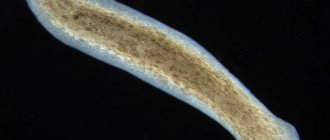
Broad tapeworm is a type of tape parasite that forms into a sexually mature individual in a human, dog, bear, or other large animal, and lives for about 20 years, sometimes without causing negative symptoms.
They penetrate into the human body through freshwater fish and are found specifically in people who consume river fish and products from it that have not undergone the necessary heat treatment, as well as in employees of fishing and processing enterprises.
Who is the wide tapeworm?
Diphyllobothrium latum is a tapeworm ranging from 2 to 10 meters in length. Some specimens exceed this length. The wide tapeworm belongs to the class of cestodes (Cestoda), family Diphyllobothriidae. It consists of a neck, on which there is a scolex (head) with two slit-like devices for attaching the helminth to the mucous membrane of the small intestine, and a body.
The body of the tapeworm consists of a huge number of segments, their number reaches 4 thousand. Large oval-shaped eggs are formed in mature segments. They are protected by a two-layer shell and have a cap on one of the poles. While in the intestines of the intermediate or definitive host, the tapeworm secretes immature eggs that reach full maturity only in fresh water.
Life cycle of helminth
Unlike other tapeworms, the wide tapeworm has a long, multi-stage life cycle, which occurs with a change of several carriers. Each intermediate host serves as a kind of incubator, in which a more advanced organism, adapted to survive in the absence of light and oxygen, is “bred” from the previous larval stage.
Life cycle of the broad tapeworm
The life cycle of the helminth begins in the human intestine. This is where adult tapeworms live. They secrete many eggs every day, which, when leaving the human digestive tract, almost immediately begin to transform in accordance with the environment:
- The initial development cycle begins when the egg enters the water. Most often it takes place in open small bodies of water. Over the course of about 4 weeks, the contents of the egg transform into the initial larval stage of the helminth, the coracidium. This mobile living organism exists for 2 weeks. During this time, it should develop its first intermediate host - a freshwater crustacean.
- After entering the body of a mollusk, the tapeworm larva undergoes a series of metamorphoses and passes into a new stage called procercoid. Upon completion, the helminth needs a new intermediate host for further development. Most often they are freshwater fish that feed on crustaceans and mollusks.
- In the digestive tract of the fish, the procercoid is freed from the membrane surrounding it and penetrates the liver, eggs or muscle fibers of the intermediate carrier. There it transforms into a new intermediate form - the plerocercoid.
The helminth then develops in the body of its final host, a human. Its habitat is the small intestine. In it, the worm larva, which has entered the digestive tract along with infected food, turns its head with suckers outward, attaches to the intestinal wall and begins the last development cycle, ending with the onset of sexual maturity of the helminth and the production of eggs.
To obtain a larval form dangerous to humans, a long development cycle is required. Until the egg goes through these stages, it remains dangerous only for intermediate carriers.
Symptoms of diphyllobothriasis
From the moment the tapeworm enters the human body until the first significant symptoms appear, it can take from 20 to 60 days. Manifestations of the disease develop gradually and may be mild for a long time.
Abdominal pain of a cramping nature;
Increased salivation (hypersalivation);
A slight increase in temperature to subfebrile levels;
Decreased or increased appetite, weight loss;
The appearance in feces of fragments of the body of the tapeworm in the form of scraps of whitish ribbons;
Intestinal obstruction due to the accumulation of helminths in the lumen of the small intestine;
Signs of anemia with vitamin B12 deficiency (weakness, tachycardia, dizziness, pale skin, swelling of the face, arms and legs, cracked tongue, atrophy of taste buds, damage to the oral mucosa);
Damage to the nervous system (numbness of the limbs, sensory disturbances, unsteady gait);
Blood composition disorders (decrease in the number of leukocytes, erythrocytes, platelets, blood hemoglobin, increase in color index, appearance of megaloblasts, megalocytes).
The intensity of symptoms depends on the degree of damage to the body, concomitant pathologies, and diet. In severe cases, hepatomegaly, enlarged spleen, and extremely low secretion of gastric juice are noted. The accumulation of many helminth individuals in the intestinal lumen leads to obstructive intestinal obstruction. There are cases of latent (hidden) infection.
Preventive actions
Prevention of diphyllobothriasis consists of the following measures:
- Good heat treatment of meat;
- Chemical processing of fish preservatives;
- Compliance with hygiene requirements;
- Regular testing of fish products for the content of parasitic larvae;
- Sanitary control over river vessels and settlements near rivers.
This will identify the parasite in the early stages of spread and protect the health of other workers. In other words, with proper treatment and following all the necessary prevention recommendations, you can quickly recover from this parasitic worm. You should be more careful about your own health and undergo appropriate medical examinations in a timely manner. Thus, it is possible to exclude the development of this pathology in the body.
Consequences of diphyllobothriasis for human health
Consequences of helminth presence in the human gastrointestinal tract:
At the site of attachment of bothry of the tapeworm scolex to the intestinal mucosa, tissue necrosis and atrophic processes develop;
Disturbances in the activity of the gastrointestinal tract occur due to damage to the nerve endings of the mucous membrane and disorders of intestinal trophism;
The waste products of the broad tapeworm sensitize the body, causing allergic reactions;
Megaloblastic anemia appears due to the fact that vitamins B1, B6, B12 are adsorbed by the parasite.
A severe form of anemia leads to neurological disorders: depression, increased irritability, hyperreflexia, paresthesia.
Routes of infection with tapeworm
Infection with the broad tapeworm occurs through the nutritional route. Invasion of the parasite occurs during the consumption of infected fish or caviar, which may be lightly salted or insufficiently thermally processed. In the muscles or internal organs of such fish (chum salmon, pink salmon, pike perch, burbot, ruffe, pike) there is a plerocercoid - an intermediate form of development of the wide tapeworm.
It is most likely that such caviar or fish was salted at home in violation of the proportions or salting technology. Sometimes infection occurs through contaminated dishes, knives, and cutting boards. Those who prefer to eat fish or caviar raw or cook fish kebab are at great risk.
Parasite development cycle:
From the small intestine of an infected person or animal, tapeworm eggs enter the external environment.
In some of the eggs that fall into the water, a tapeworm embryo develops. If the water temperature does not drop below +15°C, the embryo (coracidium) emerges into open water after 1-2 weeks.
At temperatures no higher than +20°C, it remains viable in fresh water for up to six months.
In the body of a freshwater crustacean that has swallowed the embryo, it turns into a larva (procercoid).
Predatory fish or fish of the chum family swallow crustaceans along with procercoids.
In the body of fish, the larvae penetrate through the intestinal wall into the muscles and continue their development, transforming within a month into a plerocercoid measuring from 1 to 5 cm, together with bothria. This form of tapeworm development can be seen with the naked eye.
The plerocercoid, together with the fish, enters the body of the final host (human) and continues its development in the small intestine.
After 2-4 weeks, the larva turns into a sexually mature individual and begins a new development cycle.
From the egg stage to the appearance of a mature individual, under favorable circumstances, 6-7 months pass. In the human body, the broad tapeworm can parasitize for up to 20 years. A sexually mature female tapeworm is able to produce up to 2 million eggs per day.
Further metamorphoses
If the coracidium managed to find the host it needed in the few days allotted to it by nature, the development of the broad tapeworm continues. Once in the stomach of the crustacean, the worm larva is released from the shell with cilia and, with its hooks, penetrates the body of the victim. There, in 2-3 weeks, it turns into a so-called procercoid - a worm-like creature measuring only 0.5 mm in size. At one end there is a tiny ball with hooks (cercomere). Fish that eat infected crustaceans become second intermediate hosts. These can be ruffs, pike perch, roach, perch, burbot. Once in the new host’s stomach, the procercoid drills through its walls and penetrates the muscles, liver, and other organs. It takes 3 weeks for it to develop into a plerocercoid.
This new form of tapeworm has a worm-like body up to 4cm long. At one end there is a head with bothria pressed inward. Sick fish are a source of infection for humans and other mammals (cats, dogs, foxes, bears, otters). Once in their stomach, the plerocercoid becomes an adult, sexually mature worm. The cycle repeats. If a small river fish is swallowed by a larger one, the plerocercoids also spread throughout its body, but do not develop further; they wait until this random host is eaten by a person.
Treatment of diphyllobothriasis
Before treating diphyllobothriasis, the doctor diagnoses helminthiasis. A preliminary history of epidemiological manifestations is collected. It includes such items as living near a fresh body of water, fishing, and eating independently caught and salted fish.
Fecal analysis to detect tapeworm eggs and parts of its body;
Blood test to determine signs of hyperchromic anemia;
Complete blood test to detect neuropenia and thrombocytopenia;
Biochemical blood test for haptoglobin and lactate hydrogenase levels.
After analyzing all the indicators, the helminthologist recommends effective drugs for the treatment of diphyllobothriasis. At the preparatory stage, treatment for vitamin deficiency and iron deficiency anemia is carried out. For a month, the patient takes iron supplements and receives vitamin B12 injections.
Drugs with anthelmintic action:
Praziquantel - leads to paralysis of the muscles of the parasite, is used to treat children from 4 years of age, the side effect is a decrease in concentration.
Biltricide is contraindicated for pregnant women, dosage is 60-75 mg/kg body weight, the daily dose is divided into 3 doses.
Niclosamide is used to treat children from 2 years of age (0.5 g/day), the therapeutic dose for adults and adolescents from 14 years of age is 2-3 g/day, accompanied by the use of laxatives.
To reduce the intensity of toxic poisoning and allergies, taking these drugs is accompanied by antihistamines - Tavegil, Suprastin, Cetrin, Diazolin.
How to get rid of an uninvited guest?
From the moment the diagnosis is established, treatment for tapeworm should begin as early as possible. To completely get rid of the parasite, a course of treatment is carried out, which is usually carried out on an outpatient basis. The patient is prescribed pathogenetic and specific drugs. If the anemia is significant, the doctor will prescribe folic acid tablets and intramuscular injections of vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin) before choosing an anthelmintic medication. Specific therapy for tapeworm is drugs aimed at eliminating the parasite. Medicines in this group paralyze the neuromuscular system of helminths, which is why the parasite loses its ability to cling to the intestinal walls and is expelled by peristaltic waves.
Anthelmintics acting on tapeworm include:
- biltricide;
- fenisal;
- niclosamide;
- praziquantel;
- plant-based preparations (male fern seed extract, pumpkin seeds).
Of course, the drug, its dosage and timing of treatment should be chosen by a medical specialist based on the individual condition of the sick person, taking into account contraindications, since a number of drugs are contraindicated at certain stages of pregnancy, concomitant diseases, and young children.
We should not forget that in rare cases, part of the worm may remain in the intestines and begin to develop again, so after six months you should be tested again to ensure a final cure. If eggs and fragments of the broad tapeworm are again found in the biological material, then another course of treatment will have to be carried out. If the test results are negative, then further observation is not necessary.
To restore the body and correct the condition of the digestive system, enzymes, pro- and prebiotics, multivitamins, and antihistamines are used.
In general, the prognosis with timely diagnosis and adequate therapy is favorable.
Prevention of wide tapeworm infestation
To protect yourself from infection with Latena wide, you need to carefully monitor the complete culinary processing of fish: fry it for at least 30-40 minutes, salt it for 10 days, freeze fish products to destroy parasite larvae.
Fishermen and workers in the processing industry should undergo timely medical examinations, especially during the peak activity of parasite larvae. When the first symptoms of the disease appear, you should immediately undergo an in-depth examination by a parasitologist.
Education: in 2008, received a diploma in the specialty “General Medicine (Therapeutic and Preventive Care)” at the Russian Research Medical University named after N. I. Pirogov. I immediately completed an internship and received a diploma as a therapist.
10 ways to relieve stress
15 scientifically proven beneficial properties of sesame!
It is well known that parasites in the human body strive to exist as inconspicuously as possible. However, our body is very difficult to deceive, and it gives signals to a person that an infection has occurred. The main thing is to be able to recognize these signals and interpret them correctly.
Ascariasis is a type of helminthiasis caused by roundworms belonging to the class of nematodes, family Ascarididae (roundworms). They parasitize the intestines of humans and animals. There are several types of these parasites that affect various representatives of vertebrates: cats, dogs, birds, pigs.
The symptoms of toxocariasis are so diverse that doctors practicing in various branches of medicine - neurologists, ophthalmologists, hematologists, gastroenterologists, and therapists - can encounter its manifestations. Although researchers called humans an “ecological dead end” of toxocariasis, because it is unusual.
Anthelmintic drugs are used to treat various types of helminthiasis - damage to the body by parasites. These agents can be either universal (broad-spectrum) or selectively acting on any type of helminth. Until recently, the pharmaceutical industry could not offer parasite expulsion to patients.
In case of pinworm infection, all close relatives of the infected person are subject to preventive treatment. Testing for the presence of pinworms often gives a false negative result. The ease of infection with enterobiasis through household items and shared bedding, contact with animals and handshakes, as well.
Wide tape. Morphology, routes of infection, development cycle, prevention
Broad tapeworm (Diphyllobotrium latum) is the causative agent of diphyllobothriasis . The disease occurs mainly in countries with temperate climates. In Russia - along the banks of the Volga, Dniester and other large rivers.
In the human body, the parasite is localized in the small intestine.
In the mature state, the parasite has a length of up to 7-10 m or more. The head of the parasite (scolex) is devoid of suckers. It is attached to the intestinal wall with the help of two bothria, or suction slits, which look like grooves. Proglottids are wider than long. The uterus has a characteristic rosette-shaped shape and small size. It comes into contact with the external environment through an opening at the anterior edge of each proglottid. Therefore, maturing eggs can freely come out of it. The eggs of the broad tapeworm are wide, oval, up to 70 microns in size, and yellowish-brown in color. At one pole they have a cap, at the other - a small tubercle.
The life cycle of the parasite is the most ancient among tapeworms. It retains a larval stage that actively swims in the water - coracidium . There are two intermediate hosts that live in water - small freshwater crustaceans (Cyclops and Diaptomus) and the fish that feed on them. The definitive hosts are humans and carnivorous mammals (cats, lynxes, foxes, arctic foxes, dogs, bears, etc.).
Structural features
Despite the fact that the wide tapeworm itself can grow up to 15 meters in length, its head, or scolex, is tiny (up to 5 mm). It looks like an elongated oval, flattened on the sides. There are cracks (bothria) on both sides. With them the worm attaches itself to the intestinal mucosa of its victim. At first glance, it seems that such an attachment is very unreliable, but the worm safely stays in a person for many years, sometimes up to 20 years or more, and it is impossible to remove its head from the intestines by mechanical force, such as enemas. The eggs of this parasite are also oval, slightly yellowish in color, with a cap at one end and a tubercle at the other. A huge amount of them is released into the external environment with feces every day - up to one million pieces. This is facilitated by the structure of the reproductive system. In the center of each proglottid (segment) there is a uterus, similar to a rosette and having an opening extending outward. She tirelessly produces new eggs, and throws already fertilized ones into the intestines of the victim.
Ways of infection by the parasite
The larvae and eggs of the broad tapeworm floating freely in fresh water bodies do not pose any threat to surrounding people . For invasion, which can subsequently lead to the development of diphyllobothriasis, the parasite must develop in a second intermediate host - fish.
Important! To become infected with a dangerous helminth, a person does not have to eat undisinfected fish. Since the broad tapeworm can parasitize the tissues of fish, simple contact with them may be sufficient for invasion. Therefore, after purchasing or cutting freshwater fish, you must wash your hands especially thoroughly.
You should also thoroughly wash your knife and cutting board - poorly treated kitchen utensils can carry parasite larvae, and when used to process other foods, contribute to infestation
Traditional methods
Traditional methods of treatment are most often used to destroy the larvae and even hatch the eggs of the broad tapeworm. You can safely treat yourself with folk remedies at home, since they have virtually no side effects and do not harm the body.
Wormwood contains phytoncides that paralyze the larvae and stop the general activity of helminths. To prepare a multi-remedy based on this plant, you will need: cloves, flax and wormwood - 1 teaspoon, as well as a glass of fresh carrot juice. The components must be mixed together, after grinding the herbs. Take the drink in the morning and during meals.
Wormwood is an effective remedy for worms
Onions also contain phytoncides. This product can be consumed raw, made into tinctures and even enemas.
For the first recipe you will need:
- 2-3 medium onions;
- 350-400 ml of alcohol or water (depending on the age of the patient).
- the main component must be filled with liquid, then leave the tincture in a cool, dry place for 12 hours.
Take on an empty stomach for 5 days. For adults, it is better to use alcohol as a base, as it completely extracts all the beneficial substances from the onion.
An ordinary onion will help get rid of worms
To prepare an enema you will need:
- 1 tablespoon each of onion peel and chopped wormwood, a liter of water;
- mix the ingredients and bring to a boil over low heat;
- After cooking, the mixture should be thoroughly strained.
The enema will need to be used 2 times a day for 4 days.
Broad tapeworm: symptoms of invasion
The development cycle of tapeworm in the human body begins with an incubation period, which can last from 20 to 60 days. The onset of infection may not have pronounced symptoms. Even parasitization of an already sexually mature individual, with good nutrition and the general condition of the host’s body, can be asymptomatic.
The presence of broad tapeworm in the body causes the following symptoms in humans:
- nausea;
- vomit;
- painful sensations in the abdomen;
- attacks of fever;
- bowel dysfunction;
- change in appetite (can be either decreased or increased);
- sometimes intestinal obstruction occurs (this symptom develops when the small intestine is blocked by the bodies of parasites);
- B12-deficiency anemia (characterized by general weakness, dizziness, fatigue, pale skin, numbness of the extremities)
- pain when eating.
In some patients, the broad tapeworm causes glossitis - inflammation of the tongue with atrophy of its papillae; the same damage to the gums, inner surface of the cheeks, and pharynx may occur
Note. In some cases, infection is accompanied by damage to the nervous system: patients experience sensory disturbances, numbness in certain areas of the body, and unsteady gait.
Story
Broad tapeworm has a long documented history of affecting people who regularly consume fish. Especially those whose customs include eating raw or poorly processed fish. In the 1970s, most known cases of infection with this parasite were in Europe (5 million) and Asia (4 million). Fewer reports have come from the Americas, and there have been no credible confirmations in Africa or Australia.
It is interesting to note that, despite the relatively small number of cases seen in South America today, some of the earliest archaeological evidence of tapeworm infestations comes from this part of the world. Evidence of Diphyllobothrium worms has been found in 4,000-10,000-year-old human remains on the west coast of South America. There is no clear time period when tapeworms and related species were discovered in humans. But it is clear that diphyllobothriasis has occurred in certain human populations for a very long time.
Due to changing eating habits in many parts of the world, cases of tapeworm infestation have been observed either from a long time ago or appeared later. For example, cases of diphyllobothriasis have recently been described in previously unprone regions, such as Brazil. Thus, tapeworm is becoming a cause of disease in some parts of the world, where new preferences for eating raw or undercooked fish are emerging.
Diagnosis of damage to the body by tapeworm worms
Early detection of broad tapeworm infestation contributes to quality treatment of diphyllobothriasis . The following methods are used to diagnose infection:
- studying the patient’s epidemiological history (the patient’s stay in a potentially hazardous environment, possible contact with fresh fish, consumption of insufficiently heat-treated, lightly salted products, freshwater fish caviar);
- analysis of clinical data of symptoms;
- conducting a general blood test - with helminth infestation, a reduced number of red blood cells or hemoglobin is observed, although the color indicator remains normal; the level of leukocytes and platelets decreases; altered blood elements are present;
- microscopic analysis of feces - parts of the parasite’s body can be observed in the excrement.
Treatment of diphyllobothriasis
Treatment of this type of helminthiasis, such as diphyllobothriasis, is primarily aimed at ridding the infected body of the parasitic worm. In addition, measures are often taken to combat B12 deficiency anemia or other symptoms of the disease (laxatives or painkillers are prescribed, drugs that improve intestinal motility).
After one to three months, patients are prescribed a repeat copro-ovoscopy (fecal analysis for helminth eggs).
Part of the wide tapeworm, whose length reaches 15 meters, can remain in the body and continue parasitism . If tapeworm eggs are detected again in the feces, a second course of treatment is prescribed.
Each proglottid (component segment) of the broad tapeworm has both male and female reproductive organs, so it can reproduce independently
Drug therapy
Important. All antiparasitic medications have increased toxicity and a number of contraindications and side effects. Therefore, the use and dosage of drugs should be prescribed exclusively by the attending physician, based on the patient’s age and clinical picture of the disease.
Among the medications used to rid the patient of broad tapeworm, the following are distinguished:
- Phenasal (niclosamide), which is prescribed in a dosage of 1 to 3 g, depending on age;
- Biltricide - 25 mg per kilogram of patient weight.
Vitamin B12 is used to correct related deficiency anemia. Preparations containing iron (Hemofer, Ferronate, Ferronal, Actiferrin) - also for the treatment of anemia.
During treatment of diphyllobothriasis, it is recommended to follow a diet consisting of liquid or semi-liquid dishes - broths, liquid cereals, purees, jelly, fruit juices
Treatment with folk remedies
Pumpkin seeds are most often used as a folk remedy to get rid of tapeworm, the use of which is recommended in the treatment of most types of helminthiasis . They are used as follows:
- For adult patients, take about 300 g of peeled raw pumpkin seeds (it is very important to preserve the green skin of the seeds); for children, depending on age, from 50 to 15 g. The raw materials are crushed in a mortar, using a coffee grinder or blender.
- To the resulting mass add 50 ml of boiled water, cooled to room temperature.
- To improve the taste of the drug, you can add a little honey or jam to it.
- The resulting medicine is thoroughly mixed and eaten within an hour in the morning on an empty stomach.
- Three hours later, a weak solution of magnesium sulfate is taken as a laxative, and after another 30 minutes the patient is given a cleansing enema.
According to some sources, it is best to take medicine from pumpkin seeds without getting out of bed - this is how the effect of the folk remedy is most pronounced
Male fern seed extract is also used as an aid during infestation with broad tapeworm:
- For two days before taking the drug, the patient is prescribed a light diet without fats and spicy foods, and on the eve of the dose, a light dinner and a saline laxative at night.
- Depending on age, the drug is taken in a total weight of 4 to 7 g, taking one capsule every two minutes.
- After half an hour, the patient is again given a saline laxative, and after an hour and a half - a light breakfast.
- If there is no stool for more than 3 hours, a cleansing enema is performed.
Bibliography
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Brucellosis. Parasites. Link
- Corbel MJ Parasitic diseases // World Health Organization. Link
- Young EJ Best matches for intestinal parasites // Clinical Infectious Diseases. — 1995. Vol. 21. - P. 283-290. Link
- Yushchuk N.D., Vengerov Yu.A. Infectious diseases: textbook. — 2nd edition. - M.: Medicine, 2003. - 544 p.
- Prevalence of parasitic diseases among the population, 2009 / Kokolova L. M., Reshetnikov A. D., Platonov T. A., Verkhovtseva L. A.
- Helminths of domestic carnivores of the Voronezh region, 2011 / Nikulin P. I., Romashov B. V.
An article for patients with a doctor-diagnosed disease. Does not replace a doctor's appointment and cannot be used for self-diagnosis.
The best stories from our readers
Topic: Parasites are to blame for all troubles!
From: Lyudmila S. ( [email protected] )
To: Administration Noparasites.ru
Not long ago my health condition worsened. I began to feel constant fatigue, headaches, laziness and some kind of endless apathy appeared. Problems also appeared with the gastrointestinal tract: bloating, diarrhea, pain and bad breath.
I thought it was because of the hard work and hoped that it would go away on its own. But every day I felt worse. The doctors couldn’t really say anything either. Everything seems to be normal, but I feel like my body is not healthy.
I decided to go to a private clinic. Here I was advised, in addition to general tests, to get tested for parasites. So in one of the tests they found parasites in me. According to doctors, these were worms, which 90% of people have and almost everyone is infected, to a greater or lesser extent.
I was prescribed a course of antiparasitic medications. But it didn’t give me any results. A week later, a friend sent me a link to an article where some parasitologist shared real tips on fighting parasites. This article literally saved my life. I followed all the advice that was there and after a couple of days I felt much better!
Digestion improved, headaches went away and the vital energy that I so lacked appeared. To be sure, I took the tests again and no parasites were found!
Anyone who wants to cleanse their body of parasites, no matter what types of these creatures live in you, read this article, I’m 100% sure it will help you! Go to article>>>
Still have questions? Ask them in our Anonymous group on VK
How to get rid of parasites in a week. The answer is here!
A reliable and effective remedy for combating worms. Removes all parasites in 21 days.
Go to website
Reviews
Read online
Symptoms that 100% indicate parasites! Take the Test.
How to rid your body of life-threatening parasites before it’s too late!
Read more
Website
To get a consultation
The doctor tells how to quickly get rid of parasites for adults and children!
A parasitologist explains what effective methods exist to combat helminths.
More details
Read completely
Comments
Search for cures for parasites
Other tests
We recommend reading
Is it possible to get scabies from a cat, how to prevent infection
6 days ago 03/08/202008.03.2020ecoliv94
Can only one partner have ureaplasma and is there a chance of getting sick?
6 days ago 03/08/202008.03.2020ecoliv94
How long does itching last after scabies treatment and what to do about it?
6 days ago 03/08/202008.03.2020ecoliv94
Can worms come out through a person's mouth, when can this happen?
01.02.202001.02.2020ecoliv94
Prevention of infection with tapeworm worms
As with any other disease, following preventative rules greatly reduces the risk of infection with broad tapeworm. The most common prevention methods are:
- Maintain good hygiene, wash hands thoroughly after contact with live or fresh fish.
- Elimination of raw food diet and consumption of low-salt foods.
- When preparing fish dishes, you must carefully adhere to the rules of heat treatment of carcasses: fry small portioned pieces in a large amount of fat for 15-20 minutes, large pieces - 30-40 minutes.
The vital activity of the plerocercoids of the broad tapeworm is negatively affected by low temperatures: at −15°C the parasites die in 24 hours, at −10°C - after 3 days, at −4°C - in 10 days
- It is necessary to thoroughly clean the workplace after cutting fish.
- Workers in the fishing and food industry should undergo routine helminthiasis testing on a regular basis.
- Periodically, research is carried out on fish caught in fresh water bodies and fish products of enterprises.
- Proper operation of treatment and sewerage facilities to prevent the release of fecal matter into the environment.
Infection with broad tapeworm is a fairly common type of helminthiasis in our country. However, careful monitoring of the condition of your body, timely diagnosis and proper treatment allow doctors to make favorable prognoses regarding the disease with diphyllobothriasis.
Diagnostics
The most obvious sign of tapeworm infection is proglottids in the stool. But they are not always found. The main way to diagnose diphyllobothriasis is microscopy of the patient's stool to detect eggs and tapeworm fragments.
Additional methods include laboratory blood tests.
- A general blood test can reveal anemia, which is a frequent companion to diphyllobothriasis;
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) allows you to detect antibodies formed as a response of the immune system to the presence of helminth antigens;
- Using PCR diagnostics, tapeworm DNA can be detected in the blood.