Intestinal obstruction in adults is a surgical pathology when the movement of semi-digested food masses through the intestines is partially or completely blocked. Pathology appears as a result of mechanical obstruction or failure of intestinal motor function. Most often diagnosed in old age and in people who have undergone surgery on the gastrointestinal tract.
Causes of intestinal obstruction
The movement of food masses occurs due to intestinal peristalsis, the disruption of which is caused by relaxation of the muscle layer, or prolonged spasm. In both cases, there is dynamic intestinal obstruction, developing:
- in complicated cases of acute cholecystitis, pancreatitis, appendicitis;
- after surgery on the gastrointestinal tract.
Mechanical intestinal obstruction develops if there is any obstruction in the intestine:
- tumor growth;
- adhesions;
- foreign bodies;
- food bolus formation;
- accumulation of worms.
Revealing
Most often, intestinal obstruction is diagnosed in older people due to frequent constipation, which occurs due to impaired blood supply in the pelvis.
To conduct a complete diagnosis, the doctor prescribes various directions for medical research to collect facts:
- Examination using the auscultation method, which includes palpating and tapping individual areas of the abdomen and subsequent analysis of the sounds that arise as a result. The procedure is carried out using a stethoscope - a special listening device used throughout medical practice. It will help identify the splashing noise when gently shaking the abdomen.
- Ultrasonography.
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- X-ray using barium.
- Biochemical analysis of blood and urine.
- Examination of the condition of the intestinal surface using an endoscope.
https://youtu.be/JUPGlHVoIG8
Signs of intestinal obstruction
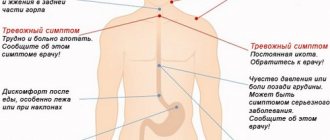
Characteristic signs of intestinal obstruction are:
- Severe pain.
- Vomit.
- Blocking the chair.
- Inability to pass gas.
Intestinal obstruction often occurs as a complication of various pathologies, but can appear suddenly in a person who feels relatively normal. The condition of obstruction begins with cramping pain in the abdominal area.
After strong seething in the stomach, vomiting appears. The patient cannot empty the intestines; gases are also retained along with the stool. The patient’s well-being deteriorates at a rapid pace: the face becomes distorted and pale, cold sweat appears, and the abdomen swells asymmetrically. The patient groans and tries to take a body position in which the pain would not be felt so strongly. Hypotension and tachycardia often develop, and painful shock may occur.
If the pain subsides, you need to be especially vigilant: this indicates that necrosis has begun, leading to the death of nerve endings. If appropriate medical assistance is not provided, peritonitis will certainly begin within a day.
Intestinal obstruction: what to do
Signs of intestinal obstruction require an immediate call to the ambulance, as in most cases the situation requires surgical intervention. Profuse vomiting does not bring relief; first, food remains are visible in the vomit, followed by bile. The appearance of fecal vomiting with intestinal contents is accompanied by a putrid odor.
Symptoms of late intestinal obstruction
If medical assistance is not provided, after 24 hours the symptoms increase alarmingly:
- there is a sharp rise in temperature due to intoxication of the body;
- urine production stops;
- the acid-base balance is disturbed;
- peritonitis increases.
If the patient is not provided with qualified medical care, death occurs from multiple organ failure.
Diagnosis of intestinal obstruction
The clinical picture and history of the disease are often not enough to correctly diagnose the patient. In such cases, hardware tests and laboratory diagnostics are used:
- An X-ray examination is performed at the slightest suspicion of intestinal obstruction. The images make it possible to examine intestinal loops with gas and liquid and, by shape and size, determine the place where there is an obstacle to the exit of feces.
- Irrigoscopy makes it possible to diagnose if the large intestine is affected.
- Ultrasound also informs about the presence of neoplasms that provoked intestinal obstruction.
- Laparoscopy makes it possible to examine the site of obstruction, and also, if necessary, to dissect adhesions and reverse the intestinal loop.
Radiography
In the early stage of obstruction, plain radiographs in the supine position will show moderately distended loops of the small intestine with a small amount of air. When shooting in a standing position or on the left side, multiple gas-liquid levels are determined. Kerkring's folds are visible in the early stages; as the obstruction progresses, the loops stretch and the folds become blurred. Sometimes it is very difficult to distinguish swollen loops of the small intestine from the large intestine.
Plain radiography of the abdomen in a standing position
Plain radiography of the abdomen in the supine position
Treatment methods
If you have the first signs of intestinal obstruction, you should consult a surgeon. Treatment at home is useless; sometimes it worsens the patient’s condition or masks the clinical picture of the disease, negatively affecting the speed of diagnosis. According to statistics, the possibility of conservative therapy in a hospital exists in 40% of patients.
First aid
Therapy for the patient begins with intestinal decompression: their contents are removed from the stomach and intestines. Endoscopes are used to clear the upper intestines. Obstruction in the colon is eliminated using siphon enemas. At the same time, the gastrointestinal tract is unloaded, the pressure in it decreases, the content of toxic substances decreases, when they enter the bloodstream, intoxication of the body occurs.
Drug therapy
Drug treatment includes the use of detoxifying and protein drugs. To detoxify the body, Reopoliglucin and Refortan are prescribed; Albumin is the most effective protein drug. The action of the drugs makes it possible to normalize vascular microcirculation, equalize blood pressure, and compensate for water and electrolyte deficiency. Painkillers and antispasmodics are also prescribed. Medicines are used to restore intestinal motility. To prevent necrosis, antibacterial drugs are prescribed.
It should be remembered: if after 3-4 hours from the start of treatment the patient’s well-being has not improved, conservative therapy is considered inappropriate, and the patient is prescribed surgical treatment.
Surgical treatment of intestinal obstruction
Surgical therapy for intestinal obstruction includes several stages. For general anesthesia, the endotracheal method is used. The duration of the operation is determined by the type and severity of obstruction and the presence of other diseases. After anesthesia, an incision is made in the middle of the anterior abdominal wall. Then cleansing is carried out from inflammatory fluid, blood, feces (in case of intestinal perforation).
After the blockade with novocaine, an examination is carried out in all areas of the intestine (especially hard-to-reach ones). When the cause is known, they move on to eliminating it. When the operation is completed, the edges of the incision are sutured. The patient is prescribed complex drug therapy necessary in the postoperative period.
Decompensated form
All the signs described in the simple form are determined, additionally pathological changes appear in the abdominal cavity: - dilated loops of the small intestine proximal to the transition zone (obstruction zone); -collapsed intestinal loops distal to the level of obstruction; - normal, non-thickened intestinal walls with homogeneous, identical contrast enhancement; - free fluid between dilated loops of intestine, often in the form of a piquant detail of a woman’s toilet - tanga panties, therefore in many sources it is described as a sign of “tanga” (tanga sign); -free fluid in mesenteric pockets; -free fluid in the abdominal cavity.
Examples of fluid accumulation between intestinal loops (tanga) and in mesenteric pockets in the decompensated form.
Folk remedies
Due to the existence of various factors that can lead to intestinal obstruction and the possibility of death, it is prohibited to use traditional methods of treatment without first consulting a doctor.
Traditional methods of treating intestinal obstruction are used with careful adherence to a diet that excludes fatty, salty, spicy, smoked, and alcoholic drinks.
Herbs
The most effective plants for intestinal pathologies are popularly considered St. John's wort and fennel. To prepare a decoction, you need to pour 1 teaspoon of dry herb into 200 ml of boiling water and leave in a thermos for 3 hours. Take instead of tea 15 minutes before meals.
Dry plantain leaves are used as a laxative. It is recommended to take a decoction of the plant: pour 1 teaspoon of plantain leaves into 200 ml of boiling water and simmer for 20 minutes. Take 1 time per day.
Vegetables
If you have intestinal problems, you need to eat as many vegetables as possible. Beetroot is especially useful when there is a threat of intestinal obstruction. It is added to vegetable salads and baked in the oven. You can prepare a decoction by boiling 3-4 beets for 30 minutes in a liter of water. It is advisable to add a little sugar. Baked pumpkin also helps with intestinal problems.
Dried fruits
To get rid of incipient intestinal obstruction, dried fruits are successfully used. To prepare the decoction, take equal parts of raisins, dried apricots and plums. Cook over low heat for 15 minutes. You can make fruit puree by grinding boiled dried fruits in a blender and adding 1 tablespoon of honey.
Prevention
To minimize the risk of developing intestinal obstruction, the following tips are recommended:
- At the first manifestation of symptoms of a gastrointestinal tract disease, you should immediately go to the doctor.
- It is necessary to carry out a preventive examination every six months.
- You should adhere to a rational diet and do not overeat.
- Overloads must be avoided.
- Do not self-medicate for abdominal pain.
- Avoid alcohol abuse.