Oncology is replete with complex and incomprehensible terms, the meaning of which is not so easy to find or understand for a person without special education, however, doctors’ opinions and already made diagnoses push us to search for the meaning of individual definitions. Malignancy is one of them. How to treat this condition? Do you urgently run to the doctor, fearing for your life, or is there time and opportunity to be cured without resorting to surgery? Patients have many questions...
Malignancy (malignancy) is the acquisition of signs of malignancy by cells. Most often, malignancy can be observed in already changed tissues against the background of some kind of inflammatory process, ulcers and erosions, benign tumors, scar changes, etc., although the possibility of its development in healthy tissues cannot be ruled out. This process is based on a genetic mutation that triggers disruption of cell differentiation and maturation.
malignancy using the example of transformation of a benign polyp into a malignant one
It is no secret that cells endowed with signs of malignancy are constantly formed in each of us, however, whether they become the beginning of a tumor or are removed depends on the state of the body and even external conditions.
Thanks to the coordinated work of the components of the immune system, pathologically altered, damaged and obviously abnormal cells are removed from the body in order to avoid their uncontrolled reproduction. Under unfavorable conditions, immunodeficiency, and a decrease in antitumor protection in old age, the likelihood of the preservation and further development of tumor cells increases, and therefore the risk of developing a dangerous disease becomes higher.
Malignization is the initial stage of the formation of a malignant tumor, so there is no need to panic when you find this term in medical documents, because timely help from a specialist will help avoid further progression of the process.
In fact, malignancy is not a diagnosis, but only a change found, as a rule, in already affected tissues or organs. However, it is impossible to let everything take its course, hoping that it will “carry away” or “dissolve on its own,” because malignancy is a step in the formation of a malignant tumor that the body has already passed.
Malignancy - what is it? Mechanism of occurrence
This process is based on a genetic failure of the program for the formation of a specialized cell phenotype and their increased division. Thus, tissue proliferation occurs.
The changed cells begin to actively grow and divide. At an early stage, cancer cells do not cause any discomfort to the patient, so it is difficult to detect pathological changes at the initial stage. Malignancy of a benign tumor, gastric ulcer or polyp often occurs. That is why such patients must undergo regular examinations so that the doctor can notice unwanted changes in time and take action.
Malignancy - what is it? There are many hypotheses about its origin, but these are only assumptions. The only fact that has been accurately established is that the combination of certain unfavorable conditions triggers the process of degeneration of healthy cells into pathological ones.
Forecast
If malignancy is detected at the very initial stage, then the prognosis is favorable. Often, simply measures to strengthen the immune system and eliminate the irritating factor are enough for the abnormal cells to self-destruct naturally. The same goes for the second stage. This condition is more dangerous, but can still be treated without much difficulty.
With the beginning of the third stage and its transition to the fourth, they speak of the development of an oncological disease, and here the prognosis will depend on how early the tumor was detected, what biological properties it has, and where it is located. An important role in this case when predicting will be played by the general health of the patient, his age, the presence of concomitant diseases and many other factors.
All we can say for sure is that the sooner the tumor is discovered and treated, the greater the chances of survival, but a more accurate prognosis depends on a combination of many factors. It can only be done by the attending physician, and in some cases even he turns out to be wrong.
https://youtu.be/4I2qpNDP6MI
Causes
Conventionally, the reasons for this process can be divided into external and internal.
External reasons:
- Unfavorable environmental conditions.
- A dose of x-ray radiation that significantly exceeds the norm.
- Chemically active substances that have a long-term effect on the body.
- Nutritional disorders, namely consumption of carcinogens, prohibited stabilizers and dyes, transgenic products, etc.
Internal reasons:
- Decreased immunity.
- Chronic inflammatory diseases.
- Endocrine disorders.
- Fungal and viral diseases.
- Prolonged stress.
- Severe psychological shock.
- Hormonal imbalances.
- Burdened heredity.
General information
Malignization (malignancy, malignant degeneration) is a complex pathomorphological process during which benign cells acquire the properties of malignant ones. Both normal cells and those already changed, but not showing signs of malignancy, can undergo malignancy. Most often, foci of malignancy occur in the area of ulcers, polyps and various benign tumors. Malignancy can be caused by genetic predisposition and harmful environmental factors.
In the initial stages, malignancy is asymptomatic, so early diagnosis of malignant neoplasms is associated with significant difficulties, however, regular preventive examinations and the use of modern laboratory and instrumental research methods can partially solve the problem of early detection of malignancy. Diagnosis and treatment are carried out by specialists in the field of oncology, gastroenterology, pulmonology, neurology, dermatology, otolaryngology, gynecology, orthopedics and doctors of other specialties (depending on the location of the tumor).
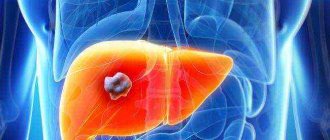
Currently, malignant tumors are the second most common cause of death after cardiovascular diseases. In 2012, more than 8 million people died from cancer. The likelihood of malignancy increases with age, however, along with elderly people, malignant tumors often affect children and patients of working age. The most common types of cancer are lung cancer, stomach cancer, breast cancer, liver cancer and colon cancer.
As a result of malignancy, approximately 150 types of malignant cells can form in the human body. About 80% of these cells are of epithelial origin, 15% are connective tissue, 5% are hematogenous. According to experts, the prevalence of malignancy will increase in the coming decades, which is associated with a number of factors, including increasing life expectancy, unfavorable environmental conditions, bad habits, the use of large amounts of chemicals, increasing levels of ionizing radiation, etc. All This makes it extremely important to study the processes of malignancy, as well as to develop optimal algorithms for identifying such processes during mass examinations, diagnosis and treatment of non-oncological diseases.
Signs
Malignancy - what is it? Let's look at its signs. The symptoms of pathological changes will depend on the location. But despite this, there are common signs that unite the process of malignancy, no matter which organ suffers.
These signs include:
- Genetic changes in cells of a certain phenotype that perform specific functions. Newly formed cells can no longer fulfill the functional load imposed on them.
- The structure of cells changes.
- Metastasis.
- Cell proliferation, i.e. their increased division.
- Cell polymorphism, i.e. their ability to perform different functions.
Treatment
Since the process of malignancy can be localized in any area of the body, there is no specific method of therapy.
The treatment method is selected based on several factors:
- affected area;
- stage of development;
- form and type of disease.
Many people live with formations such as birthmarks or papillomas, as they do not have a negative effect on the body. But in case of signs of malignancy of formations, their removal should be carried out without delay.
It is recommended to remove them in advance to reduce the risk of malignant degeneration in the future. To eliminate such formations, the following minimally invasive methods can be used:
- electrocoagulation;
- laser therapy;
- cryodestruction.
If the process of malignancy begins, the method of therapy depends directly on the affected organ. Typically, in the later stages, malignancy is treated using a complex of different methods, which includes surgery, as well as radiation and chemotherapy.
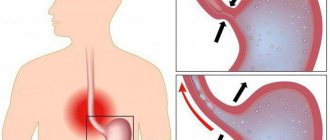
Malignancy of stomach ulcer
Statistics show that the degeneration of a stomach ulcer into a cancerous tumor occurs in 4-15% of cases. The reasons for this process have not been reliably identified. But it is known that poor nutrition plays a significant role in this transformation. First of all, this is the intake of too spicy, fried or smoked food. In sick people with a history of stomach ulcers, who abuse alcohol and smoking, the risk of malignancy increases many times.
Symptoms of ulcer malignancy include:
- Changes in taste preferences, such patients often refuse meat dishes.
- Decreased appetite.
- The connection between pain and eating is no longer observed.
- The pain in the stomach area becomes constant.
- Painful sensations do not disappear from medications that previously helped.
- Nausea is added, which is present almost constantly.
- There is belching with a foul odor.
- There are bouts of vomiting.
- There is a feeling of heaviness in the stomach area.
- The patients are exhausted.
- Pallor of the skin is observed.
- Vitality decreases.
Malignancy is diagnosed in the same way as a gastric ulcer. It is enough to do fibrogastroscopy (FGS), during which a biopsy will be taken and sent for research.
Special cases
The likelihood of developing a malignant neoplasm depends on many factors:
- Patient's age;
- The nature and localization of the pretumor pathological process;
- Heredity;
- Exposure to carcinogens and other external causes;
- The duration of existence of altered tissues in the body (inflammation, scar, benign tumor, etc.).
The following have a high risk of malignancy:
- Benign tumors that rapidly increase in size due to active cell division (adenomas with epithelial dysplasia, etc.);
- Dysplastic processes of various localization, for example, in the epithelium of the cervix if it contains an oncogenic type of human papillomavirus;
- Chronic gastric ulcers, especially in the elderly and due to infection with the bacterium H. pylori;
- Large colon polyps;
- Nevi exposed to mechanical trauma or exposure to solar radiation;
- Benign and borderline ovarian cysts, especially in young women, with hereditary forms of cancer of the reproductive organs.
These are just some examples of conditions in which the possibility of malignancy is quite high.
In the presence of familial forms of oncopathology (cancer of the colon, breast or ovaries in blood relatives), special attention should be paid to pre-tumor changes in organs, because the risk of malignancy in such individuals may be several times higher than that of other people.
It is worth noting that the same condition does not always behave the same way in different organs or tissues, so the location of the pathological focus must be taken into account. For example, absolutely benign epithelial papilloma tumors, appearing on the skin, very rarely serve as a source of cancer, and even then, as a rule, in cases of constant mechanical irritation. At the same time, papilloma of the bladder or ureter is a dangerous phenomenon, which is accompanied not only by subjective discomfort, bleeding, and impaired urine outflow, but also by a high probability of malignant transformation.
Malignancy of tumors
A tumor is a proliferation of cells of any tissue. If this growth occurs within the tissue in which it was formed, then it is a benign tumor. Examples of benign tumors include:
- Myoma - occurs in muscle tissue.
- Lipoma - forms in adipose tissue.
- Fibroma is a growth of connective tissue.
- Osteoma - occurs in bone tissue.
If the growing cells retain the properties of the tissue from which they were formed, and the tumor has clear boundaries that do not extend beyond the organ, then it is a benign tumor. But there is always a risk that the tumor will become malignant.
In this case, tumor cells grow into neighboring tissues and nearby organs. In addition, with the flow of lymph and blood, individual cells can spread throughout the body and penetrate into distant organs and tissues, forming metastases in healthy structures. This is possible when a tumor grows into a vessel. That is why doctors, at the slightest suspicion, always recommend removing the tumor if the cells begin to grow too quickly. Before this, a biopsy is always taken and a histological examination is performed.
Diagnostics
If signs of malignancy occur, the first thing the doctor does is conduct an external examination of the patient and also collect an anamnesis. If there is a suspicion of malignancy of a skin tumor, a diagnosis is carried out in dermatology. Subsequently, the patient is prescribed a biopsy followed by histological examination of the biomaterials taken from the formation.
We recommend reading What disability group is given for oncology and how to apply for it
For an accurate diagnosis, pathologists carry out diagnostics using the following studies:
- urine and blood analysis;
- bacteriological analysis;
- conducting an electrocardiogram;
- cytological examination (prescribed for polyps);
- ultrasound examination (ultrasound);
- computer and magnetic resonance imaging (CT and MRI).
All of the above diagnostic methods make it possible to accurately identify the type and form of the disease, but the most informative diagnostic test for suspected malignancy of formations is hysteroscopy. The patient is sent for treatment only after receiving the results of all studies performed.
Properties of malignant neoplasm
Tissue that has undergone malignancy acquires the ability for accelerated uncontrolled growth, which no other cell in the human body has. Such cells can be transported throughout the body by metastasis and are capable of producing toxins that have a negative effect on the patient’s body.
The first symptoms of the development of a malignant tumor are usually
- decreased appetite;
- weight loss;
- manifestations of general intoxication of the body;
- exhaustion;
- weakness.