Why does increased gas formation occur?
Every day, about 500–600 cm3 of gas is formed in the intestines of an adult, but this small amount is released naturally without any discomfort. Only the formation of a significant amount of a gas mixture (hydrocarbon, nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide) is uncomfortable, as there is a feeling of abdominal distension, pain and the need to frequently visit the toilet. The causes of excessive gas formation are quite varied. Among them, the most significant are the following:
- consuming large amounts of carbohydrates, certain dairy products, or foods that cause gas;
- a mechanical obstruction in the intestines that interferes with the natural passage of gases;
- disruption of the innervation of the gastrointestinal tract, as a result of which peristalsis slows down and the processes of rotting and fermentation in the intestines increase;
- inflammatory changes in the intestinal mucosa (enteritis, colitis), as a result of which the processes of parietal absorption and digestion of nutrients worsen;
- changes in the microbial balance of the human intestine.
Thus, it becomes clear that increased gas formation in the abdomen may simply be a consequence of a nutritional error, or may be the initial sign of a serious pathology. If measures taken on your own (more on them later) do not bring the desired relief, you should visit a gastroenterologist as soon as possible to find out why this is happening.
Classification of flatulence
Classification is carried out depending on the mechanisms causing the pathological condition. The following forms of increased flatulence are distinguished:
- Nutritional. It develops as a result of malnutrition, when the menu is dominated by foods that can cause intense fermentation and gas formation in the digestive system.
- Dynamic. Manifests itself as a result of disruption of the intestinal muscles. An example of this form of flatulence is gas formation as a result of the effects of toxins on the body during food poisoning.
- Mechanical. Occurs as a result of a violation of the excretory function of the intestine;
- Psychogenic. The appearance of this type of flatulence is typical in people with an increased psycho-emotional reaction. Flatulence appears as a result of strong experiences, stress, and hysterics.
- Circulatory. A disturbance in the blood flow of the intestinal walls is considered characteristic of this species, for example, with cirrhosis of the liver.
- Digestive. This form appears due to digestive disorders.
- High-rise. Pathological accumulation of gases in the intestines appears when rising to altitude, under the influence of changes in atmospheric pressure.
- Dysbiotic. It is formed due to an increase in the number of gas-forming bacteria in the intestines.
Increased flatulence can also appear as a result of disruption of the functioning of the digestive canal due to a deficiency of certain enzymes.
Power supply errors
The habit of eating quickly, not paying enough attention to a varied and proper diet, preference for certain (not always healthy) dishes - all this provokes severe gas formation. Among the products that provoke severe gas formation, the most significant are:
- legumes (any cabbage, beans, peas, lentils);
- nuts (in large quantities);
- dried fruits (prunes, dried apricots, raisins);
- brown bread and fresh baked goods;
- fresh (especially fat) milk;
- carbonated drinks, including kvass;
- some types of vegetables and fruits (banana, grapes with seeds, apricots).
Accordingly, avoiding these trigger foods will quickly eliminate the delicate problem that has arisen. Various tactics are possible in correcting the diet. The first method involves a complete rejection of the above products. Switching to boiled vegetables, lean baked meats and fish, soups with diluted broth, and only natural sweets in very limited quantities will undoubtedly be beneficial for the gastrointestinal tract of any person. However, such tactics will leave unresolved the main question of which product causes excessive gas formation.
It is more appropriate to eliminate provoking foods one by one. The relationship between the consumption of a certain group of foods and the occurrence of abdominal discomfort will allow you to accurately identify the triggering product and exclude only it from the diet. There is another solution to the problem - keeping a food diary. Recording the foods you eat and analyzing your own feelings will help you quickly identify the “culprit” and solve the problem.
Causes of bloating and gas formation in men
Depending on the causative agents of the disease, the degree of criticality of the situation also depends. If a person believes they are in excellent health but still exhibits symptoms, the following circumstances must be ruled out:
- fast food consumption;
- taking antibiotics;
- eating excessive amounts of berries and fruits, they cause fermentation (it is better to eat the gifts of nature an hour after eating);
- absorption of alcohol in large quantities;
- stress and depression.
Depending on the causes of flatulence in adult men, specialists select either drug treatment or diet. Disruption of the gastrointestinal tract also affects the intimate and emotional sphere of a person. Therefore, in order to avoid and develop diseases, it is necessary to take preventive measures:
- drink plenty of water (this cleanses all internal organs, nourishes them, and also improves metabolism);
- give up fatty foods;
- do simple physical exercises.
Among the main causes of intestinal flatulence in men, doctors note:
- inflammatory processes in the excretory tract (accompanied by pain when going to the toilet, in some cases bleeding);
- acute infections;
- infection with parasites (helminths);
- wearing tight belts (squeezing the intestines);
- colic.
If you belong to a risk group, that is, have one of the listed diseases, then you need to be regularly examined by gastroenterologists.
Changing microbial balance
Disruption of the natural balance between beneficial bacteria of the human intestine (lacto- and bifidobacteria) and opportunistic bacteria (clostridia, enterococci, yeast, staphylococci), as well as contamination of the gastrointestinal tract with pathogenic intestinal microflora lead to disruption of fermentation and digestion processes. As a result, a variety of clinical symptoms are noted, including constant rumbling in the abdomen and gases. Often, dysbiosis can be a consequence of a severe or insufficiently treated intestinal infection (salmonellosis, shigellosis, Proteus infection).
How to get rid of the problem of flatulence in this case is decided by the doctor (therapist, gastroenterologist or infectious disease specialist). First, it is necessary to conduct a special study (stool culture) to assess the degree of disturbances in the intestinal microbial system. To treat dysbiosis, a variety of drugs are prescribed, the action of which is aimed at restoring the disturbed microbial balance. All such drugs can be divided into two large groups:
- probiotics (lacto- and bifidobacteria) – actually beneficial bacterial flora, which displaces pathogenic flora from the intestines, due to which the microbial balance is restored;
- prebiotics are substances that create the most favorable conditions for restoring normal gastrointestinal microflora (lactulose, inulin, glutathione, chitosan, dietary fiber and others).
The duration of treatment, the specific drug or their combination are prescribed by the doctor. Buying the product you like at the pharmacy on your own can lead to even greater disturbances in the intestinal microflora.
Diagnostics
The doctor collects the patient’s complaints, data on eating habits, and conducts an examination. To determine the localization of gas accumulation, palpation and percussion are performed - the abdomen is tapped and palpated. The diagnosis is confirmed by the following methods:
- general and biochemical blood tests - with inflammation, an increased level of leukocytes is detected, with anemia, a drop in red blood cells and hemoglobin is observed;
- coprogram (stool examination) – reveals inflammation, helminthic infestations, helps assess the evacuation function of the intestines;
- radiography of the gastrointestinal tract - carried out if tumors, structural anomalies of the digestive tract, inflammatory diseases (gastritis, cholecystitis, duodenitis) are suspected;
- endoscopic examination - examination of the esophagus, stomach, colon, sigmoid or duodenum to identify obstruction, acute inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, tumors;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs - ultrasound examination of the condition of organs and tissues. The procedure allows you to identify abnormalities of the abdominal organs.
Mechanical obstruction
This is the worst and most difficult cause of excess gas. In fact, this is a confirmation of mechanical intestinal obstruction, which is most often caused by tumor growth. Having reached a significant size, the tumor node disrupts the patency of the gastrointestinal tract, feces are retained, which provokes increased processes of decay and fermentation, as well as excessive gas formation. In this case, symptoms such as loss of appetite, pain and a tendency to constipation are noted.
There are no home remedies. Only a doctor can decide what to do if such a situation develops. In the vast majority of cases, surgical intervention is required, the extent of which is determined individually. The prognosis depends on the severity of the process and the treatment performed.
Causes of appearance in women
Bloating in the lower abdomen occurs much more often in women than in men due to natural causes. Many women experience a feeling of distension of the peritoneum and accumulation of gases before the start of the active phase of the menstrual cycle. Before the onset of menstruation, fluid accumulates in the body due to hormonal changes, which increases blood flow to the pelvic organs. Liquid adds extra pounds and a small belly appears. The main causes of bloating in women include:
- menstruation;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- systematic overeating;
- increase in progesterone.
Physiological flatulence disappears immediately after the cessation of provoking factors. Treatment of bloating in this case comes down to reducing food and aggressive foods. If pregnancy or menstruation has passed, and constant bloating continues for a long time, then the following conditions can be suspected:
- development of uterine fibroids;
- functional liver disorders, up to cirrhosis;
- enterocolitis;
- intestinal diseases;
- intestinal obstruction;
- dysfunction of the pancreas.
Important! If your stomach is swollen and your lower abdomen hurts, you may suspect fibroids. Uterine fibroids in the early stages of development proceed latently, only occasionally manifesting themselves as bloating and painful menstruation. If unpleasant symptoms persist, an ultrasound of the pelvic and abdominal organs should be performed. Usually this method is the fastest and most informative for initial diagnosis.
Flatulence during pregnancy
The development of flatulence during pregnancy is due to the constant growth of the fetus and natural compression of the internal organs. Some women experience flatulence throughout pregnancy, starting from the moment the egg is fertilized. A disturbing accumulation of gases is a reason for diagnosis in order to exclude conditions potentially dangerous to the fetus. The main causes of abdominal distension during pregnancy include:
- production of progesterone (against the background of relaxation of the muscle tone of the uterus and a decrease in the motor activity of the digestive organs);
- pressure of the growing fetus on the intestines and adjacent organs;
- uncomfortable or tight clothing;
- poor nutrition, lack of routine;
- eating fruits or berries in unlimited quantities;
- desire to eat sweets, flour, sour.
Important! The body of a pregnant woman is under extreme stress, immunity is reduced to eliminate the risk of rejection of the fertilized egg. Women can help their bodies by creating a properly balanced diet.
Before eliminating bloating during pregnancy, obstetric history should be taken into account. Some drugs or herbs can cause permanent harm to the fetus. Normalizing your diet, small, frequent meals, and an active lifestyle (if necessary) will help avoid unpleasant sensations such as flatulence or heartburn.
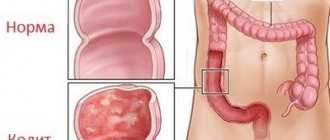
Inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
Pancreatitis, enteritis, colitis of various origins - all these diseases occur with disruption of digestion processes and, accordingly, are accompanied by increased gas formation. How to treat in each specific case depends on the cause of the disease, its severity and form. Most often, the following groups of medications are used to eliminate flatulence:
- carminatives (Simethicone, Dimethicone), which reduce the surface tension of the bubbles and their size, which facilitates the process of gases escaping;
- sorbents (Enterosgel, Polysorb, activated carbon) bind toxins and gases without being practically absorbed into the gastrointestinal tract;
- enzymes (Pancreatin and many of its commercial variants) facilitate the digestion of food, which helps reduce the amount of gases formed.
If you follow the doctor's recommendations, the problem of flatulence quickly disappears.
Traditional methods of treating flatulence
Very often, increased flatulence is treated using traditional medicine recipes. The combination of traditional medicine methods with time-tested traditional medicine recipes is recommended by doctors.
Infusion of fennel, valerian and mint
You need to take 2 parts of peppermint leaves, 1 part each of valerian root and fennel fruit. 2 tsp. The collection is poured into 200 ml of boiling water, left for 20 minutes and filtered. You need to take 100 ml in the morning and evening.
Carrot seeds
Carrot seed powder helps relieve bloating and eliminate increased gas formation. You need to take the powder 3 times a day, a teaspoon.
Currently reading: Flatulence and activated carbon: dose, contraindications, instructions and reviews
Dandelion root infusion
2st. L. Pour 250 ml of boiling water over crushed dandelion roots and leave for 24 hours, having first wrapped the container with the composition well. The finished infusion is filtered and taken 50 ml 5 times a day.
Ginger
After eating, it is useful to dissolve ginger root; it stimulates digestion, inhibits pathogenic microflora, and helps restore intestinal motility.
Camomile tea
1 tbsp. L. Chamomile flowers are poured with a glass of boiling water, the resulting composition is placed on low heat for 3 minutes, then left for 2 hours. The finished infusion is filtered and taken 2 tbsp. L. 15 minutes before eating.
Medicinal fee
You need to take 50 g of gentian herb, crushed rhubarb rhizomes, St. John's wort, angelica, calamus root, centaury herb. 2st. L. The collection should be poured with 500 ml of boiling water and the resulting composition should be kept in a water bath for 20 minutes. The finished infusion should be taken ½ glass three times a day before meals.
Infusion of dill and thyme seeds
You need to take one teaspoon each of dill and thyme seeds and mix, then pour 250 ml of boiling water. The resulting composition should be infused for 15 minutes in a closed glass container. It is recommended to take the infusion warm, 3 times a day.
Causes of pathology in men
Before using medications against gas, it is worth finding out what may be causing bloating. The sensations of flatulence in men and women are the same. Against the background of absolute health in men, increased gas formation and bloating occurs mainly for the following reasons:
- swallowing excess air with food;
- talking while eating;
- consumption of fermentation products;
- disruption of gas transportation (stress, overeating, change of usual diet);
- drinking carbonated drinks;
- the presence of semi-finished products and fast food in the diet;
- systematic intake of alcoholic beverages.
If the pathology persists for a long time, this is a reason to contact specialists for additional diagnostics. The main causes of non-physiological flatulence include:
- development of pancreatitis;
- chronic dysbacteriosis;
- colitis, enterocolitis, acute enteritis;
- symptoms of intestinal obstruction;
- stomach ulcer;
- inflammatory processes of the gastrointestinal tract.
Important! Alcohol and tobacco are more common among the male half of the population, so regular consumption of beer with any snack is a common cause of bloating. Smoking also provokes the absorption of air with smoke and the accumulation of excess gas in the intestinal cavity. If you have a burdened clinical history of gastroenterology, you should undergo additional research.