General information
Bloating is a condition that occurs in a person due to too high a level of gas formation.
The symptoms that this disease causes usually cause quite severe discomfort for the patient. It is important to realize that this condition can be corrected and prevented by following a certain diet and making some lifestyle changes. As a rule, bloating occurs quite often in people. However, in most cases this condition is not too serious a problem. However, under certain circumstances, bloating can be a sign of quite serious pathologies developing in the human body.
Mechanism of damage development
What is the cause of a dangerous surgical pathology is clear, but what happens inside the intestine when the normal movement of food through it stops?
The contents in the form of food gruel encounter an obstacle on its way, and stagnation occurs. The intestinal wall is subject to excessive stretching, and excess digestive juices, bile, pancreatic secretions, and gases accumulate in it due to the activity of microorganisms and the breakdown of organic acids.
The altered wall is unable to fully carry out absorption, the pressure in it increases, the intestinal loops increase in volume, swell, change color, become purple or cyanotic, peristalsis slows down sharply or is completely absent.
The pathogenesis of the process and its speed depends on the form of obstruction. In the strangulation form, due to a sharp disruption of blood circulation, pathological changes in the intestinal wall increase extremely quickly: its vessels are compressed, blood clots form, and death - necrosis - develops.
All processes lead to disruption of the functioning of a part of the intestine or its part. Through a non-functioning organ, pathogenic microorganisms, part of the liquid contents, and bacterial toxins can penetrate into the abdominal cavity. Peritonitis develops.
Such changes in the body cannot but affect the patient’s well-being. And if in the initial stages the process is local, limited in nature, albeit with a clear clinical picture. Then, as the disease progresses, peritonitis develops, followed by sepsis (blood poisoning) and multiple organ failure.
At the stage of systemic damage to the body, without highly qualified medical care, the disease ends in death.
Causes of bloating
In the process of swallowing liquid, food or saliva, a person simultaneously swallows a certain amount of air. This air gradually accumulates in the digestive system. A gas consisting of oxygen and also nitrogen collects there. Gas is also produced during the digestion of food: mainly in this case, hydrogen, methane, and carbon dioxide are produced. If too many of these gases accumulate, a person develops bloating.
Today, experts note that many people complain about the regular occurrence of bloating. Doctors explain this situation by the fact that modern people predominantly lead an unhealthy lifestyle. First of all, in this case, the cause is dietary errors: irregular eating, an abundance of animal proteins, too fatty foods, as well as foods containing a large number of calories. At the same time, the amount of fiber necessary for the digestion process in everyday food is very low.
As another reason that is decisive for the occurrence of intestinal bloating, experts identify too low a level of mobility in modern humans. Due to an insufficient level of physical activity, digestion slows down, and, as a result, a person experiences not only bloating, but also intestinal inflammation, peptic ulcers and even intestinal cancer . Sometimes pathological phenomena in the intestines occur as a result of taking certain medications. Thus, bloating is possible after taking certain antibiotics , anti-inflammatory drugs , and antidepressants .
Some drugs that are intended for the treatment of general diseases, as well as diabetes mellitus , thyroid pathologies and other ailments have a similar effect. Among the causes of bloating, doctors also identify constipation , celiac disease (gluten intolerance), irritable bowel syndrome , gastroenteritis , and the inability to properly absorb nutrients.
Symptoms of bloating
With the inflammatory process that develops in the intestines, a variety of events are possible. For example, inflammation can affect almost the entire digestive system. This type of illness can continue for many years. With intestinal bloating, a person begins to feel heaviness and severe distension in the abdomen. In addition, he is overcome by pain, which can be of a very different nature: the pain can be aching, stabbing, or cramping. It occurs in different parts of the abdomen and stops only after the person passes gas.
Often, intestinal bloating is accompanied by constipation, nausea, diarrhea, and belching. The patient may also periodically experience an unpleasant taste in the mouth. Accordingly, he develops bad breath . In most cases, a person experiences very poor appetite and weakness. Due to the fact that the internal organs are connected by a single nervous system, abdominal pain due to intestinal bloating sometimes provokes a response from other organs. For example, with intestinal bloating, there are often cases of pain in the heart area, uneven heart rhythm, and headache attacks. A person feels weak and overwhelmed, he periodically experiences a bad mood, a state of anxiety, and bouts of insomnia.
A patient with intestinal bloating is constantly passing gas. This condition is sometimes accompanied by loud sounds. In some cases, with intestinal bloating, gases pass intermittently, which is accompanied by rather unpleasant sensations.
Treatment of dolichosigma
After identifying the pathology, the patient is registered with a gastroenterologist, who prescribes a diet according to the examination indications and drug treatment. In case of acute manifestations of symptoms, the doctor may prescribe treatment in a hospital.
What is the treatment?
During drug treatment, the specialist prescribes the following drugs to the patient:
- Prozerin (injection);
- Dibazol (two-week courses with breaks of 1-2 months);
- B vitamins;
- Preparations aimed at improving intestinal microflora;
- Antispasmodic drugs to relieve pain;
- Abdominal massage courses.
After completing a course of medication, the patient is recommended to undergo additional rehabilitation treatment in a sanatorium, but this treatment option has a positive effect only in the early stages of the development of the pathology; in cases of progressive disease, surgical intervention is prescribed.
Surgical intervention for the formation of intestinal loops
Indications for surgery are based on the patient’s condition, as well as on the findings of the study of the course of the disease.
Surgery is prescribed to the patient only for persistent constipation that lasts more than a month, as well as in cases of progress in increasing the intestinal lumen and when conduction damage is detected at the neuromuscular level.
In cases where there is no positive reaction to medications, when the intoxication process threatens the patient’s life, this is also an indication for surgical intervention.
Patients with dolichosigma must adhere to all the instructions of the attending physician: the prescribed drug therapy and diet aimed at eliminating the possible causes of the disease and treating the patient.
Diagnosis of bloating
As a rule, diagnostics are not carried out for intestinal bloating, because patients rarely go to doctors with this problem. But if you have some other symptoms, for example, prolonged abdominal pain, blood in the stool, you should undergo a comprehensive examination. First of all, in this case, a blood test is performed, which allows you to detect infections and determine how related this condition is to the occurrence of bloating and other symptoms. In some cases, the doctor may also prescribe an endoscopy .
How to diagnose pathology
In recognizing pathology, an important role is played by the qualifications of the surgeon, his ability to correctly conduct an examination, palpate the abdomen, collect anamnesis, quickly find his bearings and decide on the tactics for managing the patient.
This diagnosis does not tolerate slowness and does not allow long thinking and waiting. As soon as possible, if obstruction is suspected, the patient should undergo the following diagnostic tests:
- X-ray examination of the abdomen in a vertical position and a horizontal position on the left side. Radiography can be performed with barium suspension contrast.
The diagnosis will be confirmed by visualized accumulations of gas in the small intestine (normally there is gas only in the colon), “inverted bowls” - gas above the liquid level, “organ pipes” - swollen loops with gas and liquid. This is how radiologists describe confirmed intestinal obstruction.
- colonoscopy
- irrigoscopy
These methods are used to clarify pathology in the final sections of the gastrointestinal tract; they will help identify the mechanical cause of closure of the lumen and more accurately determine the localization of the process.
- laparoscopy
It is used more and more often in modern surgery. Through small incisions on the anterior abdominal wall, the doctor inserts an endoscopic device with a camera into the abdominal cavity; on the monitor screen, which is connected to the endoscope, organs and pathological changes are visualized with high accuracy.
In addition to diagnostic, the method can be used for therapeutic purposes: some manipulations can be performed laparoscopically to cut adhesions, remove foreign bodies, and perform detorsion.
- Ultrasound of OBP (due to increased accumulation of gases, it may be difficult to perform)
- CT
Both methods are very informative in determining fluid in the abdominal cavity, tumors, and infiltrates.
Preventing bloating
First of all, to prevent intestinal problems, it is important to lead a healthy lifestyle and eat right. You need to eat food in small portions, and it is important to chew it thoroughly and not immediately wash it down with food and other drinks.
proteins , starchy foods , and fructose in your meals at the same time . Sometimes reducing the amount of dairy products in your diet can help prevent persistent bloating . You should not often eat very cold or very hot foods. The cause of bloating can be strong coffee and tea, or consumption of large amounts of chocolate.
It is important to get rid of bad habits that cause bloating: smoking, constant chewing of gum. If bloating does occur periodically, then recording your daily diet will help you find out what is causing this condition. Thus, you can understand which product provokes such a reaction. Walking after a meal can also prevent bloating. Therefore, after lunch you should not lie down, but at least take a walk for a few minutes.
Bloating in children
Bloating is a common problem in newborn babies. Often the disease manifests itself due to certain structural features of the digestive tract. When a child has bloating, the following symptoms are observed: the abdomen becomes very hard, enlarged and rounded. At the same time, the baby behaves very restlessly, cries, and is nervous. At the same time, he periodically shudders and moves his legs, eats poorly and sleeps restlessly.
If the child is healthy, then intestinal colic usually manifests itself in the evening. Such attacks can last about twenty minutes.
However, parents should take into account that bloating in babies can also occur in the presence of certain diseases. Therefore, it is important to consult a pediatrician in time. Among the reasons that provoke the occurrence of intestinal bloating in children, doctors identify the swallowing of a large amount of air during feeding, incorrect selection of the formula and its improper dilution during artificial feeding, the presence of lactase deficiency, enterocolitis arising from an intestinal infection, intestinal dysbiosis .
After a few months, intestinal bloating, which causes intestinal colic, ceases to bother a healthy child. As a rule, as a treatment for intestinal bloating in babies, a certain correction of the diet of mother and child is used, as well as the use of drugs for the treatment of intestinal bloating in babies.
Intestinal obstruction - what is it?
This condition is characterized by a violation (complete or partial) of the movement of contents through the intestinal sections.
This is an acute surgical pathology that is more common in the male population aged 30-60 years. But women and children with such a diagnosis are not at all uncommon in hospitals and clinics. Among all “acute abdomen”, this diagnosis is established in 5-9% of cases.
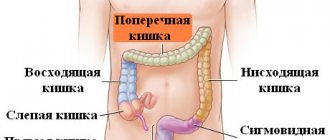
This pathology is classified according to anatomical principles into colonic (if the process affects the final sections of the gastrointestinal tract) and small intestinal (with lesions of the duodenum, jejunum and ileum). By origin - congenital and acquired.
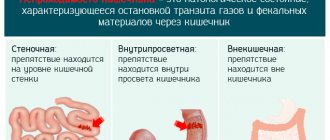
But more informative is the classification, which reveals the mechanism of the disease, according to which dynamic and mechanical obstruction are distinguished.
The occurrence of this type of obstruction is based on the following factors:
- Blockage of the intestinal lumen with objects that are foreign to the body or not anatomically related to the intestinal wall (dense feces, bezoars, gallstones, a ball of parasites, foreign objects), or pathological structures that are interconnected with internal organs and, growing, close the lumen (tumors, polyps in the intestines).
- Pinching, twisting of intestinal loops behind each other or around their axis, the formation of nodes, which results in a disruption of the blood supply to the vessels and blocking of blood flow in the areas of the loops. This is the situation that people call “volvulus.” The medical name for this phenomenon is strangulated intestinal obstruction.
- Combination of obstruction and entrapment. This is a situation in which one loop is inserted and pressed into another, being both a mechanical obstacle and a source of compression of blood vessels and cessation of normal blood flow.
It is based on functional disorders of motor activity of the gastrointestinal tract, namely:
- persistent spasm
- paresis
- paralysis
Based on the mechanism of motor disorders, this form is divided into paralytic and spastic.
Defects in muscle tone and peristalsis in the form of paralysis and paresis can be observed both throughout the intestine and in its individual sections. The following conditions can provoke motor-evacuation dysfunction and cause paralytic obstruction:
- injuries, operations on the abdominal cavity and gastrointestinal tract
- inflammatory processes: appendicitis, peritonitis, ileitis, cholecystitis
- pathological conditions occurring outside the peritoneum: myocardial infarction, spinal and skull injuries, pneumonia
- retroperitoneal hematomas, as well as thrombosis of mesenteric vessels, splenic infarctions
- metabolic diseases (diabetic precoma, cystic fibrosis)
Persistent spasm of the intestinal muscles is possible with:
- ascariasis
- hepatic and renal colic
- diseases of the nervous system (hysteria, neurasthenia)
- intoxication of the body both by products of internal metabolism (in case of severe renal and liver failure) and substances coming from outside (alcohol, heavy metals)
Adhesions can deform the structure of the organ, tighten, and disrupt the anatomical location of the intestinal loops.
Some practicing surgeons distinguish separately the adhesive form of disruption of the passage of contents through the intestine, thereby emphasizing the role of the causative factor: the presence of adhesions - connective tissue fibers formed as a result of an inflammatory process or trauma to the organ.
Other authors believe that it is more convenient to consider the adhesive process not as a separate form, but as one of the causes of obstructive and strangulation obstruction, since these structures can cause both circulatory disorders and block the intestinal lumen.
Both opinions are justified and have the right to exist.
Complications of bloating
A patient's intestinal bloating can have varying degrees of severity. If the disease is not treated in time, more severe conditions may develop. Thus, with long-term bloating of the intestine, its obstruction, as well as inflammation and subsequent suppuration, may occur. The consequence of intestinal diseases is often problems with other organs. Children suffering from constant bloating experience poor growth and development. Therefore, if bloating is a regular problem, you should seek professional help.
Genesis of loops
The formation of intestinal loops can be a congenital anomaly, but in most cases the disease is an acquired pathology.
Medical scientists still do not know exactly what causes additional intestinal loops to form during the development of the fetus in the womb, but, according to versions, this can be caused by: unfavorable heredity, the influence of toxic substances on the fetus, as well as various kinds of physical factors.