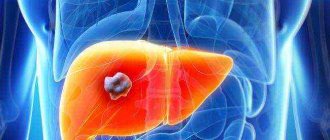
Fibrosis is a process accompanied by the replacement of healthy cells with connective tissue. Often the disease affects liver cells, which is explained by the increased load on this organ. Pathology occurs in different forms, differing in severity. When considering stage 1 liver fibrosis, what it is and how to treat it, it is necessary to understand that the disease is reversible in the initial stages of development. However, this is only possible with timely identification of symptoms and treatment.
Causes of liver fibrosis in hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a viral disease characterized by damage to the liver parenchyma. Due to its asymptomatic course, in 75-80% of cases it becomes chronic. Slow inflammation of liver cells leads to their death and replacement with scar (fibrous) tissue.
The virus provokes chronic inflammation of the liver, as a result of which fat-storing Ito cells are activated. They grow into the parenchyma and turn into myofibroblasts. Modified Ito cells synthesize an abnormal structure, which consists of:
- glycans;
- fibrillar protein;
- glycoproteins.
This leads to activation of Kupffer cells, which damage hepatocytes, white blood cells (leukocytes) and platelets. In the parenchyma, the concentration of inflammatory mediators and reactive oxygen increases. Meanwhile, myofibroblasts increase the density of the structure, resulting in the formation of fibrous cords.
Fibrosis is a consequence of chronic viral inflammation of hepatocytes. It aggravates the course of hepatitis C, as it seriously damages the liver tissue.
Risk factors
The likelihood of fibrosis and the rate of its progression depend on various factors. Children, elderly people and those who have been diagnosed with hepatitis C genotype 1 are more susceptible to pathology. It much more often becomes chronic, threatening scarring of the liver.
Factors that increase the risk of fibrosis in hepatitis:
- autoimmune disorders;
- genetic predisposition;
- drug abuse;
- parasitic infestations;
- poisoning with salts of heavy metals;
- extrahepatic blockage of the bile ducts;
- portal hypertension;
- Wilson-Konovalov disease;
- Infectious mononucleosis;
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
All patients with hepatitis C, without exception, are prescribed a therapeutic diet. It is aimed at reducing the toxic load on the digestive and hepatobiliary system - the liver, bile ducts and bladder. If it is not followed, the load on the parenchyma increases. Activation of oxidative reactions accelerates the transformation of Ito cells into myofibroblasts.
Over time, fibrous tissue replaces the functional cells of the liver and surrounding anatomical structures - hepatic and bile ducts, blood vessels. Therefore, against the background of fibrosis, portal hypertension often occurs, which can only be treated surgically.
Systematic intake of alcohol for 7-8 years leads to massive death of hepatocytes and the formation of fibrous cords in the parenchyma. Against the background of hepatitis, fibrosis progresses 2.5-4 times faster.
Symptoms
Liver fibrosis in the early stages of development is characterized by the fact that it is not expressed by any symptoms and slowly progresses. This is why diagnosing the disease in the early stages is quite difficult and often happens by accident. The clinical picture becomes more pronounced only in cases of severe disease. The initial symptoms of the disease are:
- severe fatigue of the body;
- decreased performance;
- decreased tolerance to physical and psychological stress.
At later stages other signs are added. These include:
- anemia;
- internal hemorrhages from dilated veins of the esophagus;
- decreased immune system levels;
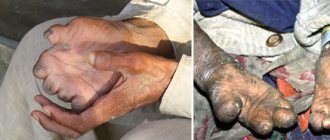
- increased tendency to form bruises and spider veins on the skin.
Traditional medicine will help eliminate some of the symptoms.
Liver fibrosis
How long does it take from infection to fibrosis?
Fibrotic changes in the liver are observed after hepatitis becomes chronic. If inflammation is not treated, it becomes chronic within 4-6 months. The rate of transition of acute hepatitis to a sluggish form is influenced by:
- body resistance to infection;
- age;
- hepatitis C genotype.
It may take 6-10 months from infection to the first fibrotic changes in the liver. In those suffering from immunodeficiency, fibrosis progresses faster, which is associated with an excessive viral load on the parenchyma.
Typically, clinical manifestations of fibrosis occur after 6-8 years. With hepatitis C, it disguises itself as a viral inflammation. Therefore, before prescribing therapy, the doctor must conduct a comprehensive examination to determine the presence and extent of scar changes.
Diagnostic procedures
Before starting treatment for stage 4 liver fibrosis, a comprehensive diagnosis is carried out. It includes instrumental and laboratory studies. These measures are used if the disease is suspected:
- urine and blood analysis;
- coagulogram;
- alpha-fetoprotein test;
- analysis to detect hepatitis;
- Ultrasound of the liver;
- ultrasound examination of other systems that are involved in pathology;
Depending on the patient’s well-being, invasive procedures may be performed, including a biopsy, which allows one to accurately indicate the extent of the lesion.
Stages and symptoms
The degree of fibrosis in hepatitis C is determined by the density of the parenchyma in kPa. The Metavir scale is used to assess the severity of lesions:
- F0 – up to 5.5 kPa. There are no fibrotic changes.
- F1 – 5.8-7 kPa. Slight proliferation of connective tissue around hepatocytes and bile duct cells.
- F2 – 7.2-9 kPa. There is mild fibrosis, in which scar tissue forms septa that connect fibrous islands around cells.
- F3 – 9.5-12 kPa. Fibrotic changes are observed within the parenchyma, in the hepatic arteries, lymphatic vessels and bile ducts.
- F4 – over 12.5 kPa. Signs of a disturbed liver structure are detected. Against the background of fibrosis, the organ is deformed, changes in its structure are revealed.
Fibrosis of the 1st degree in hepatitis can be effectively treated. In the case of the formation of nodes or blockage of the hepatic vessels, it transforms into cirrhosis of the liver.
The clinical picture depends on the extent and location of fibrosis. If changes are observed only around the liver cells, there are no symptoms. The first signs of the disease appear when the liver is severely damaged and the patency of blood vessels is impaired.
Characteristic manifestations of fibrosis caused by hepatitis C:
- decreased performance;
- chronic fatigue;
- anemia;
- digestive disorders;
- frequent colds;
- spider veins on the body;
- variceal bleeding;
- abdominal dropsy.
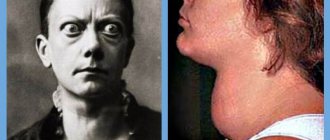
If hepatitis is complicated by cirrhosis, signs of liver failure and encephalopathy come to the fore. Mental disorders are noted - gaze fixation, irritability, forgetfulness.
Diagnostics involves laboratory and hardware tests:
- tests for ALT and AST;
- coagulogram;
- general urine analysis;
- blood test for biochemical markers of fibrosis;
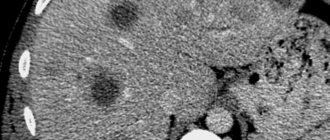
- CT scan of the peritoneum;
- Ultrasound of the liver;
- elastography;
- liver biopsy.
The choice of additional diagnostic methods is influenced by the results of laboratory tests. Based on the data obtained, the appropriate tactics for treating hepatitis and the fibrotic changes caused by it are determined.
Diagnostics
As noted above, the disease at stage 2 is quite difficult to diagnose, since most often fibrosis at this stage is not accompanied by significant problems in the functioning of the whole organism. The first signs appear only after several years in the process of sluggish development of the pathology. To determine the degree of fibrosis, experts have developed various methods:
- conducting a special blood test to determine the number of specific markers;
- Analysis of urine;
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs;
- radionuclide method of liver examination (scanning using radioactive tracers);
- biopsy.
A biopsy is the most effective and informative way to diagnose fibrosis - it allows you to establish not only the presence of the disease, but also determine its stage. A piece of tissue from the affected organ is removed with a special needle, to which a special dye is added. The sample is then examined under a microscope. This diagnostic method allows you to monitor the degree of development of fibrotic abnormalities.
Important! Experts recommend performing a biopsy at least once every three years. This will allow you to track the dynamics of the disease and timely adjust therapy.
How to treat hepatitis complicated by fibrosis
The main goal of fibrosis treatment is to eliminate the factors that cause scarring of the liver parenchyma. Therapy includes antiviral drugs that fight hepatitis. To maintain liver function, symptomatic medications are prescribed.
Particular attention is paid to a diet that reduces the load on the gastrointestinal tract and hepatobiliary system.
Medicines
Treatment of hepatitis with fibrosis begins with taking direct antiviral drugs. The basis of therapy is drugs that suppress the self-copying of three HCVirus viral proteins - NS5B polymerase, NS5A protein, NS3/4A protease:
- Sovaldi;
- Velpatasvir;
- Dasabuvir;
- Narlaprevir;
- Daclatasvir;
- Asunaprevir;
- Daklinza;
- Sofosbuvir;
- Ledipasvir.
Treatment options depend on the hepatitis C genotype and viral load. To eliminate fibrosis, the following are prescribed:
- glucocorticosteroids (Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone) – stop inflammation, which prevents scarring of the parenchyma;
- hepatoprotectors (Heptral, Hepatosan) – normalize the metabolic and neutralizing functions of the liver, protect its cells from destruction;
- choleretic drugs (Hofitol, Holosas) – stimulate bile drainage, eliminate digestive disorders;
- antioxidants (Tocopherol, Dibunol) – normalize redox reactions, remove free radicals and prevent liver scarring;
- immunostimulants (Amiksin, Wobenzym) – increase the body’s resistance to the hepatitis pathogen;
- enzymes (Pancreazim, Eurobiol) – accelerate the digestion of food in the intestines and prevent intoxication.
To slow down scarring of the parenchyma during hepatitis, all patients without exception are prescribed antifibrotic drugs - Pentoxifylline, Lecithin, Ghrelin.
Folk remedies
Fibrosis occurs in response to hepatocyte damage caused by hepatitis. Therefore, therapy is aimed at eliminating viral inflammation. To increase the body's resistance to HCV, herbal remedies with an immunostimulating effect are used. But before using them, you should consult a hepatologist. Some medicinal herbs increase the load on the liver, which only aggravates the course of hepatitis.
Traditional medicine recipes:
- Herbal collection. Mix 2 tbsp. l. crushed wheatgrass roots and rose hips. Add 1 tbsp. l. nettles Steam 750 ml of boiling water and leave in a thermos for 15-20 minutes. The filtered infusion is drunk 250 ml twice a day for 1.5 months.
- Turmeric. Dissolve 1 tsp in a glass of warm boiled water. honey Add ½ tsp. turmeric. Drink in one gulp after meals three times a day. The course of therapy is 2-3 weeks.
- White cabbage. The cabbage is chopped in a blender. Squeeze out the juice through cheesecloth. Drink 100 ml before meals twice a day for half a month.
Herbal remedies stimulate intestinal function and cleanse the blood of toxins. During a course of treatment, the toxic load on the liver is reduced and the regeneration of hepatocytes is accelerated.
Treatment with folk remedies
The most common folk remedies are:
- infusion of white cinquefoil, which slows down the process of fibrotic degeneration;
- seeds, as well as milk thistle tincture. Improves the overall outflow of bile and normalizes the functioning of the hepato-bisiological system;
- decoction of young corn leaves. Has a choleretic effect, partially helps dissolve small stones in the biliary tract;
- a mixture of honey and olive oil in equal proportions. Clears the choleretic tract, slows down the formation of scars.
All traditional methods can only be used as additional measures of influence, and not as primary ones. Fibrosis can be treated with such means only in the initial stages or during remission for a longer duration.
In conclusion, it is worth noting that liver fibrosis is a serious disease. It is impossible to stop the process once it has started, since the process is irreversible. With the help of treatment, it is possible to slow down the process of degeneration of hepatocytes, delaying the onset of some consequences. Early diagnosis is of great importance for successful treatment. If you suspect a pathology of the liver, you should immediately consult a doctor to undergo a specialized examination.
https://youtu.be/AQO-0_T-oPU
Is fibrosis curable?
If hepatitis is treated before nodes form in the parenchyma, complete recovery is possible. The success of treatment depends on:
- hepatitis C genotype;
- immune status;
- concomitant pathologies;
- age;
- literacy therapy.
After treatment, it is imperative to exclude factors that provoke massive death of hepatocytes. Otherwise, the risk of relapse of the disease increases.
Fibrosis of 1-3 degrees is reversible, but only if hepatitis is successfully treated. If it transforms into cirrhosis, recovery is only possible with a donor liver transplant.
Complications
If the disease is not detected promptly by ultrasound and the disease is not treated, a number of severe and irreversible complications may develop. These include:
- Liver cirrhosis is the most common consequence of fibrosis, which is its final stage;
- ascites;
- peritonitis;
- dilation of varicose veins of the esophagus, against which internal bleeding develops. This disorder may be accompanied by symptoms such as blood in the vomit, black stool, decreased blood pressure, and increased heart rate;
- hepatic encephalopathy;
- carcinoma - a malignant neoplasm of the liver;
- severe renal failure;
- low oxygen content in the blood;
- hepatic gastropathy and colopathy;
- male and female infertility;
- menstrual cycle disorders – in girls.
Prevention of liver degeneration due to hepatitis
The prognosis of life depends on the success of hepatitis C therapy. Proper nutrition, moderate physical activity, and taking vitamin and mineral complexes prevent structural changes in the parenchyma. To prevent fibrosis, you should:
- avoid psycho-emotional stress;
- give up alcohol and smoking;
- treat underlying diseases in a timely manner;
- take antioxidants and choleretic agents;
- Do an ultrasound of the abdominal organs 1-2 times a year.
Mild fibrosis disappears after treatment of hepatitis without any health consequences. If you follow the hepatologist's recommendations, eat a balanced diet and give up bad habits, the risk of exacerbations is reduced several times. For a long time, fibrosis is asymptomatic. Therefore, for its timely detection, it is advisable to be examined by a doctor at least once a year.