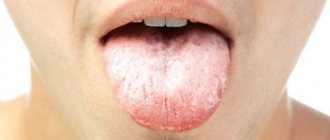
Why can the tongue be coated with a yellow coating?
The top layer of the tongue is the mucous membrane on which the taste buds are located. The epithelium of the mucous membrane, depending on various reasons, can change its parameters, thicken or slough off, forming plaque.
The main factors provoking this effect are:
- inflammation of the gastrointestinal system;
- changes that occur against the background of the development of inflammation;
- irritations of various types caused by the action of chemical compounds, mechanical damage or high temperatures.
Gastrointestinal disorders
A change in the color of the mucous membrane of the tongue due to disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract occurs due to the release of bile into the stomach. This provokes the formation of chronic gastritis and ulcers.
Main symptoms:
- pain in the duodenal area (especially at night and in the morning on an empty stomach);
- nausea, often accompanied by vomiting;
- attacks of heartburn;
- strong unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- change in color of the mucous membrane of the tongue to a yellow tint.
Liver diseases
When the tongue is covered with a yellow coating, suspicion often falls on the liver. With exacerbation of diseases, the exchange of bile pigments is disrupted, which is why the mucous membrane of the tongue and other tissues become yellow.
The following problems can provoke this effect:
- Primary hepatocellular cancer , in which metastases affect the liver, migrating from the main focus: mammary glands, pancreas, rectum, lungs. It is worth noting that this form does not occur very often.
- Hepatitis, which develops due to inflammation of the liver. The inflammatory process can be provoked by: viruses, alcohol, toxic substances. The course of the disease is characterized by damage to liver cells and disruption of the formation of bilirubin (bile pigment), which also poses a danger to the body when released into the blood due to toxicity.
Diseases of the gastric gland
The inflammatory process in the pancreas can provoke various disorders, but pancreatitis is considered the most serious disease.
You can recognize it by the following signs:
- severe pain radiating to the back;
- nausea accompanied by vomiting;
- a yellow coating that covers the tongue due to a violation of the outflow of bile.
Any infections and even respiratory diseases provoke disturbances in the formation and passage of bile.
The participation of this mechanism in the development of inflammation can be seen by the yellow coating on the tongue.
It comes in different shades: at low temperatures, a color appears that has a light tone, which becomes clearly defined and thick at elevated temperatures.
Taking certain medications
A change in the color of the mucous membrane of the tongue is also observed in the process of taking certain drugs (furazolidone, quinine, enterofuril, cardiac glycosides).
This effect occurs for two reasons: the composition of the products includes components with increased pigmentation, and due to the effect of chemicals on the gastrointestinal tract and liver, which provokes a violation of the outflow of bile.
Respiratory system infections
In case of infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract (sore throat, pharyngitis, etc.), a dense coating forms on the tongue. This is due to the continuous process of division of harmful bacteria and viruses in the oral cavity, which is why discoloration can be observed on the teeth and gums.
Bad habits
Many smokers are recognized by a characteristic brownish coating on the tongue, teeth and even nails. This effect is formed due to the influence of the resins that are part of cigarettes.
In addition to pigmentation, there is a growth of taste buds on the back third of the tongue, they become like villi.
Another bad habit is frequent drinking of coffee or strong tea.
The tissues and mucous membranes of the oral cavity turn yellow. The following can also make the mucous yellow: cola, dark chocolate, carrots, etc.
Poor oral hygiene
Improper oral hygiene or its complete absence can also provoke the formation of a yellow coating on the tongue and palate. Many people are surprised by the fact that with daily cleaning, yellowness is still observed.
After consuming coloring products, it is a good idea to rinse your mouth with a special liquid. If this is not possible, it is enough to use chewing gum with a whitening effect.
Inflammation of the tongue
The mucous membrane changes color for a simple reason - due to inflammation of the tongue. From the influence of bacteria or fungus, a white-yellow coating is formed, which is often accompanied by the formation of erosions and small ulcers.
Other reasons why yellow plaque may have appeared include:
- infectious diseases, poisonings that disrupt the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- dehydration, severe intoxication;
- pellagra, diabetic coma;
- Addisonian crisis, which occurs as a result of iron deficiency and the development of hemolysis.
Possible diseases and their symptoms
There can be many causes of tongue diseases, the main ones include:
- infection with viruses, bacteria, fungi;
- damage: thermal, chemical, mechanical;
- lack of oral hygiene;
- stress;
- smoking, alcohol, drugs.
Modern man has added piercing to the usual mechanical damage.
Diseases are divided into 3 types.
- Catarrhal glossitis - caused by acute respiratory viral infections, caries, dental plaque, smoking tobacco or mixtures. It is characterized by unpleasant sensations, loss of taste, plaque, and redness.
- Ulcerative glossitis - ulcers appear on the tongue, there is a grayish, dirty coating, and a strong odor from the oral cavity. Often the manifestation of ulcerative glossitis indicates a weakening of the body’s immune defense; it also appears with necrotizing stomatitis.
- Desquamative glossitis (geographic tongue) - characterized by an unpleasant taste in the mouth and the appearance of red spots. Indicates diseases associated with metabolic disorders in the body, gastrointestinal tract, and the occurrence of dysbacteriosis.
- An abscess appears due to mechanical, toxic, chemical, thermal damage. The tongue swells, it becomes difficult to speak, severe pain occurs, cracks and dryness may occur.
Acute inflammatory diseases on the tongue, photographs:
- Leukoplakia – the organ turns red and thickens, which causes discomfort and difficulty speaking. A common cause is smoking, advanced dental diseases, and genetic predisposition.
- Hairy leukoplakia - the papillae become like separate threads, the shape of the tongue loses its boundaries, becomes uneven, wavy, the entire tongue and its root thicken. Manifests itself in HIV infection and tuberculosis.
- Hairy black tongue - there is hypertrophy of all papillae, unpleasant sensations. Often characterizes pathological changes in the gastrointestinal tract or infection of the body with fungi.
- Diamond-shaped glossitis - a diamond-shaped, smooth, small, red lesion appears on the back of the organ. Characterizes the occurrence of immune diseases.
Photos of chronic diseases:
- Thrush (stomatitis caused by the Candida fungus) - causes itching, burning, loss of the ability to sense tastes, and fever. When the plaque is removed, red ulcers appear.
- Glossitis caused by herpes virus infection is characterized by the appearance of ulcers and small watery swellings. Severe pain occurs when eating food, water, and the temperature rises.
- Streptococcal impetigo - severe redness, rashes appear in the form of blisters. Caused by streptococcus entering the oral cavity.
- Lichen planus - rough red spots appear. Occurs when metabolic processes in the body fail, immunity is weakened, and manifests itself in stressful situations.
Photos of infectious diseases:
If any deviations from the norm are detected in the appearance of the organ or changes in taste, you should contact a specialist to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
If the changes affect not only the tongue, but also the gums and teeth, then you need to contact a dentist. If changes affect the tongue or throat, then you need to make an appointment with a family doctor or therapist who will give a specialized referral.
How to “read” plaque on the tongue to determine the cause?
Each disease is characterized by its own shades and other signs, knowing which you can determine the cause of the yellow coating on the tongue in adults.
Based on the nature of the localization of yellowness in the tongue, the affected organ is approximately determined.
You can analyze plaque on the tongue using the following criteria:
- By structure: the curdled mass that coats the tongue is a sign of a fungal infection;
- a shiny, moist surface means chronic colitis or chronic pathology of the gallbladder;
- a dry layer indicates a violation of the secretory function of the stomach.
- a thin and uniform layer on the root of the tongue and in the middle strip indicates disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, developing influenza, ARVI, side effects of medications;
- tip of the tongue - upper body;
- yellowish is observed in smokers in the morning and people who have impaired bile flow;
The presence of a yellow coating on the tongue in adults is a cause for concern
Language configuration
The determining factor in the study of language is also its form. It is necessary to pay attention to such aspects.
- A thin tongue is characteristic of blood diseases and impaired metabolism.
- The thick form indicates the presence of liver pathologies and the gastrointestinal tract system.
- Swelling makes itself felt when there are digestive problems.
- Long occurs in the presence of heart problems.
- A curved stripe in the center indicates problems with the spine.
- The bulge is observed in lung pathologies.
- The surface changes due to vitamin deficiency.
Causes of yellow plaque in children
Children are most susceptible to various problems with the gastrointestinal tract, metabolic processes, and circulatory system.
Ignoring yellow coating on the tongue can lead to complications
When a yellow coating is detected in your child, household causes are first ruled out:
- the period of introducing vegetables and cereals (yellow coating often remains on the tongue for up to a year);
- inclusion of pigment-containing foods in the diet;
- careless handling of drawing paints (pencils, felt-tip pens) by a child;
- abuse of caramel, carbonated drinks, chewing gum and other treats containing dyes.
If domestic reasons are excluded, then the answer lies in one of the following options:
- hemolytic disease (babies in the first year of life are susceptible);
- hypomotor biliary dyskinesia;
- jaundice (nuclear or physiological);
- giardiasis;
- dehydration characteristic of infectious diseases;
- the use of drugs that have a coloring effect on the mucous membrane.
If you exclude safe factors that are associated with dyes in products or household items, you should consult a doctor for diagnosis.
Ignoring the yellow coating on the tongue can lead to complications, but valuable time for quickly localizing the problem will be hopelessly lost.
In pregnant women
Pregnant women often experience the formation of yellow plaque on the oral mucosa. This is due to the increased load on the liver during pregnancy.
Also, the reason may lie in a change in the secretory function of the stomach, a violation of its motility. Often, pregnant women are diagnosed with various infections that negatively affect the process of bile secretion.
Causes of plaque with ulcers
The following factors can provoke the formation of plaque with ulcers:
- stomatitis;
- dysbacteriosis;
- insufficient oral hygiene;
- infections.
In case of any malfunctions in the body, it itself gives clues about the problems that have arisen.
You just have to pay attention and start treatment in a timely manner. To do this, at the first manifestation of alarming symptoms, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
Yellow coating on the tongue
Normally, the tongue is soft pink, covered with many papillae, mobile, without spots or grooves. If the body malfunctions, a white or yellow coating may appear.
First of all, you need to understand the reason for the appearance of plaque. Monitor the condition of your tongue for several days. Examine it in the morning before eating in natural light. The cause of plaque on the tongue may be:
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
- Dehydration
- Breathing through the mouth
- Smoking, drinking too much coffee or tea
- Taking medications (such as antibiotics)
A yellow coating on the tongue can be observed with biliary dyskinesia of the hypokinetic type. In this case, you may also be bothered by a dull, aching pain in the right hypochondrium (sometimes radiating to the back, under the right shoulder blade) and heaviness in the right hypochondrium, which intensifies after eating food, especially fatty and fried foods; nausea, bitterness in the mouth, bloating, constipation. A yellow coating on the tongue appears due to frequent contact of the tongue with bile when the contents of the duodenum are thrown into the stomach, then into the esophagus and into the oral cavity, because impaired motility of the biliary tract is often combined with impaired motility of the upper gastrointestinal tract.
Important! The diagnosis must be confirmed by ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs (exclusion of organic diseases, including cholelithiasis) with ultrasound cholecystography to assess the functional state of the gallbladder. Since similar symptoms may occur in other diseases caused by secondary dysfunction of the gallbladder:
- Chronic non-calculous cholecystitis
- Chronic hepatitis
- Cirrhosis of the liver
If the diagnosis is confirmed, the drug Hofitol can be very effective in eliminating symptoms. Hofitol simultaneously has choleretic and cholekinetic effects, i.e. At the same time it helps the production of bile and its secretion.
Hofitol stimulates bile secretion (increases the volume of bile secreted by 30%), normalizes its rheology (increases the secretion of bile acids by 15%) 1. This helps reduce the viscosity of bile, reduces its stagnation, increases evacuation due to stimulation of gallbladder contraction and relaxation of the sphincter of Oddi. In this case, excessive contraction of the gallbladder does not occur 2.
Thanks to this, Hofitol helps eliminate yellow plaque on the tongue, normalizes the motility of the biliary tract in patients with biliary dyskinesia of the hypokinetic type, chronic non-calculous cholecystitis, chronic hepatitis, and cirrhosis of the liver. . Dosage regimen: adults: 2-3 tablets (2.5-5.0 ml solution) 3 times a day before meals orally for 2-3 weeks or longer; children over 6 years old: 1-2 tablets (0.625-2.5 ml of solution) (depending on age) 3 times a day before meals for 2-3 weeks 3. Before prescribing, be sure to exclude the presence of contraindications to taking the drug: hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, cholelithiasis, biliary obstruction, acute diseases of the liver, kidneys, biliary and urinary tracts.
THERE ARE CONTRAINDICATIONS. BEFORE USE, CONSULT WITH A SPECIALIST
If plaque appears on the tongue, you should consult a doctor. The doctor will identify the disease that is causing the plaque and prescribe appropriate treatment.
It is necessary to urgently seek medical help if, along with the appearance of plaque on the tongue:
- Bleeding has occurred (including coughing with blood)
- Difficulty breathing, swallowing
- There was a high fever
- Sudden swelling of the tongue and throat, as well as the lips and around the eyes
- A blue tint appears on the lips and in the nail bed area
- There was a disturbance of consciousness
- There is a rash
- Blood pressure decreased
- Worried about nausea, vomiting
1 Increase in choleresis by means of artichoke extract. Results of randomized placebo-controlled double-blind study, Kirchhoff R. et al. Phytomedicine, 1994, 1(2): 107–115 2 Gebhardt R. Inhibition of cholesterol biosynthesis in primary cultured rat hepatocytes by artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) extracts. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997; 286: 1122-1128 3 Instructions for use of the drug
Oral diseases
Inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, including the tongue, do not always reflect the development of pathologies of internal organs - sometimes we are talking about independent diseases. If a burning sensation or the presence of a foreign body appears in the mouth, the tongue turns red and swells (the swelling tends to progress over time), salivation increases, taste sensations change (they may become dull or completely disappear), speech and eating become difficult, the patient feels pain in the tongue - these are symptoms of the development of glossitis, that is, inflammation of the tongue. This disease can take various forms, but the symptoms listed above are inherent in almost all of them.
Biliary system
The organs of the digestive tract that are responsible for transporting and collecting bile from the liver are called the gallbladder and bile ducts. In medicine, this system is called biliary, consisting of:
- sphincter systems - they regulate the flow of bile;
- gallbladder;
- bile duct systems - hepatic, cystic and common.
The cystic duct connects to the hepatic duct and the common bile duct emanates from them - it flows into the duodenum and thus bile passes from the biliary system directly into the intestine. It is precisely due to the fact that bile exists in our body that it is possible to remove heavy metal salts, fully digest fats in the intestines, absorb vitamins important for health, intestinal motor activity and the production of digestive enzymes.
Problems in the functioning of the biliary system are quite common and are typical mainly for women aged 40-50 years, although men are also subject to such disorders. The causes of the development of pathological conditions in the gallbladder and bile ducts may be:
- neurological and endocrine pathologies that lead to disturbances in the outflow of bile;
- infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, which provoke inflammation of the walls of the organs of the biliary system;
- gene mutations that provoke the formation of tumors in the biliary system of a benign and/or malignant nature;
- genetic abnormalities of the gallbladder and bile ducts;
- helminthic infestations;
- various pathologies that can lead to the formation of stones in the biliary system;
- regular intoxication;
- regular drinking and smoking;
- violations of the regime and diet;
- long-term use of certain medications.
All of these factors can lead to the development of various pathologies of the biliary system. But these same pathologies will manifest themselves with various symptoms - general and local, different in nature and intensity, supplemented by signs of diseases of the stomach, duodenum, intestines and liver. In order to promptly seek professional medical help and begin effective treatment, you need to know which symptoms indicate problems with the biliary system.
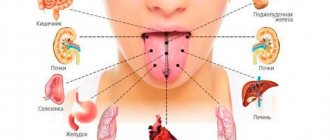
Correspondence of tongue zones to internal organs
To determine the state of health by the tongue, it should be taken into account that the tongue is conventionally divided into separate zones responsible for certain internal organs. When identifying pathologies, the doctor will first of all pay attention to the dislocation of changes in the tongue. An interesting fact is that from the point of view of ancient eastern practices, language is also divided into areas according to five “primary elements”:
- back - Water;
- central region - Earth;
- sides – Wood;
- between the tip and the central part - Metal;
- tip – Fire.
| Tongue area | Relevant authorities |
| Tip | Heart, small intestine |
| Sides | Liver, gall bladder |
| The area between the tip and the central zone (the transversely band-like part encircling the organ) | Respiratory system, immune system, large intestine |
| Central zone | Stomach, pancreas, spleen |
| Rear end | Genitourinary system |
| Longitudinal fold in the middle of the organ | Spinal column |
Seven warning signs
Only a specialist can establish an accurate diagnosis, but you still need to contact him in time! Therefore, it would be very wise to remember the 7 most alarming symptoms - they are the reason for a visit to the doctor.
Pain in the right hypochondrium
Pain syndrome in diseases of the biliary system can vary in intensity of manifestation - for example, with a kinked gallbladder or cholecystitis, pain in the right hypochondrium will be of low intensity, but acute pain is inherent in cholelithiasis.
Most often, the symptom in question is provoked by another consumption of fatty, smoked, fried foods or foods, immediately after physical activity (for example, after running or cycling) or against a background of severe stress. Patients characterize pain as dull or sharp, sharp or gradually increasing, constant or periodically appearing.
If the pain in the right side is sharp, intense or sudden, then this most likely indicates hepatic colic - this condition develops with cholelithiasis, when the stones begin to “move”. Usually, patients can pinpoint the location of pain concentration, and it is accompanied by general weakness, fever, nausea and vomiting.
With all other pathologies of the gallbladder and bile ducts, the pain is never too intense; this syndrome appears periodically and gradually increases. As a rule, pain in the right hypochondrium is accompanied by fever, dizziness and nausea with vomiting.
Please note: if pain in the right hypochondrium occurs during chronic cholecystitis, then it may be the only symptom of the pathology and have low intensity.
Separately, it is worth mentioning neoplasms of a benign and/or malignant nature, which are almost never accompanied by pain. The only caveat is that pain can occur with aggressive tumor growth.
Digestive system dysfunction
Since bile is “responsible” for the normal digestion of food, it is not surprising that problems with the gallbladder and bile ducts lead to systematic disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system. Patients note a deterioration in appetite, periodic nausea and vomiting, belching of air with a bitter taste, and bowel disorders (diarrhea or constipation).
Symptoms of dysfunction of the digestive system may indicate pathologies of the biliary system and other organs of the gastrointestinal tract. But in any case, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Yellow coating on the tongue
With some pathologies of the system under consideration, bile is released into the esophagus and oral cavity - this phenomenon is often observed in tumor processes and cholelithiasis. The result of this is a change in the color of the tongue - it becomes yellow, and absolutely any shades of this color can be present.
Bitterness in the mouth
This symptom is very common and occurs in almost all pathologies of the gallbladder and bile ducts. Some patients note the appearance of bitterness in the mouth immediately after eating food, while others complain of constant discomfort.
Yellow color of the skin and mucous membranes
This symptom is characteristic not only of diseases of the gallbladder and bile ducts, it often signals liver pathologies, but differentiation of pathologies should be carried out only by a doctor and in a clinical setting. Jaundice occurs due to the entry of bile acids into the blood and may be present with dyskinesia of the bile ducts, chronic cholecystitis, the development of benign or malignant neoplasms, and cholelithiasis.
Discolored stool
This symptom may appear with the development of the following pathologies:
- cholelithiasis;
- tumor processes in the biliary system;
- inflection of the gallbladder;
- cholecystitis of acute and/or chronic forms.
Usually, discolored feces are accompanied by pain in the right hypochondrium, jaundice, and bitterness in the mouth. But keep in mind that the symptom in question is characteristic not only of the development of diseases of the gallbladder and biliary tract, but also pathologies of the liver and other organs of the gastrointestinal tract. By the way, stool can become discolored due to prolonged use of a certain group of medications, and due to a violation of the diet/diet.
Dark color of urine
If the level of bilirubin in the blood increases, the patient’s urine takes on a distinctly dark shade. This symptom is present in many diseases of the gallbladder and biliary tract - for example, when the gallbladder is bent, in acute and chronic cholecystitis, cholelithiasis and tumor processes.
Please note: dark urine is not one of the main symptoms of biliary system diseases, so the doctor will need to conduct a thorough examination of the patient to differentiate some other conditions.
Symptoms of liver cirrhosis
Liver cirrhosis is the outcome of a long destructive mechanism and the replacement of healthy liver tissue with dense fibrous tissue has many causes. Doesn't show itself for a long time.
Deviations in tests may be discovered accidentally during a routine examination or during a medical examination.
In clarifying the causes of cirrhosis, it is important to take into account the following:
- The way of life of a person.
- Profession (long-term contact with industrial poisons, when working in agriculture, contact with infection - echinococcosis, leptospirosis).
- Food preferences and habits, vegetarianism, fasting.
- Excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages directly leads to the formation of cirrhosis.
- Taking medications that have a toxic effect on the liver.
- Diagnosis of liver pathology in close family members.
- The epidemiological history is aimed at establishing contacts with a patient with viral hepatitis, whether there was a transfusion of blood components, surgery, a trip to the dentist, injections, hemodialysis, taking narcotic substances, other interventions with damage to the skin, unprotected sexual intercourse. Travel to an epidemiologically unfavorable territory.
- Clarification of the presence of diseases from other organs and systems.
Nonspecific symptoms occur in most known diseases and cannot clearly indicate to us the organ concerned. With cirrhosis, these symptoms appear at the onset of the disease. These include:
- Dyspeptic symptoms in the form of gas formation, vomiting, heaviness in the right side, constipation, bloating, abdominal discomfort, and lack of appetite occur.
- Vegetative and asthenic syndromes are associated with low work capacity, high fatigue, and unmotivated weakness.
- Psychoneurological disorders debut in the form of sleep and mood disturbances, memory impairment, and behavioral disturbances.
- Losing weight, sometimes to the point of exhaustion.
The symptoms are specific, and based on them we assume the possibility of liver cirrhosis.
- Hepatomegaly is an increase in the size of the liver due to the formation of regenerative nodes and replacement of tissue with fibrosis. First of all, growth occurs due to the right lobe, and then due to the left. In the last stage of cirrhosis, there is a decrease in liver volume due to its compaction.
- Splenomegaly is an increase in the size of the spleen due to stagnation of venous blood, hyperplasia of the reticulohistiocytic tissue of the spleen, proliferation of fibroreticular tissue, and the formation of arteriovenous shunts. There is a feeling of heaviness in the left side and the presence of pain on the left.
- Jaundice in liver cirrhosis progresses when the metabolism of bilirubin breaks down and its excessive accumulation in the blood. Color varies from saffron yellow, lemon yellow to olive green. Primary biliary cirrhosis is an autoimmune disorder in the liver cells, which causes staining of the skin and mucous membranes.
- Itchy skin is the result of the development of jaundice and cholestasis, the cause is the accumulation of bile components and cause itchy skin.
- Cholestasis syndrome often occurs in biliary cirrhosis and is associated with impaired bile metabolism. It accumulates excessively in the liver, making its excretion difficult. Manifested by skin itching.
- Hemorrhagic syndrome, or bleeding, is the result of a drop in the number of platelets in the blood and a deterioration in blood clotting. Bruises, bruises on the skin, nasal, gingival, uterine and other bleeding occur.
- Anemia. With venous bleeding, iron deficiency anemia develops. Hemolytic anemia results from the death of red blood cells - erythrocytes. Megaloblastic, hyperchromic anemia is diagnosed with a lack of vitamins B12 and folic acid.
- Heaviness in the right side or dull pain is characteristic of a noticeable increase in the size of the liver, due to stretching of the Glyson capsule. The liver tissue itself is devoid of pain receptors, so pain in the side does not occur. Pain may appear when neighboring organs are involved in the process.
- External manifestations of liver cirrhosis: increased vascular pattern or telangiectasia - on the upper half of the body, palmar erythema. “The head of a jellyfish” is an extended anastomosis - veins on the abdomen. A violation of fat metabolism manifests itself in the form of xanthoma and xanthelasma appearing on the skin.
- A rise in temperature is recorded during an exacerbation of the process or during the active stage of the disease. Reflects the death of liver cells. Associated with the presence of active waste products of bacteria that the liver cannot neutralize. The temperature cannot be brought down; it decreases on its own as the condition of the liver improves.
Diagnosis of biliary system diseases
If at least one of the above symptoms of diseases of the gallbladder and biliary system occurs, then it is necessary to contact a medical institution. Even a specialist will not be able to make an accurate diagnosis based on symptoms alone, so you should not even stutter about some kind of self-diagnosis! And the treatment regimen will depend on what kind of pathology of the biliary system is detected - so self-medication is not suitable in this situation.
When a patient presents complaints characteristic of diseases of the gallbladder and biliary tract, the doctor will definitely prescribe a full examination of his body. As part of the diagnosis, the following is carried out:
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs;
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- laboratory blood tests (biochemical and clinical tests);
- radiography using a contrast agent;
- computed tomography;
- fine-needle biopsy, which is performed under ultrasound control.
Only after assessing all the examination results obtained, the doctor will select a treatment regimen - symptomatic, pathogenetic or etiotropic therapy can be used. For some diseases of the gallbladder and bile ducts (for example, cholecystitis of the calculous type, tumor processes of a malignant/benign nature), the patient will be prescribed surgical treatment. Absolutely all patients with diseases of the biliary system will be prescribed specific dietary nutrition; in the future, patients will have to radically reconsider their gastronomic preferences.
Almost all diseases of the gallbladder and bile ducts can be completely cured with timely consultation with a specialist and proceed without complications or any serious consequences. But in order to seek medical help in time, you need to know the main symptoms of diseases of the biliary system.
Tsygankova Yana Aleksandrovna, medical observer, therapist of the highest qualification category
9, total, today
Cold calculation
So, we see objects painted in one color or another
, our vision is color. But what is at its core?
A study of the eye has shown that the retina has three main light-sensing elements: one of them is most irritated by red rays, the other by green rays, and the third by blue rays.
Thus, in the 19th century, Goethe’s compatriot Hermann Helmholtz
I finally looked at color through human eyes and found out that the main ones should actually be considered red, green and blue, since with their help you can get all other colors of any saturation. But white and black do not exist in nature at all, and their admixture does not change the type of color, but only creates its shades.
In fact this meant
, that any shade can be synthesized by presenting it in the form of the formula “Color” = NR + NG + NB, where NR, NG and NB are the amount of red, green and blue in the mixture (the principle of operation of color TV). And in general, every color can literally be measured.
Thus, the color tone is determined by the wavelength
spectrum of visible light radiation. Tone contrast is the ratio of white and black. Saturation is the amount of chrome (color) at a constant hue contrast.
By the way, this approach formed the basis of “color coding”
, which is used today by paint manufacturers and thanks to which you can easily navigate when choosing the right shade. Let's look at the example of the Dulux color system.
Let's say there is paint of color 68YR 34/780. 68YR is just the color tone, 34 is its contrast, and 780 is saturation.
There are only 8 color tones:
RR (fuchsia to red), YR (red to orange), YY (orange to yellow), GY (yellow to green), GG (green to turquoise), BG (turquoise to blue), BB (from blue to lilac) and RB - from lilac to fuchsia.
Number indicating tone contrast
, varies from 00 to 99, and the higher the numeric code, the lighter the shade. The saturation index changes according to a similar principle (from 000 to 900) - the higher the code, the more intense the color tone.
All causes of yellow coating on the tongue
A visual examination when visiting a doctor always includes an examination of the tongue. Its condition (color, shape) can help the doctor make a diagnosis.
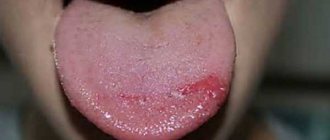
The color of the coating on the tongue can vary, but most often you can see a yellow coating with a brown or greenish tint. It can say a lot about the proper functioning and condition of the human digestive tract.
The content of the article:
The presence of a small amount of translucent deposits is considered normal - they are formed because the papillae on the tongue can retain food particles, which are a place for the proliferation of microorganisms.
However, a change in the color of plaque may indicate the presence of serious abnormalities in the functioning of the digestive system. Therefore, if you find a thick coating on your tongue, it is recommended to visit a doctor .
Features of diagnosing pathologies by language
The best time to examine the surface of the tongue is in the morning, before breakfast. First you need to determine whether there are any changes in the shape of the tongue, whether it is covered with a layer of plaque. Color and mobility are considered equally important. Attention should also be paid to various formations (ulcers, blisters, etc.), if they exist, of course.
Diagnosis of diseases by language
What should the tongue look like in an absolutely healthy patient? First of all, it should have a smooth surface, painted in a delicate pink color. The tongue itself may be covered with a small layer of plaque - this is normal, so you should not immediately sound the alarm. The tongue should look a little velvety, this is due to the presence of barely noticeable papillae on its surface.
What does a healthy tongue look like?
What can it even arise from?
The tongue is covered with a mucous membrane containing taste buds. Deposits on its surface can occur under the influence of the following factors:
- Inflammatory phenomena affecting the tongue directly;
- Inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract;
- The influence of various factors on the tongue: temperature, chemical, mechanical.
Before going to see a doctor, you should make sure that the plaque has formed due to abnormalities in the functioning of the body, since it also occurs after eating - in such a situation it can be brushed off with a toothbrush, and it will not appear regardless of food intake.
Liver pathologies
The most common reason why the tongue may become covered with a yellow coating is considered to be abnormalities in the functioning of the liver, as a result of which the concentration of bilirubin changes.
When the exchange of bile pigments is disrupted, the mucous membrane of the tongue turns yellow . This may be caused by conditions such as:
- Cirrhosis of the liver;
- Hepatitis;
- Liver cancer, or metastases of the lungs, rectum to the liver.
With hepatitis, liver cells are destroyed, accompanied by a violation of the binding of direct bilirubin, which is dangerous for the full functioning of the body. The substance enters the blood, changing the color of the whites of the eyes, tongue, frenulum and giving them a yellow color.
Additional symptoms that accompany this condition include:
- Weakness;
- Deterioration in general health;
- Deterioration in working capacity;
- Pain in the hypochondrium on the right side of the body.
With liver cirrhosis, the death of liver cells occurs, changes in its structure, and the formation of nodes.
Cell death is accompanied by improper restoration, and the resulting nodes put pressure on the bile ducts, causing the processes of production and outflow of bile to be disrupted and the cleansing ability of the liver to fail.
Enzymes formed as a result of protein metabolism enter directly into the blood, which leads to a negative effect on the nervous system.
Symptoms that characterize the condition include: an enlarged liver, skin and tongue turning dark yellow, itching, memory disturbances and sleep problems .
Biliary tract lesions
Obstructive jaundice develops due to:
- Inflammatory processes affecting the gallbladder;
- Gallstone disease;
- Neoplasms of the bile duct.
vascular stenosis occurs , which causes a disruption in the process of bile outflow. A distinctive feature is that the skin and mucous membranes become yellow with a greenish tint. The coating on the tongue acquires the same color.
The condition occurs against the background of pain (they can bother you constantly or occur from time to time), a feeling of bitterness in the mouth appears, and attacks of nausea and vomiting with bile may occur.
Provoking factors are often: fatty foods, significant physical activity, shaking on the road.
Prehepatic jaundice
With this diagnosis, the cause is the same bilirubin, which is present in concentrations that exceed the norm, since it does not have time to be eliminated from the body.
This may occur in the following cases:
- Accelerated hemolysis of red blood cells, which can be observed with acquired or congenital anemia;
- With improper synthesis of red blood cells, which can occur due to B-12 deficiency anemia, erythropoietic uroporphyria;
- The presence of significant external and internal hematomas;
- Pulmonary infarction;
- Intoxication with arsenic, hydrocarbons, hydrogen sulfide, etc.;
- Use of sulfonamides.
Diseases related to the stomach
The reason for the formation of yellow plaque can be:
- Gastric and duodenal ulcers;
- Chronic gastritis.
With these diseases, bile reflux into the stomach . In addition to a coated tongue, the following symptoms are present:
- Abdominal pain, not tied to the time of day or food intake, may occur at night;
- Nausea;
- Vomit;
- Heartburn;
- Belching with a sour taste;
- Bad breath.
Your baby is teething - every mother should know the symptoms.
In this article we will tell you how to treat periodontal disease at home.
Here: https://zubovv.ru/ortodontiya/breketyi/do-i-posle-ustanovki-foto-patsientov.html - you can see the “before and after” photos, where you can see how braces correct malocclusion.
Duodenogastric reflux
This pathology is manifested by retrograde reflux of contents from the duodenum into the stomach, which occurs due to improper functioning of the obturator muscle of the gastric outlet.
Provoking factors may be:
- Inflammatory processes in the duodenum;
- Traumatic lesions;
- Hernia;
- Tumor;
- Fetal pressure during pregnancy;
- Treatment with antispasmodic medications, as well as muscle relaxants, as a result of which muscle weakening occurs;
- Consequences of surgery.
In this case, the patient's condition will be accompanied by nausea, heartburn, vomiting with bile, and dull pain localized in the right half of the epigastrium.
Biliary dyskinesia of hypomotor type
With this pathology, the biliary tract and bladder cannot fully perform their functions, i.e. the process of bile outflow is disrupted. In this case, staining of the mucous membrane of the tongue also occurs.
This symptom manifests itself most pronouncedly when the patient does not follow a diet and consumes a large amount of unauthorized products: fatty meat, alcohol.
Acute pancreatitis
The disease can cause a violation of the outflow of bile. Accompanying symptoms in this case may be: girdling pain radiating to the back, nausea, vomiting .
Acute intestinal diseases of infectious nature
This group of diseases includes various gastroenterocolitis. The classic clinical picture includes a combination of the following symptoms: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea .
The more frequent the attacks, the more pronounced the signs of dehydration in the body become, and accordingly, the plaque becomes thicker. Staphylococcal intoxications manifest themselves in a similar way, only they are combined with a mandatory rise in temperature (the body’s reaction to the toxins produced).
In this case, as in the previous one, the formation of plaque is caused by dehydration processes in the body. The more severe the dehydration, the thicker the plaque layer. This is observed in any inflammatory diseases.
As a consequence of drug therapy
Taking cardiac glycosides, as well as some other medications (akrikhin, enterofuril) can cause the coating on the tongue to change color.
Inflammatory processes of the tongue
This group includes inflammation of the tongue of bacterial or viral origin. They appear as a white-yellow coating.
At the same time, ulcers and erosions may occur, and pronounced desquamation of the epithelium may occur.
We invite you to find out the prices of dental veneers and look at their photos.
Read here the instructions for using Kamistad, an effective drug for various dental diseases.
At this address: https://zubovv.ru/lechenie/zubyi/lz-mudrosti/simptomyi-prorezyivaniya.html - all the symptoms of wisdom teeth erupting are listed.
Treatment prognosis at the last stage
The disease affects the entire body, so it becomes impossible to cure it at the last stage. The patient has only the ability to: completely change his lifestyle, give up bad habits, change the menu, thanks to which he can extend his life. Organ replacement surgery may be required, followed by constant monitoring by doctors.
With cirrhosis of the liver, a person's appearance changes, as can be understood from the photographs. It’s not so easy to see internal changes, but it’s worth knowing that to maintain the whole body you will have to take medications, regularly give injections and IVs. The task of doctors is to prevent the development of other diseases caused by liver failure.
Medicines, notes prokishechnikRu, can only be prescribed by a doctor, having selected a suitable menu and set of remedies. Self-medication can lead to a sharp deterioration of the condition or death. Medicines prescribed by a doctor can be divided into several groups:
- diuretics;
- vitamin complexes;
- diuretics;
- hepatoprotectors;
- adsorbents;
- glucocorticoids.
For the rest of his life, it is important for the patient to maintain a certain diet, avoid alcohol, smoking, eat light, healthy foods, and lead a healthy lifestyle.