What causes the symptoms?
Entering the human body through the mouth, Giardia parasitizes the mucous membrane of the small intestine. After just a few days, the parasites begin to actively multiply, sometimes their number reaches millions. As a result of parasitism by protozoa, the absorption of vitamins, proteins and other beneficial components is disrupted.
This leads to the following changes:
- deterioration of nutrient absorption;
- disruption of the production of enzymes involved in the breakdown of food;
- development of dysbacteriosis.
As the parasites multiply, they spread throughout all parts of the intestine, and some experts point to their ability to penetrate the liver. However, this information is questionable, since there is an opinion that the pathogen cannot live in the environment of the biliary tract.
Giardia causes dyskinesia and cholecystitis, and the products of their decay and vital activity penetrate into the blood, resulting in intoxication of the body.
Methods for diagnosing giardiasis
Giardiasis has no specific symptoms, and its manifestations are varied. Therefore, a typical situation is when a person is treated by different specialists for different symptoms, but giardiasis remains undetected.
You should definitely get tested for Giardia in the following cases:
- with a tendency to intestinal diseases, as well as with their chronic course;
- with eosinophilia (the presence of an increased number of eosinophils in the blood);
- for allergic manifestations;
- in case of intestinal disorder acquired while traveling abroad, especially to southern and exotic countries;
- in case of neurotic symptoms, especially against the background of intestinal disorders.
Giardiasis is diagnosed based on laboratory tests. To diagnose giardiasis, the following are usually used:
Microscopic examination
The feces are examined for the presence of Giardia cysts, and the intestinal contents are examined for the presence of vegetative forms.
Serological blood test
Using a serological analysis, the presence of antibodies to Giardia in the blood is determined.
More information about the diagnostic method
Stool examination
An immunological test can detect a specific Giardia antigen in the stool.
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.
Signs of the disease in the acute stage
The signs of giardiasis are varied. It manifests itself as gastrointestinal, allergic-dermatological, astheno-neurotic, hepatolienal or intoxication syndromes, which depends on the form.
The incubation period is from 7 to 21 days. A characteristic clinical manifestation is gastrointestinal syndrome. Since the organ of Giardia parasitism is the small intestine, most of the symptoms are associated with disruption of the digestive system.
An acute illness is accompanied by painful manifestations in the abdomen, mainly near the navel. In addition, the pain is localized in the right hypochondrium.
The following disorders are observed:
- nausea;
- decreased appetite or its complete absence (depending on the number of parasites);
- belching;
- bloating;
- diarrhea (up to five bowel movements per day).
Often there is a feeling of fullness in the stomach, even if a small amount of food has been eaten. This feeling can occur even on an empty stomach.
Diagnosis of the disease
When the first signs of a pathological condition appear, the patient must contact a medical center for diagnosis. In most cases it consists of:
- Stool analysis. It is used to detect cysts. The procedure is carried out over two months. The interval between tests should be 2 months. This is explained by the fact that parasites have an incubation period.
- Probing of the upper intestine. After the procedure, the contents of the organ are examined.
- Interotesta. It is a modern diagnostic method. The patient needs to swallow a special gelatin capsule, which is characterized by the presence of a nylon thread. After the capsule shell dissolves, the thread comes out along with the feces. Next, a microscopic analysis is carried out, which makes it possible to detect parasites attached to the thread.
In order to clarify the preliminary diagnosis, specific diagnostics are carried out. The most common use is serological methods, which are used to determine antibodies in blood plasma to Giardia.
From this article you will learn about the treatment of trophic ulcers with folk remedies.
Here you will read about treatment for lice and nits at home.
And from this article you will learn about treating the body from roundworms.
Clinical manifestations of the disease in the chronic stage
Chronic giardiasis is characterized by more smooth symptoms, which often complicates diagnosis. Exacerbations, which are quite short-lived, alternate with periods of remission. For certain periods of time, a person ceases to be infectious because parasite eggs stop coming out in his feces, although recovery has not yet occurred.
During the protracted chronic stage of the disease, the following changes occur:
- weight loss;
- nausea;
- bloating;
- belching;
- psychopathological disorder;
- exacerbation of diseases of the digestive system;
- yellow coating on the tongue;
- paleness of the skin;
- anemia.
Even if clinical manifestations periodically appear and then disappear, you need to consult a doctor and undergo a full examination.
Methods for diagnosing the disease
Rare specialists can clinically recognize the disease and the fact of invasion. It is very difficult for doctors to identify giardiasis - the symptoms and causes are nonspecific and extremely varied. This is caused by the ability of protozoa to gain a foothold in many organs and systems, affecting them and causing intoxication of the body as a whole. Without identifying giardiasis, treatment, focusing on symptoms, is prescribed for gastroenterological and neurological diseases, allergies, and dermatitis. Studying the manifestations of the disease, doctors:
- prescribe an ultrasound examination of the hepatobiliary system, cholecystography - and identify biliary dyskinesia and cholestasis;
- do a hemogram and biochemical blood test, diagnosing “monocytosis” or “anemia”;
- examine stool for dysbacteriosis and changes in intestinal microflora - to detect cysts and confirm giardiasis, you need to do at least 3-5 tests per month;
- duodenal intubation is prescribed, and so on.
Despite the extensive laboratory research base, without diagnosing giardiasis, doctors often determine the symptoms (and treatment, accordingly) incorrectly. A parasitological examination helps to confirm the presence of protozoa, identifying cysts and antigens of protozoa in feces, trophozoids in duodenal secretions, and antibodies in blood serum (during serological diagnosis).
Having identified signs of giardiasis in adults, treatment begins with the analysis of biopsy materials obtained during endoscopy and enterotests using gelatin capsules containing nylon threads. An intestinal biopsy provides valuable information. This is one of the effective, but expensive ways to determine giardiasis in adults by changes in tissue structure or the actual presence of parasites.
Rice. 12 Giardiasis in adults
Immunological diagnostics detect protein antibodies in the blood. In the presence of IgM, an acute pathological stage is recorded, IgG indicates a chronic course of the process, the presence of two markers at the same time indicates that chronic giardiasis in adults has worsened. Irido-scanning using IridoScreen devices developed by NPK Optisalt helps determine the level of toxic load on individual internal organs and the extent of their damage. But in real practice, all these measures are rarely used or too late. Only when there is a clear suspicion of giardiasis are the symptoms classified correctly. This affects the quality of treatment and makes it difficult to prevent the disease.
Signs of the intestinal form
Intestinal giardiasis is accompanied by pain in the abdomen and right hypochondrium. They are aching or spastic in nature. After eating, the patient often feels discomfort and stool changes. Basically, the stool is mushy, has an unpleasant odor, and contains mucus impurities. Blood, as a rule, is not visible. Diarrhea gives way to constipation.
The following clinical manifestations also occur:
- weakness;
- general malaise;
- excessive fatigue;
- decreased performance;
- sleep disturbance;
- irritability;
- headache.
All these signs are a consequence of intoxication of the body and metabolic disorders. Patients often complain of heart pain and instability of blood pressure.
Diet for illness
During the course of the pathological process, the patient must adhere to a diet. In this case, it is recommended to use products that slow down the reproduction process of Giardia. It is recommended to take carbohydrates in minimal quantities.
The patient's diet should primarily consist of protein foods and foods that contain large amounts of fiber. The patient is recommended to consume dried fruits, vegetable oil, fresh vegetables and fruits.
Also, his diet should be rich in lean meat and a variety of cereals. The patient should adhere to such a diet during the first two stages of treatment.
At the third stage, it is necessary to consume foods whose effect is positively reflected on intestinal motility. The diet should consist of fresh vegetables and fruits:
- cabbage;
- pears;
- apples;
- carrots.
Experts recommend that patients consume cranberries, lingonberries, baked apples, greens, oatmeal, buckwheat and pearl barley. Also, the patient’s diet should consist of fermented milk products - yogurt, cottage cheese, kefir.
Please note: diet is a fairly important aspect in the treatment of giardiasis, so the patient must strictly adhere to it.
Clinical manifestations of the astheno-neurotic form
When the disease is astheno-neurotic, gastrointestinal disorders are mild or moderate. But the following are observed:
- severe fatigue;
- increased irritability;
- headache;
- insomnia;
- disorders of the cardiovascular system.
Since disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract are not very obvious, they can be confused with the symptoms of another disease or completely ignored. Therefore, it is important to conduct a complete diagnosis of the body in order to identify a dangerous disease and prevent serious complications.
Why is giardiasis dangerous in children?
The disease can develop not only in adult patients, but also in children. In this case, emergency treatment is recommended. Young patients must adhere to a diet. During this period, the consumption of flour products, milk, carbonated drinks, and baked goods is strictly prohibited.
Patients are treated with antiparasitic drugs:
- albendazole;
- nemozola;
- Makmir, etc.
The drugs are characterized by a high level of toxicity, so their prescription should only be carried out by a specialist. To speed up the removal of parasites from the child’s body, it is recommended to take choleretic medications.
It is worth noting: therapy for giardiasis in children must be comprehensive, which will guarantee its effectiveness.
Clinical manifestations of the toxic-allergic form
Toxic-allergic disease is accompanied by frequent and severe allergic reactions.
These include:
- urticaria (a relatively mild condition, manifested by a rash);
- Quincke's edema (a serious complication that can be fatal).
Atopic dermatitis often appears, which is constantly at the stage of relapse. Sometimes patients' joints are affected.
Toxic-allergic giardiasis in the acute stage has a protracted course. If you do not remove all Giardia, drug therapy will be ineffective.
Treatment of giardiasis in children using the method of Dr. Komarovsky
The method of treating Giardia according to Dr. Komarovsky, one of the most popular pediatricians in the former USSR, is somewhat different from generally accepted views. To begin with, he believes that it is not always necessary to treat a child when Giardia cysts are detected in his stool.
In his opinion, the most effective drug against Giardia is the antiparasitic drug Furazolidone. However, it is worth recalling that this drug has quite unpleasant side effects (allergic reaction in the form of skin rashes, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting).
They mainly appear during an overdose, so it is very important that the medicine is prescribed by a doctor.
Features of the course of the disease in women
In women of reproductive age, hormonal changes occur in the body every month. In this regard, the functions of other organs change. Thus, the immune system is either stronger or weaker throughout the month. During periods when immunity is weakened, the risk of infection is especially high. During pregnancy, you are most likely to contract an infectious disease, since during the nine months the immune system is especially vulnerable.
Symptoms of giardiasis in women may be absent for a long time, but with a decrease in the protective functions of the body, lamblia begins to actively reproduce. This leads to inflammation of the small intestine and digestive disorders. When the disease is asymptomatic, we can talk about such a thing as “giardia carrier state.”
In women, this disease occurs with symptoms similar to men.
In addition, you may experience:
- disruptions of the menstrual cycle;
- inflammation of the female organs;
- change in vaginal discharge.
Routes of infection
Giardia are overly capable microorganisms. That is why their activity is observed to persist in the environment for a long period. In the human body, the parasite in most cases lives in the upper intestines.
In their shape, vegetative Giardia resembles a pear. They are characterized by the presence of flagella and suction cups, which ensure their attachment to the intestinal mucosa.
Giardia is characterized by fairly rapid reproduction in the body. After attaching to the intestinal walls, parasites absorb nutrients. Against the background of the active activity of parasites, the release of toxins is observed, which leads to a deterioration in human health.
Infection with worms can occur in several ways:
- water;
- food;
- contact and household.
Quite often, parasites are carried by flies and domestic animals. Giardia belongs to the category of mobile parasites, which allows them to move through the intestines. The conditions of the colon are unfavorable for parasites. That's why they turn into arguments. This form is released into the environment along with feces. Cysts are characterized by an oval shape and are surrounded by a protective membrane.
Giardia can enter the body in various ways. That is why a person is advised to be careful about his lifestyle.
Signs of giardiasis in women during pregnancy
Since a woman's immunity is reduced during pregnancy, it is quite easy to get sick. Including, catching giardiasis and feeling all its symptoms costs nothing. Based on this, gynecologists advise their patients to pay special attention to personal hygiene during pregnancy.
Recommended:
- wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly immediately before consumption;
- avoid visiting open bodies of water;
- Be sure to wash your hands before every meal.
The danger during pregnancy is that, in addition to threatening the woman’s health, the disease negatively affects the development of the fetus. The fact is that the disease leads to disruption of the absorption of nutrients necessary for the child in the womb. And constant diarrhea, alternating with constipation, negatively affects the general condition of the pregnant woman and can lead to miscarriage.
Thus, a woman during pregnancy should pay special attention to every symptom that disturbs her well-being and tell the doctor. If treatment is carried out in a timely manner, you can not only restore the health of the mother, but also avoid negative effects on the child. Symptoms of the disease in a pregnant woman appear in the same way as in other patients, but can be more pronounced.
Most often, during pregnancy, women develop an intestinal form of the disease, which manifests itself in all kinds of digestive disorders.
Therapeutic diet
Giardia, like a number of other parasites, thrives in a nutrient medium of easily digestible carbohydrates that enter the child’s body with sweets (sweets, cakes, pastries), rich pastries, etc.
It is clear that for a 3-4 year old child, refusing them is problematic, but parents must have their say here, because without strict adherence to the diet, any treatment, neither medications nor folk remedies, will not have an effect.
Therefore, everything sweet, fatty, spicy, pickled and smoked, sausages, milk, and semolina are excluded from the child’s diet.
Vegetables that have an irritating effect on the intestines are also excluded: garlic, onions, radishes, radishes.
An acidic environment is extremely unfavorable for Giardia, so it is recommended to increase the consumption of fermented milk products (kefir, unsweetened yogurt, cottage cheese), sour berries and fruits (oranges, pineapples, kiwis, cranberries, blueberries, etc.) both fresh and in the form fruit drinks, compotes.
Taking such acidifiers half an hour before meals gives a good effect. The benefits of sour berries are explained by the presence of a large amount of pectin in them - these natural sorbents successfully remove toxins and harmful microorganisms deposited on them, including Giardia.
The basis of the child’s menu for the treatment of giardiasis also includes:
- vegetables - raw, boiled or stewed (carrots, white cabbage, cauliflower, broccoli, etc., cucumbers, tomatoes, zucchini);
- porridges prepared not with milk, but with water (buckwheat, corn);
- limited - lean meat and fish.
The method of preparing dishes is boiling (preferably steamed) or stewing, but frying is excluded. It is recommended to feed the child 4-5 times a day.
If you maintain such a diet for 3-4 months, while carefully monitoring personal hygiene rules to avoid re-infection, then the child’s intestinal microflora will not only be restored, but also Giardia will disappear.
Treatment
The disease must be treated in stages. It is undesirable to use anthelmintic drugs immediately after diagnosis, since this can worsen the patient’s condition due to the development of intoxication.
Primary treatment is as follows:
- elimination of endotoxicosis;
- elimination of bile stagnation;
- increasing immunity;
- deterioration of environmental conditions favorable for the reproduction of parasites.
When prescribing therapy, it is important to correctly prepare the patient’s diet. The diet should be maintained for about 1 week. The menu includes cereals, vegetables, fruits and other healthy products, and also excludes bread, meat, sugar, etc.
When the preparatory stage is completed, you can begin antiparasitic therapy. After removing all Giardia from the body, it is necessary to restore the intestinal microflora.
Treatment and prevention of giardiasis
Before giardiasis is diagnosed in adults, they are often treated for other illnesses. Suspecting the presence of parasites, patients resort to folk herbal remedies - horseradish tincture, honey-plantain mixture, flax seeds, cloves and other anthelmintic drugs. Even if doctors have identified giardiasis, how to treat it is a separate difficult question.
The classic scheme includes:
- preparatory stage: giardiasis, the causes of organ damage are identified and measures are taken to improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, eliminate choleasis, endotoxicosis, and mechanically remove parasites;
- antiparasitic therapy with medications: doctors decide how to remove Giardia from adult patients and use furazolidone, tinidazole, metronidazole and other drugs that expel protozoa;
- a special low-carbohydrate diet that prevents the proliferation of protozoa - with cereals, vegetable dishes, fruits, vegetable oil, lean meat, kefir and curdled milk instead of milk, since giardiasis manifests itself much more strongly in adults with irritable bowels;
- restoration of the body means taking enterosorbents, antihistamines, enzymes, probiotics, herbal medicine.
Traditional science has learned to answer the question of how to poison Giardia in adults. The drugs used, however, expel only vegetative forms of parasites. Doctors do not always know how to treat Giardia cysts in adults and expel them when the disease is asymptomatic. Therefore, the disease is dangerous due to relapses and reinfection.
Giardiasis (giardiasis) requires patient monitoring, persistent and systemic treatment, as well as restoration of the microelement balance that primarily suffers from parasites. Prevention of the disease requires serious social measures - filtration of drinking water, regular parasitological control. Therefore, individual prevention and treatment of giardiasis in adults and children comes to the fore.
Rice. 13 Signs of Giardia in an adult
What tests can detect Giardia:
- Signs of Giardia in the liver can be determined through a comprehensive study. First of all, these are scatological studies, that is, stool analysis. The most reliable such study will be conducted three times, with an interval of one and a half to two weeks.
- The doctor must also prescribe a serological blood test for the presence of eosinophils.
- An ultrasound examination of the liver, gallbladder and other abdominal organs, as well as examination of duodenal contents, may be prescribed. This study is more often used as a diagnosis in adults.
Important! It often happens that a person is an asymptomatic carrier of Giardia, without even suspecting that he is infected with it.
Treatment of giardiasis
Once the diagnosis is confirmed in the laboratory, treatment must begin immediately. First of all, the patient should follow some rules:
- Carefully observe the rules of hygiene, regularly wash your hands with soap;
- Establish a diet and diet that creates unfavorable conditions for the proliferation of Giardia: exclusion of dairy products, limitation of carbohydrates, especially simple ones, as well as the introduction of products with sorbent properties (bran, cereals, dried fruits, apples, pears, vegetable oil, beets, pumpkin, zucchini);
- Periodically cleanse the hepatobiliary system, gallbladder and intestines;
- Use antispasmodic drugs;
- Eliminate deficiency of B vitamins (to increase the stability of the nervous system);
- The effectiveness of treatment increases in combination with vitamin C.
For many years, metronidazole was considered the most common drug for the treatment of giardiasis. It was prescribed at a dose of 250 mg - 3 times a day for adults, and at a dose of 15 mg/kg - for children. The course of treatment is 7 days. However, recently more and more studies have appeared on the development of Giardia resistance to this drug. In addition, given its contraindications and the impossibility of use in pregnant women, their use is limited.
In this regard, the development of new, more effective drugs continues. One of the latest generation of antiprotozoal drugs is Macmiror (nifuratel). The drug has an extended spectrum of antimicrobial and antiprotozoal action and does not cause resistance to use.
In addition, the drug suppresses the growth of pathogenic flora in the intestines, increasing the growth of lacto- and bifidobacteria. Children are prescribed at a dosage of 30 mg/kg, adults – 2 tablets 2 times a day, for 7 days.
Improvement in well-being during treatment with Nifuratel from the first days has been proven, as well as a decrease in the severity of symptoms of giardiasis. No side effects are observed. It is the drug of choice in pediatrics. The effectiveness of treatment reaches 96.8%.
In addition to pathogenetic treatment, it is necessary to take care of increasing the body's defenses and creating conditions that prevent the proliferation of Giardia, eliminating dysbacteriosis and fermentopathy.
How to properly take a stool test for Giardia
A procedure called stool testing is designed to determine the presence of Giardia or cysts in an adult or child. Also, stool analysis reveals the form in which giardiasis occurs. This disease can exist in two forms: chronic and acute. Feces are the material on the basis of which not only the presence of Giardia in the body of an adult or child is detected, but also control of the disease is carried out. After completing the full course of medication, if the rules are followed and after recovery, a final analysis is carried out. Feces should be donated against the background of giardiasis symptoms such as liquid diarrhea, inflammation, and endocrine system disorders.
Fecal analysis for Giardia is by far the most accurate. The analysis reveals both the presence of lamblia and eggs.
Characteristics of the method
In order for the study to reflect correct data, it is necessary to provide stool in liquid form. Fecal analysis for Giardia is carried out in a laboratory using a microscope. If Giardia antigen is detected in the stool, an appropriate conclusion is drawn up.
Preparing for the test procedure
For correct information and accurate analysis of stool for Giardia, it is necessary to submit fresh stool that has been stored for no more than 12 hours
It is important that the material is not initiated by laxatives. In addition, a week before testing stool for Giardia, you must stop taking antiparasitic drugs
Both previously unused sealed packaging and a sterile jar are suitable as packaging for stool.
Giardiasis in children and adults in severe, advanced stages is difficult to treat and requires much more time
It is important to identify the disease in time to avoid the development of severe pathologies
The ideal condition for feces of a child or adult is two-hour freshness, when under a microscope you can see movable flagella. If the time that feces spent in the package is more than two hours, the mobile flagella begin to experience discomfort and change under the influence of an unusual environment - different acidity, humidity level and low temperature, turning into cysts.
Our readers recommend! For the prevention and treatment of parasitic infestations, our readers recommend the Bactefort parasite remedy. It consists exclusively of medicinal plants collected in environmentally friendly places, which are extremely effective in cleansing the body of parasites, and also heal and protect the body as a whole. Doctors' opinion..."
If the storage time of feces is not observed correctly, the flagella are transformed into another form - into cysts, which are characterized by a lack of movement. Despite the fact that Giardia is immersed in an unusual environment, the laboratory technician is able to detect them
The ability to detect Giardia in stool that has been collected for 12 hours is important for a child who sometimes cannot tolerate it. The study is adequate for both very fresh stool (no more than 2 hours) and 12-hour, semi-diurnal
Detect and treat giardiasis
In a family, the child will be the most vulnerable to Giardia because:
- immunity is not fully formed;
- characterized by constant interaction and contact with the environment and nature.
Giardia is dangerous for a child. They slow down proper development. To identify the disease, infectious disease doctors conduct research in the form of taking samples. Worms and other single-celled organisms are detected in the stool. The disease is more complex in children than in adults and has negative health consequences.
The ability to combat Giardia
With Giardia, the following events occur:
- parasites progress in the intestines, the intestines suffer;
- developmental disorders and the appearance of symptoms of mental retardation and developmental disorders;
- exhaustion;
- temperature;
- grinding teeth at night;
- lymph nodes are enlarged;
- cough;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract.
It will not be difficult to quickly identify and expel parasites. If you suspect giardiasis, you need to undergo an examination to completely clear yourself of parasites. When contacting an infectious disease specialist, treatment will be prescribed.
They treat worms for a month, preventing the parasites from surviving. The easiest way is to see a doctor. If an infection is found in the blood, treat until complete recovery, not giving microorganisms a chance to continue parasitizing.
Diagnostic methods
Before starting treatment, laboratory tests and tests should be performed to determine your health status. Diagnosis methods:
- Antibodies are determined in blood tests;
- study of feces;
- bile examination;
- ingestion of a special nylon thread and its subsequent study.
You can verify the presence of helminths by carrying out the following 4 stages of examination. One analysis may not give a 100% accurate result.
Giardiasis in adults: treatment
After confirming the diagnosis, the infectious disease doctor prescribes treatment. Qualified therapy consists of several stages. In this case, the main condition is careful adherence to hygiene rules, cleaning the house, boiling bedding, ironing underwear with steam. If giardiasis is detected in one of the family members, everyone living under the same roof, including pets, should be treated at the same time.
Preparatory stage of treatment
It should not be missed under any circumstances. The body, weakened by intestinal pathologies, will react painfully to the antiparasitic drug. Side effects from the medication will increase. It should be remembered that all pharmaceutical drugs load the liver and force the gallbladder to work actively. Therefore, before starting the main therapy, the adult’s body must be prepared. The stage lasts from 1 week to a month. It all depends on the severity of the pathologies.
- Detoxification. Remove toxins using sorbents. The simplest of them is activated carbon. It is enough for an adult to take 4 tablets per day. The drugs Smecta and Enterosgel are indicated.
- Improving the flow of bile. Traditional medicine recipes - a decoction of lily of the valley, immortelle, and tansy - work well with the gallbladder. You can use special choleretic drugs as prescribed by your doctor.
- Reduced allergic reaction. Especially if there are skin rashes or problems with the respiratory tract. Diazolin, Loratadine, Eden, Elcet are prescribed.
- If there is Giardia in the bile ducts , the following manipulation is carried out - they drink mineral water all day, in the evening they place a heating pad on the right side of the abdomen. They lie with her for at least 1.5 hours. Choleretic agents for cholecystitis - Allohol, Hologom, Decholin.
- Special diet. Avoid foods rich in carbohydrates and glucose from the diet. Avoid sweets and starchy foods. You should eat porridge, sour juice, dried fruit compote, and medicinal tea. The diet continues until the end of the course of treatment.
Basic treatment
Consists of taking antiparasitic drugs. The course of treatment lasts from 1 to 7 days. In parallel with them, they continue to take antihistamines and sorbents.
- Ornidazole. Known under the names Tiberal, Ornisid, Gairo, Dazolik. Available in tablet form. 90% of patient cases are completely cured. Side effects include mild nausea, dizziness, drowsiness, and headache.
- Nifuratel . The drug is better known as McMimor. In addition to Giardia, it destroys pathogenic intestinal microflora. Side effects are extremely rare. Prescribed, including during pregnancy.
- Albendazole . There are several variations of the antiparasitic drug in the pharmacy: Sanoxal, Nemozol, Aldazole. It is more often used to remove helminths, but has also shown effectiveness in the treatment of giardiasis pathologies. The active substance of the drug inhibits the production of glucose, leaving intestinal parasites without food.
The final stage is restoration
Aimed at strengthening the immune system, restoring the vitality of the body, and restoring the normal functioning of internal organs. To restore the intestinal microflora, take probiotics - Enterol, Lactiale. Hilak, Bifidumbacterin, Linex and others. To maintain the body, they drink vitamins. They stick to the same diet, but introduce more vegetables and fruits, which contain a large amount of natural vitamins and beneficial microelements. To strengthen the immune system, immunomodulators are taken in severe cases; in all other cases, herbal remedies are taken. At the recovery stage, folk remedies play a very important role.
First stage
Typically, treatment of giardiasis in children is carried out in outpatient clinics, but if the patient’s condition is severe and the clinical picture is severe, parents may be advised to hospitalize the child in the infectious diseases or gastroenterology department.
After hospitalization of the patient in a hospital, it is necessary to sanitize the home
Important! All family members who are in contact with the patient must undergo a comprehensive examination.
The duration of this stage lasts from 2 weeks to a month, which depends on the severity of intoxication, the need for mechanical removal of Giardia, the state of intestinal functioning and the level of its enzymatic activity. A prerequisite is nutritional correction, which will be discussed in more detail below. Experts prescribe the following groups of medications:
- choleretic;
- enterosorbents;
- enzymes.
Choleretic agents stimulate the release of bile, which reduces the severity of inflammatory processes in the gallbladder. Two subgroups of medications are used: cholekinetics and cholespasmolytics. The first subgroup increases the tone of the biliary tract. Representatives are magnesium sulfate solution, sorbitol, xylitol. The second subgroup relaxes the walls of the gallbladder and ducts. It is represented by No-shpa, Platifillin, Eufillin, Metacin, and preparations of common barberry.
How to get rid of lamblia
The use of agents from the group of enterosorbents accelerates the process of removing toxic substances from the child’s body, which are released during the processing of waste products of parasites. Medicines are also needed in case of prolonged diarrhea. Experts prescribe Smecta, Polyphepan, Polysorb.
If a child has diarrhea in the acute phase, the remaining medications are prescribed 3-4 days after its completion. Antipyretics may be prescribed according to indications. Enzymatic preparations are used in treatment only if scatological examination of stool shows the presence of undigested food components (this indicates reduced enzyme activity). Representatives of the group are Mezim, Creon, Festal, Pancreatin.
Experts also recommend taking hepatoprotectors - medications that protect liver cells from negative outside influences, and in the case of a number of diseases help restore the structure and function of hepatocytes. For example, Galstena, Khofitol. Antiallergic drugs are also prescribed according to indications.
Tubazh
A separate procedure that is used in a scheme that helps cure Giardia in a child is Demyanov’s tubage. Another name for manipulation is blind probing. It is carried out in the first two stages of therapy. Tubage helps cleanse the biliary system and intestinal tract. One procedure every 2 days is enough, carried out from the age of 5. This is done as follows:
- In the morning, on an empty stomach, the child is given warm mineral water (Narzan, Borjomi, Essentuki) without gas or a decoction of choleretic herbs (knotweed, immortelle, corn silk) to drink. If the patient is under 10 years old - 100 ml, 10-14 years old - 200 ml, older - 300 ml.
- You need to place the patient on his right side and apply a warm heating pad. If the water is too hot, you should wrap the heating pad in a towel to prevent burns.
- Half an hour later, along with a warm breakfast, you need to eat a raw egg (it is important to choose eggs from proven chickens to avoid infection with salmonellosis), drink warm water with a spoonful of honey or a few tablespoons of warm olive oil.
Tubage is carried out both at home and in a hospital
What properties of the pathogen must be taken into account in diagnostic methods?
The Russian doctor D.F. was the first to describe the cause of the disease. Lambl in 1859, the name of the parasite and the disease is associated with his name. In European countries, this role is given to the Frenchman A. Giard, so you can also find the name of the disease as “giardiasis.”
Giardia is the simplest unicellular flagellated microorganism. It parasitizes mainly in the initial parts of the human small intestine (duodenum and jejunum). It can exist in two forms: vegetative (trophozoite) and spores (cysts). Under a microscope, they are easy to recognize by their characteristic pear-shaped shape, suckers and four pairs of flagella.
Giardia feeds through the membrane by absorbing necessary substances from the intestines, taking them away from the body of an infected person. Reproduction is carried out quickly by division, doubling the number every 10–12 hours. Giardia cysts are equipped with a double-circuit capsule and are oval in shape.
They are found only in the large intestine and are excreted with the patient’s feces into the external environment, where they remain viable for a long time. This feature makes it relatively simple to organize the diagnosis of giardiasis by examining stool. A person becomes infected through unwashed hands, vegetables from the garden, water, contaminated food, and through the fecal-oral route at home. Possible carriers of cysts are domestic animals, flies, and cockroaches.
Therapy methods in several stages
Treating chronic giardiasis means preparing for a long and labor-intensive process consisting of several stages. Every step of the patient should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor. The result depends on how attentive a person is to the treatment process. The essence of each stage is to perform certain actions.
- To begin with, with the help of diet you need to reduce the manifestation of toxicosis. The diet is supplemented with choleretic agents, enterosorbents and antihistamines in order to prevent the further spread of parasites. The first stage is aimed at cleansing and preventing complications during the following procedures.
- At the second stage, the patient is prescribed basic antiparasitic therapy, which destroys flagellates. Various derivatives of drugs (Mikmiror, Tinidazole) may be prescribed. Independent choice of medication is impossible. Only a doctor can tell you how and in what quantity to take the medicine. Antiparasitic therapy is combined with the use of antihistamines and enterosorbents.
- The third stage is aimed at strengthening the immune system and bringing the body back to normal. For these purposes, they use multivitamins, enzymes, and probiotics. It is important to maintain a special cleansing diet.
Are there any side effects from treating the disease with drugs?
Almost every drug has a number of contraindications and side effects. Thus, synthetic medications intended for the treatment of giardiasis are completely contraindicated for pregnant and breastfeeding women. You should not take medications if you have liver pathologies, blood problems, or damage to the central nervous system.
The main side effects after taking medications for giardiasis include:
- sleep disturbance;
- migraine;
- the appearance of diarrhea and constipation;
- frequent urges of nausea, gag reflexes;
- the appearance of cramps, itching and allergies on the skin, urticaria;
- burning sensation in the vagina.
In severe cases, there is deterioration in hearing and vision, as well as complications of previously “forgotten” chronic diseases, therefore the use of certain drugs should be carried out under control. The only way you can help yourself is traditional medicine, which can be combined with taking antibiotics in order to “smooth out” their effect on the body. Non-traditional methods of treatment help cleanse the body. To combat giardiasis, you can take infusions of garlic, flax, tansy, cloves, and pumpkin seeds.
What is giardiasis
Giardiasis occurs in acute and chronic forms. The first signs begin to appear 2-3 weeks after infection. Helminths conduct their own life activities, quickly spreading throughout the organs. The acute form appears 2-3 days after infection, the chronic form can last for many months.
It is easy to remove protists from children and adults if the diagnosis is made in time. Symptoms:
- fatigue before starting work or physical activity;
- irritability;
- bowel dysfunction;
- vomiting, nausea;
- temperature fluctuates;
- pain in the bladder, stomach;
- the small intestine suffers;
- loss of appetite, weight loss;
- allergic reaction.
In children, the malaise occurs in the acute type. In adults it quickly becomes chronic. The pathogen selects unstable immunity, infected with another infection - organisms with unstable health.
Additional signs indicating the presence of worms:
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, leading to stool instability;
- change in skin color;
- dryness, flaking of skin, lips;
- nervousness;
- stagnation of bile, the bladder is deformed;
- anorexia.
Sometimes a person acts as a carrier who can transmit the disease. The transmitted parasite will begin to multiply in someone else's body.
Giardiasis in adults - a form of the disease
Giardiasis is characterized by several forms of diseases. According to the degree of activity and frequency of symptoms, acute and chronic forms are distinguished. The acute form is characterized by the rapid, noticeable development of giardiasis. It is in such cases that patients seek qualified help. The chronic form of giardiasis is disguised as the pathology of other diseases and is diagnosed by chance in most cases.
Forms of giardiasis:
- subclinical – occupies 50% of all cases;
- asymptomatic – 25%;
- manifest – up to 44%.
The last form of the disease also has its own classification. Depends on the location of Giardia.
- Intestinal form of giardiasis in adults. Indigestion, dysbacteriosis, and gastrointestinal diseases are observed. These include gastroduodenitis, gastroenteritis, duodenitis, enteritis, and other inflammatory pathologies.
- Biliary-pancreatic form . Associated with digestive and metabolic disorders, with clinical manifestations of inflammation of the biliary tract, and impaired bile discharge. The patient has problems with the gallbladder. Pathologies such as pancreatitis, cholecystitis, cholangitis, and biliary dyskinesia are diagnosed. Along with this, there is a disruption of the liver and an increase in its size.
- Extraintestinal form of giardiasis . Causes toxic-allergic symptoms. There is a change in blood composition, an increase in allergens that the body cannot cope with. Allergies manifest themselves as skin rashes, atopic dermatitis, urticaria, eczema, acne on the face and back.
- The mixed form of giardiasis in adults combines all of the above symptoms.
The clinical manifestation of symptoms depends on the presence of other chronic diseases in the body and general health.
Symptoms and manifestations of giardiasis
Infection with lambia does not give any specific manifestations and is most often disguised as symptoms of other diseases.
Signs of Giardia in the body can be manifested by the following factors:
- feeling of constant fatigue, fatigue even without active work;
- irritability, insomnia, headache and dizziness;
- long lasting subfebrile (about 37-37.5 degrees) temperature;
- constant presence of pain in the navel and/or upper abdomen, bloating, rumbling, frequent heartburn;
- constipation, followed by diarrhea with characteristic yellow, foamy stool or mixed with mucus;
- changeability of appetite, weight loss;
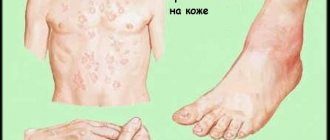
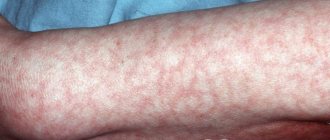
- numerous allergic manifestations - rashes in the form of hives and pimples, dryness and flaking of the skin, cracks on the lips and “jams” in the corners of the mouth;
- characteristic, terracotta (red-brick) coloring of the palms and feet, peeling of the skin on them; neurotic manifestations in the form of grimacing, frequent blinking and twitching of parts of the face or body;
- Diagnosis of Giardia infection
If you observe any signs of Giardia in children, you should immediately contact your local or family doctor, who will give you a referral for certain tests. If tests are positive and Giardia is detected, treatment is prescribed and monitored by a specialist parasitologist or infectious disease specialist. On our website there is a section about traditional treatment of all parasites that can live in the body.
How can you become infected with Giardia?
The source of infection is a person who is a carrier of these protozoa or some animals that are in close contact with people (dogs, cats, pigs, cattle and others). The mechanism of infection is fecal-oral. To understand how Giardia is transmitted, you need to know that Giardia cysts enter the environment with the feces of the carrier.
For further development, they must enter the gastrointestinal tract of a healthy person through the mouth with water, soil or unwashed fruits and vegetables. The modes of transmission of Giardia include household contact, food and water. Giardia spreads from person to person, for example, in kindergartens through contaminated toys, bedding or underwear.
Treatment with folk remedies
To treat giardiasis, traditional medicine is often used. It will not be possible to completely get rid of parasites with their help. But, this is a highly effective auxiliary method.
Medicines are prepared based on:
- Herbal Take immortelle, elecampane, cinquefoil and mint in equal proportions. 2 tbsp. It is recommended to pour the mixture with 500 milliliters of boiling water. The medicine is infused in a thermos for 12 hours. After this time, the medicine must be filtered and used orally three times a day. A single dose of the medication is 100 ml.
- Pumpkin seeds. They must be consumed raw, which will lead to the destruction of parasites. After consuming the product for 3 hours, it is strictly forbidden to take liquid.
- Rowan trees. A teaspoon of dry berries of this plant is poured with a glass of boiling water. The medicine is infused for 30 minutes. It should be taken half a glass before meals.
- Celandine. This herb is mixed with crushed burnet, birch buds, alder cones and agrimony. A tablespoon of the mixture is poured with 250 milliliters of boiling water and left for 10 hours. It is recommended to take the drug 4 times a day. A single dose of the medicine is 50 milliliters.
Traditional medicine effectively combats the symptoms of giardiasis, so it is recommended to be used simultaneously with traditional medications. Despite the safety of folk remedies, the patient should consult a doctor before using any of them.
Giardia in adults: symptoms
Since disruption of the intestines reduces immunity and irritates the nervous system, an adult develops tearfulness, loss of strength, weakness, irritability, and bad mood. According to the World Health Organization, 40% of the world's population is infected with giardiasis. In most cases, they learn about this by chance, which is due to the complex specificity of the symptoms of giardiasis. A sick person turns to specialists for help with complaints of other diseases, the provocateurs of which are Giardia. Treatment does not give the desired effect, since the true causative agent of the infection continues to develop in the intestines. In general, the symptoms of giardiasis can be divided into several groups.
Gastrointestinal tract dysfunction
In adults, symptoms of giardiasis, with acute manifestations: vomiting, nausea, diarrhea with foamy feces, bloating, pain without specific localization in the abdominal area. With mild manifestations or in a chronic form, the patient experiences constant nausea, with periodic pain in the stomach and pancreas. There is inflammatory bowel syndrome with rumbling, bloating, and pain around the navel. Bad breath, coating on the tongue. Appetite decreases or food preferences change - you crave sweets. Heartburn appears periodically. At the beginning of the disease, stools are frequent and loose – up to 5 times a day. Then it becomes half-formed. Diarrhea alternates with constipation. The duration of the acute phase is no more than 7 days.
Biliary tract disorder
Occurs when the liver ducts and gallbladder tracts are damaged. Symptoms of giardiasis: pain in the right hypochondrium, bitter taste in the mouth. There are manifestations of pancreatitis, gastritis, cholecystitis. 50% of patients experience changes in the functioning of the pancreas.
Nervous system dysfunction
Symptoms of giardiasis: disturbance of intestinal microflora, unpleasant manifestations of gastrointestinal diseases affect the state of the nervous system. A person has chronic headache, weakness, fatigue, irritability, poor sleep at night, and drowsiness during the day. Mood worsens, irritability and aggressiveness appear. Along with this - tearfulness, impressionability, and decreased self-esteem. Attacks of dizziness often occur.
Toxic - allergic symptoms of giardiasis in adults
Blood with toxins and Giardia feces causes allergies, which are manifested by dermatitis, itching, redness, swelling, and burning. In rare cases, Quincke's edema develops. The allergy is chronic with frequent relapses. Treatment with antihistamines and corticosteroids give temporary results. Acne on the face of unknown etiology can also be a symptom of giardiasis. Giardia affects the condition of the skin indirectly. Their presence disrupts metabolism, weakens the body, and allows other pathogenic microorganisms to develop. Intestinal dysfunction causes allergies, rashes on the skin of the face and back. The constant presence of toxins only deepens the problem. Inflammation of the adenoids may occur. Other manifestations of the disease are rhinitis, conjunctivitis, cheilitis, bronchial asthma, and other pathologies of allergic origin.
The mixed form of giardiasis brings all manifestations of the disease into one group. You should be tested for Giardia if you experience:
- headache;
- constant weakness;
- abdominal pain;
- dizziness;
- intestinal dysfunction;
- manifestations of gastritis, pancreatitis;
- heartburn;
- nausea;
- temperature increase;
- Bad mood;
- sleep disturbance;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- pain in the liver area;
- skin allergies;
- weak immunity, as a result of frequent colds.
With such symptoms you should go to an infectious disease specialist.
Prevention
It is always easier to prevent a disease than to get rid of it. To avoid infection with giardiasis, it is strongly recommended:
- wash fresh fruits and vegetables;
- drink boiled, filtered, bottled water;
- maintain personal hygiene;
- avoid swallowing water when swimming in bodies of water;
- do not allow pets to lick your face or hands;
- get rid of mechanical carriers of various infections (cockroaches, flies);
- carry out sanitary and hygienic measures in kindergartens, schools, and public institutions.
It is forbidden to drink from rivers, lakes, unknown bodies of water, in order to avoid infection with giardiasis.
Daily ironing of individual towels, underwear and bed linen will reduce the possibility of infection. Be sure to disinfect toilet seats, door handles, children's potties, and washbasin taps with boiling water or detergents. After wet cleaning of the room, buckets, all rags, brooms, and brushes are doused with boiling water. By carrying out sanitary and hygienic measures regularly, it will be possible to completely eliminate the source of infection, without the use of medications.
Giardiasis is not difficult to prevent; you just need to be more attentive to yourself and your health, keeping everything clean. Since children are most susceptible to giardiasis, you need to closely monitor them and teach them personal hygiene.
Classification
There are several clinical forms of giardiasis:
- asymptomatic;
- biliary-pancreatic, hepatobiliary (characterized by inflammation of the gallbladder, liver damage);
- intestinal (duodenitis, gastroenteritis, enteritis are observed);
- astheno-neurotic (extraintestinal manifestations, allergies);
- mixed.
According to severity:
- light;
- average;
- heavy.
It occurs acutely and chronically. Acute giardiasis is common in preschool children. Symptoms appear within 3-10 days. The incubation period is 5-25 days. The acute critical state is maintained for about five days.
Chronic giardiasis is more common in school-age children. Symptoms are either absent, or peri-umbilical spasms and nausea associated with intestinal damage due to the active activity of pathogens are expressed. Characterized by constant remissions and relapses.