Such an unpleasant phenomenon as constipation occurs in almost every pregnant woman. Constipation not only brings inconvenience and discomfort to a pregnant woman’s life, but also poses a significant threat to health, so it is necessary to promptly determine its cause, promptly eliminate it, and prevent its recurrence. Many people know how to deal with constipation, however, due to the physiological characteristics of a pregnant woman, most tips do not bring the desired effect. In this article we will offer recommendations and advice on nutrition, prevention, and treatment of constipation in a pregnant mother.
Why does constipation occur in pregnant women?
Constipation is a very common phenomenon, regardless of the stage of pregnancy, but the reasons for its occurrence in different trimesters may differ.
Cause of constipation in the first trimester
While some mothers in the first trimester suffer from flatulence, bloating and diarrhea, others cannot find the right remedy for stool retention.
Why do pregnant women experience constipation in the early stages?
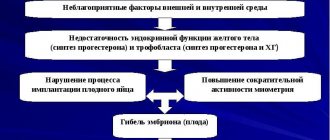
The main reason for constipation in the early stages is the body's production of the hormone progesterone, which is responsible for the development and preservation of pregnancy. Progesterone at the beginning of pregnancy, by reducing the tone of the uterus, ensures implantation of the embryo to the mucous membrane of the uterine wall. However, at the same time, the contractile activity of the muscles of the intestinal walls decreases, and this leads to the fact that the urge to go to the toilet occurs less and less often.
Another cause of constipation is nausea and vomiting, and lack of appetite. Toxicosis in pregnant women can last several weeks, as a result of which an incorrect diet may occur. In addition, many mothers note a change in taste preferences, due to which pregnant women consume less plant fiber and fiber, while more animal proteins are consumed in the diet. This eating behavior leads to disruption of the gastrointestinal tract and constipation.
For some mothers, constipation in the early stages lasts about 3-4 days, while for others, constipation is a companion throughout the entire pregnancy. The first appearance of constipation can begin as early as 5-8 weeks of pregnancy.
Cause of constipation in the second trimester
If you did not have constipation in the first trimester, then it is quite possible that it will appear in the second trimester, starting from the 16th week of pregnancy. In 95% of cases, constipation during pregnancy is caused by physiological changes in the body, such as: decreased physical activity and mobility of the pregnant woman in order to maintain pregnancy, lack of fluid in the body due to increased urination. At this time, pregnant women are highly susceptible to hormonal fluctuations, and this in turn also affects stool retention.
Another cause of constipation is taking vitamins and minerals , which contribute to constipation. For example, iron, calcium, magnesium and B vitamins can disrupt the gastrointestinal tract and lead to constipation.
Cause of constipation in the third trimester
To the already listed causes of constipation, you can add several reasons that are typical for the third trimester of pregnancy:
- pressure from the enlarged uterus on the intestines. During pregnancy, the uterus increases in size many times over. It puts pressure on the intestines, disrupting its peristalsis. In addition, it pinches the rectum, which also interferes with the passage of feces through it.
- decreased sensitivity of the pelvic plexus. As already mentioned, at the beginning of pregnancy the tone of the uterus decreases, and since the muscles of the intestines and uterus have a common nervous supply system, there is a decrease in sensitivity and the urge to defecate, so in order to empty the intestines, a stronger stimulus is required.
- insufficient fluid intake. Due to the threat of edema, doctors recommend reducing fluid intake in the later stages, and this in turn leads to constipation.
- sedentary lifestyle. Already from the 6th month of pregnancy, it becomes much more difficult for the mother to move and perform her previous duties. Mommy tries to rest more in a sitting or lying position. This image leads to slower intestinal motility and constipation.
- stressful situations. Emotional instability, anxiety, increased anxiety, etc. lead to constipation. At the same time, negative emotions very often cause an attack of acute pain in the abdomen or lower back.
- haemorrhoids. Since the uterus with the fetus puts pressure on the vessels of the rectum, venous stagnation occurs, which leads to the appearance of hemorrhoids, and bowel movements with constipation are difficult, resulting in constipation.
- abuse of laxatives. The fact is that with frequent use of laxatives, a “lazy bowel” condition may occur. It occurs due to irritation of the intestinal walls and increased peristalsis by laxatives, as a result of which the digestive tract loses sensitivity and tone.
- complications of pregnancy, such as: toxicosis, low presentation of the fetus, gestosis, hypertonicity, etc.
Treatment of constipation in late pregnancy
The occurrence of constipation in the second trimester of pregnancy, as well as during the transition to the third, is provoked by increasing pressure of the uterus on the large intestine and rectum. The use of osmotic laxatives in later stages is undesirable due to their ability to significantly increase the volume of feces, which can create additional discomfort for the expectant mother. In addition, pregnant women in the 3rd and 2nd trimesters are characterized by a tendency to swelling, and it is not possible to provide the necessary drinking regimen for osmotic drugs.
The solution for a pregnant woman may be to take prebiotic medications, in acute cases - the use of emergency laxatives, and sometimes even intestinal irritants.
Products based on disaccharides
During pregnancy, you can use a laxative based on synthetic sugar. It is not broken down by enzymes and enters the intestines in its original form. The disaccharide formula helps attract fluid, which helps soften stool. The products of enzymatic processing of sugar molecules are an excellent environment for the proliferation of beneficial bacteria, and an increase in acidity eliminates pathogenic microorganisms, and with them the processes of fermentation and decay.
The most common example of a laxative that pregnant women can drink is Duphalac syrup. The list of its analogues is wide. However, the dosages of lactulose are the same everywhere, and accordingly, the regimen for taking the syrup is the same. It is important that these drugs normalize the flora and restore peristalsis in an absolutely natural way, do not cause addiction or drug dependence, and therefore can be used both in late and early stages of pregnancy.
- Duphalac - taken 20-45 ml in the morning on an empty stomach or at night, 2 hours after dinner. Once a stable result is achieved, 20 ml is used as maintenance therapy. The effect appears on the 2-3rd day of administration. 200 ml of the drug costs from 300 rubles.
- Normaze syrup 200 ml – from 280 rubles.
- Portalak – 390 rubles.
- A preparation based on lacthiol – Exportal. Much less likely to cause bloating than Duphalac. 2 packets of the drug are dissolved in a glass of water and taken once a day. Costs about 430 rubles.
Chemical intestinal irritants
These include sodium picosulfate drops and tablets. This is a strong chemical agent that artificially causes activation of peristalsis. All picosulfate tablets are prohibited for pregnant women. The exception is Guttalax drops. The doctor decides whether pregnant women can drink them after an objective comparison of the risks and benefits for each specific case. The drug is taken 10 drops, dissolved in a small amount of water, at night. During pregnancy, taking the drug should be as short as possible.
https://youtu.be/E70ePOhW5aw
Diagnosis of constipation in pregnant women
Diagnosing constipation yourself is not difficult; it is enough to know the symptoms of constipation and its manifestations. Pregnant women suffering from constipation experience difficulty in bowel movement with dense stool consistency, no bowel movements for 2-3 days, and also bloating, pain, pain in the abdomen or lower back, nausea and weakness.
If you notice these symptoms, it is important to consult a therapist to confirm the diagnosis and prescribe treatment!
The therapist, in turn, will prescribe treatment, however, if it does not help, the doctor may refer the pregnant woman for a consultation with a gastroenterologist and proctologist (in case of hemorrhoids). To identify the causes of constipation, the pregnant woman will have to undergo a digital examination of the rectum, as well as donate blood and feces for laboratory tests. In complex cases, it may be necessary to diagnose rectal pathologies using ultrasound and endoscopic colonoscopy.
Using this procedure, you can assess the condition of the epithelium of the intestinal mucosa and study individual anatomical features; diagnose adhesions, etc. Colonoscopy is prescribed even in the first trimester if a pregnant woman has blood, mucus, pus in the stool, bleeding, anemia, polyps, colitis, and painful bowel movements.
Laxatives for pregnant women
The main rule when treating a pregnant woman is “do no harm.” Therefore, self-prescription of drugs is out of the question. For pregnant women, medications that increase intestinal contractions, such as Senade, Bisacodyl, and Regulax, are absolutely contraindicated. They tone the muscles of the uterus and can provoke labor.
There are several groups of laxatives approved for use during pregnancy. But they should also be prescribed by a doctor:
Approved for emergency use, not suitable for frequent use. The glycerin in the suppository irritates the walls of the rectum, causing increased peristalsis, and the oils included in its composition help soften stool. The action occurs quickly - after 15-30 minutes. Cannot be used if there is an existing threat of miscarriage.
The active substance sodium citrate softens and thins stool and gently enhances peristalsis. Bowel movement occurs within 15 minutes.
Lactulose preparations (Duphalak, Portalak, Normaze) are a mild laxative for pregnant women, they are broken down in the large intestine into organic acids, causing a decrease in acidity and an increase in osmotic pressure. The action of lactulose is based on increasing and softening the intestinal contents and stimulating peristalsis. The laxative effect occurs approximately one day after administration.
Treatment of constipation during pregnancy
With the appearance of difficult stool, it is important for a pregnant woman to contact her doctor, who will initially offer non-drug relief from constipation, since many remedies can harm the health of the unborn baby. In addition, treatment for constipation may differ depending on the stage of pregnancy, since the causes of constipation may vary.
As already mentioned, at the very beginning of pregnancy, hormonal changes in the body cause constipation, which is difficult to eliminate, but very important. Therefore, for complete bowel movements, a pregnant mother should adhere to the following recommendations:
- Change your lifestyle: increase physical activity, engage in light sports or physical therapy, visit the pool;
- Drink up to 2 liters of water to normalize water balance;
- Avoid emotional stress and stressful situations;
- Discontinue (after consulting with your doctor) medications that cause constipation (iron and calcium supplements).
- Consume only approved foods during pregnancy;
- Include in your diet foods with a laxative effect, containing coarse fiber and dietary fiber. We'll talk about them later.
- Taking (with the doctor's permission) medications.
For later pregnancy, methods for relieving constipation will be as follows:
- Eat meals in small portions up to 5-6 times a day. Food portions should be small (300-350 g);
- The main amount of calories should be consumed for breakfast and lunch;
- Breaks should not be long, that is, more than 3.5-4 hours;
- Dishes should be steamed, boiled, stewed, baked;
- The main part of the diet is fruits and vegetables, soups and cereals;
- You should choose a balanced diet : proteins - at least 150 g, fats - 80 g, carbohydrates - 300 g. and more;
- You can eat your last meal of the day a maximum of 3 hours before bedtime. There are 4-5 hours breaks between breakfast, lunch and dinner;
- Correct selection of diet , depending on the type of disorder and other concomitant diseases;
- Stand in the knee-elbow position at least 4 times a day (after 20 weeks).
Drug Treatment for Constipation: Be Extremely Caution
How to get rid of constipation during pregnancy? The main rule is not to self-medicate. Some medications for expectant mothers are generally prohibited, as they can lead to the most unpredictable consequences. For example, medications such as Senadexin or other tablets based on Senna leaves can cause abortion.
It is best to see a doctor who will prescribe one of the following safe medications to help relieve constipation during pregnancy:
- Duphalac syrup. It has a very delicate effect on the body, softens feces and promotes their gentle removal from the body. The presence of a prebiotic in the composition makes it possible to simultaneously restore normal microflora and eliminate the occurrence of problems in the future;
- Microlax. Another gentle remedy for constipation during pregnancy, which is used for so-called microenemas. Its main advantage is the high speed of impact. The required laxative effect appears within 10-12 minutes;
- Glycerin suppositories. A completely safe remedy for constipation during pregnancy, which gives an excellent effect. Its components do not penetrate the blood and do not pose a risk to the health of the unborn baby.
Despite the fact that these drugs are safe, treatment for constipation during pregnancy with their use can only be performed after consulting a doctor. Only he can choose a medicine that suits the characteristics of the body.
Medicines for constipation
Attention!
ALL INFORMATION ON THE SITE IS FOR INFORMATIONAL NATURE AND IS NOT A GUIDE TO ACTION! SPECIALIST CONSULTATION IS REQUIRED
Only if the above recommendations are ineffective, a pregnant woman, after consulting with a doctor, can resort to drug treatment with laxatives. Most often, the doctor prescribes the following medications to a pregnant woman:
Rectal suppositories with glycerin
This laxative softens and lubricates hardened feces, facilitates their passage through the colon, and has an irritating effect on the intestinal mucosa, reflexively stimulating intestinal motility. Suppositories are safe for pregnant women, since glycerol has only a local effect, it is not absorbed when administered rectally and does not penetrate the bloodstream.
Contraindications and side effects: hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, intestinal obstruction, hemorrhoids in the acute stage, inflammatory diseases and tumors of the rectum, undiagnosed abdominal pain, renal failure.
As we can see, the drug is not contraindicated for pregnant women, however, in the 1st trimester, suppositories can have a relaxing effect not only on the smooth muscles of the internal organs, but also on the uterus, and this can lead to miscarriage. As for the 2nd and 3rd trimesters, the use of suppositories is allowed, but it is important to take into account that frequent use of suppositories can lead to premature birth. Therefore, doctors do not recommend systematic use of this drug, and treatment should be stopped after restoration of normal intestinal motility.
Rectal suppositories with sea buckthorn oil
Suppositories with sea buckthorn oil have anti-inflammatory, antitumor and analgesic effects, as well as antimicrobial effects. The candles have regenerating and restoration-stimulating properties. The active substance accelerates the healing of damaged tissues, has a general strengthening effect, and has antioxidant and cytoprotective effects. Reduces the intensity of free radical processes and protects cellular and subcellular membranes from damage.
Contraindications for use: Hypersensitivity to the product; for oral administration - cholecystitis, cholangitis, pancreatitis, hepatitis, cholelithiasis, children under 12 years of age; for rectal use - diarrhea. Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding is possible only if the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus or child.
Therefore, suppositories can only be used with the approval of a gynecologist . It is better for a pregnant woman to be tested in advance for tolerance to the herbal preparation. If an allergic reaction occurs, there may be complications for the baby's health. Most suppositories are prohibited during pregnancy, but sea buckthorn remedy is made from natural raw materials, so it has a mild and effective effect.
Rectal suppositories "Papaverine"
Papaverine reduces the tone of the smooth muscles of the internal organs of the gastrointestinal tract and blood vessels, due to this, the arteries dilate and blood flow increases. The drug relieves tone from smooth muscles, so the walls of the digestive organs relax under its influence.
For constipation, papaverine helps remove accumulated feces by eliminating spasm from the lower parts of the large intestine. Papaverine suppositories, after entering the rectum, begin to dissolve and their active ingredients quickly penetrate the walls and general bloodstream, relieving spasms and facilitating bowel movements.
Contraindications for use: AV blockade, glaucoma, severe liver failure, old age (risk of developing hyperthermia), children under 6 months of age, hypersensitivity to papaverine. Use during pregnancy and lactation - during pregnancy, the safety and effectiveness of papaverine has not been established.
Despite the fact that suppositories with papaverine are prescribed to pregnant women to relieve uterine tone, it is also not contraindicated in any trimester of pregnancy, as a drug for prolonged constipation. Although suppositories with papaverine for constipation are considered a safe drug, you should not use them constantly without a doctor’s prescription.
Duphalac syrup
The laxative Duphalac is one of the safest remedies for constipation in pregnant women. The drug does not have any effect on the fetus, since the effect of lactulose on a pregnant woman is negligible. Duphalac contains substances that lead to an increase in the number of lactobacilli. Changes in colon flora lead to increased acidity in the colon lumen and stimulation of peristalsis. As a result, a laxative effect develops without directly affecting the mucous membrane and smooth muscles of the colon.
The lactulose contained in Duphalac retains water in the intestinal tract, and this helps soften the stool, activate motility and intestinal evacuation function. As a result, the physiological rhythm of colon emptying is restored.
How to use Duphalac: The drug is intended for oral administration. Lactulose solution can be taken either diluted or undiluted. It is necessary to immediately swallow the single dose taken without holding it in the mouth. If a single daily dose is prescribed, it must be taken at the same time, for example, during breakfast.
During laxative therapy, it is recommended to take a sufficient amount of fluid (1.5-2 liters, equal to 6-8 glasses) per day. To accurately dose the drug in vials, use the included measuring cup. When using the drug in sachets, you must tear off the corner of the sachet and immediately take the contents.
The daily dose of lactulose can be taken once, or divided into two using a measuring cup. After a few days, the initial dose may be adjusted to a maintenance dose depending on the response to the drug. The laxative effect may appear 2-3 days after starting to take the drug.
| Age | Initial daily dose | Maintenance daily dose |
| Adults and teenagers | 15-45 ml (1-3 sachets) | 15-30 ml (1-2 sachets) |
Contraindications: galactosemia; obstruction, perforation or risk of perforation of the gastrointestinal tract; hypersensitivity to any component of the drug; galactose or fructose intolerance; lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption; undiagnosed rectal bleeding; colostomy; ileostomy.
Syrup "Normaze"
Laxative. It has a hyperosmotic, hypoammonemic, laxative effect, stimulates intestinal motility, improves the absorption of phosphates and calcium salts.
Under the influence of the drug, a change in the flora of the colon occurs (an increase in the number of lactobacilli), which leads to an increase in acidity in the lumen of the colon and stimulates peristalsis. Along with this, the volume increases and the stool softens. As a result, the drug has a laxative effect without directly affecting the mucous membrane and smooth muscles of the colon. Under the influence of the drug, ammonia passes from the blood into the intestine, while the formation of nitrogen-containing toxic substances in its proximal section and, accordingly, their absorption into the vena cava system decreases. The effect may occur quickly or be delayed - after 24-48 hours.
Contraindications for use : intolerance to galactose or fructose; galactosemia; intestinal obstruction; rectal bleeding (not hemorrhoidal); colostomy, ileostomy; suspicion of appendicitis; hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding: lactulose is safe when used during pregnancy and lactation (breastfeeding).
Dosage regimen: The drug should be taken orally after meals. For constipation, adults are prescribed 15-40 ml/day in the first 3 days, then 10-25 ml/day.
Natural complex “Fitomucil Norm”
The Phytomucil Norm complex includes two components: the seed shell of a special variety of plantain Plantago Psyllium and the pulp of the domestic plum fruit - natural sources of dietary fiber (fiber). Phytomucil Norm contains 4 times more soluble fiber than ordinary bran and is a “champion” in terms of soluble fiber content*.
The complex's soluble fibers in the intestines absorb water, swell, turn into a mucous gel and soften the stool, which facilitates easy bowel movements. Insoluble dietary fiber mechanically stimulates the intestinal walls, activating its movements and excretion of feces. Thus, Fitomucil Norm simultaneously affects both the contents of the intestine and its mucous membrane, relieving constipation, bloating and a feeling of heaviness.
In addition to the laxative effect, Fitomucil Norm creates favorable conditions for the growth of its own beneficial intestinal microflora, which helps eliminate dysbiosis, which always occurs with constipation.
Contraindications for use: individual intolerance to the components of the complex; acute inflammatory diseases and gastrointestinal obstruction.
Use during pregnancy and lactation: Fitomucil Norm can be used during pregnancy and lactation. The duration of administration of the complex is selected individually.
Microenema "Mikrolaks"
Microlax is a solution for rectal use, produced in the form of a disposable microenema. Belongs to a group of laxatives that affect the digestive system and metabolic rate. The combined drug Microlax has a laxative effect.
The drug contains sodium citrate (a peptizer that displaces bound water contained in stool), sodium lauryl sulfoacetate (thin the intestinal contents) and sorbitol (increases the laxative effect by stimulating the flow of water into the intestines). Increasing the amount of water due to peptization and liquefaction helps soften stool and facilitate bowel movements.
Thus, Microlax has a mechanical and chemical effect. It is a non-toxic agent with an irritating and moisturizing effect. Penetrating into the feces, the solution liquefies them, after which the process of defecation is facilitated.
Contraindications for use: increased individual sensitivity to the components of the drug.
Can pregnant women have a microenema for constipation?
Although there is no in-depth research into how the drug affects pregnancy and breastfeeding, it is often prescribed during pregnancy and lactation. Since the components of the drug have an extremely low ability to penetrate the intestinal walls, a negative effect on the fetus and the course of pregnancy is not expected during the use of Microlax.
Method of administration and dosage regimen: the drug is administered rectally. The entire contents of 1 microenema (5 ml) are introduced, inserting the tip to its full length (the length of the universal tip is 60.6 mm). The laxative effect occurs 5-15 minutes after taking the drug.
Safe laxatives
This state of the body is not as harmless as it might seem at first glance.
- In a woman’s body, breakdown products of incoming food accumulate, which remain in the intestines for a very long time. Due to a long stay there, harmful substances are absorbed through the intestinal walls and enter the blood. This negatively affects the general condition of the pregnant woman and child. Scientists have determined that there are currently 36 types of toxic substances that form in the large intestine.
- With constant bloating, the tone of the uterus may increase.
- Healthy microflora in the intestines of a pregnant woman is the key to the formation of normal microflora in the child. Since during childbirth the baby passes through the birth canal, it receives all the bacteria from the mother.
- Constant constipation causes heaviness in the stomach and constant bloating. This may be accompanied by pain, which causes discomfort for mother and baby.
The consequences can be the most unpleasant: the general condition worsens, the rectum becomes inflamed, fecal poisoning occurs, the tone of the uterus increases, and the condition of the skin worsens (peeling, sagging).
- Duphalac. The main component is lactulose, which eliminates and prevents constipation. The drug does not penetrate the bloodstream and is excreted unchanged. When prescribed by a doctor in the form of syrup, you need to take the daily dose once or divide it into two doses.
- Defenorm is a laxative of plant origin. It has a mild effect, does not irritate the rectum, and changes the consistency of stool. Can be used after doctor's prescription.
- Fitomucil is a dietary supplement and is not a drug. With the help of natural dietary fiber, the volume of stool increases. Treatment is possible only after the recommendation of a doctor.
- Glycerin suppositories slightly irritate the colon mucosa and cause it to contract. Vaseline and glycerin soften stool. Even if the pregnancy is progressing normally, you should not self-medicate, as the tone of the uterus may increase.
- Microlax is a microenema with the active ingredient sodium citrate. The drug acts locally, does not penetrate the intestinal walls and does not enter the blood.
- Fortrans is an osmotic laxative containing polyethylene glycol and electrolytes. After oral administration, the volume of fluid in the intestines increases, which provides a laxative effect. The drug can be used during pregnancy only after a doctor's prescription.
Let's first figure out what symptoms indicate constipation, since the frequency of bowel movements can vary greatly among people. The main signs of pathology are that the number of bowel movements and the amount of feces has significantly decreased, the stools have become excessively hard and dry, it seems to you that the intestines are not completely emptied.
- An increase in progesterone - the hormone has a relaxing effect on all smooth muscles, which negatively affects peristalsis.
- Constipation during early pregnancy can occur while taking medications with iron and calcium - these substances are necessary for expectant mothers, so they are often prescribed by gynecologists.
- A sedentary lifestyle, the need to adhere to strict bed rest if there is a threat of miscarriage.
- Severe toxicosis provokes dehydration and loss of appetite, which causes the formation of a small amount of feces.
- In the second trimester, the uterus begins to actively grow, compresses and displaces nearby organs, and the digestive system suffers most from this.
- Lack of diet - overeating, long breaks between meals with severe toxicosis, craving for salty, sweet, junk food.
- Exacerbation of chronic diseases of the digestive system.
During pregnancy, almost all groups of potent drugs with a rapid and pronounced effect are prohibited. These include:
- Osmotic laxatives (magnesium sulfate). They cause increased release of fluid into the intestinal lumen, slow down absorption, and cause secretory diarrhea with loss of electrolytes and water. They have a mutagenic effect on the child.
- Drugs that stimulate peristalsis (senna preparations, Bisacodyl). Increased intestinal motility leads to the release of acetyloline, which increases the tone of the uterus and increases the likelihood of miscarriage.
- Drugs that increase the volume of intestinal contents (Mukofalk). Excessively absorb fluid, which can worsen constipation. The action develops after 10-12 days, which is unreasonably long.
The choice of laxatives for treating pregnant women is extremely limited. When determining the necessary drug, the doctor must focus on its safety and effectiveness. The medication is considered suitable if the stool returns to normal within 5-7 days.
How to deal with constipation during pregnancy and can you take laxatives? Most medications are strictly contraindicated for pregnant women, as they can cause uterine contractions and lead to miscarriage. Some medications disrupt the water-salt balance, causing digestive disorders, abdominal pain, and diarrhea, which is also very dangerous for the expectant mother and her child.
But at the same time, not treating constipation is also extremely dangerous. What to do? First of all, preventive measures should be observed (which are described in detail below). But if the problem has already arisen, then under no circumstances should you self-prescribe medications or practice treating constipation with folk remedies.
At the first symptoms of constipation, you should immediately report the problem to your doctor. Only a specialist, having assessed the severity of the condition, can prescribe medications for constipation to the expectant mother. Thus, the safest are those that are not absorbed into the bloodstream. They are aimed at loosening (due to the absorption of large amounts of liquid from tissues) and natural removal of feces.
These are so-called probiotics, which have a laxative effect. For example, Duphalac, Forlax, Tranzipek and others. In addition to their direct purpose, they help restore the intestinal microflora, which prevents the problem of constipation in the future. But even such medications have contraindications and side effects, so they should be used only in extreme cases and with great caution. In addition, you should not expect an immediate effect from the above drugs: the result can be noted only after a few days.
Laxative products for constipation
To both eliminate constipation and prevent its occurrence, a pregnant woman is recommended to include the following laxative products in her diet:
Category | Laxative product |
Dried fruits and nuts | prunesdried apricotsdatesdried apricotsfigsalmondpistachiospeanuthazelnuts and cashews |
Fruits and berries | applesapricotsavocadopineapplespearsorangesplumsgrapeblack currantstrawberryblackberrycowberrycherrymelonkiwiwatermelon |
Vegetables High in Soluble Dietary Fiber | beetcabbagezucchiniJerusalem artichokepumpkincucumberstomatoescarrotbroccoliBrussels sprouts |
Legumes and seeds | beanslentilsflax and chia seeds |
Cereals, cereals and whole grains | oat branbuckwheatcorn gritspearl barleymilletwhole grain rye breadbran bread |
Dairy products | kefirRyazhenkacurdled milkcottage cheeseyogurt |
Vegetable oils | sunflower oillinseed oilolive oilCoconut oilcorn oil |
Greens and root vegetables | spinachdillparsleygreen and onionshorseradishginger |
Beverages | fresh juicescompotesfruit drinksdecoctionsjellygreen teacoffeemineral water |
This list of products is recommended for normalizing metabolism, enhancing intestinal motility, and improving the microflora of the digestive system of a pregnant woman. For example, dried fruits contain a large amount of fiber - 3.1 g. per 100 gr. product, which is 12% of the recommended daily intake. Fresh fruits and berries also contain a lot of fiber, in addition, many fruits contain enzymes, organic sugars and acids, which are responsible for the functioning of the digestive system.
Legumes contain a mixture of both insoluble and soluble dietary fiber. This means they can relieve constipation by adding bulk and weight to stool, as well as softening it to make bowel movements easier. The dietary fiber in chia and flax seeds consists of 85% insoluble fiber and 15% soluble fiber. Insoluble fiber acts like a sponge in the colon, retaining water, adding bulk, and softening stool. Meanwhile, soluble fiber promotes bacterial growth, adding bulk to stool.
Vegetables, fresh or boiled, enhance peristalsis and soften the consistency of stool, facilitate their separation and prevent the development of hemorrhoids. Vegetables naturally cleanse the body, normalize the composition of microflora in the intestines, improve the digestion process and immunity. Thanks to insoluble fiber, plant foods attract water and increase the volume of intestinal contents. Soluble pectin compounds help eliminate toxins, radionuclides and cholesterol.
Fermented milk products fermented with “live” bacteria can improve the intestinal microflora and affect its peristalsis. Vegetable oils soften the intestinal walls, as if “lubricating them” and this facilitates the easy passage of feces. Greens stimulate the secretion of gastric juice, enhance sluggish intestinal motility, reduce gas formation during flatulence, and have a diuretic effect.
Why is it important for pregnant women to eat foods rich in fiber?
The fact is that foods rich in fiber increase the number of beneficial bacteria in the intestines that take part in food processing. As a result of these processes, short-chain fatty acids are formed - substances that play a very important role in the functioning of the intestines as a whole. They provide energy to beneficial intestinal microflora; improve the barrier function of its walls, preventing microbes from passing through them into other environments of the body; regulate his motor activity; stimulate blood flow; maintain normal pH levels, etc.
Diet and nutrition for pregnant women with constipation
In some cases, constipation during pregnancy can be treated with one of the complex treatment methods - diet. Very often, a properly organized diet can solve the problem of regular bowel movements. It is advisable for pregnant women to give preference to oatmeal and buckwheat porridge, wholemeal black bread, dried fruits, especially prunes, since food for constipation in pregnant women should first of all contain a large amount of fiber. Consuming enough fluids is essential to maintaining gut health.
Meat should contain a lot of connective tissue. Fatty varieties should be limited. Young veal, lamb, and poultry have proven themselves to be excellent for feeding pregnant women. This product perfectly helps restore intestinal function. Your daily diet should include a large amount of vegetable or olive oil.
Soups during pregnancy are best prepared from vegetables with minimal addition of potatoes and pasta. It can be cabbage soup, borscht, vegetarian soup. Puree soups are especially useful, for example, pumpkin soup with cream or cauliflower soup with the addition of grated unsalted cheese.
It is not recommended to consume foods that cause constipation:
- rice
- semolina
- semi-finished products
- canned and smoked meats
- persimmon
- bakery and confectionery products, crackers,
- pomegranate juice
- spices
- celery
- unripe fruits containing starch
- red fatty meat
- corn kernels
- pickles
- pasta
- chocolate
- canned meat and fish
- dogwood
- blueberry
- cheese
- potato
- quince
- scrambled eggs, omelette cooked in a frying pan.
What affects constipation?
Unfortunately, a pregnant woman's diet is not without its small weaknesses, especially when it comes to increased consumption of substances such as chocolate, white rice and bread.
In addition, constipation during pregnancy and its formation are influenced by the less active lifestyle of the expectant mother. The process of slowing down digestion also has a powerful effect.
What you eat stays in the intestines longer, so more nutrients are absorbed by the body. However, the sooner you think about preventing constipation, the better for you and your well-being.
Sample menu for a pregnant woman with constipation
The first menu option for constipation in a pregnant woman:
- First breakfast: steamed omelette; oat cookies; green tea;
- Second breakfast: baked green apple;
- Lunch: soup with chicken breast; cabbage, carrot and apple salad dressed with olive oil; compote;
- Afternoon snack: oatmeal cookies; dried fruits compote;
- Dinner: steamed fish with mashed potatoes; bran bread; tea.
- At night, 1-1.5 hours before bedtime: 1% kefir or fermented baked milk.
Second menu option for the day:
- First breakfast: oatmeal with milk with a handful of nuts and dried fruits;
- Second breakfast: cottage cheese with banana; tea;
- Lunch: boiled beef with buckwheat; boiled beet salad with prunes;
- Afternoon snack: vinaigrette with whole grain bread;
- Dinner: steamed pumpkin porridge;
- Before bed: a glass of 1% kefir.
Third menu option for the day:
- First breakfast: millet porridge with milk with a handful of dried fruits;
- Second breakfast: steam omelette and rosehip decoction;
- Lunch: red borscht; salad with vegetables; dried fruits compote;
- Afternoon snack: cottage cheese casserole with dried apricots;
- Dinner: chicken cutlets with steamed vegetables;
- Before bed: a glass of 1% kefir or fermented baked milk.
Fourth menu option for the day:
Folk remedies for constipation during pregnancy
A good and safe folk remedy for constipation is prune decoction . To prepare it, you need to take 100 grams of washed dried fruits, 100 grams of rolled oats and 100 grams of beets. Mix all these ingredients, place them in a saucepan and pour 2 liters of water. Boil prunes, rolled oats and beets over low heat for an hour. After this, strain the broth and put it in the refrigerator. Before going to bed you should drink 1 glass.
Prunes, dried apricots and raisins with honey also help against constipation during pregnancy . To prepare this mixture you will need dried fruits (100 g each) and 2 tbsp. l. honey Rinse prunes, dried apricots and raisins thoroughly and pass through a meat grinder. After this, add honey and mix thoroughly. It is recommended to take 2 tsp of this product before bed, washing it down with warm water. It is good for constipation to drink compote of dried apricots and prunes
. It has a mild laxative effect, which is especially important when carrying a baby.
What is the danger?
The absence of bowel movements in an expectant mother, especially if constipation is a concern during early pregnancy, is an extremely dangerous condition for both the woman and the child. Even if severe symptoms in the form of pain, fever or other signs do not cause concern, the lack of natural bowel movements can lead to uterine tone and, as a result, miscarriage.
Why is constipation dangerous during pregnancy? If defecation does not occur within 5 days, then the feces harden, thereby the possibility of independent bowel movements is significantly reduced, and the likelihood of intestinal cracks (and with them bleeding) increases. In addition, during stagnation, rotting of the masses begins to occur.
Why is constipation dangerous during pregnancy?
Constipation may seem like a minor problem at first glance, but during pregnancy it can lead to dangerous consequences, especially in the case of regular bowel retention. The main threat for a pregnant woman with constipation is the risk of miscarriage or premature birth (depending on the stage of pregnancy) due to strong and frequent straining in an attempt to empty the intestines; for the same reason, rectal prolapse cannot be ruled out.
The outflow of blood and lymph from the pelvic organs provokes the development of hemorrhoids over time, and dense feces can lead to cracks, ruptures and bleeding from the anus. Another risk is poisoning (intoxication) from accumulated toxins and harmful substances formed as a result of the decomposition of unremoved feces. This leads to severe intoxication of the maternal body and fetus. Intoxication is accompanied by weakness, nausea, headache, fever and abdominal pain.
All this can lead to dysfunction of the digestive system, intestinal obstruction and the appearance of polyps in the rectum. As a result of inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, dysbiosis can begin, which can also spread to the genitals. As a result, vulvitis and vaginitis may occur, which will lead to complications during pregnancy and the risk of fetal development.