Blood with feces in men (the reasons for this are different) may indicate the presence of various pathologies in the body. It can be either a consequence of a minor small crack caused by constipation, or a sign of intestinal cancer.
Why stool appears with blood, causes in men, treatment - all this is described in this article.
The main reasons for the discharge of blood in stool
Such a symptom should always alert you and be a reason to consult a doctor.
Why does blood appear in stool in men? The reasons may be as follows:
- Presence of hemorrhoids or anal fissures.
- Oncological lesion. In this case, we are talking about the presence of a tumor in the intestines, stomach or rectum.
- Formation of intestinal diverticulum.
- Peptic ulcer disease.
- Liver cirrhosis, in which varicose veins develop.
- Reasons of a different nature: the presence of Crohn's disease, diseases of an infectious nature, increased levels of potassium in the body.
Causes of bloody bowel movements in men
The genitourinary system of the stronger sex is a very weak point. Blood from the rectum can be a symptom of a disease such as acute prostatitis. The disease occurs as a result of bacterial infection of the prostate tissue. In this case, you cannot delay contacting a medical institution. Other symptoms include fever, chills, a significant increase in rectal temperature, pain in the back, abdomen and perineum, frequent urination, as well as signs of general intoxication of the body - weakness, fatigue, pain in the neck and muscles.
False blood discharge
Blood in the stool in men (the causes of the symptom usually lie in the presence of gastrointestinal disease) can also be a false manifestation. In this case, the stool acquires a reddish tint or includes red clots after eating a number of foods: tomatoes, beets, currants, sausages containing blood. Therefore, if an atypical color of the stool appears, do not panic. You should remember what food was consumed these days. If the diet included specific foods, then we can assume that it was not blood mixed in the stool.
If after a day the situation has not changed in any way, then you should pay attention to your health, since the admixture of blood in the stool always indicates the presence of some pathology in the gastrointestinal tract.
Before visiting a specialist, it is recommended to diagnose yourself. However, such manipulations should in no case replace a medical examination.
What to do if you find blood in your stool
If you find blood in your stool, you should act calmly and clearly:
- Analyze your diet in recent days. Eliminate the possibility of staining stool with food and medications.
- Write down other symptoms, if any (diarrhea, nausea, pain, fever).
- Visit a proctologist, undergo tests and other studies prescribed by the doctor.
To avoid such problems, not much is needed. Regularly check your health, do not develop even the most insignificant diseases in your opinion, eat properly and regularly and lead an active lifestyle.
How to diagnose yourself?
What are the causes of such manifestations as blood in feces in men? Self-diagnosis will greatly help clarify the situation. Undoubtedly, a person who does not have special medical education is not able to determine the provoking factor, but this is not required.
Self-diagnosis is needed, rather, to reassure yourself and to provide the specialist with more useful information that will help him make the correct diagnosis.
So, if you detect a symptom such as blood in stool in men (there may be different reasons), you should pay attention to the following signs:
- blood coloration;
- its volume;
- the presence of blood streaks, clots and drops;
- the place where blood accumulates (whether it is present in the stool itself or on its surface; it is also important whether the blood transfers to toilet paper or underwear).
It is on the basis of such signs that a preliminary diagnosis can be assumed, which can subsequently be confirmed by a specialist.
Why does bloody stool appear in men? The reasons may be as follows:
- Bleeding in the form of drops or streams is observed in the presence of hemorrhoids. In this case, the blood turns scarlet and does not contain any impurities or mucus. In advanced forms of hemorrhoids, not only blood, but also pus is present in the stool.
- The stool contains blood and mucus. This may be evidence of the presence of polyps, colitis and even a malignant neoplasm.
- The blood is scarlet in color and contains streaks mixed with feces. This indicates the presence of a cancerous tumor in any part of the gastrointestinal tract. The same clinical picture characterizes diverticula and colitis.
- The stool has a liquid consistency (diarrhea), and isolated inclusions of blood are noticeable in it. This indicates damage to the body by helminths, and if such symptoms occur at elevated body temperature, this signals a disease such as dysentery.
- The brighter the color of the blood, the closer to the anus the pathological process is localized.
- Scarlet blood signals the development of inflammation in the large intestine.
Why is there bleeding from the anus?
There are many reasons that can cause bleeding from the anus. Depending on the nature and origin of the factor that caused blood from the anus, the causes of pathology can be grouped into the following groups:
1. Pathologies of the digestive tract and intestines:
- rectal fissure;
- haemorrhoids;
- colon polyps;
- colon cancer;
- ulcerative colitis;
- Crohn's disease;
- endometriosis of the large intestine;
- diverticulosis of the colon.
2. Infectious diseases:
- shigellosis;
- dysentery;
- salmonellosis;
- a consequence of taking certain medications.
Bleeding from the anus during stool
In most cases, blood from the anus during bowel movements is associated with hemorrhoids. This disease is characterized by dilation of blood vessels in the anorectal region. During the act of defecation, they are often damaged due to thin walls, as a result of which the patient notices blood from the anus. Its traces may be present on toilet paper and underwear.
Chronic constipation also causes increased pressure on the walls of the intestines and rectum. When passing through the rectum, solid feces can injure the mucous membrane, which leads to the formation of cracks. In such cases, blood clots from the anus are released in small quantities, but traces of blood are clearly visible on toilet paper.
If the patient has a change in the nature of the stool and there are traces of blood in it, doctors try to rule out infectious diseases. Sudden bloody diarrhea, accompanied by a rise in body temperature to 38–40 degrees, indicates the presence of pathogenic microorganisms in the body. Fever, nausea, and increased sweating are the result of severe intoxication of the body with poisons produced by pathogenic microorganisms. Among the diseases with similar symptoms:
- amoebiasis;
- salmonellosis;
- dysentery.
Blood from the anus without defecation
As noted above, anal bleeding can occur with diseases of the intestines and digestive organs. In this case, no change in the character of the stool is observed. Often, blood from the anus becomes the only sign of pathology in the human body. Moreover, its appearance is periodic. A similar clinical picture can be observed in the following pathologies:
- varicose veins of the esophagus;
- intestinal polyps;
- Crohn's disease;
- rectal cancer;
- haemorrhoids;
- ulcerative colitis.
Bleeding from the anus without pain
Heavy bleeding from the anus without pain is observed when there is a violation of the integrity of the walls of the intestine, colon and rectum. This clinic develops when tumors and polyps appear in the intestines. Symptoms appear when the formations reach large sizes. If blood comes from the anus, this may indicate some pathology of the hematopoietic system. In most cases, they are chronic, the symptoms disappear and reappear after a while. Leukemia and Crohn's disease are diseases with a similar clinical picture.
Blood from the anus in some cases may be a consequence of mechanical damage to the epithelium that lines the inside of the wall of the rectum. This situation can occur in the presence of chronic constipation, when excess feces begin to put pressure on the rectum, which leads to disruption of the mucous membrane of the organ. Such blood in feces can go unnoticed for a long time. An occult blood test helps to identify it.
Pain and blood in the anus
When a patient bleeds from the anus and this phenomenon is accompanied by acute pain, the first thing doctors rule out is hemorrhoids. In this case, the appearance of blood may have no connection with the act of defecation. However, in most cases, pain becomes more intense when going to the toilet. The walls of the large intestine and rectum experience greater pressure, resulting in blood appearing from the anal fissure. In this case, patients note the appearance of additional symptoms - burning, itching in the anus are signs of hemorrhoids in the rectum.
Blood from the anus during pregnancy
Some expectant mothers during gestation notice the appearance of bloody discharge in the anus. Scarlet blood from the anus in pregnant women indicates the presence of microcracks in the rectum or hemorrhoids. In this case, hemorrhoids can be small or located inside the organ, so they are not visualized.
The development of pathology at this time is facilitated by the increased load on the pelvic organs, caused by the growth of the uterus and fetus. For the same reason, pregnant women often experience constipation, which aggravates the situation. Doctors advise to combat them by revising your diet: including vegetables, fruits, cereals in the menu, and increasing the volume of fluid you drink helps to cope with constipation and prevent the development of hemorrhoids.
Stool color
Stool with blood in men (the causes of the phenomenon are different) can be of different colors. Does the color of stool matter in diagnosis? This sign is also paid attention to. Black stool is evidence that blood has stagnated in the tract for a long time and has become caked. Often, a dark-colored discharge is noted in the presence of cancer tumors.
Chestnut-colored stool is evidence of a pathological process in the small intestine, located in the middle of the tract.
A visit to a specialist is extremely necessary, since blood in the stool is a very serious symptom. It's best not to put off visiting your doctor's office. Indeed, in the case of a serious disease, it is easier to stop it at an early stage than in an advanced form.
Treatment
What to do if there is bloody stool? Consult with a specialist who will prescribe the necessary treatment based on the results obtained. In addition to drug therapy, the patient is prescribed adherence to the principles of dietary nutrition. The following groups of drugs are used during therapy:
- rectal suppositories - necessary for healing injuries to the intestinal mucosa;
- venotonics - used to eliminate varicose symptoms;
- drugs containing glucocorticoids;
- antitumor;
- Sulfasalazine and its derivatives are prescribed for use when diagnosing Crohn's disease;
- antibiotics;
- antiviral, interferons;
- hemostatic;
- pro- and prebiotics.
Diagnosis of polypous and ulcerative formations is an indication for surgical treatment.
Diagnosis by a proctologist in the presence of blood in the stool
What are the causes of such a phenomenon as blood in feces in men? Diagnostics carried out by proctologists includes a number of procedures, on the basis of which a specialist can make a final diagnosis and choose the appropriate therapeutic course.
The main methods include the following:
- Anamnesis collection. In this case, a description of the signs obtained during diagnosis at home will be useful. The patient may describe the consistency of atypical discharge during bowel movements. In addition, the doctor will ask about the patient’s general well-being and complaints.
- Digital examination of the rectum. The procedure is quite unpleasant, but very necessary, since in most cases it helps in establishing the correct diagnosis.
- Diagnosis is not complete without a general analysis. Usually the hemoglobin level is determined, and stool and urine are examined.
- Additional manipulations. If the examination does not give the doctor a complete picture or the doctor has doubts about something, then he may recommend additional testing, tests or research. Similar methods include coprogram, endoscopy, colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, and radiography. In this case, the section of the large intestine is subject to examination. Manipulations will make it possible to make the correct diagnosis, on the basis of which the patient is prescribed appropriate therapy.
In most cases, the pathological processes that provoke bleeding bring discomfort to the patient, but are not fatal. But in some cases the situation can be critical. After all, the reasons for the appearance of blood in the stool in men are not the same. Sometimes such a manifestation is provoked by the presence of a cancerous tumor, metastases and other dangerous pathologies. They pose a direct threat to the patient's life. This is why an examination by a specialist is essential.
Diagnostics
In case of bloody stool in adult patients, a full medical examination is prescribed in order to identify the cause of its appearance. Initial procedures - examination by a proctologist: assessment of the condition of the anus, digital examination of the sphincter and intestinal mucosa. To diagnose the cause, a person is prescribed:
- Blood tests (general and biochemistry). Necessary for identifying signs of inflammation and anemic conditions.
- Coprogram. It is carried out to determine traces of hidden blood and helminth eggs.
- Sigmoidoscopy. Used to identify pathologies in the large intestine.
- Radiology.
- Ultrasound examination of the digestive organs.
- Colonoscopy.
- Gastroscopy. Recommended for suspected inflammatory processes in the upper intestines.
The colonoscopy procedure is an opportunity to examine the surface of the gastrointestinal tract from the inside
With minor bleeding that develops due to the removal of teeth, wounds in the oral cavity, and others, blood in the stool is visually invisible. But this does not always mean that it is not there. To confirm occult blood, a special laboratory test is performed.
Three days before donating stool, meat, fish, and iron-containing medications are excluded from the person’s menu. The collected feces are treated with acetic acid. A change in color to blue/green indicates the presence of blood.
Blood in stool due to hemorrhoids
What are the causes of such a sign as blood in stool in men? This symptom occurs without pain in the presence of microcracks. But with hemorrhoids, it causes discomfort.
Hemorrhoids are a common cause of blood appearing during bowel movements. This disease is characterized by swelling, inflammation and subsequent loss of vein nodes. All this is accompanied by the release of blood. The cause of the pathology lies in varicose veins, in which the venous outflow of blood is impaired.
As a result of this process, the rectal tissues fill with blood. Over time, it coagulates, and this is how hemorrhoids are formed. They are neoplasms filled with blood. That is why when relaxed they decrease in size, and when tense they increase.
With hemorrhoids, blood is located on the surface of the stool and appears in the form of streams. It can be seen on toilet paper or in the toilet. If a person suffers from constipation, hemorrhoids can worsen and cause bleeding.
Self-diagnosis methods
Self-diagnosis will help shed light on the current situation. Of course, the patient will not be able to identify the root cause, however, such actions can help calm down and collect the necessary information about their condition.
In the future, when contacting a competent specialist, this will help for a correct diagnosis.
If a person discovers blood in his stool after a bowel movement, you need to pay attention to:
- amount and shade of blood;
- are there any clots or blood streaks?
- where exactly the blood collected (on the surface of the feces, or inside);
- whether there are drops of blood on underwear and on toilet paper.
The above symptoms will help your doctor make an accurate diagnosis.
If the problem is caused by hemorrhoids, there is an excellent option for removing hemorrhoids using laser therapy. This method, modern and painless, will help solve the problem accurately and for a long time.
This technique is recommended in advanced cases. It consists of cauterizing the vessels of the rectum to the patient using laser radiation, thus eliminating the cause of the bleeding.
Advantages of laser technique:
- there is no need for hospitalization;
- painlessness and speed of the procedure;
- the likelihood of relapses is minimized;
- short postoperative period.
Unfortunately, the laser treatment method is not yet very widespread in Russia, and many patients resort to a conservative method - surgical intervention.
Forms of hemorrhoids
It is customary to distinguish two forms of hemorrhoids:
- Chronic appearance. It flows in waves. If proper therapy is not carried out, the disease begins to progress and over time takes an acute course.
- Acute stage. It manifests itself in sharp pain sensations that seem to burst a person from the inside. In addition, the patient complains of the presence of a foreign body in the anus. When defecating in a sitting position, this sensation becomes more acute. The disease may be accompanied by copious bleeding. Complications such as paraproctitis and tissue necrosis may also occur, which, if not properly treated, can even lead to sepsis.
What measures to take
When blood is detected during bowel movements in women without pain, the patient’s well-being can be characterized by:
- semi-fainting states;
- severe, debilitating weakness;
- feeling of discomfort.
The same conditions are typical for men.
Without wasting time, the patient should be examined by a proctologist as soon as possible.
If a pregnant woman experiences bloody discharge from the anus, she should visit an antenatal clinic to find out the possible causes.
If blood leaks out of a child’s stool, the baby should be taken to a pediatrician and tests scheduled as soon as possible. The specialist will determine which doctors to refer the little patient to and what to do.
Basic actions when bleeding from the anus is detected:
- Immobilize the patient so that he is at rest.
- In case of continuous bleeding, apply a cold bandage to the anus and swallow ice (drinking water is prohibited).
- Washing with cold water.
- Compress (cold) on the bleeding area (to constrict blood vessels and stop blood loss).
- Use of drugs to stop blood loss:
- Insertion of collagen tubes into the anus, which swell inside and prevent further bleeding. These devices exert a compressive effect on the vessels in the anus, thereby stopping bleeding. There is no need to remove the sponges - they will dissolve inside on their own.
Reasons for the development of hemorrhoids
The causes of the disease are varied. The most common ones include:
- passive lifestyle;
- increased physical activity;
- presence of constipation;
- abuse of spicy foods or spices;
- consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- inflammatory process in the gastrointestinal tract;
- oncological neoplasms in the pelvic area.
For this reason, hemorrhoids can be classified as an occupational disease. Why does blood with feces appear in men (the reasons are described in the article) during a certain type of employment? The symptom is often found in loaders, drivers, athletes, accountants and representatives of other professions who lead a sedentary lifestyle or lift heavy objects.
Rectal suppositories and treatment with their use
A very popular remedy for eliminating such problems are rectal suppositories.
This easy-to-use tool helps solve many problems:
- healing of damaged tissues;
- relief of the main symptoms;
- elimination of microcracks;
- relieving severe itching;
- elimination of pain syndrome;
- reducing the activity of proliferation of hemorrhoidal compactions.
The suppositories are inserted into the anus while lying on the back, after which the patient must roll over onto his stomach and remain in this position for at least half an hour.
The most effective in use, according to patient reviews, are suppositories such as:
- Aurobin;
- Anuzol;
- Anestezol;
- Relief.
If the patient is a pregnant woman, the attending physician will recommend the use of suppositories containing:
- papaverine;
- ichthyol;
- glycerol.
Many people wonder: how to get rid of hemorrhoidal bleeding at home? The initial stage of hemorrhoids is treated with traditional methods, so this approach is quite natural.
Healers achieve high efficiency in treating an unpleasant problem, practically guaranteeing a positive result from this approach. However, it is quite risky to use traditional methods without the supervision of a competent specialist.
It is better to use healers’ recipes as aids in professional therapy prescribed by a doctor.
The most popular folk methods are presented by the following recommendations:
- taking baths with a small amount of potassium permanganate solution for hemorrhoids;
- baths with the addition of infusion of chamomile and St. John's wort, mixed in a ratio of 1 to 1, in case of anal fissures;
- the use of microenemas with chamomile (30g of chamomile flower herb, brew with a glass of boiling water, cool, leave for 2 hours, insert into the anus using an Esmarch mug) for colitis, fissures, hemorrhoidal internal manifestations;
- if the patient has helminths, they are removed using a solution from onions: a chopped onion head is poured with warm boiled water overnight, filtered in the morning and the liquid is drunk on an empty stomach;
- you can get rid of tapeworm using the simplest available products - garlic and milk: you need to eat 10 heads of garlic and drink a glass of milk, and then, after 40 minutes, take a laxative (however, this method is not suitable for everyone);
- the use of tampons moistened with sea buckthorn oil (sea buckthorn is an effective anti-inflammatory and hemostatic agent) as lotions to the anus;
- to combat polyps in the intestines, use celandine: a decoction of the herb is used for enemas, and the infusion (1 to 4) is drunk 10-15 minutes before meals, in the morning;
- horseradish roots mixed with honey (1 to 1), take a teaspoon three times a day - also to eliminate polyps;
- orange peel boiled in boiling water will serve as an excellent remedy against bleeding: you can either eat the peel of the fruit or add sugar to the broth and drink in small portions, 3 times a day;
- A well-known hemostatic agent, nettle, will help stop severe bleeding: dry herb (30 g) should be brewed with boiling water (200 ml), cooled and taken three times a day, 1 tbsp. spoon, before eating.
To effectively eliminate bleeding, ice suppositories are often used, prepared in this way:
- Having twisted the paper into a cone, you need to pour herbal infusion or cooled, after boiling, water into it;
- place the cone in the freezer;
- after freezing, insert into the anus, being careful.
This method is good in cases where the patient does not have an inflammatory process. If there is one, such procedures are strictly prohibited.
If the bleeding does not stop on its own after bowel movement, it is recommended to use chilled herbal infusions, introducing them into the rectum using an Esmarch mug.
The following fees have proven themselves to be excellent:
- Pour 20 g of chamomile (flowers) with boiling water (1 glass), leave for at least 5 hours, apply after straining;
- Pour 50 g of yarrow into 0.5 liters of boiling water, leave for 2-3 hours, cool (this plant has an astringent effect and perfectly eliminates bacterial infections).
Presence of diverticula in the intestine
Blood in the stool of an adult man (for various reasons) can be caused by diverticulosis. This disease is characterized by protrusion of the walls of tubular and hollow organs. The pathological process can affect any organ.
The most common location for diverticula is the gastrointestinal tract. They are often localized in the esophagus, duodenum, small or large intestine.
Symptoms of the disease, as a rule, remain unexpressed. Sometimes the disease is detected completely suddenly.
Feces and food accumulate, fermentation occurs, followed by suppuration. If the stagnant mass remains for a long time in the diverticula, it causes inflammation and perforation. In addition, the process can serve as an impetus for the development of cancer.
Diverticula in the acute stage are accompanied by constipation in the chronic form. It is this kind of constipation that causes blood impurities to appear during bowel movements. At the same time, patients complain of increased body temperature and mild pain in the gastrointestinal tract.
Causes
The causes of bloody stool are numerous. The following conditions and diseases can contribute to the appearance of feces mixed with blood:
- Anal fissures. Accompanied by the appearance of scarlet blood (noted on the top of the poop). It is absent inside, since it enters them only after formation. There are few reasons for the appearance of anal fissures. Particularly common is chronic constipation and severe straining during rectal emptying. Although bleeding that begins is not life-threatening, it can bother a person for one to three days. To diagnose pathology, a digital (rectal) examination of the rectum is performed. The pathology can be quickly treated if you visit a doctor in a timely manner.
- Haemorrhoids. Fresh blood, scarlet in color, covers the passing feces because it only appears at the end of a bowel movement. Additionally, the patient is bothered by the sensation of a foreign body in the anus, itching and soreness. The condition is aggravated by too hard stools and increased intra-abdominal pressure. In males, the cause of the disease is lifting heavy objects. Hemorrhoids can be external or internal. In the latter case, the pathology is diagnosed only during examination of the rectal mucosa using a proctoscope.
- Nonspecific ulcerative colitis. The disease is accompanied by the appearance of ulcerative areas on the mucous surface of the large intestine. In this case, mucus and pus are released along with the feces. Associated symptoms include abdominal pain, diarrhea, and increased general temperature. Pathology is diagnosed after histological and endoscopic studies.
- Oncopathology. The condition is indicated by the appearance of unchanged blood. The site of localization in this case is the sigmoid or rectum. Typical signs of cancer are weight loss, pain, increased body temperature and other symptoms of intoxication of the body.
Rectal fissure is one of the causes of bloody stools
If the area of localization of bleeding is located far from the rectum, then in the case of accelerated movement of the fecal mass, the blood comes out unchanged. The following diseases may be the cause:
- Crohn's disease. The disease belongs to the group of immune inflammations. The predominant area of localization is the small intestine and transverse colon. The condition can be triggered by stressful situations, food allergies and active smoking. Symptoms are frequent diarrhea mixed with blood, mucus and pus, high body temperature, abdominal pain, ulcers on the oral mucosa, skin rashes, and blurred vision. Stool may contain blood clots.
- Intestinal pathologies. One of the characteristic symptoms is diarrhea mixed with blood. Laboratory techniques are used for diagnosis.
Important! With a constant rate of advancement of the food coma, the appearance of scarlet blood indicates pathologies of the mucous membrane of the sigmoid or rectum.
Causes of black stools (melena)
This phenomenon is caused by damage to the mucous membranes of the upper gastrointestinal tract. The hydrochloric acid and enzymes present in food coma cause a change in the color of the blood. Under their influence, the food lump is transformed into “melena”: feces look like a sticky, viscous mass of black color.
This bleeding may be accompanied by:
How to properly test stool for occult blood?
- Ulcerative pathologies. If the source of blood loss is located in the stomach cavity or the lumen of the duodenum, then black stool will be accompanied by the appearance of pain in the epigastric region. They can appear after eating or on an empty stomach. The development of attacks of nausea, belching and heartburn is also noted.
- Pathologies of the esophagus. In this case, there is not melena with a strong unpleasant odor, but also bloody vomiting.
- Tumors.
- Abdominal injuries.
- Treatment with certain groups of medications. Taking NSAIDs and drugs that reduce the rate of blood clotting can provoke the development of gastric bleeding. One of the common diagnoses is aspirin ulcer.
- Diseases of the gallbladder and ducts. Symptoms of the pathology include the development of obstructive jaundice, yellowing of the skin, and pain in the right hypochondrium. The disease is diagnosed using ultrasound and laboratory tests.
- Varicose veins of the esophagus. Blood comes from pathologically dilated vessels. The disease itself is a complication of portal hypertension, which develops against the background of liver cirrhosis. Additional symptoms are chest pain that occurs after eating, vomiting with blood, low blood pressure, bitter taste in the mouth, spider veins on the skin of the abdomen.
- Mallory-Weiss syndrome. The cause of the development of the condition is a violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane of the esophagus or the cardiac part of the stomach down to the submucous membranes. Formed against the background of vomiting after perforation of an ulcer or in people with alcohol addiction. In addition to melena, the patient experiences severe pain.
- Perforation of duodenal ulcer.
- Oncopathology of the stomach. Typical signs are aversion to food, the development of anemic conditions, weakness, rapid weight loss, bleeding, causing the appearance of melena.
- Bowel cancer. Symptoms of the pathology include alternating constipation and diarrhea, and a false urge to defecate. Late stages are characterized by the appearance of ribbon-like feces containing bloody inclusions.
In addition, the appearance of hidden blood in the stool is caused by tumors of the esophagus, intestinal tuberculosis, as well as periodontal disease, stomatitis, and nosebleeds.
The appearance of melena during drug treatment is a reason to consult a doctor
Causes of blood in a child's stool
If a child passes blood in his stool, what could be the cause? Gastrointestinal diseases in childhood are quite common, since the digestive system is not fully formed. In babies of the first year of life, the appearance of bloody spots in feces can be a sign of the development of dysbiosis.
The accompanying inflammation of the intestinal mucous membranes causes damage and bleeding of blood vessels. Additional symptoms are severe intestinal colic, bloating, foamy stools. Streaks of blood can be detected when intestinal obstruction develops - a very dangerous condition that requires urgent medical attention. In children, the disease does not exclude stool retention.
Sometimes there is a discharge of liquid stool containing blood inclusions. At the same time, the blood content gradually increases. The next reason is anal fissures. Provoking factors are constipation, helminthic infestations, an allergic reaction to milk protein and other products. You can learn more about the causes and treatment of blood in the stool in babies here.
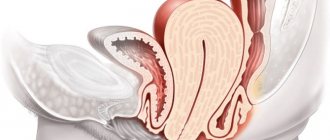
Bloody feces in women
An exclusively female reason for the appearance of blood in the stool is the development of endometriosis. It is characterized by the appearance of nagging pain in the lumbar region and lower abdomen, which intensifies during bowel movements.
Important! Similar symptoms develop after undergoing radiation therapy.
The photo shows the degree of development of endmetriosis, which often causes blood in the stool
Other reasons:
- Dark scarlet blood may indicate the presence of polyps, tumor formations and ulcerative pathologies.
- Blood after defecation often appears in the postpartum period. The cause is an exacerbation of hemorrhoids, the appearance of anal fissures caused by hard stool and past labor. There is usually no pain, but the healing period is characterized by severe itching.
- Before the onset of menstruation, it is possible that hemorrhoids may worsen, which leads to the appearance of blood on the surface of the stool.
- Red mucus found in feces during menstruation is a sign of endometriosis. The overgrown uterine endometrium, just like the normal one, begins to bleed, which explains the presence of bloody impurities.
Causes of diverticulosis
The causes of the disease can be different. The most common ones include:
- weakening of the muscles of the hollow organ;
- increased pressure in the organ;
- presence of constipation;
- development of a hernia;
- prolapse or prolapse of an organ;
- the presence of hemorrhoids or varicose veins of the lower extremities;
- injuries and inflammatory processes.
Usually, eliminating the symptoms inherent in the disease is possible only through perforation of the organ.
Self-diagnosis methods
Bloody discharge from the rectum is a dangerous symptom. It is prohibited to make any decisions on your own without finding out what was the source of the bleeding. The patient needs to seek qualified help from a therapist, proctologist, surgeon, and for women, in addition to a gynecologist. After diagnosing and establishing the cause and provoking factors, the doctor can prescribe treatment.
In case of rectal bleeding, a digital examination of the rectum is mandatory. This method helps to detect fissures, internal or external hemorrhoids and other oncological pathologies. If examination is not enough, then colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy is performed. These hardware diagnostic methods make it possible to detect even the most minor damage to the mucous membrane, and, if necessary, take a biopsy for further research.
Diagnosis is not complete without a blood test. Based on the data obtained, the doctor determines the hemoglobin level and the presence or absence of iron deficiency anemia.
Blood in the stool in the presence of a peptic ulcer
Why does blood appear in stool in men? Causes and symptoms may vary. One of them is an ulcer. It is characterized by the appearance of defects in the mucous membrane of the stomach or duodenum. The disease usually develops between the ages of 25 and 50 years.
Peptic ulcer disease has an acute and sudden onset. The disease is characterized by the presence of acute pain in the stomach, nausea, heartburn, belching and constipation. The last symptom can be so intense that even stomach pain is less of a concern.
The reasons for the development of pathology may be:
- overstrain of the nervous system and stress;
- improper diet;
- increased consumption of spicy foods and fatty foods;
- smoking;
- alcohol consumption;
- long-term use of hormonal drugs;
- predisposition to the disease at the genetic level.
Bloody stool with an ulcer looks different depending on the area in which the ulcer occurs. Usually the stool turns black. However, it should be remembered that a similar sign characterizes an intestinal tumor. Therefore, a comprehensive diagnosis is required to make an accurate diagnosis.
hidden blood
The blood that enters the stool from the upper gastrointestinal tract is black. This is due to the breakdown of hemoglobin and its conversion into iron monoxide. The shit turns dark gray or black and is called melena.
Esophageal varices
A pathology that develops as a result of impaired blood flow from the veins of the esophagus. At the same time, the vessels expand, lengthen and form nodes, the walls of which are too thin and rupture.
The main symptom of the pathological condition is bleeding from the esophagus. Before the vessels burst, the patient may feel a slight tickling in the throat and a iron taste in the mouth. As a rule, rupture of the vessel is accompanied by bloody vomiting, but it happens that this symptom is absent and black stool indicates the disease.
Mallory-Weiss syndrome
The term refers to a condition in which there are superficial ruptures in the mucous membrane of the esophagus, or rather its abdominal section, and the cardia of the stomach. The development of pathology is most often observed in patients with perforated gastric ulcers with repeated vomiting and in chronic alcoholics. The main symptom of the condition is black blood in the stool and cutting pain in the abdomen.
Ulcer of the stomach and duodenum
Bleeding from a peptic ulcer is accompanied by frequent loose tar-black stools, a feeling of debilitating nausea, bloody vomiting (black blood, reminiscent of coffee grounds), and fainting.
When the ulcer is perforated, in addition to bloody stool, the patient experiences sharp unbearable pain in the right side, increased heart rate, loss of consciousness, and cold sweat.
Stomach cancer
Bleeding, which occurs due to tissue breakdown , is manifested by the presence of blood in the stool. Also noted:
- aversion to food (meat products);
- rapid satiety when consuming a small amount of food;
- anemia;
- signs of intoxication;
- sudden weight loss.
Colorectal cancer
Oncological pathology affecting the intestines . Symptoms of the disease are:
- bowel disorder, characterized by alternating persistent constipation and diarrhea;
- false urge to poop;
- lack of feeling of relief after bowel movement;
- feeling of bloating and fullness in the intestines;
- blood (visible and hidden) in the stool;
- intestinal obstruction.
Important: in case of intestinal and stomach cancer, bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract is dangerous to human life. If any type of blood appears during stool, immediate medical attention is required.
Another article on this topic: How to prepare for an intestinal colonoscopy?
Oncology in men
The oncological process can develop in any area of the gastrointestinal tract. As a rule, the disease develops in older people, but recently it has begun to be detected in people over 40 years of age. Symptoms of cancer depend on which part of the tumor has developed. Often the pathology forms in the rectum.
There are two groups of symptoms:
- Nonspecific. A person complains of food intolerance, asthenia, fatigue, pallor, decreased and/or complete lack of appetite, sudden weight loss, impaired sense of touch and smell. These symptoms are also common to other diseases. Therefore, a diagnosis is not immediately made on its basis.
- Specific. They are typical only for oncology. Signs appear in the later stages of the disease. They are expressed in pain in the rectum, bloating and rumbling in the abdomen. These symptoms persist even after eating. In addition, patients complain of a feeling of fullness in the stomach and intestines. Moreover, after defecation, a person complains of a feeling that the intestines remain full. Disturbances such as diarrhea or constipation, increased formation of gases are noted. As the tumor increases in size, the stool changes. The stool becomes ribbon-like. The urge to have a bowel movement becomes frequent. Often they turn out to be false. There is an atypical admixture of blood, mucus, pus and pieces of tumor in the stool. At a late stage of the disease, obstruction appears.
When the pathological process spreads to the upper rectum, constant constipation, a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen, pain, and incontinence of feces and gases are a concern.
Bleeding in the presence of cancer is not so intense, but is characterized by regularity, which provokes anemia and asthenia. In this case, an admixture of blood is noticeable in the stool. The chair turns black. Such signs indicate the presence of a cancerous tumor.
Proctologist's research
Diagnostic studies by a proctologist will help to establish the root causes of the appearance of blood in the stool during defecation. The examination consists of several stages; after completing them, the patient is informed of the diagnosis and treatment for the disease is prescribed.
The most popular diagnostic methods are:
- examination of the rectum by palpation is not a very pleasant procedure, but extremely necessary for making a diagnosis;
- carrying out general tests: blood, urine, feces;
- collection of information by the doctor from the patient about the time of onset of the disease, its symptoms and duration of course;
- prescribing additional tests for a more in-depth study of the patient’s condition.
By and large, bloody discharge during bowel movements brings the patient a feeling of discomfort and pain, however, it does not pose a threat to his life. However, very serious situations leading to death are also possible.
The appearance of blood in the stool can be caused by, among other things, cancer and the growth of metastases. Therefore, in order to avoid negative consequences, you should not postpone your visit to a specialist. After all, as you know, it is better to prevent any disease than to carry out a course of lengthy and expensive therapy in the future.
Causes of the disease
The main causes of liver cirrhosis include:
- alcohol abuse;
- presence of hepatitis;
- poisoning of the body with industrial chemicals or certain groups of drugs;
- the presence of heart failure causing venous congestion in the liver;
- changes in the structure of the bile ducts;
- a genetic factor manifested in diseases such as glycogenosis, hemochromatosis, etc.
If the cause of bleeding is cirrhosis, then in addition to treating the consequences of the disease, therapy for the underlying disease is necessary. For this purpose, they turn not only to the proctologist, but also to other specialists.
Hemorrhoids or cancer
The cause of blood discharge from the anus can be a disease such as hemorrhoids or colon cancer. How to recognize these diseases at the initial stage? Hemorrhoids are inflammation and prolapse of varicose veins of the rectal plexus. Bloody discharge occurs after bowel movements. They are insignificant. They can only be seen on toilet paper or in feces. When the venous plexus ruptures, the hemorrhage is profuse.
The cause of blood during defecation is severe straining or injury to the rectal mucosa with hard feces. Blood does not mix with excrement and is on the surface. No pain is felt. Regular rectal hemorrhages can cause anemia.
If treatment is not started in time, hemorrhoids become more complicated. The patient may develop paraproctitis. The nodes are easily injured and become inflamed when infected. Symptoms include itching and burning in the anus, pain during bowel movements and the sensation of a foreign object in the anus.
Stages of development of hemorrhoids (Click on the picture)
Treatment of hemorrhoids at stages 1-2 is carried out with medication. Suppositories, ointments and gels are considered effective. They quickly relieve pain, stop bleeding, restore damaged tissue, relieve swelling and improve blood circulation. In advanced stages, medications are not effective.
If blood clots in excrement are mixed with mucus, then this is a symptom of oncology. Blood in the stool is dark brown or black. Colon cancer can be recognized by frequent urges, poor appetite, bloating and rumbling in the abdomen, weight loss, weakness, high fever, and pale skin. Many of the symptoms are characteristic of other diseases, so if discomfort occurs or changes in the nature and shape of excrement, you should consult a specialist.
Without treatment, the tumor grows rapidly and affects neighboring organs. Colon cancer requires complex treatment. The treatment plan is drawn up individually. The type of surgery depends on the size of the tumor and its location. If the tumor has metastasized, then the tumor is completely removed along with the surrounding tissues and affected lymph nodes.
Therapy
Blood in feces in men (the reasons are described in the article) is eliminated using various drugs. For complications of a number of diseases, rectal suppositories and ointments are used. This therapy is appropriate in the presence of hemorrhoids. Products containing zinc oxide, titanium or bismuth are selected. They have a hemostatic effect. Such drugs as “Relief”, “Proctosan Neo”, “Relief Advance” and “Proctosan” are used.
The presence of cracks in the anus and bleeding requires an integrated approach. Laxatives are also used: suppositories based on glycerin or sea buckthorn and Guttalax.
With the development of serious pathologies in the gastrointestinal tract, treatment of these diseases is required. This will eliminate the disease itself and the bleeding it causes. Pain and associated symptoms are also relieved.
Treatment options
Therapy is prescribed taking into account the reasons that caused the appearance of blood in the stool. To diagnose the disease, laboratory and instrumental examination of the intestines and ultrasound of the abdominal cavity are performed. The doctor interviews the patient, examines and palpates the abdomen, and finds out what complaints bother him.
For spontaneous or constipation caused by psychogenic factors, diet therapy, therapeutic exercises, and the development of a conditioned reflex to bowel movement are prescribed. To facilitate bowel movements, laxatives and cleansing enemas are used. Pro- and prebiotics are prescribed to patients to normalize intestinal microflora. Pain is relieved with antispasmodics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Medicines
Many patients turn to the doctor with the question: how to treat constipation in order to avoid the appearance of blood in the stool. Laxatives for local (suppositories, microenemas) or systemic use (drops) help to liquefy hard feces and quickly cleanse the intestines.
Laxatives for constipation:
- Bisacodyl.
- Regulax.
- Guthallax.
- Duphalac.
- Senna preparations.
In case of constipation with bleeding, it is forbidden to use laxatives for a long time, this can cause psychological addiction, intestinal atony, and electrolyte imbalance in the body. In acute inflammatory diseases, drugs for oral administration are not prescribed; in such cases, suppositories or pharmaceutical microenemas are used.
If blood flows profusely from the anus due to constipation, it is necessary to take a hemostatic agent (Vikasol, Dicynon) and call an ambulance, since such a symptom may indicate intestinal bleeding. To strengthen the veins of the rectum and prevent blood loss during defecation in patients with hemorrhoids, venotonics are prescribed: Troxevasin, Detralex. Pain is relieved with antispasmodics (No-shpa, Spazmalgon) or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Mydocalm, Nimesulide).
Patients with anal fissures, when visiting a proctologist, are interested in what to do to alleviate the condition. Ointments for external use help to remove swelling, spasm, reduce inflammation, and speed up wound healing: Levomekol, Relief, sea buckthorn ointment. To prevent infection of cracks, it is recommended to take warm sitz baths with a decoction of chamomile, calendula, a solution of baking soda, and potassium permanganate.
Cleansing enemas
If blood appears in the stool after constipation, acute symptoms of inflammation of the digestive tract are bothering you, you can cleanse the intestines at home with an enema. To do this, add sea buckthorn, vaseline or linseed oil to warm water, draw the solution into a rubber syringe and carefully inject it into the anus. Fatty liquid facilitates the passage of feces and reduces the risk of injury to the mucous membranes.
This remedy is contraindicated in the presence of purulent wounds, as it can delay the discharge of necrotic masses. For paraproctitis, it is allowed to add soap with neutral pH and herbal decoctions to the water. You can also use a pharmacy microenema - Microlax.
The importance of normal stool
Normally, each person should defecate 1-2 times a day. In the presence of various diseases and other reasons, this process may be disrupted: disappear completely or, conversely, become more frequent. In both cases, ailments arise during bowel movements, which can significantly complicate a person’s life.
Violation of the frequency of bowel movements is already a symptom of a disease that requires consultation with a proctologist, surgeon, or gastroenterologist.
At the first sign of acute pain in the rectum, you should urgently visit a proctologist. Only in this case can correct treatment and a favorable outcome be guaranteed.
Most common reasons
Haemorrhoids
About 10% of people in the middle age group suffer from hemorrhoids; men are affected 4 times more often.
Its development is facilitated by a sedentary lifestyle, heavy physical labor, and pregnancy.
At the beginning of the disease, there is discomfort and a sensation of a foreign body in the anus. Recurrent rectal bleeding then appears. They occur during defecation or immediately after it. The blood has a bright red color; it does not mix with the feces, but covers it on top. Traces of blood may be found on toilet paper and underwear. The volume of blood released varies from a few drops to a puddle. Frequent intense bleeding leads to the development of anemia.
When inflammation occurs, pain occurs during defecation and persists for some time after it.
Mucus discharge irritates the skin around the anus, causing an itchy sensation, and contributes to the development of eczema.
Anal fissure
It is a linear ulcer located in the lower part of the anal canal.
Its main symptoms are bleeding and pain that occurs during bowel movements. The pain is quite intense, burning, stabbing in nature, radiating to the perineum, sacrum, and rectum. It lasts from several minutes to several hours.
Bleeding is usually minor. In this case, the blood is on the surface of the stool in the form of stripes and does not mix with it. Sometimes blood comes out in drops at the end of a bowel movement, leaving marks on paper or underwear.
Polyposis of the colon
Polyps are benign neoplasms of epithelial nature. They can be single or multiple, localized in any part of the colon, and are prone to degeneration into malignant tumors.
The main complaints of patients with polyposis are:
- discomfort;
- abdominal pain that does not have a clear localization;
- bowel dysfunction in the form of alternating constipation with diarrhea;
- stool mixed with mucus and blood.
Bleeding with polyposis is not intense. The blood is dark, mixed with mucus and feces, however, the closer to the anus the polyp is located, the brighter the blood. Bleeding can also be hidden, and quickly leads to anemia in the patient.
Colorectal cancer
Tumors of the large intestine begin to manifest themselves only after 1.5-2 years from the moment of their occurrence. Bleeding is a delayed symptom and develops at the stage of tumor disintegration.
The first signs of rectosigmoid cancer are spastic constipation, the stool becomes ribbon-shaped, and later mucus and blood appear on its surface. Often with intestinal cancer, hemorrhoids develop, which are extremely difficult to treat. Pain is not typical for this location and appears only with the development of intestinal obstruction. The tumor may not be detected by palpation even in the late stages of the disease.
When a tumor affects the right parts of the colon, the first symptoms appear very late and are nonspecific. Signs of intoxication increase (fever, accelerated ESR), lack of appetite, rapid loss of body weight. Pathological impurities appear in the stool: mucus, blood (usually hidden), pus, and sometimes the stool takes on the appearance of “raspberry jelly.” Later, pain appears in the right half of the abdomen, and the tumor is often detected by palpation.
Rectal cancer is characterized by nagging, burning pain in the rectum, frequent urge to defecate, followed by the release of mucus and blood. Blood does not mix with feces, but unlike hemorrhoids, it is released at the beginning of defecation. Feces may include pus and tumor breakdown products.
Diverticular disease
Diverticulosis in most cases affects the large intestine, mainly its left sections. The incidence of the disease increases with age, affecting more than 60% of the population after 70 years of age.
Uncomplicated colonic diverticulosis is usually asymptomatic. Inflammation of the diverticulum manifests itself:
- pain predominantly in the left abdomen;
- unstable stool;
- decreased appetite;
- nausea;
- increased temperature;
- leukocytosis.
Diverticulitis is complicated by bleeding in 3-5% of patients. It is often profuse and develops suddenly. Signs of acute blood loss increase (weakness, pale skin, dizziness, tachycardia), and little changed blood appears in the stool.
Nonspecific ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease
Inflammatory bowel diseases with similar intestinal manifestations. They are characterized by an undulating course with periods of exacerbation and remission.
The main symptoms of the disease are:
- bloody diarrhea;
- abdominal pain;
- fever during exacerbations.
With nonspecific ulcerative colitis, diarrhea with blood can be the only symptom of the disease for a long time. With Crohn's disease, bleeding occurs less frequently; depending on the level of damage, blood in the stool may be detected in the form of dark clots or bright red streaks.
In addition to intestinal damage, there are systemic symptoms (erythema nodosum, arthritis, skin and eye damage, sclerosing cholangitis, etc.)
Intestinal and other infections
Anal bleeding is sometimes a symptom of certain infectious diseases (dysentery, typhoid fever, amoebiasis, hemorrhagic fevers).
Infectious diseases are characterized by:
- acute onset;
- febrile fever;
- weakness;
- headache, muscle pain;
- and other manifestations of intoxication: vomiting, diarrhea, severe abdominal pain.
In this case, abdominal pain always precedes bleeding. The blood is usually dark and mixed with stool and mucus.
Pseudomembranous colitis
One of the dangerous complications of antibiotic therapy. Most often it develops while taking sulfonamides, clindamycin, ampicillin, lincomycin, and cephalosporin drugs.
The disease manifests itself as cramping abdominal pain, intoxication syndrome, and severe diarrhea. The stool is copious, watery, and in severe forms it takes on the appearance of “rice water.” The stool contains pathological impurities - mucus, blood.
In what pathologies are streaks of blood present in feces?
Thin blood threads can occur in both acute conditions and chronic diseases. In fact, there is quite a large list of diseases. Each of them requires careful attention and immediate treatment. Let's look at the most common ones:
- neoplasms benign (polyps) and malignant (cancer);
- haemorrhoids;
- inflammation of the intestinal mucosa;
- diverticulitis;
- ulcerative colitis;
- helminths of different types.
Blood in the intestines always indicates problems in the digestive system. The patient’s task is not to react emotionally, but to carefully analyze where and how blood inclusions appear.
Hemorrhoids can cause blood to appear in the stool.
Streaks in the stool are diseases of the large intestine, unlike scarlet blood in hemorrhoidal problems. If you observe more or less identical staining of feces with cherry-colored blood, then this is most likely a pathology of the small intestine.
Prevention of an unpleasant symptom
To keep your pet healthy, you need to take care of it by following simple measures to prevent possible diseases. You can prevent the occurrence of pathological conditions in which blood appears in your cat’s feces by taking into account the following animal care tips:
- keep medicines, chemicals and toxic substances out of reach;
- when choosing ready-made dry food, take into account the age, weight and health status of the pet;
- when feeding dry granules, provide the cat with free access to water and change it in a timely manner;
- carry out timely treatment of your pet against parasites;
- Take your cat to the veterinarian regularly for preventive examinations.
Share with friends!
Pain during bowel movements: main causes
The causes of pain during bowel movements can be different and depend on many factors.
So, even such a banal reason as an upset stomach can cause it. An abundant amount of food, its poor quality, food unsuitable for the stomach causes indigestibility of food. As a result, problems with bowel movements arise. This situation is often observed when a person does not monitor his diet and consumes excessive amounts of fatty, spicy foods. Eliminating foods that can cause stomach upsets from your diet can solve the problem. If a person continues to lead his usual lifestyle, it is possible that more serious complications will develop, which will have to be treated under the supervision of specialists.
It is a careful attitude towards one’s health that helps a person quickly get rid of pain in the anus or never know what it is.
If we talk about diseases, then most often pain that occurs during bowel movements occurs when:
- anal fissure;
- subcutaneous and sciatic paraproctitis;
- inflammation of the rectum;
- acute form of hemorrhoids;
- colorectal cancer.
How to alleviate the condition?
If a person has gone to the toilet with blood only once, this is already a cause for concern. If the situation repeats, and for a long time, or additional symptoms appear (pain, nausea, etc.), then you should definitely consult a doctor.
This is true for cases where blood after using the toilet mostly appears in men. If bleeding is noticed by a woman of reproductive age (especially if she is pregnant or has recently given birth), then there is definitely no point in postponing a visit to the doctor.
Therapy for anal bleeding is prescribed based on diagnostic results. This means that the doctor, during a series of procedures, determines the cause as accurately as possible, and only after that makes recommendations for eliminating it.
You should not self-medicate, but you can still follow a few recommendations:
- If blood appears due to hemorrhoids or anal fissures, then local treatment is sufficient. Fat-based creams and ointments, rectal suppositories with medications, etc. help against hemorrhoids. Baths of chamomile and other herbal infusions and decoctions also have a wound-healing effect.
- If the walls of the rectum or anus are injured during the passage of compacted feces, then the situation can be corrected by normalizing the stool. To do this, we adjust the diet, excluding fixing foods, drink more liquid (up to 2 liters per day) and follow a toilet routine.
- Diets that relieve stress on the gastrointestinal tract are also effective. For most diseases, doctors recommend avoiding fatty, spicy and too salty foods, and reducing the consumption of fried foods and smoked foods. In addition, you need to completely eliminate alcohol and minimize the number of cigarettes you smoke.
- Another group of recommendations concerns compliance with personal hygiene rules. Bleeding. Especially in the lower intestines, it can provoke infection. That is why, after each visit to the toilet, the perianal area should not just be thoroughly wiped with toilet paper, but rinsed with cool water.
Haemorrhoids
This is one of the most common causes of bleeding from the anus. This pathology is not only external, when venous nodules are visible to the naked eye, but also internal - here no signs are noticeable and, accordingly, pain does not appear.
A characteristic feature of it is the absence of mixing of feces with blood - it is distributed over their surface. In advanced cases, to fix the problem
a simple operation will be required, but with timely treatment, the matter is usually limited to conservative methods.
Cancer
This disease often occurs in the large intestine. One of its main signs is the leakage of mucus and blood. Moreover, the latter can be of any shade and mixed with feces. It often comes out in the form of clots.
The disease is found both in young people and in those who have never been diagnosed with cancer in their family.
Signs of pathology are as follows:
- noticeable change in the structure of feces;
- constipation alternating with diarrhea;
- after defecation, patients often do not feel relief;
- nausea;
- frequent bloating;
- sudden weight loss;
- high fatigue;
- anemia.
What does bleeding after bowel movement mean?
If, when going to the toilet after defecation, traces of blood are found, this indicates that somewhere along the intestinal tract there is serious damage in the form of micro-tears. The nature of the bleeding and the color of the discharge indicate where the defect formed:
- black stool indicates problems in the upper gastrointestinal tract - in the esophagus, stomach or duodenum;
- red-brown stool appears due to bleeding in the small intestine;
- a bright scarlet hue indicates that the large intestine near the anus is damaged.
Bloody discharge after using the toilet, in some cases, may be accompanied by discomfort and pain. Sometimes blood literally pours from the anus, in other cases it is not visible outwardly, but it is present in the stool. The patient may also complain that traces of blood remain on the paper after defecation. Regardless of the volume and nature of the discharge, you must remember that you will not be able to cope with such a problem as “I’m walking around with a lot of blood” on your own. Consultation with a proctologist and strict adherence to his recommendations are required.
Diseases that cause bleeding after bowel movements
A person may go to the toilet with bloody discharge if he also suffers from certain internal diseases, including:
- haemorrhoids. Bloody, bright red discharge appears after defecation. As a rule, they are not mixed with feces;
- gastritis. Formed feces are observed, accompanied by profuse bleeding.
- anal fissure. After using the toilet, a scarlet liquid appears, not mixed with feces. It is released in small portions, and pain and burning are felt immediately afterwards;
- colitis. The inflammatory process in the rectum leads to the formation of periodically bleeding ulcerations, after which complaints arise such as “I go to the toilet with blood”;
- peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum. These diseases are characterized by a combination of black stools with “coffee grounds” vomiting and pain in the upper abdomen;
- polyps. When they form on the intestinal mucosa, blood is released moderately when going to the toilet, and there is no pain;
- diverticulitis. Formations on the intestinal walls in the form of pouches usually do not cause much trouble, but their presence can cause a complication such as intestinal bleeding. Discharge flows from the anus in a thin stream or falls out in the form of clots. The patient's general condition is serious, with abdominal pain, weakness, decreased blood pressure, pallor, loose stools or constipation;
- proctitis With this disease, ulcerations appear on the intestinal mucosa, which are then covered by the inflammatory process. If you go to the toilet for a long time, you will see that the feces are mixed with mucous and bloody discharge;
- rectal cancer. In the presence of malignant neoplasms, blood can be released in different ways, from barely noticeable stains on toilet paper after using the toilet to heavy bleeding. Accompanying signs can help you suspect the disease - rapid weight loss, bowel dysfunction, ribbon-like stool, abdominal pain, and a feeling of incomplete evacuation.
In addition, patients who suffer from phlebectasis may go to the toilet with blood. The disease is more common in men and is characterized by increased pressure in the portal vein. The obstructed passage of blood through the vascular bed leads to its lengthening, expansion and tortuosity, resulting in the formation of varicose nodes, on which microcracks appear over time.
Diseases such as atherosclerosis and HIV can also cause blood to appear after you go to the toilet for a long time. In the first case, the disease causes a narrowing of all blood vessels that nourish the body. As a result of blockage by a blood clot or embolism, a rupture occurs and internal bleeding begins.
The human immunodeficiency virus itself does not cause discharge from the anus; the disease leads to a decrease in immunity and the progression of other pathologies.
Colitis
This is the name for inflammation in the colon. The following symptoms are characteristic of this disease:
- flatulence;
- stomach ache;
- unpleasant odor in stool.
The acute form of colitis is characterized by severe symptoms. Chronic has more blurred signs.
The most common types of pathology include the following:
- ischemic;
- ulcerative;
- infectious;
- drug.
Children's problems
A child may have blood in their stool for the same reasons as adults. There are also some specific problems that are characteristic of childhood:
- Intestinal obstruction. This problem usually appears before 2 years of age and is very dangerous. First, after feeding, the child begins to worry and scream a lot, then vomiting begins. The stool is frequent and loose, and blood is visible. After a few hours, the stool takes on the appearance of red mucus. Intestinal obstruction can be caused by:
- congenital anomaly in the development of the intestinal tube;
- untimely introduction of complementary foods;
- switching to a different milk formula.
- Dysbacteriosis. In a baby, this problem can be caused by a poor diet. If the child is breastfed, then the problem is in the mother's nutrition. Common causes include weak immunity or unnecessary antibiotic treatment. In addition to blood, mucus is observed in the stool, and the child suffers from bloating and diarrhea.
- Allergy. The reaction is usually caused by a food product - gluten, cow's milk protein, citrus fruit, food additive or coloring. In this case, the blood in the stool appears as inclusions or streaks, the stool becomes foamy, and diarrhea begins.
- Rectal fissure. Typically, this problem occurs with chronic constipation.
Important! Any alarming symptoms in children is a reason to immediately call a doctor. The consequences can be very serious. For example, in the absence of timely help, intestinal obstruction can be fatal.
How to get rid of pain during bowel movements?
To eliminate pain after defecation, it is necessary to determine its nature.
As you can see, there are many diseases that cause this symptom. A proctologist deals with problems associated with anal diseases. Only a doctor can diagnose the disease and help get rid of the problem.
It is possible that during the diagnostic process, consultation with other specialists may be required: a surgeon, urologist, gynecologist, gastroenterologist.
Diagnostic methods such as ano-, colon-, and gastroscopy will help to study the mucous membrane of the rectum, identify hemorrhoids, fissures, benign and malignant neoplasms.
Laboratory diagnostic methods (blood, urine, stool tests, including occult blood tests) will help differentiate the pathology.
Treatment methods for painful bowel movements depend on the diagnosis:
- For constipation or diarrhea caused by poor diet, it is enough to simply eliminate the provoking factor.
- For hemorrhoids, anal fissure, proctitis and paraproctitis, conservative or surgical treatment is prescribed. The doctor chooses a treatment regimen individually, based on the severity of symptoms and the degree of advanced disease.
- If the patient suffers from severe pain in the anus before, during and after defecation, in addition to the main one, symptomatic treatment is prescribed, aimed at reducing discomfort and facilitating the act of defecation.
The patient himself plays an important role in eliminating pain. It is very important to normalize stool and avoid constipation and diarrhea by all means. To do this you need:
- carefully choose foods for your daily diet;
- drink at least two liters of water every day;
- Eat enough fiber (found in fresh vegetables and fruits), which helps soften stool.
If constipation is irregular, the doctor may recommend taking laxatives, however, for a short time, otherwise addiction to the drug may occur and the problem will only worsen.
Many people, regardless of whether they are men or women, have to experience what it’s like to experience a lot of blood. The specifics of modern life often become a determining factor for the development of diseases for which such a complaint is very characteristic. Unfortunately, most often a person is embarrassed about diseases associated with the anus or genitals and keeps silent about his condition. The realities of life are such that it is necessary to forget about false shame and turn to specialists for help in time. Quite often, the complaint: “I go to the toilet with a lot of blood” indicates the presence of a serious health problem, especially if this is repeated regularly.
Examination and diagnosis
Determining the severity of the disease in an animal and its severity involves a number of examinations:
- visual inspection of the dog;
- stool examination;
- examination of the rectum;
- ultrasound diagnostics of the peritoneum;
- performing a colonoscopy or gastroscopy (depending on the color of the blood impurity).
For a correct diagnosis, the information that is required from the dog owner also matters a lot:
- timing of the onset of symptoms of the disease;
- whether deworming was carried out in a timely manner and when;
- what kind of diet does the pet have (does it chew bones, picks up food or other objects from the ground);
- does he suffer from loss of appetite, etc.
Based on all this, a diagnosis is established, and a treatment regimen is determined accordingly. Elimination of blood from stool is possible only if the root cause that caused such a symptom is cured. Therefore, do not delay your visit to the veterinary clinic with your four-legged friend. Not only his health, but possibly his life will depend on the speed of your actions.
Hemorrhoidal bleeding
In adult dogs, varicose hemorrhoids develop as a consequence of labor and regular constipation. When these nodules are injured by hard feces, intense bleeding develops. In this case, the feces are intensely stained with fresh blood due to its large amount. Blood loss is regular, significant and leads to anemia. A dog's feces with blood scare everyone, but the bleeding stops on its own. It is necessary to urgently seek help from a veterinary hospital to prescribe adequate therapy and eliminate the risk of recurrent hemorrhage.
In case of rectal prolapse, the diagnosis is not difficult, since the defect is visible to the naked eye. When prolapsed, the intestine is visible from the anus, is easily injured, and bleeds slightly. Most often it is a complication of constipation and bladder stones. Immediate contact with a veterinarian is necessary, because the intestinal wall may be pinched, blood flow stops, and necrosis develops. This situation requires emergency surgery.
Infectious, toxic gastroenteritis
The mechanism of development of gastroenteritis with bleeding is the same during infection or damage to the gastrointestinal tract and is explained by the release of toxic products into the intestinal lumen. It often develops in puppies when they are improperly kept in a cold room or improperly fed, which lead to a decrease in immunity.
When an infectious agent or endogenous toxins is attached, for example against the background of pyelonephritis, the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract becomes edematous. Exposure to food masses, gastric juice, and pancreatic enzymes injures the delicate mucous membrane, and the dog poops blood. The severity of bleeding varies. The less pronounced the bleeding, the more dangerous it is for the dog, since it does not get to the veterinarian sooner, but only after complications develop.
As the disease progresses, the dog develops diarrhea with blood. She refuses to eat, becomes lethargic and apathetic, hides in secluded places, and periodically moans. If a dog has diarrhea with blood, then I should treat it myself; I need to urgently consult a doctor, undergo a full examination aimed at finding the source of bleeding, the cause of the disease, and select individual therapy and diet.
Tumors of the gastrointestinal tract, helminthiases
With a long-term oncological disease of the gastrointestinal tract, the tumor growing into the lumen of the organs is constantly injured by feces and gradually begins to bleed. The severity of bleeding varies. It must be remembered that blood in the stool may not be visible to the naked eye. Hidden bleeding is also dangerous for the body, as it indicates a serious pathology. Therefore, it is necessary to undergo preventive examinations by a veterinarian.
If a dog poops blood due to tumor diseases, then it is too late to ask the question of what to do. Regular examination of the dog by a veterinarian is necessary, which will allow diagnosing the disease at an early stage and preventing its progression and the development of complications. Helminthic infestation - eimeriosis develops more often in puppies at the age of 2-3 months, leading to the appearance of blood streaks in the stool.
Ulcers are the cause of bleeding
Ulceration in the stomach and duodenum with a complicated course leads to bleeding. Intense ulcerative bleeding from the stomach is accompanied by bloody vomiting. But blood loss of about 200 ml will not cause vomiting. A transformation of the blood occurs as a result of the work of enzymes and intestinal bacteria, and the dog develops tarry black liquid or mushy sticky feces. In this situation, immediate consultation with a doctor is necessary.
Treatment and nutritional advice
When choosing treatment tactics, which is carried out in the event of detection of blood in the stool, one should take into account the fact that this is a consequence of a serious illness. First of all, it is necessary to establish the cause of this disease, and only after it is eliminated, this symptom will disappear.
The presence of blood in men is usually noted between the ages of 40 and 45 years. Therefore, upon reaching 40 years of age, men are recommended to undergo an intestinal examination. This will allow you to exclude intestinal pathology, and if it is present, promptly treat it.
If rectal bleeding occurs, it is recommended to take a horizontal position (lie down in bed) and wait for the doctor to arrive.
Treatment directly depends on the type of disease:
- With the development of hemorrhoids, phlebotropic drugs , suppositories and ointments are prescribed, which have an anti-inflammatory effect and promote vasoconstriction. In severe cases, surgical treatment is resorted to.
- If bleeding occurs due to anal fissure , conservative treatment methods can be used. Drugs are used to relieve inflammation and accelerate wound healing.
- In case of ulcerative lesions of the intestines and stomach, the patient is hospitalized. Complex treatment is prescribed with drugs that eliminate the cause of pain, relieve inflammation, and regenerate the mucous membrane.
- In the case of oncology development, the surgical method of therapy is mainly used.
- For liver cirrhosis, treatment is prescribed using hepatoprotectors, painkillers, and immunomodulators.
If such a symptom develops, you need to adhere to the correct food intake:
- It should be low-fat, preferably boiled.
- Be sure to have a large amount of coarse fiber.
- The daily diet should include boiled vegetables or fruits (beets, carrots, prunes, dried apricots).
- It is best when dishes are seasoned with vegetable oil. This will ensure (in case of constipation) painless bowel movements.
- It is very important to consume fermented milk products.
- Avoid eating white bread, giving preference to black bread.
- During the day, drink at least 2 liters of water that does not contain gases.
Which doctor should I contact and how to treat?
Bloody feces are a very dangerous condition. This is always a pathological process that has different causes. Only the doctor will decide how to treat. The patient’s task is to contact a specialist as quickly as possible, very carefully describe all the symptoms and undergo diagnostics.
Doctor's appointment
Remember, the sooner you see a doctor, the more careful and thorough the tests, the greater the likelihood of proper treatment and recovery.
Treatment methods may be different, depending on the reasons that caused this condition (from conservative to surgical).
Only a doctor will be able to answer you with accuracy: “What does this mean – feces with blood?” You need to contact a therapist, gastroenterologist, surgeon, oncologist, proctologist and infectious disease specialist.
Blood color
Based on the shade of the discharge, it is not difficult to draw preliminary conclusions. So, if bright scarlet blood flows from the anus, then most likely you have:
- haemorrhoids;
- anal fissures.
The dark red color most likely indicates the appearance of a benign tumor in the rectum - a polyp. However, the same symptom also indicates cancer. The release of dark clots during defecation also indicates a neoplasm or deverticulosis.
Why does this happen
When bloody stool appears, the cause can be infectious or non-infectious. This symptom in humans is caused by:
- Nonspecific ulcerative colitis. This is a chronic disease characterized by uniform inflammation of the large intestine. The rectum, colon and sigmoid colon may be affected. The etiology of colitis has not been established. Possible predisposing factors include autoimmune disorders, infections and family history. With this pathology, blood appears as a result of injury to ulcerative defects and damage to blood vessels. It is bright red.
- Helminthiases. Parasites can damage the mucous membrane, leading to bleeding.
- Stomach ulcer.
- Esophageal bleeding.
- Acute intestinal infections.
- Benign intestinal neoplasms (polyps).
- Varicose veins of the esophagus.
- Diverticulosis.
- Inflammatory diseases. Ulcerative proctitis is a severe inflammation of the rectal mucosa, in which ulcers form and the lumen of the organ narrows. Proctitis can be caused by injuries, infections and parasites.
- Protozoa (amoebiasis).
- Malignant diseases (bowel cancer).
- Improper conduct of medical procedures (colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy).
- Previous operations on the intestines and stomach. The presence of blood in the stool only bothers you for a while, then this symptom disappears.
- Haemorrhoids.
- Crohn's disease.
- Endometriosis.
- Mechanical injury to the mucous membrane. Possible through accidental ingestion of sharp objects (needles, bones), as a result of careless anal sex or masturbation.
- Blood diseases (leukemia, hemophilia).
- Intestinal tuberculosis. Develops as a complication of the pulmonary form of the disease. The causative agents are mycobacteria.
- Exposure to ionizing radiation.
- Cryptitis (inflammation of the anal pockets).
- Anogenital condylomatosis.
A reddish tint to stool does not mean the presence of a disease. This is observed when taking certain medications or eating food (beets, watermelons, tomatoes). When taking iron supplements and activated carbon, the stool often turns black.
Anal fissure
Discharge of blood during stool is a sign of anal fissure. This is a deep defect of the mucous membrane of an ellipsoidal or linear shape. The crack can reach a length of 2 cm or more. Pathology is often detected together with hemorrhoids. The appearance of a crack provokes:
- constipation;
- severe diarrhea;
- inflammatory diseases;
- stress;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- haemorrhoids;
- having anal sex;
- errors in the diet (excess of spicy and rough foods in the menu);
- injuries during childbirth;
- heavy lifting and blood stagnation.
In patients, traces of blood are found on the surface of the feces. She stands out a little. Blood comes out at the end of defecation and does not mix with feces. Fresh blood is scarlet in color. Some people experience heavy bleeding. Along with this symptom, pain appears during and after bowel movements, discomfort and anal itching.
Haemorrhoids
Hard stool with blood means that a person has an exacerbation of hemorrhoids. Mostly people aged 20-40 years old are affected. With hemorrhoids, the veins of the anus are affected. They lose elasticity and firmness, which leads to the formation of knots. In the early stages, the nodes are located inside, and in the later stages they come out and cannot be reduced.
Bleeding occurs when the veins of the anus are damaged by hard feces.
Hemorrhoids occur in people who lead a sedentary (sedentary) lifestyle, in pregnant women and women in labor, with constipation, long journeys, poor diet and heavy physical work.
With hemorrhoids, red blood may appear in the stool. In most patients, the volume of discharge does not exceed a few drops. Stream bleeding is only occasionally observed. If left untreated, anemia often develops. Defecation is accompanied by pain and itching. When examining the anus, hemorrhoids are revealed.
Polyps in the intestines
Polyps cause scarlet blood in the stool. These are non-malignant neoplasms, which are outgrowths on a thin stalk or a wide base. The exact reasons for their appearance have not been established. Risk factors:
- dysbacteriosis;
- chronic constipation;
- gastritis with high acidity;
- cholecystitis;
- cholelithiasis;
- tumors.
The large intestine is predominantly affected.
Signs of the presence of polyps in men and women:
- bleeding;
- pain syndrome;
- intestinal obstruction;
- feeling of fullness;
- itching, burning;
- signs of anemia;
- stool instability;
- nausea and belching.
Sometimes mucus and pus come out along with the stool. Bloody stools are observed as a result of polyp enlargement, injury and ulceration. The closer to the anus the polyp is located, the brighter the blood released. This pathology can develop into cancer.
Oncology
An admixture of red blood cells in the stool is a sign of intestinal cancer. Colorectal cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer. The risk of developing the disease increases with:
- presence of cancer patients in the family;
- genetic mutations;
- chronic inflammatory diseases;
- adenomatous polyps;
- absence of cereals on the menu;
- insufficient consumption of vegetables and fruits;
- smoking;
- alcoholism;
- stagnation of feces;
- contact with carcinogens;
- Lynch syndrome.
The main symptom of colorectal cancer is the presence of bloody spots in the stool in adults. Moreover, they are not located on top of the feces, but mixed with them. Blood is released without pain. Other signs of malignant pathology are:
- tenesmus;
- alternating diarrhea with constipation;
- gas and fecal incontinence;
- signs of intoxication in the form of exhaustion, pallor and weakness.