Hepatitis C is a chronic liver disease characterized by damage to hepatocytes with disruption of their functions. In some literature you can find another name for the disease “gentle killer”.
This is due to the fact that for a long time the pathology does not manifest itself in any way and is diagnosed only at the stage of liver cirrhosis. Hepatitis C occurs several times more often in women than in men. It is worth understanding why and under what circumstances infection with a deadly virus occurs.
Symptoms of hepatitis C in women
Unfortunately, the incidence of viral hepatitis is increasing every year.
Disappointing global statistics indicate a significant increase in the number of patients with hepatitis C among young people, children, and pregnant women.
Today we will talk about the manifestations and symptoms of hepatitis C in women.
Features of the course of viral hepatitis C
In order to understand the main signs of the disease and its characteristics in women, it is important to understand the course of the disease itself.
The main distinguishing feature of hepatitis C is its hidden, so-called latent course. In the classic book version, any hepatitis is manifested by fever, pain in the right hypochondrium, nausea, vomiting and yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes.
This set of symptoms is characteristic of the acute phase. Then, due to the characteristics of the immunity of each individual person and treatment, the infection either passes or becomes chronic. It is for hepatitis C that the acute period is not characteristic.
Very often, the infection becomes primarily chronic, and the patient is unaware of his illness for years and does not receive proper treatment.
The second feature of hepatitis C is its indirect effect on liver cells.
Unlike hepatitis B or E, the virus does not destroy the cell itself. By integrating its genetic material into liver cells, hepatitis C “alarms” the immune system, which tries to kill the virus. However, the virus dies only together with the host cell. This is why hepatitis C is difficult to treat. Hepatitis C is a parenteral type of hepatitis, that is, it is transmitted through blood and body fluids.
Consequences of hepatitis C
The liver performs a huge number of functions in the body, each of which suffers in patients with hepatitis.
- Detoxification or cleansing the body of toxins, waste, poisons. Harmful substances can either come from outside (alcohol, drugs, harmful natural factors) or be produced by the body itself (bilirubin, creatinine, urea, tissue breakdown products).
- Digestive function or bile production. Bile enters the duodenum and activates a number of enzymes important for the digestion of food.
- Immune function. A huge amount of antibodies and own antioxidants are produced in the liver.
- Hematopoietic function. The liver plays an important role in the metabolism of iron in red blood cells; at an early age, together with the bone marrow, it produces blood cells.
- The hemostatic or blood clotting function consists of the synthesis of special proteins by liver cells - blood clotting factors.
- The depot function or storage function is to store glycogen, iron and fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E) and B vitamins in the liver.
Main manifestations of hepatitis C in women
Now that we understand the peculiarities of the effect of the hepatitis C virus on the liver, as well as its functions, we can better understand the symptoms of the disease. The symptoms of acute hepatitis C in women are essentially no different from those in men. The acute disease occurs the same in both sexes: fever, chills, weakness, jaundice, pain in the right hypochondrium, nausea, vomiting.
However, most often we are dealing with a chronic asymptomatic course of the disease, so we should talk about some minor symptoms. It is these small and insignificant signs that women notice more often than men.
According to global statistics, women more often listen to their bodies, visit doctors more disciplinedly and undergo examinations. This is especially true for pregnant women and patients planning pregnancy.
- Weakness, drowsiness, apathy, headaches are the consequences of intoxication of the body with external and internal products. Such a seemingly insignificant symptom as weakness is sometimes the only manifestation of the disease.
- Periodic yellowing of the skin. Disturbances in the metabolism of the bilirubin pigment and its accumulation in tissues determine this specific “icteric” color. Women look in the mirror more often, visit cosmetologists and makeup artists, and more often notice periodic yellowing of the skin, sclera of the eyes or mucous membranes.
- Pain in the right hypochondrium and nausea do not bother patients very often. Many women follow diets and the principles of proper nutrition and notice a connection between these symptoms and the intake of heavy fatty foods or alcohol.
- Paleness, flaking of the skin, hair loss, brittle nails will definitely bother any woman. These signs are the cause of vitamin and iron deficiency and manifestations of anemia.
- Bleeding will be a consequence of a lack of blood clotting factors. The appearance of small bruises, bleeding gums, heavier and longer periods definitely make a woman concerned about her condition.
- Menstrual irregularities and signs of early menopause are caused by intoxication of the body and imbalance of hormones. Women may complain of prolonged delays in menstruation or, conversely, breakthrough bleeding.
- Infertility or frequent miscarriages. This point definitely worries any patient of reproductive age. Chronic infection in the body, deficiency of vitamins and proteins, and sensitization of the immune system absolutely do not contribute to normal hormonal levels and interfere with the physiological course of pregnancy.
Coupled with heavy periods and cycle irregularities, these symptoms force the woman to consult a gynecologist. A competent doctor, as part of an examination or pregnancy planning, will definitely prescribe a blood test for viral hepatitis. That is why gynecologists are one of the first doctors to identify chronic viral hepatitis in their patients. https://gastromedic.ru
Diagnostic methods
Considering that the symptoms of the disease are scanty, they are not very informative in diagnosis. Changes are observed in general and biochemical blood tests. The diagnosis of hepatitis is confirmed by a blood test for antibodies and markers of viral hepatitis C. When the disease progresses to the stage of cirrhosis, a biopsy is performed, which allows one to assess the degree of damage to the liver cells.
Hepatitis C is a chronic, severe pathology, the main danger of which is its long-term asymptomatic course. For prevention, you should monitor your health, avoid casual sexual contact and maintain your immune system.
https://youtu.be/klxmGWsKGdE
How and how long does it take for hepatitis C to appear in women after infection?
Hepatitis C virus or HCV is caused by a small virus containing a genetic variant of material in the form of enveloped RNA.
The main feature of this virus is its tendency to genetic variability, which is expressed by mutations.
Currently, six basic viral genotypes of hepatitis C are known. It should be borne in mind that the mutational activity of the virus increases this number several times. Within one genotype, about forty subtypes of HCV can be observed, which is an important factor determining viral persistence and the high level of development of hepatitis C chronicity.
Ways of infection with hepatitis C
You can get an HVC infection in several ways. Certain groups of people are at higher risk of infection. Epidemiologists identify three levels of the highest risk of infection.
Highest risk of infection:
- for people who inject drugs;
- in persons who received blood clotting factor transfusions before 1987.
Medium-high risk of infection:
- in patients undergoing hemodialysis using an artificial kidney machine;
- in persons who have recently undergone an organ transplant or blood transfusion that took place before 1992;
- in persons who received a transfusion of blood and its components from donors who subsequently tested positive for HVC;
- in persons with unidentified liver disease;
- in infants born to hepatitis C-infected mothers.
Low risk of infection:
- from medical workers and workers of sanitary and epidemiological services;
- in persons who have sexual contacts with a large number of partners;
- in persons who have sexual contact with an infected partner.
Persons belonging to groups with indicators of high and medium risk of infection must be examined as early as possible for the presence or absence of hepatitis C.
It should be remembered that hepatitis C cannot be transmitted through airborne droplets through saliva, as well as through talking and sneezing, shaking hands, sharing utensils, eating or drinking.
How can you become infected with hepatitis C at home? This method of transmission of infection is always associated with the ingress of blood particles from an already sick person or a virus carrier. Persons with HVC, as well as carriers of this virus, are not subject to isolation from family and society.
How do the symptoms of the disease manifest themselves?
Signs and symptoms of hepatitis C infection The latent or incubation period for hepatitis C infection is on average about fifty days. There are known cases of a reduction in the period to twenty days and, conversely, a prolonged manifestation of the first symptoms after five months.
Symptoms of this disease may have an erased form or appear only at the stage of transition of hepatitis to cirrhosis of the liver.
The very first symptoms of infection with the hepatitis C virus are manifestations of asthenia, general weakness and fatigue. However, it should be remembered that such symptoms are nonspecific and may indicate the presence of a completely different disease. The main symptoms of liver cirrhosis are the appearance of jaundice, abdominal enlargement or ascites, increasing weakness and the appearance of spider veins.
The first signs of hepatitis in women
Despite the apparent asymptomatic nature, some signs can still be used to suspect hepatitis C, which in women is accompanied by the following manifestations:
- the presence of a yellowish tint to the skin and jaundice of the whites of the eyes;
- the appearance of skin itching;
- the appearance of mild joint and muscle pain;
- increased fatigue and tiredness;
- dark coloration of urine;
- the appearance of nausea due to lack of appetite;
- a sharp decrease in body weight;
- painful sensations in the right hypochondrium.
Laboratory manifestations of hepatitis C:
- high level of liver enzyme activity;
- presence of markers for hepatitis C infection;
- presence of antibodies to hepatitis C virus or anti-HCV;
- detection of viral RNA as a result of polymerase chain reaction.
The hepatitis C virus rather slowly but thoroughly affects liver tissue, which inevitably leads to cirrhosis, accompanied by the following symptoms:
- the appearance of vascular dilations and redness of the palms of the hands;
- the appearance of a bright vascular pattern on the face, chest and shoulders;
- swelling of the abdomen and legs;
- muscle spasms;
- the appearance of varicose bleeding;
- encephalopathy, accompanied by clouding of consciousness and memory problems.
Diagnosis and prevention of hepatitis C
Unambiguous confirmation of the presence of HVC virus can be obtained with positive results of the anti-HCV antibody test and the HCV-RNA test. Detection of antibodies belonging to the IgM or anti-HCV-IgM class helps differentiate active hepatitis from carriage, in which IgM antibodies are absent and ALT is within normal limits.
The basis for laboratory diagnosis of hepatitis C is PCR, which allows detection of viral RNA in the blood, which not only helps confirm the presence of infection in the body, but also confirms the fact of replication or multiplication of the virus.
The standard complete diagnostic scheme involves:
- biochemical blood test;
- PCR analysis for qualitative and quantitative HCV RNA;
- virus genotyping;
- general blood test;
- coagulogram, which determines blood clotting parameters;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- needle biopsy of the liver.
There is currently no known effective vaccine against the hepatitis C virus. It is for this reason that it is very important to follow preventive measures:
- do not use injecting drugs;
- do not use other people's needles, syringes and injection equipment;
- promptly vaccinate against hepatitis A and B;
- entrust piercings and tattoos to masters from official, trusted salons;
- Use personal protective equipment every time you have sexual intercourse.
In addition, all health care workers must strictly adhere to all safety requirements and be vaccinated against hepatitis B.
Persons exposed to infection must refrain from drinking alcoholic beverages and strictly follow all instructions of the hepatologist.
If a patient wants to stop drinking, how long will he have to see the doctor?
If a patient is convinced that he is an alcoholic, he will have to undergo treatment for the rest of his life. It is better to let the person understand that he is normal, alcoholism is treated after taking the last drink, and returns with the first. The rest of the impact is exerted by psychological factors, development, and motivation.
That is why the duration of treatment for alcoholism is always so long. There is a need to resolve some social problems and restore psychological health. There are a lot of pitfalls in alcoholism associated with the influence on a person from his wife, children, and other people. Such patients have to be in touch with specialists for approximately 3 years. There is no limit on the number of appointments. Patients who have begun rehabilitation can contact doctors at any moment to resolve the existing problem so as not to drink alcohol.
Signs of hepatitis C in women
The worst thing is that the symptoms and signs of hepatitis C in women, as well as in men, quite often go unnoticed. In such cases, the presence of the virus in the human body can only be determined by donating blood for a biochemical analysis.
However, quite often the disease still makes itself felt, and this allows you to immediately begin its treatment. What are the first signs of hepatitis?
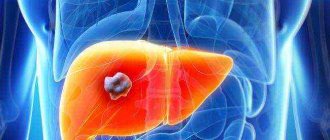
Hepatitis C destroys the human liver
What is hepatitis C?
Hepatitis C is one of the most common types of a serious and dangerous disease, which has many different types and forms, which differ in symptoms and signs of the disease.
Unfortunately, young people are most often affected by this disease. Often the hepatitis virus manifests itself in infancy, and is completely asymptomatic. And no matter how sad it is, the disease is progressing and affecting more and more people.
The infection can be transmitted in several ways:
- through blood
- along with breast milk,
- sexually.
Most often, infection occurs through blood transfusion or the use of unsterile syringes. Therefore, before contacting any medical center or beauty salon, you should make sure that they take a responsible approach to the issue of sterility and precautions.+
This disease is very dangerous - almost 80% of those infected with hepatitis C cannot be completely cured, as a result of which the disease becomes chronic. If treatment is not started in a timely manner, liver cancer or cirrhosis may develop and be fatal.
Unfortunately, today there is still no vaccine that can help in the fight against hepatitis C. However, modern medical scientists have developed a number of techniques that can improve health and ease the course of the disease.
Hepatitis C is as common in men as it is in women. However, women face more severe consequences of infection.
72% of patients find out about liver disease too late!
Signs of hepatitis in women
Symptoms of hepatitis C in women may not appear for many years. The disease does not show any obvious signs and only in the case of any other disease, when a biochemical blood test is taken during treatment, can the presence of the virus in the body be suspected. Otherwise, the liver can be destroyed asymptomatically for 20 years.
What are the first symptoms to look out for? Among the common symptoms of the disease are the following:
- fatigue, sleep disturbance;
- periodic, not too intense pain in joints and other parts of the body;
- fever, mild itching;
- jaundice, general malaise.
The liver gradually deteriorates over the years
All these signs can be the cause of other diseases, as well as accompany the period of menopause.
What are the symptoms in men?
Symptoms of hepatitis C in men are very similar to those in women. Among them are the following:
- skin rash;
- chills;
- anorexia;
- scabies;
- nervousness;
- decreased performance.
Hepatitis has several different forms and, depending on the stage of the disease, the signs of hepatitis C in men, as well as the symptoms in women, can be different.
Chronic form
It is very difficult to determine hepatitis C without a thorough medical examination. It is more hidden than other types of this disease. Therefore, almost all patients infected with this virus learn about it after the onset of a chronic form that can progress from 10 to 20 years. But still, you can pay attention to some signs of the disease.
Chronic hepatitis symptoms are as follows:
- brown or dark yellow urine;
- periodic pain in the muscles;
- slightly yellowed skin;
- joint disease;
- scabies.
If there is no treatment, the chronic disease worsens, and the symptoms of hepatitis manifest themselves as follows:
- a vascular network is observed in the chest area, face and shoulders;
- palms turn red;
- muscles contract involuntarily;
- discomfort and bulge in the abdominal area;
- impaired memory and concentration;
- noticeable manifestation of jaundice on the skin;
- yellowed whites of the eyes.
Other forms of hepatitis
Acute form . The incubation period after the development of an acute infectious disease can be about twenty-six weeks, and then become chronic. As a rule, the acute form is asymptomatic.
The patient suffers from headaches. Sometimes you can observe the first signs of hepatitis such as headache, nausea, dizziness, severe itching of the whole body or some of its parts. Fever, lack of appetite, upset and discomfort in the gastrointestinal tract occur a little less often.
Drug-induced hepatitis occurs as a result of damage to liver tissue by drug toxins. As a rule, this disease is accompanied by an increase in body temperature, disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, dizziness and skin rashes.
The autoimmune form of hepatitis can develop against the background of a sharp decrease in immunity. As a rule, it most often occurs in women during menopause. Its symptoms are malaise, colitis, skin rashes, itching, and a deep feeling of heaviness under the right rib.
The most dangerous factor of hepatitis C is that its virus can develop in the human body for many years without manifesting itself, and then manifest itself with serious complications. Therefore, you should try to pay attention to your health more often and find time to undergo a full medical examination. After all, the length and quality of life may depend on this. https://mypechen.ru
In what situations is a transplant necessary?
There are several cases when doctors think about the need for a liver transplant:
- Patients with cirrhosis, complications when the formation of scar tissue is so extensive that liver cells are completely replaced. In such cases, doctors think about transplantation.
- Patients with a tumor. Often the operation is performed at earlier stages, when the tumor is not too large and cirrhosis is still at an early stage.
In situations like this, time is always of the essence. It is important to detect diseases in the early stages. In such situations, the tumor can be completely cured.
Diagnosis and treatment of Hepatitis C(C) in women and men
The first signs of hepatitis C in women and men: symptoms, risk groups, treatment. What you need to know about the disease hepatitis C. In Greek, the word “hepatitis” is translated as “liver”. It is this organ that suffers from a disease called hepatitis.
The most severe form is considered to be post-transfusion, that is, hepatitis C. According to statistics, the incidence rates in developed countries reach approximately 2%, and if we consider the spread throughout the world, the number of patients will exceed 500 million.
Despite all the measures taken to inform and treat the population, the number of sick people only increases every year. This virus was discovered relatively recently. Until 1989, it was diagnosed as hepatitis A or B (B).
At the time of infection, the virus enters the liver cells and integrates its genetic code into their DNA structure. Once in the body, it begins to actively multiply and replicate, causing damage to liver cells (hepatocytes) and inflammation.
Due to this specificity of the disease, the immune system cannot recognize the disease and begins to direct the attack of leukocytes into its own cells, increasing the gradual death of liver tissue and replacement by connective and fatty tissues. These processes are respectively called “liver cirrhosis” and “fatty liver.”
Both the adult population of the planet and children are at risk of the disease. However, in adults, the signs of the disease are less pronounced, and the consequences pose less of a threat than in children.
Unfortunately, there is no vaccine for hepatitis C, since the virus has the ability to mutate and can adapt to medications. However, modern medicine has already developed treatment complexes with drugs that can cope with the hepatitis virus and lead patients to recovery.
It is generally accepted that hepatitis is a disease of people with drug addiction, but a person without any addictions can also become infected with it. However, it is worth noting that the percentage of drug addicts among hepatitis patients is quite high and amounts to about 40% of all patients.
Methods of infection
- Cosmetic procedures that may damage the integrity of the skin or mucous membranes (manicure, pedicure, piercing, tattooing, etc.);
- Using a shared syringe for drug injections;
- During a transfusion of blood or blood components. Now this method is not as relevant as before, since donor blood is carefully checked for the presence of the hepatitis C virus.
- During hemodialysis;
- When visiting dentists;
- Due to the use of common personal hygiene items;
- Unprotected sexual contact;
- From mother to child during childbirth. There are known cases of intrauterine disease of the fetus;
The virus can only be transmitted through blood. The following situations do not lead to infection:
- Everyday communication, sneezing, coughing;
- Using the same household items (for example, dishes), consuming the same food and drinks;
- Handshake, kisses, hugs.
The patient does not need any special living conditions, he is absolutely safe for others if he follows the rules of hygiene, or he does not need to provide emergency medical care to stop the bleeding.
If the patient's blood gets on clothing, it must be washed for thirty minutes at 60 °C. If possible, you can boil the clothes: in boiling water, the virus will die in two minutes.
If blood gets on objects, they must be thoroughly treated with chlorine-containing products.
Who is susceptible to hepatitis
- People with multiple sexual partners. The likelihood of infection increases with unsafe sexual intercourse;
- Direct sexual partners of a patient with hepatitis C
- People who have a positive HIV status;
- Men of homosexual orientation;
- Drug addicts who take drugs intravenously;
- People with sexually transmitted diseases;
- Children of infected mothers, pregnant women;
- Healthcare workers exposed to blood;
- People requiring blood transfusions, blood components or hemodialysis.
The disease is more severe in:
- Persons with alcohol dependence;
- Persons with positive HIV status;
- Persons with other viral hepatitis and liver diseases;
- Children and elderly people.
Symptoms of hepatitis C
There are five forms of the disease:
- Incubation period . It can last from three weeks to five months. The first symptoms of hepatitis are often minor or absent altogether, so detecting the disease in the early stages is quite difficult.
- Initial . During this stage, the first pronounced signs of the disease appear.
- Spicy. There is a possibility of liver coma.
- Chronic . The disease can progress for years.
- Latent. There are no signs of illness. In this case, the patient is a carrier of the virus and can spread it through the blood.
What form of hepatitis will develop depends on the individual characteristics of the human body.
The first general symptoms of hepatitis C in the early stages
- Signs of hepatitis C in women and men Feeling of physical weakness, fatigue;
- Painful sensations in joints and muscles;
- Pain in the liver area;
- Fever and constant chills;
- Stomach and intestinal disorders: constipation, chills, nausea;
- Decreased appetite;
- Yellowish skin and eye whites.
How does hepatitis C manifest in women?
The first signs of hepatitis C in women are often confused with flu symptoms. The first two weeks after infection, the disease occurs without intoxication or visible signs. In rare cases, dark urine, decreased appetite, itchy skin, pain in joints and muscles are observed.
Some women experience depression during the incubation period of hepatitis C.
It is worth noting that women are less susceptible to this disease and, in general, they tolerate it more easily than men.
How does hepatitis C manifest in men?
Hepatitis is diagnosed more often in men than in women. This is explained by the fact that among men, a larger percentage of those who suffer from alcohol addiction, violate general sanitary and hygienic standards, and have reduced immunity. In addition, the strong population of the planet suffers this disease more severely.
The male body does not produce estrogens, so their liver protection is lower than that of women.
With chronic hepatitis, men can experience complications such as:
- Enlarged mammary glands;
- Impotence;
- Ejaculation disorder.
- Cirrhosis of the liver
If hepatitis C is not diagnosed in time, then, continuing to destroy liver cells, it will inexorably lead to cirrhosis of the liver, in which the following symptoms appear:
- Vasodilation and redness of the hands;
- Bright vascular pattern on the face, shoulders and chest area;
- Swelling of the legs and abdomen;
- Muscle spasms;
- Varicose bleeding;
- Encelophathia. Loss of consciousness and memory problems
Prevention of hepatitis C
Since a vaccine against this virus has not been discovered to date, it is necessary to carefully monitor your health, taking all possible measures to protect yourself and your loved ones from infection.
- Do not use unsterile injection needles or use other people's injection equipment.
- Get vaccinated against hepatitis A and B.
- For cosmetic procedures that require damage to the skin, contact only proven, licensed salons.
- Use contraception during sexual intercourse.
- Do not share personal hygiene products with anyone.
- Diagnosis and treatment
If you notice early symptoms of hepatitis, you should urgently contact a hepatologist or gastroenterologist. The standard laboratory diagnosis of hepatitis C is a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) blood test. This test will detect viral RNA in the blood.
A complete diagnosis, which helps to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment, includes the following procedures:
- Blood chemistry;
- General blood analysis;
- Virus genotyping;
- Determination of blood clotting;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- Liver biopsy.
Although hepatitis C is a very dangerous disease for the body, positive prognosis cannot be ruled out with this diagnosis. The virus may not manifest itself for many years and not cause inconvenience to the carrier. It is important to ensure decent medical supervision, which includes regular liver checks. If the viral stage of the disease is activated, drug treatment will be prescribed.
Today, it is common to treat hepatitis C with the complex use of antiviral drugs. In case of hepatitis, you should never treat yourself; all medications, diets and procedures must be prescribed by the treating specialist.
To improve their prognosis and physical condition, a sick person must maintain a healthy lifestyle, stop taking alcohol and drugs, and also adhere to diets that cleanse the body. https://rodinkam.com
Routes of infection
Virus B is found in all biological fluids. The likelihood of infection depends on the route the virus enters the body.
Transmission routes:
- parenteral - through blood (blood transfusions, hemodialysis, intravenous drug use, operations and various manipulations using non-sterile instruments);
- sexual - through sperm;
- vertical - from mother to fetus during childbirth (but not through mother's milk, but during amniocentesis, when the integrity of the placenta is disrupted, since the large size of the virus does not allow it to penetrate into it on its own).
The main route of transmission is parenteral. Infection can occur as a result of any medical procedures (gynecological, urological, dental, blood transfusions, etc.), during manicure, pedicure, piercing, ear piercing, acupuncture, tattooing. Anything that violates the integrity of the skin provokes the appearance of the disease, provided there is a virus on the instruments and reduced immunity. Therefore, viral hepatitis B is called serum hepatitis. In the world, 2% of donors are HAV carriers.
Note! Despite the fact that infected people and carriers contain virus B in saliva, tears, urine, semen, and feces, the risk of infection with them is negligible. Infection through sexual contact is 30%.
Virus B is not transmitted through household contact or airborne droplets, so there should be no point in social isolation (this also applies to carriers of the chronic form of the disease).
Symptoms of hepatitis C in men
The liver is susceptible to many different diseases. One of the most severe is hepatitis C. This viral infection gradually destroys the cellular structure of the liver, causing irreversible degenerative tissue changes. The disease is life-threatening.
Typically, symptoms of hepatitis C in men, as in women, appear only at a late stage, often incurable.
Features and routes of infection
Studies conducted by the World Health Organization have shown that the growth rate of hepatitis B and C among the male population is near the epidemiological threshold. This disappointing result was possible because the male body is more susceptible to attacks by the virus.
This is due to the following reasons:
- High probability of contact with contaminated instruments when applying tattoos and piercings.
- Men are prone to frequent changes of partners, as well as unprotected sexual intercourse.
- The physiological process of liver cleansing occurs at a slower rate than in women. With low hepatic clearance, the virus has time to infect a much larger area of the organ.
- Infection occurs only through direct contact with the virus.
Hepatitis C has several ways of entering the body:
- Parenterally. In this case, the viral infection enters directly into the bloodstream. This can occur through contact with non-sterile invasive (surgical and injection) instruments that have come into contact with contaminated blood.
- Unprotected sexual intercourse with a carrier of the virus.
- In the prenatal period, from an infected mother.
INTERESTING! In the risk group for hepatitis C (C), 70% are men aged 16 to 50 years.
Specifics of virus development
Hepatitis C can occur in both acute and chronic forms. Long-term development of the disease has a more destructive effect on the liver and is fraught with the development of deadly cirrhosis. For the male body, an acute course of the disease is more typical.
A man is rarely a latent carrier of a chronic virus, since his body is more often susceptible to infection with aggressive genotypes HCV2 and HCV3 . These species are characterized by an active cytotoxic effect on the liver parenchyma, which causes rapid necrotization of hepatocytes (liver tissue cells).
The pathogen's RNA replicates into liver cells.
The immune system quickly recognizes foreign agents and begins to actively destroy them, along with its own cellular structures. This specific feature leads to the fact that the course of the disease is acute. NOTE! The incubation period for hepatitis C ranges from 10 days to 6 months.
Consequences
There are statistics according to which about 20% of men infected with the pathogen have an acute form of hepatitis, from which they recover on their own. In others, the disease takes a chronic course. 20% of this group are at risk of complications, the consequences of which are expressed in the form of cirrhosis or liver cancer.
There is no vaccine that modulates immunity to the disease. Hepatitis C can be re-infected, even after successful treatment.
Symptoms
The danger of acute hepatitis is that it does not have early symptoms. At the same time, active destructive processes occur in the liver. Therefore, the asymptomatic acute course of the disease often leads to chronicity of pathological processes. The first symptoms appear when diffuse changes in the liver are already pronounced.
Primary signs of the HCV virus:
- Lack of appetite.
- State of chronic fatigue.
- Decreased performance.
- Aches in the joints.
- Nagging muscle pain.
- Periodic dizziness.
With hepatitis C in a more severe form, the symptoms are complicated by the following manifestations:
- Nausea.
- Vomiting, often with bile.
- External signs include itchy skin, jaundice of the skin and whites of the eyes.
- Frequent stools of an uncharacteristic light color.
- Dark urine.
- Bloating.
- Enlarged liver.
- Venous network on the abdomen.
- Slight increase in temperature.
How does hepatitis manifest itself in later stages?
As the organ grows, a feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium and pain in the right side arise as a result of the growth of scar connective tissue. IMPORTANT! Severe hepatitis C can cause hepatic encephalopathy (failure), the symptoms of which include severe pain and confusion.
If these signs occur, the person urgently needs to be hospitalized. If he has liver failure, he can only be helped in a hospital setting.
Diagnostics
The absence of symptoms in men during the development of the acute form of the disease makes diagnosis difficult. The presence of the HCV pathogen can be determined by chance, during a routine medical examination, or already during the period of complications.
The following laboratory methods are available to diagnose hepatitis C:
- Blood chemistry . High levels of ALT, bilirubin, low liver clearance indicate liver problems.
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) , using lysate, recombinant, peptide antigens to identify pathogenic markers.
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to detect pathogen RNA. Allows you to accurately determine the type of virus.
Diagnostics also includes hardware research methods. They are used to localize the lesion and assess the severity of the disease.
Instrumental diagnostics are carried out using:
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound).
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
INTERESTING! In the same phase of hepatitis, men have higher levels of bilirubin and ALT than women.
Treatment
If at the initial stage hepatitis is treatable, then in the chronic phase it may be too late. Treatment of mild forms of the disease is successful in 95% of cases, especially with the advent of new generation drugs. The success of treatment for chronic hepatitis C depends on the severity of the pathology.
- Medicines. Treatment must be carried out under the supervision of a hepatologist. According to the patient’s condition, the doctor selects therapy. The modern approach to treatment involves the use of combination antiviral therapy. Ribavirin
The standard combination is Interferon-alpha and Ribavirin.
For interferon-resistant disease, the newest drugs Sofosbuvir, Velpatasvir, Daclatasvir, Gletsaprevir are prescribed. At different stages of the disease they are used in different combinations. IMPORTANT! Most of the newest drugs recommended by the AASLD and EASL as breakthroughs in the treatment of hepatitis are manufactured abroad.
Unfortunately, they do not have cheap analogues. Additional funds
Hepatoprotectors provide additional liver support. These include Phosphogliv, lipoic acid, Essentiale Forte. The immunomodulator Zadaxin stimulates certain parts of the immune system. Following a diet, giving up alcohol and smoking are a prerequisite for hepatitis treatment.
If treatment is carried out on time and in full, liver functions are completely restored.
The chronic form of hepatitis, which has developed into cirrhosis, cannot be cured. https://nashapechen.com/
Identification of the disease
When complaining of indigestion and pain in the right hypochondrium, women turn to a gastroenterologist. If hepatitis is suspected, the doctor will prescribe the following tests and examinations:
- General clinical blood test. Due to infectious liver damage, the concentration of leukocytes in the blood changes.
- ELISA. Contact of the body with the causative agent of hepatitis is indicated by the presence of antibodies to HCV in the blood.
- PCR. If viral RNA is detected in the plasma, the fact of HCV infection is confirmed.
- Liver tests. Due to the death of hepatocytes and the release of bioactive substances from them, the serum concentration of hepatic transaminases - AST, ALT - increases.
- Ultrasound of the liver. An extensive lesion is indicated by an increase in its size, compaction, and pathological inclusions.
Taking into account the data obtained, the doctor selects medications and determines the duration of antiviral therapy (AVT).
Risk group
The hepatitis C virus affects the population from 18 to 46 years old. This is the age of greatest risk, when there is a danger of getting difficult-to-treat liver disease. In extremely rare cases, the disease affects children and the elderly. People who can become infected with hepatitis are:
- They become addicted to drugs by using disposable syringes several times;
- Often undergo hemodialysis;
- Regularly visit dubious beauty salons and medical institutions to undergo procedures involving the use of reusable instruments;
- Forced to agree to a blood transfusion in order to restore their health;
- They work in hospitals, clinics and deal with the blood of patients.
What can the doctor prescribe?
Your doctor may offer several options for hepatitis treatment, from the most economical to the most expensive. Today there are 3 options:
- economy option. Interferon drug in 3ME dosage, exclusively in the form of injections. The injection is carried out daily or once every 3 days. Additionally, ribavirin medications are taken daily;
- average pricing option. Interferon preparations are also administered by injection, at a dosage of 6IU + ribavirin;
- the most effective option involves the use of already modified interferon (PEG-interferon), administered once a week. It has the ability to maintain a therapeutic effect for a long time.
Does everyone need treatment?
Treatment of hepatitis C is necessarily prescribed for genotype 2-3 virus, since they respond well to treatment. Patients at high risk of developing cirrhosis and liver cancer also need therapy. When the virus is in “sleep mode” and there is no negative effect on the liver, a wait-and-see approach is chosen. In this case, treatment is not required, but regular laboratory tests are mandatory.
Distinctive features of acute and chronic forms
If less than 6 months have passed since infection, an acute form of hepatitis C is diagnosed , more - a chronic form. The acute stage of hepatitis C is characterized by a short incubation period, while the chronic form often takes decades to develop.
In the acute course, the symptoms are so mild that the woman either does not notice them or does not attach any importance to them, but the main insidiousness of the disease is that in 80% of cases there are no symptoms at all. That is why hepatitis C is more often detected in the chronic stage. In addition, sometimes chronic hepatitis is detected without a previous acute stage.
Prevention
Preventive measures for hepatitis C in women include:
- Elimination of promiscuity.
- Careful selection of hairdresser, manicurist, cosmetology salon, dentistry. You should not get piercings, tattoos, or pierce your ears at home, or in salons whose reputation you are not sure of.
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules.
- Quitting bad habits (smoking, alcohol, drugs).
- Be attentive to your health, consult a doctor in a timely manner, and refrain from self-medication.
- Using gloves when working with blood (hairdresser, manicurist, doctor).