What is intestinal enterocolitis
Enterocolitis is the occurrence and development of an inflammatory process in the small and large intestines simultaneously, which at the initial stage manifests itself in an acute form, and in the absence of proper treatment, becomes chronic. The period of transition from one form to another passes quite quickly, so it is important to start treatment as quickly as possible.
Diagnostics
- Colonoscopy. An endoscopic examination allows you to carefully examine the mucous membrane of the large intestine and detect characteristic inflammatory changes in its wall. During the procedure, you can take a fragment of the organ mucosa - a biopsy sample.
- Histological examination. The resulting mucosal sample can be examined under a microscope and its cellular composition can be determined. The study allows you to confirm the diagnosis of enterocolitis and carry out differential diagnosis with other diseases.
- Coprogram. Stool examination reveals characteristic microscopic changes - the presence of leukocytes, mucus and blood.
We recommend reading:
Gastroenterocolitis: symptoms and treatment methods (diet, medications)
Differential diagnosis of the disease should be carried out with the following diseases:
- peptic ulcer of the stomach and intestines;
- botulinum toxin poisoning;
- acute intestinal obstruction;
- arsenic or mushroom poisoning;
- acute appendicitis.
It is necessary to differentiate the disease on the basis of the clinical picture of the disease, as well as data from laboratory and instrumental studies.
Causes of enterocolitis
The causes of enterocolitis may be:
- bacterial, intestinal infections of the gastrointestinal tract, such as salmonellosis, dysentery, typhoid fever, shigella);
- disturbances of intestinal and stomach microflora;
- parasitic infections: trichomonas, amoebic, lamblia;
- intoxication due to taking chemicals or medications;
- unbalanced diet, abuse of fried, spicy, salty foods, as well as long periods of time between meals;
- chronic diseases of the gallbladder, liver, pancreas, gastrointestinal tract;
- weakening of the immune system;
- abnormal intestinal structure, defective form;
- stressful situations, depression;
- hormonal disorders.
Infectious enterocolitis
Enterocolitis primarily affects the large intestine area. But there is an opinion that when this area is damaged, the inflammatory process spreads to the small intestine.
The causes of the development of the disease are of two types: infectious and non-infectious. Each of them has different symptoms.
Infectious enterocolitis occurs:
- parasitic type . Manifests itself due to the penetration of a parasitic infection in the form of worms, trichomonas, amoebas;
- bacterial type . Includes a large group of infectious agents in the form of streptococcus, staphylococcus, salmonella, shigella, and E. coli.
Infectious colitis is contagious to others.
It can be transmitted through unwashed hands, poor-quality products, and poor cooking.
In children's groups, enterocolitis caused by staphylococci is most often observed. If an infant becomes infected with it, the course of the disease will be very difficult. In adults, staphylococci colonize the intestinal canal, so the disease occurs rarely and only when the immune function is weakened.
In practice, another pathogen is also isolated in the form of clostridia. It acts directly on the mucous membrane of the intestinal canal and poisons the body with a strong poison.
Thus, the patient develops pseudomembranous colitis. It is observed against the background of long-term use of antibacterial agents, which lead to an increase in clostridia in the body.
According to statistics, approximately three percent of adults act as carriers of this pathogen. They can live for a long time and not harm the body. But as immune function weakens, their activity increases.
The causes of the disease can be various formations of a malignant and benign nature, surgical interventions, and impaired blood flow in the intestinal cavity.
Symptoms of enterocolitis
Most often, severe symptoms accompany acute enterocolitis; chronic enterocolitis is less pronounced, but is more life-threatening.
Let's look at the most obvious signs of this disease:
- Pain in the abdomen, often in the umbilical region, but can also be diffuse throughout the entire abdominal cavity; the intensity depends on the severity and severity of the inflammatory process. The small intestine gives dull and moderate sensations, while the thick intestine manifests itself in more intense and pronounced pain. The pain intensifies with minimal physical activity, hunger, fast walking, while running and before bowel movements.
- Alternation of intestinal disorders and constipation.
- Feeling of sourness in the mouth.
- Pale skin, slight feeling of nausea.
- Prolonged feeling of flatulence, as if you had swallowed a ball, increased gas formation.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system, in other words, dyspeptic syndrome, in which food remains in the intestines begin to ferment, rot, etc.
- Fatigue, lethargy, weakness, apathy, decreased concentration.
- A noticeable decrease in total body weight, as a result, lack of appetite and disorders of the digestive functions in the body, as well as inadequate work and functioning of the pancreas.
Forms of enterocolitis
There are several forms of this disease:
- Acute form . The cause of its occurrence may be severe poisoning or a certain infection. With its development, pathological conditions arise in the upper layers of the mucosa with a simultaneous exacerbation of gastritis.
- Chronic form . With this form, almost all parts of the digestive system are affected. The main cause of the disease is difficult to diagnose, so a comprehensive course is selected for treatment, which simultaneously affects all symptoms. If there is a suspicion of intestinal enterocolitis, only a specialist should study the symptoms, who will prescribe an appropriate course of treatment, including a mandatory diet.
Acute form of intestinal enterocolitis
In acute enterocolitis, symptoms develop rapidly, accompanied by active bouts of seething and bloating. Vomiting, nausea, pain in the abdominal area (cutting pains), and diarrhea occur.
Infectious enterocolitis
If the cause of enterocolitis is the development of an infection, then the following symptoms will be added to the already listed symptoms:
- stool may acquire a specific odor mixed with blood or pus;
- muscle aches;
- fever appears with chills and weakness;
- severe headaches.
Chronic form of intestinal enterocolitis
In the chronic form of enterocolitis, the clinical picture can vary significantly. Symptoms may be completely absent or, conversely, very active.
The development of this form of the disease is characterized by:
- weight loss;
- increased pain in the abdominal area;
- development of absent-mindedness and passive state;
- hair becomes dull;
- the skin becomes pale in color;
- increased nail fragility;
- constipation may be replaced by loose stools.
Treatment of enterocolitis with folk remedies, the most effective
Traditional medicine is rich in recipes for intestinal colitis; it is enough to choose the right remedy for treatment, and then you can do without additional drug therapy.
Recipe No. 1
The recipe will help in the fight against constipation and excessive heaviness in the intestines. For five days, prepare and take the following mixture: 70 milliliters of kefir + 30 ml of skate + 30 ml of castor oil.
Take in the morning on an empty stomach, once a day, after that do not drink or eat for half an hour. Fresh mixture should be prepared daily. Treatment should be carried out in this way - one five-day course, once every six months.
Recipe No. 2
Dry the pomegranate peel a little and beat with a blender, pour 2 tablespoons of the powder into 250 ml of warm water, cover with a lid and let it brew for 3-4 hours. Take a tablespoon three times a day before main meals and another 1 tablespoon 1-1.5 hours before bedtime.
The course is one week, then a two-week break and can be repeated, in total it is permissible to carry out 3 courses of treatment at a time.
Recipe No. 3
Grind 50 grams of ginger root in a blender or grate it on a fine grater, and grind with 100 grams of soft butter until smooth, put in the refrigerator until it hardens.
Take for 12 days, according to the following scheme: 1st and 12th day, 0.5 teaspoons, 2nd and 11th, 1 teaspoon, 3rd and 10th, 1.5 teaspoons, 4th and 9th, 2 teaspoons .spoons, from 5th to 8th to 2.5 teaspoons.
In just one year, two courses of treatment are allowed.
Recipe No. 4
A tasty, healthy and irreplaceable recipe for the treatment of enterocolitis. You need to mix 100 grams of walnuts, raisins, 250 grams of dried apricots, 350 grams of prunes and 50 grams of senna grass, grind through a meat grinder or grind with a blender, pour in 100 ml of liquid honey, mix well, store the mixture in the refrigerator.
Take a full teaspoon on an empty stomach in the morning and before bed for 30 days, then for another month, take half a teaspoon only in the morning, once a day. The course is carried out 1-2 times a year.
Recipe No. 5
Pour 0.5 dessert spoons of chamomile, centaury and sage herbs into a glass of boiling water, leave for 30 minutes under a closed lid, strain and divide the finished volume into 3 equal portions. Take before breakfast, lunch and dinner – 10 days. If you have constipation, you can add 10 ml of honey to the infusion.
Recipe No. 6
Blend one small, peeled potato, 1 carrot and 15-20 grams of sorrel with a blender, dilute the mixture with a glass of water at room temperature, and drink the resulting fresh juice 0.5 cups before breakfast on an empty stomach and 2 hours before bedtime. Course 10-14 days.
Recipe No. 7
Pour 200 ml of boiling water over a dessert spoon of cumin and dill seeds, leave for 1 hour, drink 2 tablespoons, 3-4 times a day, regardless of meals, for 21 days. Prepare fresh mixture every three days.
Recipe No. 8
Pour 100 grams of dried watermelon rinds and 50 grams of watermelon seeds into half a liter of boiling water and boil for 15 minutes over low heat, leave for 1 hour, strain, drink 100 ml, 4 to 6 times a day - 10-14 days.
Recipe No. 9
Place a liter of medical alcohol, 100 grams of crushed propolis in a dark aluminum or glass container, leave for 5-7 days in a dark, warm place. Take a dessert spoon three times a day, half an hour before meals, with a glass of water. The minimum course is 3 weeks, and the maximum duration of treatment can be 4 months.
Recipe No. 10
Pour 2 tablespoons of fresh elecampane roots with 0.7 liters of Cahors wine, simmer for 5 minutes, but do not bring to a boil, and cool.
Take 50 ml once a day after meals for 10-12 days, then a three-month break and the course can be repeated.
Treatment of enterocolitis in childhood
This pathological process in childhood can be caused when an infection enters the child’s body.
Drug treatment is prescribed using non-narcotic analgesics and antispasmodics to relieve a pain attack
Most often this is caused by:
- Bacteria (staphylococci, E. coli, dysentery coli, salmonella).
- Viral infection (adenovirus or rotavirus).
- Parasitic intestinal infection by helminthic infestations.
Also in the biomechanism of development there may be factors of a non-infectious process:
- Consumption of spicy foods.
- The appearance of allergies.
- Large use of antibiotics.
Factors that can trigger the development of enterocolitis are:
- Underdevelopment of the internal digestive organs.
- Infection of the fetus during pregnancy.
- Abnormal structure of the stomach and intestinal tract.
- Concomitant diseases with metabolic disorders (diathesis).
- Bad ecology.
The clinical picture of enterocolitis in children is the same as in adult patients, but it is accompanied by more severe symptoms:
- The child develops spasmodic pain in the abdominal area, sometimes localized under the right rib or in the navel area.
- Disorder of the act of defecation, in the form of diarrhea, can occur up to 10 times a day.
- The stools become watery, often streaked with blood, and contain greens and mucus. Feces have a foul odor.
- The temperature rises sharply.
- There is regurgitation of food or vomiting.
- Headache, lethargy, and apathy appear.
- In some cases, joint or muscle pain is observed.
- Bloating leads to an increase in its volume, and is accompanied by belching and heartburn.
- Diarrhea gradually stops and is replaced by constipation.
Treatment of this pathology in childhood is carried out in three areas:
- Dieting. It is imperative to limit food that is consumed raw (fruits, vegetables); eating dishes with a high concentration of table salt, hot and spicy spices is unacceptable. Food should be low-fat; when preparing meat dishes, use lean varieties of meat. It is advisable to steam fish and cutlets. Eat more slimy porridges and rare soups.
- Drug treatment is prescribed using non-narcotic analgesics and antispasmodics to relieve a pain attack. It is allowed to apply a warm heating pad to the abdominal area. In case of damage to the large intestine, it is necessary to use microenemas as therapy. For this purpose, you can use a decoction of calendula or chamomile.
- A good effect in the treatment of enterocolitis can be achieved using traditional medicine recipes. For this, decoctions and infusions of chamomile, mint, valerian roots, fennel seeds, and calendula are used.
In the youngest patients, the course of this pathological process has its own characteristics. Since their intestinal environment suffers from a deficiency of bifidobacteria. The immune system has not yet developed sufficiently and therefore infection easily penetrates into the newborn’s body.
The disease in newborns is severe, can cause significant weight loss, and take a protracted course.
Enterocolitis occurs even more complexly in children with varying degrees of prematurity. Since their swallowing and sucking reflexes are underdeveloped, their enzymatic function is reduced. The passage of feces through the intestinal lumen is significantly reduced.
An underdeveloped immune system causes a high number of pathogenic microorganisms in the intestines of a premature baby.
In premature babies, due to the above factors, several infectious pathogens may be present in the intestines at the same time.
This contributes to the development of necrotizing enterocolitis. Often this pathology causes a large number of complications and leads to death.
When treating newborns it is recommended:
- Stop eating by mouth and switch to parenteral nutrition (using IVs).
- Mandatory prescription of broad-spectrum antibiotics.
- The use of enzymatic preparations that improve digestion.
- Mandatory use of drugs from the pharmacological group of prebiotics.
Treatment of enterocolitis in adults with drugs
To treat a disease, several groups of drugs are often prescribed to relieve unpleasant symptoms, alleviate the general condition, relieve the inflammatory process, and also have a direct therapeutic effect.
Let's consider the most effective medications for the treatment of intestinal enterocolitis:
- But - Shpa, Spazmalgon - will help relieve or alleviate pain, as well as relax the intestinal muscle tissue;
- Espumisan, Kolikid, Motilium, Meteospasmil - are prescribed to eliminate bloating and increased gas formation in the body;
- Linex, Laktovit, Bififormula, Bifidumbacterin - a group of probiotics that prevent fermentation processes in the gastrointestinal tract and intestines, help maintain sufficient, normal microflora;
- Duphalac, Picolax, Normolakt - will help in the fight against constipation and facilitate the process of bowel movements.
- Mezim Forte, Pancreatin, Creon, Panzinorm - improve the functioning of the pancreas, stimulate additional production of pancreatic enzymes.
Therapeutic measures
After diagnosis, enterocolitis is treated, which depends on the course of the disease.
Acute form
If the patient has acute enterocolitis, treatment is carried out in a hospital setting. During the entire therapy, strict bed rest must be observed.
In the hospital, an adult is given:
- probing for gastric lavage. For this, ordinary boiled or distilled water is used. If the patient has no contraindications, then sodium bicarbonate can be used;
- cleaning the intestinal cavity with a saline laxative. After this, the patient undergoes enterosorption. It involves taking enterodesis up to four times a day with boiled water;
- detoxification therapy with the consumption of large amounts of fluid.
On the first day, the patient must fast. The next day, liquid dishes are gradually introduced. When the symptoms of enterocolitis subside, the diet is gradually increased.
In case of infection, the patient may be prescribed antibiotics for enterocolitis, antiparasitic drugs and antiviral agents. The duration of treatment therapy ranges from seven to ten days, depending on the severity of the disease.
After the acute phase of the disease has passed, the patient is prescribed enzymes and lactobacilli. Additional therapy is carried out for immunodeficiency and metabolic disorders.
Diet for intestinal enterocolitis in adults
This diagnosis requires some adjustments in diet, especially in the acute course of the disease; we will consider a number of permitted and prohibited foods.
Can:
- fresh or boiled vegetables, soups - pureed vegetables, everything is possible, except those that can provoke increased gas formation;
- fruits: apples, pears, peaches, either fresh or baked;
- cereals: buckwheat, oatmeal, rice, corn;
- soups with low-fat meat or vegetable broth, as well as pureed soups;
- meat and fish of low-fat varieties, boiled, baked, in the form of minced meat;
- fermented milk products - kefir, fermented baked milk, cottage cheese, sour cream are possible, but in limited quantities, and during the period of exacerbation of the disease, it is better to refuse;
- yesterday's bread, preferably from durum wheat, crackers, fresh baked goods, should be excluded;
- fruit and berry jelly, weak tea/coffee, refreshing, unsweetened compotes;
- You can have sweets, but in minimal quantities, 2 teaspoons of sugar per day is the norm, you can also have 20-30 grams of chocolate or half a marshmallow.
It is forbidden:
- fresh bread, products made from white, wheat flour, as this will only aggravate the production of gases in the intestines;
- rich fish or meat broths;
- pasta, legumes, peas;
- fatty, fried foods;
- marinades, smoking, pickling, preservation;
- semi-finished products;
- fresh pumpkin, watermelon, radish, melon;
- dairy products with high fat content, in particular homemade ones;
- strong coffee, tea, cocoa;
- peanuts, almonds;
- eggs should be kept to a minimum in your diet, you can eat 1-2 per week;
- It is better to exclude butter, but no more than 50 grams per day is allowed.
Sample menu for enterocolitis:
Option #1:
- Breakfast : oatmeal on water with two steamed lean meat cutlets, rosehip tea with a teaspoon of sugar.
- Snack : grated apple or pear.
- Lunch : beef soup with potatoes and vegetables, vegetable salad dressed with olive oil, a slice of bread.
- Snack : dried fruits (prunes, dried apricots, dates) soaked in water in the amount of 80-100 grams.
- Dinner : compote, cottage cheese casserole without sugar, with raisins, with the addition of one egg.
Option #2:
- Breakfast : weak coffee, rice porridge cooked in water with salt and a piece of butter, salad of cucumbers, onions and tomatoes.
- Snack : a glass of jelly, 2 biscuits.
- Lunch : cauliflower and potato puree, 150 grams of boiled beef or chicken.
- Snack : apple and carrot salad.
- Dinner : salad of fresh vegetables, fish, steamed or baked in the oven.
Forecast
Enterocolitis is a condition that requires medical attention. Inflammation in the body poses a danger to the digestive tract. A person must promptly detect the ailment and visit a specialist. Enterocolitis should be treated at the acute stage of development, since the chronic form is difficult to get rid of. The sick person will have to restrict himself in nutrition, take medications, and suffer from abdominal pain. The pathology also disrupts the function of other internal organs. The man is lethargic and drooping.
If you seek help in time, you can eliminate enterocolitis and prevent the development of complications. The gastrointestinal tract is very important for a person’s successful life. Healthy food will improve your mood, relieve inflammation and overcome stress. There is no need to injure the digestive system, then chronic enterocolitis will be avoided. Since this form limits the intake of many foods.
We recommend: What is gastroenteritis and what are the symptoms in children
Prevention of enterocolitis
In order not to encounter a disease such as enterocolitis, you need to take into account the rules and habits of a few simple recommendations:
- Eat nutritiously and rationally, so that your daily diet contains a sufficient amount of proteins, fats, carbohydrates and microelements.
- It is imperative to have breakfast, and not just have morning coffee on an empty stomach, this bad habit is the first provocateur of the development of the disease.
- Breaks between meals should not be more than 2.5 - 3 hours.
- Drink enough water to avoid dehydration and make bowel movements easier.
- Visit a gastroenterologist at least once a year.
- Take general strengthening medications to maintain immunity.
- Avoid overeating, eat small portions.
- Do exercises; with mobility, the intestines begin to work more actively and this prevents constipation.
Enterocolitis, a disease that can remain silent for a long time, if you periodically begin to feel heaviness in the pancreas, then this is one of the first alarm bells that it’s time to visit a doctor to confirm or refute this or that diagnosis. Lead an active lifestyle and be attentive to your health.
Rate this article: ( 9 ratings, average: 4.67 out of 5)
Classification
Depending on the origin, all enterocolitis is divided into primary and secondary diseases. Primary pathology is systematized depending on the cause and includes the following enterocolitis:
- Bacterial.
- Viral.
- Toxic.
- Fungal.
- Mechanical.
- Nutritional.
Secondary enterocolitis does not belong to independent nosological entities. They develop as a result of the development of other pathological processes in the body and belong to the corresponding syndrome.
Effective drugs for enterocolitis
Intestinal inflammation is eliminated using different groups of remedies. They can be used both in combination and separately, depending on the doctor’s recommendations and the individual course of the clinical picture. Which groups of drugs are recommended for enterocolitis:
- Antibiotics - “Enterofurin”, “Furazolidone”, “Erythromycin”, “Cefazolin”, “Zinnat”, “Cedex”, “Ampicillin”, “Lincomcin”, “Clindamycin”;
- Steroids for the absorption of protein, increasing its level in the body. Prescribed: “Lipofundin”, “Intralipid”. Dissolve the required amount of powder in warm water, 2 grams each. per 1 kg of weight;
- Vitamin mineral complexes. Prescribed to compensate for the deficiency of beneficial microelements. It is recommended to drink folic acid, ascorbic acid and any complex containing B vitamins;
- Sorbents - “black coal”, “Smecta”, “Polipefam” help remove toxins if inflammation is caused by intoxication;
- Prebiotics – restore damaged microflora. It is advisable to drink - “Linex”, “Acepol”, “Laktovit”, “Biovestin”, “Bifikol”;
- Enzyme agents help food to be well absorbed and prevent food from rotting in the intestines and stomach. Among the enzyme preparations used for enterocolitis are “Pancreatin”, “Mezim”, “Creon”
Each medicine has its own characteristics, contraindications, and side effects. Therefore, taking medications approved by a doctor is the surest path to recovery.
- Crohn's disease: symptoms and treatment in adults
- Intestinal adhesions symptoms and treatment
- Miliaria in adults photo symptoms and treatment
- Umbilical hernia in adults: symptoms and treatment
Tags: adult, intestines, treatment, symptom, enterocolitis
- Related Posts
- Cystitis in women: symptoms and treatment at home quickly
- How to treat cough during pregnancy
- Dizziness, causes and treatment with folk remedies
« Previous entry
More about intestinal problems
If the first symptoms of intestinal enterocolitis occur in a patient of any age, you should not hope that it will go away; it is important to consult a specialist in time - a family doctor or gastroenterologist, undergo a full examination and receive recommendations for treatment and care.
Enterocolitis what is it
Despite the fact that it is always difficult to treat the intestines, if time is not lost and everything passes without delay, then you can quite count on a successful outcome.
Such a diagnosis is far from a death sentence; despite certain features, the pathology is completely curable:
- Symptoms of bowel disease persist for a long period.
- The disease is characterized by a chronic process, quickly followed by an acute period.
- Even with high-quality therapy, relapses and exacerbations can occur.
- If there is negligence in following the doctor’s prescriptions and non-compliance with such things as diet for enterocolitis in adults, the process not only worsens, it rapidly worsens, new symptoms appear, and the course becomes much more severe than during the initial treatment.
- Tests for this disease are not always comfortable and painless, which is due to the specific physiology of the gastrointestinal tract.
- In the event of a complete diagnosis requiring surgical intervention, it is very dangerous to delay making a decision; this can lead to irreparable consequences.
Important! The slightest discomfort in the intestinal area, signs of indigestion and bloating with the appearance of pain and colic, constant or paroxysmal nausea, vomiting, fluctuations in body temperature, upset stool or prolonged spontaneous constipation in combination or each symptom individually may well make you think about serious problems .
Description of the disease
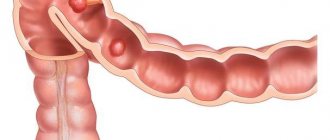
The name “enterocolitis” explains the nature of the damage to the gastrointestinal tract, “enteritis” - the small intestine, “colitis” - the large intestine. Unlike chronic enterocolitis, acute enterocolitis has pronounced symptoms, causes pain and discomfort to the patient, and worsens the quality of life.
The acute form of the disease requires timely treatment, as it can develop into a chronic form. To understand why the disease occurs, it is necessary to pay attention to the anatomical features of the structure of the gastrointestinal tract. The intestine ends in the large intestine, through which undigested food remains are removed. This happens through the rectum. In addition to it, the intestines contain the following intestines:
- sigmoid;
- colon;
- transverse;
- ascending;
- blind.
Enterocolitis is a disease that affects the lining of the colon, leading to problems in the functioning of the intestine. This is due to inflammatory or dystrophic processes in the colon. The large intestine contains a suitable environment for the residence of many microorganisms. Although most of them are positive, for example, lactobacilli, there are also opportunistic ones - E. coli and others. Infection multiplies in such an environment especially rapidly.
Prevention
Prevention of intestinal diseases consists of measures taken to avoid factors leading to the occurrence of enterocolitis. These include:
- Quickly identify intestinal problems and eliminate them.
- Maintaining a proper diet.
- Taking medications as prescribed.
From our material you learned the symptoms of enterocolitis, how treatment is carried out in children and adults. We figured out the types of enterocolitis and diets.
It is worth noting that this disease cannot be treated with folk remedies. This approach will lead to complications in most cases. This is especially true for staphylococcal and viral enterocolitis.
Enterocolitis in newborns is especially dangerous. Therefore, if you notice the symptoms described above in yourself or your child, be sure to consult a doctor!
Author: Daria Tyutyunnik, doctor, especially for Zhkt.ru
Treatment of chronic enterocolitis
To successfully treat enterocolitis, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of its occurrence in the body. To achieve this, the following activities are carried out:
- it is necessary to normalize the diet and nature of nutrition;
- discontinue medications that disrupt the functioning of the intestinal tract;
- cure parasitic or bacterial infection;
- carry out therapy for all diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
After eliminating the root cause of enterocolitis, it is necessary to cope with motility disorders, digestive disorders and dysbiosis.
Treatment of chronic enterocolitis is impossible without prescribing an individual diet. In the absence of exacerbations, table No. 2 is prescribed; for a disease that is accompanied by frequent constipation, table No. 3 is appropriate; in case of a large number of diarrhea, treatment table No. 4 is prescribed.
In case of severe dyspepsia, it is necessary to limit the consumption of foods: the putrefactive nature of the course - coarse fiber, meat, fish, fermented milk products, the fermentative nature of dyspepsia should exclude the presence of rye bread, whole milk, cabbage, and sugar in the diet.
When the main part of the inflammatory process is localized in the small intestine, it is recommended to eat foods rich in proteins, vitamins and microelements, and large amounts of calcium. It is necessary to remove from the diet everything that can irritate the mucous membranes - sour, salty, spicy and fried.
Treatment of chronic enterocolitis with medications:
- To suppress pathological flora, it is necessary to use antibacterial agents (enterofurin, furazolidone);
- Enzyme-containing products (Creon, pancintrat) will help restore normal digestion;
- For restoration, pro- and prebiotics with lacto-, bifido- and enteric bacteria, as well as media for the development of these bacteria, are also used;
- Drugs that help normalize intestinal motility (loperamide, trimebutine, mebeverine).
Local treatment of enterocolitis can be carried out using microenemas with herbs. Oak bark, bird cherry and St. John's wort will help eliminate diarrhea. Sea buckthorn oil helps against constant constipation, and chamomile will relieve flatulence.
Vinilin has been successfully used to heal ulcers and erosions; it is also advisable to use it when necessary to stop bleeding.
In case of mental depression in the treatment of chronic enterocolitis, consultation with a psychotherapist may be required.
It is necessary to consult a physiotherapist in order to select a comprehensive physiotherapeutic treatment for enterocolitis, including: procedures aimed at cleansing the intestinal tract, SMT, reflexology, magnetic therapy.
Therapy in sanatoriums at balneological resorts during remission is highly effective, as it always leads to an improvement in the general condition and consolidation of the results of the main course of treatment.
During periods of exacerbation of chronic enterocolitis, it is necessary to reduce physical activity. When clinical symptoms subside, it is important to regularly do therapeutic exercises, walk and do aerobics. It is necessary to lead a fairly active lifestyle in order to normalize digestion processes and all body functions. You should not engage in sports in which there is a high risk of abdominal injury.
It is necessary to do exercises to strengthen the abdominal muscles to improve the regulation of pressure in the abdominal cavity and have a beneficial effect on bowel function.
Treatment is medicinal
Treatment for each form is carried out in different ways, as soon as the first symptoms of the disease appear, it is necessary:
- change your diet for a positive result from treatment;
- the patient must follow a strict diet.
For the treatment of acute form:
- The patient needs to fast for the first days and follow a diet that includes only tea and water.
- The consumption of foods should be completely excluded; you can drink water with the addition of lemon, the volume should not exceed 2 liters, throughout the day.
If there is diarrhea and vomiting, to treat an illness with the following symptoms:
- the patient can have his stomach washed out;
- prescribe medications for diarrhea and medications to prevent dehydration;
- in this case, it will be useful for the patient to drink a decoction (rice) or liquid rice porridge.
To relieve pain:
- the doctor prescribes antispasmodic drugs;
- if treatment is performed inpatiently, then the patient is given droppers with these medications.
When treating chronic enterocolitis, you first need to eliminate the cause of the disease.
The cause of the disease is eliminated in this way:
- First of all, the patient needs to normalize the diet and review the daily menu.
- You need to stop taking medications that disrupt your digestion.
- It is necessary to cure all existing diseases associated with the gastrointestinal tract.
- Get rid of all pathogens of infectious and viral origin.
After the causes of enterocolitis have been eliminated, it is necessary to treat the digestive system. All patients must strictly adhere to the prescribed diet.
The doctor prescribes medications after diagnosis; these can be the following medications:
- antibacterial drugs to suppress pathological microflora;
- to restore the nutritional environment, it is recommended to take probiotics and prebiotics;
- the doctor will also prescribe medications to normalize intestinal motility;
- To normalize digestion, it is recommended to take products containing enzymes.
You can also do small-volume enemas from medicinal herbs:
- if the patient suffers from diarrhea, then it is necessary to do enemas from the infusion of St. John's wort, oak (bark) or bird cherry;
- if a person has flatulence, then the enema should be chamomile decoction; for constipation, sea buckthorn oil should be administered.
A person who has developed mental disorders due to enterocolitis needs to visit a psychotherapist.
In the chronic form, a person needs to consult a physiotherapist.
The specialist will select the necessary physiotherapeutic measures for the patient, including:
- procedures aimed at cleansing the body;
- SMT therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- reflexology.
During periods of remission, visiting a balneological resort will have a positive effect on consolidating treatment and improving the condition. In moments of exacerbation of the disease, it is necessary to exclude physical stress.
When symptoms stop appearing, the patient is advised to:
- Do physical exercises of a therapeutic nature and aerobics.
- The patient also needs to be in the fresh air every day. Thus, a person will restore the functions of the digestive system and the entire body.
- When choosing exercises for physical education (therapeutic), the patient must avoid all sports that can cause injury to the abdomen.
Diet for enterocolitis:
- After the patient limits himself to food intake for some time and drinks only water and tea, on the third day you can gradually begin to introduce apple puree into the menu; consumption is allowed only in small portions.
- A little later, the patient can gradually introduce other foods into the diet, the main thing is that they do not irritate the mucous membrane and do not contribute to excessive secretion of gastric juice.
The following foods are acceptable for consumption:
- Any cereal cooked in beef broth. The cereal must be cooked until it is softened.
- Blueberry or currant cocktails.
- Steamed cutlets or meatballs made from low-fat meats.
- Strongly brewed tea.
- Low-fat cottage cheese.
DETAILS: Treatment of amblyopia – Eye Surgery Center
After treatment for intestinal enterocolitis is completed and the disease has subsided, a person must carefully monitor the daily diet, otherwise an exacerbation of the disease may occur.
You can include the following foods in your diet:
- cottage cheese (homemade);
- tea with honey;
- white bread (preferably dried);
- dairy products;
- crackers;
- a variety of oatmeal or rice dishes (the main thing is that the cereal is well boiled);
- fruit jelly.
If after eating any food a person begins to feel unwell, he needs to remove this product from the diet or try to reduce the amount of carbohydrates consumed.
If the patient has chronic enterocolitis and there is a lack of proteins in the body, it is necessary to introduce as many protein-rich foods into the menu as possible and reduce the consumption of carbohydrates.
Protein-rich foods include:
- cheeses of different varieties;
- butter;
- potato or vegetable puree;
- chicken meat;
- low-fat fish;
- beef.
If the patient suffers from constipation, it is advisable for emu to eat more foods high in fiber, such as various vegetable salads, plums, and prunes.
A diet for intestinal enterocolitis is prescribed only by the attending physician, after analyzing all the examination results and the person’s condition.
If a person has severe dyspepsia, then he needs to limit the consumption of the following products:
- complex protein;
- coarse fiber;
- bread made from rye flour;
- cabbage;
- milk and fermented milk products;
- products containing sugar.
The decision on restrictions on the intake of any products is made only by the doctor based on the test results obtained.
If the inflammatory process occurs in the small intestine, then it is advisable for a person to eat:
- more products containing vitamins, proteins, microelements
- exclude all products that may irritate the mucous membranes.
With each form of enterocolitis, a person is haunted by quite unpleasant symptoms, if detected, it is necessary to consult a doctor as quickly as possible.
The specialist, having examined and listened to the patient’s complaints, will refer him for the necessary examination. After receiving the results, the doctor will prescribe the necessary treatment and advise how best to eat during this period of time.
You cannot treat the disease on your own; this can significantly complicate the existing situation.
Therapy for different forms of pathologies differs. Treatment of the acute form is aimed at directly eliminating pronounced symptoms and normalizing the functioning of the digestive tract. Chronic enterocolitis is eliminated in a comprehensive manner; the doctor first identifies the source of the disease and then eliminates tangible signs. Therapy for the chronic form includes the following methods:
- Drug therapy aimed at eliminating the cause and symptoms of intestinal inflammation;
- The patient’s lifestyle is normalized - nutrition is regulated (therapeutic diet), work and rest patterns are changed;
- Medicines that negatively affect the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract are eliminated or replaced.
The main methods of treatment for both forms:
- Removal of toxic substances - detoxification, if the pathology was caused by toxins, spoiled, unhealthy food;
- Medicines of different directions of action;
- Diet No. 3;
- Physiotherapeutic procedures;
- Folk remedies.
Complex therapy allows the patient to quickly recover and return to normal life.
In the remission phase of chronic enterocolitis, a number of physiotherapeutic procedures are carried out aimed at overall improvement of the intestines, reducing the number of exacerbations and their duration. What physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed:
- A set of physical therapy exercises is selected;
- Magnetic therapy is carried out;
- Reflexology sessions;
- Balneology.
During the exacerbation phase, doctors strongly advise against exercising, but when remission occurs, physical activity increases intestinal tone and improves its functioning.
The right folk recipes help improve the condition and cope with the discomfort that arises from intestinal inflammation. What traditional medicine advises:
- Dill water. You need to add 10 ml of dill oil to 100 ml of warm water. Drink 2 tsp 2-3 times a day;
- Mint decoction. Take 2 tbsp. l peppermint and brew in 250 ml of boiling water, let it brew for 2-3 hours. Drink half a glass three times a day;
- Thyme infusion. You need to pour 2 teaspoons of thyme into 3 cups of boiling water, leave to steep for 2-4 hours. Drink 50 ml of the resulting liquid;
- A decoction of chamomile and valerian. Take the ingredients in equal quantities and mix together. For 20 gr. herbal mixture requires 1 liter of boiling water. Drink 100 ml half an hour before meals 3-4 times a day.
Acute enterocolitis responds well to treatment if it is carried out in a timely manner. The first improvements are observed on days 5-7 of intensive treatment. Complete recovery with restoration of intestinal microflora is achieved after 4 weeks of treatment. The prognosis for chronic enterocolitis depends on the quality, composition of treatment, and how long the disease lasted without taking any measures.
Enterocolitis is not a diagnosis or a disease. This is a disease syndrome that manifests itself with several symptoms:
- Nausea
- Vomit
- Pain in all parts of the abdomen
- Change in stool consistency with or without pathological impurities in the stool (mucus, blood)
Depending on the individual characteristics of the body, one of the symptoms may manifest itself to a greater or lesser extent. For example, vomiting can occur 1 time or 5 times, and loose stools 7 times or 2 times, but in any combination these symptoms indicate a pathology of intestinal function.
In order to decide on treatment, it is necessary to find out the cause of the disease. To do this, several factors are assessed:
- Epidemiological anamnesis. If attacks of illness began after eating spoiled food, then most likely this is an infectious process called foodborne toxic infection.
- Life story. The manifestation of symptoms of enterocolitis several times a year means that the disease tends to be chronic and most likely associated with pancreatitis, cholecystitis or gastritis.
- Medical history. The onset of the disease after consuming large amounts of fatty foods or butter dough, sweet carbonated drinks indicates pathology not only of the pancreas and gall bladder, but also of the intestines themselves.
- Heredity. All diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are inherited to a greater or lesser extent. Therefore, in the differential diagnosis of any disease in this department, it is necessary to clarify the chronic diseases of blood relatives. Sometimes this helps in diagnosing such serious diseases as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
Patients with acute enterocolitis require hospitalization in the gastroenterology department or infectious diseases hospital. First of all, detoxification and replenishment of fluid deficiency are carried out. For this purpose, intravenous infusion of water-salt solutions is established, gastric lavage and cleansing enemas are performed. On the first day of the disease, therapeutic fasting is required, then rice water, mucous porridges, and “second” broths are introduced into the diet.
Drug treatment consists of prescribing antispasmodics, antibiotics and drugs to restore intestinal microflora. If the cause of acute enterocolitis is precisely known, therapy should be etiotropic (antibacterial drugs are not prescribed unnecessarily, antiparasitic drugs may be required, etc.).
Enzyme preparations and means for normalizing intestinal motility are used as symptomatic treatment. To wash the stomach and intestines, it is recommended to use herbal decoctions (chamomile, calendula, etc.). For severe diarrhea, a decoction of oak bark, bird cherry and St. John's wort in the form of tea will help. Sea buckthorn oil, taken orally, promotes healing of the intestinal mucosa.
The diet for acute enterocolitis depends on the level of damage (mainly the small or large intestine), the nature of the pathological processes in the intestine, and the type of dyspeptic disorders. If the small intestine is damaged, more protein, vitamins and microelements should be included in the diet. In case of putrefactive processes in the intestines, protein, on the contrary, is excluded, as are fiber and fermented milk products. If fermentation processes predominate, it is necessary to give up rye bread, milk, large amounts of sweets, cabbage and legumes.
DETAILS: Pain in the ovaries - causes and treatment methods
Prognosis and prevention of acute enterocolitis
Prevention of acute enterocolitis consists of following the rules of personal hygiene and food preparation, balanced nutrition, timely treatment of intestinal infections, and a responsible approach to taking various medications. The prognosis for acute enterocolitis is favorable, however, the lack of proper treatment or its premature termination can lead to the development of complications, bacterial carriage, and chronic forms of the disease.
Treatment
After studying all the examination results and confirming the diagnosis, an individual treatment strategy for acute enterocolitis is prescribed. Elimination of such a disease is complex and consists of several stages:
- carrying out detoxification and replenishing fluid deficiency - for this they use gastric lavage, intravenous administration of water-salt solutions and cleansing enemas;
- adherence to a diet - in the first few days, therapeutic fasting will be required, after which liquid or puree food, prepared without adding fat and salt, is gradually introduced, as well as eating foods that do not contain coarse fiber;
- taking medications is necessary to eliminate symptoms. For this purpose, antibiotics, painkillers, enzyme preparations, as well as medications to restore intestinal microflora are prescribed;
- the use of traditional medicine is permissible only after prior consultation with your doctor.
Classification of the disease
The disease is classified according to the reasons for its manifestation:
- Bacterial. There is a specific type caused by various intestinal infections (shigellosis, salmonellosis, dysentery). And nonspecific - manifesting itself after the infection is destroyed.
- Parasitic. Occurs after various parasites appear in the intestines.
- Mechanical. As a consequence of prolonged constipation.
- Toxic. It appears after damage to the mucous membrane by toxins - chemicals, poisons, drugs.
- Secondary. Develops as a result of complications of other diseases of the digestive organs.
- Nutritional. Caused by prolonged poor nutrition.
Symptoms and course of enterocolitis in children
Acute enterocolitis in children is not a specific, “children’s” infection, such as rubella, measles or mumps. But this does not diminish its severity. A child's body is not as balanced as an adult's body. Therefore, dehydration is the hardest thing for babies, and fever comes in second place.
But febrile convulsions, which inexperienced parents fear so much, are much less dangerous than exicosis, or dehydration.
At first glance, the loss of fluid through stool does not seem significant to parents, but for a baby, the loss of a liter of water is a life-threatening condition. The following signs indicate its development:
- “Dry” crying and lack of tears in the baby;
- Dry mouth;
- Hoarse and silent voice and crying resulting from dehydration of the vocal cords;
- Retraction of fontanelles on the skull;
- A sharp decrease in tissue turgor.
If these symptoms are present, urgent hospitalization in an infectious diseases hospital is required, since it is very difficult to force the baby to replenish the body with fluid through drinking.
In the smallest children, a serious complication can occur - necrotizing enterocolitis in newborns. In this case, inflammation penetrates deep into the intestinal wall, with the possible development of necrosis. The most common occurrence is the presence of ulcers and necrosis. This form occurs due to the pronounced necrotizing effect of pathogenic microflora. After all, the newborn’s body has no immunological protection other than mother’s milk.
Most often, these severe forms of the disease occur due to perinatal infection with streptococcus aureus and various types of pathogenic streptococci. Quite often, intestinal inflammation is associated with prematurity and various types of child underdevelopment.
Diagnosis and treatment of this condition must be very prompt, since without treatment, irreversible changes can develop in 1-2 days, which can cause the death of the baby.
Diet No. 4 (table No. 4): menu for the week
Diet No. 4 is varied and healthy. Below is a sample menu for the week. Dishes must be consumed in liquid or semi-liquid form, as well as pureed. Cooking method: steam or boil in water. Eat only warm.
| Breakfast | Lunch | Dinner | Afternoon snack | Dinner | |
| Monday | pureed rice, steam omelette, tea | rosehip decoction | meatball soup, steam soufflé | pear jelly | buckwheat porridge, steamed fish cutlets |
| Tuesday | oatmeal, cottage cheese, cocoa on water | applesauce | cream soup with rice and egg flakes, steamed quenelles | quince jelly | semolina porridge with meat broth, soft-boiled egg |
| Wednesday | buckwheat porridge, 2 soft-boiled eggs | rosehip decoction | fish soup with oatmeal, steamed fish | apple mousse | rice porridge, steamed quenelles |
| Thursday | cottage cheese, cocoa | blueberry decoction | broth with egg flakes, steamed chicken cutlets | semolina pudding | rice porridge with minced chicken |
| Friday | oatmeal, steamed omelette | baked apple | soup with meatballs and croutons | rosehip decoction | mashed potatoes, fish soufflé |
| Saturday | buckwheat porridge, jelly | jelly | rice porridge, buckwheat-beef meatballs | bird cherry decoction | fish balls, omelette |
| Sunday | cottage cheese with applesauce, coffee | fruit jelly | meat broth with egg flakes, croutons | rosehip decoction | liquid semolina, chicken soufflé |
Complications and prevention
With timely treatment of acute enterocolitis, complications do not develop. Frequent vomiting and diarrhea can cause dehydration. If there is no or insufficient treatment, serious complications can occur:
- bacterial carriage:
- chronicity of the disease;
- malabsorption syndrome (impaired intestinal absorption of nutrients and vitamins);
- intestinal perforation (perforation of an ulcer) with peritonitis;
- intestinal bleeding.
Video on the topic:
To prevent acute enterocolitis, it is recommended to follow several simple rules:
- Comply with sanitary and hygienic rules.
- Follow your diet.
- Treat gastrointestinal diseases and intestinal infections in a timely manner.
- Take medications prescribed by your doctor.
- Have regular medical examinations.
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Exercise.
During the period of remission of acute enterocolitis, treatment in a sanatorium or balneological resort is desirable. Sanatorium-resort treatment improves the general condition and quality of life, and consolidates the results of therapy. You need to walk more, do therapeutic exercises and aerobics. Physical activity is useful for normalizing digestive functions.
Diet for intestinal inflammation
Starvation
Therapeutic nutrition for enterocolitis consists of several stages:
- Cleansing. In case of acute enterocolitis, an enema and detoxification are performed in a hospital setting. This is especially effective if the disease is caused by intoxication of a certain group of viruses;
- Starvation. For the first two days, doctors recommend refusing to eat, drinking only clean still water and weak tea without sugar. The way out of therapeutic fasting begins with eating dilapidated porridges in water, soups of a homogeneous mass, stewed vegetables without spices;
- Diversity of food. When the body has come out of fasting and is already accustomed to eating food, you can add dishes from lean types of meat - beef, chicken. Low-fat fish is also recommended; it is rich in folic acid, vitamins B and E.
What products are allowed to be consumed for enterocolitis:
- Yesterday's dried bread (no more than 150 g);
- Oils – olive, vegetable (no more than 30-40 g);
- Sugar – 50-60 gr. day;
- Cream soups, pureed soups with rice porridge, oatmeal, buckwheat, vegetables;
- Grind cottage cheese, mixed until smooth;
- Dishes from chicken fillet, beef, low-calorie fish;
- Kissel, jelly, juices from lemon, tangerines, blueberries, cherries, black currants;
- Semolina, rice, oatmeal, buckwheat.
You need to eat 4-5 times a day. This type of diet is considered low in calories, so it does not provide much energy. This strict diet lasts throughout the entire bed rest, no more than a week.
Features of the diet for children
If an infant is sick, you must adhere to the following rules:
- reduce the volume of food, but increase the frequency of feedings - the reduction should be 20% of the total volume;
- it is necessary to exclude any complementary foods for a while, adding them gradually after the acute symptoms have resolved;
- if possible, you should feed only breast milk or fermented milk formulas based on beneficial bacteria;
- When artificial feeding, I make sure to compensate for the entire volume with liquid.
You should not feed your child formulas that are not suitable for the treatment of enterocolitis and other intestinal disorders. Children over 6 months old can be given fermented milk mixtures diluted with buckwheat or rice porridge or puree soup.
Additionally, prebiotics are used to restore the intestines. All actions must be discussed with the doctor. It is best to choose from these medications: Linex, Bifiform, Colibacterin.
How to switch to a regular diet correctly
To prevent the acute process from becoming chronic, it is recommended to follow the sequence of diet expansion. After diet 4, the following foods and dishes are added to the diet:
- soup in a weak broth of meat, fish, vegetables. Small noodles or vermicelli, pureed cereals and vegetables, and meatballs are poured into it;
- dried white bread (yesterday's), biscuits, dryers;
- milk and cream are used for sauces, soups, porridge (half diluted with water);
- low-fat homemade cottage cheese, kefir and yogurt are recommended to be made independently from milk and pharmacy starter cultures;
- mild cheese is added to dishes;
- only minced meat or beef stroganoff. First, the skin is removed from the bird, all films and tendons are removed;
- lean fish is steamed, boiled in water or used for steamed cutlets, meatballs, soufflés;
- From vegetables, the most digestible ones are first selected - seedless zucchini, cauliflower, pumpkin, potatoes and carrots;
- All previously permitted porridges remain; boiled vermicelli is also prepared as a side dish;
- You can add a little fresh herbs to dishes for taste;
- baked apples, boiled pears. gradually try fresh sweet fruits without skin;
- compotes, jelly, berry and fruit mousse;
- diluted juice of apples, tangerines, oranges, cherries.
Only after adaptation to such a diet can you gradually reduce mechanical grinding, and then gradually introduce new dishes; it is important to monitor your reaction to them.
What could cause
Often, such a disease develops along with acute gastritis and develops due to the fact that a person eats low-quality foods, which, most likely, were contaminated with substances from natural bacteria, also if you eat a lot of fatty foods, spicy or rough (constant dryness) .
Fruits or vegetables that are not yet ripe can also become one of the causes of the disease. In addition, enterocolitis accompanies a number of other diseases that are associated with the intestines.
Treatment methods[edit | edit code]
- The treatment is complex. A diet high in protein and limited carbohydrates is of great importance. For exacerbations, antibiotics and enzymes are prescribed.
- In the acute course of the disease, it is usually necessary to perform gastric lavage and prescribe the patient a diet consisting of tea and water. It is possible to consume some liquid foods, for example: liquid porridge with water and rice water. It is imperative to monitor the volume of fluid consumed by the patient. Solid food is strictly excluded.
- If acute enterocolitis is caused by an infection, antibiotics and drugs that restore the intestinal microflora are prescribed.
- In the treatment of chronic enterocolitis, eliminating the cause of the disease is of utmost importance. For this purpose, it is necessary to normalize the patient’s diet and diet. If there is a suspicion that the disease may be caused by taking any medications, these medications should be discontinued.
- When it is established that the disease has developed under the influence of infection, parasites or diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, treatment should first of all be aimed at eliminating these causes.