The liver is the body's main filter, which cleanses the blood and removes all toxins from it. This organ experiences enormous stress every day, and is therefore often susceptible to various diseases. A liver cyst is a round or oval neoplasm that has cavities filled with liquid or thick contents. It can appear in both adults and children.
If the tumor does not grow, doctors only monitor it and prescribe supportive treatment to the patient. Otherwise, surgery may be required.
A cyst on the liver is a capsular neoplasm with liquid or thick contents.
General description of the pathology
So, now we need to take a closer look at what a liver cyst is. It is a sac (capsule) made of epithelium or fibrous tissue, which often contains liquid (less often jelly-like, purulent) contents. The formation can develop both on the surface of the organ and inside it.
The size of the cyst can reach 15 mm or more. If it increases, the functionality of many internal organs may be impaired. In some cases, the cyst can rupture, which poses a great danger to human life and health.
This pathology is most often diagnosed in women. The age of maximum spread of cysts is 35 - 55 years. The disease must be monitored, since an increase in the size of the formation entails serious complications.
What is a liver cyst
A cavity tumor filled with clear fluid is considered cystic. It can be localized in all internal organs, and is prone to gradual growth. A liver cyst is a benign tumor that arises and develops not only in individual segments of the organ, but also in its ligaments. It is possible to cure the disease, but the determining factor is the size of the tumor, which varies from a few millimeters to 25 centimeters. In women, this health problem occurs much more often at the age of 35-50 years.
Reasons for the appearance of education
The appearance of a cyst in the right lobe of the liver or in its left part is provoked by the following negative factors:
- hereditary predisposition;
- inflammatory processes in the organ due to its parasitic infection;
- injury to an organ, surgical intervention on it;
- hormonal imbalance;
- alcohol or drug abuse;
- polycystic kidney or pancreatic disease;
- prolonged intoxication of the body;
- intrauterine organ development disorder;
- cirrhosis of the liver.
There are many reasons for the development of education, including cholelithiasis that can give impetus to the development of such a disease.
Parasitic infection of the organ can lead to the formation of liver cysts.
After surgery, cysts can sometimes form on the liver.
Hormonal imbalance can lead to various changes in the body, sometimes to the appearance of cystic liver cavities.
Intoxication due to improper use of drugs and alcohol abuse will certainly affect the state of the body’s “main filter”.
For what reasons does a cyst appear?
Until now, doctors have not been able to accurately determine for what reasons a liver cyst develops. Most likely, there may be several reasons.
Here are the main theories explaining the pathology:
- genetic predisposition: liver cysts often appear in children whose parents have been given a similar diagnosis;
- taking hormonal medications;
- undergone surgery;
- development of an inflammatory process in the liver;
- traumatic organ damage, such as liver rupture.
In the case of parasitic cysts, the neoplasm occurs due to human infection with helminths.
You have been diagnosed with a cyst in the liver, but you don’t know what the reasons for its formation were and what should be the treatment? Don't worry, we will help you figure it out.
The most common causes of a tumor in the liver include:
- genetic predisposition of the human body,
- hormonal disbalance,
- inflammatory process in the liver,
- liver damage (trauma) leading to such consequences.
But until now, doctors have not fully established the specific causes of this disease. Therefore, only a comprehensive diagnosis of the patient’s body can show a complete picture of the disease, thanks to which your attending physician will prescribe correct and timely treatment.
Types of cysts
If a cyst occurs on the liver, the causes must be determined before treatment is carried out.
It is equally important to determine the type of pathology:
| Group | Variety | Characteristic |
| Non-parasitic | True | It appears due to a violation of intrauterine development of the fetus. There are several types of this disease:
|
| False | It is acquired, that is, it occurs as a result of trauma or the influence of other external or internal negative factors. The inflammatory process can also push its development. | |
| Parasitic | Echinococcal | The neoplasm most often occurs in the right lobe of the organ. The main reason for its development is the development of a worm - echinococcus. |
| Alveococcal | This disease occurs in the presence of a larval stage of cystoid. | |
| Small liver cysts | In this case, you do not need to do anything other than observe the tumors. More often they can appear and disappear on their own. In most cases, even drug therapy is not needed. The reasons may be different (for example, changes in hormonal levels, disruptions in the digestive system, etc.). | |
| Abscess | Bacterial neoplasm. |
It happens that a patient has rare types of formations - for example, an avascular cyst (it is characterized by a lack of blood supply).
Cystic neoplasms can consist of a single chamber (cavity), or they can be multi-chambered. The latter are dangerous because they can be filled with various kinds of contents, so a scrupulous, specific approach to treatment is required.
Symptoms of the disease
If a patient has a cyst in the left or right lobe of the liver, a thorough diagnosis will help determine the cause. It is also necessary to record human complaints.
However, pain is not the main symptom. The liver does not have nerve endings, so this symptom appears when the grown tumor affects neighboring organs. Before this, the pathology can occur in a latent form.
The first manifestations are usually observed not when small liver cysts are present, but when they reach 7–8 cm or when a quarter of the entire organ is affected.
The symptoms of the pathology are:
- pain and feeling of heaviness on the right side;
- stomach discomfort;
- increase in abdominal volume;
- nausea and vomiting that continues for a long time;
- jaundice;
- loss of appetite, rapid weight loss;
- general weakness, loss of performance;
- sour belching (with pressure from the enlarged liver on the stomach, acidic contents and food may be “thrown back” into the esophagus);
- increased body temperature (in rare cases);
- excessive sweating.
Pain and heaviness in the right hypochondrium may indicate a progressive cystic formation in the liver.
Impaired liver function associated with a growing tumor may be indicated by jaundice (yellow discoloration of the sclera, skin, and mucous membranes).
With a rapidly growing liver cyst, the patient may notice a progressive decrease in body weight.
A patient with liver tumors may notice increased sweating with little physical exertion and even at rest.
A cyst that appears in the left lobe of the liver may not appear for years, however, if such symptoms appear, they indicate the progression of the disease. A mandatory consultation with a doctor is required here.
Classification
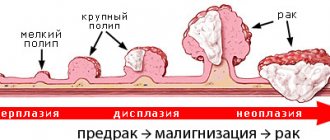
Cysts can be true or false. True congenital ones represent an internal epithelial lining. Solitary true formations can be different in their location and forms. There are simple, retention, dermoid cysts of the liver, multilocular cystadenomas.
False ones appear during life and the course of the disease. Such formations can appear after operations, injuries, or inflammatory processes. Fibrous-changed liver walls serve as their foundation.
Based on the number of cavities, multiple and single cysts of the organ are distinguished. If cysts form in each segment of the liver, then this type is called polycystic disease.
If a person has echinococcus in the body, it can cause the formation of a cyst. In other words, formations can be parasitic and non-parasitic. Parasitic also includes alveococci, which enter the body after contact with infected animals.
Before we consider in more detail the symptoms of a liver cyst and methods of treating it, we should first talk about the forms of this formation. Liver tumors are classified into two large groups, each of which has its own subtypes:
- parasitic – these include alveococcal and echinococcal cysts;
- non-parasitic - this group includes true and false tumors.
A false cyst of the left lobe of the liver or the right, as a rule, occurs as a result of trauma to the tissues of the organ. When the integrity of the tissues is violated, they become inflamed, after which they undergo fibrotic changes, which become the cause of further tumor formation.
There are certain types of cysts in the liver. The first of them implies division depending on the etiological factor. Thus, such neoplasms are divided into:
- parasitic;
- non-parasitic.
Classification of liver cysts
Neoplasms of parasitic nature are divided into:
- hydatid cyst of the liver - develops due to the penetration of tapeworms into the human body, which invade the organ and multiply in it;
- alveococcal liver cyst - is a consequence of alveococcal parasitism.
Non-parasitic liver tumors have their own classification and are:
- congenital or true - most often diagnosed. It is formed against the background of abnormalities of the bile ducts. This variety is considered harmless to humans, but only if growth dynamics are not observed;
- acquired or false - often the result of liver injury.
A true cyst in the liver has the following division:
- solitary - the cyst is usually determined in the right lobe of the liver, namely in its lower part. It differs in that it has a leg, due to which it hangs into the abdominal cavity;
- polycystic disease - this type of disease is a consequence of a genetic mutation. These neoplasms are diffusely distributed throughout the liver and are always found in its upper layers. Such cysts increase in size throughout a person’s life;
- Cystic fibrosis is the most severe form of the disease and poses a danger to the life of a newborn. This is due to the fact that it affects not only the liver, but also its main vein, the portal vein, and is also prone to growing into many bile microcysts.
Based on the number of tumors in the liver, cysts are divided into single and multiple, and based on the presence of complications - into complicated and uncomplicated.
The latest classification of the disease - depending on the size of the cyst, they are:
- small - volumes do not exceed one centimeter;
- medium - sizes vary from one to three centimeters;
- large - reach ten centimeters;
- gigantic - grow 25 centimeters or more.
https://youtu.be/v_b5T29XTXQ
Stages of development of a parasitic cyst
Before treating a liver cyst, it is necessary to consider the stages of its development. This determines whether a person needs to take medications or undergo surgery.
Since parasitic liver damage accounts for the majority of all cystic formations, we will consider the stages of progression of the disease using its example:
- First stage . Parasites have penetrated the organ, they have begun their destructive effect, a small part of the toxins penetrates the blood. At this stage, the defenses are able to maintain normal body functionality. There are practically no symptoms here.
- Second . The tumor grows and soon begins to put pressure on the organ, causing pain; waste products of foreign organisms are already entering the bloodstream more, so nausea, dizziness, etc. are possible.
- Third. The cyst progresses quite quickly. If you do nothing, the inflammatory process begins and the formation begins to fester. In this case, the risk of organ rupture increases. Poisoning of the body with toxins may occur, which makes itself felt by vomiting, fainting, fever, etc.
Regardless of the cause of the disease, it needs to be monitored. At the first signs of changes (growth of formation, changes in content, inflammation of adjacent tissues, etc.), appropriate therapeutic measures must be taken.
Consequences
Many patients are interested in the question of why a liver cyst is dangerous. In the absence of proper therapy, the following complications may occur:
- Suppuration of the formation occurs when it becomes infected. Then the likelihood of peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum) and severe poisoning increases.
- Rupture of the walls of the formation, leakage of contents into the abdominal space. Peritonitis, intoxication and even death are possible.
- Bleeding into a tumor or abdominal space.
- The parasitic disease is getting worse. Helminths, along with bile, penetrate into another segment of the liver and other organs, causing the patient’s condition to worsen.
When a pathological cavity becomes infected, it suppurates
Now you know what consequences a liver cyst can cause. To avoid them, you must strictly follow the doctor's recommendations regarding treatment.
Diagnostic features
Treatment of liver cysts begins only after a thorough examination of the patient, which includes:
- Ultrasound.
- CT or MRI. This diagnosis helps determine the size of the tumor and the number of cysts. These techniques allow us to more accurately determine the causes of the development of pathology.
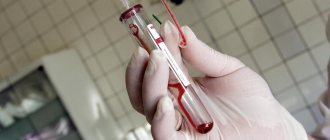
- Lab tests. Serological analysis of biological fluids makes it possible to find out the type of neoplasm. In addition, blood PCR, radioimmunoassay, enzyme immunoassay, and determination of markers for the presence of hepatitis are performed.
- Puncture of the neoplasm to determine its composition. Subsequently, bacteriological and cytological examination is carried out.
- Echography. In this way you can find out the density of the cyst contents.
- Angiography of the celiac trunk.
- Scintigraphy using radioisotope elements.
- Histological analysis of the tumor to determine whether it is malignant or not.
Ultrasound gives the doctor an idea of the presence of formations, their number, location, nature, structure.
If necessary, ultrasound diagnostic data are confirmed by CT examination.
It is not necessary to use all diagnostic methods. Ultrasound and laboratory tests are quite sufficient.
Traditional treatment
In the treatment of the liver, the classification of formation is of great importance. The treatment regimen and its type depend on this. Treatment of liver cysts with medication is required due to negative changes in the organ.
If necessary, the patient is prescribed the following medications:
- multivitamins (for example, Complivit);
- antibiotics;
- enzyme agents;
- choleretic drugs (for example, Allochol);
- sorbents: activated carbon, Enterosgel;
- hepatoprotectors (Bicyclol);
- painkillers (Amidopyrine, Analgin).
Antiparasitic medications may also be needed. The choice of medications depends on the cause of the disease and accompanying symptoms, and on the individual characteristics of the patient.
Now it is clear how to cure a cyst on the liver without surgery, but this does not always happen. If drug therapy does not help, then the hydatid cyst of the liver (or another type) is removed. Surgery is necessary in case of rupture of the walls of the tumor, disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, presence of bleeding or severe inflammation, or growth of the formation.
The most common method of combating pathology is puncture, which allows you to get rid of the contents of the tumor. After which a special drug is injected into the cavity of the formation, which promotes gluing of its walls.
There are also other types of surgical intervention:
- Laparoscopy of liver cyst. Such a gentle intervention reduces the risk of complications and reduces the person’s recovery time.
- Radical intervention. This type of surgery is necessary if the liver is too damaged to be cured. In this case, organ transplantation is used.
- Palliative effect. Only the content is deleted. The walls of the neoplasm remain inside the organ.
- Conditional radical surgery. In this case, the entire cyst is removed, as well as the affected tissue around it, but part of the patient’s organ is preserved.
If symptoms of liver cysts are detected in women, you should not self-medicate. It is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Symptoms
Disputes about the nature of cyst formation have been going on for decades. Some researchers associate the cause of the condition with inflammatory hyperplasia of the bile ducts, which occurs during fetal development.
- Long-term intoxication.
- Alcoholic hepatitis.
- Cirrhosis.
- Cholelithiasis.
- Polycystic disease in the kidneys, pancreas, ovaries.
The causes of tumors are also associated with the use of hormonal drugs, hereditary predisposition to transformations of liver tissue, and progressive echinococcosis. The etiology of such disorders is a question that is clarified by the doctor before prescribing treatment.
Due to small cysts, there are no signs of illness, since the largest gland in the human body is devoid of nerve endings. Pain appears when the enlarged tumor begins to put pressure on other organs. In addition to discomfort, a person is bothered by the following symptoms:
- Constant weakness.
- Enlarged belly.
- Yellowness of the skin.
- Lack of appetite.
- Excessive sweating.
- Dyspnea.
- Belching sour.
- Fever.
- Dyspeptic disorders.
Life-threatening parasitic cysts can fester and rupture with hemorrhage into the abdominal cavity and liver abscess. No less dangerous are conditions when the purulent contents of the blisters block the bile ducts and cause their inflammation. As a result, hepatocytes are replaced by connective tissue or atrophy.
A cyst is an asymptomatic pathology and is therefore detected at an advanced stage. Signs of the disease are nonspecific. A physical examination does not determine the diagnosis. The simplest method of detection is ultrasound, a familiar short procedure that allows you to see a bubble of a homogeneous structure or gives confidence that the most important organ is healthy.
MRI allows you to clarify the diagnosis and differentiate a cyst from metastasis, ascites, and hemangioma. Serological analysis helps determine the nature of the tumor: parasitic or not. But the most accurate diagnostic tool is laparoscopy, when using a microcamera you can see all the structural changes that have occurred in the liver.
Suspicions of a liver cyst may arise as a result of a therapeutic examination during palpation of the abdomen. If the doctor notices any suspicious lumps, asymmetry and an increase in the size of the liver, the patient is prescribed a special hardware examination to establish an accurate diagnosis.
In most cases, an ultrasound (ultrasound) is performed to identify a cyst on the liver, as well as determine its size and location. Echography shows a cyst of the right and left lobes of the liver as a round cavity, which is limited by a thin wall.
In addition, abdominal tomography is also indicated for the same purposes. In complex cases that require additional diagnostics, the patient may be asked to undergo an MRI or a blood test.
A cyst on the liver is a benign neoplasm, but in order to completely exclude the possibility of cancer, a biopsy is performed (taking a suspicious area of tissue for further examination).
Often the formation appears where the left lobe of the liver is located. The cause of parasitic cysts, of course, is parasites in the human body. This is all clear. But the reason for the appearance in another case is still being clarified by scientists.
Many argue that the cause may be an intrauterine complication. But since this disease is observed mainly in women, there is an opinion that taking hormonal drugs can affect the formation of cysts.
If there has been some kind of injury or surgery on the liver, then a cyst may appear in this case. This is all that applies to non-parasitic species.
Parasitic ones appear after parasites are introduced into the body. And this happens among dog lovers. Parasitic cysts are dangerous to human health. Forming in one of the lobes of the liver, they begin to grow over time. And this is fraught with development into oncology.
While the formation is small, there are practically no symptoms. And it is detected on an ultrasound examination completely by accident. But if the cyst has grown to a certain size, the following symptoms appear:
- nausea;
- loose stools;
- frequent belching;
- pain in the right hypochondrium.
If a person exercises or drives a car over bumps, the pain becomes more noticeable.
There are other nonspecific symptoms:
- dyspnea;
- refusal of food;
- increased sweating;
- feeling of weakness.
As the liver cyst grows, the volume of the abdomen also increases, eventually becoming convex and asymmetrical. At the same time, body weight decreases, the skin acquires a yellowish tint.
Therefore, if you feel pain in the liver area, consult a doctor. In addition, complications of the disease are possible. The cyst may rupture, and then its contents will break into nearby organs, which will entail an attack of abdominal pain.
Parasitic types are fraught with the spread of parasites through the blood to other organs. Liver lobes with polycystic disease may develop into liver failure over time.
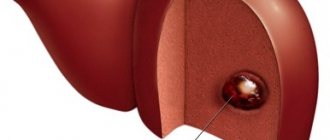
A liver cyst is a benign formation, the cavity of which is filled either with a clear liquid that has no odor or taste, or with a dark green jelly-like mass. Cystic formations are most often found in people aged 30 to 50 years, mainly in women.
The cyst can be located both on the surface and in depth, as well as in different segments and lobes of the liver. The diameter can reach 25 cm. A cyst can also occur against the background of other diseases, such as: cirrhosis of the liver, polycystic liver or ovarian disease, bile duct cysts, etc.
Classification
Liver cysts are either parasitic or non-parasitic. Non-parasitic are divided into true and false. If individual bile ducts for various reasons are not included in the biliary tract system during the period of intrauterine development, then in this case true cysts can form.
False cysts are divided into traumatic and inflammatory. A traumatic false cyst usually forms when the liver ruptures. Treatment of liver abscess, removal of echinococcus - the causes of the development of an inflammatory cyst.
We invite you to read: Red acne on the body - what is it? Red pimples appeared on the body and itched
Among parasitic liver cysts, alveococcal and echinococcal cysts are distinguished. These parasitic diseases develop in the human body after contact with a sick animal and occur without symptoms.
Causes of liver cysts
There is no clear opinion among scientists about what causes the formation of non-parasitic liver cysts. But still, the majority believes that the reasons lie in complications during intrauterine development.
The causes of parasitic liver cysts are human contact with a sick animal. Due to the danger of the disease, serious treatment is provided, since infection of internal organs is possible, because such cysts are almost always prone to enlargement.
Liver cyst symptoms
shortness of breath, weakness, loss of appetite, increased sweating. The patient's abdomen may become asymmetrically enlarged if the cyst has grown to enormous sizes. The remarkable thing is that, overall, a person is likely to lose weight. It is quite possible in this case that jaundice will develop.
A liver cyst is not a serious pathology, but nevertheless, if pain appears in the liver area, you should still consult a doctor in order to avoid various risks and unpleasant consequences.
Treatment of liver cysts
For small liver cysts, it is necessary to be observed by a gastroenterologist, and also to adhere to a diet that consists of excluding “heavy foods” from your diet. It is necessary to consume as little fatty, fried, smoked, canned and salty foods as possible.
In addition, you need to give up ice cream, carbonated drinks and strong coffee. Spicy dishes are completely excluded. Fresh vegetables and fruits should be consumed regularly. Drinking juices is also good for the liver.
Liver cysts can be treated quite successfully, including with folk remedies, which must be selected with your doctor.
It is necessary to treat a liver cyst surgically in the following cases: if the cyst has ruptured, bleeding or suppuration is detected, if the cyst has reached a diameter of more than 10 cm, if the cyst has severe symptoms (severe pain, indigestion, weight loss).
During surgery, two techniques are used depending on the situation - the traditional open technique and laparoscopy (operation through a small hole). Today, preference is given to laparoscopy, but there are cases when open surgery is the only correct solution.
Folk remedies
Many patients want to know how to treat liver cysts with folk remedies. They are not a panacea, but will help avoid surgical intervention only in rare cases (if the tumor does not progress, and if natural recipes are used with the therapy recommended by the doctor).
Please note: in our article all folk recipes are presented for informational purposes. On their own, they cannot be a treatment for progressive cystic liver formations. Before using any natural remedies, consult your healthcare professional!
The following tools will be useful:
- Celandine. An infusion is prepared from it. Requires 1 tbsp. l. dry raw materials, pour 0.5 liters of boiling water and leave for 30 minutes. The resulting volume should be drunk in small portions throughout the day. It is important to note that this plant is poisonous, so it should be used with caution. Pregnant and lactating women, children under 14 years of age, elderly and weakened people - this herbal medicine is not recommended. Drink the infusion for 7 - 10 days, then take a week's break and resume treatment.
- Salsify. To prepare the decoction, you need 3 cups of boiled water and 3 tbsp. l. raw materials. The mixture must be boiled for half an hour and left for the same amount of time. Next, the product is taken in small sips. The resulting volume should be consumed per day. The course of therapy is 1 - 2 months.
- Juice from burdock leaves. It should be drunk three times, 1 to 2 tbsp each. l. The medicine is taken 30 - 40 minutes before meals.
- If the liver is damaged, treatment with quail eggs makes it possible to improve the condition of the digestive system, increase the body's defenses, and stop the growth of cystic formations. Doctors advise drinking 5 raw eggs on an empty stomach for 2 weeks, taking a break for 14 days and repeating.
Nutrition rules
Just using medications to get rid of pathology is not enough. Diet needed for liver cyst.
It provides for the exclusion of fatty foods, canned food, as well as foods with a lot of flavoring additives; smoked and fried foods are also prohibited. It is worth giving up tomato juice, alcoholic drinks, and chocolate.
The patient is allowed to eat lean meat and fish, fruits and vegetables (they are rich in vitamins and microelements), and dairy products. Nutrition for liver cysts in women should be complete. But you should not eat foods that increase the load on the organ.
The general nutrition rules are:
- The body should receive easily digestible protein;
- Do not completely eliminate carbohydrates;
- The patient needs to eat in small portions (optimally 5 - 6 times a day);
- the menu must contain products that produce a choleretic effect;
The diet includes cereals, berries, and fermented milk products.
Prognosis and possible complications
To the question “can a cyst in the liver resolve?” - It’s quite difficult to answer. This is possible if you remove the negative factors that provoke it. Also, it itself disappears if its size is not very large, and it is not caused by parasites, or is not congenital.
The prognosis, with timely treatment, is favorable. However, in some cases, the pathology can recur and cause complications:
- formation of purulent contents inside the neoplasm;
- internal bleeding due to cyst rupture;
- spread of parasites throughout the body;
- liver failure.
With timely treatment, the risk of complications is minimal.
Risks of non-parasitic cysts
Such neoplasms can be congenital, when they are formed as a result of a developmental abnormality, or acquired. A congenital cyst is considered true, but it most often appears only in adulthood. If such a formation grows, it must be removed, otherwise the liver cells will degenerate and its function will be impaired. Congenital polycystic disease, a tendency to form multiple tumors, is also dangerous.
Acquired cysts are different. In each case, the question of the need to remove them is decided by the doctor. After all, they do not always pose a danger. For example, microcysts that form in liver tissue due to intoxication or taking certain drugs can resolve on their own.
Symptoms of the presence of worms in the liver
- A simple cyst in the liver can be congenital or acquired. This is a single formation filled with serous contents, usually clear liquid. Such tumors are usually harmless because they are small in size and do not interfere with liver function. But regular monitoring is necessary, because simple cysts can degenerate into malignant tumors.
- Traumatic cysts are formed due to mechanical damage to liver tissue. Their appearance can be caused by a strong blow or surgery. Such tumors can be large. Most often, their contents are blood or even pus. Traumatic cysts are dangerous as they can rupture, leading to infection of the abdominal cavity.
- Polycystic liver disease affects most of the organ. This leads to liver failure. Other diseases of this and neighboring organs may develop.
- Cystic fibrosis is usually congenital in origin. In this case, healthy liver cells are replaced by connective tissue. Typically, degeneration occurs in the area of the bile ducts. Therefore, pathology often causes disturbances in the outflow of bile. Such tumors can develop into malignant ones.
- Sometimes benign neoplasms are attached to the liver tissue with the help of a stalk. Such tumors are called solitary cysts. If they grow or if the patient does not comply with the doctor’s recommendations, the leg may twist and the cyst may rupture. These tumors also often degenerate into malignant ones.
Prevention of pathology
A cyst is a complex disease that in most cases does not pose a danger to the body. Whether it is dangerous depends on the type of pathology and the degree of its progression. It is better to prevent the disease.
To do this, the following preventive measures must be observed:
- avoid drinking water from unknown sources;
- if there is a suspicion of helminth infection, then it is necessary to be examined and take medications to kill worms;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- eat right and don’t drink alcohol;
- avoid liver injury;
- perform feasible physical exercises;
- observe the work and rest schedule;
- Treat diseases of the digestive system in a timely manner and undergo routine examinations.
A cyst in the liver area is an insidious disease, as it is not always detected in the early stages. However, timely treatment will get rid of the problem and prevent the risk of complications.
The video in this article will tell you about cystic liver formations - why they form, how they manifest themselves and what needs to be done in such a situation.