A healthy person normally has stool 1-2 times a day. But sometimes a malfunction occurs in the functioning of the digestive system, which affects the process of bowel movement. One of the common symptoms is false urge to defecate. Due to the sensitivity of the problem, few people immediately consult a doctor. And in vain, since this unpleasant phenomenon may be one of the signs of a serious illness.
- 6 Preventive measures
- 7 Features in women and men
- 8 Video: tenesmus - our body’s SOS signal
- 9 Patient reviews
What is false urge to defecate?
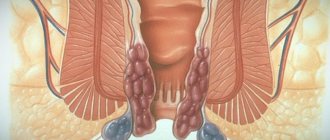
The symptom is manifested by a subjective feeling of the need to empty the intestines, while the act of defecation itself does not occur. False (imperative) urges to defecate can be painless or cause excruciating pain to a person. Such urges are called tenesmus in medicine.
Tenesmus is often accompanied by flatulence, bloating, constipation or diarrhea. The futile urge to empty is based on the high sensitivity of the rectum to pressure from the inside, so even a small amount of intestinal contents - mucus, feces, blood, foreign body, inflammatory substrates - causes an increased reflex urge to visit the toilet. In this case, the anal sphincters (compressor muscles) do not relax and defecation does not occur. Spasms of the muscle layer of the sigmoid and rectum, as well as the muscles of the perineum and abdominal press, make these urges painful.
False urges can be completely painless and bring only slight discomfort, or they can cause excruciating pain
Urgency
Imperative urges (urgency) constantly haunt a person with urinary disorders, preventing him from concentrating on ordinary everyday affairs. Do not confuse the usual strong urge to urinate with urgency. When it appears, it immediately becomes clear that not everything is in order in the body. It is characterized not only by incredibly strong urges, but also by their very frequent occurrence. Such symptoms cannot be controlled; they bother you constantly, regardless of the time of day, gender and age. Previously, statistics spoke of a more frequent susceptibility to the disease in older people, but now this phenomenon is increasingly occurring among young people.
There are cases when urgency is accompanied by nocturia (mainly night urination) or incontinence. Urgency often leads a person to an incapacitated state. Among urinary disorders, urgency is the most common, and among other diseases it occupies a fairly high position. If present, they speak of overactive bladder (OAB).
Causes and development factors
False urges to have a bowel movement can be a symptom of a number of diseases:
- hemorrhoids, which is the formation of nodes as a result of congestion, inflammation and expansion of the veins. Obesity, physical inactivity, hereditary predisposition, stress, heavy physical activity can lead to pathology;
- proctitis - inflammation of the inner lining of the rectum, which can be caused by frequent constipation, helminthic infestations, hypothermia, hemorrhoids, prostatitis, abuse of alcoholic beverages, spicy, spicy dishes;
- sigmoiditis - inflammation of the sigmoid colon due to infections, dysbiosis, Crohn's disease (granulomatous enteritis), radiation sickness, intestinal ischemia;
- rectal cracks that occur during inflammatory processes or mechanical trauma;
- fistulas, which can form as a result of chronic intestinal pathology, most often occur with paraproctitis;
- polyps - outgrowths of the mucous membrane that arise at the site of inflammation, with the growth of healthy tissue or atypical cells. The reason for the formation of polyps can be heredity, frequent constipation, poor nutrition - lack of fiber and excess protein foods;
- adenocarcinoma - a malignant neoplasm that forms from glandular cells lining the walls of the rectum;
- stenosis (or stenoses) of the rectum - a pathological narrowing that occurs as a result of inflammation, a tumor, or is a congenital anomaly;
- pararectal lymphadenitis - inflammation of the lymph nodes caused by staphylococcal or streptococcal infection;
- periproctitis - inflammation of the tissues surrounding the rectum, with the formation of purulent exudate. Often develops with hemorrhoids or proctitis.
Hemorrhoids can cause tenesmus - a reflex urge to defecate
In addition to these diseases, tenesmus can occur against the background of:
- accumulation of a large number of fecal stones in the intestines;
- irritable bowel syndrome, which occurs due to a disruption of healthy microflora and a malfunction of the autonomic nervous system;
- infectious diseases - dysentery, cholera, typhus, intestinal tuberculosis, acute intestinal infection;
- pathologies of the nervous system (rectal crisis, myelitis, anismus or desynergic defecation - uncontrolled spasm of the sphincter);
- spasms caused by frequent diarrhea, large stools, and prolonged riding in a sitting position.
To determine which disease symptom is the imperative urge to defecate, it is necessary to conduct a thorough diagnostic examination of the patient.
Etiology
The main reasons for this condition are failures in the excitability of the structures responsible for nervous regulation, which provokes a serious condition that leads to spasms of the muscles of the intestinal elements. Spasms affect the muscular elements of the pelvis, rectum, and perineum. A disorderly contraction of the intestines occurs, and this prevents the normal movement of the contents.
Rectal tenesmus is a common symptom. Many diseases of the gastrointestinal tract manifest themselves in this way.
Such a clinic may indicate the following pathologies:
- infectious diseases;
- paraproctitis.
Often the causes of tenesmus are anal fissures and fistulas. Unsafe etiological factors are neoplasms in intestinal structures. Diagnosing them is difficult because the symptoms can remain hidden for a long time. Very often, it is an infectious lesion of the lower parts of the digestive tract that becomes the cause of the disease.
Anal fissure
As you can see, the manifestation of such a syndrome can be associated with a number of reasons that must be determined before starting therapy.
The pathogenesis is based on increased excitability of the nervous system, which leads to erratic contraction of intestinal smooth muscles. Spasms can occur both in a specific area of the intestine and along its entire length, which significantly complicates the process of defecation.
The reasons for the presence of false urges to defecate are as follows:
- proctological diseases - anal fissures, hemorrhoids;
- benign or malignant formations in the gastrointestinal tract;
- inflammatory bowel diseases;
- intestinal infections;
- frequent food poisoning;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- prolonged stress, constant nervous tension.
Also, the causes of intestinal tenesmus may be a sedentary lifestyle, long-term cycling, or horseback riding. Sometimes a person may experience a similar sensation after undergoing surgery in the gastrointestinal tract.
Diagnostics
The proctologist makes the main diagnosis; if necessary, the patient is referred for consultation to a gastroenterologist and neurologist. A patient interview, examination, laboratory and instrumental examination are carried out.
Laboratory diagnostic methods:
- Clinical blood test:
- assess the level of hemoglobin and red blood cells to exclude anemia;
- leukocytosis and high ESR indicate an inflammatory process.
- A general urine test is necessary to exclude urological pathology.
- A coprogram is prescribed to assess the composition of stool, the presence of undigested food residues, and pathological elements, for example, pus.
- Feces for occult blood can exclude internal bleeding.
- A stool test for worm eggs is carried out to detect helminthic infestation.
- Stool culture is done to identify pathogenic microorganisms.
In order to find out the cause of tenesmus, you need to submit feces for coprogram
Examination of the patient consists of a digital examination of the rectum through the anus. The doctor determines muscle tone, mobility of the mucous membrane, its integrity, the absence or presence of hemorrhoids. If palpation examination is not enough, sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy are prescribed.
A visual examination of the rectal mucosa is carried out using a sigmoidoscope - a special device equipped with a light source and lenses. Colonoscopy is carried out using a thin fiber optic probe, which allows you to examine in detail all areas of the colon and detect tumors, ulcers, polyps, as well as perform a biopsy - collecting material for histological examination. In addition to these methods, the patient undergoes an ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
Sigmoidoscopy allows you to study in detail the mucous membrane of the large intestine and find out the cause of tenesmus
After studying the results of laboratory tests and evaluating the data obtained during instrumental studies, the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment for the identified pathology.
Differential diagnosis
There are a number of symptoms from which tenesmus should be distinguished:
- Proctalgia is a pain syndrome in the rectal area. This pain is not associated with the urge to have a bowel movement and usually manifests itself in the form of night attacks.
- With coccydynia (pain in the coccyx area, most often associated with injuries), the pain is also not associated with the urge to defecate, becomes stronger in a sitting position, and sometimes radiates to the hip joints.
- Proctospasm is characterized by a feeling of compression of the anal sphincter, pain radiating to the thigh or lumbar region, while the person does not experience the urge to empty the intestines.
- Impaired sensitivity - its decrease or increase (paresthesia or hyperesthesia), in the rectal area occurs with tabes dorsalis (damage to the spinal nerve endings in late neurosyphilis).
Symptoms
Symptoms of intestinal candidiasis are varied.
Determining the disease is not difficult. Despite the fact that candidiasis (one of the types of fungal infection, caused by microscopic yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida (primarily Candida albicans)) is a disease (a condition of the body expressed in a violation (Offence, action or inaction, contrary to the requirements of legal norms) and committed by a person capable of delinquency; “Violation”, one of the first stories by Sergei Lukyanenko) of his normal functioning, life expectancy, and his ability to maintain his homeostasis), caused by opportunistic flora, without proper treatment (a process whose purpose is to alleviate, remove or elimination of symptoms and manifestations of a particular disease or injury, pathological condition or other disability) is indispensable.
Intestinal candidiasis is a pathological condition of the gastrointestinal tract caused by pathogenic mycoses of the genus Candida. Normally, microorganisms are found in the normal flora of a healthy person. The development of the disease occurs against the background of uncontrollable growth of fungi. The appearance of symptoms is due to the negative influence of candida waste products.
The main manifestation of thrush in the intestines (the organ of digestion and excretion in humans and multicellular animals) will be severe pain, in addition to which you should pay attention to the following signs of invasion:
- bloating becomes chronic;
- patients complain of heaviness in the epigastric region (stomach);
- after eating, intestinal spasms are observed;
- impaired intestinal motor function (diarrhea);
- low-grade body temperature (from 37 to 37.50);
- patients complain of lack of appetite;
- impurities of blood and pus are found in the stool;
- in the anal area and stool you can find a cheesy discharge with a foul odor;
- after bowel movement there is no feeling of relief;
- pain during defecation;
- false urge to defecate;
- a rash appears on the skin.
In addition to the primary signs of pathology, fatigue, insomnia and various forms of skin diseases (acne, dermatitis, urticaria) may appear.
Regardless of the severity of the clinical picture, intestinal candidiasis can be easily determined by an experienced doctor (gastroenterologist).
As the pathological spread of fungi progresses, all symptoms intensify. Lack of treatment allows the pathology to spread to various parts, most often the disease affects the genitourinary organs and the oral cavity. In addition to the spread of candidiasis (one of the types of fungal infection, caused by microscopic yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida (primarily Candida albicans)) provokes an exacerbation of existing diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
The transition of thrush from the intestines (the organ of digestion and excretion in humans and multicellular animals) to the genitals of a woman has the following symptoms:
- cheesy discharge is detected on the genitals and underwear, having an unpleasant odor;
- unbearable itching of the vagina, turning into a burning sensation, can be observed at rest, during urination or sexual intercourse;
- in severe forms of the disease, menstrual function may be impaired; long-term infection can cause secondary infertility.
Symptoms in men are not very different:
- itching and burning of the penis and scrotum;
- discharge of a cheesy nature (outwardly reminiscent of cottage cheese);
- disturbance of urination, pathogenic fungi are detected in the urine (visually the urine has a cloudy whitish sediment).
When the oral cavity is affected, inflammation of the mucous membrane, a white coating that can be easily removed with a spatula or gauze swab, and pain during eating are determined.
In the absence of adequate treatment, serious complications may occur. The most dangerous to the life and health of the patient is considered to be perforation and penetration of the ulcer (breakthrough of the ulcer into the surrounding tissues with the subsequent entry of its contents into the cavity of the damaged organ).
Intestinal fungus does not cause problems if the immune response is good. For the development of the disease, certain conditions are necessary that favor the development of mycosis:
- decreased resistance of the body to the development of pathogenic flora under unfavorable environmental conditions (sudden time zone changes, temperature changes, high or low humidity);
- chronic infections;
- diseases of internal organs;
- immunodeficiency (congenital or acquired);
- uncontrolled treatment (a process the purpose of which is to alleviate, relieve or eliminate the symptoms and manifestations of a particular disease (this is a state of the body expressed in a violation (Offense, action or inaction, contrary to the requirements of legal norms and committed by a person capable of delinquency; “Violation”, one of the first stories of Sergei Lukyanenko) of his normal functioning, life expectancy, and his ability to maintain his homeostasis) or injury, pathological condition or other dysfunction,) antibiotics;
- suppression of immunity during the treatment of oncological processes (chemotherapy or radiation);
- imbalance in the hormonal background (the cause may be a disease (this is a state of the body, expressed in a violation of its normal functioning, life expectancy, and its ability to maintain its homeostasis) (this is a state (an abstract concept denoting a set of stable values of variable parameters of an object) of the body, expressed in violation of his normal functioning, life expectancy, and his ability to maintain his homeostasis) endocrine system, hormone intake, menopause, pregnancy);
- malnutrition (favorable conditions for candidiasis are created by lovers of flour products with a rare and inconsistent diet).
Determination of yeast fungi in the intestines is carried out by inoculating the contents of the secretions on a nutrient medium. After identifying fungi, differentiation of the type of mycosis is carried out.
In addition to culture, sigmoidoscopy can be used as a diagnostic method, which allows one to isolate plaque on the intestinal wall and confirm the preliminary diagnosis established on the basis of the patient’s sting.
Treatment
Only a doctor can determine how to treat intestinal candidiasis. Elimination of pathology should be comprehensive and carried out in two directions:
- stopping the growth of mycoses and destroying the already expanded network;
- treatment (a process the purpose of which is to alleviate, relieve or eliminate symptoms (one of the individual signs, frequent manifestations of any disease, pathological condition or disorder of any life process) and manifestations of a particular disease or injury, pathological condition or other disorder vital activity,) diseases that cause a decrease in immunity.
When choosing tactics for treating the condition, the doctor takes into account the form of the disease (this is the state of the body, expressed in the disruption of its normal functioning, life expectancy, and its ability to maintain its homeostasis), the severity, the risk of a complicated course, the state of the immune system and the background disease that gave rise to thrush.
Tenesmus has a characteristic clinical picture of the disease. As practice shows, the patient feels pain symptoms of a spastic, aching nature, localized in the lower abdomen. All this is accompanied by a strong urge to defecate. These urges are ineffective; an attack of this nature is accompanied by a small discharge of feces, which contain impurities of blood, mucus, and sometimes even undigested food particles. Spasms in the abdomen and closer to the groin area continue.
The nature of the clinical picture will depend on what exact causes caused such a pathological process in a child or adult. One of the specific symptoms of this disease is pain in the lower abdomen, which persists for a long time.
In addition, the clinical picture will include the following conditions:
- feeling of fullness in the stomach;
- rumbling, increased formation of gases;
- temperature increase;
- dizziness, headaches;
- nausea and vomiting;
- constipation can suddenly give way to diarrhea;
- general weakness, increasing malaise;
- compression of the anal sphincter muscles;
- loss of appetite.
Due to the fact that false urges to defecate provoke contraction of the anal sphincter muscles, but the act of defecation does not occur after this, this can lead to the formation of erosions and cracks. In this case, the clinical picture may be supplemented by rectal bleeding, but of a minor nature.
It should be noted that the clinical picture in women does not differ from that which occurs with a similar problem in men. If you have such symptoms, you should consult a doctor who will diagnose and prescribe effective treatment.
Treatment of tenesmus
Therapy is primarily aimed at eliminating the disease that caused the symptom.
Use of medications
Drug therapy is determined by the specific disease:
- intestinal infections require the use of antibacterial agents, for example, Nifuroxazide, enterosorbents - Sorbex, Enterosgel;
- colitis and proctitis are treated with sulfonamide drugs;
- for hemorrhoids and anal fissures, anti-inflammatory, emollient, wound-healing agents are prescribed in the form of ointments or suppositories - Proctosan, Ultraproct, Methyluracil, drugs to improve blood circulation - Detralex;
- diarrhea is treated with Imodium or Loperamide; for flatulence, Espumisan is recommended;
- constipation is eliminated with mild laxatives - Duphalac, Lactulose;
- They use sedatives - Novo-Passit, Alora syrup, valerian tincture.
Symptomatic treatment of tenesmus itself is based on the use of antispasmodics:
- No-Shpy (Drotaverina);
- Papaverina;
- Dicyclomine;
- Hyoscyamine;
- Duspatalina.
Microenemas with silver nitrate or warm vegetable oil are used.
Photo gallery: drugs for the treatment of false urges
The active ingredient of Spasmolysin is drotaverine, an antispasmodic that effectively eliminates tenesmus. The sedative Novo-Passit is used in the complex treatment of false urges to defecate. Papaverine in rectal suppositories is used to relieve spasms. If false urges are caused by diarrhea, Imodium Duphalac is prescribed - a mild laxative used to treat constipation Duspatalin - antispasmodic, prescribed to eliminate irritable bowel syndrome. Rectal suppositories Proctosan are recommended for tenesmus caused by hemorrhoids
Treatment of tenesmus as a symptom of the underlying pathology, in addition to medications, includes correction of lifestyle, nutrition and physical activity.
Diet
Therapeutic nutrition for futile urge to defecate is adjusted taking into account the underlying disease. Avoid foods that irritate the intestines:
- cold;
- hot;
- spicy;
- salty;
- fried;
- smoked;
- spicy.
It is better to boil or steam foods.
Meals should be fractional: often and in small portions.
It is imperative to remove from your diet foods that provoke processes of rotting and fermentation in the intestines:
- non-dietary meat;
- coarse vegetable fiber (cabbage, legumes);
- fresh baked goods;
- sweets;
- canned food;
- alcohol.
If you are prone to constipation, we recommend:
- vegetable purees:
- pumpkin;
- beet;
- carrots;
You can eat soups, cereals, boiled, stewed lean meat (rabbit, turkey, veal) and fish.
Depending on the underlying disease, the doctor recommends dietary nutrition to the patient
Folk remedies
Traditional recipes can serve as a complement to basic therapy. Sitz baths with a cool infusion of medicinal plants are effective: chamomile, marigold, sage. Microclysters with herbal decoctions of chamomile, St. John's wort, and sea buckthorn oil relieve inflammation and irritation of the intestinal mucosa.
If the inflammation is not limited only to the rectum, therapeutic enemas of 200–400 ml with herbal decoctions are recommended. Marshmallow root, elderberry blossom, sage leaves, and oak bark have enveloping and anti-inflammatory properties.
Herbs with antispasmodic effects can be taken orally in the form of tea:
- chamomile;
- mint;
- motherwort;
- sweet clover;
- lemon balm;
- oregano;
- valerian.
Chamomile infusion is prepared and taken as follows:
- Pour boiling water (200 ml) over a large spoon of crushed raw materials and leave for an hour.
- Strain the infusion and drink a third of a glass three times daily.
Herbal mixture for spasms:
- Take a teaspoon of centaury, chamomile and sage herbs, pour a glass of boiling water, leave for half an hour.
- Strain and take 2 tablespoons 4 times a day.
Chamomile infusion has an antispasmodic and anti-inflammatory effect; for tenesmus, it can be taken orally or made into microenemas
Preventive measures
Since false urges to defecate are often the result of poor nutrition and a violation of a healthy lifestyle, for prevention it is necessary:
- organize a complete healthy diet, minimize the amount of foods harmful to the intestines;
- make up for the lack of physical activity due to a sedentary lifestyle:
- to walk;
- do morning exercises;
- organize breaks with warm-up during the working day;
Walking in the fresh air is important for maintaining the health of all body systems, including the intestines.
Features in women and men
Tenesmus associated with hemorrhoids more often bothers men, since the stronger sex is more susceptible to this disease. Women often experience tenesmus associated not only with pathology of the large intestine, but also with gynecological problems and diseases of the urinary tract (cystitis, urethritis), which is associated with the anatomy of the female body.
Tenesmus in women can be associated not only with diseases of the rectum, but also with gynecological and urological pathologies
Human nutrition
“I go to the toilet very often, for the most part, what could be the reasons?” - some patients are interested. Sometimes increased intestinal motility and emptying can be a consequence of a peculiar diet. Moreover, if a person changes his diet, then the frequency of stool begins to decrease. What can be classified as products that cause such a reaction in the body?
Greens and leafy salads, raw vegetables and fruits, whole grain bread and bran - all these foods contain coarse fiber. These substances are very beneficial for the body. They cleanse the human intestines and bloodstream. However, it is worth remembering that their uncontrolled use can lead not only to increased stool frequency, but also to its dilution. Fresh kefir has the same effect. If you purchase a one-day product, be prepared for frequent trips to the toilet. Older products have exactly the opposite effect on the human body.