaves the patient only 1-1.5 years of life if untreated and a little more if palliative therapy is used.