First stage of the luteal phase
During ovulation, the granulosa membrane ruptures; to put it in medical terms, the wall of the Graafian follicle bursts. After rupture occurs, fluid from the follicle flows from the ovarian tubercles containing the egg into the peritoneum. This stage is called follicle decline. When there is a violation of the integrity of the vascularized epithelium, a process of destruction of the integrity of small vessels occurs in the membrane. They begin to bleed in the place where the follicle was ruptured due to the fact that the pressure inside it decreases. In this area, blood clotting occurs, and after some time, metamorphosis occurs with this blood clot.
The remaining part of the granulosa membrane, which is the follicular cells of the epithelium, connects with the theca interna, becomes profiled and hypertrophies. After which the process of germination into a clot begins, and the formation of large epithelial blastomeres begins along the edge of the burst membrane. They begin to grow larger, their bodies become rounder and their numbers increase.
Lutein is an important component of the corpus luteum
At this time, the cytoplasm accumulates spherosomes that have an orange-yellow tint (lutein) containing droplets of fat. Depending on where the cells came from, elements are distinguished that originate from the granulosa membrane (luteal follicular cells), as well as from the theca (thecal luteal blastomeres). This is how the process of formation of a fibroblast node occurs, in the center of which, in the place of the bursting gaaf follicle, a small part of a blood clot overgrown with connective tissue remains.
From blood clot to corpus luteum
This formation is called sanguinolentum. Lutein, represented by a yellowish substance, colors the membrane that begins to enlarge in a yellow-orange hue. That is why it is called the “yellow body”. The luteal phase, during which progesterone peaks and is secreted, is a favorable time for the formation of the corpus luteum. Along the edge, where the luteal cells are concentrated, thin vascular bundles and connective tissue begin to grow. During this process, a small organ is formed, the structure of which resembles an endocrine gland.
The luteal phase is represented by cellular formations with nodules and bars that fill the entire corpus luteum. The result of the appearance of these cells is the remains of a blood clot located at this site.
What it is?
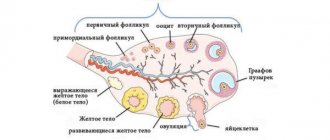
The process of ovulation in a woman’s body is regulated by hormonal levels. It is under the influence of certain concentrations of hormones that the follicle matures in the ovary in the first half of the cycle and the release of a mature egg after the rupture of the follicle. In the second half of the cycle, hormones also play a large role. The first half of the female cycle is called follicular, since during this period, under the influence of the hormone FSH, the follicle matures and enlarges, inside which the egg matures.
When the follicle reaches a large size, under the influence of estrogens and luteinizing hormone, its membrane becomes thinner and it ruptures - this is the mechanism of ovulation. The egg lives from 24 to 36 hours; after its death, conception is no longer possible . In place of the follicle that bursts at the time of ovulation, a corpus luteum is formed, producing progesterone. Therefore, the second half of the cycle is called the luteal phase or the corpus luteum phase.
The period of ovulation itself and the viability of the egg is the ovulatory phase.
- Menstruation
- Ovulation
- High probability of conception
Ovulation occurs 14 days before the start of the menstrual cycle (with a 28-day cycle - on the 14th day). Deviation from the average value occurs frequently, so the calculation is approximate.
Also, together with the calendar method, you can measure basal temperature, examine cervical mucus, use special tests or mini-microscopes, take tests for FSH, LH, estrogens and progesterone.
You can definitely determine the day of ovulation using folliculometry (ultrasound).
- Losos, Jonathan B.; Raven, Peter H.; Johnson, George B.; Singer, Susan R. Biology. New York: McGraw-Hill. pp. 1207-1209.
- Campbell NA, Reece JB, Urry LA ea Biology. 9th ed. - Benjamin Cummings, 2011. - p. 1263
- Tkachenko B. I., Brin V. B., Zakharov Yu. M., Nedospasov V. O., Pyatin V. F. Human physiology. Compendium / Ed. B. I. Tkachenko. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2009. - 496 p.
- https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ovulation
Degenerative processes in the corpus luteum
The corpus luteum, which forms and degenerates every 28th day, is called the “menstrual body.” When the luteal phase ends, progesterone, the norm of which is not exceeded, has a degenerative effect on the cells of the “yellow menstrual body”, in the place of which connective tissue is eventually formed.
After this process is completed, the corpus luteum is replaced by a whitish, slightly shiny scar consisting of dense connective tissue. It is called whitish or fibrous. If a woman becomes pregnant, then it not only does not leave the ovary, but also increases and performs its functions until the second trimester of pregnancy. Its endocrine activity suppresses the action of other membranes, in other words, it prevents blood clots from appearing. As a result, the norm of the luteal phase means that the reproductive system is functioning normally, which means that there are no obstacles to conceiving offspring.
For those wishing to get pregnant, the luteal phase, the cycle day of which falls in the middle of ovulation, is very important, because with the right calculations, the long-awaited conception can occur. But not everything is always so simple, because some women also have a disorder.
LLF or luteal phase deficiency is a fairly common disorder of ovarian function in the female half of humanity. This problem usually worries those who are unable to conceive, or those who have had repeated early miscarriages.
Luteal phase deficiency is caused by the fact that the corpus luteum does not produce progesterone in the required amount, which is necessary for fertilization and pregnancy.
Why did the pregnancy occur?
Some girls, having calculated their cycle, are surprised that conception occurred on the day when they did not have intimacy with their partner. The fact is that sperm can live in the fallopian tubes for up to 6 days. If ovulation occurs, the egg moves through the fallopian tube into the uterine cavity. There she meets sperm that remain from previous sexual intercourse.
Conception can occur if sexual intercourse occurs on the first day after the ovulatory phase, since the egg does not immediately leave the body, but lives in the fallopian tube for about a day.
About the cause of NLF
The main causes of deficiency may be several fairly common reasons, consisting in a violation of the central regulatory mechanisms of reproductive function, which has a detrimental effect on various levels of the system, from the hypothalamus and pituitary gland to the functioning of the ovaries.
In this case, the ovaries produce a small amount of hormones, and the doctor, upon examination, determines hyperprolactinemia and hyperandronemia - disorders in the thyroid gland and adrenal cortex.
Firstly, this condition causes hormonal imbalance.
Secondly, it has an inappropriate effect on the developing egg. Thirdly, degenerative changes occur in the endometrial receptor apparatus of the inner lining surface of the uterus.
This factor is influenced by infections and inflammation, adhesions after cesarean section, abortions and miscarriages, and abnormal development of the appendages and the uterus itself or delays observed during puberty may also be to blame.
In such cases, infertility will occur due to the fact that the egg fails to attach to the uterine wall, which will subsequently prevent it from receiving vital substances and other components for the development of the baby.
The second reason may be a lack of lipoproteins due to low blood density, as well as the amount of progesterone required in it, and a change in the biochemical composition of the peritoneal fluid.
About symptoms and diagnostic methods
With this problem, scanty discharge before menstruation, irregularities in the menstrual cycle, infertility, and frequent miscarriages in the first and second trimester of pregnancy appear.
In order to determine luteal insufficiency, you can use a couple of methods. Measure your basal temperature. If the hormone is observed in small quantities, then changes will be visible in the second phase. Do an ultrasound and examine the dynamics of follicular growth and the thickness of the endometrial layer, as well as examine the hormonal status and take a biopsy of the membrane lining the uterus. This method is also effective in that it will help identify other abnormalities in the menstrual cycle.
Sometimes doctors talk about hysterosalpintography to determine the level of patency of the fallopian tubes, as well as determine their tone.
Traditional methods
Some patients use traditional medicine. A popular recipe for tea made from dried raspberries. You need to pour 2 tablespoons of crushed raspberry leaves into 0.5 liters of boiling water. After an hour, filter the mixture and drink it in small sips throughout the day.
To normalize the menstrual cycle, another recipe is suitable. You need to take 1 teaspoon of crushed plantain seeds and 1 tablespoon of common mantle. The plants are mixed and brewed with 1 cup of boiling water. When the composition has cooled, filter it and drink 1 tablespoon 3 times a day.
Traditional medicine recipes can only be used as complementary therapy. Before use, you need to make sure that you are not allergic to the components and consult your doctor.
https://youtu.be/L-PuyAGctN0
About the main methods of treating luteal phase deficiency
This complication is fraught with not only hormonal disruptions, but also problems with reproductive function, which usually cause miscarriages and long-term infertility.
Often, gynecologists prefer monotherapy with various drugs that restore progesterone, but this is practically to no avail. For it to be effective, you must first regulate the follicular phase, without which normal development and maturation of eggs is impossible. This means that in treatment it is necessary to use not only drugs to increase hormone levels, but also those that will reduce prolactin and androgens to normal.
Physiotherapeutic and sanatorium-resort treatment combined with acupuncture, vitamin therapy and the use of adaptogenic drugs are also prescribed. The emotional and psychological state of a woman is no less important. A month after the procedures, a new luteal phase will begin. Which day of the cycle will be the most successful for determining the correctness of treatment can be determined using a special test. If the deficiency has been overcome, you can begin planning your pregnancy.
How to determine?
Two categories of women are interested in determining the exact day when ovulation occurs: those who under no circumstances want to get pregnant, and those who plan to conceive as soon as possible. The latter are especially interested in the exact time of a possible miracle.
Some representatives of the fair sex note certain signs that occur regularly when they enter the phases of the ovulatory cycle. Daily discharge takes on a rusty color, due to a small discharge of blood when the follicle ruptures, slight nagging pain appears in the lower abdomen and lower back, as during menstruation. Also, some young ladies observe hormonal manifestations in the form of special abundance and consistency of discharge, the appearance of acne or other skin manifestations. In some women, the breasts become enlarged and become sensitive. Mood may also change, emotionality and tearfulness may increase. There may be an increase in libido shortly before the onset of X-day.
However, if you have previously had problems with conception, and you need to determine the most favorable day for this with maximum accuracy, then there are several methods for determining ovulation:
- track using a calendar. For this purpose, a special calendar is created - you can take any one, get a special one at the antenatal clinic, or install a calendar application on your mobile phone.
After a few months, a picture of your cycle length will emerge in front of you. On average, the cycle (from the first day of one period to the first day of the next period) lasts about 28-30 days. But there are women with short (21 days) and long (35 days) cycles. These indicators may be within normal limits.
But the duration of the critical days itself is usually from three to seven days. When you already know exactly the length of your cycle, subtract 14 from this number and you will get the theoretical date of ovulation.
Using this method, a woman has the opportunity to prepare in advance for “dangerous” days, limit sex life, or, conversely, try to conceive a child. But this method does not provide a 100 percent guarantee. A woman's cycle can fluctuate, and her hormonal levels change throughout the month.
Therefore, the ovulatory phase may shift. The reason for this may be stress, fatigue, physical activity, moving, changing climate zones, changes in sex life, and even just too hot summer days.
- basal temperature. This is a very accurate method of ovulation. Basal temperature is measured with a thermometer in the rectum. When the egg is released, the temperature jumps upward and remains at this level until the start of menstruation. In order not to miss an important day, basal temperature begins to be measured from the beginning of the cycle. This should be done every day, early in the morning, preferably at 6 o’clock.
Prepare a thermometer in advance by placing it next to you on the bedside table. After the measurement, the data obtained should be recorded. By the middle of the cycle, you will already have a temperature scale drawn.
- folliculometry. Modern diagnostic method. It is carried out only in hospital conditions. A woman should visit an ultrasound doctor every couple of days and have an ultrasound examination of her follicles. The doctor identifies the dominant follicle and watches it until it ruptures, when it simply disappears. After this, a small amount of fluid appears on the posterior vaginal fornix and the corpus luteum begins to form. All this suggests that the ovulatory phase has begun.
- changes in hormonal levels. This is another medical method. During ovulation, there is a powerful release of luteinizing hormone (LH), which causes the follicle to rupture. Changes in hormonal levels can be determined using an ovulation test, which can be purchased at any pharmacy, or using laboratory tests for hormones.