Belching is the reflux of the contents of the stomach or esophagus into the oral cavity. In most cases, its appearance is preceded by discomfort in the stomach, which is caused by an increase in tone in this organ, and the release of excess contents leads to relief of this condition.
- Etiology
- Classification
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Prevention
There are quite a few reasons for the occurrence of such an unpleasant symptom, and not all of them are associated with pathologies of the digestive system. It follows from this that air belching can occur even in healthy people, for example, after eating. As for age and gender, this symptom has no restrictions, which is why it is often expressed in children and women during the period of bearing a child.
Although belching itself is often a symptom, depending on the disease, it is accompanied by other signs. For example, profuse diarrhea, attacks of nausea and vomiting, chest pain and other symptoms.
Diagnosis when air belching occurs is aimed at identifying the factors of its formation. To do this, a series of laboratory and instrumental examinations are carried out. To eliminate this manifestation, conservative methods are used, namely, taking medications, traditional medicine, diet and following general rules.
General information about the disease
Why do some people (constantly) burp air? The causes of this trouble very often lie in diseases of the digestive tract.
In medicine, air belching is the sudden and involuntary release of gases without any smell or taste from the stomach or esophagus through the oral cavity. If this process is observed rarely, then this is quite normal. After all, every swallowing movement of a person is necessarily accompanied by a certain swallowing of air (about 2-3 ml). This is necessary in order to normalize intragastric pressure. Subsequently, this air quietly escapes through the oral cavity in small portions.
But what if this process is observed constantly? Belching with air, the causes of which we will discuss below, in excessive quantities usually occurs in the presence of airbrushing or pneumatosis of the stomach.
What is burping
This is an involuntary release into the mouth of gases that entered the body during swallowing; the process of air release is beyond human control. A healthy person, when swallowing, can swallow a small portion of air along with food, which will later come out back through the esophagus, and this will not be felt at all. If the amount of air swallowed is large, then the body itself begins to regulate the removal of excess air, which is expressed in the form of belching (belching).
Normally, excess air from the stomach leaves not only through the mouth, but also through the intestines and is absorbed through its walls. Pathological regurgitation of air can be observed due to its constant excess in the stomach, which ends up there during the process of swallowing food. This may be caused by aerophagia, pneumatosis of the stomach or other phenomena. If belching is not associated with eating food and can occur at any time (sudden), then it may be associated with neurotic aerophagia (nervous swallowing of air).
Frequent belching of air is a pathological process that needs treatment, because it can be a symptom of some disease, especially if the belching is accompanied by unpleasant sensations in the intestines, the presence of some kind of taste in the mouth.
Normal and pathological: how to distinguish
Frequent or constant belching of air is a pathological human condition that needs to be treated. As a rule, in this case, the patient seeks help from a gastroenterologist.
Separate attention should be paid to such a deviation as neurotic aerophagia. This pathology is characterized by swallowing large amounts of air, which occurs outside of food consumption. As a rule, in such cases, this illness can remind itself both after eating and at other times, except during sleep.
If you constantly belch air, the causes of the phenomenon should be sought in the disrupted activity of the gastrointestinal tract, since this is a pathological syndrome that requires special attention from a specialist.
With normal functioning of the digestive tract, this process is never accompanied by unpleasant sensations. In this case, the air coming from the esophagus or stomach does not have any taste or smell. By the way, most people do not even attach any importance to this feature of the body, since it does not cause any discomfort. Otherwise, you should definitely undergo a medical examination.
Prevention
In order to prevent people from developing such an unpleasant symptom, it is necessary to adhere to several rules:
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- follow a proper, gentle diet;
- give up carbonated drinks;
- take medications only as prescribed by a doctor;
- Avoid sleeping or intense exercise immediately after eating.
In addition, it is necessary to undergo regular examinations by a gastroenterologist, since only such a specialist knows why belching occurs.
Main symptoms of pathology
What do flatulence and belching indicate? We will look at the causes, symptoms and treatment of these deviations right now.
So, in the presence of various diseases, a person may experience:
- Sour belching + flatulence. Occurs due to increased acidity of stomach juice. As a rule, this indicates abnormalities such as gastritis, the formation of ulcers in the stomach or duodenum.
- Belching rotten. It is formed during putrefactive processes in the main digestive organ (stomach) and is associated with stagnation and rotting of its contents (for example, with pyloric stenosis, cancer, gastritis, etc.).
- Belching air in large quantities. It begins to bother the patient due to increased gas formation in the gastrointestinal tract (for example, after drinking soda), as well as when swallowing air while eating dry food, talking during lunch, due to nasal congestion during a cold.
- Belching bitter. It is formed when bile flows back into the main digestive organ during cholecystitis or cholelithiasis.
If you regularly experience these abnormalities, you should definitely consult a doctor and undergo a medical examination. After a series of tests, the gastroenterologist should prescribe you one or another treatment.
Causes
There is a whole range of reasons that provoke stomach cramps. Some of them lie in the excess supply of air, and the other lies in the fact that the organ itself cannot cope with the incoming food and drinks. In healthy people, belching of odorless air most often occurs; its causes are:
- Swallowing food too quickly.
- The use of sour spices - ketchups, sauces; eating sour foods - for example, berries or citrus fruits.
- Overeating is accompanied by a characteristic heaviness in the stomach.
- Intense physical activity immediately after eating - it is recommended to wait at least an hour between meals and exercise.
- Alcoholic drinks, even without additional carbon dioxide, provoke stomach cramps, and beer, cider, and champagne cause air belching in any person.
- In women, symptoms may occur in the second or third trimester of pregnancy due to the fact that the fetus partially compresses all internal organs.
Nobody likes belching, this manifestation of physiology is considered indecent in society, but still, not a single person can live without removing excess air from the stomach. If the symptoms do not attract excessive attention and disappear after changing the eating style and food selection, then the individual reaction of the body should not be considered a pathology. Although if there is excessive gas production in response to sour foods, eating sour foods can check the acidity of the stomach.
It is worth thinking about diseases of the gastrointestinal tract if belching of air becomes constant, occurs in a state of hunger, causes discomfort or even pain, and the air coming out has a characteristic unpleasant odor. A sour taste in the mouth may also occur. Additional symptoms that should not be ignored:
- heaviness in the stomach;
- nausea;
- heartburn - in this case, belching occurs with partial reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus;
- pain in the epigastric region - at the level of the sternum;
- belching of air after eating is accompanied by spasms.
Belching rotten eggs
Any of these additional signs indicates a disease of the gastrointestinal tract. You can correlate symptoms and make assumptions, although a final diagnosis always requires a visit to a gastroenterologist and a full examination:
- Heartburn is gastritis with high acidity. If partial reflux of contents into the esophagus occurs, reflux esophagitis is a common disease associated with overeating, excess weight, and structural features of the esophagus. It lasts for years, people get used to it, but this is wrong: the acid that enters the esophagus destroys it, which leads to erosions and even cancer.
- Belching rotten eggs sometimes occurs in generally healthy people due to overeating and simultaneous drinking of alcohol. This symptom indicates that the stomach cannot cope with the amount of food received; it has begun to rot and form hydrogen sulfide. An isolated case after an excessively rich feast is not a pathology, but a persistent condition indicates gastritis with low acidity, weak stomach activity, which sometimes occurs in the early stages of an ulcer or cancer.
- A weak lower sphincter separating the esophagus from the stomach or a hernia provokes constant belching of air, not associated with meals, often accompanied by painful sensations. If this is a congenital feature, then it is detected in infancy: the child spits up, cries, sleeps poorly. In adults, a hernia develops slowly; one of the early symptoms is the release of air.
- Achalasia cardia is a disease of the esophagus, accompanied by a subjective sensation of a “lump in the throat”, swallowing is difficult. This disease occurs against the background of injuries, burns, degenerative changes in the mucosa, and polyps.
- Chronic pancreatitis is also one of the diseases that can be associated with burping air. A deficiency of pancreatic enzymes causes the stomach to become underactive, causing gas to form before food can pass further into the intestines.
- With constant manifestation and severe pain against the background of belching, we can talk about Zenker's diverticulum - a pathological pouch-like formation at the junction of the pharynx and esophagus. Additionally, pharyngitis-like symptoms appear: cough, sore throat.
The list of painful conditions, one of the manifestations of which is belching, is very long. Among them are not only “recognized” diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, but also pathologies not related to this system: for example, involuntary release of air from the stomach is typical for people with neuroses exposed to stressful situations. This occurs against the background of a spasm of the sympathetic nervous system, which, in turn, is transmitted from the central one.
Body type and anatomical features play a role. Belching is more common in obese people because fatty tissue puts pressure on the stomach. The symptom is typical for smokers: when inhaling smoke, part of it enters the digestive organs, irritating them and causing discomfort.
Frequent belching of air: causes, diagnosis of pathology
The causes of regular belching of air are identified after a thorough examination, namely:
- Analysis of the patient’s medical history and complaints (for example, when did it appear, how often does it bother you, is the appearance related to food intake, how long does it last, etc.).
- Analysis of life history (for example, does a person suffer from diseases of the gastrointestinal tract).
- Laboratory research.
- Biochemical and clinical blood tests to identify signs of inflammatory processes, dysfunction of internal organs, etc.
- Fecal occult blood test. As a rule, it is performed when serious intestinal diseases are suspected.
- Fecal analysis, or rather a coprogram, thanks to which undigested food, undigested fats, dietary fiber, etc. are easily detected.
Diagnostics
Establishing the correct diagnosis for the expression of belching and accompanying symptoms is aimed at finding the causes of their occurrence. To do this, the following complex of examinations is carried out:
- studying the patient’s medical history and life history;
- a gastroenterologist performs a thorough physical examination and questioning, which will determine the intensity and first time of onset of symptoms;
- control of general and biochemical blood tests - to determine acute inflammation;
- general urine analysis;
- microscopic examination of feces;
- cultures on nutrient media to determine the presence of pathogens.
If necessary:
- Ultrasound and MRI;
- CT and radiography;
- endoscopic diagnostic procedures and biopsy.
It is these diagnostic methods that will make it possible not only to identify pathologies, but also to assess the degree of damage and the functioning of the affected organ.
Treatment methods
What to do if you belch air? The causes and treatment of this phenomenon should not be identified or carried out if it is episodic.
Constant belching that continues for too long requires special attention. After visiting a doctor, the patient should undergo a thorough examination. After making a diagnosis, the gastroenterologist is obliged to treat those diseases that, in fact, led to the occurrence of this pathology.
- Gastritis or inflammation of the stomach lining.
- Diseases of the esophagus (can be different):
- diaphragmatic hernia;
- GERD or so-called gastroesophageal reflux disease. 3. Cholecystitis, that is, the formation of inflammatory processes in the gallbladder. 4. Peptic ulcer of the stomach or duodenum.
Treatment
Elimination of air belching is carried out conservatively:
- diet therapy;
- taking medications;
- the use of traditional medicine.
Treatment of belching with air
Proper nutrition plays the main role in treatment, since it can save a person from such an unpleasant manifestation as belching. Doctors often prescribe that patients follow dietary rules No. 1 and No. 5.
Drug treatment is individual and depends on what symptoms accompany such a symptom. In most cases, patients are shown:
- painkillers and antispasmodics;
- gastroprotectors;
- antacids;
- antibiotics;
- antimicrobials;
- stimulants of motor function of the stomach and intestines;
- enzymes.
You can also achieve good results by using herbal decoctions and infusions. Important rules for such treatment are consultation with a doctor and complexity.
Surgical intervention is resorted to when conservative therapy is ineffective or when the course of the disease that caused the belching of air is complicated.
Non-drug methods
Frequent belching of air (the causes, treatment of the deviation are described in detail in this article) is sometimes eliminated using non-drug methods. As a rule, they come down to reducing intra-abdominal pressure. For this it is recommended:
- sleep on a fairly high pillow;
- never tighten the belt or waistband too tightly;
- walk after eating for 40-60 minutes;
- do not do physical exercises to train the abdominal muscle tissue (for example, lifting the body, bending, twisting, etc.).
How to deal with belching
If this symptom is episodic, then treatment is not required. In other cases, you can get rid of painful, incessant belching after eating with the help of Gastal, Rennie, Almagel - drugs that normalize the acidity of gastric juice and the level of enzymes, and also have an enveloping and moderate anesthetic effect. When diagnosing neurotic aerophagia, psychotherapy sessions are prescribed.
If the belching was caused by some diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, then the gastroenterologist will prescribe treatment applicable to this disease. In addition to drugs that reduce acidity (Immodium, Motilium and others), antacids can also be prescribed to soften the mucous membrane, prokinetics to normalize digestion and bile ducts.
To eliminate air belching, non-drug methods are also used, which boil down to reducing intra-abdominal pressure:
- move after eating (walk) for at least 40-60 minutes;
- sleep on a high headboard;
- do not perform abdominal exercises after eating;
- Do not tighten the belt too much;
- follow a diet;
- limit the consumption of carbonated drinks;
- eat slowly, chew food thoroughly;
- do not talk while eating.
The main causes of belching in children
Surely every mother knows that belching in an infant is quite common. As a rule, the reason for this process is that during feeding he swallows too much air. Most often this happens if the baby's body is positioned incorrectly during breastfeeding. Also, those mothers who purchased a bottle or pacifier of an irrational shape for their child (with artificial feeding) may encounter a similar problem.
Often belching milk in infants is caused by weakness of the muscle tissues that are located at the entrance to the stomach. As the child grows, they become stronger, and the belching goes away on its own.
If a baby experiences frequent regurgitation of breast milk, you should contact your pediatrician, as this may indicate the presence of a disease.
Symptoms
In cases where belching without or with odor is a manifestation of a disease, it will not be the only symptom.
The most common is considered to be a combination of belching and nausea, which, in turn, is accompanied by vomiting. The expression of such signs individually is harmless, but if they appear complexly, this may indicate serious pathologies. Such diseases can be duodenitis, inflammation of the gastric mucosa, pancreatitis, ulcerative lesions of the duodenum or gastroduodenitis, acute intestinal infection. Nausea and belching of air are the initial signs of diseases for which you should immediately seek help from a medical facility.
Pain in the stomach and belching of air indicate any changes in one organ of the gastrointestinal tract or the entire digestive system. If such a set of symptoms begins to appear more and more often, then this may indicate serious digestive pathologies. These include peptic ulcers, pancreatitis and cancerous tumors. In such cases, it is strictly forbidden to attempt self-medication, but you should immediately consult a gastroenterologist.
Belching and heaviness in the stomach are alarming signs, especially if they appear after eating a small amount of light food, as well as at rest.
Belching with air and an increase in the size of the abdomen - in most cases, are expressed against the background of overeating, enzyme deficiency, or in the presence of diseases of the gallbladder and bile ducts.
Belching with foul air and diarrhea are some of the key symptoms that indicate an infectious process or food poisoning. Their appearance is explained by the process of decay and fermentation with the release of ammonia and hydrogen sulfide. Almost all of these symptoms indicate the presence of very serious gastrointestinal disorders that require immediate treatment.
In addition, depending on the causes of its occurrence, constant belching may be accompanied by symptoms such as:
- feeling of a lump in the throat;
- heartburn and burning in the chest area;
- hoarseness of voice;
- increase in temperature indicators;
- discomfort in the throat;
- change in skin tone;
- shingles pain syndrome;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- cough and shortness of breath;
- chest pain;
- bowel dysfunction in the form of alternating constipation and diarrhea;
- decreased or complete absence of appetite, which is caused by the occurrence of unpleasant symptoms after meals.
Folk remedies
There are quite a large number of recipes for folk remedies that can help a person with severe belching of air after eating.
Popular recipes:
- In a small container you need to combine 1 glass of water, 25 grams of honey, half a glass of cranberry juice and the same amount of aloe juice. The resulting product should be taken three times a day, 25 g for a week. Then you need to take a two-week break, after which the course must be repeated in the next six months;
- The following herbal mixture helps well: watch (2 g), fennel seeds (15 g), yarrow (15 g), St. John's wort (30 g) and mint (15 g). 1 large spoon of this mixture should be brewed with 1 tbsp. boiling water. After 20–30 minutes, the infusion will be ready. It is taken several times during the day, 1 large spoon;
- Powder made from calamus root is also used. It should be taken every quarter of an hour before a meal, 5 grams;
- Elecampane decoction. To prepare it, you need to combine 1 liter of boiling water and 50 grams of elecampane. The mixture should be boiled slightly over low heat and allowed to brew for 15–30 minutes. You need to take the drug 2 times a day, 150 milligrams before meals. Treatment should last 7 days;
- Fresh milk (goat). You need to drink 1 glass of milk three times a day for 3 months;
- Carrot and potato juice. You will need freshly squeezed juices, which are taken in equal parts. Take this remedy half a glass 3 times a day;
- After the meal is finished, it is recommended to eat a fresh apple or carrot;
- Do not drink during or immediately after meals.
Currently reading: What does constant burping tell you?
Description of action
Almost every internal human organ contains air; some organs have more of it, while others have less. In this case, the stomach is no exception, especially since the average volume of gases in it is about one and a half liters.
The presence of such a fairly large volume of air can be explained by the fact that the stomach is not sealed from the external environment. That is, air enters it along with the food consumed, through the mouth and esophagus. It is also worth considering that the gases accumulated in the stomach create the necessary pressure in it, which is necessary for digestion.
Excess gas can leave the gastrointestinal tract in the following ways:
- through the esophagus - belching;
- rectum and anus - flatulence;
- through the walls of the intestinal tract - by absorption.
For a healthy person, all three methods of removing excess gases from the gastrointestinal tract should work equally. Otherwise, this indicates a disease of the digestive system.
Belching sour
Almost every person at least once in his life has felt a taste of acid in his mouth - such belching is usually preceded by eating lemon or another sour dish.
However, if you constantly suffer from belching with an unpleasant aftertaste, it is better to carefully reconsider your diet. Products that have the ability to reduce intestinal motor functions and provoke fermentation and sour belching:
- a large number of sweets;
- mushrooms and pearl barley;
- lamb and sauerkraut;
- strong coffee and alcoholic drinks.
Of course, you shouldn’t completely abandon them. Just consume with caution - in small portions, 1-2 times a week, alternate with other dishes.
A person's passion for carbonated water has a negative effect on the production of hydrochloric acid. It may be present on the table, but not in huge quantities.
The time of appearance of sour belching after eating is also important in diagnosis. Thus, the immediate passage of air through the esophagus is a symptom of a malfunction of the gastric cardia. It is unable to close completely and prevent gas escape.
A lack of digestive juices will be expressed by regurgitation 25-30 minutes after eating food. An accumulation of gases forms in the stomach, looking for an opportunity to escape. Late belching - after 2-2.5 hours indicates the formation of a chronic course of gastritis or bulbitis . Pathology is often accompanied by increased acidity. Food is digested with considerable difficulty. Remains of stagnant foods with air masses tend to move not only lower through the intestines, but also back into the esophagus. How to get rid of such air belching will be decided by the attending physician - after diagnostic procedures have been performed.
Belching with gastrointestinal pathologies
To determine the presence of pathologies when belching air, doctors use radiography, ultrasound, and FGDS. Among the main gastrointestinal diseases are:
- Gastritis. The disease can be of different types. If the disease is acute, the patient will not only have belching, but also heaviness of the stomach, vomiting and nausea, as well as aching pain. A person loses his appetite, and after a small portion of food he becomes quickly full. In some cases, there is upset stool immediately after a meal. Additional symptoms in adults include pale skin, nails become brittle, and decreased performance.
- Ulcer. With pathology, a large number of scars and other lesions appear on the gastric mucosa. More often with a peptic ulcer, belching and heartburn appear, and there may be a sour taste. An ulcer can be recognized by its characteristic symptoms that occur 30 minutes after a meal. These include dull or sharp pain, vomiting and nausea, and bowel dysfunction.
- Transformation of the output department. When the disease occurs, increased pressure appears in the stomach, causing food to stagnate and begin to ferment. People will burp loudly and have a rotten, sour smell. As the disease progresses, body weight decreases and water balance is disrupted. The heart rhythm often goes astray and shortness of breath occurs.
- Tumors. With stomach cancer, there are almost no symptoms; there may only be heartburn, belching and other symptoms, as with gastritis. Over time, patients lose weight, quickly get full, and cannot eat meat. Before eating, there is often a strong release of gas from the mouth and pain.
Another problem arises due to disturbances in the intestinal microflora, pancreatitis and other pathologies that a doctor can diagnose.
Types of belching and their causes
Belching occurs for physiological or pathological reasons. The phenomenon is also observed in a healthy person who does not have problems with the functioning of the gastrointestinal system. Regurgitation of air, which is periodically accompanied by the smell of food eaten shortly before, certain moments appear:
- a person eats quickly, swallows pieces without properly chewing them;
- there is a heated conversation while eating;
- when overeating;
- when swallowing excess air (aerophagia).
The pathological “culprits” for the release of gases from the stomach are considered to be diseases of the digestive system:
- gastritis, ulcer;
- pancreatitis;
- gallbladder problems;
- hiatal hernia;
- gastroduodenitis.
Today, the causes of unpleasant, debilitating belching are classified into five main types, which are determined independently, according to sensations:
- bitter;
- rotten;
- with a sour taste;
- air (empty);
- tasteless and odorless.
Gorkaya
Belching often occurs, after which a bitter feeling remains in the mouth. There are several common reasons for this phenomenon. Reasons for frequent belching with a bitter taste:
- Gastroduodenal reflux. If bile is properly excreted from the body, it flows from the liver to the duodenum and then to the lower intestine. Sometimes there is a malfunction of the pylorus and the pressure in the duodenum increases. Bile enters the stomach, causing a bitter taste.
- Use of certain groups of medications. For example, the cause of frequent belching may be the use of antispasmodics, which negatively affect the sphincter muscles. Result: a space is formed between the stomach and duodenum.
- Surgical intervention. If during the operation the doctor dissects part of the sphincter muscles, then from that moment bile will constantly enter the stomach.
- Various injuries and diseases of the abdominal organs.
- The period of bearing a child (strong fetal pressure on the duodenum affects).
- Chronic form of duodenitis. The inflammatory process of the mucous membrane of the duodenum causes an increase in pressure. The duodenal “stuffing” enters the stomach.
With the smell of rotten eggs
The main reasons for frequent belching with a rotten “aroma” are often inflammation of the gastric mucosa with a decrease in acidity, stenosis of the pyloric part of the stomach, and a decrease in the volume of one of the sections of the duodenum. If such pathologies appear, the normal digestive process becomes difficult. As a result, the food breaks down to some extent and hydrogen sulfide is released, which smells like rotten chicken eggs. “Rotten” belching can also be caused by the following deviations:
- stomach ulcers;
- aerophagia;
- Gluten enteropathy is the body’s inability to digest gluten from cereal plants (a chronic disease).
With a sour taste
Belching after eating may also have a sour taste. The presence of “sourness” signals: there is significantly more acid in the stomach than the amount necessary for normal digestion of food. Most cases of release of gastric gases into the oral cavity are associated with the following ailments:
- stomach ulcer, gastritis;
- gastroesophageal reflux - a disruption of the esophagus due to the fact that the contents of the duodenum and stomach enter it;
- oncological diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Air with food
The reason for frequent belching of air often lies in excessive swallowing. When the volume of air that a person takes in with food is higher than normal, this phenomenon is called aerophagia (pneumatosis). Such regurgitation becomes the result of a physiological or pathological nature of the deviation. Physiological pneumatosis is caused by:
- absorption of carbonated drinks;
- quickly eating food;
- conversations while eating;
- long-term and constant use of chewing gum;
- regular overeating;
- a large number of spicy, fatty dishes in the daily menu;
- Often constant belching of air and a lump in the throat appear due to physical activity that follows immediately after eating.
The source of pathological aerophagia is considered to be:
- hysterical psychosis;
- severe decrease in gastric tone and disturbance of gastric motility;
- hiatal hernia;
- aneurysm of part of the cardiac aorta;
- frequent inhalation of air through the mouth;
- excessive salivation;
- cardiospasms of the esophagus;
- cardiovascular failure.
No smell or taste
Sometimes a person may be bothered by the “empty” secretion of gastric gases, which have no taste and do not smell of anything. In this case, the motives that cause belching are also divided into physiology and pathology. Physiological causes of “empty” regurgitation:
- diseases of the nose and mouth;
- frequent consumption of too cold or, on the contrary, hot drinks;
- pneumatosis;
- carbonated alcoholic and non-alcoholic drinks, whipped cocktails;
- constant snacking on the go;
- binge eating;
- second trimester of pregnancy;
- food that is not chewed thoroughly;
- physical activity immediately after eating.
Pathological sources of regurgitation:
- chronic form of gastritis, stomach ulcers;
- significant narrowing of the esophagus;
- neurotic aerophagia;
- disruptions in the functioning of the stomach;
- Cardiospasms.
Medicines
If belching becomes a frequent occurrence, then you will have to undergo a comprehensive course of treatment, which will eliminate both the belching and the cause that caused it. The most effective medications are used for this purpose. The best proven ones:
- Omez is a universal drug that reduces the acidity of gastric juice. Most often it is prescribed for the treatment of reflux esophagitis, hypersecretory conditions, ulcers of stress origin, and NSAID gastropathy.
The drug is produced in capsules, and if taken in the correct dosage, it will eliminate belching very quickly. It is best to take Omez in the morning with a small amount of water.
- Rennie is a sugar-free chewable tablet that is therefore suitable for diabetics. This drug effectively fights belching and eliminates the symptoms that arise from increased acidity of juice in the stomach. In the process of taking Rennie, sour belching, heartburn, and a feeling of heaviness in the epigastrium will go away. It can be used to treat people 12 years of age and older. When belching occurs, you must take the tablet, holding it in the mouth until completely dissolved. If there is no improvement within two hours, you need to take another pill. The maximum daily dose is 11 pieces.
- Gaviscon - has an antacid effect, acts symptomatically, and is not able to eliminate the cause of the pathology. The drug is produced in two forms - suspension and chewable tablets, thereby giving people the opportunity to choose the most preferable one for themselves.
Most often, the drug is prescribed for the treatment of dyspepsia, which occurs when the acidity of the juice in the stomach is increased. Gastroesophageal reflux is a direct indication for taking the drug. Excellent for sour belching and heartburn.
Gaviscon tablets are taken 1-2 times a day, 1-2 pieces, and the suspension – 10-20 ml for adults. It can also be used by pregnant women. Violation of the dosage may cause bloating.
- Simethicone is a carminative drug that has proven itself in the fight against belching. Although the drug has a chemical composition, it is not absorbed into the blood and does not harm the human body. It can also be used to treat women in an interesting position and those who are breastfeeding.
The drug destroys gas bubbles in the digestive tract and thereby helps eliminate belching. It is prescribed for dyspepsia, aerophagia and poisoning. In the pharmacy, Simethicone can be found in the form of capsules, drops, emulsion and suspension, so each person can choose the one that best suits them. Depending on the form, the dosage of the drug is calculated.
Whatever drug is chosen to treat belching, do not neglect to study the instructions for its use. This will avoid side effects.
Classification
This symptom may be accompanied by unpleasant odors, namely:
- sour – often indicates increased secretion of hydrochloric acid;
- belching with bitterness after eating is a sign of reflux;
- rotten or acetone - indicates stagnation and the development of fermentation of undigested food particles in the stomach, and may also indicate diabetes;
- belching of food after eating - with the smell of recently consumed food;
- without smell. This manifestation is accompanied by aerophagia.
Classification of belching
Treatment of heaviness in the stomach
Take care of your health - save the VKontakte link
If belching of air is accompanied by heaviness in the stomach, the patient has dyspepsia. From an additional clinic, heartburn, flatulence, and nausea may appear.
In this case, the causes of belching are various gastrointestinal diseases.
If belching of air is caused by a problem with the stomach, the patient is prescribed the following treatment:
- after meals, a soda solution is prepared;
- after meals, drink magnesium dissolved in water;
- a mixture of sugar and clove essential oil.
To regulate the activity of the stomach, it is recommended to take a course of Mezim, Omez, Almagel. In parallel, treatment includes diet therapy.
The patient needs to give up sweets. This is due to the fact that sugar provokes food fermentation, increasing gas formation, causing flatulence with belching.
It is harmful to eat sweets immediately after eating. Fatty foods are another provocateur of PT dysfunction. Eating such food causes belching of air and heaviness in the stomach.
With frequent such clinics, gastroenterologists advise adhering to a special diet once a week.
It is recommended to drink 6-10 tablets of Activated Carbon once a day. During this day you can eat porridge with water.
The patient must drink plenty of water between meals. In this case, the time interval after the meal is observed - 2 hours.
Drink water 30 minutes before meals. If you constantly follow such a diet, you can normalize the activity of the gastrointestinal tract, quickly eliminating heaviness in the abdomen and belching.
If the patient follows the above recommendations, but the symptoms do not disappear and the pain only increases, the functionality of the pancreas may be impaired and dysbiosis has developed.
With such pathologies, the help of a gastroenterologist is required. To confirm dysbiosis, it is recommended to undergo laboratory tests. Treatment consists of diet and medication.
If there is belching of air with a sour taste, the patient suffers from a pathology of the digestive system. More often, the symptom in question appears after eating.
In this case, the patient may be bothered by heartburn and a burning sensation in the stomach. To make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe competent treatment, the patient must be observed by a doctor for a long period.
If such a clinic appears after eating, the diagnosis is “valve dysfunction”. It can close partially, which allows food to penetrate out. This provokes a sour taste and heartburn.
If belching air with a sour taste appears 30 minutes after eating, the patient has developed an enzymatic deficiency. This is due to the inability of natural enzymes to digest all food.
In this way, fermentation occurs and gases are formed, which are released through the mouth. This phenomenon is popularly called indigestion. Treatment should be prescribed by a gastroenterologist.
Belching air with a sour taste indicates pancreatitis. With this pathology, there is insufficient production of enzymes that are necessary for digestion.
To understand the etiology of this disease, it is recommended to undergo a complete examination.
Pancreatitis is characterized not only by the release of gases from the stomach into the esophagus, but also by the entry of food particles into this organ with gastric juice. The last component has a sour taste.
Treatment of such belching is carried out under the supervision of a gastroenterologist. Self-therapy can only make the situation worse.
Before the examination, the patient is recommended to:
- establish a dietary regime - breakfast, lunch and dinner should take place at certain hours. As the patient becomes accustomed to meal times, the production of the necessary enzymes is activated. Unsystematic nutrition provokes stagnation of food and subsequent formation of gases;
- eating small portions;
- frequent food consumption – more than 4 times;
- creating a menu of enveloping and tender food;
- After lunch, you should not lie down, as the horizontal position of the body impairs digestion, causing belching.
If belching air with a sour smell often bothers you, it is recommended to drink Mezim, Festal, an antacid medication.
Alternative treatment should be carried out only after consultation with the treating gastroenterologist. More often, with sour belching, drink freshly squeezed juice. It is consumed 20 minutes before meals.
Frequent belching of air is a symptom of certain gastrointestinal diseases:
- various forms of gastritis, including chronic;
- ulcer;
- GRB.
Scientists have proven that belching air accompanies dysfunction of the liver and gallbladder. Inoperability of the cecum can cause the symptom in question. Therefore, treatment should be carried out after determining the etiology.
Features of treatment
If periodic belching is associated with errors in food intake, or if this complaint occurs during pregnancy, special therapy is not needed. In this case, it is recommended to eat slowly, in small portions, chewing everything thoroughly. If necessary, you should exclude drinks with gases, milk and foods that promote gas formation (beans, peas, cabbage, fresh bread, apples).
The following exercise also helps to relieve physiological belching. You need to lie on your back, raise your straightened legs at an angle of 45 ° and try to hold them in this position for 3 - 4 minutes.
If belching is a sign of a certain disease, then only adequate treatment of the underlying pathology will effectively get rid of this unpleasant symptom. So, with the neurological genesis of this problem, it is recommended to get enough sleep, try not to overwork, avoid stressful situations and take sedatives.
If you are constantly worried about belching due to damage to the digestive organs, you should undergo appropriate examinations. As a rule, patients are prescribed:
- blood analysis;
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs (to identify lesions of the liver, pancreas, gallbladder, etc.);
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy and colonoscopy (to exclude peptic ulcers or intestinal pathologies);
- X-ray examination (for timely detection of diaphragmatic hernia or esophageal diverticulum);
- esophagotonokymography (allows you to determine the presence of low tone of the cardiac sphincter);
- pH-metry to determine the acidity of gastric juice (with this study you can identify reflux esophagitis against the background of low acidity).
Based on the results of these studies, the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes therapy according to the identified disorders.
Treatment of belching after eating - how to get rid of it?
Unfortunately, there is no symptomatic drug that could get rid of such an “indecent” symptom in a few doses. If belching is caused by a pathological process in the body, then the only way to cure it is to begin therapy for the underlying disease.
Belching with a sour odor can be eliminated by prescribing an appropriate diet, antacid and antisecretory medications; these drugs neutralize hydrochloric acid and reduce its production in the stomach. In addition, to improve motor skills, the doctor prescribes prokinetics.
- Very rarely, surgery may be necessary (stenosis, hiatal hernia).
For belching after eating associated with problems in the liver and gall bladder, the same drugs are prescribed as for sour belching, and also depending on the diagnosis: choleretic, antispasmodics, litholytics, bile acid inhibitors. We recommend dietary table No. 5.
Sometimes it is necessary to carry out surgical interventions (duodenostasis, cholelithiasis). For chronic pancreatitis, enzyme replacement, analgesics, and drugs that reduce the production of gastric juice and block the pancreas' own enzymes are prescribed.
Atrophic gastritis is treated with antibiotics that act against the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, vitamins and gastric juice preparations.
Oncological diseases of the gastrointestinal tract almost always require tumor removal followed by chemotherapy. If the belching is caused by aerophagia, then you need to contact a neurologist and undergo a course of treatment from this specialist.
When a person is healthy and the belching is physiological, you just need to follow certain rules to prevent this symptom.
Etiology
Belching after eating can be caused by many factors, both physiological and pathological.
From time to time, belching appears during the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, often with the release of air or a mild smell of recently consumed foods. The first group of reasons includes:
- conversations during meals;
- hasty consumption of food with poor chewing;
- frequent overeating;
- states of severe stress;
- abuse of chewing gum;
- sports, sleep or drinking cold drinks immediately after eating;
- a condition called aerophagia.
In addition, there are several foods that certainly cause belching of air after eating, which is often expressed against the background of increased gas formation. These ingredients and drinks include:
- whole milk;
- onion and garlic;
- ice cream;
- beer;
- sweet sodas or oxygen cocktails;
- legumes;
- White cabbage.
Foods and drinks that cause belching
However, gastroenterologists do not advise ignoring belching, especially if it is frequent. This is due to the fact that it can be part of the clinical symptoms of some disorders.
Disorders that are accompanied by belching:
- pancreatitis;
- gastritis of any etiology;
- gallbladder pathology;
- gastroduodenitis;
- ulcerative lesions of the stomach or duodenum;
- hiatal hernia;
- neuroses or congenital pathologies of the nervous system;
- diseases of the biliary or pancreatic ducts;
- esophagitis;
- GERD;
- narrowing of the esophagus;
- gurgle;
- stomach oncology.
Severe belching after eating can be not only a symptom, but also an unpleasant consequence, for example:
- abdominal injuries;
- uncontrolled use of certain medications, in particular antispasmodics;
- surgical interventions in the abdominal cavity.
If an adult experiences constant belching after eating, this may indicate not only improper functioning of the digestive system, but also malfunctions of other body systems, for example, the cardiovascular system. It is because of this that if belching occurs frequently, it is worth undergoing a comprehensive examination.
In addition, there are several specific predisposing factors for the occurrence of belching in a child:
- immature gastrointestinal tract;
- dysfunction of the nervous system;
- increased salivation;
- poor nutrition that does not correspond to the child’s age group;
- emotional stress;
- adenoids;
- watching TV or playing on the computer while eating.
However, it is worth noting that for babies under one year old, belching after eating is considered normal.
Belching after eating in females during pregnancy is isolated separately. Often the main reason for this is the physiological changes in the body that occur when carrying a baby. During this period, the fetus is actively growing, which becomes a factor in compression and displacement of internal organs.
Only a gastroenterologist can find out why belching occurs after eating, after performing a series of laboratory and instrumental diagnostic examinations.
Belching of air accompanied by pain
If belching air is accompanied by pain in the stomach, we can say with confidence that gastrointestinal disease begins to develop in the body. Typically, these symptoms develop as a result of:
- smoking after a meal: most smokers are accustomed to finishing their meal with a cigarette, but when smoking the smoker swallows the smoke;
- eating fruit for dessert. Traditionally, it is customary to finish a meal with fruit, but gastroenterologists advise eating fruit after a meal a couple of hours later. Otherwise, fruit organic acids interact with mineral elements from other foods eaten, having an undesirable effect on the digestive process;
- traditional tea drinking after meals: the tea leaf contains enzymes that weigh down proteins and prevent digestion;
- a bath after dinner is not at all beneficial for digestion, since the blood drains from the stomach, which weakens the digestive process;
- the habit of unfastening your belt while eating has a negative effect on the intestines;
- drinking a cold drink after a meal (traditional cola after a burger or finishing a meal with a milkshake) interferes with the fermentation process and the absorption of lipids;
- Sleeping after a heavy meal can also lead to gastroenterocolitis, since the digestion process is disrupted during sleep.
Diseases characterized by belching air along with pain:
- peptic ulcer;
- chronic cholecystitis;
- inflammation of the pancreas;
- gurgle;
- malignant tumors with numerous symptoms.
If belching occurs with painful sensations in the stomach, you should contact a gastroenterologist to identify the causes.
Lump in throat and belching
The feeling of a lump in the throat, accompanied by belching, is characteristic of a wide range of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, thyroid gland, as well as neurological disorders. The patient should be examined not only by a gastroenterologist, but also by an endocrinologist and a neurologist. This symptomatology is typical for:
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- VSD;
- laryngeal tumors.
The body's response to a problem
What are the causes of burping air? The human body reacts in a similar way to the following symptoms:
- regular dietary violations;
- improper behavior at the table during meals;
- neurotic dysfunctions associated with constant swallowing of air;
- the presence of any pathologies.
Constant belching may indicate problems that affect the following organs:
- organs of the gastrointestinal tract;
- organs of the cardiovascular system.
Causes of belching air:
- dysfunction of the lower digestive sphincter due to developing hernia of the diaphragm;
- ulcerative lesions of the duodenum or stomach;
- functional disorders of the stomach of a non-ulcer nature;
- diseases that contribute to the reverse movement of food from the stomach;
- due to pathological lesions of the biliary tract or pancreas.
Video about the causes and treatment of constant burping of air
Belching with air and its treatment is carried out after determining the cause of its occurrence. Belching air is a physiological process.
But this phenomenon can cause discomfort to the patient, since the air may have an unpleasant odor. Frequent regurgitation indicates gastrointestinal pathology.
If the patient is bothered by repeated oral gas, it is recommended to make an appointment with a gastroenterologist. This article will discuss how to treat belching with air.
Preventing belching with food
Compliance with certain “living conditions” allows you to reduce the frequency of episodes of regurgitation, and they are as follows:
- When eating food, temperature contrasts should be avoided;
- form a diet mainly from easily digestible and liquid dishes;
- avoid heavy physical activity, especially bending and squatting, immediately after eating (slow walking is encouraged);
- freshen your breath not with chewing gum, but with careful oral hygiene;
- do not drink food;
- do not eat protein foods at the same time as carbohydrate foods;
- Do not combine dairy products with anything;
- Do not take a horizontal position immediately after eating.
When correcting nutrition, the factor of individual intolerance to a number of foods should be excluded.
Prevention and prognosis
To eliminate regurgitation or minimize the number of its occurrences, it is necessary to adhere to basic preventive methods:
- Avoid eating whipped soufflés and milkshakes;
- When eating food, it is important to chew food slowly and thoroughly to prevent swallowing air;
- It is advisable to drink liquid from a glass and not from a straw;
- in some cases, it may be necessary to limit the consumption of dairy products.
Belching food particles has a prognosis depending on the effectiveness of therapy specific to each disease. If belching is an individual symptom, then it does not lead to changes in the person’s condition, which means the prognosis will be as positive as possible.
What is regurgitation: physiological aspect
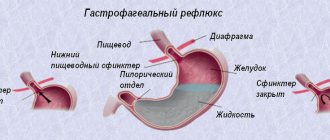
Belching food or involuntary regurgitation that occurs reflexively without a feeling of nausea is called gastroesophageal regurgitation. This term refers to the movement of fluids (or gases) in the body in the direction opposite to their natural, physiological flow. Under certain conditions, regurgitation occurs from any hollow organ with intense muscle contraction of its walls.
Under normal physiological conditions, the release of food into the oral cavity (reverse motion) is prevented by the tight closure of a special valve through which food enters the stomach. It is located in the lower part of the esophagus at the line of its separation with the stomach and opens reflexively only with the direct movement of food. This determined its name - lower esophageal sphincter (LES) or cardia (cardiac valve). The closing force of the cardia is called its muscle sphincter. Pathological opening of the LES and belching of food is caused by excess gastric pressure and a number of organic reasons.