Bile is a liquid produced by the liver and used for digestion. But the diet of an ordinary person does not always meet the requirements of a healthy lifestyle. Eating in a hurry on the way to work, fast food, carbonated drinks, lack of routine - all this contributes to various digestive disorders. Against this background, one of the most common complaints is a bitter taste in the mouth, constant belching and burning spasms in the esophagus. This is evidence that there is bile secretion in the stomach. In turn, bile in the stomach is also harmful: it damages cells, contributing to the appearance of gastritis, esophagitis and other inflammatory diseases.
Kinds
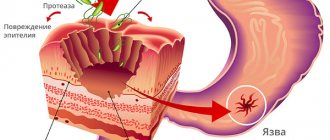
Bile, consisting of acids, enters the cavity and dissolves the epithelial membranes, which leads to irreversible metabolic processes in the cells. The gastric mucosa swells and becomes inflamed, which provokes a number of different lesions that differ in structure, volume and type of damage. In this regard, there are several classifications of the pathological process.
Based on the volume of the affected area of the mucosa, they are distinguished:
- focal form - individual areas of the stomach are affected;
- diffuse form - the lesion covers the mucous membrane of the entire muscular organ.
According to the type of lesion, reflux is divided into:
| Surface | Characterized by a chronic course with gradual damage to the epithelial layer of the stomach. The damaged cells are replaced by intestinal epithelium. |
| Erosive | Erosion occurs, which can increase in size and affect the deeper layers of the mucosa, forming ulcers. |
| Atrophic | There is a thinning of the mucous membrane and an increase in hypersensitivity of the stomach walls to the effects of acidic acid. |
Stages and degrees
There are 3 degrees of the pathological process that provokes bile reflux:
- I degree. A moderate process, which is characterized by the reflux of a small volume of duodenal contents. The gastric mucosa is irritated without the appearance of additional symptoms or damage.
- II degree. The reflux of intestinal contents into the cavity of the muscular organ causes inflammation, which provokes diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- III degree. The launch of destructive processes in the epithelium of the stomach with the manifestation of accompanying symptoms.
Symptoms
Bile in the stomach (causes and treatment are interrelated and influence the choice of further therapy) damages the protective barrier of the mucous membrane.
The acids contained in bile provoke the backflow of hydrogen ions into the tissue of the gastric walls and increase acidity. The lipid membranes of cells are also damaged, which leads to sensitivity to the components of gastric juice, as well as increased pressure in the stomach cavity.
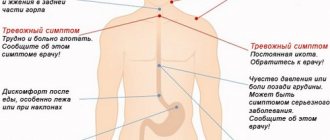
All this causes the appearance of characteristic symptoms:
- spasmodic pain in the upper abdomen or right hypochondrium, radiating to the spine;
- frequent attacks of nausea;
- heartburn;
- increased gas formation;
- vomit containing bile;
- increased belching;
- regurgitation of food debris;
- yellow coating on the tongue.
The longer the period during which bile is thrown into the stomach, the more pronounced the clinical picture of the pathology is.
Reasons for appearance
The stomach passes into the duodenum through the pylorus, in the area of which there is a sphincter that transports the intestinal contents in the desired direction. The reflux of bile into the stomach cavity indicates that the main reason provoking this process is the failure of the sphincter apparatus.
The following factors can lead to dysfunction of the sphincter:
- increased pressure in the upper intestines;
- impaired gastric motility;
- the presence of tumors in the stomach or intestines;
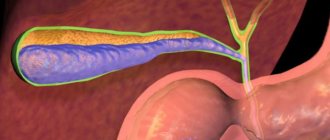
- disruption of the gallbladder;
- changes in the nervous coordination of the gastrointestinal tract;
- pathological processes in the liver, bile ducts.
External factors that increase the risk of pathological processes include:
- long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- frequent overeating;
- surgical interventions: removal of the gallbladder, suturing of a duodenal ulcer;
- smoking;
- excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages.
https://youtu.be/VdXzgwi4f78
What is reflux gastritis
Immediately behind the stomach is the duodenum, into which the pancreatic passage and bile duct drain. This includes all the enzymes and digestive enzymes that break down food into fatty components, proteins and carbohydrates. In normal conditions, bile helps to emulsify and break down fats to a state where they can be conveniently digested.
If there are malfunctions of the duodenum, then the digestion process stops, inflammation of the stomach occurs: this phenomenon is called reflux gastritis. During this dangerous disease, bile contents are refluxed into the stomach, where the latter accumulates and stagnates, leading to severe discomfort. If the symptoms of the disease are not treated in time and the symptoms of the disease are ignored, this will quickly lead to a chronic course.
Symptoms
At the initial stage of the disease, a person does not always feel the symptoms of the disease. A slight feeling of discomfort often does not make one think about serious health problems. It is necessary to detect a stomach problem in time, because... Important organs are located next to the stomach: duodenum, gallbladder, liver. Due to this anatomical feature of the human body, the diagnosis of reflux gastritis is accompanied by concomitant diseases: pancreatitis, cholecystitis, duodenitis, which have characteristic symptoms.
Bitterness in the mouth and throat
When the bile ducts are clogged, their contents do not enter the duodenum and begin to leak through the walls of the bladder. A lot of bile in the stomach can give a feeling of bitterness in the mouth and throat, especially this feeling complicates life in the morning, on an empty stomach, when the stomach is empty. A bitter taste on the tongue should alert a person and force him to see a doctor.
Vomiting bile
A series of festive feasts, which involve consuming large amounts of fatty foods and alcohol, lead to unpleasant consequences, especially for people with problems with the digestive system. When you feel sick, vomiting bile after drinking alcohol, or diarrhea - this means that the digestive organs are working hard and cannot cope with the problem themselves.
Stomach pain
Due to the fact that there are a large number of nerve endings on the walls of the stomach, in case of any disease, a person feels abdominal pain. They can give to any part of it. A person should be alert to high fever, stomach pain and belching that appears even after eating a small amount of food: this indicates an inflammatory process.
Release of bile into the oral cavity
Along with belching, reflux of the contents of the stomach with bile components may occur through the esophagus. This happens at night, during sleep, when the overfilled gallbladder and its ducts relax. Bitter belching with an unpleasant odor indicates the presence of stones in this organ, which requires immediate medical intervention, otherwise there will be complications.
Heartburn
A burning sensation, a rush of heat, or a tingling sensation behind the breastbone is called heartburn. It occurs when there is increased acidity and the reflux of aggressive stomach contents into the esophagus; this phenomenon is called reflux gastritis. This symptom is often confused with a disease of the cardiovascular system, so it is important that a person seeks help from a doctor in a timely manner.
Pimples
Inflammation of the skin is a direct consequence of the uncoordinated work of the stomach with nearby organs. Poor nutrition, constant stress, and starvation diets can cause an uncontrolled release of bile, which leads to the appearance of purulent acne throughout the body. Even proper hygiene cannot cope with this symptom, only an integrated approach to treatment.
Causes of bile reflux into the stomach
Chewed food is processed by gastric juice and hydrochloric acid, after which it moves to the duodenum, where complete digestion of food occurs with the help of incoming bile and pancreatic juice. If any digestive organ malfunctions, these enzymes are not released or enter the intestine at the wrong time, when it is not yet filled with food. Why do unwanted substances enter the stomach?
- eating according to the schedule without the appearance of appetite;
- binge eating;
- pregnancy;
- frequent stress.
Diagnostics
Bile in the stomach (causes and treatment affect the effectiveness of further therapy) can manifest itself in the presence of many diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, so it is quite difficult to differentiate the diagnosis at an appointment with a gastroenterologist.
At the initial stage of diagnosis, the patient is interviewed to compile an anamnesis, as well as an examination to determine the clinical manifestations of the disease. In order to determine the cause of duodenogastric reflux, it is necessary to apply a number of diagnostic measures, both laboratory and instrumental.
Instrumental research methods include:
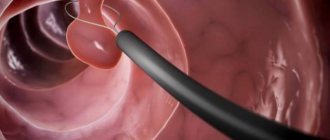
- Gastric endoscopy (FGDS) is a visual examination of a hollow organ using an optical device - a fiber gastroscope, which allows you to examine the upper parts of the digestive tract from the inside, take a photo and collect biomaterial for further research. Using FGDS, small mucosal defects are determined, their prevalence, boundaries and structural characteristics are detailed. The cost of the diagnostic method is from 2000 rubles.
- Intragastric pH-metry is a method for studying the functional state of the upper gastrointestinal tract. With its help, the level of acidity in the esophagus, stomach and duodenum is measured using a device - an acidogastrometer. A PH probe is inserted into the patient through the nasal passage, which is gradually advanced through the esophagus into the stomach cavity. The probe data on acidity is sent to the recorder in the form of an electrical signal. Information is recorded within 24 hours. The cost of the method is from 700 rubles.
- Antroduodenal monometry is a study of peristalsis of the upper gastrointestinal tract by measuring pressure in the stomach and intestines. Pressure is measured using a thin catheter that is inserted through the nasal passage. A device connected to a catheter records the frequency of contractions of the walls of the stomach and duodenum. The study is carried out for 4 hours on an empty stomach, and for 2 hours after eating. Cost – from 4000 rubles.
- Electrogastrography is a study that evaluates the peristaltic activity of the stomach using external electrodes placed on the skin in the abdominal area. Diagnostics is carried out in several stages. First, signals from an empty stomach are recorded for 40-60 minutes using 3 electrodes on the stomach. Then, after a break of 1.5 hours, the patient eats and the study is repeated. The cost of the diagnostic method is from 1600 rubles.
- Ultrasound of the stomach and intestines makes it possible to obtain information about the structural and functional state of the gastrointestinal tract. The method is used when it is impossible to conduct FGDS and is characterized by a lesser degree of information content. The cost of ultrasound is from 1200 rubles.
Laboratory research methods include analysis of gastric juice for the content of pancreatic elements and bile. Biomaterial from the stomach cavity is collected using a thin probe, which is swallowed by the patient. The procedure is carried out on an empty stomach after 12 hours of fasting. Gastric juice is collected every 15 minutes for 1 hour.
Next, secretion enhancers are introduced into the stomach cavity - meat broth, cabbage juice or medications. After 45 minutes, gastric juice is collected again. Examination of the stomach contents reveals a number of chemical indicators: acidity, volume of hydrochloric acid, amount of pepsin. Cost – from 300 rubles.
Nutrition
Treatment of bile reflux into the stomach area is recommended to be carried out in combination with proper nutrition:
- Before eating, you must drink a glass of still mineral water, but in no case after it;
- It is recommended to eat in small portions, but often;
- dishes must be at normal temperature, not hot or excessively cold;
- the basis of the diet is boiled food (porridge, vegetables, soups);
- fried and fatty foods should be excluded from the diet, as well as smoked foods, fruits and vegetables, which contribute to increased gas formation;
- Pickled foods, chocolate, jam, baked goods, strong coffee and tea are prohibited.
Maintaining proper nutrition is one of the most effective methods in the treatment of reflux and its prevention. The main goal of the diet is to reduce the load on the gastrointestinal tract and normalize general health.
Fried and fatty foods are specially prohibited during the period of treatment of pathology
When to see a doctor
The reflux of bile secretion into the stomach is not always a sign of pathology. More than 10% of healthy people experience one-time cases of bile reflux that occurs during night sleep. This condition does not manifest symptoms and does not require medical intervention.
Bile can be released into the stomach due to various gastrointestinal diseases that require further treatment.
You should consult a gastroenterologist if you have the following complaints:
- constant nausea;
- heartburn;
- the presence of a yellow coating on the tongue;
- feeling of bitterness in the mouth;
- flatulence;
- periodic spasmodic pain localized in the upper abdomen.
Treatment methods
https://youtu.be/4lX1sO3zJ7U
Treatment of bile reflux is aimed at reducing symptomatic manifestations and improving the general condition of the patient. To do this, it is necessary to normalize digestive function, restore normal sphincter tone and eliminate pain. Complex therapy consists of taking medications, following a diet and using physical therapy methods.
Medications
The therapeutic regimen contains several groups of medications:
- selective prokinetics;
- non-absorbable antacids;
- proton pump inhibitors;
- choleretic agents;
- adsorbents.
Selective prokinetics are necessary to normalize gastrointestinal motility and increase muscle tone of the sphincters.
This group of medications includes:
- Motilium is a drug in tablet form that increases the duration of antral and duodenal contractions and accelerates the process of gastric emptying. The drug is taken 30 minutes before meals, 1 tablet. 3 times a day. The maximum daily dose is 30 mg. Cost – about 700 rubles.
- Cerucal is a solution for intravenous or intramuscular administration. The drug affects the tone and motor activity of the upper gastrointestinal tract, increases intestinal tone. The drug is administered intravenously and intramuscularly, 1 ampoule 3-4 times a day. Cost – 221 rub.
Antacids are used to reduce acidity in the stomach.
These include:
- Maalox is an oral suspension that neutralizes free hydrochloric acid of the stomach and does not cause its repeated secretion in an increased volume. The product has an adsorbing and enveloping effect. Maalox is taken 1 sachet 1-2 hours after meals, and also, if necessary, if heartburn and pain in the stomach occur. The maximum permissible daily dose is 6 sachets. Price – about 360 rubles.
- Almagel a is a suspension to neutralize hydrochloric acid and reduce the digestive activity of gastric juice. The therapeutic effect occurs 3-5 minutes after taking the drug and lasts for 1 hour. The drug is taken 1-3 dosage spoons 3-4 times a day 30 minutes before meals. Cost – 328 rubles.
Proton pump inhibitors are needed to control acid levels by reducing the activity of secreting glands.
Among this group are:
- Controloc is a drug in tablet form that has antisecretory activity. The drug is prescribed at 20 mg per day. Duration of therapy is 7-14 days. Cost – from 450 rubles.
- Pariet is a benzimidazole derivative that suppresses the secretion of gastric juice. The therapeutic effect is achieved within 1 hour after taking the drug. The drug is prescribed 20 mg 1 time per day. The duration of treatment is from 4 to 8 weeks. Price – about 2200 rubles.
Choleretic agents help dilute bile:
- Allochol is a choleretic agent that reduces the processes of putrefaction and fermentation in the intestines, as well as increases the secretory and motor activity of the gastrointestinal tract. Tablets are taken in quantities of 1-2 pieces. 3-4 times a day. Duration of treatment is 3-4 weeks. The course of therapy for exacerbation is 1-2 months. Cost – 50 rub.
- Cholenzym is a combined remedy that has a choleretic effect. The drug improves the functional state of the gastrointestinal tract and improves the digestion process. The drug is taken orally after meals 1-3 times a day. Price – from 200 rub.
Adsorbents neutralize hydrochloric acid and also bind bile acids and pepsin.
These drugs include:
- Endosorb is a powder for preparing a suspension that has pronounced adsorbing and enveloping effects. The daily dose of the drug should not exceed 9 g. The cost is about 200 rubles.
- Smecta is a drug in powder form for the preparation of a suspension that stabilizes the mucous barrier of the gastrointestinal tract. Adults are prescribed 3 sachets per day. The maximum duration of treatment is 7 days. Cost - about 150 rubles.
Traditional methods
Bile in the stomach (causes and treatment are determined after diagnosis) provokes unpleasant symptoms in the form of nausea, heartburn, bloating and discomfort, which can be eliminated with the help of traditional medicine.
The following recipes are considered the most effective among them:
- Potato juice. It is necessary to peel 2 potatoes, grate them on a fine grater and squeeze out the juice, wrapping the pulp in cheesecloth. Take 50 ml of juice 30 minutes before meals.
- Herbal decoction of thyme and St. John's wort. Take 1 tbsp. l. thyme and St. John's wort, as well as 1 tsp. plantain and immortelle. The mixture of dried herbs should be poured into 1 liter of boiling water and boiled for 3-5 minutes. The resulting decoction should be filtered and taken in small portions throughout the day.
- Rosehip decoction. You need 2 tsp. rose hips pour 500 ml of water, and then put on fire, bring to a boil and simmer for 15-20 minutes. Leave the resulting broth for 1 hour and strain. Take throughout the day.
- Propolis tincture . 10 g of propolis should be dissolved in 100 ml of vodka and infused for 3 days. The resulting infusion should be filtered and taken 15 drops before each meal.
- Infusion of flax seeds. 50 g of flax seeds must be crushed and poured with warm water so that the resulting consistency resembles gruel. Allow the mixture to swell for 2 hours and take in the morning.
Diet
Diet therapy for bile reflux plays an important role, as it significantly improves the general condition and reduces the symptomatic manifestation of the pathology. The principle of nutritional therapy is fractional nutrition. Food should be taken in small portions 5-6 times a day.
In this case, it is prohibited to consume the following products:
- carbonated drinks;
- fatty, fried, spicy foods;
- smoked meats;
- bakery products and sweet pastries.
Preference should be given to:
- vegetables;
- fruits and dried fruits;
- lean varieties of meat and fish;
- fermented milk products;
- jelly;
- light soups.
Steam cooking should be chosen as a heat treatment method. It is not advisable to consume vegetables and fruits raw, as they provoke increased gas formation.
After each meal, it is recommended to maintain an upright position for 1 hour and avoid physical activity.
Other methods
Bile in the stomach (causes and treatment affect the degree of manifestation of symptoms) is not a separate disease, but manifests itself as a symptom that arises against the background of pathological processes of the gastrointestinal tract. One of the effective methods of combating diseases of the gastrointestinal tract is physiotherapy, the elements of which are hardware therapy and mud therapy.
Device therapy includes:
- Electrophoresis is a method in which medications are introduced into the body through current. Often the method is used to eliminate pain and relieve the inflammatory process. The drugs used are papaverine, gangleron, and novocaine.
- Galvanization is a method based on the use of constant, continuous low voltage electric current. Galvanic current improves blood circulation and metabolism in tissues, stimulating the biological and physiological functions of the body. For bile reflux, galvanization in the stomach area with the electrode placed in the epigastric region is indicated.
- Amplipulse therapy is an effect on the body using low-power alternating sinusoidal currents. These currents have an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect, affect gastric motility and improve blood circulation in the tissues.
- Electrosleep is the use of low-frequency pulsed current with a minimum pulse duration that affects the central nervous system. This method is indicated for patients with increased neurovegetative excitability, which arose against the background of the development of pathology.
Diet
When suffering from gastritis, for a speedy recovery, the patient must adhere to the principles of proper nutrition and follow a therapeutic diet:
- Eliminate fried foods from your diet.
- During treatment, it is recommended to avoid food of animal origin: meat, fish, dairy products.
- You should include in your diet stewed or steamed vegetables that have the ability to coat the stomach: pumpkin, zucchini, carrots, sweet potatoes, beets.
- Eat seasonal fruits and greens.
Possible complications
The reflux of bile into the stomach has a negative effect on the condition of the mucous membrane, destroying it.
Prolonged course of pathological processes can lead to the development of complications:
- Barrett's esophagus is a disease in which bile acid permanently damages the lower esophagus. As a result, the normal multilayered epithelium is replaced by cylindrical epithelium, which can lead to the development of a malignant tumor - adenocarcinoma.
- Reflux gastritis is an inflammation of the gastric mucosa caused by exposure to bile. The disease progresses and causes the development of erosion, dysplasia, duodenitis, and ulcers.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease is an inflammation of the lower esophagus.
Bile in the stomach is a syndrome caused by diseases of the upper digestive canal. Bile, in contact with the mucous membranes of the stomach and esophagus, provokes the development of additional inflammatory processes in the surface epithelium. The process requires timely treatment to avoid complications.
Folk remedies
Treatment of bile reflux into the esophagus using folk remedies comes down to the use of various medicinal decoctions. Herbal mixtures consisting of plantain, immortelle, thyme and St. John's wort have proven themselves to be the best. To prepare, you need to pour boiling water over the herbs and boil them for no more than a minute. Then the broth should stand for a while in a cool place. After this, the medicinal product is ready for use.
The recommendations given in the text are not a guide to action. To obtain detailed information about your disease, you should consult a specialist.