When it comes to a disease such as esophageal cancer, the epidemiology of its spread is quite extensive. This is an oncological disease accompanied by the appearance of a malignant formation on the wall of an organ. The tumor develops from epithelial cells that form the mucous membrane. The main risk group for this dangerous disease is represented by people who have crossed the 60-year age limit.
In men, this condition is diagnosed 3 times more often than in women. Currently, cancer of this type is an extremely common pathology, accounting for 5–7% of all cancers. If the first symptoms of the condition were noticed in a timely manner, comprehensive diagnosis and treatment were carried out, the prognosis is usually favorable.
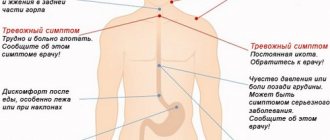
Symptoms of the disease
The condition of patients with a benign disease does not differ from the ordinary condition of a healthy person. There may be slight fluctuations in weight due to anxiety. The infected cell grows slowly and does not appear for a long time. To determine the presence of the disease, you will need to undergo an x-ray and endoscopic procedure.
Signs of the disease
The reasons for the appearance of a tumor are alcohol abuse, frequent smoking and neglect of the rules of heat treatment of consumed food, chronic diseases of the mucous membrane, and the presence of benign formations in the body. Regardless of the location of the tumor, the symptoms are the same.
Leiomyoma of the esophagus
General features of the disease:
- Dysphagia. The process of swallowing food is difficult. The first signs of the disease occur in 90% of patients. Occurs not only due to a mechanical obstruction in the passage of food, but also due to a violation of the reflexes of the upper parts of the digestive tract. It happens that violations arise due to two of the listed factors. A mechanical obstruction manifests itself as discomfort when eating solid food passing through the esophagus. When the disease begins to progress, the patient has to drink water with each dose. So the portion size is gradually reduced and gradually reduced to zero. Moreover, there is a refusal not only from solid food, but also from liquid consistency.
- Odynophagy. The occurrence of pain in the lower part of the neck and pain in the chest. Regardless of food intake, a burning, stabbing, tearing pain is felt in the chest area, radiating to the area between the shoulder blades.
- Hypersalivation. Profuse salivation. It is a protective reflex to facilitate the passage of food. It has a thick foamy consistency.
- Bad breath. When the tissue begins to disintegrate and necrosis occurs, a purulent, unpleasant odor is felt from the mouth, which is difficult to hide.
- Regurgitation. Reverse swallowing process. Different from vomiting. Swallowed food does not have time to reach the stomach to be treated with acid, but immediately returns to the oral cavity.
- Heartburn. Increased acidity is caused by an enlarged lumen of the esophagus and improper functioning of the nervous system.
A hoarse voice, pain when eating, persistent cough while eating and varying degrees of dysphagia will help the doctor pay attention to the possible presence of a tumor of the esophagus. After conducting a series of diagnostic examinations, the doctor will make an accurate diagnosis. Cancer of the digestive tract ranks sixth among neoplasms of other organs and, unfortunately, ranks third in cases of death.
The presence of a benign tumor in the esophagus is 1% and reveals a number of varieties. These include polyp, myxoma, hemangioma, adenoma, which can be located in any part of the organ with a smooth or tuberous structure.
Neighboring organs and systems - characteristics of the lesion
When the neoplasm crosses the borders, clinical symptoms of other organs arise. It happens that the symptoms appear much brighter than those of the underlying disease. In such cases, types of esophageal tumors are distinguished.
- Laryngotracheal. Occurs in patients with a tumor in the cervical spine. Accompanied by a cough, the frequency of the voice decreases, complete loss is possible, and there are troubling hot flashes of suffocation. At short intervals, particles of undigested food are visible in the cough sputum.
- Gastric. Present in the lower third of the esophagus. The characteristic features are similar to gastritis. Discomfort in the upper abdomen, heartburn, nausea, pain.
- Neuralgic. The vagus and phrenic nerves are affected. It manifests itself in malfunctions of the heart muscle, unstable blood pressure, chest pain, leading to angina pectoris.
- Pulmonary. Manifests itself in frequent pneumonia, bronchial fistulas, and bronchitis.
In addition to the above organs, growth occurs in vessels located nearby.
https://youtu.be/F1jN93Ogaf8
Common symptoms of esophageal cancer
The clinical picture of many patients is dominated by general signs of the disease, which manifest themselves as:
- weaknesses;
- severe fatigue;
- decreased ability to work;
- loss of appetite;
- causeless heavy sweating at night;
- insomnia;
- slight hyperthermia (the appearance of a feverish state may indicate an advanced malignant process).
If the disease develops for a long time without obvious signs, the patient loses a lot of weight, the skin becomes dry and pale, and anemia appears. When choosing approaches to treating esophageal cancer abroad, specialists take into account the patient’s complaints and the present clinical picture.
Why does a tumor occur?
Until now, the exact reasons for the appearance of cancer cells in the esophagus have not been established. But the research and experiments of scientists have led to the conclusion that the occurrence of foreign formations is influenced by external factors. An example is the consumption of alcohol and hot food. Statistics show that benign and malignant tumors of the esophagus are encountered by people living in Iran, Central Asia, and China. In these geographic locations, the consumption of a huge number of foods that provoke the formation of tumors is common.
Causes of the disease
The causes of cancer in the esophagus have been well studied, in particular, the sources lie in the following factors:
- Excess body weight provokes pressure on the abdominal walls, this leads to the occurrence of reflux with the subsequent development of various pathologies.
- Strict diets have a negative effect on the body and organs of the digestive tract.
- Abuse of fatty, salty, canned, fried foods provokes the development of tumor-like formations.
- Chemical solutions accidentally entering the body leave severe burns.
- Addiction to alcoholic beverages and tobacco products.
- Genes that are inherited mutate and become the cause of the disease.
- The presence of papillomavirus in the blood causes the development of malignant diseases.
- The use of minimal nutrients and microelements necessary for the normal functioning of the body and the structure of a strong immune system.
Classification
Any changes in the cellular composition of the esophagus are 99% malignant. Medicine has recorded four hundred cases of benign tumors in this organ. Therefore, when it comes to tumor-like diseases in the digestive organs, they most likely mean cancer.
Classification of tumor growth:
- Endophytic - the appearance of neoplasms in the thickness of the tissue walls or from the submucosal layers in the glands.
- Exophytic – the appearance of tumor-like cells inside an organ, which, due to their location in the mucous membrane, block the lumens.
- Mixed formations - the occurrence of formations in all layers, as a result of which the tissues disintegrate.
There are two types of tumors: benign and malignant. Pathologies of non-cancer cases most often demonstrate a non-epithelial structure.
Benign – determined by the growth rate of the affected cells and the presence of a pathomorphological sign.
Benign:
- intramural - located inside the wall of the esophagus;
- polyp-shaped - located in the lumen of the organ.
Polyp-like formations affect the epithelium of the esophagus, namely:
- adenomatous polyps;
- papillomas;
- cysts.
Intramural formations are not related to epithelial origin:
- lipoma;
- fibroma;
- angioma;
- leiomyoma;
- neurofibroma.
Malignant
Among malignant formations, they are classified by such characteristics as location, structure, morphology and pathological anatomy.
Epithelial:
- keratinizing and non-keratinizing cancer cell damage can be 95% squamous cell;
- basal cell;
- transitional cell;
- anaplastic and mucoepidermoid cancer;
- less than 5% of lesions are adenocarcinoma.
Non-epithelial:
- sarcoma;
- lymphoma;
- melanoma.
Malignant tumors quickly affect the lymph nodes and other organs associated with the symptoms of the disease.
Type of malignant neoplasms:
- Cancer is a malignant formation of the epithelium: basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma.
- Leiomyosarcoma - affects smooth muscle tissue.
- Rhabdomyosarcoma - affects the upper part of the striated muscles.
- Lymphosarcoma - lymph nodes and lymphatic tissue in the wall of the esophageal tube.
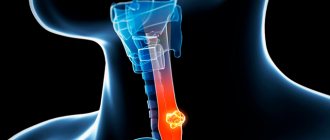
What does the pathology look like in the photo?
The presented photograph clearly shows the narrowing of the lumen of the esophagus when a malignant formation of the epithelial type occurs. This pathology has a complicated course and requires immediate treatment.
In order to begin the necessary treatment, a thorough diagnosis is necessary, identifying the possibility of tumor resectability and prescribing combination therapy using radiation and potent chemicals.
Diagnostics
During a visual examination, the doctor does not diagnose the presence of the disease. Before prescribing productive treatment, a diagnosis is carried out using special tools. A tumor of the esophagus can be detected by X-ray with a contrast agent (barium). The solution envelops the organ, and the image shows disturbances in the normal structure.
X-rays help visually determine the degree of narrowing of the esophagus, identify any changes in wall thickness or the presence of ulcerative wounds.
Using an endoscope, the doctor examines whether the wall has spasms or swelling. This examination technique helps to identify the stage of the oncological process, the presence or absence of metastases in the lymph nodes and nearby organs.
Using ultrasound, the exact size of the tumor and secondary formations, if any, are recorded.
To determine the presence of histology, an abdominal biopsy is performed. A laparoscope equipped with a video camera is inserted through a puncture near the navel, and biological material is collected.
To determine an accurate diagnosis, they take a general biochemical test of blood and urine and monitor the dynamics of changes in indicators. Such studies are needed during chemotherapy to monitor the level of red blood cells, platelets, and white blood cells. Diagnosis of tumor-like formations is carried out for comparison with diseases that cause dysphagia.
Stages
- The first stage is set if the detected neoplasm is localized only in the mucous and submucous membrane. There is no germination of cancer into the muscle layer, as well as no metastases and narrowing of the lumens.
- The second stage - the tumor spreads to the muscle layer, there is a moderate narrowing of the lumen. At this stage, the cancer does not extend beyond the esophagus. Single foci of metastases may be detected in nearby lymph nodes.
- Stage three – all layers of the organ walls are affected by cancer. The tumor spreads to the periesophageal tissue and the adjacent serous membrane. At this stage, there is no cancer spreading to neighboring organs yet, but there are numerous metastases in regional lymph nodes.
- At the fourth stage, the tumor not only grows into all layers of the esophagus, but also spreads to neighboring organs. Metastases are found in separated organs and lymph nodes.
Treatment
Treatment of tumor-like formations in the esophagus is carried out depending on the degree and size of the affected cells, as well as the stage of progression of the process. Common treatments for esophageal masses rely on combination therapy. Prescribed individually by the attending physician.
The fight against esophageal tumors involves surgery and the method of endoscopic surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Endoscopic surgery
It is performed during the course of the disease in an uncomplicated form, by inserting an endoscope, which is equipped with appropriate devices. During the procedure, bougienage is performed. This is required to eliminate the narrowing of the esophagus and to restore the lumen.
Radiation therapy
One of the effective methods of struggle. It is performed in the absence of contraindications for diseases of the respiratory organs and cardiovascular system. As a rule, such treatment is indicated to avoid relapse of the disease and infection of the lymph nodes and adjacent organs. Radiation therapy plays an important role in reducing tumors by affecting only the affected cells, leaving healthy ones without negative effects on them.
Chemotherapy
The main method of combating malignant tumors. Based on the principle of using a cytostatic substance with toxic substances that can destroy cancer cells. When carrying out this procedure, there are a number of side effects due to the effect of the drug on both diseased and healthy cells of the body. The consequences include: hair loss, damage to the oral cavity with stomatitis, a significant decrease in the body's immunity. But all these factors return to normal immediately upon completion of treatment.
Carrying out a chemotherapy procedure
Chemotherapy is necessary for the following forms:
- small cell and granular cell;
- oncological process with a poorly differentiated form.
Treatment algorithm
- All drugs that the doctor prescribes are aimed at destroying cancer cells and the further possibility of new ones arising. Effective in the second and third stages.
- The entire treatment process is palliative in nature and, as a rule, is aimed at maintaining a person’s life and significantly slowing tumor growth.
Surgery, radiation and polychemotherapy procedures. The dosage of radiation therapy before surgery is 3000-5000 rads. The procedure will be effective when the affected cells have not invaded nearby organs. Remember that you should resort to alternative medicine treatment methods only when you have the consent of doctors.
Surgery is only possible for benign tumors and is performed using a gastroscope. When performing abdominal surgery, the entire affected organ is removed or partially removed. If the surgeon finds that the lymph nodes are also affected, they will be removed.
The operation at the last stage is not performed. It is important to diagnose the disease as early as possible. Based on a first stage diagnosis, the survival rate is high. However, the listed signs do not confirm a formation in the esophagus, and the diagnosis is made by an experienced doctor.
During the operation, the surgeon removes part of the affected organ or the entire esophagus. In some cases, the doctor may have to remove part of the stomach. It should be taken into account that surgical intervention is performed if the tumor is located in the middle or lower part of the organ. If during surgery it is necessary to remove the upper part, then an alternative to the removed organ is a part of the intestine or a gastrostomy is formed.
Unconventional treatment
This type of treatment for this disease is ineffective, and sometimes can cause colossal harm to the body. Traditional medicine, unfortunately, is powerless in the fight against cancer. Therefore, you should strictly follow the recommendations and instructions of your doctor.
On the Internet there are a lot of methods that verbally promise to get rid of the disease. But rest assured that the recommendations posted on dubious sites have not been confirmed in any way by top-category specialists in the field of oncology!
Contraindications for surgery:
- metastases in lymph nodes and organs located nearby, the number of which is much greater than normal;
- patients whose age is over 70 years;
- the presence of chronic diseases occurring in the body;
- disruptions in the functioning of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
Medical examinations suggest that the probability of death from esophageal cancer and surgical intervention does not cross the line of 10%. This does not mean that the patient can fully perform physical and mental labor. Productivity decreases significantly or becomes completely questionable.
With a tumor of the esophagus, the patient should pay attention to food intake. Strictly follow and adhere to the doctor’s recommendations. Rough food is excluded from the diet; the amount of food consumed per day does not exceed three kilograms, and portions should be divided into 6 or 7 times. In this case, the temperature of the food consumed should be warm and accompanied by an additional vitamin complex.
Symptomatic picture
Symptoms of esophageal esophagitis directly depend on the form of the disease. In the acute form of the disease, the patient may complain of some symptoms such as:
- acute painful sensations in the chest area. May radiate to the chest or back;
- increased secretion of saliva;
- heartburn. It is difficult to eliminate even with the help of special medications;
- difficulty swallowing. This symptom is more often observed with catarrhal esophagitis;
- decreased appetite;
- weakness.
In more complex cases, vomiting occurs. You can see streaks of blood in the vomit.
Symptoms of inflammation of the esophagus in chronic form are characterized by:
- frequent occurrence of heartburn after eating hot, spicy and fatty foods;
- belching;
- nausea;
- disruptions in the digestive tract;
- exacerbations and subsidence of the disease;
- aching painful sensations in the chest and shoulder blades.
If the disease is protracted, then scar changes form on the mucous membrane. Very often, chronic esophagitis leads to difficulty breathing. This process can affect the development of pneumonia or bronchial asthma.
With each inflammation of the esophagus, a person often shows signs of herpes or stomatitis in the form of ulcers in the mouth. The cause of this condition is considered to be a sharp decrease in immunity and infection.
Complications and prognosis
Tumors that are benign in nature suggest a favorable outcome. But due to the high degree of possible relapse, lifelong observation at the dispensary is necessary.
In case of malignant neoplasms, the time at which the disease is detected and treatment is prescribed plays a role. Unfortunately, the absence of metastases does not guarantee a favorable outcome.
Until now, the specifics of preventing tumor-like formations of the esophagus have not been identified.
What does improper treatment or lack thereof lead to:
- partial obstruction of the alimentary canal or complete blockage;
- lack of passage of food;
- due to tissue breakdown, hemorrhage is possible;
- death.
It all depends on the degree of the disease. If the disease is detected in time, there is a high chance of complete recovery of the body and relapse in the future. If the disease is detected at an early stage, 90% of patients have a chance to live for five years. The subsequent stage will be favorable only for half of cancer patients. 10% of 100 expect full recovery of the body. And no matter how disappointing it may sound, patients with the fourth stage are incurable. After diagnosis, the patient dies soon after.
It happens that a benign tumor develops into a malignant stage. It proceeds slowly. If surgical intervention is no longer advisable, the average life expectancy of the patient is 5-10 months.
Prevention of occurrence
If we take into account the causes of the tumor, it is possible to identify preventive measures. This is medical and personal prevention of the disease.
Personal prevention consists of giving up bad habits: using tobacco products, alcoholic beverages, abstaining from spicy foods and spices, maintaining a normal temperature for the food consumed.
The diet includes the required amount of vegetables and fruits that facilitate the movement of food, foods rich in fiber. Don't forget about your oral health. Food that enters the esophagus must be chewed well so that there is no difficulty in swallowing.
Medical prevention consists of periodic examination and treatment of timely detected chronic diseases associated with the gastrointestinal tract, leading to inflammation of the esophageal mucosa.