Ulcers affecting the gastrointestinal tract are becoming more and more common in people. At the moment, these diseases are the most common among all. The most serious problem of the disease is that this disease is practically incurable. About 30% of the population faces this problem.
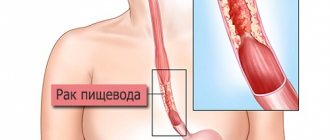
One of the most common gastrointestinal ulcers is an esophageal ulcer.
How does the disease progress?
The first symptoms of an ulcer are the presence of unpleasant sensations. Thus, a violation of the trophism of the walls of the esophagus occurs. It should also be noted dysfunction of gastric peristalsis and excessive increase in sphincter tone, which contributes to the frequent reflux of acidic contents into the esophagus.
Most often, this disorder appears after operations in the gastric junction area. The disease can also occur with cardia insufficiency and gastroesophageal reflux.
Important: Ignoring the first symptoms of the disease for a long time is one of the common factors leading to the formation of peptic ulcers of the esophagus. Complicated forms of the disease cannot be treated with folk remedies.
Preventive measures
To prevent the occurrence of an ulcer, it is necessary to exclude the influence of unfavorable factors in advance: it is advisable to completely quit smoking, reduce the negative load on the nervous system, and regularly undergo routine examinations with a doctor. To generally strengthen the body, it is useful to follow a diet, have dinner no later than 2-3 hours before bedtime, and maintain a healthy lifestyle. The occurrence of inflammatory processes in neighboring organs can also provoke esophageal ulcers, so it is necessary to cure all abnormalities in advance.
Symptoms
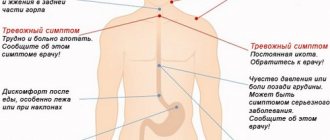
In most cases, the symptoms of an esophageal ulcer appear unobtrusively. Over time, their severity worsens, which begins to significantly affect the quality of life and general well-being of a person.
Thus, an esophageal ulcer can be identified by the following symptoms:
- Severe dysphagia - impaired swallowing function, cough when eating;
- Frequent belching sour;
- Nausea;
- Vomiting blood;
- Pain when swallowing directly;
- Heartburn during active physical activity, namely when bending over in a lying position;
- Pain in the chest area that occurs sharply after eating;
- Weight loss;
- Weakness;
- Fast fatiguability.
Important: Quite often, people diagnose themselves on their own, hoping that the obsessive symptoms will disappear in a couple of days. However, delaying treatment provokes the development of complications leading to the development of oncology. An esophageal ulcer can be easily treated if its signs are detected early.
Menu and delicious recipes
Below are recipes for preparing dishes during different periods of the disease. Dietary dishes have different preparation and heat treatment technologies.
Dietary mucous soups are used in the initial stages of the disease with severe inflammation. They are strained decoctions of long-cooked cereals, but without pureing the cereal itself. The decoctions are lightly salted, seasoned with an egg-milk mixture and butter is added. The finished dish has a uniform consistency of cream, without food particles or flakes of curdled eggs.
Milk soups are used in Diets 1A and 1B. They are prepared with cereals, in milk with the addition of water (1:1). The cereals are pre-cooked until tender, and then boiling milk is added. The grains in the finished dish should not retain their shape, so they are pureed, the color of the soups is white, and they have a sweetish, slightly salty taste.
Puree soups are the basis of the first table. They are boiled in water with cereals, potatoes and carrots. Well-cooked ingredients are pureed, salted and butter is added.
For ulcer sufferers, the preferred method of cooking is steaming and boiling in a water bath. For greater removal of extractive substances, the meat should be cooked in small pieces, then the primary broth should be drained, and the meat should be cooked in fresh hot water until tender. It is used as a semi-finished product for stewed and chopped dishes.
When cooking with steam, the product should not come into contact with the liquid, therefore there is less loss of nutrients. Cooking in a water bath is carried out at a temperature of 40-70°C in a container lowered into a larger container with water. In the diet, omelettes, sauces, egg porridge and puddings are prepared in this way.
First meal
Below are recipes for preparing dishes during different periods of the disease. Dietary dishes have different preparation and heat treatment technologies.
Dietary mucous soups are used in the initial stages of the disease with severe inflammation. They are strained decoctions of long-cooked cereals, but without pureing the cereal itself. The decoctions are lightly salted, seasoned with an egg-milk mixture and butter is added. The finished dish has a uniform consistency of cream, without food particles or flakes of curdled eggs.
Milk soups are used in Diets 1A and 1B. They are prepared with cereals, in milk with the addition of water (1:1). The cereals are pre-cooked until tender, and then boiling milk is added. The grains in the finished dish should not retain their shape, so they are pureed, the color of the soups is white, and they have a sweetish, slightly salty taste.
Puree soups are the basis of the first table. They are boiled in water with cereals, potatoes and carrots. Well-cooked ingredients are pureed, salted and butter is added.
Treatment of esophageal ulcers with folk remedies also demonstrates a pronounced effect. However, the traditional method of therapy and folk recipes must be used in combination.
In search of a solution to how to treat such an ailment, people tried various methods, and here are some of them that have gained the most popularity:
- Potato juice. It should be drunk raw and on an empty stomach. It has alkaline properties and thereby promotes tissue regeneration. The course of treatment should be at least one and a half months.
- Flax seeds. This recipe is actively used in the treatment of esophagitis and its complications. Just pour a teaspoon of seeds into a glass of hot water and then strain. The resulting mucous decoction gently envelops the affected areas and quickly relieves inflammation.
- Propolis. This beekeeping product has pronounced healing properties. It is recommended to mix the thoroughly crushed substance with olive oil in a ratio of 40g/500 ml and heat it in a water bath. Take a tablespoon before meals.
With a fairly strict limitation on the range of food baskets, there is no reason to be upset. Delicious dishes can be prepared even with this diet, and a healthy diet will only bring benefits to the whole body.
Forms of ulcers
An esophageal ulcer can have several types. The thing is that this disorder appears in connection with the most unpredictable factors, which can represent serious violations in the diet, or even relate to a undermined emotional state. Each case of ulcer has its own individual symptoms.
Symptomatic ulcers
- Stressful - appear when the body is in a critical condition, namely with serious burns of the body, complex diseases of the heart, kidneys and others.
- Medicinal - occur due to side effects from incorrectly selected drugs. A malignant effect is also possible after oncology radiation.
- Decubital - the use of a probe in the esophagus for a long time forms an excellent basis for the appearance of a defect.
- Congestive - may appear after an enlargement of a tumor located in the human esophagus.
Peptic ulcers
- Chronic - an ulcer is formed due to the presence of another ailment - reflux, which, due to the constant reflux of acidic contents, provokes the development of inflammation, irritation and the subsequent appearance of wounds.
- Acute - manifests itself as an additional disorder accompanying serious gastrointestinal diseases or the postoperative period.
Stages of disease development
There are several stages in the development of esophageal ulcers, and all of them are considered an acute form of the disease.
- There are no deep scars on the mucous membrane of the esophagus yet. The ulcer is quite small, but has an inflamed field of mucous membrane with swelling around it.
- The scar begins to grow deeper, causing the nearby cells of the mucous membrane to die. Edema folds form, which bring discomfort in the stomach area.
- Complete deformation of the esophagus begins. Cells die deeper than the mucous membrane, causing bleeding. The swelling is constantly increasing.
- The mucous membrane is already completely damaged. Every scar bleeds profusely.
Causes
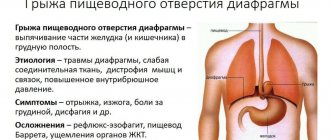
An esophageal ulcer does not always appear for standard reasons. Quite often, in order to identify the factor in the onset of the disease, it is necessary to conduct a complex diagnostic analysis. Often this causal diversity makes early treatment difficult.
Causes for peptic ulcers
- Scleroderma is a specific disease of connective tissues, manifested by a decrease in the elasticity of the skin and its excessive thickening.
- Bad habits such as smoking and alcohol abuse.
- Diseases of ulcerative type;
- Side effects from drugs that interfere with the proper functioning of the sphincter;
- Cardiac dysfunction;
- Reflux;
- Esophageal hernia.
Causes for symptomatic ulcers
- Tumor in the esophagus;
- Mechanical damage to the esophagus;
- Serious terminal conditions of certain organs and tissues;
- Side effects from radiation therapy;
- Incorrect use of certain medications, side effects;
- Diverticulum (protrusion of the walls of the esophagus, which leads to stagnation of swallowed food).
Important: Only a qualified doctor can determine the cause of the disease. Treatment with improvised means will not bring results and will only worsen the existing condition.
Diagnostics
A gastroenterologist knows how to treat and diagnose such a disease. The basis of diagnostic measures is instrumental and laboratory examinations. But before prescribing them, the specialist needs to familiarize himself with the patient’s medical history, conduct a thorough survey and an external examination. This will help determine the causes of the disease, the presence and intensity of symptoms. After which laboratory tests are prescribed, which include:
- performing a general and biochemical blood test to search for concomitant disorders and possible changes in its composition;
- microscopic examination of feces will make it possible to determine the presence of internal hemorrhage, as well as identify undigested food fragments.
Instrumental examinations are of greatest diagnostic value:
- EGDS is a procedure for examining and assessing the surface of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract. It necessarily includes a biopsy - for subsequent histological studies of a small piece of the membrane of the affected organ;
- radiography with contrast – makes it possible to accurately detect the location of the ulcerative defect;
- manometry - study of the activity of the lower esophageal sphincter;
- Ultrasound, CT and MRI - to identify concomitant gastrointestinal diseases;
- measuring the acidity of the environment in the esophagus.
EGDS
After studying all the results of tests and examinations, the specialist prescribes an individual treatment course.
Treatment
Treatment of ulcers, as in cases of therapy for other diseases, begins with the preparatory stage. This stage consists of cleansing the body, namely the liver and intestines, of toxins and parasites. Why is cleansing necessary? This procedure is necessary to prevent dysbacteriosis.
This process interferes with the normal digestion of food and leads to its rotting. At the same time, poisons accumulate in the human body, which can lead to poisoning of the entire body, entering and spreading throughout the body through the circulatory system. If the body is poisoned, a person may experience discomfort from constant headaches, malaise, intestinal upset and nausea. If a person experiences certain symptoms, the doctor will definitely prescribe a colon cleanse. These symptoms include:
- Constipation and diarrhea.
- Bloating and gas formation.
- Unpleasant smell of sweat.
- Unhealthy skin.
- Bad breath.
- General malaise.
- Frequent occurrence of colds.
- Worm infestations and more.
They also use natural remedies for cleansing, including herbal tinctures and decoctions. They perfectly soothe the esophagus, stomach and their mucous membranes.
In addition to instrumental bowel cleansing, the patient is also prescribed therapeutic fasting. Its result is not only cleansing of the intestines, but also cleansing of the blood, renewal of numerous body cells, as well as rejuvenation of the body and replacement of the skin.
The next stage involves intensive treatment. During it, the body is restored with the help of an active lifestyle and light physical activity for optimal health. Patients are advised to go in for sports and constantly walk in the fresh air.
After this, there comes a period when treatment is based on several exceptions and occurs at home:
- Elimination of alcohol.
- Exclusion of tobacco.
- Exclusion of unnatural medicines.
- Eliminating junk food with numerous unnatural additives.
- Elimination of overeating.
Surgical treatment is prescribed to the patient only if the above classical treatment does not work sufficiently or does not bring results. The use of traditional methods to cure this type of disorder, even as an additional remedy, is unacceptable.
ICD 10 code
Often the final diagnosis given to the patient includes many designations that are incomprehensible to the common person, which can take up more than one line. Therefore, for a convenient description of the underlying disease and its accompanying pathologies, the list of the international classification of diseases ICD-10 is used, where the number ten indicates the date of the last revision, i.e. 2010. This classification includes codes indicating all existing diseases. Currently, instead of the name of the disease, the corresponding code is entered into the patient’s chart and into all medical documents issued for him, so the code K22.1 is assigned to an esophageal ulcer.
Currently reading: How to treat mouth ulcers in children and adults
Code classification of diseases allows you to monitor the state of the country's health care, have an idea of the level of health of the population, monitor the activities of hospitals and medical institutions, know which diseases most often affect the population, and anticipate the possibility of these conditions. And also this code system contains a list of possible injuries and causes of death. These lists are reviewed once every ten years.
The ICD is a unified normative document, the use of which makes it possible to choose a technique and method for diagnosing a particular disease from a unified point of view at the international level. During the last revision, along with the traditional structure of the document, a new alphanumeric code system was introduced, the use of which is more convenient than the simple digital one that was used before. Important additions were made during the revision. Thus, the main main part of the classification included external factors that affect the state of human health, which were previously considered additional.
The document contains a detailed list of all diseases, which are arranged in alphabetical order. It is divided into headings, sub-headings, includes necessary notes, lists for exclusion, as well as determining the causes of death. It contains a list of conditions for the patient's inpatient regime.
With the help of this list, it became possible to obtain objective data on diseases of the population, the frequency of visits to medical institutions, the cause and number of deaths.
Possible complications
With timely treatment, the patient recovers fairly quickly. However, for progress to be noticeable in the near future, strict adherence to diet and drug therapy is necessary.
If left untreated, an esophageal ulcer can develop complications:
- The appearance of a hole in the esophagus;
- Severe narrowing of the esophagus in the lower section;
- Spread of ulcers to other organs;
- The appearance of internal bleeding;
- The emergence of malignant cells;
- Severe weight loss.
Important: The appearance of oncology in all cases means surgical intervention. In the future, the patient’s condition will be under year-round doctor’s supervision.
Drug therapy
Often, drugs that have antibacterial, antacid and astringent effects are used in therapy. You will also need medications that accelerate the regeneration of the affected areas, and in extreme cases, analgesics will also come in handy.
The main goal of drug therapy is to reduce pain, gastric acidity and irritability of the mucous membrane on which the esophageal ulcer has formed. Symptoms and treatment are related, since the disappearance of negative manifestations indicates an improvement in the clinical picture.
Medicines that accelerate the healing of ulcers play an important role. Such drugs contain a substance that stimulates regeneration, which restores the correct structure of the tissue. Antacids are required to reduce the aggressive effect of hydrochloric acid on the esophagus by neutralization, and prokinetics effectively restore gastrointestinal motility.
Prevention
To avoid long-term and intrusive treatment, a person should adhere to simple rules of prevention. They consist in preventing the occurrence of a hiatal hernia and preventing the occurrence of heartburn. Doctors give examples of several basic preventive canons:
Proper nutrition.
Nutrition is an underrated aspect of human life. It is very important to follow a meal schedule. You must eat at least five times. At the same time, the portion size consumed should be gentle, not too large and not too small. It is also worth remembering that the feeling of fullness from food does not come immediately, but only 10-15 minutes after eating. Thus, you need to eat gradually and slowly, chewing every piece of food thoroughly. You should not eat on the go and snack on dry food. With severe heartburn, its elimination will proceed much faster if meals are taken by the hour.
Proper sleep.
To prevent the occurrence of the disease, it is very important to maintain a sleep schedule. You also need to get enough sleep correctly. That is, the best option would be to sleep on a comfortable bed, with your head and torso elevated above your legs. If the legs are higher than the body during sleep, then gastric juice is thrown into the esophagus and larynx, which leads to heartburn. There is one more rule that we have been taught since childhood: you should not overeat before going to bed. This habit has a very bad effect on the functioning of the stomach and often leads to acute reflux.
The right products.
A balanced diet and high-quality products are the key to energy and excellent well-being. Very often, eating certain foods leads to excessive acid formation. These include oranges, tomatoes, onions and garlic, carbonated and alcoholic drinks, as well as fatty, fried meat. Smoking is also highly discouraged. Smoke irritates not only the lungs and larynx, but also the mucous membrane of the esophagus and stomach, which very often leads to the appearance and reflux of acid in the opposite direction.
Thus, the treatment of esophageal defects is a whole range of measures, the observance of which will allow you to achieve the desired results and achieve a full recovery in the shortest possible time. The use of traditional methods is possible only as preventive measures.
Diet
The diet for esophageal ulcers must be strictly followed. Systematic adherence to the correct menu significantly improves the patient’s well-being from the very beginning. If you have an ulcer of the esophagus, you should exclude foods that increase gastric secretion. Preference should be given to steamed or boiled food.
The following products should be strictly excluded:
- fatty meats;
- fatty fish and dishes made from them;
- mushrooms and dishes made from them;
- freshly baked bread and flour products;
- alcohol;
- ice cream and similar foods.
Instead, your daily diet should include the following:
- lean meat, without tendons;
- eggs (no more than 2 pieces per day);
- porridge;
- dairy products (but low-fat);
- vegetables and fruits.
Diet for esophageal ulcers
You should also drink at least 1.5 liters of fluid daily. It doesn't have to be water. You can replace it with not too sweet compotes, rosehip decoctions, and non-acidic juices.
Compliance with all doctor’s instructions and proper nutrition will in any case give a positive result. The main thing is to consult a doctor at the first signs of illness and not self-medicate.