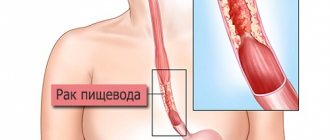
A polyp in the esophagus is a proliferation of the epithelial membrane with the formation of a benign seal on the stalk. Men over forty are susceptible to this pathology more often than other segments of the population. The tumor forms in the upper third of the digestive canal or near the gastric sphincter. If there is an elongated leg, it can fall into the pharynx or into the stomach if it develops in the lower region of the esophagus.
Often the formation is penetrated by blood vessels. Injury to blood vessels leads to bleeding. The formation is discovered by chance during an examination of the gastrointestinal tract or during a preventive medical examination.
Description
An esophageal polyp is a compacted growth of a benign nature.
A tumor grows from the cells of the epithelial lining of the esophageal tract. Esophageal polyps always grow from any place on the mucous membrane of the organ. The neoplasm occurs in places of physiological narrowing in the upper third of the hollow tube, on the epithelial mucosa in the lower part of the esophagus or near the sphincter muscle (in the area of the transition of the esophagus to the stomach). Esophageal polyp comes in two forms:
- in the form of a rounded cap on a stem;
- protrusion on a broad base.
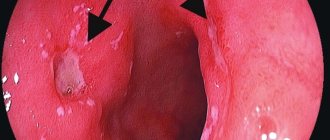
Pedicled growths are often pinched near the cardia of the stomach, that is, at the valve connecting the esophagus to the hollow digestive organ. If the growth grows in the upper part of the esophagus, it may fall out of the esophageal lumen into the pharynx. Externally, a glandular polyp is a three-dimensional structure with a lobed or smooth convex roundness of red color. From a slight touch of the endoscopic instrument, the growth begins to bleed.
In size, esophageal polyps rarely reach large sizes. The growth is diagnosed by fibrogastroscopy or other examinations of the digestive tract and stomach. Large polyps are characterized by a specific clinical picture.
In order to provide uniform approaches to the treatment of various pathological processes in the body, there is an International Classification of Diseases - ICD, according to which growths in the esophagus are classified as diseases K22 in the revised version of ICD 10.
Polyp in the esophagus: symptoms
If there is a polyp of the esophagus, symptoms become noticeable only when it reaches impressive dimensions. Small polyps often do not cause any special conditions in the patient and may be an unexpected discovery during a gastroenterological examination.
However, even minor delays in the treatment of these tumors can lead to cell transformation and the appearance of cancer, so it is important to pay attention in time to even the slightest manifestations of this pathology:
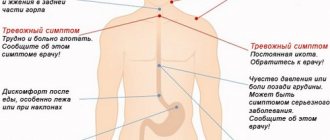
- dysphagia - a violation of the swallowing process, is a primary alarming sign, the polyp reduces the esophageal lumen and prevents the normal passage of food masses;
- feeling of discomfort behind the sternum;
- pain while eating;
- feeling of nausea and frequent gag reflexes;
- spasms of the esophageal walls;
- decreased appetite and, as a result, noticeable weight loss;
- increased irritability of the patient, against the background of the inability to fully eat.
Causes of the disease
The polyp looks like a benign red growth on a wide base. A hat in the form of a hemisphere can be placed on a stem. According to its structure, it is divided into a voluminous smooth or lobed pouch of a small size of a few millimeters. There are specimens whose diameter reaches tens of centimeters. Small growths are rarely diagnosed.
The prerequisites for the formation of polyps are:
- Inflammatory processes of the gastric mucosa;
- Inflamed mucous layer of the digestive canal (esophagitis);
- Rough, hot food;
- Smoking, alcohol addiction;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Reflux gastritis;
- Unhealthy, heavy food;
- Sedentary daily routine, stressful situations, environmentally unfavorable environment.
Clinical manifestations
A person cannot determine the presence of a polyp in the esophagus on his own. Basically, it is detected as a finding during contrast fluoroscopy or endoscopy (esophagogastroduodenoscopy) - procedures that are done for a completely different reason. The polyp in the esophagus, as a rule, is very small in size. In this regard, it shows little clinical activity. There may be no symptoms at all. The general state of health is not affected. Mild dysphagia, a swallowing disorder that has not been observed before, should alert you and requires attention.
Polyps, unlike malignant tumors, practically do not grow or enlarge. If the spasm has subsided, swallowing is restored, since the polyp cannot completely block the esophagus. Its size does not allow this.
There are cases when, for certain reasons, a polyp in the esophagus reaches significant sizes. Then clinical symptoms appear: difficulty breathing and a sensation of a foreign body behind the sternum. While eating, there may be pain when swallowing, and sometimes nausea and vomiting. A man is losing weight.
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy
When conducting a fibrogastroduodenoscopy examination, the growth according to ICD 10 is visualized as a round or oval formation. Its outer surface is smooth and has clear, even contours. The color of the polyp is red and darker than nearby tissues. When the endoscopic probe touches the tumor, slight bleeding occurs.
The method allows for a targeted biopsy of a growth in the esophagus. A fragment of tumor tissue taken is sent for histological analysis to determine the morphological structure of the sample tissue.
Diagnostics
The World Health Organization makes changes to the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Injuries every ten years. Classification is needed to form a unified system of approach to the treatment of diseases. In accordance with the ICD, the disease called esophageal polyp is assigned the number K22.
Methods for studying the alimentary canal
A gastroenterologist will make the correct diagnosis after studying the medical history and conducting an examination. What is the diagnosis of esophageal diseases based on:
- Analysis of patient complaints, lifestyle and diet. This allows you to determine the causes of polyps and set priorities when choosing further actions.
- The upper part of the digestive canal is examined using endoscopy. Inspection of the mucous layer, identification of damage and epithelial growths helps in making a diagnosis.
- The polypoid formation is biopsied. Histological examination will suggest the tactics of immediate action.
- If endoscopic examination is not available, the chest is subjected to radiography. The image is contrasted to see the outer outline of the esophagus and to distinguish possible changes in the typical structure. The size of the seal up to 1 cm will show a fold in the picture. If the polyp is relatively larger than one cm, then the contour is clearer.
Complications
The occurrence of an esophageal polyp is usually associated with frequent exposure to various damaging factors on the mucous membrane of the organ. A certain etiological role is played by the patient's hereditary tendency to hyperregeneration, accompanied by multiple polyposis. According to experts in the field of modern gastroenterology and oncology, the main prerequisites for the formation of esophageal polyps are:
- Inflammatory processes. In 80-85% of cases, polyps occur against the background of gastroesophageal reflux disease, allergic, dysmetabolic and other chronic esophagitis, and are provoked by damage to the mucosa under the influence of infectious agents and inflammatory mediators. Polyposis of the lower esophagus is often associated with reflux gastritis.
- Traumatic injuries. The impetus for neogenesis can be mechanical injuries to the epithelium, the action of thermal and chemical factors, including acute chemical burns with potent reagents (acids, alkalis). In rare cases, polyps form after linear ruptures of the esophageal mucosa in patients who have had Mallory-Weiss syndrome.
- Eating habits. A potentiating factor for polyp formation is constant irritation of the epithelial layer with spicy, hot, sour and rough foods, which stimulates the processes of hyperregeneration of the mucous membrane and facilitates the development of inflammation. The risk group also includes patients who abuse strong alcoholic beverages.
We suggest you read: Is it possible to rinse your nose if you have nasal polyps?
Risk factors
The appearance of polyps is facilitated by prolonged exposure to unfavorable environmental conditions, frequent stressful situations, and smoking. Some authors consider the cause of polyp formation at the site of the cardioesophageal junction to be a violation of mucosal embryogenesis, leading to dystopia of embryonic tissues from which epithelial neoplasias are formed.
With a long course of the disease, constant maceration of polyps with food particles occurs, which over time leads to erosions and ulcerations. Sometimes massive bleeding occurs from the esophageal vessels, which poses a danger to the patient’s life. Low-intensity repeated blood loss causes iron deficiency hyporegenerative anemia with characteristic pallor of the skin and mucous membranes, dizziness, flashing “spots” before the eyes, and general weakness.
The most dangerous complication of esophageal polyps is malignancy with the formation of esophageal cancer or adenocarcinoma: malignancy of hyperplastic neoplasms occurs in 0.25-7.1% of cases, adenomatous - in 18-75%. Patients may also experience cachexia, which is caused by the inability to receive adequate enteral nutrition in the later stages of the disease.
Not a single symptom of the disease manifests itself for a long time. However, the discovery of polyps in the esophagus plays a cruel joke when visiting a doctor late. The greatest danger is cancer. The benign appearance of the growth turns into a malignant tumor, and malignancy occurs. Adenocarcinoma of the digestive tube often develops. The wall of the hollow canal grows, bleeds, and metastases spread to neighboring organs and tissues. Sometimes the intestine or lymph node is affected.
When a tumor is injured, due to lack of treatment and diet, the body loses a volume of blood sufficient to cause anemia. The disease threatens oxygen starvation of the body, lack of vitamins, and the risk of developing heart pathologies.
Localization
If the esophageal polyp is located in the lower third, it may also appear in the stomach. If there are several tumors in the esophagus and stomach, the condition is called polyposis. In the stomach, they are mainly localized in the cardiac or antral regions and look like a mushroom or cauliflower.
In the presence of polyposis, the possibility of malignancy—transition into a malignant, uncontrollably growing tumor—cannot be excluded.
It is believed that any benign formation in the body from the moment of its growth can potentially become malignant. This is especially true if the polyp in the esophagus is large and has a thick stalk.
Treatment methods
If a polyp is detected in the esophagus, treatment is not always prescribed. Specific therapy is not required when the tumor does not cause discomfort and has a low risk of transforming into a malignant tumor. In most cases, therapy is carried out using conservative methods.
Surgery is required when the neoplasm causes severe symptoms or has signs of malignant degeneration. If polyps are up to 1 cm in size and do not show signs of becoming cancerous, operations are performed endoscopically.
For malignant tumors, surgery is performed using the open method. During the intervention in this case, regional lymph nodes and secondary tumors formed from metastases are removed.
Drug treatment does not eliminate tumors from the wall of the esophagus. If necessary, patients are given antacids to reduce the acidity of gastric juice.
In addition, you may need to use anti-nausea medications. Surgery is performed under local or general anesthesia. Anesthesia drugs are selected for patients individually.
Folk remedies
Traditional treatment can be used as an auxiliary method. To eliminate the manifestations of this disease, you can use a honey-oil mixture. To prepare this composition, mix 1 kg of ghee and 1 kg of honey. The mixture should be stored in the refrigerator.
Every morning you need to take 1 tbsp. facilities. The course of treatment must be continued until the remedy runs out.
After removal of the polyp, there is a possibility of replacing the damaged areas with connective tissue. This process can lead to narrowing of the esophagus and disruption of the swallowing process. Complications associated with the risk of malignancy are especially dangerous. Trauma to the mucous membrane of the esophagus is associated with the risk of further malignant degeneration.
To reduce the risk of complications, it is necessary to undergo a rehabilitation course after surgery. For at least 7 days, preference should be given to liquid and soft foods. Throughout the entire rehabilitation period, a gentle regimen should be followed. You need to stop playing sports and activities that involve increased physical exertion.
Treatment with folk remedies is effective when a polyp is detected at an early stage of development. The rest of the time, alternative medicine is used as an auxiliary or preventive measure, prescribed in combination with surgical and drug therapy. Popular recipes for treating pathology with folk remedies:
- Honey-oil mixture. You will need 1 kg of honey, 1 kg of melted butter. The resulting mixture is stored in the refrigerator and taken 25 g on an empty stomach every morning. The course of treatment ends when the mixture is completely used.
- Decoction of celandine. 25 g of plant is poured with 500 ml of boiling water. Taken orally three times a day before meals. The decoction can be used in the form of microenemas.
- Sea buckthorn oil. Take 25 g on an empty stomach every morning.
- A decoction of spruce needles and hops. 50 g of spruce needles are poured into 250 ml of boiling water. Then 10 g of dry hops is added. The mixture is brought to a boil over heat. You need to take 250 ml per day for 3 days. Then you need a break of 6 days. 3 treatment courses will be required.
- Juice from young burdock leaves. Three healing courses of 1 month are required with breaks of 30 days.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with Fluconazole in the treatment of intestinal candidiasis
Treatment with traditional methods helps with the early diagnosis of polyps in the esophagus. When the formations are enlarged and their localization is spread over a large area of the mucous membrane, alternative medicine is relevant as an adjuvant. What traditional therapy recipes are in demand among the sick:
- Sea buckthorn oil is taken in the morning on an empty stomach, 25 grams.
- Burdock juice will overcome the disease in three courses of treatment a month later.
- Three times a day before meals, drink a decoction of celandine herb.
- A mixture of ghee and honey is used orally, 25 g on an empty stomach in the morning.
There are other options for supporting the body with folk recipes. Do not forget that polyps in the food tube carry the risk of developing cancer. Therefore, when diagnosing the symptoms of the disease, a person is able to prevent the worsening of the pathology by going to the hospital. The doctor will decide what means and methods of treatment will be used after studying the picture of the disease.
Useful video
If there are polyps in the esophagus, the symptoms and treatment of which are clear, their removal is not so traumatic, as can be seen in this video.
If the growth is removed in a timely manner, the postoperative wound heals within 4-5 days, and the functions of the esophageal canal are restored after a short rehabilitation period. The postoperative prognosis is usually good, relapses and complications are practically excluded.
If there is a polyp of the esophagus, treatment with folk remedies is very effective, but only at the initial stages of the development of the pathology, and also as preventive measures.
Recipe No. 1. Burdock juice.
A useful remedy used for neoplasms on the mucous membranes of internal organs. Preference should be given to young burdock leaves, then cut them off, wash and dry. Next, we pass the burdock leaves through a juicer, and put the resulting nectar in a cool place. It is recommended to drink juice 2-3 times a day, a teaspoon, after meals. The course of treatment is 1 month, after which you need to take a two-week break.
Recipe No. 2. A decoction of hop cones and spruce needles.
This drug will help eliminate the unpleasant symptoms of growths in the gastrointestinal tract, as well as completely rid the body of small growths. To prepare a healing decoction, you need to pour 3 tablespoons of spruce needles with boiling water and let it brew for 20 minutes.
Then you need to add a small spoon of dry raw material from hop cones to the broth and bring everything to a boil, and then strain. You need to take the decoction internally, 1 glass per day, for 3 days, after which it is important to take a 5-day break. In total you need to take 3 courses.
Source: GastrituNet.online
Surgery
When choosing surgical tactics, one should be guided by the data obtained during histological examination of tissue samples taken from the tumor. Protrusions are removed with extreme care to eliminate the risk of seeding nearby tissues with polyposis cells.
The growth (less than 1 cm in diameter) will be removed surgically with minimal trauma. This will eliminate complications and postoperative consequences that may require more extensive surgery in the future.
The generally accepted technique for removing a polyp from the esophagus is endoscopic. To do this, an esophagoscope is inserted into the esophageal tract, through which a special electrical loop is launched. The instrument is equipped with high-quality optics and light, which allows you to visualize the pathology and transmit the image to a large screen.
After the growth has been removed, the doctor performs electrocoagulation (cauterization) of the leg and damaged vessels. Measures are necessary to minimize blood loss and eliminate bleeding that may occur in the postoperative period. The wound at the site of polyp removal heals within the first 3-5 days after the operation. The esophagus completely restores function. The patient's quality of life does not change.
Resection of large polyps with a diameter of more than 1 cm is carried out openly due to the high risk of malignancy of the growth. Operation stages:
- the esophagus opens through a wound on the front of the neck;
- tumor boundaries are assessed;
- the growth and nearby tissues are cut off;
- wounds on the esophagus are sutured.
Polyps with high growth rates were removed by esophagotomy or partial/complete resection of the esophagus. This is necessary due to the maximum likelihood of malignancy. A malignant growth requires complete removal along with the esophagus. In this case, preliminary and subsequent chemotherapy and/or radiation are necessary. After any type of operation, a biopsy is again performed with histological analysis of the esophageal tissue.
Symptoms
Hyperplasiogenic polyp is prone to asymptomatic development. The first signs of pathology appear at the stage when the neoplasm has reached an impressive size.
In some cases, they fall into the throat. These processes are accompanied by the following symptoms:
- A lump in the throat that causes a lot of discomfort when swallowing, breathing, or talking.
- When eating food or drinking liquids, pain is felt.
As the growth increases in size, there is an aggravation of discomfort.
The patient is concerned about the feeling of the presence of a foreign body in the organ. How is this expressed:
- The patient is constantly nauseous.
- Gag reflexes.
- Pain syndrome, discomfort in the sternum.
- Poor appetite.
- The patient is rapidly losing weight.
If such manifestations occur, you should immediately seek help from specialists. The doctor will conduct a diagnosis and refer you for laboratory tests.
Features and classification
Polyps most often form at the junction of the stomach and esophagus. Such neoplasms are benign in nature, but under the influence of unfavorable factors they can become malignant tumors. Such neoplasms rarely rise above the mucous membrane of the esophageal tract by more than 0.5 cm. The growth of a tumor of this type in the esophagus can cause severe symptoms, but such an unfavorable course is rarely observed.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Acne pills - on the face, hormonal, contraceptive, for teenagers. What birth control pills help with acne and acne?
There are several approaches to the classification of such neoplasms. In shape, polyps can have a thin stalk or a wide base. The first option is the most common. The formation of a polyp with a wide base is more dangerous, because Such neoplasms often develop malignantly. Depending on the nature of changes in tissues that provoke the proliferation of pathological tissues, esophageal polyps are divided into:
- inflammatory;
- neoplastic;
- hyperplastic.
Inflammatory neoplasms most often form in areas of the esophageal mucosa that were once exposed to chemical or thermal burns. In addition, a small formation may appear in an area where there is a chronic inflammatory process.
Neoplastic polypous growths are formed from cells that have an atypical structure or have undergone degenerative changes.
A hyperplastic esophageal polyp is formed as a result of the proliferation of healthy tissue lining the esophagus. A feature of polyps of this type is the low degree of possibility of malignant degeneration. Cancerous tumors form from such tumors only in isolated cases.
Causes of polyp formation
The reasons for its occurrence are not fully understood. We can only guess what the predisposing factors are. The most common of them:
- chronic esophagitis - inflammation of the esophagus;
- drinking alcohol;
- microtrauma of the sensitive epithelium of the esophageal wall after eating rough food, certain medications;
- insufficiency of the esophageal-gastric sphincter, which can result in reflux: reflux of hydrochloric acid from the stomach into the esophagus;
- genetic predisposition.
General factors also contribute to the formation of a polyp in the esophagus:
- unhealthy diet (rough food, dry food);
- stress;
- physical inactivity;
- ecology.
Danger when occurring
Polyps in the esophagus in most cases do not cause any discomfort to a person, but they cannot be ignored, since the appearance of such neoplasms is associated with the risk of their further degeneration into a malignant tumor. In most cases, it is impossible to determine exactly why a patient has such esophageal tumors.
When it comes to esophageal polyps, the reasons may lie in genetic predisposition. Often such neoplasms are detected in representatives of several generations of a family at once. The following diseases can provoke polypous growth:
- gastritis;
- burns of the esophagus;
- microtraumas;
- reflux disease.
It is believed that frequent drinking and smoking can contribute to the formation of polyps.
Reviews
Dear readers, your opinion is very important to us - therefore, we will be glad to receive feedback about esophageal polyps in the comments, this will also be useful to other users of the site.
Sergey
When difficulties appeared when swallowing food, I thought it was due to nerves. Gradually the condition worsened. I went to the doctor, and after a special examination they diagnosed an esophageal polyp. The neoplasm was single and medium in size. They offered surgery, I agreed. A minimally invasive intervention was performed using an endoscopic device. The results were good. Three years have passed and there have been no relapses.
Kirill
Problems with the esophagus arose as a result of reflux - esophagitis. Constant inflammation of the mucous membrane led to the formation of a polyp in the digestive tube. A neoplasm was discovered during examination of the esophagus. He immediately agreed to have it removed because the doctor said that the disease did not require any other treatment.
Source: ogkt.ru
Diet
- improvement and acceleration of regeneration of damaged esophageal tissue;
- prevention of wall trauma;
- stabilization of the evacuation function;
- prevention of gastroesophageal reflux disease.
The diet for esophageal polyps is designed to reduce trauma to the mucous membrane of the lower part of the damaged organ. All ingredients are prepared by steaming and then grinding to a puree consistency. Products are selected based on two requirements:
- food should help accelerate the regeneration of damaged tissues after surgery;
- preventing the development of gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Nutrition for polyps should promote cell restoration.
Prohibited:
- foods containing fiber: legumes (beans, peas), radishes, asparagus;
- all types of canned food;
- fatty, stringy meat, fish with bones;
- flour products: wholemeal bread, pasta, baked goods and muffins;
- coarse porridges: pearl barley, millet, barley.
Diet:
- every day at the same time;
- frequent split meals;
- small portions;
- increased volume of liquid consumed per day over 1.5 liters.
Classification of polyps according to ICD 10
Published: August 24, 2020 at 09:57
In the broad sense of the word, gastric polyps are defined as formations protruding above the surface of the mucous membrane. The clinical manifestations of such formations are not specific, defining specifically for this disease, which makes their diagnosis difficult. The first classification of polyps was proposed by Menetrier in 1886, who divided them according to the type of attachment. Classification based on the morphological characteristics of these formations in the stomach was proposed in 1939 by A.D. Rybinsky. According to the International Statistical Qualification of Diseases, growths in the stomach are classified in the tenth revision of the morphology of neoplasms - ICD 10.
Basically, different subtypes of formations can be divided into tumor and non-tumor. In addition, they can be divided into:
- single growths with a diameter of less than 10 mm, located in the antrum of the stomach;
- multiple presence of small formations, numbering dozens, under the general name of polyposis.
The World Health Organization defines the adenomatous appearance of ICD 10 formations as tubular or glandular structures lined with dysplastic epithelium. Neoplastic changes in the epithelium create conditions for the development of cancer. They can be identified by their velvety lobular surface, which sharply contrasts with the smooth surface of the adjacent mucous membrane. ICD 10, based on the shape and severity of the pedicle, defines 4 types of polyps:
- Hemispherical in shape, representing flat plaque-like formations with a wide base, 3-6 mm in diameter.
- Round or oval in shape in the form of a hemisphere on a stalk with a diameter of up to two centimeters, with a bright color, often ulcerated.
- Nipple-shaped with a cone-shaped tip on a short stalk.
- Formation of an elongated stalk-like shape with a clearly formed stalk of different sizes.
According to ICD 10, these include adenomas:
- villous with finger-like projections;
- tubular with branched glands, surrounded by mucous membrane;
- papillotubular adenoma combines tubular and papillary structures.
ICD 10 codes:
- K62.0 Polyp of the anal canal.
- K62.1 Polyp of the rectum.
- D13.1 Benign neoplasms of the stomach.
According to the Paris classification of polyps, the concept of early gastric cancer is defined as a tumor on the surface of the mucous membrane of the stomach or on the submucosal layer of its wall. In this regard, ICD 10 additionally identified type “O”, which describes types of gastric cancer without metastases, with subtypes depending on the type of neoplasm. Considering the high degree of danger of adenomatous polyposis turning into cancer according to this classification, the treatment tactics for the disease are determined.
zhkt.guru
Prognosis and prevention
The outcome of the disease depends on the timeliness of diagnosis and the morphological variant of the formation. With a hyperplastic polyp of the esophagus, which has a benign course, the prognosis is favorable. With adenomatous neoplasia, there is a high risk of malignant transformation, which, if surgical treatment is refused, significantly worsens the prognosis for the patient.
Anyone who has had polyps removed from the esophagus knows that after the operation the patient returns to normal life and becomes practically healthy. The only condition is to undergo control examinations at least once a year in order to exclude relapses. Small tumors are safely removed with minimal risk of recurrence.
Postoperative monitoring of patients with excised large polyps is carried out more carefully and for a long time. If the growths turn out to be malignant, the prognosis is less comforting and depends on the degree of cancer.
Polyp in the esophagus: treatment
Making a final diagnosis is possible only after carrying out instrumental diagnostic methods, such as:
- Radiography.
- Endoscopic examination.
If there is a polyp of the esophagus, treatment can only consist of surgical removal of the growth; the main task of instrumental diagnostic methods is to determine the nature of the neoplasm: benign or cancerous. A histological examination of its tissue will help to definitively verify the nature of the growth.
Removal of the esophageal polyp is carried out endoscopically, using an esophagoscope. The presence of a constant video image of the internal organs during the surgical process helps to reduce blood loss to a minimum. Surgical intervention is necessary only if the neoplasm disrupts the functions of the esophagus and is accompanied by symptoms that are painful for the patient.